Pattern Recognition of Functional Neuroimage Data of the Human Sensorimotor System after Stroke
|
|
|
- Derrick Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pattern Recognition of Functional Neuroimage Data of the Human Sensorimotor System after Stroke Camille Gómez-Laberge, M.A.Sc., B.Eng., B.Sc. Ph.D. Candidate Faculty of Engineering, Carleton University Neuroscience Program, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute May 13, 2010
2 Outline 1. Cerebral microcirculation 2. Experimental protocol 3. Pattern recognition of neuroimage data 4. Space-time structure of BOLD response signals 5. Bayesian hierarchical correlation model 6. Results from normal and stroke participants 7. Conclusion
3 The cerebral microcirculation
4 Cerebral microcirculation Microcirculation plays a critical role in brain function neurons need a continuous blood supply of oxygen and glucose the human brain is a highly perfused organ being 2% of body mass and getting 15% of cardiac output the microcirculation is endowed with cellular mechanisms that control cerebral blood flow cerebrovascular autoregulation functional hyperemia
5 Cerebral microcirculation The neurovascular unit Unit members in the cerebral cortex are neurons astrocytes vascular pericytes [adapted from Hamel, J Appl Physiol, 2006] Neurons & glia release vasoactive chemicals to influence vessel tone via pericytes
6 Cerebral microcirculation Functional hyperemia is a complex phenomenon regional microvessels do not possess sufficient vascular resistance to account for flow changes a retrograde vasodilation propagates upstream to relax the feeding pial artery the smooth muscle neurovascular units at all levels release signalling chemicals that act in concert to produce a timely and focused hemodynamic response
7 Impairment of functional hyperemia takes place after stroke Ischemic stroke [adapted from Rossini et al, Brain, 2003]
8 Vascular signal Neural signal Impairment of functional hyperemia takes place after stroke Ischemic stroke Contralesional hemisphere Ipsilesional hemisphere 20 ms Nerve stimulation [adapted from Rossini et al, Brain, 2003] 20 s Nerve stimulation others report functional hyperemic alterations including attenuation, time delays, and absence in either hemisphere
9 Ischemic stroke Motivating question for my research: Since the cerebral microcirculation is altered in cerebrovascular disease, then is it possible to locally characterise the state of the disease by monitoring functional hyperemia? require a method that can simulatneously monitor neuronal and vascular signals the method must be non-invasive to enroll subjects in normal and patient populations the analysis must be flexible to identify a signal whose shape is unknown a priori
10 Ischemic stroke Motivating question for my research: Since the cerebral microcirculation is altered in cerebrovascular disease, then is it possible to locally characterise the state of the disease by monitoring functional hyperemia? require a method that can simulatneously monitor neuronal and vascular signals the method must be non-invasive to enrol subjects in normal and patient populations the analysis must be flexible to identify a signal whose shape is unknown a priori
11 Experimental protocol
12 Experimental protocol Experimental objectives: 1. to reproducibly induce functional hyperemia 2. to simultaneously observe the nervous system response and the cerebrovascular response
13 Experimental protocol The sensorimotor system Why this system? evoked via basic sensorial and motor stimuli motor responses can be monitored has been previously studied [adapted from Gray, Anatomy, 1977 and Kandel et al, Prinicples of Neural Science, 2000]
14 Experimental protocol Event-related visual feedback controlled motor task Display Training: - MVC calibration - motor task training Rest Event Response Hand grip device MRI: Tesla - 5 minute scan - both hands monitored - single-handed response - target force: 25% MVC
15 Experimental protocol Event-related visual feedback controlled motor task Data sources: - Images: 160 GE-EPI 1 T2 FLAIR - Timing: Scanning trigger Event schedule - Motor: Left hand Right hand
16 Experimental protocol Event-related visual feedback controlled motor task -- Left -- Right
17 Pattern recognition of neuroimaging data
18 Pattern Recognition Pattern recognition is a search for structure in the data The search: subjective assessment (eg human intuition) statistical modelling (eg estimation of the data generating process) component analysis (eg representation of the whole by its parts) The structure: how information is organised within a data set
19 Pattern Recognition data X
20 Pattern Recognition data X + + assume k=3 +
21 Pattern Recognition data X + + assume k=3 form a 3-partition by NN +
22 Pattern Recognition data X + + assume k=3 form a 3-partition by NN + Question: how to validate our choice of k=3? is this the optimal k-partition?
