Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children
|
|
|
- Robyn Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of the M.Sc degree in Pediatrics Submitted by Ahmed Ibrahim Abulkhir Khayyal Under supervision of Prof. Dr. Neveen Abd El Monem Soliman Professor of Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine - Cairo University Prof. Dr. Hafez Mahmoud Bazaraa Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine - Cairo University Dr. Inas Abdalla Ali Lecturer of Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine - Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 2012
2 Acknowledgement First of all thanks to ALLAH the most gracious and the most merciful for helping me to complete this study. I am greatly honored to express my feelings of appreciation and sincere gratitude to Prof. Dr. Neveen Soliman, Professor of pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, for her valuable, scientific and moral support. Her eminent supervision and endless motivation was giving me a great potential and I will remember her overwhelming kindness with respect forever. I would like to express my greatest and deepest appreciation to Prof. Dr. Hafez Bazaraa, Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, for his valuable effort and endless help in this work. He gave me too much of his time. I am in great debt to him. I offer my deepest appreciation to Dr. Marwa Nabhan, Lecturer of pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, for her valuable supervision and guidance. I also wish to thank all staff members and colleagues in the Center of Pediatric Nephrology and Transplantation (CPNT), for their constant encouragement and cooperation during my work. Finally, special thanks and gratitude to all my lovely patients and their cooperative families.
3 Abstract Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder characterized by bilaterally enlarged cystic kidneys without dysplasia. The two major forms, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) and autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), have significant overlap in clinical presentation and radiographic features. This descriptive study was designed to assess the clinical phenotypes of Egyptian infants and children with PKD, presenting to Cairo University Center of Pediatric Nephrology and Transplantation as a referral center. We have studied 36 cases with PKD; 32 patients with ARPKD (89%) and 4 patients with ADPKD (11%). The most important clinical morbidities were urinary tract infection (44%), systemic hypertension (42%), portal hypertension (17%) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (14%). Abdominal ultrasonography was the most helpful diagnostic test, while CT scan, renal biopsy and investigations for extra-renal manifestations were required in selected cases. Early and proper diagnosis is important for genetic counseling and for proper management of comorbidities for better survival and for delaying progression to ESRD. Key words: Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, inherited renal diseases, chronic renal failure, ultrasonography.
4 CONTENTS List of Abbreviations. I List of Tables. II List of Figures III Introduction and Aim of the Work. 1 Review of Literature.. 3 Polycystic kidney diseases; Introduction and differential 3 diagnosis. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney 8 disease Epidemiollogy. 8 Molecular genetics.. 8 Pathogenesis. 10 Pathology. 10 Clinical features. 12 Diagnosis. 15 Imaging Laboratory studies. 21 Prenatal features and diagnosis.. 22 Prognosis. 24 Treatment. 24 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Epidemiology and genetics.. Pathogenesis.... Pathological features..... Clinical features.. Diagnosis Imaging... Antenatal diagnosis.. Prognosis Treatment.. Patients and Methods.. 39 Results.. 44 Discussion. 71 Summary & Conclusion. 78 Recommendations.. 81 References. 82 Arabic Summary
5 List of Abbreviations ACE: ACEi: ADPKD: ARPKD: camp: CCB: CHF: CKD: ESRD: GCKD: GFR: Hx&E: ICAs: IHBR: LVH: LVMI: MCD: MCDK: PC-2: PKD: Angiotensin converting enzyme Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Calcium channel blockers Congenital hepatic fibrosis Chronic kidney disease End-stage renal disease. Glomerulocystic kidney disease Glomerular filtration rate Hematoxylin and Eosin Intracerebral/intracranial aneurysms Intrahepatic biliary radicles Left ventricular hypertrophy Left ventricular mass index Medullary cystic disease Multicystic dysplastic kidney Polycystin-2 Polycystic kidney disease PKHD1: Polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 SPSS: TRPP2: UTI: Statistical Package for Social Sciences Transient receptor potential channel P2 Urinary tract infection I
6 List of Tables Table (1) Renal length in children using ultrasound. 41 Table (2) Sex distribution in the studied patients. 44 Table (3) Age of onset of symptoms, current age and age of end stage renal disease. 45 Table (4) The main presenting symptoms in polycystic kidney disease cases. 46 Table (5) The main clinical features in polycystic kidney disease cases. 48 Table (6) Clinical data of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease cases. 50 Table (7) Extra-renal manifestations in the studied cases. 51 Table (8) Details of hepatic involvement in the studied cases. 52 Table (9) Cases presenting with hepatic manifestations. 52 Table (10) Cardiac manifestations in the studied cases. 54 Table (11) Family history of the studied subjects. 54 Table (12) Laboratory data (initial) in the studied cases. 57 Table (13) Incidence of proteinuria and hyponatremia in PKD cases. 57 Table (14) Ultrasonographic data in the studied cases. 58 Table (15) Correlation between ESRD and age of the patients. 69 Table (16) Correlation between abdominal distension & age of onset. 70 Table (17) Correlation between hypertension & age. 70 Table (18) Correlation between portal hypertension & age. 70 III
