Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses
|
|
|
- Brianna May Mosley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had had a significant exposure to a blood borne virus (BBV) then they should be referred urgently to the paediatric on-call team. A risk assessment of the injured person and the source should be completed by whomever the injured person presents to (primary care, emergency department, minor injuries unit, infectious diseases, sexual health etc). Sexual exposure incidents presenting between 9am to 5pm except weekends and public holidays should be asked to attend Tayside Sexual and Reproductive Health Services; South Block, Level 7, Ninewells Hospital or Drumhar Health Centre, Perth. The majority of exposure events do not require onward referral for HIV post exposure prophylaxis (PEP) as following assessment they are usually found not to be of sufficiently high risk to require HIV PEP. Where there is a significant risk and HIV PEP is this is available for nonsexual exposure and out of hours at the Emergency Department s of Ninewells Hospital, Dundee and Perth Royal Infirmary, Perth. Follow up will be arranged within the Infectious Diseases Department, Ninewells Hospital, Dundee. HIV PEP is not beyond 72 hours post exposure. Hepatitis B PEP can be given up to a week after exposure but is ideally started within 48 hours. PEP is available against HIV and Hepatitis B and early diagnosis of Hepatitis C allows treatment with a high chance of cure. INTRODUCTION Healthcare Improvement Scotland Standards for HIV Services (July 2011) state that Scottish Health Boards must have a policy in place for the 24 hour availability of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), including for sexual exposure (PEPSE). This guidance has been produced to meet the requirements of the HIS Standards and are in accordance with the recommendations from the UK Chief Medical Officers Expert Advisory Group on AIDS (2008) and includes the Change to regimen for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) September 2014 and Updated recommendation for HIV post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) following occupational exposure to a source with undetectable HIV viral load December In addition these guidelines were produced using the British Association of Sexual Health and HIV UK Guideline for the use of postexposure prophylaxis for HIV following sexual exposure (2011) and the UK Department of Health s Green Book on Immunisation against Infectious Diseases. This guidance is aimed at all NHS Tayside staff, including Primary Care, Sexual Health Clinics, Minor Injuries Units and the Emergency Department, where people may present who think they may have been exposed to a blood borne virus (BBV). There is separate guidance for NHS Tayside workers who sustain a contamination/needlestick injury available on Staffnet. Preventing exposure to BBVs is not always possible but reducing the risk of transmission is possible using PEP. The management of exposure events where there is a risk of BBV transmission, including the use of PEP, is complex and members of the public can present to a number of sites for advice following an event. Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 1
2 The majority of exposure injuries do not require onward referral, as following careful risk assessment they are usually found not to be of sufficiently high risk to require PEP. PEP is available against HIV and Hepatitis B. HIV PEP is most likely to be effective if initiated within hours of exposure and is not beyond 72 hours post exposure. Hepatitis B PEP can be initiated up to a week after exposure though ideally it should be started within 48 hours of exposure. An early diagnosis of Hepatitis C allows for treatment with a high chance of cure. Exposure events that have a risk of BBV transmission include needlestick injuries (percutaneous), body fluids on open skin or in the eyes, nose and mouth (mucocutaneous exposure) and sexual exposure. The risk of BBV transmission and thus the management of these injuries varies based on the source patient, type of injury and the body fluid involved. For an exposure to be considered of sufficient risk of transmitting HIV, the type of exposure, the body fluid involved must be highrisk plus the source individual will be known to have HIV or come from a high prevalence group. Table the risk of transmission of the BBVs in an untreated source patient by different exposure events. Data is not available for all BBVs and exposure event. Receptive Anal Sex Needlestick injury Receptive Vaginal Sex Mucocutaneous exposure HIV 1 in 50 1 in in in 1000 Hepatitis C 1 in 30 Hepatitis B 1 in 3 ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE EVENTS 1. First aid 2. Document timing and nature of exposure 3. Risk assessment of the injury and body fluids involved 4. Risk assessment of the source individual 5. Indications for HIV PEP 6. Indications for Hepatitis B PEP 7. Referral for PEP 8. Use of HIV post exposure prophylaxis in the Emergency Department 9. Onward referral and appropriate follow up and testing 1. FIRST AID If the skin is punctured gently encourage the wound to bleed. Thoroughly wash the wound with soap and warm water. Do not scrub. Cover with a waterproof plaster. For splashes to mucous membranes or broken skin, irrigate with lots of water. 