Bile Acids and Liver Fibrosis Causative Agent and Therapeutic Tool
|
|
|
- Augustine Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bile Acids and Liver Fibrosis Causative Agent and Therapeutic Tool Peter Fickert, Andrea Fuchsbichler, Tarek Moustafa, Gernot Zollner, Emina Halilbasic, Ulrike Stöger, Cord Langner, Helmut Denk, and Michael Trauner Laboratory of Experimental and Molecular Hepatology, Departments of Medicine and Pathology, Medical University of Graz, Austria
2 Questions YOU are currently entertaining Are there different types of liver fibrosis? What are the current concepts of the biliary type of liver fibrosis? What have we learned from mouse models? How could bile acids be a therapeutic tool in liver fibrosis?
3 Questions YOU are currently entertaining Are there different types of liver fibrosis?
4 Normal Liver Modified Silver Stain
5 ASH Modified Silver Stain
6 ASH Sirius red
7 PSC Sirius red hv pv
8 pv PSC Sirius red hv
9 PSC Modified Silver Stain pv
10 Summary I: Fibrosis Patterns Yes, there are different patterns of liver fibrosis Related to kind of trigger? Related to activated cell type?
11 Questions YOU are currently entertaining What are the current concepts of biliary type of liver fibrosis?
12 Pathogenetic Concepts of Cholangiopathies and Biliary Fibrosis autocrine/paracrine stimulation Reactive Cholangiocytes TGF-β, MCP-1, Osteopontin PDGF,TNF-α NGFs VCAM, ICAM NO
13 Pathogenetic Concepts of Cholangiopathies and Biliary Fibrosis IL-4 IL-5 IL-8 INF-γ ICAM VCAM FasL CD8 CD4 autocrine/paracrine stimulation Reactive Cholangiocytes TGF-β, MCP-1, Osteopontin PDGF,TNF-α NGFs VCAM, ICAM NO PMNs Source of ROS?
14 Pathogenetic Concepts of Cholangiopathies and Biliary Fibrosis IL-4 IL-5 IL-8 INF-γ ICAM VCAM FasL CD8 CD4 autocrine/paracrine stimulation Reactive Cholangiocytes TGF-β, MCP-1, Osteopontin PDGF,TNF-α NGFs VCAM, ICAM NO Activated Myofibroblasts ECM production Wound healing? PMNs Source of ROS?
15 Pathogenetic Concepts of Cholangiopathies and Biliary Fibrosis TRIGGER? IL-4 IL-5 IL-8 INF-γ ICAM VCAM FasL CD8? CD4 autocrine/paracrine stimulation? Reactive Cholangiocytes TGF-β, MCP-1, Osteopontin PDGF,TNF-α NGFs VCAM, ICAM NO Activated Myofibroblasts ECM production Wound healing?? PMNs Source of ROS?
16 Do Bile Acids Activate Myofibroblasts (MFBs)? Isolation of MFBs from Mdr2 -/- Characterization of MFBs: Vimentin +, Desmin +, α-sma +, CK 19 - Treatment: Proinflammatory cytokines α-sma Bile Acids Parameters: BrdU ELISA mrna collagen1a1, MMP2, osteopontin, TGF-β
17 PSC Collagen Ring around Bile Ducts pv
18 Are MFBs Fibrosers? Activated BECs produce collagen I Xia et al, Am J Pathol 2006
19 Summary II: Concept of Biliary Fibrosis Bile acids do not induce MFB activation/proliferation MFBs have low expression levels for transporters and NRs Bile acids do not induce collagen expression in bile duct epithelial cells (BECs) TGF-β induces collagen expression in BECs Questions: Interplay between different cell types? Primary trigger for activation of BECs?
20 Questions YOU are currently entertaining What have we learned from mouse models?
21 Mdr2 -/- Develop SC and Biliary Fibrosis 4 CD4 CD4 TNF-α IL-1β CD8 5 CD4 CD4 CD4 TGF-β bd 6 Fickert et al, Gastroenterology 2004;12:261
22 Periductal Fibrosis in LCA-fed Mice Ki-67 α-sma Sirius red ha bd ha bd bd pv ha pv Control pv ha ha bd pv ha bd pv ha bd LCA Fickert et al, Am J Pathol 2006; 168:410
23 Summary III: Mouse Models for Biliary Fibrosis Several mouse models for biliary fibrosis established: CBDL, DDC, LCA, Mdr2 -/- There are reactive BECs Questions: Causes and Consequences? Role of bile acids? Cytokines/Chemokines? Inflammatory cells?
