Timing Impairments and Neural Dysfunction in Basal Ganglia Disorders
|
|
|
- Bryan Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Timing Impairments and Neural Dysfunction in Basal Ganglia Disorders Deborah L. Harrington University of California, San Diego Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System Co-Investigators University of California, San Diego Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System, California USA Gabriel N. Castillo, David D. Song, Christopher H. Fong, Jason D. Reed, and Roland R. Lee Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio USA Stephen M. Rao, Katherine A. Koenig, Svetlana Primak, and Sally Durgerian University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa USA Jane S. Paulsen
2 Time expansion/compression Properties of stimuli intensity novelty magnitude sensory modality Behavioral context externally versus internally guided timing predictability Core cognitive functions attention memory executive functions (decision making)
3 Corticostriatal anatomical connectivity Clock Signal (tonic dopamine/glutamate) phasic dopamine Core Timer Striatal Beat Frequency Model (Matell & Meck, 2004) Striatum Receives cortical oscillatory activity, which evolves as function of event duration Detects state of oscillatory pattern & responds when pattern matches reinforced state Dopamine (DA) Tonic DA & glutamate alter cortical oscillation frequencies Phasic DA signals onset/offset of timed event & strengthens synapses in striatum activated by beat frequency pattern
4 Parkinson s Disease (PD) Neuropathology Dopamine cell loss in nigrostriatal and to lesser extent, mesocortical pathway Symptoms Motor (tremor, rigidity, slowness, postural instability, freezing) Cognitive (executive, processing speed, visuospatial) Other (speech, sensation, sleep, mood, smell) Clinical Heterogeneity of Symptoms motor (tremor vs non-tremor dominant) domains of cognitive symptoms response to medication day-to-day fluctuation in symptoms
5 Timing in Parkinson s disease (PD) Temporal processing deficits in PD [Pastor et al, 1992; Rammsayer 1997; Harrington et al, 1998, 2011; Malapani et al, 2002; Elsinger, et al, 2003; Perbal et al, 2005; Smith et al., 2007; Jones et al., 2008, 2011; Merchant et al, 2008; Koch et al, 2008] Timing dysfunction is clinically relevant Freezing of gait or finger movements improved by pacing cues [McIntosh et al, 1997; Vercruysse et al, 2012] Brain mechanisms not well understood Time reproduction (fmri and PET) [Cerasa et al, 2006; Yu et al., 2007; Jahanshahi et al, 2010] Functional significance of abnormal activity in classic motor systems unclear (e.g., striatum, cerebellum) Effect of dopamine on brain activation not understood [Jahanshahi et al, 2010]
6 percent signal change Neural control of time perception in PD Study Participants 19 neurologically intact adults 21 PD without cognitive impairment groups similar in age and education level UPDRS motor subscale OFF (29.6, SD=10.4) ON (22.8, SD=8) Cortical & striatal volume normal in PD BOLD fmri detects localized changes in cerebral blood volume, flow, & oxygenation correlates with neural activity excellent spatial resolution, sluggish temporal resolution Time Perception Task Time (seconds) Image Acquisition n
7 fmri task design and hypotheses Phase of Trial DECISION 12 to 24 s post-trial onset 6 sec ENCODING 0 to 12 s post-trial onset Phase Processes Neural Systems Dopamine Encoding timing WM maintenance striatum, SMA improve striatal activation Decision timing executive processes striatum, SMA, MFG improve striatal activation cortex?