23 Pattern Recognition - a data point either belongs to A or B but not both - points in A are considered equivalent - thus set membership is uninformative of partition validity
24 Pattern Recognition - data points have fuzzy membership-- belong to some extent to both sets - the points are now distinguishable - set membership is now informative of partition validity
25 Pattern Recognition - form a k-partition and represent membership by pixel intensity - then different k lead to distributions of membership values
26 Pattern Recognition - form a k-partition and represent membership by pixel intensity - then different k lead to distributions of membership values k = 2
27 Pattern Recognition - form a k-partition and represent membership by pixel intensity - then different k lead to distributions of membership values k = 3
28 Pattern Recognition Dunn (1973) derived fuzzy k-means clustering algorithm based on a least-squares minimisation problem input: data X, metric d, and partition number k output: cluster memberships U and centroids V Dunn, (1973), J. Cybern., 3,
29 Pattern Recognition The major caveat of fuzzy sets is the missing link between cluster validity and probability theory cannot say given X, we reject the null hypothesis that k = 1 if p < 0.05 Unique advantages: systematically analyses complex data yielding results in a human-readable form does not require model pattern a priori quantitatively determines optimal k value
30 z Neuroimage Analysis Subject x x y
31 z Neuroimage Analysis Subject x x y t t
32 Neuroimage Analysis z Subject X = (x,t) x x y t t u1(x) u2(x) uk(x)
33 Neuroimage Analysis block flashes when subject grips device with the right hand data from this region have been processed to help you see the response video is played at 4x
34 Neuroimage Analysis
35 Neuroimage Analysis
36
37 Correlation = 0.48 (sd 0.035) Delay = 2.3 (sd 0.8) seconds Time (s) Time (s)
38 Space-time structure of BOLD response signals
39 Space-time structure Space: cluster contiguity function measures the spatial contiguity of a cluster based on the position of its member voxels
40 Space-time structure Space: cluster contiguity function measures the spatial contiguity of a cluster based on the position of its member voxels
41 Space-time structure Time: causal cross-correlation function stimulus response measured by correlation between delayed voxel and motor time series
42 Space-time structure Time: causal cross-correlation function stimulus response measured by correlation between delayed voxel and motor time series
43 Space-time structure Comments on the proposed features spatial contiguity function: + indicates presence of focused responses + responses can be of any shape - requires input for minimum group & clique size causal cross-correlation function: + indicated presence of delayed responses + responses can be positive or negative - is not suitable if delay varies during session
44 Bayesian hierarchical model for cluster analysis
45 Bayesian hierarchical model Bayesian hierarchical correlation model w.r.t. the motor signal Model Parameters 1 2 k
46 Bayesian hierarchical model Bayesian hierarchical correlation model w.r.t. the motor signal Model Parameters 1 2 k
47 Bayesian hierarchical model Bayesian hierarchical correlation model w.r.t. the motor signal Parameters Global signal
48 Bayesian hierarchical model Bayesian hierarchical correlation model w.r.t. the motor signal Parameters Cluster signals Global signal
49 Bayesian hierarchical model Model implementation we seek the joint posterior probability density for the parameters modelling global signal and each cluster the model (alpha, beta) is fit to the data (y) by Bayesian methods (see ref.) we used MCMC simulations to sample the posterior density we consider a cluster (i) significantly different from the global signal when
50 Bayesian hierarchical model Model implementation we seek the joint posterior probability density for the parameters modelling global signal and each cluster the model (alpha, beta) is fit to the data (y) by Bayesian methods used Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation to sample the posterior density we consider a cluster (i) significantly different from the global signal when
51 Bayesian hierarchical model Model implementation we seek the joint posterior probability density for the parameters modelling global signal and each cluster the model (alpha, beta) is fit to the data (y) by Bayesian methods used Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation to sample the posterior density we consider a cluster significantly different from the global signal when
52 Bayesian hierarchical model Demonstration using simulated data
53 Bayesian hierarchical model Demonstration using simulated data
54 Bayesian hierarchical model Demonstration using simulated data
55 Results
56 Results Motor task performance
57 Results Motor task performance left hand right hand
58 Results Motor task performance left hand right hand
59 Results Motor task performance Normal group responded to all events without extra responses Performance from stroke patients varied widely: - event responses 92-98% across group - patients 2 & 3 often performed extra responses - patient 2 often performed mirror responses - patient 3 exhibited cognitive deficit during task - patient 4 has a plegic left hand
60 Results Bayesian hierarchical cluster analysis
61 Results Bayesian hierarchical cluster analysis
62 Results Bayesian hierarchical cluster analysis - the factors for cluster selection: difference & certainty - rejected clusters fall evenly around alpha - most normal selected clusters are positively correlated - 58% more selected clusters from stroke group than normal - many stroke group selected clusters are negative correlated
63 Results Space-time structure of BOLD response signals
64 Results Space-time structure of BOLD response signals Space - stroke clutsers are significantly less contiguous than normal - both groups have comparable signal-to-noise ratio
