SCHIZOPHRENIA, AS SEEN BY A
|
|
|
- Magdalene Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCHIZOPHRENIA, AS SEEN BY A DEPTH CAMERA AND OTHER SENSORS Daphna Weinshall 1 School of Computer Science & Engin. Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel
2 RESEARCH GOAL Motivation: current psychiatric diagnosis and monitoring is based on subjective evaluations by clinicians, without being able to base judgment on measurable physical properties Goal: investigate physical qualities, including measurements of facial expressions, movement and speech, as a physical biomarker for mental disorders (Schizophrenia and Depression) 2
3 Audio Recording Bodily Movement Non verbal behavior Machine learning Diagnostic Tools Descriptive Tools Facial Expressions 3
4 SCHIZOPHRENIA One of the most severe mental disorders Lifetime prevalence of about 1% worldwide. Negative Symptoms - loss of functions and abilities (e.g. lack of speech and motivation, blunted affect) Positive symptoms - pathological functions not present in healthy individuals (e.g. auditory hallucinations, delusions and paranoid thoughts) 4 John Forbes Nash Vincent Willem van Gogh
5 SCHIZOPHRENIA Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) BACKGROUND 5
6 OUTLINE OF TALK 1. Automated facial expression analysis in Schizophrenia: a continuous dynamic approach 2. Prosodic analysis of speech and the underlying mental state (schizophrenia and depression) 3. The dawn of big data: using accelerometer data, as measured by wearable sports watches 6
7 AUTOMATED FACIAL EXPRESSION ANALYSIS IN SCHIZOPHRENIA: A CONTINUOUS DYNAMIC APPROACH Talia Tron Shaar Menashe hospital: Avi Peled 7
8 STUDY OBJECTIVE Characterize the way schizophrenia is manifested in facial activity Develop automatic tools for quantitatively describing and analyzing relevant measures of this activity 8
9 FACIAL EXPRESSIONS? Reflect mental and emotional state Impaired in patients (flat affect, incongruity) Integral part of mental status examination Possible relation to neural mechanism Direct, non invasive measurement Challenges Technology Computational 9
10 TECHNOLOGY (FACIAL AND BODILY EXPRESSIONS) Structured light 3D camera (Carmine 1.09) Action Units - a system to taxonomize human facial movements Facial Action Units extraction out of 3D video with Faceshift TM 10
11 STRUCTURED LIGHT
12 WHAT ARE ACTION UNITS 12
13 EXTRACTED FEATURES Faceshift TM returns 4 output types: Intensity level of 51 faceshift Action Units (fs-aus): BROWS (up, down) CHEEK (squint, puff) NOSE (sneer) CHIN (raise) EYES (blink, squint, up, down, in, out) LIPS (stretch, close, open, up, down, funnel, pucker) MOUTH (left, right, frown, smile, dimple) Eye gaze and position 3D head coordinates 3D position of facial markers JAW (forward, left, right, open) 13 In our research we used only Intensity level of 51 AUs
14 FACESHIFT IN ACTION 14
15 METHOD Characterize Record Interview 3D Data Extract Facial Activity Compute Facial Features Richness Typicality Affect Predict time Patients / Control Symptom Severity 15
16 DATA ACQUISITION 34 schizophrenia patients and 33 control subjects Recorded with structured light 3D camera 15 minutes long structured Interview by trained psychiatrist Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) RGB + Depth data Carmine
17 Personal Details PANSS STRUCTURED INTERVIEW RGB + Depth data IAPS X 60 Sound איך הרגשת בזמן שהסתכלת בתמונה? 6 sec RESTING STATE 1 min EMBD X 3 איך הרגשת בזמן שצפית בסרט? 40 sec
18 OUTLINE Record Interview 3D Data Extract Facial Activity Compute Facial Features Characteriz Richness e Typicality Affect Predict time Patients / Control Symptom Severity 18
19 FACIAL ACTIVITY EXTRACTION Facial Action Coding System (FACS) Ekman and Rosenberg (1997) 19
20 FACIAL ACTIVITY EXTRACTION Raw interview data Control Patient 20 time time
21 FACIAL ACTIVITY EXTRACTION 23 Faceshift Action Units (AUs) were selected based on tracking sensitivity and noise level. 21
22 OUTLINE Characterize Record Interview 3D Data Extract Facial Activity Compute Facial Features Richness Typicality Affect Predict time Patients / Control Symptom Severity 22
23 FACIAL ACTIVITY CHARACTERIZING FEATURES We measured the diversity in facial activity throughout the video: typicality the range of subtle changes in facial activity richness the range of prototypical expressions used 23
24 RESULTS CONTROL PATIENTS 1 1. Neutral, flat 4. Sadness, fear, anger 7. Happiness, content 24
25 PREDICTION, LEARNING DETAILS Two step learning algorithm SVM for patients vs. controls classification Regularized regression (ridge) for symptom severity prediction Leave One Out (LOO) train-test paradigm 25
26 RESULTS- PREDICTION Patients vs. Control Classification Symptom Severity Prediction Predicted Score (R=0.53, p<<0.01) Psychiatrist Score 26
27 RESULTS - DESCRIPTIVE CURRENT WORK Dynamic Vs. intensity features 27
28 RESULTS - DESCRIPTIVE Dynamic Vs. intensity features Emotional affect analysis Activation Level Activation Level p<0.01 Pleasant emotions,happy Sadness, Fear, Disgust 28 Wallace V Friesen and Paul Ekman. Emfacs-7: Emotional facial action coding system. Unpublished manuscript, University of California at San Francisco, 2:36,. 1983
29 RESULTS - DESCRIPTIVE CURRENT WORK Dynamic Vs. intensity features Emotional affect analysis Smile charactarization 29
30 PART 1, RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS We measured the co-existence of flat affect and inappropriate affect in patients Flat affect is expressed by reduction of intensity, slowdown of dynamic and reduced variability of expression Facial expressions of patients showed reduced consistency ( inappropriateness ), without evidence of impaired emotional experience 30
31 PROSODIC ANALYSIS OF SPEECH AND THE UNDERLYING MENTAL STATE Roi Kliper McLean hospital, Boston: Shirley Portuguese 31
32 Audio Recording Bodily Movement Non verbal behavior Machine learning Diagnostic Tools Descriptive Tools Facial Expressions 32
33 A HISTORICAL NOTE dementia preacox patients indifferent tone and distorted turns of speech Dr. Emil Kraepelin (1913) Long held belief/observation: the human voice (prosody) conveys information about people s feelings, emotions and mental state 33
34 Standard part of the repertoire of mental status examination Reported changes in acoustic characteristics of speech prosody in the course of different mental disorders, notably depression and schizophrenia Negative symptoms Alogia poverty of speech, including the manner of speech Affective Flattening the lack of vocal inflections MADRS: Montgomery Åsberg Depression Rating Scale Apparent sadness - gloom and despair reflected in speech (as well) 34
35 SPEECH ANALYSIS Speech = prosody + content Prosody, the acoustic properties of speech Frequency of the sound wave [pitch - fundamental frequency] Amplitude of sound wave (decibels) Timing (length of speech and gaps) we measure these properties, and how they change Focus of this research: investigate properties of speech prosody which can be used to characterize and monitor mental illnesses 35