8 Percent Longer Behavioral results Time discrimination worse in PD than controls [group X comparison interval, p<.005] Dopamine therapy did not improve time discrimination No group differences in reaction time 100 Auditory Visual Control Group PD OFF PD ON Comparison Interval (% difference from standard interval) Harrington et al, PLoS One, 6(2), 2011
9 Regional activation results (PD OFF & controls) Encoding motor circuit executive circuit limbic system & vermis Decision striatum memory retrieval network sensory (vermis) No group difference Group difference Harrington et al, PLoS One, 6(2), 2011
10 Regional activation and dopamine (encoding) PSC PSC PSC PSC PSC PSC PSC Executive Motor Circuit Dopamine restores limbic and sensory system activation Sec post-trial onset Sec Sec post-trial onset onset Harrington et al, PLoS One, 6(2), 2011
11 Regional activation and dopamine (decision) PSC PSC PSC PSC PSC Dopamine improves putamen and normalizes vermis activation Striatum and Vermis Memory System Sec post-trial onset Harrington et al, PLoS One, 6(2), 2011 Sec post-trial onset
12 Effective connectivity of striatum Regional activation is impoverished measure of brain functioning Does dopamine alter connectivity of striatum with cortex and cerebellum? Psychophysiological interaction (PPI) method Seed regions caudate and putamen PPI regressor deconvolved time series for seed X medication status (OFF, ON) Tests if correlation of a seed time-series with time series of other brain voxels differs OFF and ON medication [Friston et al., 1997] Harrington et al, PLoS One, 6(2), 2011
13 Connectivity modulated by dopamine in decision phase Connectivity typically stronger OFF than ON medication Left Putamen SFG insula SMA precuneus Left Caudate MFG precentral SP Right Putamen pre/postcentral Right Caudate MFG precentral IP pre/postcentral precentral pre/postcentral Harrington et al, PLoS One, 6(2), 2011
14 Conclusions PD disrupts functional activity in core-timing, executive, memory, and sensory-integration systems Encoding phase core timing system (striatum) motor circuit (SMA, precentral) executive circuit (MFG, IPL, cerebellum) limbic (insula, parahippocampus) sensory (vermis) Decision phase core timing system (striatum) memory retrieval hub (posterior cingulate, parahippocampus) sensory (vermis) Is corticostriatal connectivity altered in PD during timing? Timing emerges from interactions among brain regions, not isolated process within a specific region
15 Conclusions DA did not alter timing proficiency and effects on regional activation were limited insula, parahippocampus, & vermis (encoding) putamen & vermis (decision) DA altered striatal connectivity Encoding phase No effect on connectivity does not mean that that corticostriatal connectivity is absent Decision phase DA reduced connectivity strength of striatum with motor circuit, middle frontal-parietal cortices, and insula DA depletion produces excessive synchronicity in corticostriatal circuits (Costa et al., 2006; Gatev et al., 2006; Hammond et al., 2007) Stronger resting-state connectivity (fmri, MEG) in PD OFF than ON medication (Stoffers et al., 2008; Baudrexel et al., 2011; Kwak et al., 2010) Why does DA alter connectivity only in decision phase? Mesocortical dopamine (tonic) stabilizes cortical oscillatory activity; important for encoding/maintenance Nigrostriatal dopamine (phasic) improves updating/integrative functions of basal ganglia; important for decision making Cools, Neurosciences and Biobehavioral Reviews, 2006
16 Preclinical Huntington Disease (prehd) PREDICT-HD Study PI: Jane Paulsen, University of Iowa Longitudinal observational study, now in 10 th year 32 sites (US, Canada, Australia, UK, Spain, Germany) Potential clinical and biological markers of HD in non- diagnosed gene-positive individuals (preclinical HD) Gene-negative individuals with family history of HD (control subjects) Estimated time to diagnosis varies from 5 to 25 years
17 Huntington Disease genetics and symptoms Caused by polyglutamine (CAG) expansion in coding region of huntington gene on chromosome 4 Usually manifests in midlife, but wide variation in age of onset Inverse correlation between age of onset and CAG repeat length HD diagnosis made at appearance of unequivocal motor signs (dyskinesias, oculomotor and gait abnormalities, rigidity, bradykinesia, hyper-reflexia)
18 Pathological changes Mutant huntingtin protein expressed throughout brain, yet disease is regionally specific Medium spiny neurons of caudate most vulnerable, but also putamen Less marked neuronal loss in cortex and other subcortical regions Pathological changes decades before diagnosis (striatal and cortical atrophy, cortical thinning, white-matter changes) Preclinical HD: Estimated Years to Diagnosis > 15 years 9 to 15 years < 9 years Figure adapted from Nopoulos et al, Neurobiology of Disease, 40, 2010.