65 Results Space-time structure of BOLD response signals Space Time - stroke clutsers are significantly less contiguous than normal - both groups have comparable signal-to-noise ratio - 80% normal clusters are positive correlated (2-4 s delay) - 44% stroke clusters are negative correlated (0-2 s delay)
66 Results Identified brain regions: NORMAL GROUP
67 Results Identified brain regions: NORMAL GROUP Basal ganglia Sensorimotor cortex
68 Results Identified brain regions: NORMAL GROUP Basal ganglia Sensorimotor cortex
69 Results Identified brain regions: NORMAL GROUP Basal ganglia Sensorimotor cortex
70 Results Identified brain regions: NORMAL GROUP Basal ganglia Putamen & globus pallidus: - Turner et al. (2003), J Neurophysiol Cerebral cortex Contralateral SMC: - Kandel et al. (2000) Princ Neur Sci SMA: - Nachev et al. (2008), Nat Neurosci Ipsilateral premotor & parietal: - Reis et al. (2008), J Neurophysiol
71 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP
72 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP - as expected, responses are sparse and inconsistent - Rossini et al (2003), Brain provide compelling evidence of neurovascular dysfunction in both hemispheres - Ward et al (2003), Brain, also describe sparse activation patterns in longitudinal stroke cohorts where best motor recovery correlated with SMC focused BOLD responses
73 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP - as expected, responses are sparse and inconsistent - Rossini et al (2003), Brain provide compelling evidence of neurovascular dysfunction in both hemispheres - Ward et al (2003), Brain, also describe sparse activation patterns in longitudinal stroke cohorts where best motor recovery correlated with SMC focused BOLD responses
74 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP - as expected, responses are sparse and inconsistent - Rossini et al (2003), Brain provide compelling evidence of neurovascular dysfunction in both hemispheres - Ward et al (2003), Brain, also describe sparse activation patterns in longitudinal stroke cohorts where best motor recovery correlated with SMC focused BOLD responses
75 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP paretic hand non-paretic hand
76 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP paretic hand non-paretic hand
77 Results Identified brain regions: STROKE GROUP paretic hand non-paretic hand
78 NORMAL GROUP left Results Identified brain regions References: Contralateral SMC: - Kandel et al. (2000) SMA: - Nachev et al. (2008) Ipsilateral premotor & parietal: - Reis et al. (2008) STROKE GROUP non-paretic paretic Contralateral SMC after stroke: - Cramer et al. (1999) SMA after stroke: - Carusone et al. (2002) Ipsilateral premotor & parietal: - Ward et al. (2003) Ipsilateral SMC after stroke: - Cramer et al. (1999) - Carusone et al. (2002) - Ward et al. (2003)
79 Results Proposed method is useful for case study
80 Results Proposed method is useful for case study
81 Conclusion
82 Conclusion Experimental protocol & data acquisition Event-related visual feedback motor task: + reproducible BOLD signal in normal group + identify sensorimotor network + potential for wide range of stroke population - results limited to sensorimotor network only - no simulataneous neural activity images Data simulation: + physiologically-based BOLD signals + noise based on fmri autocorrelation estimates + block bootstrap simulation as simulation standard - block bootstrap is computationally intensive
83 Proposed analysis method Conclusion Fuzzy cluster analysis: + to identify and distinguish different BOLD signals + membership informative of optimal k-value - link to probabilistic framework is still missing - lacking accountability for temporal dependence Space-time structure: + features can separate normal and stroke groups - insensitive to signal magnitude and delay change Bayesian hierarchical model: + multilevel approach to data analysis + no multiple comparisions corrections necessary - first application: will improve with further development
84 Proposed analysis method Conclusion Fuzzy cluster analysis: + to identify and distinguish different BOLD signals + membership informative of optimal k-value - link to probabilistic framework remains elusive - lacking accountability for temporal dependence Space-time structure: + features can separate normal and stroke groups - insensitive to signal magnitude and delay change Bayesian hierarchical model: + multilevel approach to data analysis + no multiple comparisions corrections necessary - first application: will improve with further development
85 Proposed analysis method Conclusion Fuzzy cluster analysis: + to identify and distinguish different BOLD signals + membership informative of optimal k-value - link to probabilistic framework remains elusive - lacking accountability for temporal dependence Space-time structure: + features can separate normal and stroke groups - insensitive to signal magnitude and delay change Bayesian hierarchical model: + multilevel approach to data analysis + no multiple comparisions corrections necessary - first application: will improve with further development
86 Conclusion Interpretation of results A pilot study with small sample size - hence, our clinical interpretation is very limited Changes in BOLD responses in stroke group - our results corroborate the changes observed in previous research Are these changes directly caused by stroke? - we cannot provide a definite answer due to uncontrolled factors e.g., age, co-morbidity, drugs, etc... Neurovascular dysfunction or neural plasticity? - literature & our normal group results suggest that neurovascular dysfunction is likely to persist after stroke
87 Conclusion Future work should take place in a larger stroke trial: longitudinal stroke rehab with age-matched normals are there distinct BOLD indicators of CVD? can BOLD be related to degree of impairment? can neural plasticity be distinguished from neurovascular dysfunction? Optimisation of stroke recovery: to apply these answers to help monitor and develop stroke rehabilitation programmes
