Journal of Nephropathology
|
|
|
- Jonas Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /jnp J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4): Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease Mitra Naseri 1*, Nona Zabolinejad 2, Syed Ali Alamdaran 3, Reza Shojaeian 4 1 Pediatric Nephrology Department, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran 2 Pediatric Pathology Section, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran 3 Pediatric Radiology Section, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran 4 Pediatric Surgery Department, Dr. Sheikh Children Hospital, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Article type: Case Report Article history: Received: 5 March 2017 Accepted: 3 July 2017 Published online: 19 July 2017 DOI: /jnp Keywords: ADPKD ARPKD Childhood Nephromegaly Background: Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) associates with significant renal and liver-related morbidity and mortality in children. Rarely severe enlargement of kidneys necessitates nephrectomy and initiating dialysis. Case Presentation: A 5-day-old newborn boy with prenatal ultrasonography suggestive of ARPKD admitted in the hospital due to anuria from first day of life. One week after admission, left nephrectomy was conducted because of severe enlargement of kidneys accompanied by respiratory distress and repeated vomiting. Patient was placed on peritoneal dialysis. Pathology of kidney revealed cystic lesions consisted of dilated collecting duct, with lack of involvement of glomeruli and other parts of the nephrons. Patient died at age 17 days with respiratory hemorrhage. Conclusions: Our case is interesting because of progressive increase in kidney sizes requiring nephrectomy. Such huge nephromegaly in ARPKD has not been reported yet. Case Report Implication for health policy/practice/research/medical education: The course of the disease in our case emphasizes on respiratory problems as the main medical concerns in neonatal onset ARPKD, even if the patients have no respiratory symptoms at birth. Please cite this paper as: Naseri M, Zabolinejad N, Alamdaran SA, Shojaeian R. Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4): DOI: /jnp Introduction Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) belongs to a group of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes which result in significant renal and liverrelated morbidity and mortality in children. In the majority of cases, the disease presents as bilateral enlarged kidneys in neonatal period. Renal involvement is characterized by nephromegaly, hypertension, and varying degrees of renal dysfunction. Within the first decade of life, the disease progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in >50% of affected cases. Approximately 30% of cases die within the first year of life from respiratory insufficiency due to pulmonary hypoplasia or superimposed pulmonary infections (1). 2. Case Presentation A 5-day-old newborn boy was admitted in hospital because of anuria from first day of life. An obstetrical ultrasound (US) was performed in last month of gestation and has been reported bilateral hyper-echogenic enlarged kidneys and decreased amniotic fluid volume. According to the abnormal US findings, the patient was admitted in a local hospital for more evaluation. He was borne by normal vaginal delivery and no respiratory distress. In fifth day of birth, the patient was discharged from local hospital and transferred to our center because of persistent anuria. Parents presented a history of death in one of their sons in neonatal period with diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease. At the time of admission, the mother complained on poor feeding of the neonate, however, the neonatal reflexes were intact. In physical examination, systolic blood pressure (BP) was 80 mm Hg with no measurable diastolic BP. Pulse and respiratory rates were 110/min and 35/min respectively and temperature was *Corresponding author: Mitra Naseri, address: Naserim@mums.ac.ir
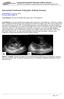
2 Naseri M et al 37 C. Physical examination of abdomen revealed severe abdominal distension due to bilateral nephromegaly. The majority of the abdominal cavity was occupied by enlarged kidneys (Figure 1). Urinary catheterization was unsucceful. The patient received two doses of normal saline (40 cc/each dose) and then intravenous furosemide 1 mg/kg. Few hours after administrating normal saline and diuretic, urine output established (35 cc in the first day of admission). Abdominal US showed normal liver and spleen with enlarged kidneys. Lengths of right and left kidneys were reported 97 and 100 mm. Increased parenchymal echogenicity and abundant microcysts were other findings (Figures 2A-B). Again, in third day of admission, the patient had no urination. Abdominal distension rapidly increased and edema in lower extremities was detected. In fifth day, frequent vomiting, decreased BP (systolic BP = 60 mm Hg) and increased in respiratory rates added to previous findings. Infusion of dopamine, 50 mg in 24 hours was started