19 Preclinical HD and cognition Pathological changes produce subtle motor, psychiatric, and cognitive changes more than a decade before diagnosis Poorer attention, working memory, processing speed, learning, executive functions, sensory-perceptual processing, emotion perception Impaired motor timing (self-paced) and time perception [Rowe, et al., Neuropsychology, 24, 2010; Paulsen et al., AJNR, 25, 2004; unpublished internal analyses of PREDICT-HD data] Timing dysfunction is clinically relevant Cross-sectional studies: Motor timing variability one of most sensitive measures of proximity to diagnosis Longitudinal studies: Motor timing variability worsens as individuals approach diagnosis Brain mechanisms not understood
20 Neural bases of timing deficits in prehd estimated years to Dx Control (n=32) Age 50.5 (9.4) Low (n=21) Medium (n=21) High (n=17) > < (10.0) CAP score (33.1) 39.0 (9.7) (21.9) 49.8 (13.9) (63.7) Basal Ganglia Volume All prehd groups L caudate & GP atrophy High prehd group B putamen, r caudate, & r GP atrophy Time Perception Task Response: longer/shorter Comparison (960 to 1500 ms) 1 sec delay Standard (1200 ms) Sensorimotor Control Task Response: press key 2 nd Tone (1200 ms) 1 sec delay 1 st Tone (1200 ms) Warning Warning
21 fmri design and hypotheses froi Methods To adjust for low-level sensory and motor activation, control task subtracted from time perception task Regions showing greater activation in the time perception task than the control task identified for each group served as froi in the data analyses Main Hypotheses Timing impairments will be more marked in prehd closer to diagnosis Timing deficits will be notable in the executive circuit (caudate, middle frontal and posterior parietal cortex)
22 Behavioral results Percent longer responses lower in high group Point of subjective equality (PSE) higher in high group No group effects for difference limen (DL) or coefficient of variation (CV) PreHD close to diagnosis underestimated time * ** *p<.05; **p<.01
23 froi associated with time discrimination bilateral caudate and thalamus R middle frontal, bilateral inferior parietal SMA/preSMA, anterior cingulate bilateral insula left inferior frontal, precentral left cerebellum (culmen, pyramis)
24 Preliminary fmri results Hyperactivation: Executive Circuit * * * * * * * * * * No group differences in caudate activation
25 Preliminary fmri results Hyperactivation: Anterior Insula & SMA/preSMA * * * * * * *
26 Genetic burden and brain activation Disease burden (CAP score) correlates with activation r age p value Executive Circuit R middle frontal (BA 9, 46) L inferior parietal (40) R thalamus L thalamus Motor Circuit SMA/preSMA (6) Limbic System L anterior insula.31.02
27 Preliminary conclusions PreHD close to diagnosis underestimate time Compensatory activity typically more than a decade before diagnosis in thalamus, executive circuit (MFG, parietal), SMA/preSMA, and anterior insula Hyperactivation correlates with genetic burden Functional changes precede timing impairments in prehd further from diagnosis Unknown if functional changes in cortex precede structural changes Functional role of striatum unclear adjust for individual differences in striatal volume (fmri analyses) investigate striatal connectivity
28 Overall summary Time discrimination deficits in PD and prehd Time underestimated in prehd Timing variability increased in PD Abnormal cortical activity seen in some common systems SMA/preSMA, MFG, inferior parietal, insula [e.g., Harrington et al, 1998; Pouthas et al, 2005; Wittmann et al, 2010] typically hypoactivation in PD hyperactivation in prehd (compensation?) Other sources of neuronal dysfunction in PD functional changes in striatum memory hub (parahippocampus, posterior cingulate) [Olton et al, 1987; Melgire et al, 2005] working memory (lateral cerebellum) [e.g., Desmond et al, 1997; Desmond, 2001; Chen & Desmond, 2005]
29 Future directions Functional connectivity of brain networks Many different connectivity approaches Advance understanding of how timing emerges from functional integration in brain circuits More sensitive to changes in core timing systems in neurodegenerative disorders More sensitive to pharmacotherapy effects specific brain networks Brain mechanisms of time compression/expansion Properties of stimuli affect perceived duration [Harrington et al, 2012; Wittmann et al, 2010] Modality effects on time are altered with maturation and in schizophrenia [Droit-Volet et al, 2007; Penney et al, 2005; Carroll et al, 2008] Intersensory timing Experience of time emerges through synthesis of information between senses Animal models: striatum involved in multisensory integration [Nagy et al, Euro J Neurosci, 2006] Corticostriatal networks support intersensory timing [Harrington et al, Frontiers Integrative Neurosci, 2012]
