Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
|
|
|
- Hillary Newman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e
2 In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal. We said that the peritoneum cavity consists of two sacs, greater sac and lesser sac. We said also that the two layers of peritoneum together make: - 1. Omenta: greater omentum (policeman of the abdomen) or lesser omentum. 2. Mesenteries: mesentery of small intestine, mesocolon which is the mesentery of transverse colon or mesentery of sigmoid. 3. Ligaments We said also that the functions of the two layers of the peritoneum: - 1. Delivering blood supply. 2. Delivering nerve supply. 3. They contain lymph nodes, lymph vessels and fat. In this lecture we will talk about the ligaments of peritoneum. the ligaments of the liver 1. The falciform ligament of liver 2. The ligamentum teres hepatis 3. The coronary ligament 4. The right triangular ligament 5. The left triangular ligament 6. The hepatogastric ligament 7. The hepatoduodenal ligament 1 P a g e
3 All of these ligaments composed of two layers of peritoneum, most of them are fibrous tissue. The liver is an interperitoneal organ, because it is not covered completely by the peritoneum, the bare area of the liver is not covered. - The falciform ligament: Sickle in shape It divides the liver into right and left lobes it is attached to the anterior abdominal wall, which means that the falciform ligament divides the space under the diaphragm into subdiaphragmatic space on the right side and subdiaphragmatic space on the left side. we can notice this division between the spaces when someone for example has appendicitis and no appendectomy was done to him, in this case usually pus starts to form and move up in the right side toward the diaphragm which accumulates under it developing what we call subdiaphragmatic abscess, this abscess cannot be on the left side because there are organs that prevent the pus to reach to it and also because of the falciform ligament that divides it from the right side. - ligamentum teres In the free edge (the end) of the falciform ligament we have the ligamentum teres also called round ligament of liver, it is an obliterated umbilical vein which means that the umbilical vein was existing in the fetus but it got obliterated and transformed into a fibrous tissue which we call ligamentum teres. 2 P a g e
4 - The coronary ligament It consists of two layers (anterior and posterior). between the two layers there is the bare area of the liver, which means that this area doesn t have peritoneum. The connection of the coronary ligament at the edges of the liver (right or left) makes on the left side the left triangular ligament and on the right side the right triangular ligament. - The hepatogastric and the hepatodudenal ligaments Together they form the lesser omentum. The hepatogastric ligament connects to the lesser curvature of the stomach. The hepatoduodenal ligament connects to the duodenum. The foramen of winslow located under the free edge of lesser omentum, this foramen has important contents which are the portal vein, common bile duct and hepatic artery. 3 P a g e
5 Ligaments of spleen - Gastrosplenic ligament We said that the spleen is the lateral boundary of the lesser sac, this ligament Connects the fundus of stomach to hilum of spleen. Contents of this ligament: 1. Short gastric arteries: they are five to seven branches that arise from the splenic artery, they supply the fundus of the stomach. 2. Left gastroepiploic artery: it is also a branch from the splenic artery, runs in the greater omentum to supply the body of stomach. - Splenorenal ligament Extends between the hilum of the spleen and the left kidney. Contents: 4 P a g e 1. The splenic artery: arises from the celiac trunk which is a branch from the abdominal aorta, it supplies the foregut. 2. The splenic vein 3. Lymphatic vessels, nodes and nerve 4. The tail of pancreas
6 This ligament is important in surgeries (splenectomy). Any trauma in the left side of the body especially on the level of the 9 th, 10 th and 11 th ribs, can cause rupture in the spleen, the spleen is considered the reservoir of the blood so any trauma in it can cause bleeding, also we cannot place stiches in it, so the only solution is splenectomy, in this surgery the doctors open the splenorenal (lienorenal) ligament and they find between the two layers the splenic vessels, so they do two ligations (to prevent bleeding) and a cut to each vessel and by that there is no more blood supply to the spleen, after that they will find in their way the tail of pancreas which is friable, so it secretes whenever there is trauma or friction, this secretion causes peritonitis, so the surgeon must be cautious in dealing with it, at the end the surgeon removes the spleen, the patient can live without it because it is considered a lymphatic organ and there are other organs that can do the rest of its functions. - Phrenicosplenic ligament: it is between the diaphragm and the spleen, it keeps the spleen in its place. - Splenocolic ligament: it is between the spleen and the left colic flexure of the transverse colon, it keeps the spleen in its place above it. 5 P a g e