36 - Data Collection McLean Hospital Boston - healthy, depressed and Schizophrenic individuals - Feature Extraction Select the most informative subset of features for the task - Algorithm for Mental state evaluation Train from data with machine learning tools - Gain insight regarding the phenomenon Meta-analysis: look for biomarkers for mental illnesses 36
37 DATA COLLECTION Healthy Schizophrenia Depression Male Female tasks: North American Adult Reading Test (NART) list of irregularly pronounced words Passage Reading the rainbow passage all 40 phonemes of American English are utilized in proportion to their representation in everyday conversation Interview 37
38 ALTERATIONS OF SIGNAL CAN OCCUR AT DIFFERENT TIME-SCALES Macro Scale > 1 sec [semantic level] Meso-Scale 25 ms 1 sec Control Time Micro Scale [least voluntary] <10 ms 38
39 utterance gap utterance gap 39
40 UTTERANCE segment of continuous speech which exceeds 0.5 s Time (sec) 40
41 FEATURES OF SPEECH PROSODY Macro scale >1s Mean utterance duration Mean gap duration Mean spoken ratio (all utterances) Meso scale 0.25ms 1s Pitch Range Pitch standard deviation power standard deviation Micro scale Mean waveform correlation Mean jitter Mean shimmer < 10ms 41
42 RESULTS SINGLE FEATURES, MACRO SCALE Spoken ratio Utterance Length Gap length 42
43 RESULTS SINGLE FEATURES, MESO SCALE Pitch Range STD Pitch STD Power 43
44 RESULTS SINGLE FEATURES, MICRO SCALE MWC Jitter Shimmer 44
45 CORRELATION WITH STANDARD SCALES SANS alogia SANS affective flatening Spoken ratio Utterance duration Gap duration
46 46
47 PART 2, SUMMARY Investigate the potential use of speech to provide biomarkers for mental illnesses Motivation: the development of a reliable, objective, low-priced, and readily applicable assessment tool would enhance the accuracy of the clinical evaluation for diagnosis and severity Suitable technological apparatus including speech recognition software could allow this tool to be applied for screening or monitoring mental health status remotely 47
48 PART 3: THE DAWN OF BIG DATA Data: movement (accelerometer data) is recorded 24/7 by wearable sport watches Work in progress Sensor: geneactive wearable watch Measures acceleration, temperature, light 48
49 CORRELATION ANALSYS Correlation between our measurements and clinical measures: 49
50 DETECTING CHANGE OF MEDICATION 50
51 SUMMARY Results: Automatic facial activity has predictive power for diagnosis and symptom severity assessment in schizophrenia Speech prosody can be used to monitor depression and schizophrenia New technology may enable the continuous monitoring of patients 24/7 We seek to develop: Biomarkers for poorly understood mental disorders Tools for scientific investigation of the underlying causes and manifestations of the disorders 51
Prosodic Analysis of Speech and the Underlying Mental State
 Prosodic Analysis of Speech and the Underlying Mental State Roi Kliper 1, Shirley Portuguese, and Daphna Weinshall 1 1 School of Computer Science and Engineering, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 91904
Prosodic Analysis of Speech and the Underlying Mental State Roi Kliper 1, Shirley Portuguese, and Daphna Weinshall 1 1 School of Computer Science and Engineering, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 91904
Automated Analysis of Non-verbal Behavior in Schizophrenia
 HEBREW UNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM Automated Analysis of Non-verbal Behavior in Schizophrenia by: Talia TRON Thesis for the degree "Doctor of Philosophy" in Brain Sciences: Computation and Information Processing
HEBREW UNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM Automated Analysis of Non-verbal Behavior in Schizophrenia by: Talia TRON Thesis for the degree "Doctor of Philosophy" in Brain Sciences: Computation and Information Processing
Analysis of Emotion Recognition using Facial Expressions, Speech and Multimodal Information
 Analysis of Emotion Recognition using Facial Expressions, Speech and Multimodal Information C. Busso, Z. Deng, S. Yildirim, M. Bulut, C. M. Lee, A. Kazemzadeh, S. Lee, U. Neumann, S. Narayanan Emotion
Analysis of Emotion Recognition using Facial Expressions, Speech and Multimodal Information C. Busso, Z. Deng, S. Yildirim, M. Bulut, C. M. Lee, A. Kazemzadeh, S. Lee, U. Neumann, S. Narayanan Emotion
Virtual Reality Testing of Multi-Modal Integration in Schizophrenic Patients
 Virtual Reality Testing of Multi-Modal Integration in Schizophrenic Patients Anna SORKIN¹, Avi PELED 2, Daphna WEINSHALL¹ 1 Interdisciplinary Center for Neural Computation, Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
Virtual Reality Testing of Multi-Modal Integration in Schizophrenic Patients Anna SORKIN¹, Avi PELED 2, Daphna WEINSHALL¹ 1 Interdisciplinary Center for Neural Computation, Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION FROM IMAGE SEQUENCES USING SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS
 International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Vol. XXXII, Part 5. Hakodate 1998 FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION FROM IMAGE SEQUENCES USING SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS Ayako KATOH*, Yasuhiro FUKUI**
International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Vol. XXXII, Part 5. Hakodate 1998 FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION FROM IMAGE SEQUENCES USING SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS Ayako KATOH*, Yasuhiro FUKUI**
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUDIO, SPEECH, AND LANGUAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 19, NO. 5, JULY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUDIO, SPEECH, AND LANGUAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 19, NO. 5, JULY 2011 1057 A Framework for Automatic Human Emotion Classification Using Emotion Profiles Emily Mower, Student Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUDIO, SPEECH, AND LANGUAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 19, NO. 5, JULY 2011 1057 A Framework for Automatic Human Emotion Classification Using Emotion Profiles Emily Mower, Student Member, IEEE,
Effect of Sensor Fusion for Recognition of Emotional States Using Voice, Face Image and Thermal Image of Face
 Effect of Sensor Fusion for Recognition of Emotional States Using Voice, Face Image and Thermal Image of Face Yasunari Yoshitomi 1, Sung-Ill Kim 2, Takako Kawano 3 and Tetsuro Kitazoe 1 1:Department of
Effect of Sensor Fusion for Recognition of Emotional States Using Voice, Face Image and Thermal Image of Face Yasunari Yoshitomi 1, Sung-Ill Kim 2, Takako Kawano 3 and Tetsuro Kitazoe 1 1:Department of
Face to Face: Technology to support exercises for facial weakness
 Face to Face: Technology to support exercises for facial weakness Edmans J 1, Logan P 1, Breedon P 2, Hall P 3, Newell O 1, Childs B 3, Russell A 2, O Brien B 4, Watts P 2. 1 Division of Rehabilitation
Face to Face: Technology to support exercises for facial weakness Edmans J 1, Logan P 1, Breedon P 2, Hall P 3, Newell O 1, Childs B 3, Russell A 2, O Brien B 4, Watts P 2. 1 Division of Rehabilitation
An assistive application identifying emotional state and executing a methodical healing process for depressive individuals.