7 Table (19) Correlation between hepatic involvement & age. 70 Table (20) Correlation between Current CKD stage & sex. 71 Table (21) Correlation between CKD stage & hepatic involvement. 71 IV
8 Fig. (1) List of Figures Cut section in a kidney of a case of ARPKD, the diffuse cystic appearance of the kidneys is noticed. 11 Fig. (2) ARPKD cysts at low power. 11 Fig. (3) The appearance of congenital hepatic fibrosis at low power. 12 Fig. (4) Hepatic sonogram of a neonate with Caroli disease. 15 Fig. (5) Sonogram of both kidneys in a case of ARPKD. 17 Fig. (6) Fig. (7) Fig. (8) Sagittal sonogram through the enlarged right kidney of a newborn with ARPKD. CT shows bilaterally smooth enlarged kidneys in a case of ARPKD. Coronal T1-W turbo spin-echo MR image in the plane of the liver hilum shows portal hypertension associated with ARPKD Fig. (9) Obstetric sonogram demonstrates massively enlarged kidneys in this fetus with ARPKD. 23 Fig. (10) Right kidney from a 15-year-old boy with ADPKD. 30 Fig. (11) Microscopic picture of ADPKD. 31 Fig. (12) Fig. (13) Fig. (14) Sonogram shows cysts with bilaterally enlarged kidneys in a case of ADPKD. CT shows bilateral renal and liver cysts with enlarged kidneys in a case of ADPKD. The incidence of different clinical features in the studied cases Fig. (15) Photo of case (36) with ARPKD. 48 Fig. (16) Incidence of recurrent UTI in cases of ARPKD. 49 Fig. (17) Incidence of hypertension in cases of ARPKD. 49 V
9 Fig. (18) Photo of case (23) with ADPKD and tuberous sclerosis. 51 Fig. (19) Family pedigree of cases 2 and Fig. (20) CKD stage at presentation of the PKD cases. 55 Fig. (21) Current CKD stage of the PKD cases. 56 Fig. (22) Renal USS of case (23) with ARPKD. 59 Fig. (23) Renal USS of case (36) with ARPKD. 59 Fig. (24) Renal USS of case (35) with ARPKD. 60 Fig. (25) Renal USS of case (11) with ARPKD. 60 Fig. (26) Renal USS of case (25) with ARPKD. 61 Fig. (27) Renal USS of case (21) with ARPKD. 61 Fig. (28) Renal USS of case (5) with ARPKD. 62 Fig. (29) Renal USS of case (26) with ARPKD. 62 Fig. (30) Renal USS of case (2) with ARPKD. 63 Fig. (31) Renal USS of case (29) with ADPKD. 63 Fig. (32) Liver USS of case (1) with ADPKD. 64 Fig. (33) Liver USS of case (1) with ADPKD. 64 Fig. (34) Liver USS of case (24) with ARPKD. 65 Fig. (35) Abdominal CT of case (11) with ARPKD. 66 Fig. (36) Abdominal CT of case (7) with ARPKD. 66 Fig. (37) Abdominal CT of case (7) with ARPKD. 67 Fig. (38) Abdominal CT of case (20) with ARPKD. 67 Fig. (39) Brain CT of case (23) with ARPKD. 68 Fig. (40) Renal histopathological examination of case (36) with ARPKD. 69 VI
10 Introduction & Aim of the Work Introduction Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disease that involves bilateral renal cysts without dysplasia. The condition is broadly divided into 2 forms: autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (Verghese et al., 2012). Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is a frequently severe form of pediatric cystic kidney disease that affects the kidneys and the biliary tract. It has an estimated incidence of approximately 1:20,000 live births (Zerres et al., 1998). All typical forms of ARPKD result from mutations in the same gene, PKHD1 (Polycystic Kidney and Hepatic Disease1) (Ward et al., 2002). The diagnosis of ARPKD can be performed in the intrauterine period, neonatal period or in the first months of life, through ultrasound detection of bilateral diffuse kidney enlargement. Its clinical presentation, however, is highly variable and can be identified in the perinatal, infantile, or juvenile period (Dias et al., 2010). Pulmonary insufficiency with respiratory distress due to oligohydramnios that is worsened by large renal masses is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in neonates. Babies who survive the neonatal period may still develop chronic kidney disease, which occurs at varying ages depending on the degree of renal involvement but renal prognosis has improved over time because of renal transplantation. Congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF) still causes considerable morbidity (Verghese et al., 2012). 1
11 Introduction & Aim of the Work Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most commonly inherited renal disease, occurring in 1/1000 to 1/500 living births. Two genes have been identified to date: PKD1which is responsible for the majority of cases and PKD2 responsible for about 15%o of cases. The possible existence of a third gene remains under discussion (Peters et al., 1993). ADPKD is characterized by a progressive cystic enlargement of the kidneys, leading to end-stage renal disease in the fifth or sixth decade, associated to various extra-renal manifestations. It was first denominated adult polycystic disease as in the vast majority of cases, no clinical manifestations occur before adulthood. However, the development of renal ultrasonography and other renal imaging techniques enabled this disease to be detected at a presymptomatic stage, and it is currently being diagnosed in children, newborns and even fetuses (Boyer et al., 2007). Aim of the work The aim of this work was to study the clinical phenotypic features of PKD in infants and children with respect to clinical presentation, chronic kidney disease stage as well as extra-renal associations. 2