7 These two legaments keep the spleen above and separate it from the other organs like the descending colon. Also they prevent the pus from accumulation on the left side of the subdiaphragmatic space, we said before it is because of the organs but now it is much clearer that the ligaments that connect between the diaphragm and the spleen and the left colic flexure prevent the formation of the abscess on the left side. Ligaments of stomach They are important to hold the stomach in its place 1. Hepatogastric ligament 2. Gastrosplenic ligament: between greater curvature of the stomach and the spleen. 3. Gastrophrenic ligament: between the stomach and diaphragm. 4. Gastrocolic ligament: between the stomach and transverse colon. 5. Gastropancrestic ligament: connects the stomach from behind with the pancreas. 6 P a g e
8 The suspensory ligament of duodenum It is also called ligament of Treitz, it is placed at the junction between jejunum and last inch of duodenum, it ascends upward and to the right because it is attached to the right crus of diaphragm. The diaphragm has vertebral, costal and sternal origins, the right crus originates from the lateral side of the bodies of the upper three lumber vertebra while the left crus originates from the upper two lumber vertebra, so the right crus has a bigger origin which gives it two features: 1. Sling around the esophagus which means its fibers goes around the esophagus. 2. It attaches to the ligament of Treitz This ligament is considered the landmark to the beginning of the jejunum, so it is important in the gastrojejunostomy operation, so basically the surgeon makes an opining in the stomach and the jejunum and connects the two openings together so the food begins to go directly from the stomach to the jejunum. So how the surgeon knows where the jejunum is? He goes to ligament of Treitz which is placed in the beginning of the jejunum and in the end of the duodenum. The duodenum is retroperitoneal so the surgeon cannot move it while the jejunum has mesentery so the surgeon can move it and connect it to the stomach. 7 P a g e
9 The phrenicocolic ligament It connects the left colic flexure to the diaphragm, it is related to the 10 th, 11 th and 12 th ribs on the lateral side. This ligament is important in separation, so no material can go up under the diaphragm. The peritoneal recesses and fossa Recess or fossa means if the organ was retroperitoneal (peritoneum only on the anterior wall) and becomes intraperitoneal (peritoneum completely surrounds the organ) like duodenojejunal or iliocical, this conversion forms fossa or recess which is space surrounded by peritoneum. For example, the appendix can be in many places, it can be parailial which means next to the ilium, or It can be rertocecal which means behind the cecum there is a recess that can enter in it. Another example, surrounding the duodenum we can find paraduodenal recess or space. The recesses have disadvantages, sometimes the small intestine either the jejunum or ilium goes in the recess and puts pressure on it, this might lead to something we call an internal hernia, the internal hernia is entering of the small intestine (mostly) in the recesses either the paraduodenal or retrocecal recess, this may cause cut in the blood supply of the intestine, by that the internal hernia becomes strangulated hernia (degeneration also called gangrene), so if the surgeon found out that some of the intestine had become gangrene, he remove it and connect the two ends of intestine together, if it was viable the surgeon get it out of the fossa then he close it (the fossa). These recesses mainly exist around the duodenum, cecum and sigmoid colon in the pelvis, sometimes around the epiploic foramen. 8 P a g e
10 Duodenal Recesses 1. The superior duodenal recess 2. The inferior duodenal recess 3. The paraduodenal recess 4. The duodenojejunal recess Cecal recesses 1. The superior ileocecal recess 2. The inferior ileocecal recess 3. The retrocecal recess: we said that the appendix goes in this fossa in 70% of the cases, this does not lead into any complications because it has the mesoappendix, but when we want to do appendectomy we should get it out from the fossa. 4. The rectocolic recess: between the sigmoid colon and the rectum. The intersigmoid recess: exists in the pelvis, it has a V shape attachment, we will talk about it with the sigmoid colon. Hepatorenal recess: it exists between the liver and the right kidney, it is important because sometimes when pus forms from the appendix, instead of going in the subdiaphragmatic space, it may go between the right kidney and the liver in what we call Morison s pouch. 9 P a g e