2. DOCUMENT TIMING AND NATURE OF EXPOSURE To make a thorough assessment of the injury a clear history including the timing of the exposure should be documented. The history should include any on-going risk of BBV acquisition. As Hepatitis B can be prevented by the use of a vaccine plus immunoglobulin post-exposure, documenting the person s vaccination history is vital to optimise use of PEP. For tetanus prophylaxis please refer to the Department of Health Green Book; Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 2
3 3. RISK ASSESSMENT OF THE EXPOSURE Only certain events are thought to carry significant risk of transmitting BBVs. Therefore both the injury and the body fluid involved need to be considered. The tables below outline what exposures and body fluids are considered high or low risk for HIV transmission. Only a high risk exposure involving a high risk fluid with a known and untreated HIV positive source or a source from a high prevalence group would warrant the use of HIV PEP. Please note that there are differences in the way the risk is assessed for HIV and Hepatitis B and the assessments for PEP should be made separately. High risk exposures Needle, surgical instrument or other sharp (bone spike, broken tooth) penetrating skin Fluid onto broken skin Fluid on to mucous membrane (eye, nose or mouth) Insertive anal sex without condom Insertive vaginal sex without condom Receptive anal sex Receptive vaginal sex without a condom Human bite Receptive oral sex with ejaculation * * Penis inserted into presenting/injured person s oral cavity Low risk exposures Fluid onto intact skin Any other sex with or High risk body fluids Amniotic fluid Blood Cerebrospinal fluid Exudative or other tissue fluid from burns or skin lesions Human breast milk Pericardial fluid Peritoneal fluid Pleural fluid Saliva in association with dentistry Semen Synovial fluid Unfixed human tissues and organs Vaginal secretions Any other body fluid if visibly bloodstained Low risk body fluids Faeces Saliva (in absence of dentistry) Sputum/phlegm Tears Urine Vomit Non-blood-stained or no fresh/wet blood on discarded needle In the case of an injury sustained with a discarded needle, where the source cannot be identified, HIV PEP is not indicated. There may be a need for Hepatitis B PEP. If EITHER the exposure OR the body fluid/materials are low risk HIV PEP is not indicated. There may be a need for Hepatitis B PEP. Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 3
4 Even when the assessment of the exposure indicates that HIV or Hepatitis B PEP is not indicated there is an opportunity to provide advice (including information leaflets) on risk and harm reduction. Specialist services are available and should be appropriately signposted including Tayside Sexual and Reproductive Health Department for risk reduction advice and to the Drug Problem Services around safer use of needles. 4. RISK ASSESSMENT OF THE SOURCE If the exposure AND the body fluid is high risk and the source individual is known to have HIV or is from a HIV high prevalence group then HIV PEP may be indicated. The source individual should be asked the questions below or when unavailable or unknown the exposed individual should be asked to answer to the best of their knowledge. Is the source known to have HIV? If the source has HIV, understanding whether they are on treatment and their last viral load helps refine the risk assessment. If any of the below questioned are answered Yes then the source is from a HIV high prevalence group. Is the source known to have Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C? Does the source come from an endemic region (sub-saharan Africa, Caribbean, Thailand)? Has the source had a sexual partner from or had sex in an endemic region (sub-saharan Africa, Caribbean, Thailand)? Has the source ever injected drugs? If the source is male have they had sex with other men? Does the source have a sexual partner known to have HIV? Does the source have a current illness compatible with HIV/AIDS? If the source is available and agrees to testing the exposed individual can often have post-exposure prophylaxis stopped preventing side effects, worry and cost. When a high risk injury, with a high risk fluid, has been sustained