12 Review Review Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a ciliopathy that can be diagnosed in adult and pediatric patients. It is an inherited disease that involves bilateral renal cysts without dysplasia. The condition is broadly divided into 2 forms: autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), previously known as infantile polycystic kidney disease and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) previously known as adult polycystic kidney disease. ARPKD and ADPKD can involve the presence of renal cysts at any time during an affected person's life, from the prenatal period to adolescence or older. The clinical and radiologic manifestations of both types of polycystic kidney disease have considerable overlap (Verghese et al., 2012). ARPKD is the most common childhood ciliopathy (Avni & Hall, 2010). It is characterized by cystic dilatation of renal collecting ducts associated with hepatic abnormalities of varying degrees, including biliary dysgenesis and periportal fibrosis. The clinical spectrum is variable and depends on the age at presentation, ranging from stillbirth and neonatal demise to survival into adulthood. The most severely affected fetuses have enlarged echogenic kidneys and oligohydramnios attributable to poor fetal renal output. These fetuses develop the "Potter" phenotype, characteristic facies (consists of wide-set eyes, squashed nose, micrognathia, and large, floppy, low-set ears deficient in cartilage) with pulmonary hypoplasia, and deformities of the spine and limbs ( Verghese et al 2012). Clinical and radiological features suggesting ARPKD rather than ADPKD include neonatal presentation, progression to end-stage renal disease as a child, hepatosplenomegaly, portal hypertension and esophageal varices, bacterial cholangitis, parental consanguinity suggestive of autosomal recessive inheritance, 3
13 Review negative family history and decreased corticomedullary differentiation. (Dell et al., 2009). ADPKD is the most common inherited kidney disease in humans. It is a multisystem disorder characterized by progressive cystic dilatation of both kidneys, with variable extrarenal manifestations in the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, reproductive organs, and brain (Verghese et al., 2012). Although most ADPKD presents in adulthood, 1%-2% present as newborns, often with signs and symptoms indistinguishable from those of ARPKD (Sweeney & Avner, 2011). Clinical features suggesting ADPKD rather than ARPKD include positive family history, extrarenal cysts, cerebral aneurysms, asymptomatic presentation, unilateral renal presentation and hematuria (Dell et al., 2009). Renal ultrasonography may distinguish between the two: bilateral macrocysts are typical of ADPKD. Early in the course of ADPKD, especially in younger children, renal involvement may be unilateral. As ADPKD progresses involvement becomes bilateral; cysts can become massive. Congenital hepatic fibrosis, an invariable finding in ARPKD, is rarely observed in ADPKD (O'Brien et al., 2011). MRI imaging if the kidneys and liver, may clearly distinguish ARPKD and ADPKD in some cases. Findings on MRI include enlarged kidneys with hyperintense T 2 -weighted signals.a characteristic hyperintense, linear radial pattern in the cortex and medulla representing microcystic dilatation has been described on RARE-MR urography (Kern et al., 2000). 4
14 5 Review Although molecular diagnostic testing is available the diagnosis usually relies on imaging studies, a complete family history, clinical findings and, rarely, biopsy findings. Molecular testing for PKD either by linkage analysis or direct sequencing is not recommended for patients in whom a diagnosis can be obtained by imaging analysis alone. Molecular genetic testing for ARPKD and ADPKD is indicated for the subset of patients in whom the clinical and/or tissue diagnosis is equivocal (Sweeney & Avner, 2011). Differential Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis of Polycystic and/or Echogenic Kidneys in the Pediatric Patient Autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPRD) Glomerulocystic kidney disease (GCKD) Inherited Disorders Associated with Polycystic Kidneys: Tuberous sclerosis complex, Meckel_Gruber syndrome, Jeune syndrome and other chondrodysplasia syndromes, Ivemark syndrome, Bardet_Biedl syndrome, oro-facial-digital syndrome Type I, Zellweger cerebrohepatorenal syndrome, Beckwith_Wiedemann syndrome, trisomy 9 and 13, juvenile nephronophthisis/ (MCD) complex, Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome and Hajdu-Cheney Syndrome Sporadic Disorders Associated with Cystic Kidneys: Isolated cystic dysplasia, multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK), unilateral/localized cystic kidney disease and caliceal diverticula. Miscellaneous Causes of Cystic and/or Enlarged Echogenic Kidneys: Nephroblastomatosis, bilateral Wilms tumor, leukemia or lymphoma, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, radiocontrast nephropathy,bilateral renal
