UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Silencing of HIV-1 co-factors Eekels, J.J.M. Link to publication
|
|
|
- Douglas O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Silencing of HIV-1 co-factors Eekels, J.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Eekels, J. J. M. (11). Silencing of HIV-1 co-factors General rights It is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), other than for strictly personal, individual use, unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Disclaimer/Complaints regulations If you believe that digital publication of certain material infringes any of your rights or (privacy) interests, please let the Library know, stating your reasons. In case of a legitimate complaint, the Library will make the material inaccessible and/or remove it from the website. Please Ask the Library: or a letter to: Library of the University of Amsterdam, Secretariat, Singel 5, 11 WP Amsterdam, The Netherlands. You will be contacted as soon as possible. UvA-DARE is a service provided by the library of the University of Amsterdam ( Download date: 16 Jul 18
2 Chapter The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter Julia J.M. Eekels, Rienk E. Jeeninga and Ben Berkhout Manuscript in preparation Laboratory of Experimental Virology, Department of Medical Microbiology, Center for Infection and Immunity Amsterdam (CINIMA), Academic Medical Center of the University of Amsterdam
3
4 The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter Abstract The RNA helicase has a plethora of cellular functions and has been implicated as a co-factor or inhibitor in some types of cancer. can also influence the replication of human pathogenic viruses, including human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). We show that stable RNA interference (RNAi) mediated knockdown of inhibits HIV-1 replication with minor effects on cell proliferation. As is involved in the transcriptional control of different promoters, we studied the effect of overexpression and knockdown on the activity of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat (LTR) promoter. Knockdown of reduces both the basal and Tat-induced LTR transcription levels. Overexpression of has no effect on basal transcription, but enhanced Tatinduced transcription from the HIV-1 LTR. The protein thus seems to facilitate optimal LTR transcription and may play a role as cellular co-factor of the viral Tat protein. Introduction The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) caused by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) remains a serious global health threat, although combined antiretroviral therapy (cart) is highly active against the virus. Despite the clinical success of cart, the emergence of drug-resistant viral strains is another major problem. To avoid viral drug resistance, it has been proposed to target cellular co-factors that HIV-1 requires for its replication cycle. One of the many possible therapeutic targets is the RNA helicase. is a member of the family of DEAD box RNA helicases (DEAD = AspGluAlaAsp) that possesses RNAdependent ATPase and helicase activity (39). Members of this family are involved in a wide range of cellular processes that deal with RNA; e.g. splicing, mrna export, transcription and translation (89). has been implicated in many of these cellular functions as summarized in Figure.1 and reviewed in (38). interacts with the transcription factor Sp1 and binds to several promoters, e.g. the interferon-β promoter to execute a transcriptional role (;39). shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus and nuclear export is mediated via interaction with the CRM1 protein, which also implicates in the nuclear export of other RNAs (388). A function in mrna translation is executed via an interaction with the translation initiation factor eif3 (196). In most cases the exact molecular mechanism of action remains unclear. also plays a role in innate immunity. is involved in the intracellular signaling upon activation of pathogen recognition receptors (PPRs) such as Toll-like receptors and cytoplasmic viral RNA sensors like RIG-I. When PPRs sense the presence of a pathogen, several signaling pathways are triggered, eventually resulting in activation of the transcription factors NF-κB and interferon regulatory factors (IRF) 3 and. NF-κB activation leads to the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines, IRF3 and activation leads to the induction of type I interferons. Cytokines and type I interferons are known to be potent antiviral mediators. Several specific -virus interactions have been reported in literature as summarized in Figure.1. Vaccinia virus (VACV) inhibits the induction of interferon-β (IFNβ) by the viral protein K, which binds to, to inhibit the - mediated induction of the IFNβ promoter (39). plays a similar role in hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication. The HBV polymerase protein binds to and blocks INFβ 13