88 Conclusion Future work should take place in a larger stroke trial: longitudinal stroke rehab with age-matched normals are there distinct BOLD indicators of CVD? can BOLD be related to degree of impairment? can neural plasticity be distinguished from neurovascular dysfunction? Optimisation of stroke recovery: to apply these answers to help monitor and develop stroke rehabilitation programmes
89 Acknowledgements Supervisors: M. Hogan MD PhD (Neuroscience) Ottawa Hospital Research Institute A. Adler PhD (Biomedical Engineering) Carleton University Co-investigators: I. Cameron PhD (MR Physics) The Ottawa Hospital T. Nguyen MD (Radiology) The Ottawa Hospital M. Sharma MA (Neurology) The Ottawa Hospital Funding: - Behavioural Research and Imaging Network (BRAIN) - Ontario Research Fund - Heart and Stroke Foundation Centre for Stroke Recovery
90 Pattern Recognition of Functional Neuroimage Data of the Human Sensorimotor System after Stroke Camille Gómez-Laberge, M.A.Sc., B.Eng., B.Sc. Ph.D. Candidate Faculty of Engineering, Carleton University Neuroscience Program, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute May 13, 2010
Biophysical and physiological bases of fmri signals: challenges of interpretation and methodological concerns
 Biophysical and physiological bases of fmri signals: challenges of interpretation and methodological concerns Antonio Ferretti aferretti@itab.unich.it Institute for Advanced Biomedical Technologies, University
Biophysical and physiological bases of fmri signals: challenges of interpretation and methodological concerns Antonio Ferretti aferretti@itab.unich.it Institute for Advanced Biomedical Technologies, University
Experimental Design. Outline. Outline. A very simple experiment. Activation for movement versus rest
 Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION. Alternatives to BOLD for fmri
 PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION Quick Review for fmri HST-583, Fall 2002 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION Quick Review for fmri HST-583, Fall 2002 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
Neuroimaging. BIE601 Advanced Biological Engineering Dr. Boonserm Kaewkamnerdpong Biological Engineering Program, KMUTT. Human Brain Mapping
 11/8/2013 Neuroimaging N i i BIE601 Advanced Biological Engineering Dr. Boonserm Kaewkamnerdpong Biological Engineering Program, KMUTT 2 Human Brain Mapping H Human m n brain br in m mapping ppin can nb
11/8/2013 Neuroimaging N i i BIE601 Advanced Biological Engineering Dr. Boonserm Kaewkamnerdpong Biological Engineering Program, KMUTT 2 Human Brain Mapping H Human m n brain br in m mapping ppin can nb
MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience
 MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience School of Psychological Sciences Faculty of Medical & Human Sciences Module Information *Please note that this is a sample guide to modules. The exact
MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience School of Psychological Sciences Faculty of Medical & Human Sciences Module Information *Please note that this is a sample guide to modules. The exact
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 10: Brain-Computer Interfaces Ilya Kuzovkin So Far Stimulus So Far So Far Stimulus What are the neuroimaging techniques you know about? Stimulus So Far
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 10: Brain-Computer Interfaces Ilya Kuzovkin So Far Stimulus So Far So Far Stimulus What are the neuroimaging techniques you know about? Stimulus So Far
The Contribution of TMS-EEG Coregistration in the Exploration of the Human Connectome
 IRCCS San Giovanni di Dio Fatebenefratelli The Contribution of TMS-EEG Coregistration in the Exploration of the Human Connectome Marta Bortoletto Carlo Miniussi Cognitive Neuroscience Section, The Saint
IRCCS San Giovanni di Dio Fatebenefratelli The Contribution of TMS-EEG Coregistration in the Exploration of the Human Connectome Marta Bortoletto Carlo Miniussi Cognitive Neuroscience Section, The Saint
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch!
 Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Stroke Patients After Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy: A Pilot Study
 Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Stroke Patients After Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy: A Pilot Study N. Kinany 1,3,4(&), C. Pierella 1, E. Pirondini 3,4, M. Coscia 2, J. Miehlbradt 1, C. Magnin
Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Stroke Patients After Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy: A Pilot Study N. Kinany 1,3,4(&), C. Pierella 1, E. Pirondini 3,4, M. Coscia 2, J. Miehlbradt 1, C. Magnin
Population Inference post Model Selection in Neuroscience
 Population Inference post Model Selection in Neuroscience Genevera I. Allen Dobelman Family Junior Chair, Department of Statistics and Electrical and Computer Engineering, Rice University, Department of
Population Inference post Model Selection in Neuroscience Genevera I. Allen Dobelman Family Junior Chair, Department of Statistics and Electrical and Computer Engineering, Rice University, Department of
fmri Acquisition: Temporal Effects
 Functional MRI Data Acquisition: Temporal fmri Acquisition: Temporal Effects Session length Repetition time Fixed vs. distributed temporal sampling Sparse temporal sampling Noise source recording Prospective
Functional MRI Data Acquisition: Temporal fmri Acquisition: Temporal Effects Session length Repetition time Fixed vs. distributed temporal sampling Sparse temporal sampling Noise source recording Prospective
Progress Report. Author: Dr Joseph Yuan-Mou Yang Qualification: PhD Institution: Royal Children s Hospital Date: October 2017
 Author: Dr Joseph Yuan-Mou Qualification: PhD Institution: Royal Children s Hospital Date: October 2017 Progress Report Title of Project: Brain structural and motor function correlations in childhood arterial
Author: Dr Joseph Yuan-Mou Qualification: PhD Institution: Royal Children s Hospital Date: October 2017 Progress Report Title of Project: Brain structural and motor function correlations in childhood arterial
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Applications with Bayesian Approach
