British Journal of Nutrition
|
|
|
- Brook Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol supplementtion Mrine L. Croze 1,2,3,4 *, Alin Géloën 2,3,4 nd Christophe O. Soulge 1,2,3,4 1 Lyon University, F-696 Oullins, Frnce 2 CrMeN Lortory, INSERM U16, Bâtiment IMBL, INSA-Lyon, 2 Avenue Alert Einstein, F Villeurnne Cedex, Frnce 3 Lyon 1 University, F Villeurnne, Frnce 4 INSA-Lyon, IMBL, F Villeurnne, Frnce (Sumitted 3 Novemer 214 Finl revision received 1 Mrch 215 Accepted 17 Mrch 215 First pulished online 2 My 215) British Journl of Nutrition Astrct We previously reported tht chronic supplementtion with myo-inositol (MI) improved insulin sensitivity nd reduced ft ccretion in mice. We then tested the potency of such dietry intervention in the prevention of insulin resistnce in C57BL/6 mle mouse fed high-ft diet (HFD). In ddition, some normlities in inositol metolism were reported to e ssocited with insulin resistnce in severl niml nd humn studies. We then investigted the presence of such nomlies (i.e. inosituri nd n inositol intr-tissue depletion) in this diet-induced oesity (DIO) mouse model, s well s the potentil enefit of MI supplementtion for inositol intr-tissue deficiency correction. HFD (6 % energy from ft) feeding ws ssocited with inosituri nd inositol intr-tissue depletion in the liver nd kidneys. MI supplementtion ( 58 mg/g per d) restored inositol pools in kidneys (prtilly) nd liver (fully). HFD feeding for 4 months induced ectopic lipid redistriution to liver nd muscles, fsting hyperglycemi nd hyperinsulinemi, insulin resistnce nd oesity tht were not prevented y MI supplementtion, despite significnt improvement in insulin sensitivity prmeter K insulin tolernce test nd reduction in white dipose tissue (WAT) mss (217 %, P, 5). MI supplementtion significntly reduced ftty cid synthse ctivity in epididyml WAT, which might explin its eneficil, ut modest, effect on WAT ccretion in HFD-fed mice. Finlly, we found some normlities in inositol metolism in ssocition with dietic phenotype (i.e. insulin resistnce nd fsting hyperglycemi) in DIO mouse model. Dietry MI supplementtion ws efficient in the prevention of inositol intr-tissue depletion, ut did not prevent insulin resistnce or oesity efficiently in this mouse model. Key words: myo-inositol: Insulin resistnce: Dietes: Oesity: High-ft diet: Inosituri Dietes mellitus is complex metolic disorder chrcterised y chronic hyperglycemi resulting from defects in insulin secretion (insulin deficiency), insulin ction (skeletl muscle, liver nd/or dipose tissue resistnce to insulin) or oth. Type 2 dietes represents out 9 % of dietes cses; lthough trditionlly considered disese of dults, it is incresingly dignosed in children in prllel with rising oesity rtes. Insulin resistnce is cliniclly defined s the inility of known quntity of exogenous or endogenous insulin to increse glucose uptke nd utilistion in n individul s much s it does in norml popultion (1). Insulin resistnce eing the first committed step in the development of type 2 dietes, the use of insulin-sensitising gents should prevent or dely pncres filure nd consecutive type 2 dietes development. Inositol, formerly referred to s vitmin B 7, is cyclitol nturlly occurring in nture nd foodstuffs. Inositol exists under nine distinct stereoisomers (nmed llo-, D-chiro-, L-chiro-, cis-, epi-, muco-, myo-, neo- nd scyllo-inositol) through epimeristion in hydroxyl group configurtion. Severl inositol isomers (e.g. D-chiro- nd myo-inositol) nd derivtives (e.g. D-pinitol nd sequoyitol) hve shown insulin mimetic properties such s lowering postprndil lood glucose level nd stimulting glucose uptke y muscle cells when given Arevitions: BW, ody weight; C, chow; DIO, diet-induced oesity; FAS, ftty cid synthse; HF, high-ft diet without myo-inositol; HFD, high-ft diet; HF-MI, high-ft diet with myo-inositol; HOMA-IR, homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistnce; ITT, insulin tolernce test; MI, myo-inositol; MIOX, myo-inositol oxygense; PCOS, polycystic ovry syndrome; PIP, phosphtidyl inositol phosphte lipids (phosphoinositides); SMIT, sodium/myo-inositol trnsporter; SREBP, sterol regultory element-inding protein; WAT, white dipose tissue. * Corresponding uthor: M. L. Croze, fx þ , emil mrine.croze@gmil.com Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
2 myo-inositol nd diet-induced oesity 1863 British Journl of Nutrition cutely in different niml models (2 5). myo-inositol is y fr the most undnt isomeric form of inositol in living cells nd in foodstuffs, mking this isomer s one of the est cndidte for nutritionl strtegy. We recently reported its insulin-sensitising potentil in chronic tretment in mice (6). Interestingly, this insulin-sensitising effect hs een ssocited with sustntil reduction in ft ccretion, nd good correltion etween insulin sensitivity nd white dipose tissue (WAT) mss hs een oserved. As the risk of dietes is reportedly incresed y 7 3 % upon ech kg of weight gined in humns (7), reducing ft ccretion constitutes vlule strtegy to improve insulin sensitivity nd control dietes. Hence, first im of the present study ws to evlute the ility of dietry myo-inositol supplementtion to prevent or dely insulin resistnce development nd ft ccretion in diet-induced oesity (DIO) mouse model: the C57BL/6 mle mouse fed high-ft diet (HFD). This DIO mouse model hs een chosen ecuse it is more representtive of the humn form of the metolic syndrome thn re genetic mouse models of oesity nd/or dietes (8). In ddition, some normlities in inositol metolism hve een oserved in severl dietic sujects nd would e ssocited with hyperglycemi nd/or insulin resistnce (for review, see Croze & Soulge (9) ). These normlities include (1) n excessive urinry excretion of inositol (i.e. inosituri) (1 12) ; (2) n intrcellulr myo-inositol depletion in some tissues, in prticulr, in tissues susceptile of developing dietes complictions (13) (e.g. kidneys, nerves, retin nd lens); nd (3) decresed D-chiro-inositol: myo-inositol rtio in some insulin trget tissues (e.g. skeletl muscles) nd urine (11,14). To the est of our knowledge, there re no dt in the literture regrding the presence of such nomlies in diet-induced rodent model of insulin resistnce. We then tested the presence of inosituri nd/or inositol depletion in C57BL/6 mouse fed HFD for 1 or 4 months. Little is known out the consequences of such metolic ltertions; however, given the importnt role of myo-inositol in cells s precursor of phosphtidylinositol nd its derived secondry messengers (in prticulr phosphtidylinositol 4,5-isphosphte/phosphtidylinositol (3,4,5)- trisphosphte (PIP 2 /PIP 3 ) nd inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphte (IP 3 )), it cn e expected tht inositol intr-tissue depletion hs deleterious consequences tht should e prevented or fought. Noteworthy, it hs een suggested tht inositol intr-tissue depletion could contriute to the progression or development of some dietes microvsculr complictions such s neuropthy, nephropthy or ctrct. Therefore, the present study lso imed to test the cpility of dietry myo-inositol supplementtion to prevent inositol intr-tissue depletion ssocited with hyperglycemi nd/or insulin resistnce. Mterils nd methods Chemicls nd ntiodies myo-inositol ws purchsed from Sigm Aldrich, nd recominnt humn insulin (1 IU/ml (3 5 mg/ml); Actrpid w ) ws from Novo Nordisk. Other chemicls were otined from Sigm Aldrich when no other origin is specified. Animls All experiments were crried out ccording to the guidelines lid down y the French Ministère de l Agriculture (no ) nd the Europen Union Council Directive for the Cre nd Use of Lortory Animls of 24 Novemer 1986 (86/69/EEC). Animl experiments were performed under the uthoristion no (INSA-Lyon, DDPP-SV, Direction Déprtementle de l Protection des Popultions Services Vétérinires du Rhône), ccording to the guidelines lid down y the French Ministère de l Agriculture (no ) nd the Europen Union Council Directive for the Cre nd Use of Lortory Animls of 24 Novemer 1986 (86/69/EEC). MLC (no ), AG (no ) nd COS (no ) hold specil licenses to experiment on living vertertes issued y the French Ministry of Agriculture nd Veterinry Service Deprtment. Mle C57Bl/6 JRj mice (15 2 g) were purchsed from Jnvier-Ls SA nd housed in n ir-conditioned room with controlled environment of 21 ^ 58C nd humidity of 4 7 %, under 12 h light 12 h drk cycle (lights on from 