24 Questions YOU are currently entertaining How could bile acids be a therapeutic tool in liver fibrosis?
25 Sirius Red norudca Reverses Biliary Fibrosis in Mdr2 -/- (KO) Mice WT Hydroxyproline (μg/g Liver) bd WT KO * KO KO+UDCA KO+UDCA * KO+norUDCA KO+norUDCA p<005 * vs WT vs KO Fickert et al, Gastroenterology 2006; 130: 465
26 Summary III: Bile Acids as a Therapeutic Tool in Biliary Fibrosis Some bile acids are antifibrotic in animal models Questions: Is there a direct antifibrotic effect? Consequence of rescuing the reactive phenotype of BECs?
27 Problems we have to resolve: What drives ductular proliferation? Is ductular reaction/proliferation a prerequisite for portal-portal bridging/biliary type of liver fibrosis? Are bile acids engaged in the proliferative response of MFBs? Are the effects of norudca direct/indirect?
28 Experimental and Molecular Hepatology Graz Center of Basic Medical Research
Mario Strazzabosco MD, PhD
 Mario Strazzabosco MD, PhD Professor of Medicine & Gastroenterology Deputy Director, Yale Liver Center, Director, Hepatobiliary Cancer Program Yale University School of Medicine Director Master Program
Mario Strazzabosco MD, PhD Professor of Medicine & Gastroenterology Deputy Director, Yale Liver Center, Director, Hepatobiliary Cancer Program Yale University School of Medicine Director Master Program
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target
 Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis
 10/1/12 Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis Hepatitis C Virus Mild inflammation Inflammation Fibrosis Cirrhosis 1 10/1/12 Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Steatosis Steatohepatitis
10/1/12 Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis Hepatitis C Virus Mild inflammation Inflammation Fibrosis Cirrhosis 1 10/1/12 Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Steatosis Steatohepatitis
Molecular mechanisms of Fibrosis: Targets of Therapy. John P Iredale University of Edinburgh, UK
 Molecular mechanisms of Fibrosis: Targets of Therapy John P Iredale University of Edinburgh, UK Take home messages: The wound healing MFBs of the liver and the hepatic macrophages are key players in progressive
Molecular mechanisms of Fibrosis: Targets of Therapy John P Iredale University of Edinburgh, UK Take home messages: The wound healing MFBs of the liver and the hepatic macrophages are key players in progressive
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9
 Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
Effects of Melittin Treatment in Cholangitis and Biliary Fibrosis in a Model of Xenobiotic-Induced Cholestasis in Mice
 Toxins 2015, 7, 3372-3387; doi:10.3390/toxins7093372 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins Effects of Melittin Treatment in Cholangitis and Biliary Fibrosis in a Model of
Toxins 2015, 7, 3372-3387; doi:10.3390/toxins7093372 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins Effects of Melittin Treatment in Cholangitis and Biliary Fibrosis in a Model of
Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by
 Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by normalizing the gene expression number to those of HPRT, then comparing the samples to untreated or naive mice.
Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by normalizing the gene expression number to those of HPRT, then comparing the samples to untreated or naive mice.