15 Review vein thrombosis, transient nephromegaly, congenital nephrotic syndrome, glycogen storage disease and acquired cystic kidney disease (Sweeney & Avner, 2011). Glomerulocystic kidney disease, a rare disorder that typically presents in the neonatal period with large palpable flank masses, may be clinically indistinguishable from ARPKD. Findings on renal ultrasound examination may also resemble those seen in ARPKD: diffusely enlarged echogenic kidneys and occasional macrocysts. Histologic examination shows dilatation of Bowman's capsule and dysplasia with abnormal medullary differentiation. GCKD also occurs as part of genetic disorders including the tuberous sclerosis complex, orofacial digital syndrome type 1, trisomy 13, brachymesomelia-renal syndrome, and short-rib-polydactyly syndrome (Dell & Avner, 2011). Diffuse cystic dysplasia is characterized by ultrasonographic findings of large echogenic kidneys and histologic findings of disorganized, poorly differentiated nephron segments with primitive elements such as cartilage (Watkins et al., 1999). Diffuse cystic dysplasia can occur sporadically or more commonly as a component of numerous syndromes (e.g., Joubert syndrome, Meckel-Gruber syndrome, Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy) (Limwongse et al., 1999).In these syndromes, the extrarenal or extrahepatic abnormalities clinically predominate; the diffuse cystic dysplasia remains a more minor feature (Dell & Avner, 2011). A syndrome of neonatal diabetes mellitus, congenital hypothyroidism, hepatic fibrosis, PKD, and congenital glaucoma has been described in two siblings. Liver biopsy confirmed the classic findings of congenital hepatic fibrosis; histologic evaluation of the kidneys was not performed (Dell & Avner, 2011). 6
16 Review Other hepatorenal disorders characterized by renal cystic changes and hepatic fibrosis to consider include a number of disorders already mentioned: juvenile nephronophthisis and multisystem disorders such as Meckel-Gruber syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Joubert syndrome, and Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy Johnson et al In these autosomal recessive disorders the kidneys are usually small or normal in size, in contrast to the enlarged kidneys of ARPKD (Dell & Avner, 2011). Medullary cystic kidney disease is characterized by bilaterally shrunken kidneys, cysts restricted to the renal medulla, salt wasting, and polyuria. It is inherited as autosomal dominant trait and is clinically milder, and typically first appear in adulthood (Dell & Avner, 2011). 7
17 Autosomal recessive polycysyic kidney disease Review ARPKD is an inherited disorder characterized by cystic dilations of renal collecting ducts and varying degrees of hepatic abnormalities consisting of biliary dysgenesis and periportal fibrosis (Verghese et al., 2012). Epidemiology Based on published reports, the incidence of ARPKD is 1:10,000 1:40,000. The frequency of the gene in the population is estimated to be approximately 1:70. Consistent with autosomal recessive disease, heterozygotes (carriers) are unaffected. The recurrence risk for subsequent pregnancies is 25%, and unaffected siblings have a 66% risk of being a carrier for ARPKD. Males and females are affected equally and ARPKD affects all racial and ethnic groups (Dell et al 2009). Molecular genetics ARPKD is caused by mutations in PKHD1 (polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1), a large, novel gene that localizes to chromosome 6p21. Intrafamilial variability in ARPKD disease phenotype was originally reported to be unusual in contrast to the wide variability often seen in some ADPKD kindreds. However recent data suggest that up to 20% of ARPKD multiplex pedigrees exhibit significant intrafamilial phenotypic variability. Among families with at least one neonatal survivor, the risk for perinatal demise of a subsequent affected child is 37%. These data are important for appropriate genetic counseling (Dell et al., 2009). PKHD1 8
18 9 Review The PKHD1 gene is an extremely large gene, extending over about 472kb, with the longest open reading frame comprising 67 exons and encoding a protein of 4074 amino acids (Ward et al,. 2002). Spectrum of Mutations More than 270 mutations have been described in the PKHD1 gene, the majority of which are private. Detection rates of up to 85% have been described in the more severely affected groups, with lower rates in the more moderate cases, which may indicate inclusion of clinical phenotypes not representing ARPKD. Mutations are spread thoughout the gene with no evidence of clustering at specific sites Furu et al., 2004, and include missense, nonsense, frameshift insertion or deletion and in frame deletions as well as mutations altering splicing. Thus, the size and complexity of the PKHD1 gene in combination with marked allelic heterogeneity and compound heterozygosity makes gene-based molecular diagnostics complicated and not routinely available (Harris and Rossetti, 2004). Modifier genes Recent molecular advances have not answered questions around the factors that modulate gene expression. The variability in clinical phenotype, found even within families, is likely to be influenced by modifier genes as well as the environment. Although a human homologue has not yet been identified, a modifying gene complex on mouse chromosome 4 is suggested (Mrug et al., 2005). Genotype-phenotype correlations In ARPKD, the combination of mutations is critical to the phenotypic outcome. Patients with two truncating mutations have a lethal phenotype, whereas the presence of at least one missense change can be compatible with life, indicating that many missense changes are hypomorphic alleles that generate partially functional protein (Rossetti and Harris, 2007).