7. to 19. hours) with free ccess to food (chow diet: 12 6 kj/g 216C, Hrln Tekld; for composition nd vitmin nd minerl content, see Tle 1 nd online Supplementry Tle S1) nd wter. Diet nd myo-inositol supplementtion Mice (n 1 per group) were rndomly ssigned to e either under stndrd diet (control group with chow diet C) or under HFD with (HF-MI) or without (HF) myo-inositol supplementtion ( 58 mg/g ody weight (BW)) in drinkingwter for 4 months. The myo-inositol (MI) dose ws chosen to mimic the effect of the mximl dose tested nd tolerted in humn clinicl trils (i.e. 2 g/d; indeed, only mild side effects such s nuse, fltus or mild insomni were reported t doses up to 12 2 g/d nd mild grde 1 gstrointestinl symptoms were oserved t dose of 34 g/d) (15,16). In the HF nd HF-MI groups, the chow diet (216C; Hrln) ws replced y the HFD (TD.6 414, Reserch diets; Hrln Lortories, Inc.; for composition, see Tle 1 nd online Supplementry Tle S1) when mice were out 25 g Tle 1. Diet composition* Stndrd diet High-ft diet Reference 216C TD.6414 Nutrient composition (g/1 g) Crohydrtes Proteins Lipids Energy density (kj/g) From (%) Crohydrtes Proteins Lipids * Men composition of the stndrd nd high-ft diets from Hrln Lortories, Inc. Dt were otined from Hrln Lortories, Inc. Aville crohydrtes only. Note tht energy density is clculted from ingredient nlysis or mnufcturer dt. Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
3 1864 M. L. Croze et l. British Journl of Nutrition (i.e. 3 weeks fter rndomistion). At the sme time, myo-inositol ws dded to drinking-wter (6 g/l) in the HF-MI group. HFD nd myo-inositol supplement were given for 4 months. Food intke nd BW were mesured twice weekly. Food consumption ws clculted s the difference etween the mount given nd tht removed from the cge. Wter consumption ws mesured to clculte dily intke of myo-inositol. Insulin tolernce test Insulin tolernce test (ITT) ws performed fter 8 d of HFD feeding with or without myo-inositol supplementtion. After n overnight fst, nimls were injected intrperitonelly with 5 IU/kg BW (17 5 mg/kg BW) of recominnt humn insulin. Blood glucose ws mesured efore nd 15, 3 nd 6 min fter insulin injection. The glucose disppernce rte for ITT (K ITT ; %/min) ws clculted using the formul given y Lundek (17) : K ITT ¼ 693 1/t 1/2 where t 1/2 ws clculted from the slope of the plsm glucose concentrtion, considering n exponentil decrement of glucose concentrtion during the 3 min fter insulin dministrtion. Urine collection 24 h-diuresis ws collected fter 1 month of stndrd or HFD feeding in polycronte metolic cges (Chrles River Lortory). During urine collection, nimls were given free ccess to food nd wter. The volume of ech 24 h urine smple ws mesured grvimetriclly. Urine smples were centrifuged for 1 min t 3 g to discrd cells nd insolule mterils, nd liquots of superntnt were removed nd stored t 288C until nlysis. Scrifice nd tissue dissection Animls were deeply nesthetised with pentoritl (6 mg/kg intrperitonel). BWnd length were mesured. Terminl crdic lood (75 ml) punctures were relised on heprinised tue nd lood ws centrifuged for 2 min t 35 g to prepre plsm. Plsm smples were liquoted, snp frozen in liquid N 2 nd stored t 288C until nlysis. Liver, hert, kidneys, gstrocnemius muscles, epididyml, retroperitonel nd sucutneous inguinl WAT were dissected out ccording to ntomicl lndmrks, weighed to the nerest mg, snp frozen in liquid N 2 nd stored t 288C. Pieces of liver were fixed into prformldehyde for histologicl sections nd 3 4 mg of retroperitonel WAT were fixed in osmium tetroxide for mesurement of dipose cell size s descried elow. Liver histopthologicl study Liver slices were fixed in 1 % (w/v) formlin solution for t lest 24 h. Fixed tissues were then emedded in prffin, nd 5 6 mm sections were relised with microtome nd stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin. Non-lcoholic stetoheptitis ws ssessed under light microscope (Zeiss). Cellulrity of retroperitonel white dipose tissue: mesurement of dipocyte sizes nd numers Preprtion of dipose tissue for the determintion of cell size ws performed essentilly s descried y Etherton et l. (18). Briefly, 3 4 mg of retroperitonel WAT were immeditely fixed in osmium tetroxide, nd incuted t room temperture for 96 h. Smples were wshed with sline for 24 h, then the sline ws replced y 1 ml of 8 M-ure for 72 h with occsionl swirling to lierte the cells. Smples were then wshed with 1 % Triton X-1 (v/v) in NCl uffer. Before nlysis, superntnt ws discrded nd cells were resuspended in glycerol. Cells were then diluted. The dipocyte size distriution ws determined using Beckmn Coulter Counter Multisizer IV with 4 mm perture nd from the mesurement of t lest 1 cell dimeters per niml (men of 22 (SEM 18) cell dimeters mesured per niml). DNA content in retroperitonel WAT pds ws mesured, fter delipidtion of the smples with hexne, y stndrd fluorimetric method using isenzimide nd clf thymus DNA s stndrd (19). Ftty cid synthse ssy WAT (3 5 mg) ws homogenised in 1 ml of ice-cold sucrose uffer ( 25 M-sucrose, 1 mm-dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mm-edta nd mixture of protese inhiitors), ph 7 4. Homogentes were centrifuged t 15 g (8C) for 6 min, ft cke ws discrded, nd the cler infrntnt ws liquoted nd freezed t 228C for the determintion of ftty cid synthse (FAS) ctivity. FAS ctivity ws mesured spectrophotometriclly y monitoring the oxidtion of NADPH t 34 nm s descried y Bzin & Ferré (2). Briefly, 1 ml of infrntnt were mixed with 7 ml of 1 mm-potssium phosphte uffer (ph 6 5) contining 2 mm-nadph nd 1 mm-cetyl-coa. Asornce t 34 nm ws monitored in heted chmer spectrophotometer t 378C for 3 min to mesure ckground NADPH oxidtion. The rection ws strted with 1 ml of 1 mm-potssium phosphte uffer (ph 6 5) contining 6 mm-mlonyl-coa, nd rection ws ssyed for 5 min t 378C to determine the FAS-dependent oxidtion of NADPH (molr extinction coefficient of NADPH t 34 nm: 1 ¼ 622 M/cm). Results re expressed s nmol NADPH oxidised per min per mg of tissue. White dipose tissue gene expression y quntittive PCR Totl RNA from epididyml WAT smples (8 15 mg) were extrcted using TRI Regent (Sigm Aldrich). Totl RNA quntities nd qulities were ssessed using the Agilent 21 Bionlyzer nd the RNA 6 LChip Kit (Agilent Technologies). Reverse trnscriptions (RNAse H, Tkr enzyme) were performed on 1 mg of totl RNA. Rel-time PCR ssys for cetyl coenzyme A croxylse (Acc), ftty cid synthse (Fs), Adiponectin, Leptin, Glut-4, sterol regultory element-inding protein (Srep)1, Srep1c nd TATA ox inding protein (tp) genes were performed using Rotor-Genee 6 (Qigen). Vlues were normlised to tp gene expression. The full list of genes nd corresponding primer sequences is shown in online Supplementry Tle S2. Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
4 myo-inositol nd diet-induced oesity 1865 British Journl of Nutrition myo-inositol oxygense ssy Kidneys were homogenised in lysis uffer (1 mg/1 ml) contining 2 mm-sodium cette, 1 mm-feso 4, 2mM-L-cysteine, 1mM-glutthione nd 1 inhiitor cocktil, ph 6, followed y rief soniction. Lystes were then centrifuged for 3 min t 13 g, 48C. Superntnt (1 ml) ws dded to 9 ml of myo-inositol oxygense (MIOX) rection uffer (5 mm-sodium cette, 2 mm-cysteine, 1 mm-feso 4 nd 6 mm-myo-inositol, ph 6 ), nd MIOX ssys were then performed t 38C for 3 min. MIOX rection ws terminted y incuting smples in oiling wter for 5 min. Smples were then centrifuged for 1 min t 12 g, 48C to remove precipittes. The D-glucuronte formed from MI y MIOX rection ws then determined in the superntnt y the orcinol ssy. Briefly, doule volume of freshly prepred orcinol regent (28 mm-orcinol nd 3 mm-fecl 3 dissolved in 12-M HCl) ws dded to the superntnt (nd to stndrd solutions of D-glucuronic cid) nd incuted in oiling wter for 3 min. Rection ws stopped y incution on ice, 5 min. Colorimetric redings were mde t 67 nm. For ech smple, negtive control ws prepred following the sme procedure; however, negtive smples were oiled directly 5 min efore MIOX rection (i.e. just fter ddition of the lyste superntnt to the MIOX rection uffer nd so efore rection t 38C). MIOX ctivity of the smple ws then expressed s the quntity of D-glucuronic cid formed during the 3 min of rection (clculted from the difference etween the smple nd its negtive control) per mg of kidneys. myo-inositol mesurement in urine nd tissues myo-inositol ws determined y the GC