NASH Bench to Bedside
 NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Biliary Atresia. Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s
 Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
CCN1 induces hepatic ductular reaction through integrin α v. mediated activation of NF-κB
 CCN1 induces hepatic ductular reaction through integrin α v mediated activation of NF-κB Ki-Hyun Kim, 1 Chih-Chiun Chen, 1 Gianfranco Alpini, 2,3,4 and Lester F. Lau 1 1 Department of Biochemistry and
CCN1 induces hepatic ductular reaction through integrin α v mediated activation of NF-κB Ki-Hyun Kim, 1 Chih-Chiun Chen, 1 Gianfranco Alpini, 2,3,4 and Lester F. Lau 1 1 Department of Biochemistry and
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Connective Tissue Response in IBD
 Connective Tissue Response in IBD Dr I C Lawrance MB BS, PhD FRACP School of Medicine and Pharmacology, University of Western Australia, Fremantle Hospital Intestinal response to Chronic Inflammation Control
Connective Tissue Response in IBD Dr I C Lawrance MB BS, PhD FRACP School of Medicine and Pharmacology, University of Western Australia, Fremantle Hospital Intestinal response to Chronic Inflammation Control
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic,
 LIVER BIOLOGY/PATHOBIOLOGY Integrin avb6 Critically Regulates Hepatic Progenitor Cell Function and Promotes Ductular Reaction, Fibrosis, and Tumorigenesis Zhen-Wei Peng, 1,2 Naoki Ikenaga, 2 Susan B. Liu,
LIVER BIOLOGY/PATHOBIOLOGY Integrin avb6 Critically Regulates Hepatic Progenitor Cell Function and Promotes Ductular Reaction, Fibrosis, and Tumorigenesis Zhen-Wei Peng, 1,2 Naoki Ikenaga, 2 Susan B. Liu,
Current pharmacological strategies for chronic
 Dual Farnesoid X Receptor/TGR5 Agonist INT-767 Reduces Liver Injury in the Mdr2 2/2 (Abcb4 2/2 ) Mouse Cholangiopathy Model by Promoting Biliary HCO 3 2 Output Anna Baghdasaryan, 1 Thierry Claudel, 1,2
Dual Farnesoid X Receptor/TGR5 Agonist INT-767 Reduces Liver Injury in the Mdr2 2/2 (Abcb4 2/2 ) Mouse Cholangiopathy Model by Promoting Biliary HCO 3 2 Output Anna Baghdasaryan, 1 Thierry Claudel, 1,2
Successful reactivation of hepatic Mrp transporters in endotoxininduced cholestasis in mice by the CAR activator 6,7-Dimethylesculetin
 Successful reactivation of hepatic Mrp transporters in endotoxininduced cholestasis in mice by the activator 6,7-Dimethylesculetin Ina V. Martin *, Sebastian Voigt*, Michael Trauner, Christian Trautwein
Successful reactivation of hepatic Mrp transporters in endotoxininduced cholestasis in mice by the activator 6,7-Dimethylesculetin Ina V. Martin *, Sebastian Voigt*, Michael Trauner, Christian Trautwein
Mesothelin/mucin 16 signaling in activated portal fibroblasts regulates cholestatic liver fibrosis
 Mesothelin/mucin 16 signaling in activated portal fibroblasts regulates cholestatic liver fibrosis Yukinori Koyama,, David A. Brenner, Tatiana Kisseleva J Clin Invest. 2017;127(4):1254-1270. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci88845.
Mesothelin/mucin 16 signaling in activated portal fibroblasts regulates cholestatic liver fibrosis Yukinori Koyama,, David A. Brenner, Tatiana Kisseleva J Clin Invest. 2017;127(4):1254-1270. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci88845.
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Fibrosis is a highly conserved response to hepatic
 NEW HORIZONS Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis: Functional Links and Key Pathways Ekihiro Seki 1,2 and Robert F. Schwabe 3,4 Inflammation is one of the most characteristic features of chronic liver disease
NEW HORIZONS Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis: Functional Links and Key Pathways Ekihiro Seki 1,2 and Robert F. Schwabe 3,4 Inflammation is one of the most characteristic features of chronic liver disease
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases
 Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication. Bile Acids Trigger Cholemic Nephropathy in Common Bile-Duct Ligated Mice
 Bile Acids Trigger Cholemic Nephropathy in Common Bile-Duct Ligated Mice Peter Fickert, 1,2* Elisabeth Krones, 1* Marion J. Pollheimer, 1,2 Andrea Thueringer, 2 Tarek Moustafa, 1 Dagmar Silbert, 1 Emina
Bile Acids Trigger Cholemic Nephropathy in Common Bile-Duct Ligated Mice Peter Fickert, 1,2* Elisabeth Krones, 1* Marion J. Pollheimer, 1,2 Andrea Thueringer, 2 Tarek Moustafa, 1 Dagmar Silbert, 1 Emina
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease
 Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease JPEMS 2014, Physiopathology Module Corentin Bessy (Nantes) _ Gabrielle Cepella (Amsterdam) _ Charly Gaisne (Angers) _ Gwladys Guilloineau (Angers)