11 The pouches The peritoneum contains pouches, the pouch is a large fossa, clinically important because it may cause internal abdominal hernia and pus can accumulate in it. rectovesical pouch (in male) the rectum is divided into upper middle and lower thirds, the upper third is surrounded completely by peritoneum, in the middle third the peritoneum is only anterior, the lower third has no peritoneum. When the peritoneum goes in front of the middle third of the rectum toward the superior border of urinary bladder, before the urinary bladder there is the rectovesical pouch. Or when the peritoneum goes from the anterior abdominal wall to the upper surface of urinary bladder, it forms the rectovesical pouch then it goes posteriorly. The sigmoid colon or the ilium may fill up this pouch, or the pus may also do so. 10 P a g e
12 Pouches in female - Rectouterine pouch (Douglas pouch) between rectum and uterus, it also covers the posterior fornix of vagina - Vesicouterine pouch (Uterovesical pouch): between bladder and uterus Peritoneal subdivisions When the peritoneum goes from the transverse colon and transverse mesocolon to the anterior border of pancreas it divides the greater sac into: - Supracolic compartments: divided into Subphrenic space: it is located under the diaphragm, Divided by the attachment of Falciform ligament into: 1. Right subphrenic space: it is opened 2. Left subphrenic space: it is closed Subhepatic space: it is located under the liver, divided into: 1. right subhepatic space (morison s pouch): the pus accumulates in it. 2. left subhepatic space (lesser sac) 11 P a g e
13 When someone sleeps on the back, the two biggest cavities will be in the pelvis and the thorax because the lumber vertebra will be raised upward, in contrast when someone sits with his back straight, the biggest cavity will be in the pelvis. So when someone has chronic appendicitis, the pus starts to accumulate, so this patient always sleeps on his right side with his knees on his abdomen by that the fluid instead of staying in the pelvis, it goes to the,(قرفصاء) subhepatic or subphrenic space on right side. - Infracolic compartments The ascending and descending colons are retroperitoneal which means the peritoneum covers them anteriorly and laterally, by that they are fixed in the posterior abdominal wall. Around them there will be what we call gutters. Gutter means groove around the ascending or descending colon, the fluids run in this groove, the peritoneum fixes these grooves (gutters) in their places. Infracolic compartments are divided into: - Right paracolic sulcus (gutter): Subdivided into: - 1. Right medial paracolic 2. Right Lateral paracolic 12 P a g e
14 Left paracolic gutter: Subdivide into: - 1. Left medial paracolic 2. Left Lateral paracolic The Right medial paracolic gutter is closed by the transversed colon and the ilium, while the Left medial paracolic gutter is open so the fluid can move toward the pelvis from it. In the Left Lateral paracolic gutter, the fluid cannot go upward because there is the phrenicocolic ligament between the diaphragm and the left colic flexure, so it goes downward to the pelvis. But in the appendicitis case, the right lateral paracolic gutter is open so the pus goes upward to the subdiaphragmatic space or morison s pouch. So, if acute appendicitis develops into chronic appendicitis, there will be accumulation of pus in the subdiaphragmatic space which will cause subdiaphragmatic abscess or it will accumulate in morison s pouch which will cause morison s abscess, the only solution is drainage of the pus. 13 P a g e BEST OF LUCK
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
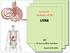
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal. - Dana AF
 - 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
- 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES. Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga
 ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
The Spleen. Dr Fahad Ullah
 The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment. Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD
 Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Anatomy of the spleen. Oluwadiya KS
 Anatomy of the spleen Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The spleen is an ovoid, usually purplish, pulpy mass about the size and shape of one's fist. It is the largest lymphoid tissue in the body
Anatomy of the spleen Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The spleen is an ovoid, usually purplish, pulpy mass about the size and shape of one's fist. It is the largest lymphoid tissue in the body
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II
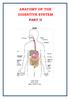 ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer
 Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Applied Peritoneal Anatomy - A Pictorial review.