method descried y Kw et l. (21). Briefly, one volume of ethnol ws dded to n equl volume of urine. Smples were vortexed nd evported to dryness under N t 48C. For the determintion of free myo-inositol, tissues were deproteinised with n equl mount of 15 M-B(OH) 2 nd 3 M-ZnSO 4 nd centrifuged nd the superntnt ws evported to dryness. Dried smples were sonicted for 5 min with 1 ml of trimethylsilylimidzole pyridine (1:1, v/v) contining 2 mg of phenyl--d-glucoside s n internl stndrd, nd were derivtised for 1 h t 88C. Derivtised smples or stndrds (2 ml) were injected into gs chromtogrph (Shimdzu) equipped with flme ionistion detector nd split injector. Inositols were seprted on silic cpillry SP-238 column (6 m 22 mm). Column temperture ws progrmmed from 15 to 28C t the rte of 38C/min, nd then to 3258C t the rte of 78C/min. Initil nd finl tempertures were held for 5 nd 2 min, respectively. The injector nd detector tempertures were held t 27 nd 358C, respectively. The crrier gs ws H t 1 5 ml/min, nd the split rtio used ws 1:4. Biochemicl mesurements Fsting nd non-fsting lood glucose levels were mesured with glucometer (Accu Check Perform; Roche Dignostics). The plsm insulin (mouse/rt insulin no. EZRMI-13K; Merck Millipore), leptin nd diponectin (rt/mouse leptin no. A5176 nd mouse diponectin no. A5187; SPI-Bio) levels were determined with mouse enzyme immunossy (EIA) kits ccording to the mnufcturer s instructions. The detection limits were 1 ng/ml for diponectin, 5 pg/ml for leptin nd 2 ng/ml for insulin immunossys. Inter-ssy coefficients were 3 9, 8 5 nd 8 2 % for diponectin, leptin nd insulin immunossys, respectively. The homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistnce (HOMA-IR) ws clculted using glucose nd insulin concentrtions otined fter 16 h of food withdrwl, using the following formul: fsting lood glucose ðmmol=lþ fsting insulin ðmu=mlþ=22 5: Plsm totl cholesterol, TAG, NEFA nd ure levels were mesured with the following commercil kits, cholesterol RTU (iomérieux), TAG PAP (iomérieux), NEFA-C (WAKO; Soiod) nd ccording to the mnufcturer s recommendtions. All ssys were performed t lest in duplictes. The muscle nd heptic lipids were extrcted ccording to the procedure of Folch et l. (22) using chloroform methnol (2:1, v/v) nd totl lipid content ws mesured grvimetriclly. Sttisticl nlyses Dt re expressed s mens with their stndrd errors. All dt were nlysed using GrphPd Prism version 5. softwre (GrphPd Softwre) nd Sttview 4.5 (Acus Concepts, Inc.). Multiple comprisons were performed using ANOVA followed when pproprite y post hoc Fisher protected lest significnt difference (PLSD) tests. Simple comprisons were performed using Student s t test. When pproprite, Welch s correction for inequlity of vrinces ws pplied. Differences were considered significnt t the P, 5 level. Results Altered inositol metolism in high-ft diet-fed mice Insulin resistnce nd hyperglycemi re reported to e ssocited with incresed myo-inositol urinry excretion (often referred to s inosituri) nd inositol intr-tissue depletion (9,23). We thus mesured urinry excretion, intrcellulr content of inositol in kidneys nd liver fter 1 or 4 months of norml or dietogenic (HF) diet. HFD feeding for 1 month induced striking glycosuri (P¼ 11) nd inosituri (3 9 folds, P¼ 6; Tle 2). The myo-inositol urinry excretion ws strongly correlted with the glucose urinry excretion s shown in Fig. 1(D). No significnt difference ws found in cretinine urine level etween chow diet-fed mice nd HFD-fed mice. Finlly, urinry myo-inositol:cretinine rtio ws significntly higher in high-ft-fed mice (5 25, P¼ 14). HFD feeding for 4 months induced significnt reduction of myo-inositol content in liver (Fig. 1(A): 246 %, P, 5) nd kidneys (Fig. 1(B): 235 %, P, 5). This intrcellulr myo-inositol depletion ws totlly prevented y myo-inositol supplementtion in liver nd prtilly corrected in kidneys. Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
5 1866 M. L. Croze et l. Tle 2. Urinry inositol excretion in mice fed chow (C) or high-ft (HF) diet (Men vlues with their stndrd errors, n 5 per group) C HF Men SEM Men SEM Chnge (folds) P Urine glucose (mmol/24 h) * Urine inositol (nmol/24 h) * Urine cretinine (mmol/24 h) Inositol:cretinine rtio * * Men vlue ws significntly different from tht of the group fed the C diet (P, 5). Dt were compred using Student s t test nd when pproprited Welch correction for vrince in homogeneity. British Journl of Nutrition High glucose level cn increse myo-inositol ctolism in kidney cells y enhncing MIOX expression nd ctivity (23). We mesured MIOX ctivity in the kidneys nd found lower MIOX ctivity in kidneys from HFD-fed mice (3 2 (SEM 3) nd 3 2 (SEM 4) mmol D-glucuronic cid produced in 3 min/g of kidneys for HF nd HF-MI, respectively) compred with kidneys from stndrd diet-fed mice (5 (SEM 2) mmol D-glucuronic cid produced in 3 min/g of kidneys, so chnge of 236 nd 232 % for HF nd HF-MI, respectively, v. C, P, 1; Fig. 1(C)). myo-inositol supplementtion reduces ft deposition in mice fed high-ft diet To evlute myo-inositol cpcity to reduce ft ccumultion under oesogenic diet, mice were fed HFD (6 % energy (A) Inositol content (µmol/g) from ft) with or without dietry myo-inositol supplement ( 58 (SEM 2) mg/g BW per 24 h) for 4 months. BW, energy intke nd myo-inositol intke were monitored throughout the study (see Fig. 2(A) nd (B)). Note tht no difference of ody growth or cumultive energy intke ws oserved etween HF nd HF-MI groups throughout the study period; however, significntly higher vlues were oserved for those prmeters in HFD groups compred with control group s erly s 2 weeks of diet for BW. Biometric dt for ech group fter 4 months of diet re presented in Tle 3. Lee index, common index of diposity in rodents, ws mrkedly incresed in HFD-fed nimls (P, 1). No significnt difference ws found, however, etween the two HFD groups (HF nd HF-MI). The men dily energy intke ws higher in high-ftfed mice compred with chow diet-fed mice, ut ws not different etween HF nd HF-MI groups (53 9 (SEM 8) kj/d (B) Inositol content (µmol/g) , Chow HF HF-MI (C) 8 (D) 5 MIOX ctivity (µmol DGA produced per 3 min/g of kidney) x y y Urine MI (nmol/24 h) Urine glucose (µmol/24 h) Fig. 1. Inositol metolism imlnce ssocited with insulin resistnce nd hyperglycemi in high-ft (HF) diet mice. myo-inositol (MI) content in liver (A) nd kidneys (B) of C57BL6J/Rj mice ws determined y HPLC fter 4 months of chow or HF (6 % energy from ft) diet feeding with or without MI supplementtion ( 58 mg/g ody weight). Vlues re mens (n 7 9), with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs., Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 5; one-wy ANOVA). (C) myo-inositol oxygense (MIOX) ctivity ws mesured s descried in the Mterils nd methods section in the kidneys of mice fter 4 months of diet with or without MI supplement. Vlues re mens (n 4 5), with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs. x,y Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 1; one-wy ANOVA). (D) Urinry excretion of inositol ws determined y HPLC quntifiction of inositol in the 24 h urine smples collected with metolism cges fter 1 month of chow diet or HF diet feeding (n 5, P, 1, Student s t test). Inosituri ws correlted with glycosuri in mice fter 1 month of chow or HF diet feeding (n 1, R 2 915, y ¼ 7558 þ 16 8, liner regression). Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