5 Chapter production (369;395). Interestingly, interaction with the viral polymerase leads to incorporation of into the virion particle and inhibits the first step of reverse transcription in the newly infected cell, thus augmenting the antiviral effect (368). In contrast, other viruses such as hepatitis C virus (HCV) use as a cellular co-factor for its replication, although the precise mechanism remains unclear. interacts with the HCV structural core protein and may modulate viral or cellular gene expression (1;3;65). Cellular functions -Virus interactions Translational control mrna nuclear export Transcription Transcription HBV (Pol) VACV (K) HCV (Core) HIV-1 (Rev) HIV-1 (Tat)? Tumor suppressor Viral RNA sensing Oncogene Interferon-β induction Cancer Innate immunity Figure.1. Different functions of the protein has been implicated in many cellular processes and we grouped the specialized functions in innate immunity, virus replication and cancer. indicates a process positively influenced by, indicates processes negatively influenced by. Functions of that are linked are depicted in the same colour. Red: nuclear RNA export. Blue: Upregulated transcription. Green: Downregulated transcription. Purple: Interferon-β induction. The effect of on Tat-mediated transcription is the focus of this study (grey box). binds CRM1 and this interaction is important in HIV-1 replication as unspliced and incompletely spliced viral transcripts require nuclear export via the CRM1 pathway that is controlled by the viral Rev-RRE axis (388). Furthermore, expression was found to be induced by the HIV-1 protein Tat. It has been reported that does not influence transcription from the HIV-1 LTR promoter, but these experiments were performed exclusively in the absence of Tat (388). Two recent studies confirmed that expression is enhanced by Tat and that the two proteins physically interact (6;19). Opposing roles have also been described for in cancer. acts as an oncogene in breast cancer cells by reducing transcription from the E-cadherin promoter, which has been associated with progression to cancer and metastasis (). acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, where it upregulates the expression of the tumor suppressor p1 via an interaction with the transcription factor Sp1 (). As has been implicated in transcriptional control in diverse settings, we wanted to readdress a putative role in HIV-1 transcription (see box in Figure.1). We and others have previously shown that stable knockdown of inhibits HIV-1 replication (13;158). This result was confirmed in this study, with additional experimentation to 1
6 The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter document the mrna knockdown level and the impact on cell growth. We subsequently tested the effect of overexpression or knockdown on transcription from the HIV-1 LTR promoter. overexpression enhances transcription from the LTR in the presence of the viral Tat protein, while knockdown of has the opposite effect. The ATPase and helicase activities of are critical for this role as HIV-1 co-factor. We thus propose that functions at two steps of the HIV-1 replication cycle, via Tat in transactivation of the HIV-1 LTR promoter and via CRM1/Rev in the nuclear export of HIV-1 RNAs. This double action as co-factor makes a promising target for anti-hiv-1 therapy, of which the impact may be broader as is also a co-factor for HCV, which is frequently seen as co-infection in HIV-1 infected individuals. Materials and methods Plasmids ShRNA-expressing constructs (plko.1) are from the MISSIONTM TRC-Hs 1. library (Sigma- Aldrich) and were obtained as bacterial clones (93). Target sequences can be found on the website of Sigma-Aldrich [ Plasmid DNA was isolated with Nucleobond Midiprep columns according to the manufacturer s protocol (Macherey- Nagel). For the competitive cell growth assay it was necessary to replace the gene for the puromycin selection marker in plko.1 for the GFP gene, as described earlier (Eekels et al, Chapter ). pcmv-myc- encodes with a Myc tag and pcmv-myc-k3e encoding a mutant form of. Both plasmids were kindly provided by dr. M. Schröder (National University of Ireland, Maynooth). psuper-sh was constructed as described (9). pbluescript3 LTRLuc (16) was used to study HIV-1 LTR activity and the empty vector pbluescript KS(-) was used to control for input DNA amounts in transfections. ptatexon contains the Tat coding sequence under control of the constitutive CMV promoter (36). Cell culture, DNA transfection, lentiviral vector production and transduction Human embryonic kidney 93T (HEK93T) adherent cells were grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 1% fetal calf serum, 1 U/ml penicillin and 1 μg/ml streptomycin. Human SupT1 suspension T cells were grown in Rosewell Park Memorial Institute medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 1% fetal calf serum, 1 U/ml penicillin and 1 μg/ml streptomycin. For puromycin selection the final concentration in the culture medium was 1 µg/ml. Cell lines were cultured in a humidified chamber at 3 C and 5% CO. DNA transfections were performed with Lipofectamine according to manufacturer s instructions (Invitrogen). In short, x 1 5 cells per well (-wells) were seeded a day before transfection. The next day cells were transfected, where necessary the empty plasmid pbluescript KS (-) was used to obtain an equal amount of DNA per well. Cells were harvested hours post transfection. All transfections were performed in four-fold, of which two wells were analyzed for luciferase activity and two wells were harvested for RNA isolation. Luciferase activity was measured using the DualGlo Luciferase kit (Promega). 15