all available source individuals with unknown blood borne virus status should be asked to consent to HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C testing. This could be through the source s own GP; by TSRH if related to a sexual exposure; or if the exposed individual is referred for PEP testing of a known source can be arranged via the Infectious Diseases Department. If the source is unavailable, but known to the injured person, information on how the source can be tested for HIV, Hepatitis B and C should be offered (LINK). What to tell the source (gaining consent for BBV testing) 1. An injury/incident has occurred that has been assessed as having the potential of transmitting infections to the exposed individual. 2. We can test you (the source) for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C to understand what the best treatment is for the exposed individual. By having the tests you will also understand whether there is a risk you could pass on an infection in the future and also you would be able to access treatment and care. 3. Your test results will be shared with the doctor treating the exposed individual. 4. If any of the tests are positive you will be informed and referred to a specialist for assessment and care (referrals to Dr Morgan Evans, Consultant physician, Ninewells Hospital, Dundee). Testing the source Should the source consent to BBV testing, obtain blood in gold-topped Vacutainer. On ICE the 3 tests required are described as "HIV screening test", "Hepatitis B (HBsAg) infection screen" and "Hepatitis C antibody screen" indicate in the clinical details Contamination injury. Source Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 4
5 individual. Urgent HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C testing. The request should include the name and contact details for the responsible staff member to whom the results should be communicated. Offer an information leaflet to the source whether they consent to testing or not (LINK). 5. INDICATIONS FOR HIV POST EXPOSURE PROPHYALXIS Using the information gathered the table below outlines when HIV PEP is indicated. This combines the injury, body fluid and the initial assessment of the source s risk. Needle, or other sharp item contaminated with fresh, wet blood penetrating skin. Viral load detectable or unknown HIV positive Viral load undetectable ++ unless viral load last checked more than 6 months ago or result not immediately available. Source HIV status Unknown HIV-status High prevalence group + Low prevalence group High risk fluid onto broken skin. High risk fluid on to mucous membrane (eye, nose or mouth). Human Bite * Receptive anal sex ** Insertive anal sex *** Receptive vaginal sex ** *** ** Insertive vaginal sex *** Fellatio (giving) with ejaculation without a *** condom Splash of semen into eye *** Fellatio (giving) without ejaculation Fellatio (receiving) Cunnilingus Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 5
6 * Recent guidance has indicated that a human bite is unlikely to transmit HIV. In the context of a source individual with known HIV infection, especially with blood in the mouth prior to the bite (for example in association with dentistry) or where there is significant tissue trauma the risk may be greater and PEP should be prescribed. ** In the context of sexual assault PEP may be considered and this should be discussed with a genito-urinary medicine consultant. *** These patients require a specialist assessment within Tayside Sexual and Reproductive Health at the earliest opportunity. With further assessment, continuation of HIV PEP may not be required and this will be discussed with the patient. + High prevalence groups include Having sex in, or a partner from, or coming from, an endemic region (sub-saharan Africa, Caribbean, Thailand); A person who injects or has injected drugs; A man who has sex with other men; A current clinical illness compatible with HIV/AIDS; A sexual partner of known HIV infected person. ++ Viral load undetectable is where the source is known to have HIV and has a viral load below 200 copies per ml within the last 6 months, and is adherent to medication. 6. INDICATIONS FOR HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Significant exposure is defined as (i) percutaneous exposure (needlestick or other contaminated sharp object injury, a bite which causes bleeding or other visible skin puncture) (ii) mucocutaneous exposure to blood (contamination of non-intact skin, conjunctiva or mucous membrane) (iii) sexual exposure (unprotected sexual intercourse) Taken from Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 6
