Laura Figueroa, M.D. a and Federico Laffaye, M.D. a
|
|
|
- Randell Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief reports / Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115(3): / 277 Early use of continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of moderate to severe acute lower respiratory tract infections among patients younger than 2 years old Laura Figueroa, M.D. a and Federico Laffaye, M.D. a ABSTRACT Objective. To analyze the characteristics of patients younger than 2 years old who had a moderate to severe acute lower respiratory tract infection and were treated early with bubble continuous positive airway pressure, and factors associated with a successful intervention. Method. Retrospective and descriptive study. Children younger than 2 years old admitted to the Pediatric Intermediate Care Unit of Hospital Provincial Neuquén between June 2009 and December Bubble continuous positive airway pressure was used, and the following outcomes were measured: heart rate, respiratory rate, Tal s score, oxygen saturation, and fraction of inspired oxygen at 0, 2, 6, 24, and 48 h. Results. One hundred and twenty patients were included. Their median age was 3 months old. The intervention was successful in 72% of patients. At 2 h, a 15% reduction in respiratory rate, and a 2-point decrease in Tal s score were predictors of success, with an odds ratio of 6.41 (95% confidence interval: ), and of 9.07 (95% confidence interval: ), respectively. Conclusions. A reduction in respiratory rate, heart rate, and Tal s score at 2 hours of starting the intervention were predictors of success. Key words: bubble CPAP, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, children. To cite: Figueroa L, Laffaye F. Early use of continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of moderate to severe acute lower respiratory tract infections among patients younger than 2 years old. Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115(3): INTRODUCTION Acute lower respiratory tract infections (ALRTIs) are an important cause of morbidity and mortality in our setting. 1 a. Pediatric Intermediate Care Unit. Hospital Provincial Neuquén Dr. E. Castro Rendón. address: Laura Figueroa, M.D.: lauritafigueroa@yahoo.com.ar The main clinical conditions included under the definition of ALRTI are bronchiolitis and pneumonia, which have a greater impact on childhood mortality, 2 and set the basis for this study. Non-invasive ventilation is an alternative for patients with moderate to severe ALRTIs. 3-6 Different publications have mentioned a reduction in the length of hospital stay and a lower proportion of failure (less than 30%), defined as the need for endotracheal intubation. 7 The objective of this study was to analyze the characteristics of patients younger than 2 years old who had a moderate to severe ALRTI and treated early with bubble continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), and factors associated with a successful intervention. POPULATION AND METHODS Retrospective and descriptive study. Children younger than 2 years old hospitalized between June 2009 and December Bubble CPAP was used, and the following outcomes were measured: heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), Tal s score, oxygen saturation, and fraction of inspired oxygen ( ) at 0, 2, 6, 24, and 48 h. Inclusion criteria for the use of bubble CPAP were as follows: Age between 1 and 24 months old. Weight < 12 kg. Tal s score > 5 points. Admission to the pediatric intermediate care unit. Exclusion criteria were the following: Cardiorespiratory arrest. Hemodynamic instability in spite of intravenous treatment with volume expanders. Inotrope requirement. Absence of gag and/or cough reflex. Funding: None. Conflict of interest: None. Received: Accepted: Collaborators: Mario González, Germán Kaltenbach, Viviana Arias y Eugenia Cerda.
2 278 / Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115(3): / Brief reports Bubble CPAP consists of an interface (nasal cannula), inspiratory tubing, and expiratory tubing immersed in an underwater bottle system. The patient breaths spontaneously with positive pressure air flow, during both inspiration and expiration. Thus, continuous positive airway pressure is maintained throughout the breathing cycle. CPAP includes an oxygen blender connected to a source of oxygen and compressed air used to supply an appropriate concentration of inspired oxygen ( ). The humidified blended oxygen is then circulated through corrugated tubing. is estimated based on the liters of air and oxygen delivered. Blended oxygen is delivered via a nasal cannula, and pressure in the circuit is maintained by immersing the distal end of the expiratory tubing in water. The depth to which the tubing is immersed underwater determines the pressure generated in the patient s airways (Figure 1). Prior to placing the nasal interface, airway secretions were cleared and, if deemed convenient, a dose of sedative was given (chloral hydrate or benzodiazepines). The Hudson RCI CPAP Cannula System (USA), sizes 1-5, was used. Bubble CPAP was first connected at 5 cm H 2 O and, eventually, this level was progressively increased up to 8 cm H 2 O, although a higher initial pressure could be used at the discretion of the treating physician. In addition, initial was 100% and then reduced based on the patient s saturation. Comorbidities were recorded: congenital heart disease, prematurity, malnutrition, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and high social risk (unmet basic needs). The presence of complications, such as abdominal distension, pressure injury, and pneumothorax, was determined. I n a d d i t i o n, p a t i e n t s w e i g h t, a g e, sex, diagnosis, virological tests (indirect immunofluorescence assay [iifa], polymerase chain reaction [PCR]), culture results, sedative administration, length of bubble CPAP use, and length of stay in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) were recorded. CPAP was considered successful if the RR reduced by 15% from the previous value and Figure 1. Bubble continuous positive airway pressure flow 1. Nasal prongs. 2. Underwater bottle. 3. Heater. 4. Air-oxygen source. 5. Pressure gauge. 6. Expiratory tubing.