7 Chapter Lentiviral vectors were produced as previously described (9). Briefly, HEK93T cells were co-transfected with the shrna-construct and the packaging plasmids (prsv-rev, pmdlg/prre and pvsv-g) using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen). One day after transfection the medium was refreshed and the supernatant was harvested the next day. The virus containing supernatant was centrifuged and aliquots were stored at 8 C. A sample was taken for CA-p enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to monitor lentiviral particle production. SupT1 T cells were seeded in a -wells plate (1 x 1 5 cells/well), lentiviral vector was added and incubated overnight. Excess virus was washed away the next day. Stably transduced cells were selected for either by addition of 1 µg/ml puromycin to the culture medium or by FACS sorting based on GFP expression, depending on the selection marker encoded by the lentiviral vector. CA-p ELISA Culture supernatant was heat-inactivated at 56 C for 3 min in the presence of.5% Empigen-BB (Calbiochem). The CA-p concentration was determined by a twin-site ELISA with D3 (Biochrom) as the capture antibody and the alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-ca-p monoclonal antibody EH1-AP (International Enzymes) as the detection antibody. Detection was performed with the Lumiphos plus system (Lumigen) in a LUMIstar Galaxy luminescence reader (BMG Labtechnologies). Recombinant CA-p produced in a baculovirus system was used as reference standard. CCG assay and FACS analysis To study the effects of shrna expression on cell proliferation, the CCG assay was used as described earlier (Eekels et al, Chapter ). Briefly, cells were transduced with 1 or 1 µl of lentiviral vector encoding a shrna and the GFP selection marker. The percentage of GFPexpressing cells was monitored over time with FACS analysis. To do so, a sample was taken from the cell culture and cells were collected by centrifugation ( min, rpm, Eppendorf centrifuge). The cell pellet was resuspended in FACS solution (Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) + % FCS). FACS analysis was performed with the FACScanto (BD Biosciences). Live cell population was based on forward and side scatter parameters and GFP-positive population was determined based on unstained and untransduced cells. HIV-1 replication and single cycle infection experiments HIV-1 was produced by transfection of HEK93T cells with the molecular clone HIV-1 LAI () and virus production was measured by CA-p ELISA. SupT1 T cell cultures (5 ml in T5 format,.5 x 1 6 cells/flask) were infected with HIV-1 (.5 ng of CA-p). Every day virus replication was monitored by scoring syncytia formation and supernatant samples were taken for CA-p ELISA. For single cycle infection experiments, SupT1 cells were incubated with HIV-1 for hours, after which excess virus was washed away. Cells were subsequently cultured in complete medium supplemented with.1 µg/ml fusion inhibitor T19 to block new infections (Eggink et al., 8). Cells were analyzed 8 hours post infection for intracellular CA-p by FACS. Therefore cells were collected by centrifugation (as above) and fixated in 5 µl % formaldehyde for 5 minutes at room temperature. 5 µl Perm/Wash (BD Biosciences) was added and cells were again pelleted by centrifugation. Cells were stained 16
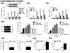
8 The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter for at least 1 hour at C in 5 µl BD Perm/WashTM buffer containing 5 µl 1:1 diluted antibody against CA-p conjugated with PE (monoclonal mouse, clone KC5, Coulter). Excess antibody was washed away by washing twice with 5 µl FACS solution, cells were resuspended in 5 µl FACS solution and analyzed on a FACScanto. Uninfected and unstained samples were used as negative controls. Western blot Cell lysates that were prepared for luciferase measurement were mixed 1:1 with SDS- PAGE loading buffer, boiled for 5 minutes and run in a 1% SDS-PAGE gel. Proteins were transferred to an Immobilon-P membrane (Millipore) via semi-dry transfer. Membranes were treated for 1 hour at room temperature in blocking solution (PBS + 5% milk +.1% Tween-) and detection was performed with anti- (Abcam, ab53, mouse, 1:1), anti-β-actin (Sigma, clone AC-, mouse, 1:5) and HRP-labeled goat antimouse IgG (1:5). Luminometric detection of proteins was performed with Western Lightning ECL (PerkinElmer Life Sciences) and membranes were analyzed on a LAS imager (GE Healthcare). RNA isolation and RT-qPCR RNA was isolated from.5 x 1 6 cells with the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer s instructions, including the optional DNase I treatment on column. 