Evaluating the roles of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum in time perception
 Sundeep Teki Evaluating the roles of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum in time perception Auditory Cognition Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging SENSORY CORTEX SMA/PRE-SMA HIPPOCAMPUS BASAL
Sundeep Teki Evaluating the roles of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum in time perception Auditory Cognition Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging SENSORY CORTEX SMA/PRE-SMA HIPPOCAMPUS BASAL
On the nature of Rhythm, Time & Memory. Sundeep Teki Auditory Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging University College London
 On the nature of Rhythm, Time & Memory Sundeep Teki Auditory Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging University College London Timing substrates Timing mechanisms Rhythm and Timing Unified timing
On the nature of Rhythm, Time & Memory Sundeep Teki Auditory Group Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging University College London Timing substrates Timing mechanisms Rhythm and Timing Unified timing
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale
 Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Neurobehavioral Mechanisms of Temporal Processing Deficits in Parkinson s Disease
 Neurobehavioral Mechanisms of Temporal Processing Deficits in Parkinson s Disease Deborah L. Harrington 1,2 *, Gabriel N. Castillo 2, Paul A. Greenberg 2, David D. Song 1,3, Stephanie Lessig 1,3, Roland
Neurobehavioral Mechanisms of Temporal Processing Deficits in Parkinson s Disease Deborah L. Harrington 1,2 *, Gabriel N. Castillo 2, Paul A. Greenberg 2, David D. Song 1,3, Stephanie Lessig 1,3, Roland
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN PARKINSON S DISEASE
 1 GENERAL INTRODUCTION GENERAL INTRODUCTION PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative movement disorder, named after James Parkinson who described some of its characteristic
1 GENERAL INTRODUCTION GENERAL INTRODUCTION PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative movement disorder, named after James Parkinson who described some of its characteristic
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Brain Structure and Function in Nephropathic Cystinosis
 Brain Structure and Function in Nephropathic Cystinosis Doris A. Trauner M.D. Professor, Depts. of Neurosciences and Pediatrics University of California San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA USA Cystinosis
Brain Structure and Function in Nephropathic Cystinosis Doris A. Trauner M.D. Professor, Depts. of Neurosciences and Pediatrics University of California San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA USA Cystinosis
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Connections of basal ganglia
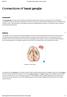 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Neurochemical changes in basal ganglia affect time perception in parkinsonians
 Magalhães et al. Journal of Biomedical Science (2018) 25:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-018-0428-2 REVIEW Neurochemical changes in basal ganglia affect time perception in parkinsonians Francisco Magalhães
Magalhães et al. Journal of Biomedical Science (2018) 25:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-018-0428-2 REVIEW Neurochemical changes in basal ganglia affect time perception in parkinsonians Francisco Magalhães
funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura Avanzino
 Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
BINGES, BLUNTS AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT
 BINGES, BLUNTS AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Why delaying the onset of alcohol and other drug use during adolescence is so important Aaron White, PhD Division of Epidemiology and Prevention Research National Institute
BINGES, BLUNTS AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Why delaying the onset of alcohol and other drug use during adolescence is so important Aaron White, PhD Division of Epidemiology and Prevention Research National Institute
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Lecture 42: Final Review. Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D.