 Applied Peritoneal Anatomy - A Pictorial review. Poster No.: C-1925 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Patel, I. Beal, K. Planche; London/UK Keywords: MR, CT, Anatomy, Abdominal wall,
Applied Peritoneal Anatomy - A Pictorial review. Poster No.: C-1925 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Patel, I. Beal, K. Planche; London/UK Keywords: MR, CT, Anatomy, Abdominal wall,
The subperitoneal space and peritoneal cavity: basic concepts
 Abdominal Imaging ª The Author(s) 2015. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Published online: 26 May 2015 Abdom Imaging (2015) 40:2710 2722 DOI: 10.1007/s00261-015-0429-5 The
Abdominal Imaging ª The Author(s) 2015. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Published online: 26 May 2015 Abdom Imaging (2015) 40:2710 2722 DOI: 10.1007/s00261-015-0429-5 The
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
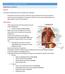 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
Peritoneal cavity anatomy in CT Peritoneography: a comprehensive description.
 Peritoneal cavity anatomy in CT Peritoneography: a comprehensive description. Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Calvo Blanco, R. Menendez de Llano, A. Mesa Alvarez,
Peritoneal cavity anatomy in CT Peritoneography: a comprehensive description. Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Calvo Blanco, R. Menendez de Llano, A. Mesa Alvarez,
Anatomy of the peritoneum: What for?
 Anatomy of the peritoneum: What for? Poster No.: C-2152 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Lima, R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, A. Cardoso, Z. Seabra; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
Anatomy of the peritoneum: What for? Poster No.: C-2152 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Lima, R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, A. Cardoso, Z. Seabra; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
Al-Mohtaseb. Saba Alfayoumi. Mo Alfarra
 8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
Done by: nisreen obeidat
 Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space
 Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
THE ORAL CAVITY
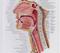 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
-the stones will obstruct the common bile duct and it might also be precancerous. -so the best treatment is chlolycyctoctomy.
 At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
Common Bile Duct (CBD)
 Liver Last time we talked about the liver and the doctor started by revising some information about it: It has five surfaces. It reaches the 5 th intercostal space ; some books write that it reaches the
Liver Last time we talked about the liver and the doctor started by revising some information about it: It has five surfaces. It reaches the 5 th intercostal space ; some books write that it reaches the
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib
 8 Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib This sheet is a remake from 2015 s sheet for the same lecture; I have checked the record, added, omitted, edited & illustrated all what the Professor mentioned in
8 Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib This sheet is a remake from 2015 s sheet for the same lecture; I have checked the record, added, omitted, edited & illustrated all what the Professor mentioned in
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Lesser sac: Anatomy and non-neoplastic processes
 Lesser sac: Anatomy and non-neoplastic processes Poster No.: C-0027 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, R. Moschona, S. Paschalidou ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3 GR, Rethymno/GR,
Lesser sac: Anatomy and non-neoplastic processes Poster No.: C-0027 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, R. Moschona, S. Paschalidou ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3 GR, Rethymno/GR,
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut
 Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2
 Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2 Last time we talked about embryology of the GIT. We said that the development of the stomach is accompanied with the development of the duodenum and the pancreas. Also we talked
Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2 Last time we talked about embryology of the GIT. We said that the development of the stomach is accompanied with the development of the duodenum and the pancreas. Also we talked
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai
 Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 21.12.2017 Internal surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall The internal ( posterior ) surface of the anterolateral
Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 21.12.2017 Internal surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall The internal ( posterior ) surface of the anterolateral
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures would have been cut EXCEPT the:
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
Anatomy of Liver and Spleen
 Anatomy of Liver and Spleen Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of Liver and Spleen Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
Liver o The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety of functions. - It s an accessory organ of GIT
 بسم رلاهللا You don t need to refer to the slides, we included everything here In this lecture we will talk about Liver & Gallbladder Liver o The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety
بسم رلاهللا You don t need to refer to the slides, we included everything here In this lecture we will talk about Liver & Gallbladder Liver o The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety
Anatomy of the renal system. Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi
 Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Peritoneal cavity compartments: A pictorial review
 Peritoneal cavity compartments: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1516 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: T. C. Fernandes, R. H. Castro, N. P. Silva, A. B. Almeida, R.
Peritoneal cavity compartments: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1516 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: T. C. Fernandes, R. H. Castro, N. P. Silva, A. B. Almeida, R.
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
The Foregut. At first the esophagus is short. but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly
 GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
General Surgery Anatomy Course
 General Surgery Anatomy Course May 2018 Course will meet on Wednesdays during May in Fee Hall in East Lansing from 12:00 5:00 May 2 12:00 1:00 Abdomen Lecture 1:15 5:00 dissection Dr. Mary Bee May 9 12:00
General Surgery Anatomy Course May 2018 Course will meet on Wednesdays during May in Fee Hall in East Lansing from 12:00 5:00 May 2 12:00 1:00 Abdomen Lecture 1:15 5:00 dissection Dr. Mary Bee May 9 12:00
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Posterior Abdominal wall-
 Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Peritoneum: Anatomy, physiology and pathology
 Peritoneum: Anatomy, physiology and pathology Poster No.: C-417 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and Gastrointestinal Authors: C. L. Fernandez Rey, I. Gutierrez Lopez, E. Montes
Peritoneum: Anatomy, physiology and pathology Poster No.: C-417 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and Gastrointestinal Authors: C. L. Fernandez Rey, I. Gutierrez Lopez, E. Montes
Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University
 Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Understand the components and functions
Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Understand the components and functions
Liver. Function of the liver
 Liver & Gallbladder Liver The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety of functions Weight: 1/50 of body weight in adult & 1/20 of body weight in infant It is exocrine(bile) & endocrine
Liver & Gallbladder Liver The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety of functions Weight: 1/50 of body weight in adult & 1/20 of body weight in infant It is exocrine(bile) & endocrine
Chapter 8: The abdomen and perineum
 Chapter 8: The abdomen and perineum The abdomen is that part of the trunk between the diaphragm and pelvis. For descriptive purposes the anterior abdominal wall is divided into nine regions by two horizontal
Chapter 8: The abdomen and perineum The abdomen is that part of the trunk between the diaphragm and pelvis. For descriptive purposes the anterior abdominal wall is divided into nine regions by two horizontal
ii. Atrioventricular c. A-V valve i. Cusps ii. Chordae tendinae iii. Papillary muscles d. Interventricular septum e. Wall i. Trabeculae carnae 5.
 Viscera I. Viscera of the thorax A. Respiratory system 1. Trachea a. carina [L. keel of boat] 2. Bronchi a. right and left main b. lobar c. segmental 3. Lungs a. Right i. Apex ii. Lobes (upper, middle
Viscera I. Viscera of the thorax A. Respiratory system 1. Trachea a. carina [L. keel of boat] 2. Bronchi a. right and left main b. lobar c. segmental 3. Lungs a. Right i. Apex ii. Lobes (upper, middle
Pathways for the Spread of Disease in the Abdomen and Pelvis
 Pathways for the Spread of Disease in the Abdomen and Pelvis 6 James A. Brink and Brent J. Wagner Learning Objectives To discuss the ligamentous anatomy of the upper abdomen and how it can inform the spread
Pathways for the Spread of Disease in the Abdomen and Pelvis 6 James A. Brink and Brent J. Wagner Learning Objectives To discuss the ligamentous anatomy of the upper abdomen and how it can inform the spread
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE LIVER
 THE LIVER DEVELOPMENT OF THE LIVER THE LIVER The hepa-c diver-culum develops as an outgrowth of the endoderm of the foregut in the region of the second por-on of duodenum. This diver-culum enters the ventral
THE LIVER DEVELOPMENT OF THE LIVER THE LIVER The hepa-c diver-culum develops as an outgrowth of the endoderm of the foregut in the region of the second por-on of duodenum. This diver-culum enters the ventral
Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13
 Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