 An assistive application identifying emotional state and executing a methodical healing process for depressive individuals. Bandara G.M.M.B.O bhanukab@gmail.com Godawita B.M.D.T tharu9363@gmail.com Gunathilaka
An assistive application identifying emotional state and executing a methodical healing process for depressive individuals. Bandara G.M.M.B.O bhanukab@gmail.com Godawita B.M.D.T tharu9363@gmail.com Gunathilaka
ANALYSIS OF FACIAL FEATURES OF DRIVERS UNDER COGNITIVE AND VISUAL DISTRACTIONS
 ANALYSIS OF FACIAL FEATURES OF DRIVERS UNDER COGNITIVE AND VISUAL DISTRACTIONS Nanxiang Li and Carlos Busso Multimodal Signal Processing (MSP) Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering, The University
ANALYSIS OF FACIAL FEATURES OF DRIVERS UNDER COGNITIVE AND VISUAL DISTRACTIONS Nanxiang Li and Carlos Busso Multimodal Signal Processing (MSP) Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering, The University
Who Needs Cheeks? Eyes and Mouths are Enough for Emotion Identification. and. Evidence for a Face Superiority Effect. Nila K Leigh
 1 Who Needs Cheeks? Eyes and Mouths are Enough for Emotion Identification and Evidence for a Face Superiority Effect Nila K Leigh 131 Ave B (Apt. 1B) New York, NY 10009 Stuyvesant High School 345 Chambers
1 Who Needs Cheeks? Eyes and Mouths are Enough for Emotion Identification and Evidence for a Face Superiority Effect Nila K Leigh 131 Ave B (Apt. 1B) New York, NY 10009 Stuyvesant High School 345 Chambers
Computational models of emotion
 HUMAINE Plenary Newcastle, May 24-27, 2004 Computational models of emotion Klaus R. Scherer University of Posing the problem: Three types of computational models Appraisal cirteria Integration rules Sequential
HUMAINE Plenary Newcastle, May 24-27, 2004 Computational models of emotion Klaus R. Scherer University of Posing the problem: Three types of computational models Appraisal cirteria Integration rules Sequential
Valence and Gender Effects on Emotion Recognition Following TBI. Cassie Brown Arizona State University
 Valence and Gender Effects on Emotion Recognition Following TBI Cassie Brown Arizona State University Knox & Douglas (2009) Social Integration and Facial Expression Recognition Participants: Severe TBI
Valence and Gender Effects on Emotion Recognition Following TBI Cassie Brown Arizona State University Knox & Douglas (2009) Social Integration and Facial Expression Recognition Participants: Severe TBI
Spotting Liars and Deception Detection skills - people reading skills in the risk context. Alan Hudson
 Spotting Liars and Deception Detection skills - people reading skills in the risk context Alan Hudson < AH Business Psychology 2016> This presentation has been prepared for the Actuaries Institute 2016
Spotting Liars and Deception Detection skills - people reading skills in the risk context Alan Hudson < AH Business Psychology 2016> This presentation has been prepared for the Actuaries Institute 2016
Drive-reducing behaviors (eating, drinking) Drive (hunger, thirst) Need (food, water)
 Instinct Theory: we are motivated by our inborn automated behaviors that generally lead to survival. But instincts only explain why we do a small fraction of our behaviors. Does this behavior adequately
Instinct Theory: we are motivated by our inborn automated behaviors that generally lead to survival. But instincts only explain why we do a small fraction of our behaviors. Does this behavior adequately
Atypical processing of prosodic changes in natural speech stimuli in school-age children with Asperger syndrome
 Atypical processing of prosodic changes in natural speech stimuli in school-age children with Asperger syndrome Riikka Lindström, PhD student Cognitive Brain Research Unit University of Helsinki 31.8.2012
Atypical processing of prosodic changes in natural speech stimuli in school-age children with Asperger syndrome Riikka Lindström, PhD student Cognitive Brain Research Unit University of Helsinki 31.8.2012
R Jagdeesh Kanan* et al. International Journal of Pharmacy & Technology
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com FACIAL EMOTION RECOGNITION USING NEURAL NETWORK Kashyap Chiranjiv Devendra, Azad Singh Tomar, Pratigyna.N.Javali,
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com FACIAL EMOTION RECOGNITION USING NEURAL NETWORK Kashyap Chiranjiv Devendra, Azad Singh Tomar, Pratigyna.N.Javali,
Discovering Facial Expressions for States of Amused, Persuaded, Informed, Sentimental and Inspired
 Discovering Facial Expressions for States of Amused, Persuaded, Informed, Sentimental and Inspired Daniel McDuff Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA This work was performed while at Affectiva damcduff@microsoftcom
Discovering Facial Expressions for States of Amused, Persuaded, Informed, Sentimental and Inspired Daniel McDuff Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA This work was performed while at Affectiva damcduff@microsoftcom
The innate hypothesis
 The innate hypothesis DARWIN (1872) proposed that the facial expression of emotion evolved as part of the actions necessary for life: Anger: Frowning (to protect eyes in anticipation of attack) Surprise:
The innate hypothesis DARWIN (1872) proposed that the facial expression of emotion evolved as part of the actions necessary for life: Anger: Frowning (to protect eyes in anticipation of attack) Surprise:
Understanding Facial Expressions and Microexpressions
 Understanding Facial Expressions and Microexpressions 1 You can go to a book store and find many books on bodylanguage, communication and persuasion. Many of them seem to cover the same material though:
Understanding Facial Expressions and Microexpressions 1 You can go to a book store and find many books on bodylanguage, communication and persuasion. Many of them seem to cover the same material though:
Emotion Affective Color Transfer Using Feature Based Facial Expression Recognition
 , pp.131-135 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013.39.24 Emotion Affective Color Transfer Using Feature Based Facial Expression Recognition SeungTaek Ryoo and Jae-Khun Chang School of Computer Engineering
, pp.131-135 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013.39.24 Emotion Affective Color Transfer Using Feature Based Facial Expression Recognition SeungTaek Ryoo and Jae-Khun Chang School of Computer Engineering
Towards Socio- and Neuro-feedback Treatment for Schizophrenia. By: PhD Student: Yasir Tahir Supervisor: Asst.Prof Justin Dauwels
 Towards Socio- and Neuro-feedback Treatment for Schizophrenia By: PhD Student: Yasir Tahir Supervisor: Asst.Prof Justin Dauwels 1 Introduction Schizophrenia is a chronic and disabling mental disorder that
Towards Socio- and Neuro-feedback Treatment for Schizophrenia By: PhD Student: Yasir Tahir Supervisor: Asst.Prof Justin Dauwels 1 Introduction Schizophrenia is a chronic and disabling mental disorder that
Perception of Music: Problems and Prospects
 A neuroscience perspective on using music to achieve emotional objectives Perception of Music: Problems and Prospects Frank Russo Ryerson University Frank Russo SMARTLab Ryerson University Room 217 February
A neuroscience perspective on using music to achieve emotional objectives Perception of Music: Problems and Prospects Frank Russo Ryerson University Frank Russo SMARTLab Ryerson University Room 217 February
A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition
 RESEARCH ARTICLE A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition Sameer Sethi 1 *, Dr. Simon Rigoulot 2, Dr. Marc D. Pell 3 1 Faculty of Science, McGill University,
RESEARCH ARTICLE A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition Sameer Sethi 1 *, Dr. Simon Rigoulot 2, Dr. Marc D. Pell 3 1 Faculty of Science, McGill University,
This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source:
 This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source: Bellocchi, Alberto (2015) Methods for sociological inquiry on emotion in educational settings.