7 HBIG is used after exposure to give rapid protection until hepatitis B vaccine, which should be given at the same time, becomes effective. The use of HBIG in addition to vaccine is only in high-risk situations or in a known non-responder to vaccine. Whenever immediate protection is required, immunisation with the vaccine should be given. When appropriate, this should be combined with simultaneous administration of HBIG at a different site. HBIG should be given as soon as possible, ideally within 48 hours, although it should still be considered up to a week after exposure. 7. REFERRAL FOR PEP If a child has had a significant exposure they should be referred urgently to the paediatric team. All sexual exposure incidents presenting between 9am to 5pm except weekends and public holidays should be asked to attend Tayside Sexual and Reproductive Health Services at either; South Block, Level 7 Ninewells Hospital or Drumhar Health Centre, Perth. Where HIV PEP is indicated please contact the closest Emergency Department and arrange for the injured person to attend with all information documented at the earliest opportunity. HIV PEP is most likely to be effective when initiated as soon as possible, within hours, allowing for careful risk assessment. HIV PEP is not beyond 72 hours post exposure. 8. USE OF HIV PEP IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT HIV PEP PRESCRIPTION HIV PEP is available in the Emergency Department at PRI and Ninewells Hospital as a 7 day starter pack of Truvada (tenofovir and emtricitabine) ONE every 24 hours and Raltegravir 400mg ONE tablet every 12 hours. There is a prescriber s guidance sheet within the PEP pack that should be followed and the injured person should also be given the information leaflet, again within the PEP pack. There are no significant drug interactions with contraceptives. Follow up whilst on HIV PEP will be arranged by the Infectious Diseases team and can be arranged by (Tay-UHB.id@nhs.net), which should include the nature and timing of injury and the injured person s details including date of birth, CHI plus contact details including the injured person s phone number. The Infectious Diseases team will refer appropriate cases to the Sexual Health Service for follow-up. CONTRAINDICATIONS TO HIV PEP The only absolute contraindication for use of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis is if the injured person is already known to have HIV. Pregnancy and known chronic kidney disease are relative contraindications and a pregnancy test should be performed if there is doubt. Where there is a relative contraindication to PEP, the benefits of PEP may still outweigh the risks. The first dose of PEP should be taken and the 7 day pack issued. Individuals with renal impairment may need dose reduction based on creatinine clearance. Follow up should be ensured within 24 hours if creatinine clearance is <50ml/min or in pregnancy. If HIV PEP is declined or indicated but not prescribed the rationale should be clearly documented. BASELINE BLOOD TESTS All individuals started on HIV PEP should have baseline blood tests: FBC, U+E, LFT, PO4, glucose and a serum sample for storage (gold top tube to microbiology). A urinalysis should be documented. Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 7
8 9. ONWARD REFERRAL AND APPROPRIATE FOLLOW UP AND TESTING All individuals prescribed HIV PEP will be offered support whilst they are on treatment. Infectious Diseases team will offer all individuals started on HIV PEP for non-sexual exposure an initial meeting to discuss continuing HIV PEP and will communicate this to primary care. The Infectious Diseases team will perform a review of the injured person s risk for BBVs and arrange testing if required. If HIV PEP is continued ID will arrange the remaining 21 days to be collected from the hospital pharmacy and will arrange an appointment two weeks after starting HIV PEP to check side effects and toxicity (FBC, U+Es, LFTs, Phosphate, Glucose, and urinalysis). Infectious Diseases will outline the routine blood screening that is required to be completed in primary care. (Testing for Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV at 12 weeks after exposure event or if PEP was taken 12 weeks from when PEP was stopped. If known chronic Hepatitis C positive source, HCV PCR should also be requested 6 and 12 weeks after exposure. Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C serology should be repeated again at 6 months. Hepatitis B serology not required in Hepatitis B vaccine responder). Infectious Diseases will also advise on whether any additional action is required after the initial assessment with regard to Hepatitis B vaccination. For all HIV PEP started for sexual exposure ID will forward on to Tayside Sexual and Reproductive Health Service for all follow up. For immediate advice or early follow up please contact Dr Sarah Allstaff or Dr Morgan Evans through the hospital switchboard. References HIV post-exposure prophylaxis Guidance from the UK Chief Medical Officers Expert Advisory Group on AIDS nce/dh_ UK guideline for the use of post-exposure prophylaxis for HIV following sexual exposure (2011) The Green Book Immunisation against infectious diseases Department of Health Exposure to hepatitis B virus: guidance on post-exposure prophylaxis. CDR Review Volume 2, Review Number 9, 14 August Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 8