and the patient received fresh frozen plasma (FFP) 40 cc for inducing volume expansion and correcting abnormal prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT). Birth weight was 3.6 kg which reached to 4.2 kg on the fifth day of admission (age of 10 days). According to severe abdominal distension and severe nephromegaly, which resulted to compressive effects on stomach and diaphragm, a unilateral nephrectomy and insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter was conducted and then the patient transferred to pediatric ICU. Figures 3A-B presents the macroscopic and microscopic details of kidney tissue. Two days after nephrectomy acute peritoneal dialysis was started to control severe hypertension (BP of 150/110 mm Hg) which continued despite stopping dopamine administration. Hypertension was controlled by administrating intravenous labetalol, high doses of furosemide and acute peritoneal dialysis. Despite respiratory support and acute dialysis, on 12th day of admission, the patient died following tracheal hemorrhage, severe hypoxemia and hypotension. Table 1 shows the laboratory tests and their changes during different days of admission. Kidney US was requested for parents, but unfortunately it did not perform due to lack of cooperation A summary history of other affected son of the family He was admitted in our center in first day of life with generalized edema, severe abdominal distension due to kidneys enlargement and oliguria. Prenatal US was not performed and post-natal US revealed hyper-echogenic kidneys with increased sizes (length of each kidney was 106 mm) with multiple microcysts, and normal liver sonography. The case was hypoxemic; the respiratory Figure 1. Thoracic and abdominal X- ray of the patient. It shows no abnormal finding in lungs fields, bone and soft tissues of the chest. Abdominal cavity is severely distended and shadows soft tissues in flanks observes that pushes the bowels to the middle of abdominal cavity. A B Figure 2. Ultrasound images of kidneys; a longitudinal lowfrequency ultrasound image shows a markedly enlarged (longitudinal diameter; 97 mm) echogenic kidney with loss of corticomedullary differentiation (A). The linear high-frequency transverse image reveals numerous tiny cystic structures and relatively hypoechoic peripheral cortex (B). Figures 3. Left nephrectomy consisting of enlarged Reni form shaped kidney with persistent fetal lobation, measuring cm and weighing 513 g, its attached proximal ureter measuring cm. On the cut surface, sponge-like renal parenchyma with radially oriented and fusiform cysts in cortex and more rounded cysts in medulla. The normal pattern of cortex and medulla is replaced by innumerable, radially arranged cysts. The calyces, ureter and pelvis are unremarkable (A). Sections of kidney show elongated, variable cystic collecting ducts, normal glomeruli and tubules seen between cysts (B) (H&E 40). 364 Journal of Nephropathology, Vol 6, No 4, October
3 Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in ARPKD Table 1. Laboratory findings in the patient before and after initiating dialysis and before death Laboratory parameters First day 7th day (before initiating dialysis) 9th day of admission (starting dialysis) 12th day Serum urea (mg/dl) Serum creatinine (mg/dl) Serum sodium (meq/l) Serum potassium (meq/l) a 3.4 b 2.6 c Serum calcium (mg/ dl) Serum phosphorus (mg/ dl) Serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), U/L 34 Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (SGPT), U/L 10 Serum albumin (g/dl) Serum prothrombin time (PT; second) >40 (control =12) 24 d 25 e 22 e Serum partial thromboplastin time (PTT; second) 46 (control = 30) 58 d 58 e 50 e Hematocrit (%) f Serum hemoglobin (g/dl) f Platelet count (cell/µl) Blood culture Negative Negative Urine culture Negative Negative a The dose of furosemide reduced; b potassium chloride was added to dialysis solution (3 meq/l) and furosemide was discontinued; c Potassium chloride was added to dialysis solution (4 meq/l) and also potassium chloride was added to serum (20 meq/l); d Patient received FFP and intravenous vitamin K. There were no apparent hemorrhage; e Patient received FFP. There were no apparent hemorrhage; f Patient received packed cells. rate at admission was 54/min and blood pressure was within normal ranges. Serum creatinine and sodium levels were 1.3 mg/dl and 133 meq/l in the first day of admission respectively which reached to 1.5 and 133 in the fifth day of hospitalization. The chest X-ray was normal. The parents did not consent for more evaluation and treatment of their boy and discharged the patient. Few days later he died in a local hospital probably due to respiratory failure. 