1 µg RNA was reverse transcribed with the Thermoscript kit (Invitrogen) and oligo-dt primers. cdna synthesis was performed at 5 C for 1 hour. The resulting cdna was diluted 1 times and 5 µl of the dilution was used as template in a SYBR Green based RT-qPCR assay (Qiagen). Primers for and the internal control β-actin were obtained from Quantitect Primer Assays (Qiagen). Primers for Firefly luciferase were Forward 5 - GGATTACCAGGGATTTCAGTC-3' and Reverse: 5'-CTCACGCAGGCAGTTCTAT-3. The levels of luciferase, and β-actin mrna were measured in duplo using Ct (threshold cycle) for every sample and the equation -ΔΔCt was used for relative quantification of luciferase and mrna expression levels (). Results knockdown inhibits HIV-1 replication We previously demonstrated inhibition of HIV-1 replication by stable RNAi-mediated knockdown of cellular proteins in the human T cell line SupT1 (13). One of the tested candidate co-factors was the helicase and 5 anti- shrnas were tested for their impact on HIV-1 replication. In this study we used shrna1 that gave the best results. The SupT1 T cell line was transduced with a lentiviral vector encoding the anti- shrna and control cell lines were generated with the empty lentiviral vector SHC1 to test for potential effects of vector integration and SHC that expresses a scrambled shrna molecule. The three cell lines were challenged with HIV-1 and virus replication was monitored over a period of 13 days (Figure.A). Both controls cells support HIV-1 replication with peak infection at 9 days post infection, while HIV-1 replication is inhibited in the knockdown cell line (sh). 1
9 Chapter To test whether the knockdown of has any effect on cell proliferation, a competitive cell growth (CCG) assay was performed (Eekels et al, Chapter ). This assay is performed directly on the lentivirus transduced culture that contains transduced GFP-expressing cells and non-transduced cells. The percentage of GFP-positive cells was analyzed longitudinally by simple FACS analysis. A reduced cell growth rate due to shrna expression is scored as a gradual decrease in the fraction of GFP-positive cells. Knowing the doubling time of untransduced SupT1 cells, the relative proliferation rate of transduced cells can be calculated. The relative proliferation rate of SHC1 cells was set at 1% and knockdown resulted in a moderate loss of 1% (Figure.B). The mrna level was measured in the three cell lines using RT-qPCR. A knockdown percentage of 55% was scored in the sh cells compared to the empty SHC1 control. The scrambled shrna in SHC had no effect on mrna expression level (Figure.C). It has in fact been reported that a knockdown percentage above 5% is difficult to achieve for (39;388). Nonetheless, this relative modest knockdown efficiency has a clear effect on HIV-1 replication. A B C CA-p (ng/ml) Days post infection SHC1 SHC sh Cell growth rate (%) SHC1 SHC mrna expression level (%) SHC1 SHC Figure.. Stable knockdown of delays HIV-1 replication without inducing cytotoxicity A. Stable knockdown SupT1 cells were generated with a shrna against (sh). Two control cells were generated in parallel: SHC1, with an empty lentiviral vector and SHC, expressing a scrambled shrna molecule. The cell lines were infected with HIV-1LAI and viral replication was monitored in the culture supernatant by ELISA for CA-p over a period of 13 days. B. The relative cell growth rate was measured to score adverse effects of knockdown. Cellular proliferation rate of SHC1 was set at 1%. A minor reduction of 1% was observed in the knockdown cell line. C. mrna levels were measured with RT-qPCR. Three independent cell samples were analyzed and the data was pooled. The mean relative gene expression levels are shown (SHC1 set at 1%), error bars represent standard deviation. knockdown in single cycle infection experiments To assess which step of the replication cycle HIV-1 is blocked by knockdown, we performed single cycle infection experiments in stably transduced SupT1 cells. To do so, cells were incubated with HIV-1 for hours, after which excess virus was washed away and the fusion inhibitor T19 was added to prevent new rounds of infection. After 8 hours, the cells are harvested and intracellularly stained for viral gene expression in the form of CA-p protein. With flowcytometry the percentage of cells positive for CA-p can be analyzed, as well as the mean production of CA-p per positive cell, expressed as the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Extracellular virus production was analyzed by CAp ELISA in the culture supernatant. When expression is reduced, we observe a reduction in the percentage of cells that become positive for intracellular CA-p (Figure.3, left panel), which indicates that less cells were productively infected. The amount of CA-p produced by these infected cells is 18
10 The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter also modestly reduced upon knockdown (Figure.3, middle panel). As less cells become productively infected and those cells produce less CA-p, the reduction of extracellular CA-p in the culture supernatant is expected (Figure.3, right panel). The fact that less cells are productively infected upon knockdown indicates that an early step in HIV-1 replication is inhibited. However, the small reduction in CA-p production by infected cells indicates an additional effect on a late HIV-1 replication step. CA-p positive cells (%) SHC1 SHC MFI SHC1 SHC CA-p (ng/ml) 6 SHC1 SHC Figure.3. knockdown in single round HIV-1 infections Control and knockdown cells were incubated with HIV-1 for hours, after which excess virus was washed away. Cells were further cultured in the presence of the fusion inhibitor T19 to prevent new rounds of infection. The percentage of cells positive for intracellular CA-p production was measured by FACS analysis 8 hours post infection (left panel). The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is plotted as a measure of CA-p production per infected cell (middle panel). The CA-p concentration in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (right panel). The average of independent experiments that were performed in duplicate are shown, error bars represent the