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease JPEMS 2014, Physiopathology Module Corentin Bessy (Nantes) _ Gabrielle Cepella (Amsterdam) _ Charly Gaisne (Angers) _ Gwladys Guilloineau (Angers)
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Unique Aspects of the Neonatal Immune System Provide Clues to the Pathogenesis of Biliary Atresia. Disclosures. Objectives
 Unique Aspects of the Neonatal Immune System Provide Clues to the Pathogenesis of Biliary Atresia Cara L. Mack, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Pediatric GI, Hepatology & Nutrition Children s Hospital
Unique Aspects of the Neonatal Immune System Provide Clues to the Pathogenesis of Biliary Atresia Cara L. Mack, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Pediatric GI, Hepatology & Nutrition Children s Hospital
Inhibition of Integrin v 6 on Cholangiocytes Blocks Transforming Growth Factor- Activation and Retards Biliary Fibrosis Progression
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:660 670 Inhibition of Integrin v 6 on Cholangiocytes Blocks Transforming Growth Factor- Activation and Retards Biliary Fibrosis Progression ELEONORA PATSENKER,*, YURY POPOV, FELIX
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:660 670 Inhibition of Integrin v 6 on Cholangiocytes Blocks Transforming Growth Factor- Activation and Retards Biliary Fibrosis Progression ELEONORA PATSENKER,*, YURY POPOV, FELIX
Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury
 Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Cytotoxic
Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Rothenberg et al. Adv Immunol; 2001 Triggers Allergens Allografts Helminths Viruses Tissue Injury Cytotoxic
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates inflammatory response. and liver fibrosis in a murine model of hepatic schistosomiasis
 Supplementary data to: 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates inflammatory response and liver fibrosis in a murine model of hepatic schistosomiasis Martina Sombetzki, Claudia D. Fuchs, Peter Fickert,
Supplementary data to: 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates inflammatory response and liver fibrosis in a murine model of hepatic schistosomiasis Martina Sombetzki, Claudia D. Fuchs, Peter Fickert,
Pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Extracellular matrix
 Pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction Extracellular matrix Javier Díez, MD, PhD. Full Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine and Director Division of Cardiovascular Sciences Centre
Pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction Extracellular matrix Javier Díez, MD, PhD. Full Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine and Director Division of Cardiovascular Sciences Centre
University of Groningen. Non-anastomotic biliary strictures after liver transplantation Hoekstra, Harm
 University of Groningen Non-anastomotic biliary strictures after liver transplantation Hoekstra, Harm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Non-anastomotic biliary strictures after liver transplantation Hoekstra, Harm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
We recently described the development of sclerosing
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2004;127:261 274 Regurgitation of Bile Acids From Leaky Bile Ducts Causes Sclerosing Cholangitis in Mdr2 (Abcb4) Knockout Mice PETER FICKERT,* ANDREA FUCHSBICHLER, MARTIN WAGNER,* GERNOT
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2004;127:261 274 Regurgitation of Bile Acids From Leaky Bile Ducts Causes Sclerosing Cholangitis in Mdr2 (Abcb4) Knockout Mice PETER FICKERT,* ANDREA FUCHSBICHLER, MARTIN WAGNER,* GERNOT
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Inflammation in heart failure: biomarker, bystander or mediator
 Inflammation in heart failure: biomarker, bystander or mediator Novel matricellular proteins to target Javier Díez, MD, PhD. Centre of Applied Medical Research and University Clinic School of Medicine,
Inflammation in heart failure: biomarker, bystander or mediator Novel matricellular proteins to target Javier Díez, MD, PhD. Centre of Applied Medical Research and University Clinic School of Medicine,
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. Presented at: of new drugs for respiratory diseases. Barcelona, Spain, September 7-11, 2013 Page 1
 PBI-4050, a novel first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound, reduces lung fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model: a comparative study with pirfenidone Presented at: Thematic Poster Session:
PBI-4050, a novel first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound, reduces lung fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model: a comparative study with pirfenidone Presented at: Thematic Poster Session:
Original Article Notch signaling affects biliary fibrosis via transcriptional regulation of RBP-jκ in an animal model of chronic liver disease
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(10):12688-12697 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014069 Original Article Notch signaling affects biliary fibrosis via transcriptional regulation of RBP-jκ in an animal model
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(10):12688-12697 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014069 Original Article Notch signaling affects biliary fibrosis via transcriptional regulation of RBP-jκ in an animal model
Virchow s Hypothesis lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation
 Virchow s Hypothesis 1863 lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation Barrett s esophagus/ Esophageal adenocarcinoma PSC / Cholangiocarcinoma Viral hepatitis
Virchow s Hypothesis 1863 lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation Barrett s esophagus/ Esophageal adenocarcinoma PSC / Cholangiocarcinoma Viral hepatitis
Altered expression and function of canalicular transporters during early development of cholestatic liver injury in Abcb4-deficient mice
 Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 306: G670 G676, 2014. First published January 30, 2014; doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00334.2013. Altered expression and function of canalicular transporters during early development
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 306: G670 G676, 2014. First published January 30, 2014; doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00334.2013. Altered expression and function of canalicular transporters during early development
Laura Smart 9/22/2011
 Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Oral Methylthioadenosine Administration Attenuates Fibrosis and Chronic Liver Disease Progression in Mdr22/2 Mice
 Oral Methylthioadenosine Administration Attenuates Fibrosis and Chronic Liver Disease Progression in Mdr22/2 Mice M. Ujue Latasa 1., Carmen Gil-Puig 1,2., Maite G. Fernández-Barrena 1,3, Carlos M. Rodríguez-Ortigosa
Oral Methylthioadenosine Administration Attenuates Fibrosis and Chronic Liver Disease Progression in Mdr22/2 Mice M. Ujue Latasa 1., Carmen Gil-Puig 1,2., Maite G. Fernández-Barrena 1,3, Carlos M. Rodríguez-Ortigosa
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Är diabetes mellitus en autoimmun sjukdom? Olle Korsgren
 Är diabetes mellitus en autoimmun sjukdom? Olle Korsgren Type 1 Diabetes is currently regarded as a T cell mediated autoimmune disease, a notion expressed in over 50 000 scientific publications. Acute
Är diabetes mellitus en autoimmun sjukdom? Olle Korsgren Type 1 Diabetes is currently regarded as a T cell mediated autoimmune disease, a notion expressed in over 50 000 scientific publications. Acute
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Pathology and pathogenesis of intrahepatic bile duct loss
 J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg (2001) 8:303 315 Pathology and pathogenesis of intrahepatic bile duct loss Yasuni Nakanuma, Koichi Tsuneyama, and Kenichi Harada Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University
J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg (2001) 8:303 315 Pathology and pathogenesis of intrahepatic bile duct loss Yasuni Nakanuma, Koichi Tsuneyama, and Kenichi Harada Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University
Portal Fibroblasts in Biliary Fibrosis
 Curr Pathobiol Rep (2014) 2:185 190 DOI 10.1007/s40139-014-0054-y MYOFIBROBLAST (TATIANA KISSELEVA, SECTION EDITOR) Portal Fibroblasts in Biliary Fibrosis Rebecca G. Wells Published online: 14 September
Curr Pathobiol Rep (2014) 2:185 190 DOI 10.1007/s40139-014-0054-y MYOFIBROBLAST (TATIANA KISSELEVA, SECTION EDITOR) Portal Fibroblasts in Biliary Fibrosis Rebecca G. Wells Published online: 14 September
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA
 LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
USTEKINUMAB and BRIAKINUMAB
 USTEKINUMAB and BRIAKINUMAB Andrew Blauvelt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Dermatology and Dept. of Molecular Microbiology & Immunology Oregon Health & Science University Chief, Dermatology Service Veteran
USTEKINUMAB and BRIAKINUMAB Andrew Blauvelt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Dermatology and Dept. of Molecular Microbiology & Immunology Oregon Health & Science University Chief, Dermatology Service Veteran
contributes to reversal of biliary fibrosis by Popov et al.