3. Discussion ARPKD is a rare (1/ live birth) hepatorenal fibrocystic disease commonly diagnosed in uterus or at birth. Enlarged echogenic kidneys with loss of corticomedullary differentiation due to fusiform dilatation of the collecting ducts are the typical findings on kidney US. Clinical findings in the proband and the absence of renal disease in the proband s biological parents are the main basic findings needed for suspecting to ARPKD. However establishing the diagnosis needs to identify biallelic pathogenic variants in PKHD1 in the affected individuals (1). A detailed history, complete physical examination, imaging, and rarely genetic testing or biopsy are usually sufficient to distinguish ARPKD from neonatal onset ADPKD. In macroscopy, the cut surface of kidneys reveals a radial pattern of the spindle-shaped collecting duct cysts that extended into the renal cortex. The glomeruli and other tubular segments appears to be decreased in proportion due to collecting duct ectasia and interstitial changes that squeeze and atrophy of renal parenchyma (2-4). Symptomatic hepatic involvement is present in only 40%-50% of neonates with ARPKD (1). Distinguishing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) from ARPKD by US is very difficult or impossible. The classic US appearance in ARPKD is enlarged kidneys with increased echogenicity of the renal parenchyma. Cysts are rarely seen. The renal borders are usually poorly defined. In ADPKD renal cysts may or may not be present initially, but the cysts usually increase in size and proportion with increasing age. One or more renal cysts within enlarged kidneys are typical US appearance of ADPKD in children. Kidney cysts form in glomeruli and in all tubular segments (5). Slow but progressive enlargement of the kidneys with renal failure occurring between 5 to 6 decades of life is characteristic of ADPKD. The disease presents with hypertension, flank pain, hematuria, and renal cysts infection in adults. However ARPKD typically presents in younger patients, and is characterized by cystic dilation of the collecting ducts of the kidneys, along with dysgenesis of the biliary ductal plate, resulting in congenital hepatic fibrosis and often death in the perinatal period due to respiratory failure. Despite different and variable clinical presentations, a single gene, PKHD1 is responsible for the disease. The diagnosis of ARPKD typically is based on clinical findings alone, with liver and kidney biopsies needed only in rare instances (6). In 1%-2% of cases, ADPKD presents in newborns, often with signs and symptoms indistinguishable from ARPKD (7-9). Congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF), Journal of Nephropathology, Vol 6, No 4, October
4 Naseri M et al an invariable finding in ARPKD, is rarely observed in ADPKD (10). Pretorius et al (11) reported five cases of ADPKD diagnosed in the fetus by sonographic evaluation and a positive family history. In first case the left and right renal lengths at 8-day age were 8.1 cm and 6.2 cm respectively with a cyst in the left upper pole measured 3.3 cm in diameter, and no liver cysts. Case 2 was the sibling of case 1 who underwent therapeutic abortion at gestational age of 24 weeks because of US findings consistent with ADPKD. Case 3 had Potter s facies and moderate pulmonary hypoplasia and died few hours after birth with respiratory failure. The pathology of this case showed findings consistent with classic ADPKD such as enlarged kidneys with variable sized cysts involving all portions of the nephrons. Other case was a neonate with normal sized echogenic kidneys and no liver cyst in prenatal and neonatal US. Ultrasonography conducted at 25th day of age showed two cortical cysts. In case 5, the neonatal US showed enlarged, echogenic kidneys with several 2-3 mm cysts with no liver cyst. Severely progressive increase in kidney sizes immediately after birth which needed unilateral nephrectomy noted in our case were not reported in any of these cases. In our patient, during a week (from age 5 to 12 days) the lengths of kidneys increased about 50 mm (5 cm) and resulted in respiratory problems and repeated vomiting and symptoms that seem partially related to compressive effects of enlarged kidneys. During delivery and also the first days of admission, our patient had no respiratory problem. In chest X-ray, the lungs parenchyma were normal with no evidences of hypoplasia. Zerres et al (12) reviewed clinical courses of 66 boys and 49 girls with ARPKD over a mean period of 4.92 years. It was a selected group of children who mostly survived the neonatal period, presenting the largest group of case series of ARPKD that have not been reported yet. The age at diagnosis was prenatal period up to 14.5 years (median age of 29 days). Ten cases (8.7%) were prenatal forms. They found decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in 72%, while 9.5% of cases developed endstage renal disease. Kidneys lengths were above the 97th percentile in 68% of patients. Furthermore, none of their cases needed to nephrectomy due to massive nephromegaly. Clinical signs of hepatic fibrosis were detected in 46% of their patients. Thirteen patients (11%) died during the observation period. In our case, a history of PKD in proband with early neonatal presentation was existed. However we did not succeed to check parents for cystic lesions in kidney US. Early presentation of the disease in two members of a family, and laboratory evidence of hepatic dysfunction (abnormal PT and PTT tests ) which were not corrected by several times infusion of fresh frozen plasma (FFP), all were supportive findings for suspecting to ARPKD. We established the final diagnosis by pathology that showed cystic lesions consisted of dilated collecting ducts, lack of involvement of glomeruli and other parts of the nephrons, pathologic findings consistent with ARPKD. However hepatic US was normal with no evidence of periportal fibrosis, prolonged PT and PTT tests which did not improve by several times FFP infusion indicated hepatic dysfunction. 