6 myo-inositol nd diet-induced oesity 1867 (A) Body weight (g) * Time (d) (B) Cumultive energy intke (kj per mouse) Time (d) 1 *** British Journl of Nutrition (C) WAT weight (mg) 4 (D) 3 c 3 c 2 c 2 c 1 1 c ewat rwat scwat Fig. 2. myo-inositol (MI) effect on white dipose tissue (WAT) nd ody weight (BW) in high-ft (HF) diet mice. (A) BW nd (B) cumultive energy intke monitoring in C57BL6J/Rj mice during the 4 months of chow ( ) or HF (6 % energy from ft) diet feeding with ( ) or without MI ( ) supplementtion ( 58 mg/g BW; n 1). (C) Sucutneous WAT (scwat), epididyml WAT (ewat), retroperitonel WAT (rwat) weights nd (D) ftty cid synthse ctivity in ewat fter 4 months of diet with or without MI (n 9 1). One unit of FAS ctivity is the mount of enzyme needed to ctlyse the oxidtion of 1 nmol of NADPH. Vlues re mens, with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs.,,c Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 5; one-wy ANOVA). Men vlues were significntly different from those of the group fed the chow diet: * P, 5, *** P, 1., Chow;, HF;, HF-MI. for HF mice, 54 (SEM 9) kj/d for HF-MI mice v. 46 (SEM 1 5) kj/d for chow diet-fed mice, n 29 3, P, 5). Of note, myo-inositol ddition to drinking-wter did not chnge mice wter consumption s no significnt difference in the men dily wter consumption ws noticed etween HF nd HF-MI groups (2 8 (SEM 1) nd 2 9 (SEM 1) ml/d nd per mouse for HF nd HF-MI groups, respectively; dt not shown). Orgn (liver, hert, kidneys nd muscles) weights, tken s representtive of len mss, were not significntly different etween FAS ctivity (mu/mg protein) the three groups with exception of kidneys tht were igger in high-ft groups (significnt difference for HF-MI group). HFD shrply incresed ft storge (totl WAT weight 4 5-fold higher in HF, P, 1), nd myo-inositol supplement significntly restrined this ft ccumultion in WAT (3 7-fold, i.e. reduction of out 17 % in the totl WAT weight compred with HF group without MI, P, 5; Tle 3). This difference etween HF nd HF-MI groups ws sttisticlly significnt for the retroperitonel nd sucutneous ft pds (Fig. 2(C)). Tle 3. Biometric dt nd orgn weights in C57Bl6 mice fed high-ft (HF) diet nd supplemented with myo-inositol (MI, 58 mg/g ody weight (BW)) (Men vlues with their stndrd errors, n 1 per group) C HF HF-MI Men SEM Men SEM Men SEM P Biometric dt BW (g) * * 1 2, 1 Body length (cm) , 1 Lee index ( 1 3 ) * 2 351* 3, 1 Orgn weights Liver (mg) Hert (mg) Kidneys (mg) * 25 6 Gstrocnemius (mg) * 5 17 Adipose tissue weight Totl WAT (mg) *** * 323, 1 C, chow diet; WAT, white dipose tissue. Men vlue ws significntly different from tht of the group fed the C diet: * P, 5, *** P, 1. Men vlue ws significntly different from tht of the group fed the HF diet (P, 5). Dt were compred using one-wy ANOVA nd when pproprited PLSD Fischer post hoc tests. Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
7 1868 M. L. Croze et l. Tle 4. Cellulrity of epididyml nd retroperitonel white dipose tissue (rwat) in C57Bl6 mice fed high-ft (HF) diet nd supplemented with myo-inositol (MI, 58 mg/g) for 4 months (Men vlues with their stndrd errors, n 8 1 per group) C HF HF-MI Men SEM Men SEM Men SEM P rwat Pd weight (mg) *** * 77, 1 Cell dimeter (mm) Cell weight (ng) *** * 236, 1 Numer of cells ( 1 6 ) * * 38, 1 DNA (mg/pd) * * 2 5, 1 C, chow diet. Men vlue ws significntly different from tht of the group fed the C diet: * P, 5, *** P, 1. Men vlue ws significntly different from tht of the group fed the HF diet (P, 5). Dt were compred using one-wy ANOVA nd when pproprited PLSD Fischer post hoc tests. British Journl of Nutrition myo-inositol supplementtion decresed ftty cid synthse ctivity in white dipose tissue HFD cused importnt ft ccumultion in the different WAT depots (i.e. inguinl, retroperitonel nd epididyml ft pds), which led to oth hypertrophi (i.e. increse in cell size) nd hyperplsi (i.e. increse in cell numer) of these tissues. Indeed, mice from HF group hd four to five times more totl WAT thn mice from C group (4 5-folds), nd this ws relted to significnt increse in dipocyte cell numer nd size/ volume (see Tle 4). myo-inositol supplementtion significntly reduced this ft ccumultion under HFD, nd this result is confirmed y decrese in dipocyte volume of HF-MI dipocytes compred with HF dipocytes. Of note, no significnt difference ws oserved in retroperitonel WAT cell numer etween HF nd HF-MI groups. To get insights into myo-inositol mechnism of ction in reducing ft storge, we mesured the ctivity of the min lipogenic enzyme, nmely ftty cid synthse (FAS; see Fig. 2(D)). FAS ctivity ws reduced in HF group compred with C group (258 %, P, 5, n 9) ecuse of FAS repression y ft overlod. Indeed, under HFD, leptin is produced y dipocytes in response to excess ft storge nd represses FAS expression. FAS ctivity ws further nd significntly reduced in HF-MI group compred with HF group (246 %, P, 5, n 9), which could contriute to the decresed WAT ft ccumultion oserved in HF-MI mice. myo-inositol supplementtion did not prevent insulin resistnce ssocited with oesity The plsm metolite levels for ech group re shown in Tle 5. HFD induced hyperglycemi with compenstory hyperinsulinemi s ssessed y the mrked increse in HF nd HF-MI fsting plsm levels of glucose nd insulin. The HOMA-IR ws clculted s clinicl prmeter for the insulin resistnce. The HOMA-IR indexes for HF nd HF-MI groups were similr etween them, ut significntly higher thn tht of control group, suggesting insulin resistnce in HFD-fed mice. High ft-fed groups lso displyed incresed fsting plsm levels of totl cholesterol (P, 1) nd decresed fsting plsm levels of TAG compred with control group (P, 1). No significnt difference ws found etween the three groups concerning the fsting plsm NEFA level (P¼ 322). Insulin sensitivity ws evluted y ITT nd their results re shown in Fig. 3. Exogenous insulin dministrtion ( 5 IU/kg; 17 5 mg/kg) triggered significntly greter hypoglycemic response in control mice (237 % in lood glucose level t 3 min compred with seline) thn HFD mice (24%; Fig. 3(A)). However, HF-MI mice glycemic response to this exogenous insulin stimultion ws improved compred with HF mice, s ssessed y the significnt difference in their glucose disppernce rtes (K ITT, P, 5; Fig. 3(B)). Tle 5. Plsm metolites in C57Bl6 mice fed high-ft (HF) diet nd supplemented with myo-inositol (MI, 58 mg/g) for 4 months* (Men vlues with their stndrd errors, n 1 per group) C HF HF-MI Men SEM Men SEM Men SEM P Fsting glucose (mm) , 1 Fsting insulin (pm) , 1 HOMA-IR , 1 TAG (g/l) , 1 Totl cholesterol (g/l) , 1 NEFA (mm) C, chow diet; HOMA-IR, homeostsis model ssessment-insulin resistnce;, Men vlues with unlike superscript letters were significntly different (P, 5). * Dt were compred using one-wy ANOVA nd when pproprited PLSD Fischer post hoc tests. Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
8 myo-inositol nd diet-induced oesity Plsm glucose (% of seline) (A) 12 myo-inositol did not prevent ectopic lipid redistriution to liver nd muscle 1 Ectopic lipid redistriution to insulin-sensitive tissues other thn WAT (i.e. skeletl muscle nd liver) ws evluted y mesurement of tissue totl lipid content (see Fig. 4(A)) nd y direct oservtion of lipid droplets in histologicl liver sections (Fig. 4(B)). Livers of oth HF nd HF-MI groups displyed stetosis s reveled y the presence of numerous lipid droplets in the liver sections of these mice compred with the livers of chow diet-fed mice, nd to the huge mount of lipids found in their liver compred with control livers (12 6 % for HF mice; 12 7 % for HF-MI v. 4 1 % of liver weight for C mice, P, 1). Ectopic lipid redistriution ws lso oserved in gstrocnemius muscles of HF nd HFMI mice tht contined nerly s much intrcellulr lipids s norml liver (4 7 nd 4 4 %, respectively, compred with 1 6 % for control mice muscles, P, 1). 8 *** 6 * Time (min) (B) 2 KITT (%/min) c myo-inositol normlised plsm dipokine levels 5 In ccordnce with the high diposity of HF nd HF-MI mice, leptinemi ws drmticlly incresed in those mice groups compred with the chow diet group (P, 1; Fig. 5(A)); Chow HF HF-MI (A) (C) 2 Tissue lipid content (mg/1 mg of tissue) Chow 1 5 KITT (%/min) British Journl of Nutrition HF-MI 5 HF Liver Totl WAT mss (mg) Fig. 3. myo-inositol (MI) effect on insulin sensitivity in high-ft (HF) diet mice. Insulin sensitivity ws explored through insulin tolernce test fter 8 d of HF diet feeding with or without MI supplementtion. (A) After n overnight fst, lood glucose ws mesured efore nd 15, 3 nd 6 min fter mice were injected intrperitonelly with 5 IU/kg (17 5 mg/kg) ody weight of recominnt humn insulin., Chow;, HF;, HF-MI. Vlues re mens, with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs. Men vlue of the HF diet-fed group ws significntly different from tht of the group fed the chow diet: * P, 5, *** P, 1 (two-wy ANOVA). (B) The glucose disppernce rte for insulin tolernce test (ITT) (KITT, %/min) ws clculted s descried in the Mterils nd methods section. Vlues re mens, with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs.,,c Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 5; one-wy ANOVA). (C) Negtive correltion etween KITT nd totl white dipose tissue (WAT) mss (C; liner regression, r , P¼ 3). Noteworthy, the glucose disppernce rte (KITT) tht reflects insulin sensitivity ws negtively correlted with totl WAT mss (Fig. 3(C), r , P¼ 3). Hence, the improvement in insulin sensitivity y myo-inositol supplementtion could result from the reduction oserved in ft mss ccretion in tht group compred with the other HF group. (B) Chow Muscle HF HF-MI 1 4 Fig. 4. myo- Inositol (MI) did not prevent ectopic lipid redistriution to liver or skeletl muscles in high-ft (HF) diet mice. (A) Intrcellulr lipid content in liver nd gstrocnemius muscles. Vlues re mens (n 1), with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs., Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 1; ANOVA). (B) Liver histologicl sections (opticl zoom 13 nd 43 ) stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin of C57BL6J/Rj mice fter 4 months of chow or HF (6 % energy from ft) diet feeding with or without MI supplementtion ( 58 mg/g ody weight). (A colour version of this figure cn e found online t org/jn). Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