3 Brief reports / Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115(3): / 279 Tal s score decreased by 2 points. CPAP was considered to fail if Tal s score did not reduce (HR, RR, intercostal retraction, wheezing) and/or desaturation (< 90%) and/or sensory deficit occurred, at the discretion of the treating physician. Criteria to remove bubble CPAP were as follows: CPAP at 4 cm H 2 O, < 40%, Tal s score of 4 points. Simple descriptive statistics were used to describe the sample: mean, median, standard deviation (SD), and range. Percentages corresponding to qualitative outcome measures were estimated and compared using a χ² test for independence to establish the association among outcome measures, with a significance level < 5%. Odds ratios (ORs) were analyzed for all possible cases. In addition, box-and-whisker plots were used to describe how quantitative outcome measures behaved. Sensitivity and specificity curves were used to establish cut-off points for bubble CPAP failure predictive outcome measures. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and their corresponding tests were used to establish which outcome measures worked better to determine bubble CPAP failure. The study protocol was assessed and approved by the Advisory Commission for Biomedical Research in Humans (Comisión Asesora en Investigación Biomédica en Seres Humanos, CAIBSH). RESULTS One hundred and twenty patients were included. The intervention was successful in 72% of cases, and failed in 28%. Table 1 describes the demographic and clinical outcome measures of enrolled patients before CPAP use and compares successful and failed interventions. All patients had an indirect immunofluorescence assay (IIFA), and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) was detected in 70 cases. H1N1 was detected in 5% of patients. CPAP was established at 5-8 cm H 2 O, with an average of 6 cm H 2 O. Complications were observed in 3.3% of cases (abdominal distension, pneumothorax). Mean bubble CPAP duration was h (95% confidence interval [CI]: ). Mean length of stay in the intermediate care unit was 10 days (95% CI: ); in the success group, it was 8.33 days (SD 3.36), and in the failure group, it was days (SD 5.19) (the latter included the length of stay in the intensive care unit). Table 2 shows outcome measures recorded during the hours after initiating bubble CPAP. The subsequent analysis identified that a 15% reduction in HR and a 2-point decrease in Tal s score at 2 hours of non-invasive ventilation (NIV) initiation were the factors related to success, with an OR of 6.41 (95% CI: ), and of 9.07 (95% CI: ), respectively. Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the sample and each group as per CPAP success or failure. Age is stated as median and range; the other outcome measures, as mean ± standard deviation All (n= 120) Success group (n= 86) Failure group (n= 34) p Age (months old); X (range) 3 (1-22) 6.08 ( ) 5.4 (2.9-12) > 0.05 Female Weight (kg) 6.49 ± ± ± 2.43 Baseline RR ± ± ± Baseline HR ± ± ± Baseline (%) ± ± ± 2.39 Oxygen saturation ± ± ± 2.69 Tal s score 9.26 ± ± ± 1.19 Bronchiolitis Pneumonia Predisposing clinical condition Prematurity 29 (24%) 23 (79%) 6 (21%) > 0.05 Malnutrition 11 (9.16%) 8 (73%) 3 (27%) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia 6 (5%) 5 (83%) 1 (17%) Congenital heart disease 8 (7%) 5 (62.5%) 3 (37.5%) High social risk 14 (12%) 8 (57%) 6 (43%) RR: respiratory rate; HR: heart rate; FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen.