 Lecture 42: Final Review Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D. Lecture 33 cortex Heilbronner 5 lobes of the cortex Lateral view (left side) Mid-saggital view (right side) Cellular organization of cortex White matter
Lecture 42: Final Review Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D. Lecture 33 cortex Heilbronner 5 lobes of the cortex Lateral view (left side) Mid-saggital view (right side) Cellular organization of cortex White matter
Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4
 Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4 Table S1: Brain regions involved in the adapted classification learning task Brain Regions x y z Z Anterior Cingulate
Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4 Table S1: Brain regions involved in the adapted classification learning task Brain Regions x y z Z Anterior Cingulate
What goes wrong with balance in Parkinson s Disease? Fay B Horak, PhD, PT Professor of Neurology Oregon Health and Science. CoM
 What goes wrong with balance in Parkinson s Disease? Fay B Horak, PhD, PT Professor of Neurology Oregon Health and Science CoM CoM Course Objectives Understand different types of balance systems affected
What goes wrong with balance in Parkinson s Disease? Fay B Horak, PhD, PT Professor of Neurology Oregon Health and Science CoM CoM Course Objectives Understand different types of balance systems affected
Neuroscience 410 Huntington Disease - Clinical. March 18, 2008
 Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
FINAL PROGRESS REPORT
 (1) Foreword (optional) (2) Table of Contents (if report is more than 10 pages) (3) List of Appendixes, Illustrations and Tables (if applicable) (4) Statement of the problem studied FINAL PROGRESS REPORT
(1) Foreword (optional) (2) Table of Contents (if report is more than 10 pages) (3) List of Appendixes, Illustrations and Tables (if applicable) (4) Statement of the problem studied FINAL PROGRESS REPORT
FDG-PET e parkinsonismi
 Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Standing strong in the roaring 40s ANZFPS November HOBART. Credit: Tourism Tasmania and Garry Moore
 Standing strong in the roaring 40s ANZFPS November 18-20 2018 HOBART Credit: Tourism Tasmania and Garry Moore Thinking on your feet the interplay between cognition, gait and falls Dr Michele Callisaya
Standing strong in the roaring 40s ANZFPS November 18-20 2018 HOBART Credit: Tourism Tasmania and Garry Moore Thinking on your feet the interplay between cognition, gait and falls Dr Michele Callisaya
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse. Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver
 Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease
 Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease Alexander Hui Department of Bioengineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 alexhui@ucsd.edu Abstract Parkinson s disease is a slowly progressing
Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease Alexander Hui Department of Bioengineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 alexhui@ucsd.edu Abstract Parkinson s disease is a slowly progressing
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D.
 HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pediatrics University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa The information provided
HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pediatrics University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa The information provided
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps
 Training course: Real-time fmri: Fundamental Principles for Clinical Applications Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps David Linden Cardiff University 1) What is your clinical
Training course: Real-time fmri: Fundamental Principles for Clinical Applications Clinical applications of real-time fmri neurofeedback in 6 steps David Linden Cardiff University 1) What is your clinical
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention
 Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
The Neurobiology of Attention
 The Neurobiology of Attention by Nadia Fike, MD/PhD Pediatric Neurology Center for Neurosciences Disclosures Nadia Fike, MD/PhD No relevant financial or nonfinancial relationships to disclose. Objectives
The Neurobiology of Attention by Nadia Fike, MD/PhD Pediatric Neurology Center for Neurosciences Disclosures Nadia Fike, MD/PhD No relevant financial or nonfinancial relationships to disclose. Objectives
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions
 Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
The Brain on ADHD. Ms. Komas. Introduction to Healthcare Careers
 The Brain on ADHD Ms. Komas Introduction to Healthcare Careers Ms. Komas Period 9/2/2016 Komas 1 HOOK: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) plagues between 5% and 7% of children and less than
The Brain on ADHD Ms. Komas Introduction to Healthcare Careers Ms. Komas Period 9/2/2016 Komas 1 HOOK: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) plagues between 5% and 7% of children and less than
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders
 Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
MANAGING YOUR COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS. Dr. Valerie Suski University of Pittsburgh Medical Center HDSA COE Director
 MANAGING YOUR COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS Dr. Valerie Suski University of Pittsburgh Medical Center HDSA COE Director The information provided by speakers in workshops, forums, sharing/networking sessions and any