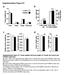
9 187 M. L. Croze et l. British Journl of Nutrition (A) Plsm leptin (ng/ml) (B) Plsm diponectin (ng/ml) Chow however, leptinemi of HF-MI mice ws significntly lower thn tht of HF mice (P, 5). This decrese in leptin concentrtion is in good greement with the lower totl WAT mss. HF mice exhiited reduced diponectinemi compred with C (P, 5; Fig. 5(B)). Noteworthy, diponectinemi of HF-MI mice ws similr to tht of C mice. myo-inositol did not lter expression of lipogenic enzymes or dipokines in white dipose tissue Since myo-inositol significntly reduced ft ccretion nd FAS ctivity, expression levels of two min lipogenic enzymes (cetyl-coenzyme A croxylse, FAS) nd trnscription fctors (SREBP-1 nd SREBP-1c) were studied y quntittive PCR in epididyml WAT (Fig. 6). HFD feeding strongly reduced SREBP-1c expression (P, 1; Fig. 6(D)) nd nerly switched off tht of cetyl-coenzyme A croxylse 1 nd FAS (P, 1 nd P, 1, respectively; Fig. 6(A) nd (B)). However, myo-inositol tretment hd no dditionl effect on ll those gene expressions. Of note, expression of SREBP-1 ws not ltered, neither y diet nor y myo-inositol supplement (P¼ 733; Fig. 6(C)). Regrding dipokine expression profiles in dipose tissue, HFD feeding incresed leptin (P, 5; Fig. 6(E)) nd decresed diponectin (P, 1; Fig. 6(F)) expressions. Finlly, HFD feeding lso HF c HF-MI Fig. 5. myo- Inositol (MI) eneficil effect on leptin nd diponectin plsm levels in high-ft (HF) diet mice. (A) Leptin nd (B) diponectin plsm levels in C57BL6J/Rj mice fter 4 months of chow or HF (6 % energy from ft) diet feeding with or without MI supplementtion ( 58 mg/g ody weight). Vlues re mens (n 9 1), with stndrd errors represented y verticl rs.,,c Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 5; one-wy ANOVA). down-regulted GLUT-4 expression (P, 1; Fig. 6(G)). myo-inositol tretment did not ffect dipokines or GLUT-4 expression levels in mice under high ft feeding. Ultimtely, HFD feeding-regulted dipokines, GLUT-4 nd lipogenesis gene expressions, ut myo-inositol supplementtion, hd no dditionl effect. Discussion We previously reported tht 2-week myo-inositol supplementtion sustntilly reduced ft ccretion nd improved insulin sensitivity nd glucose tolernce in mice (6). In the present study, we tested the ility of such nutritionl intervention to prevent insulin resistnce nd/or oesity development in mice fed HFD. However, dietry myo-inositol supplementtion ( 58 mg/g dily for 4 months) improved insulin sensitivity nd reduced ft ccretion in mice (217 %), ut (A) Expression (fold/tbp) (C) Expression (fold/tbp) (E) Expression (fold/tbp) (G) Expression (fold/tbp) (B) Expression (fold/tbp) (D) Expression (fold/tbp) (F) Expression (fold/tbp) Chow HF HF-MI Fig. 6. Effects of diet nd myo-inositol (MI) on lipogenic, dipokines nd GLUT-4 gene expressions in epididyml white dipose tissue of high-ft (HF) diet mice. Gene expression of lipogenic enzymes or trnscription fctors, dipokines or GLUT-4 ws mesured y quntittive PCR s descried in the Mterils nd methods section in epididyml white dipose tissue of C57BL6J/Rj mice fter 4 months of chow or HF (6 % energy from ft) diet feeding with or without MI supplementtion ( 58 mg/g ody weight). Expression rtes of (A) cetyl-coenzyme A croxylse (ACC1); (B) ftty cid synthse (FAS); (C) sterol-regultory element inding protein (SREBP)- 1; (D) SREBP-1c; (E) leptin; (F) diponectin nd (G) GLUT-4, re expressed in folds compred with expression level of the TBP (TATA ox inding protein) gene. Vlues re mens (n 9 1), with the rnge indicted y the oxes., Men vlues with unlike letters were significntly different (P, 5; ANOVA). Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
10 myo-inositol nd diet-induced oesity 1871 British Journl of Nutrition did not prevent insulin resistnce or oesity development in this DIO mouse model. In ddition, insulin resistnce nd/or hyperglycemi were reported to e ssocited with nomlies in inositol metolism, including inosituri nd inositol intrcellulr depletion in some tissues (e.g. nerves nd kidneys), in severl humn nd niml studies (1,11,13). Here, we show for the first time tht such metolic ltertions re lso concomitntly present with insulin resistnce nd hyperglycemi in C57BL6 mouse fter 1 or 4 months of HFD feeding. In ddition, we show tht inositol intrcellulr depletion cn e reduced or fully prevented in kidneys or liver y dietry myo-inositol supplementtion. Insulin resistnce is ssocited with inositol metolism ltertions in high-ft diet-fed C57BL/6 mice nd myo-inositol supplementtion prevents inositol depletion Mice fed HFD exhiited mrkedly incresed urinry excretion of inositol (i.e. inosituri) from 1 month of diet, which ws well correlted with the incresed excretion of glucose (i.e. glycosuri). An inositol intrcellulr depletion ws oserved in their kidneys nd liver fter 4 months of diet, which ws prtilly (kidneys) or fully (liver) prevented y myo-inositol supplementtion. This difference could e explined y the fct tht liver is the first orgn supplied y dietry myo-inositol through the portl vein, while kidneys re the primry site of inositol ctolism (especilly y MIOX) nd excretion. However, fter 4 months of HFD (6 % energy from ft), we found tht MIOX ctivity ws not enhnced ut rther significntly reduced. This result my e explined y the prole ltertion in kidney structure nd function due to the dietic phenotype fter 4 months of HFD feeding. In prticulr, it cn e expected tht the chronic hyperglycemi, lipotoxic environment nd the consecutive cellulr stresses (e.g. oxidtive stress nd endoplsmic reticulum stress) proly present t this stge in kidney cells lter some cellulr functions, including myo-inositol ctolism y MIOX. MIOX ctivity reduction oserved fter 4 months of HFD my then e relted to erly structurl nd functionl chnges in kidneys of oese nd insulin-resistnt mice (i.e. glomerulosclerosis, renl lipid ccumultion nd other erly stges of dietic nephropthy). It is worth noting tht study of Hu et l. (24) hs lso reported down-regultion of MIOX (decresed mrna level of MIOX) in the kidneys of rodents with cute kidney injury. Chng (25) reported, in n unpulished study, tht MIOX gene ws first overexpressed in the kidneys of streptozotocin-induced dietes rt model (incresed MIOX mrna level 4 weeks fter streptozotocin injection), ut tht this gene ws down-regulted t lter time point in the course of dietes development (8 weeks fter streptozotocin injection), nd despite n inositol depletion in kidneys t oth time points. This reversl in MIOX expression/ctivity over the course of dietes is uncler, ut it could e relted to renl ltertion progression. In contrst, competitive inhiition of inositol uptke y glucose (inhiition of renl tuulr resorption nd cellulr uptke y cells) could e nother cuse of intrcellulr myo-inositol depletion under hyperglycemic conditions nd could lso hve contriuted to inosituri t 1 month of HFD feeding. Indeed, glucose nd myo-inositol exhiit structurl similrities so tht glucose is competitive inhiitor of myo-inositol trnsport through its trnsporters SMIT (sodium/myo-inositol trnsporter) or H þ /myo-inositol trnsporter. For this reson, excess urine glucose (glycosuri) cn inhiit inositol tuulr resorption through SMIT, therefore fvouring inositol urinry excretion nd cusing inosituri, which possily contriutes to inositol intr-tissue depletion. Accordingly, we found strong correltion etween glycosuri nd inosituri (see Fig. 1(D)). Similrly, hyperglycemi cn inhiit inositol import from