4. Conclusions Our case is interesting and also unique because of rapidly progressive enlargement of kidneys requiring nephrectomy to minimize compressive effects on diaphragm and abdominal viscerals. Such huge nephromaly in ARPKD has not been reported yet. Acknowledgements The authors would appreciate the advocated helps of Dr. Khademi, Dr. Akhavan, the pediatric ICU specialist for management of the patient. Authors contribution All authors contributed to different stages of the preparation of the case report. Ethical considerations Ethical issues (including plagiarism, data fabrication, double publication) have been completely observed by the authors. Informed consent was obtained from the parents of patient for publication of this case report. Funding/Support There was no source of funding for this publication. References 1. Sweeney WE, Avner ED. Polycystic kidney disease, autosomal recessive. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJH, et al, eds. Gene Reviews. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; De Almeida E, Martins Prata M, de Almeida S, Lavinha J. Long-term follow-up of a family with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type 3. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14(3): Bogdanova N, Dworniczak B, Dragova D, Todorov V, Dimitrakov D, Kalinov K, et al. Genetic heterogeneity of polycystic kidney disease in Bulgaria. Hum Genet. 1995;95: McConnell RS, Rubinsztein DC, Fannin TF, McKinstry CS, Kelly B, Bailey IC, et al. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease unlinked to the PKD1 and PKD2 loci presenting as familial cerebral aneurysm. J Med Genet. 2001;38(4): Journal of Nephropathology, Vol 6, No 4, October
5 Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in ARPKD 5. Boal DK, Teele RL.Sonography of infantile polycystic kidney disease. AJR. 1980;135: Halvorson CR, Bremmer MS, Jacobs SC. Polycystic kidney disease: inheritance, pathophysiology, prognosis, and treatment. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2010;3: Sweeney WE Jr, Avner ED. Diagnosis and management of childhood polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 5(226;2011.): doi: /s Sweeney WE Jr, Avner ED. Pathophysiology of childhood polycystic kidney diseases: new insights into disease-specific therapy. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26(5): doi: /s Sweeney W Jr, Gunay-Aygun M, Patil A, Avner ED. Childhood polycystic kidney disease. In: Avner ED, Harmon WE, Niaudet P, Yoshikawa N, Francesco E, Goldstein S, eds. Pediatric Nephrology. 7th ed. Berlin: Springer; 2016: O Brien K, Font-Montgomery E, Lukose L, Bryant J, Piwnica-Worms K, Edwards H, et al. Congenital hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54(1):83-9. doi: / MPG.0b013e c. 11. Pretorius DH, Lee ME, Manco-Johnson ML, Weingast GR, Sedman AB, Gabow PA. Diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney diseases in utero and in the young infants. J Ultrasound Med. 1987;6(5): Zerres K, Rudnik-Schöneborn S, Deget F, Holtkamp U, Brodehl J, Geisert J, et al. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in 115 children: clinical presentation, course and influence of gender. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85(4): Copyright 2017 The Author(s); Published by Society of Diabetic Nephropathy Prevention. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Journal of Nephropathology, Vol 6, No 4, October
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Hereditary polycystic kidney diseases in children: changing sonographic patterns through childhood
 Pediatr Radiol (2002) 32: 169 174 DOI 10.1007/s00247-001-0624-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fred E. Avni Gretel Guissard Michelle Hall Franc oise Janssen Viviane DeMaertelaer Franc oise Rypens Hereditary polycystic
Pediatr Radiol (2002) 32: 169 174 DOI 10.1007/s00247-001-0624-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fred E. Avni Gretel Guissard Michelle Hall Franc oise Janssen Viviane DeMaertelaer Franc oise Rypens Hereditary polycystic
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Kidney Disorders. Renal cysts. Policystic Kidney Diseases. Cystic Renal Dysplasia. Autosomal-Dominant (Adult) Polycystic
 Policystic Kidney Diseases Kidney Disorders CONGENITAL CYSTIC GLOMERULAR TUBULES/INTERSTITIUM BLOOD VESSELS OBSTRUCTION TUMORS Lecture : Genito-urinary system. 11 08 2010. Renal cysts Cystic Renal Dysplasia
Policystic Kidney Diseases Kidney Disorders CONGENITAL CYSTIC GLOMERULAR TUBULES/INTERSTITIUM BLOOD VESSELS OBSTRUCTION TUMORS Lecture : Genito-urinary system. 11 08 2010. Renal cysts Cystic Renal Dysplasia