MANAGING YOUR COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS Dr. Valerie Suski University of Pittsburgh Medical Center HDSA COE Director The information provided by speakers in workshops, forums, sharing/networking sessions and any
Neuropathology of Neurodegenerative Disorders Prof. Jillian Kril
 Neurodegenerative disorders to be discussed Alzheimer s disease Lewy body diseases Frontotemporal dementia and other tauopathies Huntington s disease Motor Neuron Disease 2 Neuropathology of neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative disorders to be discussed Alzheimer s disease Lewy body diseases Frontotemporal dementia and other tauopathies Huntington s disease Motor Neuron Disease 2 Neuropathology of neurodegeneration
Biomedical Technology Research Center 2011 Workshop San Francisco, CA
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Postural instability Hypokinesia Rigidity Tremor Forward flexed posture. pain million people 50+ years old 10 most populated countries
 4.1-4.6 million people 50+ years old 10 most populated countries Cyndi Robinson, PT, PhD University of Washington Seattle, Washington, USA Progressive neurodegenerative disorder Selective neuronal loss
4.1-4.6 million people 50+ years old 10 most populated countries Cyndi Robinson, PT, PhD University of Washington Seattle, Washington, USA Progressive neurodegenerative disorder Selective neuronal loss
Cognition in Parkinson's Disease and the Effect of Dopaminergic Therapy
 Cognition in Parkinson's Disease and the Effect of Dopaminergic Therapy Penny A. MacDonald, MD, PhD, FRCP(C) Canada Research Chair Tier 2 in Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging Assistant Professor
Cognition in Parkinson's Disease and the Effect of Dopaminergic Therapy Penny A. MacDonald, MD, PhD, FRCP(C) Canada Research Chair Tier 2 in Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging Assistant Professor
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND
 THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD How did I get here? What did I do? Start driving home after work Aware when you left
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD How did I get here? What did I do? Start driving home after work Aware when you left
The Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience. Sensory Systems and Perception: Auditory, Mechanical, and Chemical Senses 93
 Contents in Brief CHAPTER 1 Cognitive Neuroscience: Definitions, Themes, and Approaches 1 CHAPTER 2 The Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience CHAPTER 3 Sensory Systems and Perception: Vision 55 CHAPTER 4 CHAPTER
Contents in Brief CHAPTER 1 Cognitive Neuroscience: Definitions, Themes, and Approaches 1 CHAPTER 2 The Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience CHAPTER 3 Sensory Systems and Perception: Vision 55 CHAPTER 4 CHAPTER
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
How to Effectively Manage the Motor Symptoms of HD
 How to Effectively Manage the Motor Symptoms of HD Yvette Bordelon, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA The information provided by speakers in workshops,
How to Effectively Manage the Motor Symptoms of HD Yvette Bordelon, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA The information provided by speakers in workshops,
Using Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Basal Ganglia as a Biomarker for Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease
 Illinois Math and Science Academy DigitalCommons@IMSA Student Publications & Research Student Works 4-2015 Using Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Basal Ganglia as a Biomarker for Symptoms of
Illinois Math and Science Academy DigitalCommons@IMSA Student Publications & Research Student Works 4-2015 Using Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Basal Ganglia as a Biomarker for Symptoms of
Part 1 Parkinson s Disease. COGS 172: Brain Disorders and Cogni5on
 Part 1 Parkinson s Disease COGS 172: Brain Disorders and Cogni5on Background: Neuroanatomy of the motor system Note: Given short time to the final the details of the anatomy will not be in the exam, but
Part 1 Parkinson s Disease COGS 172: Brain Disorders and Cogni5on Background: Neuroanatomy of the motor system Note: Given short time to the final the details of the anatomy will not be in the exam, but
Huntington s Disease. An Update on Latest Research. HD Center of Excellence
 Huntington s Disease An Update on Latest Research HD Treatment gcurrent treatments are symptomatic. gseveral compounds have delayed onset and slowed progression in mouse models. gquestion remains to translate
Huntington s Disease An Update on Latest Research HD Treatment gcurrent treatments are symptomatic. gseveral compounds have delayed onset and slowed progression in mouse models. gquestion remains to translate
Study of Verbal Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson s Disease
 Study of Verbal Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson s Disease Gilbert, Belleville, Bherer, & Chouinard, 2005 presented by Jonathan Reinharth May 2, 2005 Parkinson s Disease Symptoms: resting tremors,
Study of Verbal Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson s Disease Gilbert, Belleville, Bherer, & Chouinard, 2005 presented by Jonathan Reinharth May 2, 2005 Parkinson s Disease Symptoms: resting tremors,
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
doi: /brain/aws024 Brain 2012: 135; Altered brain mechanisms of emotion processing in pre-manifest Huntington s disease
 doi:10.1093/brain/aws024 Brain 2012: 135; 1165 1179 1165 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Altered brain mechanisms of emotion processing in pre-manifest Huntington s disease Marianne J. U. Novak, 1 Jason D.