extrcellulr sources nd led to inositol intrcellulr depletion. Dietry myo-inositol supplementtion proly prevents intrcellulr depletion y enhncing inositol lood level, therey fvouring its cellulr uptke despite high level of lood glucose. However, if hyperglycemi per se my contriute to inositol intr-tissue depletion nd urinry inositol excretion through competition etween glucose nd inositol for cellulr uptke, it my not e the only cuse. In prticulr, the consequence of chronic hyperglycemi on kidney function my e more importnt cuse of inosituri thn hyperglycemi per se nd could lso explin the good correltion etween glycosuri nd inosituri. Indeed, study of Chng et l. (26) on isolted kidneys hs shown tht perfusion conditions replicting hyperglycemi (2 mm-glucose) significntly potentited D-chiro-inositol (DCI) ut not MI urinry excretion in oth non-dietic nd dietic kidneys. The dietic kidneys, however, presented 2-fold incresed urinry excretion of myo-inositol compred with the non-dietic kidneys. These findings show tht (1) high glucose mience per se hs finlly miniml overll effect on inosituri (s MI is the predominnt circulting stereoisomer in vivo), ut it cn potentite urinry excretion of the less undnt stereoisomer DCI, nd it shows tht (2) ltertion of kidney function nd/or structure due to chronic exposition to hyperglycemi, i.e. dietic kidney per se, seems to e sufficient to lter tuulr resorption of inositol nd induce inosituri in this niml model of dietes. In this context, inosituri ws then primrily relted to dietic kidney-specific fctors rther thn from systemic fctors (e.g. high glucose mience, incresed plsm inositol levels due to incresed dietry intke or sorption). However, the underlying mechnisms through which inositol resorption is ltered in dietic kidneys nd induces inosituri re still uncler, s SMIT expression in kidneys ws incresed t this time point of the disese (4 weeks fter streptozotocin injection). As the HFD used in the present study (6 % energy from ft) induced hyperglycemi nd the rpid development of dietic phenotype, it cn e presumed tht the kidneys of HF nd HF-MI mice were impired y this chronic high glucose mience nd y the excessive lipid supply. Indeed, Jing et l. (27) reported n increse in renl intr-lipid ccumultion, glomerulosclerosis nd proteinuri in C57BL/6J mice fter 12 weeks of similr HFD (251 kj (6 kcl) percentge sturted (lrd) ft diet) feeding. The impired kidney function proly ssocited with the dietic phenotype in our mouse Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
11 1872 M. L. Croze et l. British Journl of Nutrition model ws then proly the min contriutor to the oserved inosituri, nd hyperglycemi per se proly potentited it. Finlly, chronic hyperglycemi nd ssocited glycosuri hve proly contriuted to oth inosituri nd inositol intr-tissue depletion in the short nd long term, through direct competition of glucose with inositol for cellulr uptke, nd proly more importntly through long-term impirment of renl function. myo-inositol supplementtion decresed ft ccretion ut did not prevent oesity development In ccordnce with our previous study (6), we found tht myoinositol supplementtion reduced ft ccumultion nd WAT hypertrophy under HFD feeding. Nonetheless, this nutritionl intervention did not prevent oesity development. The inhiitory effect of myo-inositol supplementtion on WAT ccretion seems to e relted to its cpcity to inhiit de novo lipogenesis in vivo, s reveled y the reduced FAS ctivity in HF-MI mice compred with HF mice (Fig. 2(D)). However, FAS ctivity (nd thus de novo lipogenesis) is lredy strongly inhiited y the excess in ftty cids provided y the HFD (inhiition of lipogenesis gene expression (Fig. 6(A), (B) nd (D))). Indeed, in the context of excessive dietry intke of ftty cids, lrge mount of NEFA is ville for TAG synthesis nd other cell functions so tht de novo synthesis of ftty cids from cette or glucose (i.e. de novo lipogenesis) is downregulted. In this context, de novo lipogenesis is no more mjor contriutor to ft ccretion, which could explin why myo-inositol supplementtion did not prevent efficiently ft ccretion nd oesity development in this DIO mouse model. Consequently, out of use in complement of lnced diet nd regulr physicl ctivity (which is y the wy recommended for most nti-oesity strtegies), myo-inositol supplementtion cnnot e n efficient strtegy to prevent weight gin nd oesity development. myo-inositol supplementtion improved insulin sensitivity ut did not prevent insulin resistnce development HFD feeding induced peripherl nd liver insulin resistnce with compenstory hyperinsulinemi s evidenced y the reduced response to insulin during the ITT (Fig. 3), the fsting hyperglycemi nd hyperinsulinemi nd so the incresed HOMA-IR index (Tle 5). This insulin resistnce ws ssocited with centrl oesity (Fig. 2(A) nd (C), nd Tle 3) nd ectopic lipid deposition in liver nd skeletl muscle (Fig. 4). Lipotoxicity nd chronic low-grde inflmmtion were very proly the mjor cuses of this diet- nd oesityinduced insulin resistnce. myo-inositol supplementtion did not prevent this insulin resistnce nd only slightly improved insulin sensitivity in mice fed HFD. The lrge extent of ectopic lipid redistriution to liver or muscles in this mouse model, nd the inility of MI to prevent or fight this phenomenon my explin MI supplementtion filure in the prevention of this insulin resistnce. The modest improvement in insulin sensitivity seemed to e of the sme extent s the reduction in WAT ccretion, s shown y the good correltion etween the men K ITT nd the men WAT weights for ech group (Fig. 3(C)). In this context, possile meditor of myo-inositol eneficil effect on insulin sensitivity could e diponectin. Indeed, MI supplementtion reduced WAT expnsion, which my e responsile for the improvement in diponectinemi in HF-MI mice (Fig. 5(B)); nd diponectin hs well-recognised nti-dietic ctivities, so the improvement in diponectinemi my hve contriuted to the improvement in insulin sensitivity. The greter insulin response in the HF-MI group could lso potentilly rise from the effects of myo-inositol on heptic glucose output. However, Whiting et l. (28) demonstrted tht myo-inositol hd no insulin-like effect on epinephrineinduced heptic glucose output. In ddition, the insulin-sensitising effect of myo-inositol supplementtion oserved in our previous study (6) y n ITT on normlly sensitive mice minly rised from peripherl (i.e. skeletl muscle nd/or dipose tissue) insulin sensitivity improvement. Indeed, in normlly insulin-sensitive mice, exogenous insulin stimultion switches off heptic glucose output so tht this phenomenon does not contriute sustntilly to the difference in hypoglycemic response etween normlly or more insulin-sensitive mice groups during ITT. The little improvement in HF-MI mice response to insulin then minly rise from n insulinsensitising effect of myo-inositol on dipose tissue or skeletl muscle, thn from n ction on liver. Incorportion of myo-inositol, s such or fter in vivo conversion to D-chiro-inositol, into inositolphosphoglycns, puttive second messengers of insulin, is commonly proposed hypothesis for insulin-sensitising ctivities of inositol isomers or derivtives. If myo-inositol supplementtion indeed enhnced the production nd relese of inositolphosphoglycns in response to insulin, this could hve slowed down the progression of insulin resistnce nd e responsile for the little difference oserved in insulin sensitivity etween the two HF groups (for further detils on inositolphosphoglycns insulin-like effects nd puttive mechnisms of ction, see Croze & Soulge (9) review rticle). myo-inositol ws fr less efficient in this DIO mouse model of insulin resistnce, thn it hd een in our previous study on normlly sensitive mice. Severl issues could ccount for these differences: (1) hyperglycemi induced y the 6 % HFD (nd then mintined y insulin resistnce) inhiits inositol uptke y cells nd so possily reduces the effect of myoinositol supplementtion. A 4 % HFD might hve provided more grdul insulin resistnce phenotype in the sence of hyperglycemi, which could hve provided greter cellulr myo-inositol uptke nd thus greter enefits of myo-inositol supplementtion; (2) the HFD-induced ftty cid overlod inhiits de novo lipogenesis from cette nd/or glucose nd so proly dmpens myo-inositol effect on WAT mss; nd reduction in ft mss seemed to e n importnt contriutory fctor to insulin sensitivity improvement with chronic myoinositol supplementtion; (3) s the HFD used (6 % energy from ft) ws cricturl, with rpid insulin resistnce development (1 month), it my e difficult to counterct with simple nutritionl intervention. A more pproprite physiologicl window to oserve greter insulin-sensitising effect Downloded from IP ddress: , on 6 Apr 217 t 5:28:, suject to the Cmridge Core terms of use, ville t