This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source: Bellocchi, Alberto (2015) Methods for sociological inquiry on emotion in educational settings.
I Can Read You Like a Book: The Craft of Reading Body Language
 I Can Read You Like a Book: The Craft of Reading Body Language By: Greg Hartley Mind at War Presented at: ACLEA 47 th Mid Year Meeting January 22 25, 2011 San Francisco, California Greg Hartley Mind at
I Can Read You Like a Book: The Craft of Reading Body Language By: Greg Hartley Mind at War Presented at: ACLEA 47 th Mid Year Meeting January 22 25, 2011 San Francisco, California Greg Hartley Mind at
Gender Based Emotion Recognition using Speech Signals: A Review
 50 Gender Based Emotion Recognition using Speech Signals: A Review Parvinder Kaur 1, Mandeep Kaur 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 2 Department
50 Gender Based Emotion Recognition using Speech Signals: A Review Parvinder Kaur 1, Mandeep Kaur 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 2 Department
A Dynamic Model for Identification of Emotional Expressions
 A Dynamic Model for Identification of Emotional Expressions Rafael A.M. Gonçalves, Diego R. Cueva, Marcos R. Pereira-Barretto, and Fabio G. Cozman Abstract This paper discusses the dynamics of emotion
A Dynamic Model for Identification of Emotional Expressions Rafael A.M. Gonçalves, Diego R. Cueva, Marcos R. Pereira-Barretto, and Fabio G. Cozman Abstract This paper discusses the dynamics of emotion
Emotion Recognition using a Cauchy Naive Bayes Classifier
 Emotion Recognition using a Cauchy Naive Bayes Classifier Abstract Recognizing human facial expression and emotion by computer is an interesting and challenging problem. In this paper we propose a method
Emotion Recognition using a Cauchy Naive Bayes Classifier Abstract Recognizing human facial expression and emotion by computer is an interesting and challenging problem. In this paper we propose a method
This is the accepted version of this article. To be published as : This is the author version published as:
 QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/ This is the author version published as: This is the accepted version of this article. To be published as : This is the author version published as: Chew,
QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/ This is the author version published as: This is the accepted version of this article. To be published as : This is the author version published as: Chew,
Affective Game Engines: Motivation & Requirements
 Affective Game Engines: Motivation & Requirements Eva Hudlicka Psychometrix Associates Blacksburg, VA hudlicka@ieee.org psychometrixassociates.com DigiPen Institute of Technology February 20, 2009 1 Outline
Affective Game Engines: Motivation & Requirements Eva Hudlicka Psychometrix Associates Blacksburg, VA hudlicka@ieee.org psychometrixassociates.com DigiPen Institute of Technology February 20, 2009 1 Outline
Routine For: Stroke Oral Motor Routine
 GENERAL TIPS FOR PATIENTS, STUDENTS, OR CAREGIVERS GENERAL TIPS (Continued) ALWAYS wash hands before practicing. Practice while sitting in chair. Head should be in midline and chin parallel to floor Use
GENERAL TIPS FOR PATIENTS, STUDENTS, OR CAREGIVERS GENERAL TIPS (Continued) ALWAYS wash hands before practicing. Practice while sitting in chair. Head should be in midline and chin parallel to floor Use
Brain and Cognition, 48(2-3), (2002) Evaluation of nonverbal emotion in face and voice: some preliminary findings on a new battery of tests
 Brain and Cognition, 48(2-3), 499-514 (2002) Evaluation of nonverbal emotion in face and voice: some preliminary findings on a new battery of tests Marc David Pell McGill University, Montréal Abstract
Brain and Cognition, 48(2-3), 499-514 (2002) Evaluation of nonverbal emotion in face and voice: some preliminary findings on a new battery of tests Marc David Pell McGill University, Montréal Abstract
Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors
 Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors Guoying Zhao, Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, P. O. Box
Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors Guoying Zhao, Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, P. O. Box
Prediction of Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia from Facial Expressions and Speech Signals
 Prediction of Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia from Facial Expressions and Speech Signals Debsubhra CHAKRABORTY PhD student Institute for Media Innovation/ Interdisciplinary Graduate School Supervisor:
Prediction of Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia from Facial Expressions and Speech Signals Debsubhra CHAKRABORTY PhD student Institute for Media Innovation/ Interdisciplinary Graduate School Supervisor:
Audio-based Emotion Recognition for Advanced Automatic Retrieval in Judicial Domain
 Audio-based Emotion Recognition for Advanced Automatic Retrieval in Judicial Domain F. Archetti 1,2, G. Arosio 1, E. Fersini 1, E. Messina 1 1 DISCO, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca, Viale Sarca,
Audio-based Emotion Recognition for Advanced Automatic Retrieval in Judicial Domain F. Archetti 1,2, G. Arosio 1, E. Fersini 1, E. Messina 1 1 DISCO, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca, Viale Sarca,
Autism. Childhood Autism and Schizophrenia. Autism, Part 1 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-IV-TR) Behavioral Characteristics of Autism
 Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Human Emotion Recognition from Body Language of the Head using Soft Computing Techniques
 Human Emotion Recognition from Body Language of the Head using Soft Computing Techniques Yisu Zhao Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies In partial fulfillment of the requirements
Human Emotion Recognition from Body Language of the Head using Soft Computing Techniques Yisu Zhao Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies In partial fulfillment of the requirements
Facial Behavior as a Soft Biometric
 Facial Behavior as a Soft Biometric Abhay L. Kashyap University of Maryland, Baltimore County 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 abhay1@umbc.edu Sergey Tulyakov, Venu Govindaraju University at Buffalo
Facial Behavior as a Soft Biometric Abhay L. Kashyap University of Maryland, Baltimore County 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 abhay1@umbc.edu Sergey Tulyakov, Venu Govindaraju University at Buffalo
Introduction to Psychology. Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS
 Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS o Derived from the Latin word Emovere emotion means to excite, stir up or agitate. o A response that includes feelings such as happiness, fear, sadness, grief, sorrow etc: it is
Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS o Derived from the Latin word Emovere emotion means to excite, stir up or agitate. o A response that includes feelings such as happiness, fear, sadness, grief, sorrow etc: it is
Speech (Sound) Processing
 7 Speech (Sound) Processing Acoustic Human communication is achieved when thought is transformed through language into speech. The sounds of speech are initiated by activity in the central nervous system,
7 Speech (Sound) Processing Acoustic Human communication is achieved when thought is transformed through language into speech. The sounds of speech are initiated by activity in the central nervous system,
REAL-TIME SMILE SONIFICATION USING SURFACE EMG SIGNAL AND THE EVALUATION OF ITS USABILITY.