 Supplementary data to MS Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cholangiocytes contributes to reversal of biliary fibrosis by Popov et al. Supplementary table 1. Primers and probes used in quantitative
Supplementary data to MS Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cholangiocytes contributes to reversal of biliary fibrosis by Popov et al. Supplementary table 1. Primers and probes used in quantitative
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Materials and Methods
 Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Review Article T Helper 17 Cells in Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 607073, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/607073 Review Article T Helper 17 Cells in Autoimmune Liver Diseases Masanori Abe, Yoichi Hiasa,
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 607073, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/607073 Review Article T Helper 17 Cells in Autoimmune Liver Diseases Masanori Abe, Yoichi Hiasa,
Bile acids initiate cholestatic liver injury by triggering a hepatic specific inflammatory response. Supplementary Results
 Bile acids initiate cholestatic liver injury by triggering a hepatic specific inflammatory response Shi-Ying Cai 1, Xinshou Ouyang 1, Yonglin Chen 1, Carol J. Soroka 1, Juxian Wang 2, Albert Mennone 1,
Bile acids initiate cholestatic liver injury by triggering a hepatic specific inflammatory response Shi-Ying Cai 1, Xinshou Ouyang 1, Yonglin Chen 1, Carol J. Soroka 1, Juxian Wang 2, Albert Mennone 1,
EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES
 EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES JAMES M. ANDERSON, MD, PhD DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR DEPARTMENTS OF PATHOLOGY, MACROMOLECULAR SCIENCE, AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING CASE WESTERN
EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES JAMES M. ANDERSON, MD, PhD DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR DEPARTMENTS OF PATHOLOGY, MACROMOLECULAR SCIENCE, AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING CASE WESTERN
Research in IBD at University of Colorado Denver
 Research in IBD at University of Colorado Denver Blair Fennimore, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology UCH Crohn s and Colitis Center Mucosal Inflammation Program
Research in IBD at University of Colorado Denver Blair Fennimore, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology UCH Crohn s and Colitis Center Mucosal Inflammation Program
The biliary epithelium is a complex network of. Forkhead Box A2 Regulates Biliary Heterogeneity and Senescence During Cholestatic Liver Injury in Mice
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 65, NO. 2, 2017 AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE Forkhead Box A2 Regulates Biliary Heterogeneity and Senescence During
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 65, NO. 2, 2017 AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE Forkhead Box A2 Regulates Biliary Heterogeneity and Senescence During
Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο
 Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Σ. ΓΟΥΜΕΝΟΣ Νεφρολογικό και Μεταμοσχευτικό Κέντρο Πανεπιστημιακό Νοσοκομείο Πατρών Causes of chronic
Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Σ. ΓΟΥΜΕΝΟΣ Νεφρολογικό και Μεταμοσχευτικό Κέντρο Πανεπιστημιακό Νοσοκομείο Πατρών Causes of chronic
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
WHAT THE EXPERIMENTAL MODELS CAN TEACH US IN NAFLD/NASH? Claudio Tiribelli, MD PhD Scientific Director FIF
 WHAT THE EXPERIMENTAL MODELS CAN TEACH US IN NAFLD/NASH? Claudio Tiribelli, MD PhD Scientific Director FIF ctliver@fegato.it Worldwide estimated prevalence of NAFLD distribution of PNPLA3 genotypes 2017-Younussi
WHAT THE EXPERIMENTAL MODELS CAN TEACH US IN NAFLD/NASH? Claudio Tiribelli, MD PhD Scientific Director FIF ctliver@fegato.it Worldwide estimated prevalence of NAFLD distribution of PNPLA3 genotypes 2017-Younussi
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Lessons from the toxic bile concept for the pathogenesis and treatment of cholestatic liver diseases
 Wien Med Wochenschr (2008) 158/19 20: 542 548 DOI 10.1007/s10354-008-0592-1 Ó Springer-Verlag 2008 Printed in Austria Lessons from the toxic bile concept for the pathogenesis and treatment of cholestatic
Wien Med Wochenschr (2008) 158/19 20: 542 548 DOI 10.1007/s10354-008-0592-1 Ó Springer-Verlag 2008 Printed in Austria Lessons from the toxic bile concept for the pathogenesis and treatment of cholestatic
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Liver Fibrosis: Which Mechanisms Matter?