19 Review Pathogenesis PKHD1 gene encodes several alternatively spliced isoforms predicted to form both membrane-bound and secreted proteins. The largest protein product, termed fibrocystin or polyductin, contains one membrane spanning domain and an intracellular C-terminal tail. Recent reports demonstrate that fibrocystin/polyductin localizes, at least in part, to the primary cilium and the centrosome in renal epithelial cells. The basic defects observed in ARPKD suggest that fibrocystin/polyductin mediates the terminal differentiation of the renal collecting duct and intrahepatic biliary ducts. However, the exact function of the numerous isoforms has not been defined, and the widely varying clinical spectrumofarpkdmay depend, in part, on the nature and number of splice variants that are disrupted by specific PKHD1 mutations (Guay-Woodford, 2006). Pathology In infants and young children, the kidneys are reniform but grossly enlarged. Pinpoint dots are visible on the capsular surface and correspond to cystic cortical collecting ducts. Microscopically the cysts are usually less than 2 mm in size and have been shown to be dilated collecting ducts lined by low columnar or cuboidal epithelium. The glomeruli and other tubular structures appear to be decreased in number because of marked collecting duct ectasia and interstitial edema. Unlike ADPKD, the cystic tubules in ARPKD are fusiform in shape and remain in contact with the urinary stream. In older children the development of larger renal cysts, interstitial fibrosis, and hyperplasia produces a pattern more like ADPKD. Some degree of biliary dysgenesis and hepatic fibrosis is always present in ARPKD. Hepatic invovement is invariably present microscopically at birth. The classic liver lesion shows a typical ductal plate abnormality consisting of portal 10
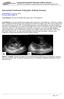
20 Review fibrosis surrounding increased numbers of hyperplastic, ectatic biliary ducts with normal hepatocellular histology (Dell et al., 2009). Figure (1) shows cut section in a kidney of a case of ARPKD, the diffuse cystic appearance of the kidneys is noticed. Figure (2) ARPKD cysts at low power, the radially arranged cysts in collecting tubules of the kidney are seen prominently. 11
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Genetics in Nephrology. Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory
 Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Polycystic Kidney Disease, Autosomal Dominant OMIM number for disease 173900 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Polycystic Kidney Disease, Autosomal Dominant OMIM number for disease 173900 Disease
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease: Issues Regarding the Variability of Clinical Presentation1
 EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Tomas Berl. Editor William Heinrich Mark Paller Fred Silva Denver. CO Dallas. TX Minneapolis. MN Oklahoma City. OK DESCRIPTION OF THE NEPHROLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF
EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Tomas Berl. Editor William Heinrich Mark Paller Fred Silva Denver. CO Dallas. TX Minneapolis. MN Oklahoma City. OK DESCRIPTION OF THE NEPHROLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF
Kidneycentric. Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry
 ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
UAB P30 CORE A: The Hepato-Renal Fibrocystic Diseases Translational Resource
 PKD Foundation UAB P30 CORE A: The Hepato-Renal Fibrocystic Diseases Translational Resource http://www.arpkdstudies.uab.edu/ Director: Co-Director: Lisa M. Guay-Woodford, MD William E. Grizzle, MD, PhD
PKD Foundation UAB P30 CORE A: The Hepato-Renal Fibrocystic Diseases Translational Resource http://www.arpkdstudies.uab.edu/ Director: Co-Director: Lisa M. Guay-Woodford, MD William E. Grizzle, MD, PhD
Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System
 A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Dr. Najla a Aldaoud. Omar Ayman Khasawneh
 Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
A Primer to Cystic Kidney Diseases and Ciliopathies
 A Primer to Cystic Kidney Diseases and Ciliopathies ERKNet Webinar Max Liebau 04.09.2018 Liebau Pediatric Nephrology, Center for chronically ill children, Center for Molecular Medicine WG CAKUT and Ciliopathies
A Primer to Cystic Kidney Diseases and Ciliopathies ERKNet Webinar Max Liebau 04.09.2018 Liebau Pediatric Nephrology, Center for chronically ill children, Center for Molecular Medicine WG CAKUT and Ciliopathies
Journal of Nephropathology
 www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.60 J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4):363-367 Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease
www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.60 J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4):363-367 Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island
 Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island Disclosure Honorarium for Consulting on the Reprise trial from Otsuka Mayo clinic preceptorship for PKD with
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island Disclosure Honorarium for Consulting on the Reprise trial from Otsuka Mayo clinic preceptorship for PKD with
Hereditary polycystic kidney diseases in children: changing sonographic patterns through childhood
 Pediatr Radiol (2002) 32: 169 174 DOI 10.1007/s00247-001-0624-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fred E. Avni Gretel Guissard Michelle Hall Franc oise Janssen Viviane DeMaertelaer Franc oise Rypens Hereditary polycystic