 REAL-TIME SMILE SONIFICATION USING SURFACE EMG SIGNAL AND THE EVALUATION OF ITS USABILITY Yuki Nakayama 1 Yuji Takano 2 Masaki Matsubara 3 Kenji Suzuki 4 Hiroko Terasawa 3,5 1 Graduate School of Library,
REAL-TIME SMILE SONIFICATION USING SURFACE EMG SIGNAL AND THE EVALUATION OF ITS USABILITY Yuki Nakayama 1 Yuji Takano 2 Masaki Matsubara 3 Kenji Suzuki 4 Hiroko Terasawa 3,5 1 Graduate School of Library,
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
A framework for the Recognition of Human Emotion using Soft Computing models
 A framework for the Recognition of Human Emotion using Soft Computing models Md. Iqbal Quraishi Dept. of Information Technology Kalyani Govt Engg. College J Pal Choudhury Dept. of Information Technology
A framework for the Recognition of Human Emotion using Soft Computing models Md. Iqbal Quraishi Dept. of Information Technology Kalyani Govt Engg. College J Pal Choudhury Dept. of Information Technology
Detection of Facial Landmarks from Neutral, Happy, and Disgust Facial Images
 Detection of Facial Landmarks from Neutral, Happy, and Disgust Facial Images Ioulia Guizatdinova and Veikko Surakka Research Group for Emotions, Sociality, and Computing Tampere Unit for Computer-Human
Detection of Facial Landmarks from Neutral, Happy, and Disgust Facial Images Ioulia Guizatdinova and Veikko Surakka Research Group for Emotions, Sociality, and Computing Tampere Unit for Computer-Human
GfK Verein. Detecting Emotions from Voice
 GfK Verein Detecting Emotions from Voice Respondents willingness to complete questionnaires declines But it doesn t necessarily mean that consumers have nothing to say about products or brands: GfK Verein
GfK Verein Detecting Emotions from Voice Respondents willingness to complete questionnaires declines But it doesn t necessarily mean that consumers have nothing to say about products or brands: GfK Verein
Research Proposal on Emotion Recognition
 Research Proposal on Emotion Recognition Colin Grubb June 3, 2012 Abstract In this paper I will introduce my thesis question: To what extent can emotion recognition be improved by combining audio and visual
Research Proposal on Emotion Recognition Colin Grubb June 3, 2012 Abstract In this paper I will introduce my thesis question: To what extent can emotion recognition be improved by combining audio and visual
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Overview. Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions
 Emotion Overview Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions Definition of Emotion Emotions are biologically-based responses
Emotion Overview Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions Definition of Emotion Emotions are biologically-based responses
MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION
 MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION EMOTION: a response of the whole organism, involving 1. physiological arousal 2. expressive behaviors, and 3. conscious experience A mix of bodily arousal
MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION EMOTION: a response of the whole organism, involving 1. physiological arousal 2. expressive behaviors, and 3. conscious experience A mix of bodily arousal
CHAPTER 1 MULTIMODAL EMOTION RECOGNITION
 CHAPTER 1 MULTIMODAL EMOTION RECOGNITION Nicu Sebe 1, Ira Cohen 2, and Thomas S. Huang 3 1 Faculty of Science, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands E-mail: nicu@science.uva.nl 2 HP Labs, USA E-mail:
CHAPTER 1 MULTIMODAL EMOTION RECOGNITION Nicu Sebe 1, Ira Cohen 2, and Thomas S. Huang 3 1 Faculty of Science, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands E-mail: nicu@science.uva.nl 2 HP Labs, USA E-mail:
Unit III Verbal and Non-verbal Communication
 (1) Unit III Verbal and Non-verbal Communication Communication by using language is called Verbal communication. Communication through other symbols without using words is called Non-verbal communication.
(1) Unit III Verbal and Non-verbal Communication Communication by using language is called Verbal communication. Communication through other symbols without using words is called Non-verbal communication.
Negative Symptom Assessment-16 (NSA-16) Long Form
 Negative Symptom Assessment-16 (NSA-16) Long Form 1. Prolonged time to respond. After asking the subject a question, he/she pauses for inappropriately long periods before answering. Rate severity of the
Negative Symptom Assessment-16 (NSA-16) Long Form 1. Prolonged time to respond. After asking the subject a question, he/she pauses for inappropriately long periods before answering. Rate severity of the
EMOTION CLASSIFICATION: HOW DOES AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM COMPARE TO NAÏVE HUMAN CODERS?
 EMOTION CLASSIFICATION: HOW DOES AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM COMPARE TO NAÏVE HUMAN CODERS? Sefik Emre Eskimez, Kenneth Imade, Na Yang, Melissa Sturge- Apple, Zhiyao Duan, Wendi Heinzelman University of Rochester,
EMOTION CLASSIFICATION: HOW DOES AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM COMPARE TO NAÏVE HUMAN CODERS? Sefik Emre Eskimez, Kenneth Imade, Na Yang, Melissa Sturge- Apple, Zhiyao Duan, Wendi Heinzelman University of Rochester,
Automatic Emotion Recognition Using Facial Expression: A Review
 Automatic Emotion Recognition Using Facial Expression: A Review Monika Dubey 1, Prof. Lokesh Singh 2 1Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Technocrats Institute of Technology, Bhopal, India 2Asst.Professor,
Automatic Emotion Recognition Using Facial Expression: A Review Monika Dubey 1, Prof. Lokesh Singh 2 1Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Technocrats Institute of Technology, Bhopal, India 2Asst.Professor,
K ING'S. Derek Goldsmith LONDON. College. FoundedI 82. Neuroscience & Emotion INSTITUTE OF PSYCHIATRY
 K ING'S College LONDON INSTITUTE OF PSYCHIATRY FoundedI 82 Neuroscience & Emotion Derek Goldsmith Remediation of poor emotion processing in schizophrenia: behavioural and eye movement findings Tamara Russell
K ING'S College LONDON INSTITUTE OF PSYCHIATRY FoundedI 82 Neuroscience & Emotion Derek Goldsmith Remediation of poor emotion processing in schizophrenia: behavioural and eye movement findings Tamara Russell
Accessible Computing Research for Users who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH)
 Accessible Computing Research for Users who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) Matt Huenerfauth Raja Kushalnagar Rochester Institute of Technology DHH Auditory Issues Links Accents/Intonation Listening
Accessible Computing Research for Users who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) Matt Huenerfauth Raja Kushalnagar Rochester Institute of Technology DHH Auditory Issues Links Accents/Intonation Listening
Study on Aging Effect on Facial Expression Recognition
 Study on Aging Effect on Facial Expression Recognition Nora Algaraawi, Tim Morris Abstract Automatic facial expression recognition (AFER) is an active research area in computer vision. However, aging causes
Study on Aging Effect on Facial Expression Recognition Nora Algaraawi, Tim Morris Abstract Automatic facial expression recognition (AFER) is an active research area in computer vision. However, aging causes
Schizophrenia. This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available.
 This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
Selection of Emotionally Salient Audio-Visual Features for Modeling Human Evaluations of Synthetic Character Emotion Displays
 Selection of Emotionally Salient Audio-Visual Features for Modeling Human Evaluations of Synthetic Character Emotion Displays Emily Mower #1, Maja J Matarić 2,Shrikanth Narayanan # 3 # Department of Electrical
Selection of Emotionally Salient Audio-Visual Features for Modeling Human Evaluations of Synthetic Character Emotion Displays Emily Mower #1, Maja J Matarić 2,Shrikanth Narayanan # 3 # Department of Electrical
Audiovisual to Sign Language Translator
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series July 17, 2018 Audiovisual to Sign Language Translator Manikandan Gopalakrishnan Follow this and additional works at: https://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series July 17, 2018 Audiovisual to Sign Language Translator Manikandan Gopalakrishnan Follow this and additional works at: https://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Autism is not a single condition but a collection of conditions that have common behavioural characteristics.
 AUTISM Autism is not a single condition but a collection of conditions that have common behavioural characteristics. Autism can affect people across a wide range of intellectual abilities and skills. All
AUTISM Autism is not a single condition but a collection of conditions that have common behavioural characteristics. Autism can affect people across a wide range of intellectual abilities and skills. All
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Duran, N.D. and Street, Chris N. H. Nonverbal cues Original Citation Duran, N.D. and Street, Chris N. H. (2014) Nonverbal cues. In: Encyclopedia of Deception. Sage,
University of Huddersfield Repository Duran, N.D. and Street, Chris N. H. Nonverbal cues Original Citation Duran, N.D. and Street, Chris N. H. (2014) Nonverbal cues. In: Encyclopedia of Deception. Sage,
Debsubhra Chakraborty Institute for Media Innovation, Interdisciplinary Graduate School Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
 Debsubhra Chakraborty Institute for Media Innovation, Interdisciplinary Graduate School Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 20 th November 2018 Introduction Design of Experiment System Overview
Debsubhra Chakraborty Institute for Media Innovation, Interdisciplinary Graduate School Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 20 th November 2018 Introduction Design of Experiment System Overview
Culture and Emotion THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN EMOTION. Outline
 Outline Culture and Emotion The Evolution of Human Emotion Universality in Emotion- The Basic Emotions Perspective Cultural Differences in Emotion Conclusion Chapter 8 THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN EMOTION Emotion:
Outline Culture and Emotion The Evolution of Human Emotion Universality in Emotion- The Basic Emotions Perspective Cultural Differences in Emotion Conclusion Chapter 8 THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN EMOTION Emotion:
CAINS (v1.0) DATE: RATER:
 CAINS (v1.0) 1 ID: DATE: RATER: Overall Introduction: In this interview, I ll be asking you some questions about things you have been doing over the past week. In the first section, I m going to ask you
CAINS (v1.0) 1 ID: DATE: RATER: Overall Introduction: In this interview, I ll be asking you some questions about things you have been doing over the past week. In the first section, I m going to ask you
Generalization of a Vision-Based Computational Model of Mind-Reading
 Generalization of a Vision-Based Computational Model of Mind-Reading Rana el Kaliouby and Peter Robinson Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge, 5 JJ Thomson Avenue, Cambridge UK CB3 FD Abstract.
Generalization of a Vision-Based Computational Model of Mind-Reading Rana el Kaliouby and Peter Robinson Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge, 5 JJ Thomson Avenue, Cambridge UK CB3 FD Abstract.
Assistive Wearable Technology
 Assistive Wearable Technology Stephan Koster skoster@student.ethz.ch 21.05.2013 Distributed Systems Seminar 1 Assistive Wearable Technology: Principles Measure Sensors Deduce Activity/Environment Walking?
Assistive Wearable Technology Stephan Koster skoster@student.ethz.ch 21.05.2013 Distributed Systems Seminar 1 Assistive Wearable Technology: Principles Measure Sensors Deduce Activity/Environment Walking?
Quantification of facial expressions using high-dimensional shape transformations
 Journal of Neuroscience Methods xxx (2004) xxx xxx Quantification of facial expressions using high-dimensional shape transformations Ragini Verma a,, Christos Davatzikos a,1, James Loughead b,2, Tim Indersmitten
Journal of Neuroscience Methods xxx (2004) xxx xxx Quantification of facial expressions using high-dimensional shape transformations Ragini Verma a,, Christos Davatzikos a,1, James Loughead b,2, Tim Indersmitten
Facial Expression and Consumer Attitudes toward Cultural Goods
 Facial Expression and Consumer Attitudes toward Cultural Goods Chih-Hsiang Ko, Chia-Yin Yu Department of Industrial and Commercial Design, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, 43 Keelung
Facial Expression and Consumer Attitudes toward Cultural Goods Chih-Hsiang Ko, Chia-Yin Yu Department of Industrial and Commercial Design, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, 43 Keelung
Voice. What is voice? Why is voice important?
 Voice What is voice? Voice is the sound that we hear when someone talks. It is produced by air coming from the diaphragm and lungs passing through the voice box (vocal folds) causing them to vibrate and
Voice What is voice? Voice is the sound that we hear when someone talks. It is produced by air coming from the diaphragm and lungs passing through the voice box (vocal folds) causing them to vibrate and
Health Behavior Informatics
 Health Behavior Informatics Louis-Philippe (LP) Morency CMU Multimodal Communication and Machine Learning Laboratory [MultiComp Lab] PhD students: Chaitanya Ahuja, AmirAli BagherZadeh, Volkan Cirik, Sayan
Health Behavior Informatics Louis-Philippe (LP) Morency CMU Multimodal Communication and Machine Learning Laboratory [MultiComp Lab] PhD students: Chaitanya Ahuja, AmirAli BagherZadeh, Volkan Cirik, Sayan
Sociable Robots Peeping into the Human World
 Sociable Robots Peeping into the Human World An Infant s Advantages Non-hostile environment Actively benevolent, empathic caregiver Co-exists with mature version of self Baby Scheme Physical form can evoke
Sociable Robots Peeping into the Human World An Infant s Advantages Non-hostile environment Actively benevolent, empathic caregiver Co-exists with mature version of self Baby Scheme Physical form can evoke
EMOTION DETECTION THROUGH SPEECH AND FACIAL EXPRESSIONS
 EMOTION DETECTION THROUGH SPEECH AND FACIAL EXPRESSIONS 1 KRISHNA MOHAN KUDIRI, 2 ABAS MD SAID AND 3 M YUNUS NAYAN 1 Computer and Information Sciences, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Malaysia 2 Assoc.
EMOTION DETECTION THROUGH SPEECH AND FACIAL EXPRESSIONS 1 KRISHNA MOHAN KUDIRI, 2 ABAS MD SAID AND 3 M YUNUS NAYAN 1 Computer and Information Sciences, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Malaysia 2 Assoc.
A comparison of acoustic features of speech of typically developing children and children with autism spectrum disorders
 * A comparison of acoustic features of speech of typically developing children and children with autism spectrum disorders Elena Lyakso, Olga Frolova, Aleksey Grigorev Saint Petersburg State University,
* A comparison of acoustic features of speech of typically developing children and children with autism spectrum disorders Elena Lyakso, Olga Frolova, Aleksey Grigorev Saint Petersburg State University,
Longitudinal aspects of emotion recognition in patients with traumatic brain injury
 Neuropsychologia 46 (2008) 148 159 Longitudinal aspects of emotion recognition in patients with traumatic brain injury Magdalena Ietswaart a,, Maarten Milders b, John R. Crawford b, David Currie c, Clare
Neuropsychologia 46 (2008) 148 159 Longitudinal aspects of emotion recognition in patients with traumatic brain injury Magdalena Ietswaart a,, Maarten Milders b, John R. Crawford b, David Currie c, Clare
What is Emotion? Emotion is a 4 part process consisting of: physiological arousal cognitive interpretation, subjective feelings behavioral expression.
 What is Emotion? Emotion is a 4 part process consisting of: physiological arousal cognitive interpretation, subjective feelings behavioral expression. While our emotions are very different, they all involve
What is Emotion? Emotion is a 4 part process consisting of: physiological arousal cognitive interpretation, subjective feelings behavioral expression. While our emotions are very different, they all involve
Description and explanation of the major themes of The Curious Incident of the Dog in the other people, dealing with new environments, and making
 How To Analyze People: Reading People, Body Language, Recognizing Emotions & Facial Expressions (Analyzing People, Body Language Books, How To Read Lies, Reading Facial Expressions) By Bradley Fairbanks
How To Analyze People: Reading People, Body Language, Recognizing Emotions & Facial Expressions (Analyzing People, Body Language Books, How To Read Lies, Reading Facial Expressions) By Bradley Fairbanks
Edge Level C Unit 4 Cluster 1 Face Facts: The Science of Facial Expressions
 Edge Level C Unit 4 Cluster 1 Face Facts: The Science of Facial Expressions 1. Which group has been taught to read the clues in facial expressions? A. firefighters B. judges C. DEA agents D. border patrol
Edge Level C Unit 4 Cluster 1 Face Facts: The Science of Facial Expressions 1. Which group has been taught to read the clues in facial expressions? A. firefighters B. judges C. DEA agents D. border patrol
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Emotional recognition in ASD from voices and faces Citation for published version: Stewart, ME, McAdam, C, Ota, M, Peppe, S & Cleland, J 2013, 'Emotional recognition in ASD
Edinburgh Research Explorer Emotional recognition in ASD from voices and faces Citation for published version: Stewart, ME, McAdam, C, Ota, M, Peppe, S & Cleland, J 2013, 'Emotional recognition in ASD
Karen G. Pounds PhD, APRN, BC Northeastern University Bouve College School of Nursing Boston, Massachusetts
 Karen G. Pounds PhD, APRN, BC Northeastern University Bouve College School of Nursing Boston, Massachusetts 1. Identify one feature of social dysfunction for the client with schizophrenia. 2. Verbalize
Karen G. Pounds PhD, APRN, BC Northeastern University Bouve College School of Nursing Boston, Massachusetts 1. Identify one feature of social dysfunction for the client with schizophrenia. 2. Verbalize
PainChek. Solving the silence of pain in dementia
 PainChek Solving the silence of pain in dementia Mustafa Atee Research Fellow Faculty of Health Sciences, School of Pharmacy & Biomedical Sciences Curtin University, WA Conflict of Interest Research Fellow,
PainChek Solving the silence of pain in dementia Mustafa Atee Research Fellow Faculty of Health Sciences, School of Pharmacy & Biomedical Sciences Curtin University, WA Conflict of Interest Research Fellow,
Non-verbal Cues of Dutch Soccer Players After a Match
 Non-verbal Cues of Dutch Soccer Players After a Match Kweku Ndamah-Arthur, Vera van den Hanenberg, Yvonne Leijten, Quinty Martens and Simone Schaffelaars Abstract The purpose of this study was to understand
Non-verbal Cues of Dutch Soccer Players After a Match Kweku Ndamah-Arthur, Vera van den Hanenberg, Yvonne Leijten, Quinty Martens and Simone Schaffelaars Abstract The purpose of this study was to understand
A Sleeping Monitor for Snoring Detection
 EECS 395/495 - mhealth McCormick School of Engineering A Sleeping Monitor for Snoring Detection By Hongwei Cheng, Qian Wang, Tae Hun Kim Abstract Several studies have shown that snoring is the first symptom
EECS 395/495 - mhealth McCormick School of Engineering A Sleeping Monitor for Snoring Detection By Hongwei Cheng, Qian Wang, Tae Hun Kim Abstract Several studies have shown that snoring is the first symptom
A Methodology for Recognition of Emotions Based on Speech Analysis, for Applications to Human-Robot Interaction. An Exploratory Study
 DOI 10.2478/pjbr-2014-0001 Paladyn, J. Behav. Robot. 2014; 5:1 11 Review Article Open Access Mohammad Rabiei and Alessandro Gasparetto A Methodology for Recognition of Emotions Based on Speech Analysis,
DOI 10.2478/pjbr-2014-0001 Paladyn, J. Behav. Robot. 2014; 5:1 11 Review Article Open Access Mohammad Rabiei and Alessandro Gasparetto A Methodology for Recognition of Emotions Based on Speech Analysis,
Public Speaking. Practice for Your Summative Final
 Public Speaking Practice for Your Summative Final Giving A Speech Giving a formal speech goes beyond just reading your essay to the class For this practice speech we will focus on: Approach (the walk to
Public Speaking Practice for Your Summative Final Giving A Speech Giving a formal speech goes beyond just reading your essay to the class For this practice speech we will focus on: Approach (the walk to
Blue Eyes Technology
 Blue Eyes Technology D.D. Mondal #1, Arti Gupta *2, Tarang Soni *3, Neha Dandekar *4 1 Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunication, Sinhgad Institute of Technology and Science, Narhe, Maharastra,
Blue Eyes Technology D.D. Mondal #1, Arti Gupta *2, Tarang Soni *3, Neha Dandekar *4 1 Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunication, Sinhgad Institute of Technology and Science, Narhe, Maharastra,
AUDIO-VISUAL EMOTION RECOGNITION USING AN EMOTION SPACE CONCEPT
 16th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 28), Lausanne, Switzerland, August 25-29, 28, copyright by EURASIP AUDIO-VISUAL EMOTION RECOGNITION USING AN EMOTION SPACE CONCEPT Ittipan Kanluan, Michael
16th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 28), Lausanne, Switzerland, August 25-29, 28, copyright by EURASIP AUDIO-VISUAL EMOTION RECOGNITION USING AN EMOTION SPACE CONCEPT Ittipan Kanluan, Michael
REFERRAL AND DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF HEARING ACUITY. Better Hearing Philippines Inc.