 REVIEW Liver Fibrosis: Which Mechanisms Matter? Ralf Weiskirchen, Ph.D.,* and Frank Tacke, M.D., Ph.D. HEPATIC FIBROSIS Historically, fibrosis was defined by a World Health Organization expert group in
REVIEW Liver Fibrosis: Which Mechanisms Matter? Ralf Weiskirchen, Ph.D.,* and Frank Tacke, M.D., Ph.D. HEPATIC FIBROSIS Historically, fibrosis was defined by a World Health Organization expert group in
Mitosis. Single Nano Micro Milli Macro. Primary. PCNA expression
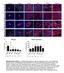 a b c DAPI YFP CC3 DAPI YFP PCNA DAPI YFP ph3 DAPI YFP KI67 e 6 Mitosis f 1 PCNA expression %ph3 + /YFP + n= 63 87 61 3 13 8 n= 15 3 9 1 5 %PCNA+/YFP+ 8 6 Supplementary Figure 1. Proliferation/apoptosis
a b c DAPI YFP CC3 DAPI YFP PCNA DAPI YFP ph3 DAPI YFP KI67 e 6 Mitosis f 1 PCNA expression %ph3 + /YFP + n= 63 87 61 3 13 8 n= 15 3 9 1 5 %PCNA+/YFP+ 8 6 Supplementary Figure 1. Proliferation/apoptosis
Supplementary Information File
 Supplementary Information File Supplementary Table 1. List of synthesized sirna sequences for target genes sirna Species Sequence Ctrl sirna mouse sense 5 -UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3 Antisense 5 -ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3
Supplementary Information File Supplementary Table 1. List of synthesized sirna sequences for target genes sirna Species Sequence Ctrl sirna mouse sense 5 -UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3 Antisense 5 -ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3
Study Design to Validate Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in NASH Due to Cirrhosis
 Study Design to Validate Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in NASH Due to Cirrhosis Detlef Schuppan Institute of Translational Immunology and Research Center for Immune Therapy, University Medical Center
Study Design to Validate Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in NASH Due to Cirrhosis Detlef Schuppan Institute of Translational Immunology and Research Center for Immune Therapy, University Medical Center
Osteopontin a bioactive milk protein with immunological properties
 Osteopontin a bioactive milk protein with immunological properties Esben S. Sørensen Section for Molecular Nutrition Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics Aarhus University, Denmark Proteins in
Osteopontin a bioactive milk protein with immunological properties Esben S. Sørensen Section for Molecular Nutrition Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics Aarhus University, Denmark Proteins in
E2F1 Is a Novel Fibrogenic Gene That Regulates Cholestatic Liver Fibrosis Through the Egr-1/SHP/EID1 Network
 AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE E2F1 Is a Novel Fibrogenic Gene That Regulates Cholestatic Liver Fibrosis Through the Egr-1/SHP/EID1 Network Yuxia Zhang, 1 * Ningyi Xu, 2 * Jun Xu, 1,3 Bo Kong,
AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE E2F1 Is a Novel Fibrogenic Gene That Regulates Cholestatic Liver Fibrosis Through the Egr-1/SHP/EID1 Network Yuxia Zhang, 1 * Ningyi Xu, 2 * Jun Xu, 1,3 Bo Kong,
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Healing & Repair. Tissue Regeneration
 Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Foxa1 and Foxa2 regulate bile duct development in mice
 Foxa1 and Foxa2 regulate bile duct development in mice Zhaoyu Li,, Sara Sackett, Klaus H. Kaestner J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1537-1545. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci38201. Research Article Hepatology The
Foxa1 and Foxa2 regulate bile duct development in mice Zhaoyu Li,, Sara Sackett, Klaus H. Kaestner J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1537-1545. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci38201. Research Article Hepatology The
HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL
 The Role of the Various Monocyte Types in Atherothrombotic Disease Protective vs. Detrimental Effects and Therapeutic Implications Matthias Nahrendorf MGH Center for Systems Biology http://csb.mgh.harvard.edu/investigator/matthias_nahrendorf
The Role of the Various Monocyte Types in Atherothrombotic Disease Protective vs. Detrimental Effects and Therapeutic Implications Matthias Nahrendorf MGH Center for Systems Biology http://csb.mgh.harvard.edu/investigator/matthias_nahrendorf
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
New Frontiers in Atherosclerotic Disease and Myocardial Infarction: From local inflammation to systemic stem and progenitor cell reaction
 New Frontiers in Atherosclerotic Disease and Myocardial Infarction: From local inflammation to systemic stem and progenitor cell reaction Matthias Nahrendorf MGH Center for Systems Biology http://csb.mgh.harvard.edu/investigator/matthias_nahrendorf
New Frontiers in Atherosclerotic Disease and Myocardial Infarction: From local inflammation to systemic stem and progenitor cell reaction Matthias Nahrendorf MGH Center for Systems Biology http://csb.mgh.harvard.edu/investigator/matthias_nahrendorf
HMGB1 promotes ductular reaction and tumorigenesis in autophagy-deficient livers
 HMGB1 promotes ductular reaction and tumorigenesis in autophagy-deficient livers Bilon Khambu,, Zheng Dong, Xiao-Ming Yin J Clin Invest. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci91814. Research Article Cell biology