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry
 ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
Dr. Najla a Aldaoud. Omar Ayman Khasawneh
 Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease: Issues Regarding the Variability of Clinical Presentation1
 EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Tomas Berl. Editor William Heinrich Mark Paller Fred Silva Denver. CO Dallas. TX Minneapolis. MN Oklahoma City. OK DESCRIPTION OF THE NEPHROLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF
EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Tomas Berl. Editor William Heinrich Mark Paller Fred Silva Denver. CO Dallas. TX Minneapolis. MN Oklahoma City. OK DESCRIPTION OF THE NEPHROLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL. Living well with Kidney Disease
 HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System
 A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children
 Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of the M.Sc degree in Pediatrics Submitted by Ahmed Ibrahim Abulkhir Khayyal Under
Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of the M.Sc degree in Pediatrics Submitted by Ahmed Ibrahim Abulkhir Khayyal Under
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE. Jules B. Puschett, M.D.
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE Jules B. Puschett, M.D. Diuretic Resistance A clinical circumstance in which patients do not respond to a combination of salt restriction and even large
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE Jules B. Puschett, M.D. Diuretic Resistance A clinical circumstance in which patients do not respond to a combination of salt restriction and even large
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound. Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE. Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham What are polycystic kidneys and livers?! Cystic degenerative condition!
SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham What are polycystic kidneys and livers?! Cystic degenerative condition!
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in infancy and childhood: Progression and outcome 1
 Kidney International, Vol. 68 (25), pp. 2218 2224 CLINICAL NEPHROLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY CLINICAL TRIALS Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in infancy and childhood: Progression and outcome 1 ABDOLLAH
Kidney International, Vol. 68 (25), pp. 2218 2224 CLINICAL NEPHROLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY CLINICAL TRIALS Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in infancy and childhood: Progression and outcome 1 ABDOLLAH
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
2 nd ARPKD Family Information Day Saturday 6 th July Welcome!
 2 nd ARPKD Family Information Day Saturday 6 th July 2013 Welcome! Programme - morning Welcome - Tess Harris, Chief Executive PKD Charity Overview of ARPKD and Programme Dr Larissa Kerecuk, Consultant
2 nd ARPKD Family Information Day Saturday 6 th July 2013 Welcome! Programme - morning Welcome - Tess Harris, Chief Executive PKD Charity Overview of ARPKD and Programme Dr Larissa Kerecuk, Consultant
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Learning Objectives: At the end of this exercise, the student will be able to:
 Applications in Transfusion Medicine- A CBL Exercise- Student Guide 1 Title: Applications in Transfusion Medicine A CBL Exercise Purpose: At the conclusion of this exercise, students will be able to apply
Applications in Transfusion Medicine- A CBL Exercise- Student Guide 1 Title: Applications in Transfusion Medicine A CBL Exercise Purpose: At the conclusion of this exercise, students will be able to apply
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA
 Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Robert W. Schrier, MD University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Prevalence of acute renal failure in Intensive
Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Robert W. Schrier, MD University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Prevalence of acute renal failure in Intensive
16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children
 16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
What is ARPKD/CHF? A Brief Overview of ARPKD and CHF:
 What is ARPKD/CHF? A Brief Overview of ARPKD and CHF: Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects approximately 1:6,000 to 1:40,000 persons in the general
What is ARPKD/CHF? A Brief Overview of ARPKD and CHF: Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects approximately 1:6,000 to 1:40,000 persons in the general
Shuma Hirashio 1,2, Shigehiro Doi 1 and Takao Masaki 1*
 Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Nephrology Grand Rounds. Vasishta Tatapudi, MD January 24 th, 2013
 Nephrology Grand Rounds Vasishta Tatapudi, MD January 24 th, 2013 Case Summary Chief complaint: A twenty-six year old African American female veteran presented to ER with left flank pain for two days.