doi:10.1093/brain/aws024 Brain 2012: 135; 1165 1179 1165 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Altered brain mechanisms of emotion processing in pre-manifest Huntington s disease Marianne J. U. Novak, 1 Jason D.
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Cognitive-Motor Interference in Persons with Parkinson Disease
 Cognitive-Motor Interference in Persons with Parkinson Disease Tara L. McIsaac, PhD, PT Associate Professor of Physical Therapy A.T. Still University Arizona School of Health Sciences October 11, 2014
Cognitive-Motor Interference in Persons with Parkinson Disease Tara L. McIsaac, PhD, PT Associate Professor of Physical Therapy A.T. Still University Arizona School of Health Sciences October 11, 2014
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Auditory Processing Of Schizophrenia
 Auditory Processing Of Schizophrenia In general, sensory processing as well as selective attention impairments are common amongst people with schizophrenia. It is important to note that experts have in
Auditory Processing Of Schizophrenia In general, sensory processing as well as selective attention impairments are common amongst people with schizophrenia. It is important to note that experts have in
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review
 The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/324/5927/646/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Self-Control in Decision-Making Involves Modulation of the vmpfc Valuation System Todd A. Hare,* Colin F. Camerer, Antonio
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/324/5927/646/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Self-Control in Decision-Making Involves Modulation of the vmpfc Valuation System Todd A. Hare,* Colin F. Camerer, Antonio
Brief Communication Nuclear Medicine. In-Uk Song, MD 1, Sang-Won Ha, MD 2, Young-Soon Yang, MD 2, Yong-An Chung, MD 3 INTRODUCTION
 Brief Communication Nuclear Medicine http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.967 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):967-972 Differences in Regional Glucose Metabolism of the Brain
Brief Communication Nuclear Medicine http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.967 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):967-972 Differences in Regional Glucose Metabolism of the Brain
Parkinson e decadimento cognitivo. Stelvio Sestini
 Parkinson e decadimento cognitivo Stelvio Sestini Patients with PD can develop a spectrum of cognitive symptoms Heterogeneity of cognitive deficits The cognitive symptoms can evolve to dementia (Mov Disorder
Parkinson e decadimento cognitivo Stelvio Sestini Patients with PD can develop a spectrum of cognitive symptoms Heterogeneity of cognitive deficits The cognitive symptoms can evolve to dementia (Mov Disorder
Investigating molecular mechanisms of progression of Parkinson s Disease in human brain
 Investigating molecular mechanisms of progression of Parkinson s Disease in human brain Murray ; C.E., Pressey ; S.N., Heywood 2 ; W.E., Hargreaves 3 ; I.P., Neergheen 3 ; V., Wauters ; S., Palkovits 4
Investigating molecular mechanisms of progression of Parkinson s Disease in human brain Murray ; C.E., Pressey ; S.N., Heywood 2 ; W.E., Hargreaves 3 ; I.P., Neergheen 3 ; V., Wauters ; S., Palkovits 4
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines
 Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines Altmann A. 1,2,7 *, Schröter M.S. 1,3 *, Spoormaker V.I. 1, Kiem S.A. 1, Jordan D. 4, Ilg R. 5,6,
Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines Altmann A. 1,2,7 *, Schröter M.S. 1,3 *, Spoormaker V.I. 1, Kiem S.A. 1, Jordan D. 4, Ilg R. 5,6,
Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk
 Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk... and corresponding risk prediction errors Peter Bossaerts 1 Contents 1. Reward Encoding And The Dopaminergic System 2. Reward Prediction Errors And TD (Temporal
Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk... and corresponding risk prediction errors Peter Bossaerts 1 Contents 1. Reward Encoding And The Dopaminergic System 2. Reward Prediction Errors And TD (Temporal
Piano playing skills in a patient with frontotemporal dementia: A longitudinal case study
 International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-94-90306-01-4 The Author 2009, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Piano playing skills in a patient with frontotemporal dementia: A longitudinal