Pediatr Radiol (2002) 32: 169 174 DOI 10.1007/s00247-001-0624-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fred E. Avni Gretel Guissard Michelle Hall Franc oise Janssen Viviane DeMaertelaer Franc oise Rypens Hereditary polycystic
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
What is ARPKD/CHF? A Brief Overview of ARPKD and CHF:
 What is ARPKD/CHF? A Brief Overview of ARPKD and CHF: Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects approximately 1:6,000 to 1:40,000 persons in the general
What is ARPKD/CHF? A Brief Overview of ARPKD and CHF: Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects approximately 1:6,000 to 1:40,000 persons in the general
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Prag. Polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD & ADPKD. Max Christoph Liebau
 Prag Polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD & ADPKD Max Christoph Liebau Department of Pediatrics and Center for Molecular Medicine, University Hospital of Cologne Glasgow, 06th of September 2017 Cystic kidney
Prag Polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD & ADPKD Max Christoph Liebau Department of Pediatrics and Center for Molecular Medicine, University Hospital of Cologne Glasgow, 06th of September 2017 Cystic kidney
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD. Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018
 Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Ultrasound examination of fetuses with cystic renal changes or hyperechoic kidneys includes assessment of [1]:
![Ultrasound examination of fetuses with cystic renal changes or hyperechoic kidneys includes assessment of [1]: Ultrasound examination of fetuses with cystic renal changes or hyperechoic kidneys includes assessment of [1]:](/thumbs/84/90654767.jpg) Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of cystic renal disease Author: Tulin Ozcan, MD Section Editors: Louise Wilkins-Haug, MD, PhD, Deborah Levine,
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of cystic renal disease Author: Tulin Ozcan, MD Section Editors: Louise Wilkins-Haug, MD, PhD, Deborah Levine,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice
 Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Genetics in Primary Care Curriculum Statement 6. Dr Dave Harniess PCME Stockport
 Genetics in Primary Care Curriculum Statement 6 Dr Dave Harniess PCME Stockport Learning Objectives Understanding of genetic component of disease Screening for genetic conditions and risk assessment in
Genetics in Primary Care Curriculum Statement 6 Dr Dave Harniess PCME Stockport Learning Objectives Understanding of genetic component of disease Screening for genetic conditions and risk assessment in
Genetics in Pediatric Nephrology. S Alexander J Fletcher Children s Hospital at Westmead National Kidney Transplant Institute
 Genetics in Pediatric Nephrology S Alexander J Fletcher Children s Hospital at Westmead National Kidney Transplant Institute OBJECTIVES 1 2 3 To understand the basis of inheritance of genetic diseases
Genetics in Pediatric Nephrology S Alexander J Fletcher Children s Hospital at Westmead National Kidney Transplant Institute OBJECTIVES 1 2 3 To understand the basis of inheritance of genetic diseases
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree
 Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Genetics of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic syndrome. Velibor Tasic University Children s Hospital Skopje, Macedonia
 Genetics of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic syndrome Velibor Tasic University Children s Hospital Skopje, Macedonia Nephrotic syndrome - definition Oedema Massive proteinuria (> 50mg/kg/d or> 40mg/m2/h Hypoalbuminemia
Genetics of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic syndrome Velibor Tasic University Children s Hospital Skopje, Macedonia Nephrotic syndrome - definition Oedema Massive proteinuria (> 50mg/kg/d or> 40mg/m2/h Hypoalbuminemia
Kidney Disorders. Renal cysts. Policystic Kidney Diseases. Cystic Renal Dysplasia. Autosomal-Dominant (Adult) Polycystic
 Policystic Kidney Diseases Kidney Disorders CONGENITAL CYSTIC GLOMERULAR TUBULES/INTERSTITIUM BLOOD VESSELS OBSTRUCTION TUMORS Lecture : Genito-urinary system. 11 08 2010. Renal cysts Cystic Renal Dysplasia
Policystic Kidney Diseases Kidney Disorders CONGENITAL CYSTIC GLOMERULAR TUBULES/INTERSTITIUM BLOOD VESSELS OBSTRUCTION TUMORS Lecture : Genito-urinary system. 11 08 2010. Renal cysts Cystic Renal Dysplasia
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound. Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
2 nd ARPKD Family Information Day Saturday 6 th July Welcome!
 2 nd ARPKD Family Information Day Saturday 6 th July 2013 Welcome! Programme - morning Welcome - Tess Harris, Chief Executive PKD Charity Overview of ARPKD and Programme Dr Larissa Kerecuk, Consultant
2 nd ARPKD Family Information Day Saturday 6 th July 2013 Welcome! Programme - morning Welcome - Tess Harris, Chief Executive PKD Charity Overview of ARPKD and Programme Dr Larissa Kerecuk, Consultant
Imaging in cystic renal disease
 Arch Dis Child 2000;83:401 407 401 CURRENT TOPIC Department of Radiology, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, Great Ormond Street, London WC1N 3JH, UK RdeBruyn I Gordon Correspondence
Arch Dis Child 2000;83:401 407 401 CURRENT TOPIC Department of Radiology, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, Great Ormond Street, London WC1N 3JH, UK RdeBruyn I Gordon Correspondence
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter?
 Clinical Research Facility Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter? Nicholas J A Webb BMedSci DM FRCP FRCPCH Honorary Professor of Paediatric
Clinical Research Facility Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter? Nicholas J A Webb BMedSci DM FRCP FRCPCH Honorary Professor of Paediatric
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Research Introduction
 Research Introduction 9.17.13 Altered metabolism in polycystic kidney disease Telomerase activity in polycystic kidney disease cells Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common
Research Introduction 9.17.13 Altered metabolism in polycystic kidney disease Telomerase activity in polycystic kidney disease cells Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name OMIM number for disease Disease alternative names please provide any alternative
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name OMIM number for disease Disease alternative names please provide any alternative
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen. Jonathan Swanson, MD
 Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Biliary Atresia. Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s
 Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA
 Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
on PKD Originally Created by Patricia Gabow, MD Jared J. Grantham, MD University of Kansas Medical Center
 Q & on PKD A Originally Created by Patricia Gabow, MD Jared J. Grantham, MD University of Kansas Medical Center Reviewed and Updated (2002) by Arlene Chapman, MD Robin Post, RN Joan Allen, RD Emory University
Q & on PKD A Originally Created by Patricia Gabow, MD Jared J. Grantham, MD University of Kansas Medical Center Reviewed and Updated (2002) by Arlene Chapman, MD Robin Post, RN Joan Allen, RD Emory University
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 587 591 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenoma(s), adrenal, gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging in, 533 534 hyperfunctioning versus
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 587 591 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenoma(s), adrenal, gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging in, 533 534 hyperfunctioning versus
ESRD Dialysis Prevalence - One Year Statistics
 Age Group IL Other Total 00-04 12 1 13 05-09 5 2 7 10-14 15 1 16 15-19 55 2 57 20-24 170 10 180 25-29 269 14 283 30-34 381 9 390 35-39 583 14 597 40-44 871 20 891 45-49 1,119 20 1,139 50-54 1,505 35 1,540
Age Group IL Other Total 00-04 12 1 13 05-09 5 2 7 10-14 15 1 16 15-19 55 2 57 20-24 170 10 180 25-29 269 14 283 30-34 381 9 390 35-39 583 14 597 40-44 871 20 891 45-49 1,119 20 1,139 50-54 1,505 35 1,540
Renal tumors of adults
 Renal tumors of adults Urinary Tract Tumors 2%-3% of all cancers in adults. The most common malignant tumor of the kidney is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors of the lower urinary tract are twice as common
Renal tumors of adults Urinary Tract Tumors 2%-3% of all cancers in adults. The most common malignant tumor of the kidney is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors of the lower urinary tract are twice as common
Predictors of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression
 Predictors of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression Robert W. Schrier,* Godela Brosnahan,* Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Michel Chonchol,* Keith Friend, Berenice Gitomer,* and Sandro
Predictors of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression Robert W. Schrier,* Godela Brosnahan,* Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Michel Chonchol,* Keith Friend, Berenice Gitomer,* and Sandro
Cystic Disease of the Liver Work Up and Management. Louis Ferrari MD, PGY 3 6/9/16 SUNY Downstate Medical Center
 Cystic Disease of the Liver Work Up and Management Louis Ferrari MD, PGY 3 6/9/16 SUNY Downstate Medical Center The Case 73F presents to clinic after diagnostic laparoscopy at OSH. Known liver mass for
Cystic Disease of the Liver Work Up and Management Louis Ferrari MD, PGY 3 6/9/16 SUNY Downstate Medical Center The Case 73F presents to clinic after diagnostic laparoscopy at OSH. Known liver mass for
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Foreword: Our Kidneys: A Lot Is Riding on Their Shoulders. Preface: Renal and Urologic Abnormalities in the Perinatal Period
 Renal and Urologic Issues Foreword: Our Kidneys: A Lot Is Riding on Their Shoulders Lucky Jain xv Preface: Renal and Urologic Abnormalities in the Perinatal Period Michelle N. Rheault and Larry A. Greenbaum
Renal and Urologic Issues Foreword: Our Kidneys: A Lot Is Riding on Their Shoulders Lucky Jain xv Preface: Renal and Urologic Abnormalities in the Perinatal Period Michelle N. Rheault and Larry A. Greenbaum
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except
 1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
Some renal vascular disorders
 Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Classifications of genetic disorders disorders
 Classifications of genetic disorders Dr. Liqaa M. Sharifi Human diseases in general can roughly be classified in to: 1-Those that are genetically determined. 2-Those that are almost entirely environmentally
Classifications of genetic disorders Dr. Liqaa M. Sharifi Human diseases in general can roughly be classified in to: 1-Those that are genetically determined. 2-Those that are almost entirely environmentally
Liver Tumors. Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy
 Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children
 16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
Renal Ultrasonography in Neonates. Abstract: Introduction:
 Renal Ultrasonography in Neonates. Mahmoud Adel Abdel-Moneim, Mahmoud Mohi-Eldin El-Kersh, Mohamed Alaa Thabet, Magdy Abdel-Fattah Ramadan and Hossam H. Zeid. From Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of
Renal Ultrasonography in Neonates. Mahmoud Adel Abdel-Moneim, Mahmoud Mohi-Eldin El-Kersh, Mohamed Alaa Thabet, Magdy Abdel-Fattah Ramadan and Hossam H. Zeid. From Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of
Shuma Hirashio 1,2, Shigehiro Doi 1 and Takao Masaki 1*
 Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Hereditary tubulointerstitial disease approach to biopsy diagnosis
 Hereditary tubulointerstitial disease approach to biopsy diagnosis Kerstin Amann Nephropathology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Krankenhausstr. 12 D - 91054 Erlangen Kerstin.amann@uk-erlangen.de maternally
Hereditary tubulointerstitial disease approach to biopsy diagnosis Kerstin Amann Nephropathology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Krankenhausstr. 12 D - 91054 Erlangen Kerstin.amann@uk-erlangen.de maternally
New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we?