HMGB1 promotes ductular reaction and tumorigenesis in autophagy-deficient livers Bilon Khambu,, Zheng Dong, Xiao-Ming Yin J Clin Invest. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci91814. Research Article Cell biology
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Efficacy and Safety of Seladelpar in Primary Biliary Cholangitis 52-Week Analysis of a Dose-Ranging Phase 2 Study
 Efficacy and Safety of Seladelpar in Primary Biliary Cholangitis 52-Week Analysis of a Dose-Ranging Phase 2 Study Bowlus CL, Neff G, Aspinall R, Galambos M, Goel A, Hirschfield G, Kremer AE, Mayo MJ, Swain
Efficacy and Safety of Seladelpar in Primary Biliary Cholangitis 52-Week Analysis of a Dose-Ranging Phase 2 Study Bowlus CL, Neff G, Aspinall R, Galambos M, Goel A, Hirschfield G, Kremer AE, Mayo MJ, Swain
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
The inflammatory process and immune reactions associated with implant use
 The inflammatory process and immune reactions associated with implant use Professor Peter A Revell Implant Biology Research Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering Division Eastman Dental Institute London
The inflammatory process and immune reactions associated with implant use Professor Peter A Revell Implant Biology Research Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering Division Eastman Dental Institute London
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. No conflicts of interest
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest University Heart Centre Tübingen Angiogenic actions of platelets Meinrad Gawaz, MD, FESC Tübingen, Germany ESC 2011 Paris GPIb GPIb GPVI TxA2
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest University Heart Centre Tübingen Angiogenic actions of platelets Meinrad Gawaz, MD, FESC Tübingen, Germany ESC 2011 Paris GPIb GPIb GPVI TxA2
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Protects From Liver Injury and Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Sclerosing Cholangitis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2010;138:2499 2508 Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Protects From Liver Injury and Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Sclerosing Cholangitis MARKUS MAIR,* GERNOT ZOLLNER, DORIS
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2010;138:2499 2508 Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Protects From Liver Injury and Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Sclerosing Cholangitis MARKUS MAIR,* GERNOT ZOLLNER, DORIS
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology
 Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Dioscin Exerts Protective Effects Against Crystalline Silica-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
 Ivyspring International Publisher 4255 Theranostics Research Paper 2017; 7(17): 4255-4275. doi: 10.7150/thno.20270 Dioscin Exerts Protective Effects Against Crystalline Silica-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Ivyspring International Publisher 4255 Theranostics Research Paper 2017; 7(17): 4255-4275. doi: 10.7150/thno.20270 Dioscin Exerts Protective Effects Against Crystalline Silica-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Cholangiopathies are a broad spectrum of disorders
 Activation of the Developmental Pathway Neurogenin-3/MicroRNA-7a Regulates Cholangiocyte Proliferation in Response to Injury Marco Marzioni, 1 Laura Agostinelli, 1 Cinzia Candelaresi, 1 Stefania Saccomanno,
Activation of the Developmental Pathway Neurogenin-3/MicroRNA-7a Regulates Cholangiocyte Proliferation in Response to Injury Marco Marzioni, 1 Laura Agostinelli, 1 Cinzia Candelaresi, 1 Stefania Saccomanno,
Topically Applicable Stromal Cell Growth Factors - Encapsulated Cosmeceuticals
 Topically Applicable Stromal Cell Growth Factors - Encapsulated Cosmeceuticals Stem cells move to injured area, differentiate into neighboring cells, and replace the damaged cells Cell Eons Stem cells
Topically Applicable Stromal Cell Growth Factors - Encapsulated Cosmeceuticals Stem cells move to injured area, differentiate into neighboring cells, and replace the damaged cells Cell Eons Stem cells
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, M.D., Ph.D Department of Hematopathology The University of Texas M.
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, M.D., Ph.D Department of Hematopathology The University of Texas M.
Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15.
 Supplementary Table 1. Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15. Male Female Cytokine Control C-26 Control C-26 IL-1β 2.0 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 1.5* 1.8 ± 0.2 6.8 ± 1.4*
Supplementary Table 1. Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15. Male Female Cytokine Control C-26 Control C-26 IL-1β 2.0 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 1.5* 1.8 ± 0.2 6.8 ± 1.4*
Management of cholestatic diseases Today and tomorrow
 12th Paris Hepatology Conference Management of cholestatic diseases Today and tomorrow Paris 15 January 2019 U. Beuers Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Tytgat Institute for Liver and Intestinal
12th Paris Hepatology Conference Management of cholestatic diseases Today and tomorrow Paris 15 January 2019 U. Beuers Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Tytgat Institute for Liver and Intestinal
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