 REFERRAL AND DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF HEARING ACUITY Better Hearing Philippines Inc. How To Get Started? 1. Testing must be done in an acoustically treated environment far from all the environmental noises
REFERRAL AND DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF HEARING ACUITY Better Hearing Philippines Inc. How To Get Started? 1. Testing must be done in an acoustically treated environment far from all the environmental noises
11 Music and Speech Perception
 11 Music and Speech Perception Properties of sound Sound has three basic dimensions: Frequency (pitch) Intensity (loudness) Time (length) Properties of sound The frequency of a sound wave, measured in
11 Music and Speech Perception Properties of sound Sound has three basic dimensions: Frequency (pitch) Intensity (loudness) Time (length) Properties of sound The frequency of a sound wave, measured in
A Review on Dysarthria speech disorder
 A Review on Dysarthria speech disorder Miss. Yogita S. Mahadik, Prof. S. U. Deoghare, 1 Student, Dept. of ENTC, Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engg Pune, Maharashtra, India 2 Professor, Dept. of ENTC, Pimpri
A Review on Dysarthria speech disorder Miss. Yogita S. Mahadik, Prof. S. U. Deoghare, 1 Student, Dept. of ENTC, Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engg Pune, Maharashtra, India 2 Professor, Dept. of ENTC, Pimpri
Researchers seek patterns in the sounds of autism
 NEWS Researchers seek patterns in the sounds of autism BY KELLY RAE CHI 15 MARCH 2010 1 / 7 Not just babble: Researchers are analyzing the grunts, squeals and early chatter of children with autism. 2 /
NEWS Researchers seek patterns in the sounds of autism BY KELLY RAE CHI 15 MARCH 2010 1 / 7 Not just babble: Researchers are analyzing the grunts, squeals and early chatter of children with autism. 2 /
PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION. Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS
 PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS Mental Status Examination General Considerations Based on Observations During the Assessment Process Spontaneity
PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS Mental Status Examination General Considerations Based on Observations During the Assessment Process Spontaneity
What's in a face? FACIAL EXPRESSIONS. Do facial expressions reflect inner feelings? Or are they social devices for influencing others?
 Page 1 of 6 Volume 31, No. 1, January 2000 FACIAL EXPRESSIONS What's in a face? Do facial expressions reflect inner feelings? Or are they social devices for influencing others? BY BETH AZAR Monitor staff
Page 1 of 6 Volume 31, No. 1, January 2000 FACIAL EXPRESSIONS What's in a face? Do facial expressions reflect inner feelings? Or are they social devices for influencing others? BY BETH AZAR Monitor staff
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
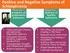 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
INTRODUCTION TO MENTAL HEALTH. PH150 Fall 2013 Carol S. Aneshensel, Ph.D.
 INTRODUCTION TO MENTAL HEALTH PH150 Fall 2013 Carol S. Aneshensel, Ph.D. Topics Subjective Experience: From the perspective of mentally ill persons Context Public attitudes toward the mentally ill Definition
INTRODUCTION TO MENTAL HEALTH PH150 Fall 2013 Carol S. Aneshensel, Ph.D. Topics Subjective Experience: From the perspective of mentally ill persons Context Public attitudes toward the mentally ill Definition
EDUCATIONAL CAREGIVERS PAIN PERCEPTION 1
 EDUCATIONAL CAREGIVERS PAIN PERCEPTION 1 Understanding Educational Caregivers Accuracy in Detecting Facial Expressions of Pain in Children: An Eye-Tracking Study Karlie Foster Laurentian University EDUCATIONAL
EDUCATIONAL CAREGIVERS PAIN PERCEPTION 1 Understanding Educational Caregivers Accuracy in Detecting Facial Expressions of Pain in Children: An Eye-Tracking Study Karlie Foster Laurentian University EDUCATIONAL
A Multilevel Fusion Approach for Audiovisual Emotion Recognition
 A Multilevel Fusion Approach for Audiovisual Emotion Recognition Girija Chetty & Michael Wagner National Centre for Biometric Studies Faculty of Information Sciences and Engineering University of Canberra,
A Multilevel Fusion Approach for Audiovisual Emotion Recognition Girija Chetty & Michael Wagner National Centre for Biometric Studies Faculty of Information Sciences and Engineering University of Canberra,
Fudan University, China
 Cyber Psychosocial and Physical (CPP) Computation Based on Social Neuromechanism -Joint research work by Fudan University and University of Novi Sad By Professor Weihui Dai Fudan University, China 1 Agenda
Cyber Psychosocial and Physical (CPP) Computation Based on Social Neuromechanism -Joint research work by Fudan University and University of Novi Sad By Professor Weihui Dai Fudan University, China 1 Agenda
A Possibility for Expressing Multi-Emotion on Robot Faces
 The 5 th Conference of TRS Conference 26-27 May 2011, Bangkok, Thailand A Possibility for Expressing Multi-Emotion on Robot Faces Trin Veerasiri 1*, Djitt Laowattana 2 Institute of Field robotics, King
The 5 th Conference of TRS Conference 26-27 May 2011, Bangkok, Thailand A Possibility for Expressing Multi-Emotion on Robot Faces Trin Veerasiri 1*, Djitt Laowattana 2 Institute of Field robotics, King