9 CONFIDENTIAL Follow up of needlestick injury or other accidental exposure to body fluid in the community Dear Doctor: Your patient attended the Emergency Department after a needlestick/accidental exposure to body fluids. Name : CHI: Date attended: Your patient's exposure was deemed to be significant / non-significant. (Circle as appropriate) Summary of Bloodborne Virus Status of Source. (Circle appropriate box) Hepatitis B Status of HBsAg positive HBsAg negative Unknown Source Hepatitis C Status of Antibody positive Antibody negative Unknown Source HIV Status of Source Antibody positive Antibody Negative Unknown Action taken (circle appropriate box) HIV post exposure prophylaxis Initiated (follow up with ID arranged) indicated Indicated and declined Hepatitis B vaccine (single dose) Given indicated Indicated and declined Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Given indicated Indicated and declined Your patient will require to complete a Hepatitis B vaccine course in the following circumstances: He or she has had a significant injury and not completed a course of Hepatitis B vaccination; He or she is at risk of future exposures. Further guidance can be obtained from the Green Book; We would recommend after a significant exposure the following tests: Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV serology at 12 weeks post exposure or if HIV post exposure prophylaxis was taken, 12 weeks from when PEP was stopped. Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C serology should be repeated 6 months post exposure. Signed Name Designation Date Please ensure a copy of this letter is also given to the patient and the patient should make appointments at their GP practice for the required additional vaccinations or follow up tests as outlined above. Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 9
10 BBV Exposure Risk Assessment Form for Community Use Please print this page to document your assessment and send with patient if referral is required. Name of exposed individual CHI Address Contact telephone number Date and time of exposure (24 hour clock) HH:MM DD/MM/YY Date and time of assessment HH:MM DD/MM/YY If the exposed individual is a child please refer to the paediatric registrar on-call In the case of an injury sustained with a discarded needle, where the source cannot be identified, HIV PEP is not indicated. There may be a need for Hepatitis B PEP HIV PEP is only indicated within 72 hours of exposure, Hepatitis B PEP may be used up to one week after exposure HIV PEP Assessment What was the exposure high risk? Yes/No Details Was the body fluid involved high risk? Yes/No Details - Was the source known to have HIV or is from a high prevalence group? Yes/No Is HIV PEP? Yes/No If Yes ask the patient to attend, for sexual exposure, the closest TSRH department or, for non-sexual exposure or out of hours, the closest Emergency Department. Hepatitis B PEP Assessment Was the exposure significant? Percutaneous, mucocutaneous with blood or sexual exposure. Is Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG) indicated? Yes/No Is Hepatitis B Vaccination indicated? Yes/No If there is a continuing risk of exposure to Hepatitis B a full course of vaccination should be completed. If No ensure the Hepatitis B assessment is completed and offer risk reduction information or signpost local services. testing for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C to all available source individuals. After a significant exposure testing for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C three and six months after the event is. Advice available from: Infectious Diseases On-call Doctor available via Ninewells Hospital Switchboard bleep 5075 Tayside Sexual and Reproductive Health Departments Ninewells Hospital Drumhar HC Perth }}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}} Endorsed: May 2015 (links updated 2016) 10
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions
 Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis).
 LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE
 Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure. Marsh Gelbart 2010
 HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
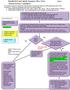 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES
 NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG.
 POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG. Reference Number: PPG CUH CUH Revision No: 1 Review Cycle: 2 Years Author (Lead): Dr Colm Kerr, Infectious Owner: Dr A Jackson, Infectious
POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG. Reference Number: PPG CUH CUH Revision No: 1 Review Cycle: 2 Years Author (Lead): Dr Colm Kerr, Infectious Owner: Dr A Jackson, Infectious
Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting
 Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
Greater Glasgow and Clyde. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts
 Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines
 Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
EQuIP 5 - This version June 2011 Revision Due June 2014
 Preamble Rockingham Peel Group Non-Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (NPEP) To Prevent HIV in Western Australia Protocol The purpose of this protocol is to clarify the appropriate use and methods
Preamble Rockingham Peel Group Non-Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (NPEP) To Prevent HIV in Western Australia Protocol The purpose of this protocol is to clarify the appropriate use and methods
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Post Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV following Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Assessment Proforma PART A: FOR COMPLETION AT INITIAL PRESENTATION
 Addressograph or Name D.O.B Address Clinic no DOB Post Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV following Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Assessment Proforma PART A: FOR COMPLETION AT INITIAL PRESENTATION The use of PEP following
Addressograph or Name D.O.B Address Clinic no DOB Post Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV following Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Assessment Proforma PART A: FOR COMPLETION AT INITIAL PRESENTATION The use of PEP following
Non-Occupational Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis npep
 Non-Occupational Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis npep Peter Meacher MD (Chief Medical Officer) Anthony Vavasis MD (Director of Medicine) Callen-Lorde Community Health Center Objectives - at the end of the
Non-Occupational Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis npep Peter Meacher MD (Chief Medical Officer) Anthony Vavasis MD (Director of Medicine) Callen-Lorde Community Health Center Objectives - at the end of the
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS
 TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGAMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSUE TO HIV, HBV AND HCV: POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR HIV (PEPSE) AND HEPATITIS B
 PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGAMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSUE TO HIV, HBV AND HCV: POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR HIV (PEPSE) AND HEPATITIS B Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGAMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSUE TO HIV, HBV AND HCV: POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR HIV (PEPSE) AND HEPATITIS B Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL
SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES
 Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: NON- OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOOD-BORNE PATHOGENS (HIV, Hepatitis B, AND Hepatitis C)
 General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016 Contents Section Topic Page
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016 Contents Section Topic Page
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
HIV and PEP. LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED
 HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
Village By Village HIV/AIDS Policy
 The Old Sweet Shop Teme Street, Tenbury Wells, Worcs. WR15 8BB Phone: 07887 870090 Web: villagebyvillage.org.uk Email: neil@villagebyvillage.org.uk Registered Charity Number 1116952 18/9/07 Village By
The Old Sweet Shop Teme Street, Tenbury Wells, Worcs. WR15 8BB Phone: 07887 870090 Web: villagebyvillage.org.uk Email: neil@villagebyvillage.org.uk Registered Charity Number 1116952 18/9/07 Village By
Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP:
 Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
Guidance for Health Care Workers on managing Needlestick/Sharp Injuries and Human Bites In members of the General Public
 Guidance for Health Care Workers on managing Needlestick/Sharp Injuries and Human Bites In members of the General Public Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY
Guidance for Health Care Workers on managing Needlestick/Sharp Injuries and Human Bites In members of the General Public Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS.
 SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
determine need but regimen does not change based on risk factor ED medicine attending meets
 HIV PEP Guidelines after Sexual Assault Harborview Medical Center January 2015 Initial risk assessment and discussion with patient about risk and PEP is by clinician who does exam (SANE, Ob-Gyn resident,
HIV PEP Guidelines after Sexual Assault Harborview Medical Center January 2015 Initial risk assessment and discussion with patient about risk and PEP is by clinician who does exam (SANE, Ob-Gyn resident,
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure
 Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses
 Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] 2014 Aim To raise awareness of the key information and procedures in NHS Lanarkshire's Control of Infection
Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] 2014 Aim To raise awareness of the key information and procedures in NHS Lanarkshire's Control of Infection
Bloodborne Pathogens. Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
A. Background for Trainer: B. What OSHA Requires: Bloodborne Pathogens. Lesson Plan 6080a
 Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
For. Correctional. Officers. Your. Health Risks. in Correctional Settings. Facts. About HIV
 For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