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Chronic high-sodium diet intake after weaning lead to neurogenic hypertension in adult Wistar rats
 Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
The Effect of Substituting Sugar with Artificial. Sweeteners on the Texture and Palatability of Pancakes
 The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS
 Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Supplemental Materials
 Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY
 METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 4010 is procedure for screening solids such s soils, sludges, nd queous medi such s wste wter nd lechtes
METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 4010 is procedure for screening solids such s soils, sludges, nd queous medi such s wste wter nd lechtes
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (2012), 108, 2166 2175 q The Authors 2012 doi:10.1017/s0007114512000347 Differentil effects of low-dose resvertrol on diposity nd heptic stetosis in diet-induced oese mice Su-Jung
British Journl of Nutrition (2012), 108, 2166 2175 q The Authors 2012 doi:10.1017/s0007114512000347 Differentil effects of low-dose resvertrol on diposity nd heptic stetosis in diet-induced oese mice Su-Jung
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Chromium Alleviates Glucose Intolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic ER Stress in Obese Mice
 nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
 Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
How adaptations of substrate utilization regulate body composition
 (27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
(27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
Excessive fructose intake causes 1,25-(OH) 2 D 3 -dependent inhibition of intestinal and renal calcium transport in growing rats
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 3: E33 E33, 3. First pulished April 9, 3; doi:.5/jpendo.58.. Excessive fructose intke cuses,5-(oh) D 3 -dependent inhiition of intestinl nd renl clcium trnsport in growing rts
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 3: E33 E33, 3. First pulished April 9, 3; doi:.5/jpendo.58.. Excessive fructose intke cuses,5-(oh) D 3 -dependent inhiition of intestinl nd renl clcium trnsport in growing rts
Inheritance of cholesterol metabolism of probands with high or low cholesterol absorption
 Inheritnce of cholesterol metolism of pronds with high or low cholesterol sorption Helen Gylling* nd Ttu A. Miettinen 1, Deprtment of Clinicl Nutrition,* University of Kuopio, nd Kuopio University Hospitl,
Inheritnce of cholesterol metolism of pronds with high or low cholesterol sorption Helen Gylling* nd Ttu A. Miettinen 1, Deprtment of Clinicl Nutrition,* University of Kuopio, nd Kuopio University Hospitl,
Input from external experts and manufacturer on the 2 nd draft project plan Stool DNA testing for early detection of colorectal cancer
 Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Synergistic effects of metformin, resveratrol, and hydroxymethylbutyrate on insulin sensitivity
 Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance
 Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Consumer perceptions of meat quality and shelf-life in commercially raised broilers compared to organic free range broilers
 Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND POLOXAMER 407 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF PIROXICAM
 IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
Bright Futures Medical Screening Reference Table 2 to 5 Day (First Week) Visit
 Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
Supporting Information
 Supporting Informtion Yun et l. 1.173/pns.1523236113 SI Mterils nd Methods Humn Sujects. All prticipnts in our study were recruited from the Center for Reproductive Medicine, Shndong Provincil Hospitl
Supporting Informtion Yun et l. 1.173/pns.1523236113 SI Mterils nd Methods Humn Sujects. All prticipnts in our study were recruited from the Center for Reproductive Medicine, Shndong Provincil Hospitl
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
Agilent G6825AA MassHunter Pathways to PCDL Software Quick Start Guide
 Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Roughage Type & Level & Grain Processing Interactions with Distiller s s Grains Diets. Matt May High Plains Bio Fuels Co-Product Nutrition Conference
 Roughge Type & Level & Grin Processing Interctions with Distiller s s Grins Diets Mtt My High Plins Bio Fuels Co-Product Nutrition Conference Why do we flke grin? Stem-flked corn (SFC) vs. dry-rolled rolled
Roughge Type & Level & Grin Processing Interctions with Distiller s s Grins Diets Mtt My High Plins Bio Fuels Co-Product Nutrition Conference Why do we flke grin? Stem-flked corn (SFC) vs. dry-rolled rolled
Enhanced glutathione peroxidases (GPx) activity in young barley seedlings enriched with selenium
 Africn Journl of Biotechnology Vol. 10(55), pp. 11483-11487, 21 Septemer, 2011 Aville online t http://www.cdemicjournls.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.1480 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Acdemic Journls Full Length Reserch
Africn Journl of Biotechnology Vol. 10(55), pp. 11483-11487, 21 Septemer, 2011 Aville online t http://www.cdemicjournls.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.1480 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Acdemic Journls Full Length Reserch
Effects of Sini San used alone and in combination with fluoxetine on central and peripheral 5-HT levels in a rat model of depression
 Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Implication of fermentable carbohydrates targeting the gut microbiota on conjugated linoleic acid production in high-fat-fed mice
 British Journl of Nutrition, pge 1 of 14 q The Authors 213 doi:1.117/s7114513123 Impliction of fermentle crohydrtes trgeting the gut microiot on conjugted linoleic cid production in high-ft-fed mice Céline
British Journl of Nutrition, pge 1 of 14 q The Authors 213 doi:1.117/s7114513123 Impliction of fermentle crohydrtes trgeting the gut microiot on conjugted linoleic cid production in high-ft-fed mice Céline
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Effect of Different Dietary Energy Sources on Induction of Fatty Liver-Hemorrhagic Syndrome in Laying Hens
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Science 7 (12): 1232-1236, 2008 ISSN 1682-8356 sin Network for Scientific Informtion, 2008 Effect of Different Dietry Energy Sources on Induction of Ftty Liver-Hemorrhgic
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Science 7 (12): 1232-1236, 2008 ISSN 1682-8356 sin Network for Scientific Informtion, 2008 Effect of Different Dietry Energy Sources on Induction of Ftty Liver-Hemorrhgic
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Food & Function Accepted Manuscript
 Food & Function Accepted Mnuscript This is n Accepted Mnuscript, which hs een through the Royl Society of Chemistry peer review process nd hs een ccepted for puliction. Accepted Mnuscripts re pulished
Food & Function Accepted Mnuscript This is n Accepted Mnuscript, which hs een through the Royl Society of Chemistry peer review process nd hs een ccepted for puliction. Accepted Mnuscripts re pulished
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
Physical training prevents oxidative stress in L-NAME-induced hypertension rats
 cell iochemistry nd function Cell Biochem Funct 2013; 31: 136 151. Pulished online 7 Septemer 2012 in Wiley Online Lirry (wileyonlinelirry.com) DOI:.02/cf.2868 Physicl trining prevents oxidtive stress
cell iochemistry nd function Cell Biochem Funct 2013; 31: 136 151. Pulished online 7 Septemer 2012 in Wiley Online Lirry (wileyonlinelirry.com) DOI:.02/cf.2868 Physicl trining prevents oxidtive stress
Response of Commercial Egg-Type Pullets to Diets Varying in Protein and Energy Content in Arid Hot Climate