standard deviation. acts in synergy with Tat to transactivate the HIV-1 LTR Because plays multiple s in the regulation of cellular transcription, we tested the effect of knockdown on the HIV-1 LTR promoter. To monitor the exclusive effects on LTR activity, experiments were performed with a luciferase reporter gene under control of the LTR promoter (LTR-luc) in HEK93T cells. We initially transduced these HEK93T cells with the shrna-expressing lentiviral vectors but did not obtain significant knockdown. We therefore decided to use transient DNA transfection. Cells were cotransfected with LTR-luc and increasing amounts of the psuper plasmid encoding the shrna against. The effect of knockdown on LTR-luc activity was analyzed in the absence and presence of the viral protein Tat that activates transcription from the LTR (Figure.A). The basal luciferase activity without Tat was set at 1. In the absence of Tat, an increasing amount of sh-expression construct and thus increased knockdown level gradually decreased the basal Luciferase activity. When the LTR-promoter is activated by Tat, knockdown again decreased Luciferase activity. has been reported to be important in many cellular mechanisms such as nuclear export of RNAs and translation. In fact, the firefly luciferase mrna requires the CRM1 RNA export pathway, in which has been implicated (1). To show that the observed effect was due to decreased transcription activity rather than e.g. nuclear RNA export, the luciferase mrna level was measured by RT-qPCR. Both in the presence and absence of Tat a gradual decrease of luciferase mrna expression was observed when is knocked down (Figure.B). The knockdown of protein was confirmed by Western blot analysis, on which the cellular β-actin protein acts as loading control (Figure.C). 19
11 Chapter We next tested the impact of overexpression by co-transfection with a CMV-driven expression vector (Figure.D). overexpression further boosted Tat-activated Luciferase activity, but it has no significant effect on the basal Luciferase activity. The latter finding is similar to those of Yedavalli et al, but that study did not test the effect with Tat (388). RT-qPCR analysis confirmed that the increase in Luciferase activity is due to increased luciferase mrna expression (Figure.E), and the overexpression of was confirmed by Western blot analysis (Figure.F). A Luciferase activity D Luciferase activity -Tat +Tat 1 -Tat +Tat sh B luciferase mrna E luciferase mrna 8 -Tat +Tat 3 -Tat +Tat 6 1 sh C - Tat F - Tat +Tat +Tat Figure.. influences LTR transcription in a Tat-dependent manner A. HEK93T cells were co-transfected with 5 ng LTR-luciferase construct and increasing amounts of psupersh (1, 5, 1 and 5 ng), in the absence and presence of Tat (5 ng). Knockdown of decreases both basal and Tat-inducted LTR activity. The basal Luciferase activity without Tat was set at 1. B. RT-qPCR was performed to measure luciferase mrna levels. Basal luciferase mrna level without Tat was set at 1.C. Knockdown of was confirmed by Western blot analysis, with β-actin as loading control. D. HEK93T cells 11
12 The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter were co-transfected with 5 ng LTR-luciferase construct and increasing amounts of pcmv--myc (1, 5, 1 and 5 ng), in the absence and presence of Tat (5 ng). Overexpression of has no effect on basal LTR activity, but enhances Tat-induced LTR activity. E. The increase in luciferase mrna levels was confirmed by RTqPCR. F. The overexpression of was confirmed by Western blot analysis. The ATPase and helicase capacity of is necessary for LTR activation To test whether the catalytic functions of are required for the effect on HIV-1 LTR transcription, we used the K3E mutant. This mutant has a single amino acid substitution in the Walker A motif and is not able to hydrolyse ATP and to unwind RNA (388). -K3E overexpression did not increase the Luciferase activity (Figure.5A) and the level of luciferase mrna (Figure.5B), but expression of the K3E mutant was confirmed by Western blotting (Figure.5C). Parallel experiments with wild-type reproduced the activation phenotype (Figure.5D and.5e) and protein expression levels were similar to that of the mutant (Figure.5F). The ATPase and helicase activity of are therefore important for the stimulatory effect on Tat-mediated transcription from the HIV-1 LTR promoter. A Luciferase activity 1 -Tat +Tat 8 6 K3E - - B luciferase mrna 1 -Tat +Tat K3E - - C - Tat + Tat D E F Luciferase activity 1 -Tat +Tat luciferase mrna 1 -Tat +Tat Tat + Tat Figure.5. The ATPase and helicase activity of are required for modulation of the HIV-1 LTR A and B. HEK93T cells were co-transfected with 5 ng LTR-luciferase reporter construct and increasing amounts of -K3E expression construct (1 and 5 ng), in the absence or presence of Tat (5 ng). No effect was observed on basal and Tat-induced LTR Luciferase activity (A) and the luciferase mrna levels (B). C. Overexpression of the mutant K3E protein was confirmed by Western blot, with β-actin as loading control. D and E. Overexpression of wildtype (1 and 5 ng) has no effect on basal LTR transcription, but enhanced Tat-induced LTR transcription, as apparent in Luciferase activity assays (D) and luciferase mrna assays (E). F. Overexpression of wildtype was confirmed by Western blot analysis. 111