Hepatitis C Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C NHS Dumfries & Galloway would like to acknowledge NHS Greater Glasgow for the use of information contained in this leaflet. This leaflet is also available on request in other formats by phoning
Hepatitis C NHS Dumfries & Galloway would like to acknowledge NHS Greater Glasgow for the use of information contained in this leaflet. This leaflet is also available on request in other formats by phoning
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
FAMILY HIV CENTER NJ CARES SANE
 HIV, Hepatitis B & C Postexposure Prophylaxis for Sexual Assault Victims Update for Case Managers Susan Burrows-Clark, RN, MSN, CNS, C. 10/17/11 Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis After Sexual, Injection-Drug
HIV, Hepatitis B & C Postexposure Prophylaxis for Sexual Assault Victims Update for Case Managers Susan Burrows-Clark, RN, MSN, CNS, C. 10/17/11 Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis After Sexual, Injection-Drug
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Sue Sebazco, Arlington, Texas A Webber Training Teleclass
 Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C
 Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C January 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to:- Demonstrate an increased knowledge and
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C January 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to:- Demonstrate an increased knowledge and
National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after non-occupational exposure to HIV
 National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after non-occupational exposure to HIV These guidelines outline the management of individuals who have been exposed (or suspect they have been exposed)
National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after non-occupational exposure to HIV These guidelines outline the management of individuals who have been exposed (or suspect they have been exposed)
Supervisors, Department Heads and Principals will:
 The Greater Victoria School District is committed to each student s success in learning within a responsive and safe environment. REGULATION 4213 UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS Preamble Universal Precautions are
The Greater Victoria School District is committed to each student s success in learning within a responsive and safe environment. REGULATION 4213 UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS Preamble Universal Precautions are
Sharps Injuries Management
 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
Module 1: HIV epidemiology, transmission and prevention
 Session 2 Module goals Module 1 Participants will be able to: -offer an insight into the epidemiological situation in the country and worldwide -present the HIV transmission modes and the broad approaches
Session 2 Module goals Module 1 Participants will be able to: -offer an insight into the epidemiological situation in the country and worldwide -present the HIV transmission modes and the broad approaches
Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft:
 Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft: 10-2-2015 Clinical studies demonstrate that when a person without HIV infection takes
Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft: 10-2-2015 Clinical studies demonstrate that when a person without HIV infection takes
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep)
 Projeto Praça Onze Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Mauro Schechter Principal Investigator, Projeto Praça Onze Professor of Infectious Diseases Universidade
Projeto Praça Onze Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Mauro Schechter Principal Investigator, Projeto Praça Onze Professor of Infectious Diseases Universidade
TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING
 POST ASSAULT MEDICATIONS Terri Stewart RN Naomi Sugar MD TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING Pregnant STDs Chlamydia Gonorrhea Trichomonas Hep B HIV EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION Plan B Levonorgestrel PLAN B Plan
POST ASSAULT MEDICATIONS Terri Stewart RN Naomi Sugar MD TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING Pregnant STDs Chlamydia Gonorrhea Trichomonas Hep B HIV EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION Plan B Levonorgestrel PLAN B Plan
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY
 CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE HEPATITIS B
 DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
I. PROCEEDINGS AFTER EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (OPIM) WHICH MIGHT TRANSFER AN INFECTION WITH HAEMATOGENOUS VIRUSES
 Annex no. 1 to the enactment No. 13/XIV R/2010 of the Rector of the Medical University in Wrocław dated April 12, 2010 Proceedings after occupational exposure to HIV, HBV and HCV 1 LEGAL GROUNDS: 1. The
Annex no. 1 to the enactment No. 13/XIV R/2010 of the Rector of the Medical University in Wrocław dated April 12, 2010 Proceedings after occupational exposure to HIV, HBV and HCV 1 LEGAL GROUNDS: 1. The
HIV Treatment as Prevention (TasP) Guideline and protocol
 HIV Treatment as Prevention (TasP) Guideline and protocol Who can use this guidance? This guidance is for clinical staff working within the HIV and sexual health services, NHS Tayside. Staff using this
HIV Treatment as Prevention (TasP) Guideline and protocol Who can use this guidance? This guidance is for clinical staff working within the HIV and sexual health services, NHS Tayside. Staff using this
The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV]
![The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV]](/thumbs/93/112976583.jpg) The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] Control of Infection Manual Section G Study Morning 25 th November 2014 Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] Aim To raise awareness
The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] Control of Infection Manual Section G Study Morning 25 th November 2014 Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] Aim To raise awareness
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: F:
 University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
 Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C
 Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C Presentation 5 October 2018 0 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to: Demonstrate an increased knowledge and understanding of opportunities
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C Presentation 5 October 2018 0 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to: Demonstrate an increased knowledge and understanding of opportunities
3/23/2016. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures
 This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
Antonio E. Urbina, M.D. Associate Medical Director Center for Comprehensive Care, West 17 th Street Clinic St. Luke s Roosevelt Hospital DISCLOSURES
 PROPHYLAXISFOLLOWINGHIV, HEPB ANDC EXPOSURES: WHAT SNEW Antonio E. Urbina, M.D. Associate Medical Director Center for Comprehensive Care, West 17 th Street Clinic St. Luke s Roosevelt Hospital DISCLOSURES
PROPHYLAXISFOLLOWINGHIV, HEPB ANDC EXPOSURES: WHAT SNEW Antonio E. Urbina, M.D. Associate Medical Director Center for Comprehensive Care, West 17 th Street Clinic St. Luke s Roosevelt Hospital DISCLOSURES
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens
 Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions
 Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005
 Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005 Version Date Date of Next Reason for Change (eg. full rewrite, No. Ratified/ Implementation Review amendment
Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005 Version Date Date of Next Reason for Change (eg. full rewrite, No. Ratified/ Implementation Review amendment
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
Advice and Information about HIV
 Advice and Information about HIV For patients, carers and the public What is HIV? (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) HIV is a virus which attacks the body s defence (immune) system. A person who is infected
Advice and Information about HIV For patients, carers and the public What is HIV? (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) HIV is a virus which attacks the body s defence (immune) system. A person who is infected
Dr Helena Nixon Specialist Occupational Physician University Hospital Birmingham
 A Study in Scarlet Dr Helena Nixon Specialist Occupational Physician University Hospital Birmingham World Map April 2006 World developing nations World life expectancy Why the interest in BBVs? Estimated
A Study in Scarlet Dr Helena Nixon Specialist Occupational Physician University Hospital Birmingham World Map April 2006 World developing nations World life expectancy Why the interest in BBVs? Estimated
Blood Borne Pathogens. Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N.
 Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Answering basic questions about HIV
 Answering basic questions about HIV Sixth Edition This booklet is for you if you have basic questions about HIV such as what it is, how it is transmitted and how it affects the body. If you have HIV and
Answering basic questions about HIV Sixth Edition This booklet is for you if you have basic questions about HIV such as what it is, how it is transmitted and how it affects the body. If you have HIV and
Question 1. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts 6. What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based Virus. B. Blood Borne Viruses
 Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based Virus B. Blood Borne Viruses C. Basic Blood Viruses Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts 6 Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based
Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based Virus B. Blood Borne Viruses C. Basic Blood Viruses Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts 6 Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based
SHARPS MANAGEMENT AND INOCULATION INJURIES
 Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Sharps Management and Inoculation Injuries Version 1.01 May 15 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Sharps Management
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Sharps Management and Inoculation Injuries Version 1.01 May 15 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Sharps Management
Colgate University. Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
An International Antiviral Society-USA
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA University of Arizona, Phoenix dougco@email.arizona. edu A look at new guidelines for HIV treatment and prevention Start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible after HIV
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA University of Arizona, Phoenix dougco@email.arizona. edu A look at new guidelines for HIV treatment and prevention Start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible after HIV
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
B. Tasks and Procedures where employees, students or contractors can be exposed to bloodborne pathogens:
 Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
PrEP in Scotland. PrEP. in Scotland. PrEP. PrEP. PrEP. PrEP is a combination pill that prevents HIV.
 PrEP in Scotland PrEP PrEP PrEP PrEP is a combination pill that prevents HIV. 1 Contents Introduction 3 What is PrEP 3 Who should take PrEP 4 Getting PrEP in Scotland 5 Side effects and interactions with
PrEP in Scotland PrEP PrEP PrEP PrEP is a combination pill that prevents HIV. 1 Contents Introduction 3 What is PrEP 3 Who should take PrEP 4 Getting PrEP in Scotland 5 Side effects and interactions with
Infection Control Standard Precautions. CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients
 Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
 Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
patients with blood borne viruses Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled Document Lead:
 CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy
 Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
 Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Version: 8 Status: Owner: In review Infection Prevention
Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Version: 8 Status: Owner: In review Infection Prevention
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure STUDENT. Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure. Student. Rev:
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