 New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we? Leicester General Hospital 28 Jan 2012 Professor Albert Ong a.ong@sheffield.ac.uk The cystic degeneration of the kidneys, once it reaches the point where it can
New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we? Leicester General Hospital 28 Jan 2012 Professor Albert Ong a.ong@sheffield.ac.uk The cystic degeneration of the kidneys, once it reaches the point where it can
Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children
 Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children David A. Mong, MD SUNDAY Andrew Mong MD Beyond the interstitium (path includes airways/airspace) Radiographic diffuse disease Adult Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children David A. Mong, MD SUNDAY Andrew Mong MD Beyond the interstitium (path includes airways/airspace) Radiographic diffuse disease Adult Interstitial Lung Disease
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions. American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course
 Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Fellow Seminar. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease F2 吳逸文醫師, 25/08/2004
 Fellow Seminar Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease F2 吳逸文醫師, 25/08/2004 Familial Nephronophthisis ARPKD Polycystic Kidney Disease ADPKD @ Genetics @ Cell biology and pathogenesis @ Clinical picture
Fellow Seminar Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease F2 吳逸文醫師, 25/08/2004 Familial Nephronophthisis ARPKD Polycystic Kidney Disease ADPKD @ Genetics @ Cell biology and pathogenesis @ Clinical picture
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking a Mass: Report of Three Cases
 Case Report Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):54-60 Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking
Case Report Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):54-60 Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: the prototype of the hepato-renal fibrocystic diseases
 Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library, The George Washington University Health Sciences Research Commons Pediatrics Faculty Publications Pediatrics 2014 Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: the
Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library, The George Washington University Health Sciences Research Commons Pediatrics Faculty Publications Pediatrics 2014 Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: the
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant ( 1997) 12: 2284 2288 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Neonatal presentation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with a maternal history of tuberous
Nephrol Dial Transplant ( 1997) 12: 2284 2288 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Neonatal presentation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with a maternal history of tuberous
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Molecular pathology and genetics of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes
 311 REVIEW ARTICLE Molecular pathology and genetics of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes C A Johnson, P Gissen, C Sergi... The hepatorenal fibrocystic (HRFC) syndromes are a heterogeneous group
311 REVIEW ARTICLE Molecular pathology and genetics of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes C A Johnson, P Gissen, C Sergi... The hepatorenal fibrocystic (HRFC) syndromes are a heterogeneous group
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Renal Tubular Acidosis
 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis Mohammad Tariq Ibrahim 6 th Grade Diyala College Of Medicine supervisor DR. Sabah Almaamoory 2 *Renal Tubular Acidosis:- RTA:- is a disease state characterized by a normal anion
1 Renal Tubular Acidosis Mohammad Tariq Ibrahim 6 th Grade Diyala College Of Medicine supervisor DR. Sabah Almaamoory 2 *Renal Tubular Acidosis:- RTA:- is a disease state characterized by a normal anion
Clinical History. 29 yo woman with polyhydramnios Cardiac mass at fetal ultrasound At 35 weeks, newborn died 30 minutes after delivery
 CASE 1 a Clinical History 29 yo woman with polyhydramnios Cardiac mass at fetal ultrasound At 35 weeks, newborn died 30 minutes after delivery Interface between tumor and normal myocardium Smaller well-demarcated
CASE 1 a Clinical History 29 yo woman with polyhydramnios Cardiac mass at fetal ultrasound At 35 weeks, newborn died 30 minutes after delivery Interface between tumor and normal myocardium Smaller well-demarcated
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems. Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017
 Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017 Not the heart Dextroposition Heart in the right chest with the apex to the left Often caused by left sided chest mass
Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017 Not the heart Dextroposition Heart in the right chest with the apex to the left Often caused by left sided chest mass