 Applications with Bayesian Approach Feng Li feng.li@cufe.edu.cn School of Statistics and Mathematics Central University of Finance and Economics Outline 1 Missing Data in Longitudinal Studies 2 FMRI Analysis
Applications with Bayesian Approach Feng Li feng.li@cufe.edu.cn School of Statistics and Mathematics Central University of Finance and Economics Outline 1 Missing Data in Longitudinal Studies 2 FMRI Analysis
HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION
 HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION Neural Signal Processing for Functional Neuroimaging Neuroscience Statistics Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School/MIT Division
HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION Neural Signal Processing for Functional Neuroimaging Neuroscience Statistics Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School/MIT Division
Ch.20 Dynamic Cue Combination in Distributional Population Code Networks. Ka Yeon Kim Biopsychology
 Ch.20 Dynamic Cue Combination in Distributional Population Code Networks Ka Yeon Kim Biopsychology Applying the coding scheme to dynamic cue combination (Experiment, Kording&Wolpert,2004) Dynamic sensorymotor
Ch.20 Dynamic Cue Combination in Distributional Population Code Networks Ka Yeon Kim Biopsychology Applying the coding scheme to dynamic cue combination (Experiment, Kording&Wolpert,2004) Dynamic sensorymotor
Water immersion modulates sensory and motor cortical excitability
 Water immersion modulates sensory and motor cortical excitability Daisuke Sato, PhD Department of Health and Sports Niigata University of Health and Welfare Topics Neurophysiological changes during water
Water immersion modulates sensory and motor cortical excitability Daisuke Sato, PhD Department of Health and Sports Niigata University of Health and Welfare Topics Neurophysiological changes during water
Online appendices are unedited and posted as supplied by the authors. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 Appendix 1 to Sehmbi M, Rowley CD, Minuzzi L, et al. Age-related deficits in intracortical myelination in young adults with bipolar SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Intracortical Myelin (ICM)
Appendix 1 to Sehmbi M, Rowley CD, Minuzzi L, et al. Age-related deficits in intracortical myelination in young adults with bipolar SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Intracortical Myelin (ICM)
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits
 Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications.
 Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? brain. deprived of sight?
 How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
5th Mini-Symposium on Cognition, Decision-making and Social Function: In Memory of Kang Cheng
 5th Mini-Symposium on Cognition, Decision-making and Social Function: In Memory of Kang Cheng 13:30-13:35 Opening 13:30 17:30 13:35-14:00 Metacognition in Value-based Decision-making Dr. Xiaohong Wan (Beijing
5th Mini-Symposium on Cognition, Decision-making and Social Function: In Memory of Kang Cheng 13:30-13:35 Opening 13:30 17:30 13:35-14:00 Metacognition in Value-based Decision-making Dr. Xiaohong Wan (Beijing
Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps
 Training course: Real-time fmri: Fundamental Principles for Clinical Applications Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps David Linden Cardiff University 1) What is your clinical
Training course: Real-time fmri: Fundamental Principles for Clinical Applications Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps David Linden Cardiff University 1) What is your clinical
BOLD signal dependence on blood flow and metabolism. Outline
 BOLD signal dependence on blood flow and metabolism R. Hoge, MGH NMR Center Outline physiological events accompanying neuronal activation factors affecting BOLD signal sensitivity BOLD response dynamics
BOLD signal dependence on blood flow and metabolism R. Hoge, MGH NMR Center Outline physiological events accompanying neuronal activation factors affecting BOLD signal sensitivity BOLD response dynamics
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods
 Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Daniel Bulte. Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain. University of Oxford
 Daniel Bulte Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain University of Oxford Overview Signal Sources BOLD Contrast Mechanism of MR signal change FMRI Modelling Scan design details Factors
Daniel Bulte Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain University of Oxford Overview Signal Sources BOLD Contrast Mechanism of MR signal change FMRI Modelling Scan design details Factors
Introduction to Functional MRI
 Introduction to Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory University of Michigan Outline Brief overview of physiology and physics of BOLD fmri Background
Introduction to Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory University of Michigan Outline Brief overview of physiology and physics of BOLD fmri Background
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Chapter 5. Summary and Conclusions! 131
 ! Chapter 5 Summary and Conclusions! 131 Chapter 5!!!! Summary of the main findings The present thesis investigated the sensory representation of natural sounds in the human auditory cortex. Specifically,
! Chapter 5 Summary and Conclusions! 131 Chapter 5!!!! Summary of the main findings The present thesis investigated the sensory representation of natural sounds in the human auditory cortex. Specifically,
Theoretical Neuroscience: The Binding Problem Jan Scholz, , University of Osnabrück
 The Binding Problem This lecture is based on following articles: Adina L. Roskies: The Binding Problem; Neuron 1999 24: 7 Charles M. Gray: The Temporal Correlation Hypothesis of Visual Feature Integration:
The Binding Problem This lecture is based on following articles: Adina L. Roskies: The Binding Problem; Neuron 1999 24: 7 Charles M. Gray: The Temporal Correlation Hypothesis of Visual Feature Integration:
1 Introduction Synchronous ring of action potentials amongst multiple neurons is a phenomenon that has been observed in a wide range of neural systems
 Model-free detection of synchrony in neuronal spike trains, with an application to primate somatosensory cortex A. Roy a, P. N. Steinmetz a 1, K. O. Johnson a, E. Niebur a 2 a Krieger Mind/Brain Institute,
Model-free detection of synchrony in neuronal spike trains, with an application to primate somatosensory cortex A. Roy a, P. N. Steinmetz a 1, K. O. Johnson a, E. Niebur a 2 a Krieger Mind/Brain Institute,
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Hebbian Plasticity for Improving Perceptual Decisions
 Hebbian Plasticity for Improving Perceptual Decisions Tsung-Ren Huang Department of Psychology, National Taiwan University trhuang@ntu.edu.tw Abstract Shibata et al. reported that humans could learn to
Hebbian Plasticity for Improving Perceptual Decisions Tsung-Ren Huang Department of Psychology, National Taiwan University trhuang@ntu.edu.tw Abstract Shibata et al. reported that humans could learn to
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity. Overview
 Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
Announcements. Exam 1. VII. Imaging techniques of the brain. Anatomical/Structural Scans. Structural Scans: CT. Structural Scans: CT 2/17/2014
 Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Exam 1. Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6%
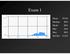 Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan. Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1
 The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
Effects Of Attention And Perceptual Uncertainty On Cerebellar Activity During Visual Motion Perception
 Effects Of Attention And Perceptual Uncertainty On Cerebellar Activity During Visual Motion Perception Oliver Baumann & Jason Mattingley Queensland Brain Institute The University of Queensland The Queensland
Effects Of Attention And Perceptual Uncertainty On Cerebellar Activity During Visual Motion Perception Oliver Baumann & Jason Mattingley Queensland Brain Institute The University of Queensland The Queensland
Event-Related fmri and the Hemodynamic Response
 Human Brain Mapping 6:373 377(1998) Event-Related fmri and the Hemodynamic Response Randy L. Buckner 1,2,3 * 1 Departments of Psychology, Anatomy and Neurobiology, and Radiology, Washington University,
Human Brain Mapping 6:373 377(1998) Event-Related fmri and the Hemodynamic Response Randy L. Buckner 1,2,3 * 1 Departments of Psychology, Anatomy and Neurobiology, and Radiology, Washington University,
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Neurovascular Physiology and Pathophysiology
 Neurovascular Physiology and Pathophysiology The physiological questions aim at understanding the molecular and biochemical mechanisms, by which the brain adapts local blood flow to neuronal activity and
Neurovascular Physiology and Pathophysiology The physiological questions aim at understanding the molecular and biochemical mechanisms, by which the brain adapts local blood flow to neuronal activity and
Comparing event-related and epoch analysis in blocked design fmri
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com R NeuroImage 18 (2003) 806 810 www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Technical Note Comparing event-related and epoch analysis in blocked design fmri Andrea Mechelli,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com R NeuroImage 18 (2003) 806 810 www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Technical Note Comparing event-related and epoch analysis in blocked design fmri Andrea Mechelli,
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity
 Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Dynamic 3D Clustering of Spatio-Temporal Brain Data in the NeuCube Spiking Neural Network Architecture on a Case Study of fmri Data
 Dynamic 3D Clustering of Spatio-Temporal Brain Data in the NeuCube Spiking Neural Network Architecture on a Case Study of fmri Data Maryam Gholami Doborjeh (B) and Nikola Kasabov Knowledge Engineering
Dynamic 3D Clustering of Spatio-Temporal Brain Data in the NeuCube Spiking Neural Network Architecture on a Case Study of fmri Data Maryam Gholami Doborjeh (B) and Nikola Kasabov Knowledge Engineering
Source Memory is not Properly Differentiated from Object Memory in Early Schizophrenia An fmri study using virtual reality
 Source Memory is not Properly Differentiated from Object Memory in Early Schizophrenia An fmri study using virtual reality Colin S. Hawco, PhD Lisa Buchy Michael Bodnar, Sarah Izadi, Jennifer Dell Elce,
Source Memory is not Properly Differentiated from Object Memory in Early Schizophrenia An fmri study using virtual reality Colin S. Hawco, PhD Lisa Buchy Michael Bodnar, Sarah Izadi, Jennifer Dell Elce,
Edinburgh Imaging Academy online distance learning courses. Functional Imaging
 Functional Imaging Semester 2 / Commences January 10 Credits Each Course is composed of Modules & Activities. Modules: BOLD Signal IMSc NI4R Experimental Design IMSc NI4R Pre-processing IMSc NI4R GLM IMSc
Functional Imaging Semester 2 / Commences January 10 Credits Each Course is composed of Modules & Activities. Modules: BOLD Signal IMSc NI4R Experimental Design IMSc NI4R Pre-processing IMSc NI4R GLM IMSc
Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique in Epilepsy Subjects
 22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique
22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique
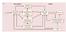 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Carnegie Mellon University Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Carnegie Mellon University Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period January 1, 2012 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Carnegie Mellon University received $943,032 in formula funds
Carnegie Mellon University Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period January 1, 2012 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Carnegie Mellon University received $943,032 in formula funds
ERA: Architectures for Inference