4 280 / Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115(3): / Brief reports When two qualitative outcome measures are combined, i.e., a 15% reduction in RR and a 2-point decrease in Tal s score at 2 hours, OR increased to (95% CI: ). No statistically significant findings were made at 24 and 48 h. DISCUSSION In our study, we described bubble CPAP use among patients younger than 2 years old with ALRTIs as a treatment strategy to avoid conventional mechanical ventilation. The intervention was successful in 72% of cases, and failed in 28%. Success percentage was similar to that published by other authors (83% and 75.5%). 8,9 In this study, at 2 hours of NIV initiation with bubble CPAP, a 15% reduction in RR from the previous value and a 2-point decrease in Tal s score were predictors of success. Other authors have also identified a reduction in RR as a predictor of NIV success. 6 This fact highlights the importance of monitoring clinical parameters and ongoing assessment of these patients. Unlike other studies, 8-11 Tal s score was used in this study. Modified Tal s score has demonstrated to be highly useful in practice for a standardization of clinical management and decision-making. 12 Although HR significantly reduced at 2 hours, this outcome measure was an adequate predictor of failure as of 6 h, unlike what has been reported by Mayordomo-Colunga et al., 8 who mentioned that HR reduction in the first hour was an adequate predictor of success. In this study, no statistically significant differences were observed between both groups in terms of weight, age, predisposing factors, or bronchiolitis or pneumonia diagnosis. Mayordomo-Colunga et al. indicated that the presence of apnea, a lower weight, and a younger age were predictors of failure, 8 as well as Antonelli et al., 9 who also identified a younger age, a higher Woods score, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or pneumonia. In our experience, NIV given through bubble CPAP was a highly successful intervention among children with moderate to severe ALRTIs. CONCLUSION The early use of bubble CPAP works as a strategy to optimize patients access to quality care and the utilization of available resources. Table 2. Results. Respiratory rate, heart, rate,, oxygen saturation, and Tal s score Outcome measure Overall sample Success group Failure group p h n X ± SD n X ± SD n X ± SD RR ± ± < RR ± ± ± RR ± ± ± RR ± ± ± HR ± ± ± HR ± ± ± HR ± ± ± HR ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± Sat ± ± ± Sat ± ± ± Sat ± ± ± Sat ± ± ± Tal ± ± ± 1.69 < Tal ± ± ± 1.91 < SD: standard deviation; RR: respiratory rate; HR: heart rate; FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen; Sat: oxygen saturation; Tal: Tal s score; h: hours since non-invasive ventilation initiation.
5 Brief reports / Arch Argent Pediatr 2017;115(3): / 281 In this study, RR, HR at 2 hours, and Tal s score at 2 and 6 hours after NIV initiation were predictors of the success or failure of the intervention. REFERENCES 1. Ministerio de Salud de la Nación. Estadísticas Vitales. [Accessed on: January 9 th, 2017]. Available at: deis.msal.gov.ar/index.php/estadisticasvitales/. 2. Comité Nacional de Neumología, Comité Nacional de Infectología, Comité Nacional de Medicina Interna. Recomendaciones para el manejo de las infecciones respiratorias agudas bajas (IRAB) en menores de 2 años. Arch Argent Pediatr 2015;113(4): Fortenberry JD, Del Toro J, Jefferson LS, Evey L, et al. Management of pediatric acute hypoxemic respiratory insufficiency with bilevel positive pressure (BiPAP) nasal mask ventilation. Chest 1995;108(4): Teague WG. Noninvasive ventilation in the pediatric intensive care unit for children with acute respiratory failure. Pediatr Pilmonol 2003;35(6): Medina Villanueva A, Prieto Espuñes S, Los Arcos Solas M, Rey Galán M, et al. Aplicación de la ventilación no invasiva en una unidad de cuidados intensivos pediátricos. An Pediatr (Barc) 2005;62(1): Essouri S, Chevret l, Durand P, Haas V, et al. Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation: five years of experience in a pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2006;7(6): Bernet V, Hug MI, Frey B. Predictive factors for the success of noninvasive mask ventilation in infants and children with acute respiratory failure. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2005; 6(6): Mayordomo-Colunga J, Medina A, Rey C, Los Arcos M, et al. Predictores de éxito y de fracaso en la ventilación no invasiva en la bornquiolitis aguda. An Pediatr (Barc) 2009;708(1): Larrar S, Essouri S, Durand P, Chevret L, et al. Place de la ventilation non invasive nasale dans la prise en charge des broncho-alvéolites sévéres. Arch Pediatr 2006;13(11): Javouhey E, Barats A, Richard N, Stamm D, et al. Non-invasive ventilation as primary ventilatory support for infants with severe bronchiolitis. Intensive Care Med 2008;34(9): Antonelli M, Conti G, Moro M, Esquinas A, et al. Predictors of failure of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: a multicenter study. Intensive Care Med 2001;27(11): Tal A, Bavilski C, Yohai D, Bearman J, et al. Dexamethasone and salbutamol in the treatment of acute wheezing in infants. Pediatrics 1983;71(1):13-8.