Nephrology Grand Rounds Vasishta Tatapudi, MD January 24 th, 2013 Case Summary Chief complaint: A twenty-six year old African American female veteran presented to ER with left flank pain for two days.
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Contrast Induced Nephropathy
 Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD. Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018
 Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Genetics in Nephrology. Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory
 Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1035 1039 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.112 Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report D. Jain*, S. Dorairajan, and
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1035 1039 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.112 Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report D. Jain*, S. Dorairajan, and
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree
 Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Smith D, Chudgar A, Daly B, Cooper M. Evaluation of potential renal transplant recipients with computed tomography angiography. Arch Intern Med. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2012.1466.
Supplementary Online Content Smith D, Chudgar A, Daly B, Cooper M. Evaluation of potential renal transplant recipients with computed tomography angiography. Arch Intern Med. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2012.1466.
Acute Kidney Injury. Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1
 Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
Definitions. You & Your New Transplant ` 38
 Definitions Acute Short, relatively severe Analgesic Pain medicine Anemia A low number of red blood cells Anesthetic Medication that dulls sensation in order to reduce pain Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
Definitions Acute Short, relatively severe Analgesic Pain medicine Anemia A low number of red blood cells Anesthetic Medication that dulls sensation in order to reduce pain Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management
 AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function. GI Tract and Kidneys
 Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1
 ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
What s Your Diagnosis??? Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012
 Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Urinary System. Dr. Thorson
 Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
What Your Kidneys Do
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
Kidneycentric. Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Renal Disease Survey Bracco Italiano Club of America Heath Committee, November 2012
 Renal Disease Survey Bracco Italiano Club of America Heath Committee, November 2012 Kidney disease is currently one of the most pressing health issues for the Bracco Italiano breed, as the etiology is
Renal Disease Survey Bracco Italiano Club of America Heath Committee, November 2012 Kidney disease is currently one of the most pressing health issues for the Bracco Italiano breed, as the etiology is
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II
 MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
A Primer to Cystic Kidney Diseases and Ciliopathies
 A Primer to Cystic Kidney Diseases and Ciliopathies ERKNet Webinar Max Liebau 04.09.2018 Liebau Pediatric Nephrology, Center for chronically ill children, Center for Molecular Medicine WG CAKUT and Ciliopathies
A Primer to Cystic Kidney Diseases and Ciliopathies ERKNet Webinar Max Liebau 04.09.2018 Liebau Pediatric Nephrology, Center for chronically ill children, Center for Molecular Medicine WG CAKUT and Ciliopathies
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
Nephrotic Syndrome. Sara Alsharhan PharmD candidate, KSU 2014
 Nephrotic Syndrome Sara Alsharhan PharmD candidate, KSU 2014 Outline Introduction Nephrotic syndrome classifications Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Management Complications Monitoring Case presentation Introduction
Nephrotic Syndrome Sara Alsharhan PharmD candidate, KSU 2014 Outline Introduction Nephrotic syndrome classifications Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Management Complications Monitoring Case presentation Introduction
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen. Jonathan Swanson, MD
 Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
27-Apr-15 1 UAF ANOMALIES OF DEVELOPMENT RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED UAF UAF
 RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder
 Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder Nilam J. Soni, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Divisions of Hospital Medicine and Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine University
Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder Nilam J. Soni, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Divisions of Hospital Medicine and Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine University
network of thin-walled capillaries closely surrounded by a pear-shaped epithelial membrane called the Bowman s capsule
 Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES
 3 Original article A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES Dr. Urvish R. Parikh [1], Dr Sudhir B. Chandana [], Dr Vinay M. Rohra [3],, Dr Jay B. Pandya [5], Dr Ankit B. Kothari [4] Assistant
3 Original article A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES Dr. Urvish R. Parikh [1], Dr Sudhir B. Chandana [], Dr Vinay M. Rohra [3],, Dr Jay B. Pandya [5], Dr Ankit B. Kothari [4] Assistant
HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Journal of Aging Research & Clinical Practice Volume 6, 2017 J Aging Res Clin Practice 2017;inpress Published online in press HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE
Journal of Aging Research & Clinical Practice Volume 6, 2017 J Aging Res Clin Practice 2017;inpress Published online in press HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE
HEDIS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE: DOCUMENTATION TIPS FOR ADULT MEASURES
 HEDIS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE: DOCUMENTATION TIPS FOR ADULT MEASURES For Health Care Providers January 2018 Helping you improve your scores, as you improve the health of your patients. Healthcare Effectiveness
HEDIS QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE: DOCUMENTATION TIPS FOR ADULT MEASURES For Health Care Providers January 2018 Helping you improve your scores, as you improve the health of your patients. Healthcare Effectiveness
1. Disorders of glomerular filtration
 RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island
 Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island Disclosure Honorarium for Consulting on the Reprise trial from Otsuka Mayo clinic preceptorship for PKD with
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island Disclosure Honorarium for Consulting on the Reprise trial from Otsuka Mayo clinic preceptorship for PKD with
Pediatric GU Dysfunction
 Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
Prag. Polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD & ADPKD. Max Christoph Liebau
 Prag Polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD & ADPKD Max Christoph Liebau Department of Pediatrics and Center for Molecular Medicine, University Hospital of Cologne Glasgow, 06th of September 2017 Cystic kidney
Prag Polycystic kidney disease: ARPKD & ADPKD Max Christoph Liebau Department of Pediatrics and Center for Molecular Medicine, University Hospital of Cologne Glasgow, 06th of September 2017 Cystic kidney
azilsartan medoxomil
 azilsartan medoxomil edarbi 40mg Tablet 80mg Tablet ANTIHYPERTENSIVE Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist FORMULATION: Each tablet contains 40mg Azilsartan medoxomil (as potassium) Each tablet contains 80mg
azilsartan medoxomil edarbi 40mg Tablet 80mg Tablet ANTIHYPERTENSIVE Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist FORMULATION: Each tablet contains 40mg Azilsartan medoxomil (as potassium) Each tablet contains 80mg
Chronic Kidney Disease. Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management Review the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) Review how CKD develops Review populations at risk for CKD Review CKD diagnosis Objectives
Chronic Kidney Disease Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management Review the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) Review how CKD develops Review populations at risk for CKD Review CKD diagnosis Objectives
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
CMQCC Preeclampsia Tool Kit: Hypertensive Disorders Across the Lifespan
 CMQCC Preeclampsia Tool Kit: Hypertensive Disorders Across the Lifespan Carol J Harvey, MS, BSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, CS Northside Hospital Atlanta Cherokee - Forsyth New! Improving Health Care Response to Preeclampsia:
CMQCC Preeclampsia Tool Kit: Hypertensive Disorders Across the Lifespan Carol J Harvey, MS, BSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, CS Northside Hospital Atlanta Cherokee - Forsyth New! Improving Health Care Response to Preeclampsia:
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131
 Julia Kaesberg Counseling Session KNH 413 February 27 th, 2014 Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131 pounds and her usual body weight is 125 pounds. Her %UBW
Julia Kaesberg Counseling Session KNH 413 February 27 th, 2014 Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131 pounds and her usual body weight is 125 pounds. Her %UBW
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Patient Education Kidney Early Education Program (KEEP) Chapter 2 bjectives: Overview 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Acute Liver Failure: Supporting Other Organs
 Acute Liver Failure: Supporting Other Organs Michael A. Gropper, MD, PhD Professor of Anesthesia and Physiology Director, Critical Care Medicine University of California San Francisco Acute Liver Failure
Acute Liver Failure: Supporting Other Organs Michael A. Gropper, MD, PhD Professor of Anesthesia and Physiology Director, Critical Care Medicine University of California San Francisco Acute Liver Failure