 ERA: Architectures for Inference Dan Hammerstrom Electrical And Computer Engineering 7/28/09 1 Intelligent Computing In spite of the transistor bounty of Moore s law, there is a large class of problems
ERA: Architectures for Inference Dan Hammerstrom Electrical And Computer Engineering 7/28/09 1 Intelligent Computing In spite of the transistor bounty of Moore s law, there is a large class of problems
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011
 Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011 I. Purpose Drawing from the profile development of the QIBA-fMRI Technical Committee,
Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011 I. Purpose Drawing from the profile development of the QIBA-fMRI Technical Committee,
Presence of AVA in High Frequency Oscillations of the Perfusion fmri Resting State Signal
 Presence of AVA in High Frequency Oscillations of the Perfusion fmri Resting State Signal Zacà D 1., Hasson U 1,2., Davis B 1., De Pisapia N 2., Jovicich J. 1,2 1 Center for Mind/Brain Sciences, University
Presence of AVA in High Frequency Oscillations of the Perfusion fmri Resting State Signal Zacà D 1., Hasson U 1,2., Davis B 1., De Pisapia N 2., Jovicich J. 1,2 1 Center for Mind/Brain Sciences, University
5/2/2013. Real-time fmri: Methods and applications
 Real-time fmri: Methods and applications Frank Scharnowski Non-invasive imaging technique PET Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) NIRS EEG MEG Functional MRI Structural MRI Perfusion MRI Diffusion MRI MR
Real-time fmri: Methods and applications Frank Scharnowski Non-invasive imaging technique PET Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) NIRS EEG MEG Functional MRI Structural MRI Perfusion MRI Diffusion MRI MR
Model-free detection of synchrony in neuronal spike trains, with an application to primate somatosensory cortex
 Neurocomputing 32}33 (2000) 1103}1108 Model-free detection of synchrony in neuronal spike trains, with an application to primate somatosensory cortex A. Roy, P.N. Steinmetz, K.O. Johnson, E. Niebur* Krieger
Neurocomputing 32}33 (2000) 1103}1108 Model-free detection of synchrony in neuronal spike trains, with an application to primate somatosensory cortex A. Roy, P.N. Steinmetz, K.O. Johnson, E. Niebur* Krieger
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Neuroimaging biomarkers and predictors of motor recovery: implications for PTs
 Neuroimaging biomarkers and predictors of motor recovery: implications for PTs 2018 Combined Sections Meeting of the American Physical Therapy Association New Orleans, LA February 21-24, 2018 Presenters:
Neuroimaging biomarkers and predictors of motor recovery: implications for PTs 2018 Combined Sections Meeting of the American Physical Therapy Association New Orleans, LA February 21-24, 2018 Presenters:
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Hemodynamics and fmri Signals
 Cerebral Blood Flow and Brain Activation UCLA NITP July 2011 Hemodynamics and fmri Signals Richard B. Buxton University of California, San Diego rbuxton@ucsd.edu... The subject to be observed lay on a
Cerebral Blood Flow and Brain Activation UCLA NITP July 2011 Hemodynamics and fmri Signals Richard B. Buxton University of California, San Diego rbuxton@ucsd.edu... The subject to be observed lay on a
4/25/2014. Real-time fmri. Real-time fmri Methods. What is special about real-time fmri? ... data analysis keeps up with image acquisition!
 Non-invasive imaging technique : Methods and applications Functional MRI PET Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Structural MRI Perfusion MRI Diffusion MRI NIRS EEG MEG MR angiography Frank Scharnowski Real-time
Non-invasive imaging technique : Methods and applications Functional MRI PET Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Structural MRI Perfusion MRI Diffusion MRI NIRS EEG MEG MR angiography Frank Scharnowski Real-time
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Moriguchi and Hiraki 10.1073/pnas.0809747106 SI Text Differences in Brain Activation Between Preswitch and Postswitch Phases. The paired t test was used to compare the brain activation
Supporting Information Moriguchi and Hiraki 10.1073/pnas.0809747106 SI Text Differences in Brain Activation Between Preswitch and Postswitch Phases. The paired t test was used to compare the brain activation
Causality from fmri?
 Causality from fmri? Olivier David, PhD Brain Function and Neuromodulation, Joseph Fourier University Olivier.David@inserm.fr Grenoble Brain Connectivity Course Yes! Experiments (from 2003 on) Friston
Causality from fmri? Olivier David, PhD Brain Function and Neuromodulation, Joseph Fourier University Olivier.David@inserm.fr Grenoble Brain Connectivity Course Yes! Experiments (from 2003 on) Friston
Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics
 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'18 85 Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics Bing Liu 1*, Xuan Guo 2, and Jing Zhang 1** 1 Department
Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'18 85 Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics Bing Liu 1*, Xuan Guo 2, and Jing Zhang 1** 1 Department
Modeling Individual and Group Behavior in Complex Environments. Modeling Individual and Group Behavior in Complex Environments
 Modeling Individual and Group Behavior in Complex Environments Dr. R. Andrew Goodwin Environmental Laboratory Professor James J. Anderson Abran Steele-Feldman University of Washington Status: AT-14 Continuing
Modeling Individual and Group Behavior in Complex Environments Dr. R. Andrew Goodwin Environmental Laboratory Professor James J. Anderson Abran Steele-Feldman University of Washington Status: AT-14 Continuing
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization
 Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Inverse problems in functional brain imaging Identification of the hemodynamic response in fmri
 Inverse problems in functional brain imaging Identification of the hemodynamic response in fmri Ph. Ciuciu1,2 philippe.ciuciu@cea.fr 1: CEA/NeuroSpin/LNAO May 7, 2010 www.lnao.fr 2: IFR49 GDR -ISIS Spring
Inverse problems in functional brain imaging Identification of the hemodynamic response in fmri Ph. Ciuciu1,2 philippe.ciuciu@cea.fr 1: CEA/NeuroSpin/LNAO May 7, 2010 www.lnao.fr 2: IFR49 GDR -ISIS Spring
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 5: Data analysis II Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis II 6 Single
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 5: Data analysis II Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis II 6 Single
Control of visuo-spatial attention. Emiliano Macaluso
 Control of visuo-spatial attention Emiliano Macaluso CB demo Attention Limited processing resources Overwhelming sensory input cannot be fully processed => SELECTIVE PROCESSING Selection via spatial orienting
Control of visuo-spatial attention Emiliano Macaluso CB demo Attention Limited processing resources Overwhelming sensory input cannot be fully processed => SELECTIVE PROCESSING Selection via spatial orienting
An Overview of BMIs. Luca Rossini. Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications
 An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
DeSTIN: A Scalable Deep Learning Architecture with Application to High-Dimensional Robust Pattern Recognition
 DeSTIN: A Scalable Deep Learning Architecture with Application to High-Dimensional Robust Pattern Recognition Itamar Arel and Derek Rose and Robert Coop Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
DeSTIN: A Scalable Deep Learning Architecture with Application to High-Dimensional Robust Pattern Recognition Itamar Arel and Derek Rose and Robert Coop Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Objectives. Objectives Continued 8/13/2014. Movement Education and Motor Learning Where Ortho and Neuro Rehab Collide
 Movement Education and Motor Learning Where Ortho and Neuro Rehab Collide Roderick Henderson, PT, ScD, OCS Wendy Herbert, PT, PhD Janna McGaugh, PT, ScD, COMT Jill Seale, PT, PhD, NCS Objectives 1. Identify
Movement Education and Motor Learning Where Ortho and Neuro Rehab Collide Roderick Henderson, PT, ScD, OCS Wendy Herbert, PT, PhD Janna McGaugh, PT, ScD, COMT Jill Seale, PT, PhD, NCS Objectives 1. Identify
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
PIB Ch. 18 Sequence Memory for Prediction, Inference, and Behavior. Jeff Hawkins, Dileep George, and Jamie Niemasik Presented by Jiseob Kim
 PIB Ch. 18 Sequence Memory for Prediction, Inference, and Behavior Jeff Hawkins, Dileep George, and Jamie Niemasik Presented by Jiseob Kim Quiz Briefly describe the neural activities of minicolumn in the
PIB Ch. 18 Sequence Memory for Prediction, Inference, and Behavior Jeff Hawkins, Dileep George, and Jamie Niemasik Presented by Jiseob Kim Quiz Briefly describe the neural activities of minicolumn in the
Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control
 Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control How Your Brain Works - Week 10 Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net The Story So Far In the first few lectures we introduced you to some
Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control How Your Brain Works - Week 10 Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net The Story So Far In the first few lectures we introduced you to some
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lingnau et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902262106 Fig. S1. Material presented during motor act observation (A) and execution (B). Each row shows one of the 8 different motor acts. Columns in
Supporting Information Lingnau et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902262106 Fig. S1. Material presented during motor act observation (A) and execution (B). Each row shows one of the 8 different motor acts. Columns in
MORNING COFFEE
 Final on-site schedule for 5. October MICCAI 2015 BrainLes: Brain-lesion workshop (BrainLes) Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation Challenge (ISLES) Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Challenge (BRATS) MORNING
Final on-site schedule for 5. October MICCAI 2015 BrainLes: Brain-lesion workshop (BrainLes) Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation Challenge (ISLES) Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Challenge (BRATS) MORNING
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
Oscillatory Neural Network for Image Segmentation with Biased Competition for Attention
 Oscillatory Neural Network for Image Segmentation with Biased Competition for Attention Tapani Raiko and Harri Valpola School of Science and Technology Aalto University (formerly Helsinki University of
Oscillatory Neural Network for Image Segmentation with Biased Competition for Attention Tapani Raiko and Harri Valpola School of Science and Technology Aalto University (formerly Helsinki University of
Memory, Attention, and Decision-Making
 Memory, Attention, and Decision-Making A Unifying Computational Neuroscience Approach Edmund T. Rolls University of Oxford Department of Experimental Psychology Oxford England OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
Memory, Attention, and Decision-Making A Unifying Computational Neuroscience Approach Edmund T. Rolls University of Oxford Department of Experimental Psychology Oxford England OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain
 Motivating Questions Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory COGS1 class How do our brains perceive the mental states of others
Motivating Questions Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory COGS1 class How do our brains perceive the mental states of others
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Hemodynamics and fmri Signals
 Cerebral Blood Flow and Brain Activation UCLA NITP July 2010 Hemodynamics and fmri Signals Richard B. Buxton University of California, San Diego rbuxton@ucsd.edu... The subject to be observed lay on a
Cerebral Blood Flow and Brain Activation UCLA NITP July 2010 Hemodynamics and fmri Signals Richard B. Buxton University of California, San Diego rbuxton@ucsd.edu... The subject to be observed lay on a
Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using Linear Discriminative Analysis and Quadratic Discriminative Analysis
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