High-flow nasal cannula use in a paediatric intensive care unit over 3 years
 High-flow nasal cannula use in a paediatric intensive care unit over 3 years Tracey I Wraight and Subodh S Ganu Respiratory illness and/or distress is the commonest reason for non-elective paediatric intensive
High-flow nasal cannula use in a paediatric intensive care unit over 3 years Tracey I Wraight and Subodh S Ganu Respiratory illness and/or distress is the commonest reason for non-elective paediatric intensive
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Post-extubation non-invasive ventilation in the pediatric intensive care unit: a multicenter study
 Original article Arch Argent Pediatr 2018;116(5):333-339 / 333 Post-extubation non-invasive ventilation in the pediatric intensive care unit: a multicenter study Juan P. Bonora, B.S. a, Judith Frydman,
Original article Arch Argent Pediatr 2018;116(5):333-339 / 333 Post-extubation non-invasive ventilation in the pediatric intensive care unit: a multicenter study Juan P. Bonora, B.S. a, Judith Frydman,
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call
 AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด
 Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Provide support without
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Provide support without
Respiratory Management in Pediatrics
 Respiratory Management in Pediatrics Children s Hospital Omaha Critical Care Transport Sue Holmer RN, C-NPT Objectives Examine the differences between the pediatric and adults airways. Recognize respiratory
Respiratory Management in Pediatrics Children s Hospital Omaha Critical Care Transport Sue Holmer RN, C-NPT Objectives Examine the differences between the pediatric and adults airways. Recognize respiratory
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Non-Invasive Ventilation in Pediatric Medicine. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Non-Invasive Ventilation in Pediatric Medicine. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Trial protocol - NIVAS Study
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
Bronchiolitis (BRO) Overview
 Bronchiolitis (BRO) Overview Common lower respiratory tract infection and leading cause of infant hospitalization Significant impact on the elderly with >220k hospitalizations per year in the US No drugs
Bronchiolitis (BRO) Overview Common lower respiratory tract infection and leading cause of infant hospitalization Significant impact on the elderly with >220k hospitalizations per year in the US No drugs
Practical Application of CPAP
 CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither?
 Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Nasal continuous positive airway pressure with heliox in infants with acute bronchiolitis
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 1458 1462 SHORT COMMUNICATION Nasal continuous positive airway pressure with heliox in infants with acute bronchiolitis Federico Martinón-Torres a,b,, Antonio Rodríguez-Núñez
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 1458 1462 SHORT COMMUNICATION Nasal continuous positive airway pressure with heliox in infants with acute bronchiolitis Federico Martinón-Torres a,b,, Antonio Rodríguez-Núñez
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants. Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid
 Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Nottingham Children s Hospital
 High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Guide line for the use of HFNCT (High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy) Contact Name
High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Guide line for the use of HFNCT (High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy) Contact Name
Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach
 Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach Suchada Sritippayawan, MD. Div. Pulmonology & Crit Care Dept. Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Kanokporn Udomittipong, MD.
Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach Suchada Sritippayawan, MD. Div. Pulmonology & Crit Care Dept. Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Kanokporn Udomittipong, MD.
CPAP failure in preterm infants: incidence, predictors and consequences
 CPAP failure in preterm infants: incidence, predictors and consequences SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT METHODS Study setting The Royal Hobart Hospital has an 11-bed combined Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
CPAP failure in preterm infants: incidence, predictors and consequences SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT METHODS Study setting The Royal Hobart Hospital has an 11-bed combined Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
Estimating RSV Disease Burden in the United States
 Estimating RSV Disease Burden in the United States Brian Rha, MD, MSPH Medical Epidemiologist, Division of Viral Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Severe Acute Respiratory Infection Surveillance
Estimating RSV Disease Burden in the United States Brian Rha, MD, MSPH Medical Epidemiologist, Division of Viral Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Severe Acute Respiratory Infection Surveillance
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During. Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Summary and algorithms
 Chapter 23 Summary and algorithms A. Medina, M. Pons and F. Martinón-Torres INTRODUCTION The demands that non-invasive ventilation (NIV) places on hospital staff require that hospital wards develop clear
Chapter 23 Summary and algorithms A. Medina, M. Pons and F. Martinón-Torres INTRODUCTION The demands that non-invasive ventilation (NIV) places on hospital staff require that hospital wards develop clear
SECTION 1: INCLUSION, EXCLUSION & RANDOMISATION INFORMATION
 SECTION 1: INCLUSION, EXCLUSION & RANDOMISATION INFORMATION DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Given name Family name Date of birth Consent date Gender Female Male Date of surgery INCLUSION & EXCLUSION CRITERIA YES
SECTION 1: INCLUSION, EXCLUSION & RANDOMISATION INFORMATION DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Given name Family name Date of birth Consent date Gender Female Male Date of surgery INCLUSION & EXCLUSION CRITERIA YES
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices
 Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Guidelines and Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide
 Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Basics of NIV. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC. Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Basics of NIV Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Objectives: Definitions Advantages and Disadvantages Interfaces Indications Contraindications
Basics of NIV Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Objectives: Definitions Advantages and Disadvantages Interfaces Indications Contraindications
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Use of NIV 1998-2010 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1998
NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Use of NIV 1998-2010 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1998
POLICY. Number: Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Authorization
 POLICY Number: 7311-60-024 Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Authorization [ ] President and CEO [ x ] Vice President, Finance and Corporate Services Source:
POLICY Number: 7311-60-024 Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Authorization [ ] President and CEO [ x ] Vice President, Finance and Corporate Services Source:
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) NICU POCKET GUIDE
 Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
 The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1. Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure 2. Purpose of Procedure/ Guidelines/ Protocol Guideline for
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1. Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure 2. Purpose of Procedure/ Guidelines/ Protocol Guideline for
Elective nasal continuous positive airway pressure to support respiration after prolonged ventilation in infants after congenital cardiac surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elective nasal continuous positive airway pressure to support respiration after prolonged ventilation in infants after congenital cardiac surgery Hemang Gandhi, Amit Mishra 1, Rajesh Thosani,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elective nasal continuous positive airway pressure to support respiration after prolonged ventilation in infants after congenital cardiac surgery Hemang Gandhi, Amit Mishra 1, Rajesh Thosani,
Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis
 Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis Gal S, Riskin A, Chistyakov I, Shifman N, Srugo I, and Kugelman A Pediatric Department and Pediatric Pulmonary Unit Bnai Zion
Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis Gal S, Riskin A, Chistyakov I, Shifman N, Srugo I, and Kugelman A Pediatric Department and Pediatric Pulmonary Unit Bnai Zion
Name and title of the investigators responsible for conducting the research: Dr Anna Lavizzari, Dr Mariarosa Colnaghi
 Protocol title: Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Nasal CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Prematurity. Protocol identifying number: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02570217 Name and title of
Protocol title: Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Nasal CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Prematurity. Protocol identifying number: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02570217 Name and title of
PUMANI bcpap GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS. An Overview of the Pumani bcpap, Indications for bcpap, and Instructions for Use
 An Overview of the Pumani bcpap, Indications for bcpap, and Instructions for Use What is bcpap? bcpap stands for bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Sometimes called Continuous Distending Pressure,
An Overview of the Pumani bcpap, Indications for bcpap, and Instructions for Use What is bcpap? bcpap stands for bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Sometimes called Continuous Distending Pressure,
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim
 Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
A Trust Guideline for the Management of. Bronchiolitis in Infants and Children under the age of 24 months
 A Clinical Guideline recommended Children s Assessment Unit (CAU), Buxton Ward, For use in: Children s Day Ward, Jenny Lind Out-patients Department, Accident and Emergency Department By: Medical and Nursing
A Clinical Guideline recommended Children s Assessment Unit (CAU), Buxton Ward, For use in: Children s Day Ward, Jenny Lind Out-patients Department, Accident and Emergency Department By: Medical and Nursing
Difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation
 Difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation Paolo Biban, MD Director, Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit Division of Paediatrics, Major City Hospital Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata
Difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation Paolo Biban, MD Director, Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit Division of Paediatrics, Major City Hospital Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION. Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018
 NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018 Learning objectives What is NIV The difference between CPAP and BiPAP The indication of the use of NIV Complication of NIV application Patient monitoring
NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018 Learning objectives What is NIV The difference between CPAP and BiPAP The indication of the use of NIV Complication of NIV application Patient monitoring
Interdisciplinary Care of the Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Respiratory Therapy Care
 Peggy Cox, RRT, RN Frazier Rehab Institute Pulmonary Rehab Interdisciplinary Care of the Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Respiratory Therapy Care Disclosure I have the following relevant financial
Peggy Cox, RRT, RN Frazier Rehab Institute Pulmonary Rehab Interdisciplinary Care of the Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Respiratory Therapy Care Disclosure I have the following relevant financial
Kugelman A, Riskin A, Said W, Shoris I, Mor F, Bader D.
 Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
ERJ Express. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi: /
 ERJ Express. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00076912 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a non intubated patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Olaf Wiesner, *
ERJ Express. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00076912 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a non intubated patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Olaf Wiesner, *
Oscillatory High Frequency Ventilation in severe Pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome after to Fibrosis stage.
 International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 10-2018 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.10.004 Oscillatory
International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 10-2018 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.10.004 Oscillatory
Respiratory Management of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Nicholas S. Hill, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 Respiratory Management of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Nicholas S. Hill, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA Respiratory Involvement in FSHD Very variable time of onset rate of progression Muscles
Respiratory Management of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Nicholas S. Hill, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA Respiratory Involvement in FSHD Very variable time of onset rate of progression Muscles
Surgery Grand Rounds. Non-invasive Ventilation: A valuable tool. James Cromie, PGY 3 8/24/09
 Surgery Grand Rounds Non-invasive Ventilation: A valuable tool James Cromie, PGY 3 8/24/09 History of mechanical ventilation 1930 s: use of iron lung 1940 s: First NIV system (Bellevue Hospital) 1950 s:
Surgery Grand Rounds Non-invasive Ventilation: A valuable tool James Cromie, PGY 3 8/24/09 History of mechanical ventilation 1930 s: use of iron lung 1940 s: First NIV system (Bellevue Hospital) 1950 s:
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
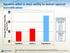 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Advantages and disadvantages of different nasal CPAP systems in newborns
 Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
You are caring for a patient who is intubated and. pressure control ventilation. The ventilator. up to see these scalars
 Test yourself Test yourself #1 You are caring for a patient who is intubated and ventilated on pressure control ventilation. The ventilator alarms and you look up to see these scalars What is the most
Test yourself Test yourself #1 You are caring for a patient who is intubated and ventilated on pressure control ventilation. The ventilator alarms and you look up to see these scalars What is the most
Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience
 Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Facilitating EndotracheaL Intubation by Laryngoscopy technique and Apneic Oxygenation Within the Intensive Care Unit (FELLOW)
 Facilitating EndotracheaL Intubation by Laryngoscopy technique and Apneic Oxygenation Within the Intensive Data Analysis Plan: Apneic Oxygenation vs. No Apneic Oxygenation Background Critically ill patients
Facilitating EndotracheaL Intubation by Laryngoscopy technique and Apneic Oxygenation Within the Intensive Data Analysis Plan: Apneic Oxygenation vs. No Apneic Oxygenation Background Critically ill patients
Landmark articles on ventilation
 Landmark articles on ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity ARDS AECC DEFINITION-1994 ALI Acute onset Bilateral chest infiltrates PCWP
Landmark articles on ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity ARDS AECC DEFINITION-1994 ALI Acute onset Bilateral chest infiltrates PCWP
INPATIENT ASTHMA CARE PROTOCOL
 INPATIENT ASTHMA CARE PROTOCOL When ordered by a physician, an eligible child 2 years of age or older who is admitted to the General Pediatric Inpatient Unit at the Children s Hospital of Georgia with
INPATIENT ASTHMA CARE PROTOCOL When ordered by a physician, an eligible child 2 years of age or older who is admitted to the General Pediatric Inpatient Unit at the Children s Hospital of Georgia with
Respiratory Distress During RSV Season
 Respiratory Distress During RSV Season Carroll King, MD, FAAP Disclosure : Carroll King, MD, FAAP has nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives At the end of this educational activity, participants should be able
Respiratory Distress During RSV Season Carroll King, MD, FAAP Disclosure : Carroll King, MD, FAAP has nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives At the end of this educational activity, participants should be able
Respiratory support for children in the emergency department
 bs_bs_bannerbs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jpc.13078 REVIEW ARTICLE Respiratory support for children in the emergency department Andreas Schibler and Donna Franklin Paediatric Critical Care Research Group, Mater
bs_bs_bannerbs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jpc.13078 REVIEW ARTICLE Respiratory support for children in the emergency department Andreas Schibler and Donna Franklin Paediatric Critical Care Research Group, Mater
10/17/2016 OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT COURSE OBJECTIVES COMMON CAUSES OF RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT J U L I E Z I M M E R M A N, R N, M S N C L I N I C A L N U R S E S P E C I A L I S T E L O I S A C U T L E R, R R T, B S R C C L I N I C A L / E D U C
OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT J U L I E Z I M M E R M A N, R N, M S N C L I N I C A L N U R S E S P E C I A L I S T E L O I S A C U T L E R, R R T, B S R C C L I N I C A L / E D U C
Discuss the benefits for developing an outpatient bronchiolitis clinic.