13 Chapter Discussion HIV-1 requires many cellular co-factors to complete its replication cycle and one of these co-factors is the RNA helicase. This protein has been described as a co-factor of the HIV-1 Rev protein, which facilitates the export of HIV-1 transcripts from the nucleus via the CRM1 pathway. has also been implicated in many cellular mechanisms, including transcription and translation (Figure.1). We first tested the effect of knockdown in T cells on HIV-1 replication. A relatively modest knockdown of did significantly inhibit HIV-1 replication, with only a minor effect on cell proliferation. We next tested the effect of knockdown and overexpression on transcription from the HIV-1 LTR promoter. We measured transcription levels of a luciferase reporter construct under control of the HIV-1 LTR and show that LTR-driven transcription is decreased when is knocked down, both in the presence and absence of the Tat protein. This result is consistent with a supportive role of in HIV-1 gene expression. Overexpression of leads to enhanced levels of LTR transcription, but only in the presence of Tat. This result could indicate that endogenous expression is sufficient for basal LTR transcription, but that more is beneficial for high-level Tat activated LTR transcription. RT-qPCR analyses of luciferase mrna expression indicated that the observed effects are due to regulation at the transcriptional level. It was obviously important to rule out that acts on nuclear RNA export or mrna translation, mechanisms known to be influenced by. To test if the enzymatic ATPase and associated helicase activity of are involved in the enhancement of Tat-mediated transcription, we used the previously described K3E mutant. This mutant has a single amino acid substitution in the Walker A motif that abrogates ATPase and helicase activity (36). When overexpressed, the K3E mutant had no effect on both basal and Tat-induced transcription from the HIV-1 LTR, as opposed to the wild-type protein. Because the mutant is stably expressed in cells, we conclude that the enzymatic helicase activity is important for enhancement of HIV-1 LTR transcription levels. Interestingly, it has been shown that the K3E mutant is fully able to enhance transcription from the IFNβ promoter (39), indicating that different molecular interactions and mechanisms are at play during transcriptional activation of these promoters. For instance, HIV-1 LTR transcription may be special because of the multiple binding sites for the Sp1 transcription factor, which interacts directly with. Sp1 is required for both basal and Tat-mediated activation of the LTR promoter (38;33). has recently been the focus of many studies because of its role in cancer development and the replication of at least two pathogenic human viruses (HIV-1 and HCV). Inhibition of such a cellular co-factor has obvious therapeutic potential and different antiviral strategies can be proposed. We and others showed that RNAi mediated knockdown inhibits HIV-1 replication, with only minor effects on cell proliferation. could thus be placed on the shortlist of candidate targets for a gene therapy approach to silence critical co-factors of pathogenic viruses, although the CCR5 receptor remains the primary target for anti-hiv therapies (13). Other studies have used small-molecules inhibitors of to achieve potent inhibition of HIV-1 replication (9;3). The notion that contributes to two important steps of HIV-1 replication, that is Tat-mediated LTR transcription and Rev-mediated RNA export, makes it an even more attractive therapeutic target. 11
14 The RNA helicase is involved in trans-activation of the HIV-1 Long Terminal Repeat promoter Acknowledgements This research was supported by the Dutch AIDS fund (grant 66 and 8). We thank Berend Hooibrink for FACS sorting, Stephan Heynen for CA-p ELISA experiments, Dirk Geerts for providing the shrna-expression constructs and Dr. Martina Schöder for the -expression constructs. We also thank the Belgian Federal Government for financial support through the Inter-University Attraction Pole grant P6/1. 113
~Lentivirus production~
 ~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside Von Eije, K.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside Von Eije, K.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay
 Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A. Link to publication Citation for published
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Improving aspects of palliative care for children Jagt, C.T. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Improving aspects of palliative care for children Jagt, C.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Jagt, C. T. (2017). Improving aspects of palliative
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Improving aspects of palliative care for children Jagt, C.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Jagt, C. T. (2017). Improving aspects of palliative
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for NF-κB Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Bos, J.M. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Bos, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bos, J. M. (2010). Genetic basis of hypertrophic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Bos, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bos, J. M. (2010). Genetic basis of hypertrophic
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc.
 CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc. Copyright (c) 2018 Cellecta, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents 1. CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator
CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc. Copyright (c) 2018 Cellecta, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents 1. CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Vascular factors in dementia and apathy Eurelings, Lisa. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Vascular factors in dementia and apathy Eurelings, Lisa Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Eurelings, L. S. M. (2016). Vascular factors in
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Vascular factors in dementia and apathy Eurelings, Lisa Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Eurelings, L. S. M. (2016). Vascular factors in
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) An electronic nose in respiratory disease Dragonieri, S. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) An electronic nose in respiratory disease Dragonieri, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Dragonieri, S. (2012). An electronic nose in respiratory
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) An electronic nose in respiratory disease Dragonieri, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Dragonieri, S. (2012). An electronic nose in respiratory
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document
 Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document
 Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
Supplementary Information. Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases
 Supplementary Information Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases Ulrike Mock 1, Kristoffer Riecken 1, Belinda Berdien 1, Waseem Qasim 2, Emma Chan
Supplementary Information Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases Ulrike Mock 1, Kristoffer Riecken 1, Belinda Berdien 1, Waseem Qasim 2, Emma Chan
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems
 ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins
 Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The artificial pancreas Kropff, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The artificial pancreas Kropff, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kropff, J. (2017). The artificial pancreas: From logic to life General
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The artificial pancreas Kropff, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kropff, J. (2017). The artificial pancreas: From logic to life General
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening
 Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Gezinskenmerken: De constructie van de Vragenlijst Gezinskenmerken (VGK) Klijn, W.J.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Gezinskenmerken: De constructie van de Vragenlijst Gezinskenmerken (VGK) Klijn, W.J.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Klijn, W. J. L. (2013).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Gezinskenmerken: De constructie van de Vragenlijst Gezinskenmerken (VGK) Klijn, W.J.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Klijn, W. J. L. (2013).
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
FIG S1 Examination of eif4b expression after virus infection. (A) A549 cells
 Supplementary Figure Legends FIG S1 Examination of expression after virus infection. () 549 cells were infected with herpes simplex virus (HSV) (MOI = 1), and harvested at the indicated times, followed
Supplementary Figure Legends FIG S1 Examination of expression after virus infection. () 549 cells were infected with herpes simplex virus (HSV) (MOI = 1), and harvested at the indicated times, followed
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
VIRAL TITER COUNTS. The best methods of measuring infectious lentiviral titer
 VIRAL TITER COUNTS The best methods of measuring infectious lentiviral titer FLUORESCENCE CYCLES qpcr of Viral RNA SUMMARY Viral vectors are now routinely used for gene transduction in a wide variety of
VIRAL TITER COUNTS The best methods of measuring infectious lentiviral titer FLUORESCENCE CYCLES qpcr of Viral RNA SUMMARY Viral vectors are now routinely used for gene transduction in a wide variety of
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
QuickTiter Lentivirus Titer Kit (Lentivirus-Associated HIV p24)
 Product Manual QuickTiter Lentivirus Titer Kit (Lentivirus-Associated HIV p24) Catalog Number VPK-107 VPK-107-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Product Manual QuickTiter Lentivirus Titer Kit (Lentivirus-Associated HIV p24) Catalog Number VPK-107 VPK-107-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins
 Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins www.vectalys.com/products/ Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Catalog Number referring to this User Manual: 0008VCT; 0009VCT;
Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins www.vectalys.com/products/ Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Catalog Number referring to this User Manual: 0008VCT; 0009VCT;
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Certificate of Analysis
 Certificate of Analysis Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631987 10 μg Specified on product label. Product Information plvx-ef1α-ires-mcherry is a bicistronic lentiviral expression vector that can be used
Certificate of Analysis Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631987 10 μg Specified on product label. Product Information plvx-ef1α-ires-mcherry is a bicistronic lentiviral expression vector that can be used
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Citation for published version (APA): Sivapalaratnam, S. (2012). The molecular basis of early onset cardiovascular disease
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The molecular basis of early onset cardiovascular disease Sivapalaratnam, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Sivapalaratnam, S. (2012).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The molecular basis of early onset cardiovascular disease Sivapalaratnam, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Sivapalaratnam, S. (2012).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Large Scale Infection for Pooled Screens of shrna libraries
 Last modified 01/11/09 Large Scale Infection for Pooled Screens of shrna libraries Biao Luo, Glenn Cowley, Michael Okamoto, Tanaz Sharifnia This protocol can be further optimized if cells being used are
Last modified 01/11/09 Large Scale Infection for Pooled Screens of shrna libraries Biao Luo, Glenn Cowley, Michael Okamoto, Tanaz Sharifnia This protocol can be further optimized if cells being used are
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Citation for published version (APA): van Munster, B. C. (2009). Pathophysiological studies in delirium : a focus on genetics.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Pathophysiological studies in delirium : a focus on genetics van Munster, B.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Munster, B. C. (2009).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Pathophysiological studies in delirium : a focus on genetics van Munster, B.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Munster, B. C. (2009).
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the solubility of amylin and huntingtin in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
Prediction of toxicity in concurrent chemoradiation for non-small cell lung cancer Uijterlinde, W.I.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction of toxicity in concurrent chemoradiation for non-small cell lung cancer Uijterlinde, W.I. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Uijterlinde,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction of toxicity in concurrent chemoradiation for non-small cell lung cancer Uijterlinde, W.I. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Uijterlinde,
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Citation for published version (APA): Parigger, E. M. (2012). Language and executive functioning in children with ADHD Den Bosch: Boxpress
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Language and executive functioning in children with ADHD Parigger, E.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Parigger, E. M. (2012). Language
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Language and executive functioning in children with ADHD Parigger, E.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Parigger, E. M. (2012). Language
Ubiquitination and deubiquitination of NP protein regulates influenza A virus RNA replication
 Manuscript EMBO-2010-74756 Ubiquitination and deubiquitination of NP protein regulates influenza A virus RNA replication Tsai-Ling Liao, Chung-Yi Wu, Wen-Chi Su, King-Song Jeng and Michael Lai Corresponding
Manuscript EMBO-2010-74756 Ubiquitination and deubiquitination of NP protein regulates influenza A virus RNA replication Tsai-Ling Liao, Chung-Yi Wu, Wen-Chi Su, King-Song Jeng and Michael Lai Corresponding
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN No Treatment. EZN-3920, 2 μm. Time, h
 Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Building blocks for return to work after sick leave due to depression de Vries, Gabe
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Building blocks for return to work after sick leave due to depression de Vries, Gabe Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): de Vries, G. (2016).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Building blocks for return to work after sick leave due to depression de Vries, Gabe Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): de Vries, G. (2016).
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/366/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Viral entry route determines how human plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons Daniela Bruni, Maxime
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/366/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Viral entry route determines how human plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons Daniela Bruni, Maxime
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Superinfection with drug-resistant HIV is rare and does not contribute substantially to therapy failure in a large European cohort Bartha, I.; Assel, M.; Sloot, P.M.A.;
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Superinfection with drug-resistant HIV is rare and does not contribute substantially to therapy failure in a large European cohort Bartha, I.; Assel, M.; Sloot, P.M.A.;
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Standaarden voor kerndoelen basisonderwijs : de ontwikkeling van standaarden voor kerndoelen basisonderwijs op basis van resultaten uit peilingsonderzoek van der
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Standaarden voor kerndoelen basisonderwijs : de ontwikkeling van standaarden voor kerndoelen basisonderwijs op basis van resultaten uit peilingsonderzoek van der