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Science 8 (9): 90-98, 2009 ISSN 682-8356 sin Network for Scientific Informtion, 2009 Response of Commercil Egg-Type Pullets to Diets Vrying in Protein nd Energy Content in
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Science 8 (9): 90-98, 2009 ISSN 682-8356 sin Network for Scientific Informtion, 2009 Response of Commercil Egg-Type Pullets to Diets Vrying in Protein nd Energy Content in
Physiology & Behavior
 Physiology & Behvior 1 (1) 376 387 Contents lists ville t SciVerse ScienceDirect Physiology & Behvior journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/ph Physiologicl nd ehviorl responses to intermittent strvtion
Physiology & Behvior 1 (1) 376 387 Contents lists ville t SciVerse ScienceDirect Physiology & Behvior journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/ph Physiologicl nd ehviorl responses to intermittent strvtion
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Effects of Dietary Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Biopolymer Encapsulation on Lipid Metabolism in Mice
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6848-6862; doi:10.3390/ijms14046848 Article OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleculr Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journl/ijms Effects of Dietry Conjugted Linoleic
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6848-6862; doi:10.3390/ijms14046848 Article OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleculr Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journl/ijms Effects of Dietry Conjugted Linoleic
Effects of Recombinant Bovine Somatotropin Administration at Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus and Subsequent Offspring Performance of Beef Cattle
 Effects of Recominnt Bovine Somtotropin Administrtion t Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus nd Susequent Offspring Performnce of Beef Cttle V. R. G. Mercdnte 1, F. M. Cirico 1, D. D. Henry 1, P. L. P. Fontes
Effects of Recominnt Bovine Somtotropin Administrtion t Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus nd Susequent Offspring Performnce of Beef Cttle V. R. G. Mercdnte 1, F. M. Cirico 1, D. D. Henry 1, P. L. P. Fontes
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
Health-Related Quality of Life and Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Obese Persons Seeking Bariatric Surgery
 Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Supporting information
 Supporting informtion Multiple Univrite Dt Anlysis Revels the Inulin Effects on the High-ft-diet Induced Metolic Altertions in Rt Myocrdium nd Testicles in the Pre-oesity Stte Yixun Dun #, Ynpeng An #,
Supporting informtion Multiple Univrite Dt Anlysis Revels the Inulin Effects on the High-ft-diet Induced Metolic Altertions in Rt Myocrdium nd Testicles in the Pre-oesity Stte Yixun Dun #, Ynpeng An #,
The different mechanisms of insulin sensitizers to prevent type 2 diabetes in OLETF rats
 RESEARCH ARTICLE DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Dietes Met Res Rev 2007; 23: 411 418. Pulished online 30 My 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).756 The different mechnisms
RESEARCH ARTICLE DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Dietes Met Res Rev 2007; 23: 411 418. Pulished online 30 My 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).756 The different mechnisms
Responses of skeletal muscle lipid metabolism in rat gastrocnemius to hypothyroidism and iodothyronine administration: a putative role for FAT/CD36
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 33: E1222 E1233, 212. First pulished Septemer 11, 212; doi:1.1152/jpendo.37.212. Responses of skeletl muscle lipid metolism in rt gstrocnemius to hypothyroidism nd iodothyronine
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 33: E1222 E1233, 212. First pulished Septemer 11, 212; doi:1.1152/jpendo.37.212. Responses of skeletl muscle lipid metolism in rt gstrocnemius to hypothyroidism nd iodothyronine
Sterolsland the Production of Oospores by Phytophthova cactovum
 Journl of Generl Microiology (I972), 72, 321-327 Printed in Gret Britin 321 Sterolslnd the Production of Oospores y Phytophthov cctovum By C. G. ELLIOTT Deprtment of Botny, The University of Glsgow, Glsgow,
Journl of Generl Microiology (I972), 72, 321-327 Printed in Gret Britin 321 Sterolslnd the Production of Oospores y Phytophthov cctovum By C. G. ELLIOTT Deprtment of Botny, The University of Glsgow, Glsgow,
Flaxseed Lignan Increased Glucose Uptake by Human Red Blood Cells
 The Open Nutrceuticls Journl, 29, 2, 81-85 81 Open Access Flxseed Lignn Incresed Glucose Uptke y Humn Red Blood Cells Yeong Rhee * nd Ardith Brunt 351 EML, NDSU Dept. # 262, PO Box 65, North Dkot Stte
The Open Nutrceuticls Journl, 29, 2, 81-85 81 Open Access Flxseed Lignn Incresed Glucose Uptke y Humn Red Blood Cells Yeong Rhee * nd Ardith Brunt 351 EML, NDSU Dept. # 262, PO Box 65, North Dkot Stte
Effect of Inhibition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and/or Neutral Endopeptidase on Neuropathy in High-Fat-Fed C57Bl/6J Mice
 Effect of Inhiition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme nd/or Neutrl Endopeptidse on Neuropthy in High-Ft-Fed C7Bl/J Mice The Hrvrd community hs mde this rticle openly ville. Plese shre how this ccess enefits
Effect of Inhiition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme nd/or Neutrl Endopeptidse on Neuropthy in High-Ft-Fed C7Bl/J Mice The Hrvrd community hs mde this rticle openly ville. Plese shre how this ccess enefits
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
Serum nesfatin-1 levels are decreased in pregnant women newly diagnosed with gestational diabetes
 originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
Optimizing Metam Sodium Fumigation in Fine-Textured Soils
 Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Effect of processing on in vitro bioaccessibility of phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant activity of vegetables with/without yoghurt
 Effect of processing on in vitro ioccessiility of phenolics, flvonoids nd ntioxidnt ctivity of vegetles with/without yoghurt Assoc. Prof. Dr. Esr ÇAPANOĞLU GÜVEN Deprtment of Food Engineering Istnul Technicl
Effect of processing on in vitro ioccessiility of phenolics, flvonoids nd ntioxidnt ctivity of vegetles with/without yoghurt Assoc. Prof. Dr. Esr ÇAPANOĞLU GÜVEN Deprtment of Food Engineering Istnul Technicl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Cytochrome P450-2E1 promotes fast food-mediated hepatic fibrosis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INRMATION Cytochrome P-E1 promotes fst food-medited heptic fibrosis Mohmed A. Abdelmegeed, Youngshim Choi, Grzegorz Godlewski b, Seung-Kwon H, Atryee Bnerjee, Sehwn Jng, nd Byoung-Joon Song
SUPPLEMENTARY INRMATION Cytochrome P-E1 promotes fst food-medited heptic fibrosis Mohmed A. Abdelmegeed, Youngshim Choi, Grzegorz Godlewski b, Seung-Kwon H, Atryee Bnerjee, Sehwn Jng, nd Byoung-Joon Song
Preliminary results were communicated at the Falk Symposium on Bile Acids, Freiburg, 1996, and Titisee,
 Cholesterol, ile cid, nd lipoprotein metolism in two strins of hmster, one resistnt, the other sensitive (LPN) to sucrose-induced cholelithisis 1 Jcqueline Férézou, 2, * Murielle Comettes-Souverin, 3,
Cholesterol, ile cid, nd lipoprotein metolism in two strins of hmster, one resistnt, the other sensitive (LPN) to sucrose-induced cholelithisis 1 Jcqueline Férézou, 2, * Murielle Comettes-Souverin, 3,
Effects of Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon cinnamon) on blood glucose and lipids in a diabetic and healthy rat model
 PHCOG RES. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Cinnmomum zeylnicum (Ceylon cinnmon) on lood glucose nd lipids in dietic nd helthy rt model Priyng Rnsinghe, Snj Perer, Mngl Guntilke 1, Erng Aeywrdene, Nuwn Gunpl,
PHCOG RES. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Cinnmomum zeylnicum (Ceylon cinnmon) on lood glucose nd lipids in dietic nd helthy rt model Priyng Rnsinghe, Snj Perer, Mngl Guntilke 1, Erng Aeywrdene, Nuwn Gunpl,
SYNOPSIS Final Abbreviated Clinical Study Report for Study CA ABBREVIATED REPORT
 Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Effect of Oral Administration of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrations in Periparturient Dairy Cows
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