 Diana L Mark, RRT Pediatric Clinical Specialist Respiratory Care Wesley Medical Center Discuss the benefits for developing an outpatient bronchiolitis clinic. 1 Definition Inflammation of the bronchioles
Diana L Mark, RRT Pediatric Clinical Specialist Respiratory Care Wesley Medical Center Discuss the benefits for developing an outpatient bronchiolitis clinic. 1 Definition Inflammation of the bronchioles
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Objectives. Health care significance of ARF 9/10/15 TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE OF VARIABLE CAUSES: INVASIVE VS. NON- INVASIVE VENTILATION
 TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE OF VARIABLE CAUSES: INVASIVE VS. NON- INVASIVE VENTILATION Louisa Chika Ikpeama, DNP, CCRN, ACNP-BC Objectives Identify health care significance of acute respiratory
TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE OF VARIABLE CAUSES: INVASIVE VS. NON- INVASIVE VENTILATION Louisa Chika Ikpeama, DNP, CCRN, ACNP-BC Objectives Identify health care significance of acute respiratory
Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study
 D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
PEDIATRIC ACUTE ASTHMA SCORE (P.A.A.S.) GUIDELINES. >97% 94% to 96% 91%-93% <90% Moderate to severe expiratory wheeze
 Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
BRONCHIOLITIS. See also the PSNZ guideline - Wheeze & Chest Infections in infants under 1 year (www.paediatrics.org.nz)
 Definition What is Bronchiolitis? Assessment Management Flow Chart Admission Guidelines Investigations Management Use of Bronchodilators Other treatments Discharge Planning Bronchiolitis & Asthma References
Definition What is Bronchiolitis? Assessment Management Flow Chart Admission Guidelines Investigations Management Use of Bronchodilators Other treatments Discharge Planning Bronchiolitis & Asthma References
A study of non-invasive ventilation in acute respiratory failure
 Original Research Article A study of non-invasive ventilation in acute respiratory failure Nilima Manohar Mane 1, Jayant L. Pednekar 2, Sangeeta Pednekar 3* 1 Consultant Physician and Diabetologist, Apollo
Original Research Article A study of non-invasive ventilation in acute respiratory failure Nilima Manohar Mane 1, Jayant L. Pednekar 2, Sangeeta Pednekar 3* 1 Consultant Physician and Diabetologist, Apollo
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Protocol Update 2019
 Protocol Update 2019 There have been several questions revolving around protocol updates and how they are to be conducted. As many of you are aware there is a protocol submission process in the appendix
Protocol Update 2019 There have been several questions revolving around protocol updates and how they are to be conducted. As many of you are aware there is a protocol submission process in the appendix
COMPLICACIONS DE LA VENTILACIÓ MECÀNICA NO INVASIVA
 COMPLICACIONS DE LA VENTILACIÓ MECÀNICA NO INVASIVA Dr. Miquel Ferrer UVIIR, Servei de Pneumologia, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, CibeRes, Barcelona. E- mail: miferrer@clinic.ub.es Barcelona, 3 de novembre
COMPLICACIONS DE LA VENTILACIÓ MECÀNICA NO INVASIVA Dr. Miquel Ferrer UVIIR, Servei de Pneumologia, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, CibeRes, Barcelona. E- mail: miferrer@clinic.ub.es Barcelona, 3 de novembre
British Thoracic Society Paediatric Pneumonia Audit National Audit Period: 1 November January 2017 Dr Julian Legg and Dr Charlotte Rampton
 British Thoracic Society Paediatric Pneumonia Audit National Audit Period: 1 November 2016 31 January 2017 Dr Julian Legg and Dr Charlotte Rampton Number of records submitted: 7302 Number of participants:
British Thoracic Society Paediatric Pneumonia Audit National Audit Period: 1 November 2016 31 January 2017 Dr Julian Legg and Dr Charlotte Rampton Number of records submitted: 7302 Number of participants:
Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality?
 Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality? Clinical problem and domain I selected this case because although this was the second patient we had proned in our unit within a week,
Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality? Clinical problem and domain I selected this case because although this was the second patient we had proned in our unit within a week,
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the
 Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
NI 60. Non-invasive ventilation without compromise. Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia. Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support
 NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. This online publication has been corrected. The corrected
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. This online publication has been corrected. The corrected
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre
 PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
Acute Paediatric Respiratory Pathway
 Guideline for the use of high Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy (Optiflow or Airvo) in Children with Bronchiolitis or an acute respiratory illness Introduction: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen enables
Guideline for the use of high Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy (Optiflow or Airvo) in Children with Bronchiolitis or an acute respiratory illness Introduction: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen enables
Clinical Update. Non-invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation in children
 DOI-10.21304/2018.0503.00398 Kundan Mittal *, N Rungta **, Vinayak Patki ***, H K Aggarwal**** * Senior Professor Pediatrics, ****Senior Professor & Head of Unit Medicine and Nephrologist,Pt B D Sharma,
DOI-10.21304/2018.0503.00398 Kundan Mittal *, N Rungta **, Vinayak Patki ***, H K Aggarwal**** * Senior Professor Pediatrics, ****Senior Professor & Head of Unit Medicine and Nephrologist,Pt B D Sharma,
Learning Objectives. 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence
 Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities
 Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis. Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine
 Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC. Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand
 786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP
 I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP II. Policy: PSV with BiPAP device/nasal CPAP will be initiated upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel trained
I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP II. Policy: PSV with BiPAP device/nasal CPAP will be initiated upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel trained
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution
 Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Liberation from Mechanical Ventilation in Critically Ill Adults
 Liberation from Mechanical Ventilation in Critically Ill Adults 2017 ACCP/ATS Clinical Practice Guidelines Timothy D. Girard, MD, MSCI Clinical Research, Investigation, and Systems Modeling of Acute Illness
Liberation from Mechanical Ventilation in Critically Ill Adults 2017 ACCP/ATS Clinical Practice Guidelines Timothy D. Girard, MD, MSCI Clinical Research, Investigation, and Systems Modeling of Acute Illness
PAPER DE LA VNI EN LA RETIRADA DE LA VENTILACIÓ INVASIVA I FRACÀS D EXTUBACIÓ
 PAPER DE LA VNI EN LA RETIRADA DE LA VENTILACIÓ INVASIVA I FRACÀS D EXTUBACIÓ Dr. Miquel Ferrer UVIIR, Servei de Pneumologia, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, CibeRes, Barcelona. E- mail: miferrer@clinic.ub.es
PAPER DE LA VNI EN LA RETIRADA DE LA VENTILACIÓ INVASIVA I FRACÀS D EXTUBACIÓ Dr. Miquel Ferrer UVIIR, Servei de Pneumologia, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, CibeRes, Barcelona. E- mail: miferrer@clinic.ub.es
PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DEFINITIONS AND BACKGROUND Uncomplicated influenza illness is characterized by the abrupt onset of constitutional and respiratory signs and symptoms. Signs
PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DEFINITIONS AND BACKGROUND Uncomplicated influenza illness is characterized by the abrupt onset of constitutional and respiratory signs and symptoms. Signs
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC)
 Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
Video Cases in Pediatrics. Ran Goldman, MD BC Children s Hospital University of British
 Video Cases in Pediatrics Ran Goldman, MD BC Children s Hospital University of British Columbia @Dr_R_Goldman Bronchiolitis Viral infection of the lower respiratory tract characterized by acute inflammation,
Video Cases in Pediatrics Ran Goldman, MD BC Children s Hospital University of British Columbia @Dr_R_Goldman Bronchiolitis Viral infection of the lower respiratory tract characterized by acute inflammation,
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System
 County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress
 Flow Chart Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM As staff therapist assigned to a Level 2 NICU in a 250 bed rural medical center you are called
Flow Chart Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM As staff therapist assigned to a Level 2 NICU in a 250 bed rural medical center you are called
STATE OF OKLAHOMA 2014 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PROTOCOLS
 3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME
 FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME Guillaume CARTEAUX, Teresa MILLÁN-GUILARTE, Nicolas DE PROST, Keyvan RAZAZI, Shariq ABID, Arnaud
FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME Guillaume CARTEAUX, Teresa MILLÁN-GUILARTE, Nicolas DE PROST, Keyvan RAZAZI, Shariq ABID, Arnaud
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease 1.1 Short title Motor
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease 1.1 Short title Motor