International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-94-90306-01-4 The Author 2009, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Piano playing skills in a patient with frontotemporal dementia: A longitudinal
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Text to brain: predicting the spatial distribution of neuroimaging observations from text reports (submitted to MICCAI 2018)
 1 / 22 Text to brain: predicting the spatial distribution of neuroimaging observations from text reports (submitted to MICCAI 2018) Jérôme Dockès, ussel Poldrack, Demian Wassermann, Fabian Suchanek, Bertrand
1 / 22 Text to brain: predicting the spatial distribution of neuroimaging observations from text reports (submitted to MICCAI 2018) Jérôme Dockès, ussel Poldrack, Demian Wassermann, Fabian Suchanek, Bertrand
Pushing the plasticity: The role of exercise in the management of neurological illness
 Pushing the plasticity: The role of exercise in the management of neurological illness Michael Gaetz Ph.D. Associate Professor, Kinesiology Department Faculty of Health Sciences University of the Fraser
Pushing the plasticity: The role of exercise in the management of neurological illness Michael Gaetz Ph.D. Associate Professor, Kinesiology Department Faculty of Health Sciences University of the Fraser
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32078 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Pannekoek, Nienke Title: Using novel imaging approaches in affective disorders
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32078 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Pannekoek, Nienke Title: Using novel imaging approaches in affective disorders
Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load
 Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load Intro Examine attention response functions Compare an attention-demanding
Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load Intro Examine attention response functions Compare an attention-demanding
9/13/2018. Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
 DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Neil P. Jones 7th Annual Conference on ADHD and Executive Function September 14, 218 Diagnosis Child
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Neil P. Jones 7th Annual Conference on ADHD and Executive Function September 14, 218 Diagnosis Child
Motor Fluctuations in Parkinson s Disease
 Motor Fluctuations in Parkinson s Disease Saeed Bohlega, MD, FRCPC Senior Distinguished Consultant Department of Neurosciences King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre Outline Type of fluctuations
Motor Fluctuations in Parkinson s Disease Saeed Bohlega, MD, FRCPC Senior Distinguished Consultant Department of Neurosciences King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre Outline Type of fluctuations
Final Report 2017 Authors: Affiliations: Title of Project: Background:
 Final Report 2017 Authors: Dr Gershon Spitz, Ms Abbie Taing, Professor Jennie Ponsford, Dr Matthew Mundy, Affiliations: Epworth Research Foundation and Monash University Title of Project: The return of
Final Report 2017 Authors: Dr Gershon Spitz, Ms Abbie Taing, Professor Jennie Ponsford, Dr Matthew Mundy, Affiliations: Epworth Research Foundation and Monash University Title of Project: The return of
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function:
 Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Attention, Academic Achievement and the Brain Boss
 Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Attention, Academic Achievement and the Brain Boss James B. Hale, PhD, MEd, ABSNP, ABPdN Visiting Professor of Educational Neuroscience Division of Psychology
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Attention, Academic Achievement and the Brain Boss James B. Hale, PhD, MEd, ABSNP, ABPdN Visiting Professor of Educational Neuroscience Division of Psychology
Original Articles. Calne, resting tremor. Mortimer, Pirozzolo, Hansch, & Webster, postural disturbance III
 2004 97-106 Original Articles 1 2 3 1 1 2 3 47 22 III I II muscular rigidity postural disturbance resting tremor bradykinesia Calne, 2001 Mortimer, Pirozzolo, Hansch, & Webster, 1982 Tel: 02-23627076 E-mail:
2004 97-106 Original Articles 1 2 3 1 1 2 3 47 22 III I II muscular rigidity postural disturbance resting tremor bradykinesia Calne, 2001 Mortimer, Pirozzolo, Hansch, & Webster, 1982 Tel: 02-23627076 E-mail:
