Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
|
|
|
- Norma Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Regular experiment schedule and primary skull surgery. (a) Weekly experiment schedule for two Long-Evans rats (A, B). The schedule includes primary skull surgery (S; 1st week), operant task training (1-8; 2nd and 3rd weeks), room transfer (T; 4th week), secondary dura-opening surgery (D), and a recording experiment (R). Two task-trained rats were available for final recording experiments every week using this schedule. (b) Handling to habituate rats to the experimenters (15 min). (c) Adaptation to the body-supporting cylinder (dummy) in their home cage (2-3 days before surgery). (d) Lightweight, reusable, sliding head-attachment (13 g, aluminum). (e) Primary surgery, under isoflurane anesthesia, to mount the head-attachment on the animal s skull. Exposed skull surface (1) was covered with silicon sealant (2). FL is showing the skull surface above the forelimb (FL) area of motor cortex. (f) Full recovery from skull surgery. The treated animals behaved normally in their home cage (e.g., eating, drinking, running, sleeping). See the Methods for details.
2 Y. Isomura et al. 2 Supplementary Figure 2. Efficient multi-rat task-training system. (a) Six task-training boxes (1-6) were controlled by one computer (inset). Note that all doors are shown open with the stereotaxic frames slid out. (b) The same training boxes are shown with the doors closed. Syringe pumps (red objects) were placed on the top of training boxes. (c) Spatial layout of the lever (1), water spout (2), sliding head-receptacles (3), body-supporting cylinder (4), side handrail (5), and optional armrest (6). The layout was properly adjusted for each animal. (d) Basement layout (1, infrared video camera; 2, horn tweeter; 3, arrow, lever-lock bar) below the stereotaxic frame with the head-receptacle and cylinder, which was removed for demonstration purposes. (e) Water spout for reward delivery was carefully placed into the left side of the mouth (circle). (f) Optimal angle of the right forelimb (shown by black lines) for pulling and pushing the lever. Note that the animal is stepping on the edge of the cylinder with both hindlimbs in the best sitting posture (circle; see non-slip edge in panel c, 4). (g) Typical posture of task-learning rat holding the side handrail with his left forelimb in the first training week. (h) Relaxed posture with the left forelimb on the optional armrest (circle) in the second training week.
3 Y. Isomura et al. 3 Supplementary Figure 3. Operant learning of voluntary forelimb movement task. (a) Scheduled criteria required for reward acquisition: start (hold) and goal (release) lever positions (left; final 0-20% and %, respectively) and lever hold time (right; final 1 s). (b) Body weight was maintained at more than 80% of pre-surgery weight. (c) Lever trajectories in a trainee (1 min trace; upward trace, pull; downward trace, push; bottom, holding) on the 1st, 2nd, 4th, 6th, and 8th training days. (d) Typical task performance (upper, histograms showing the trial number with actual lever-holding times; lower, temporal changes in trial number during 2-h task-training sessions; filled columns represent rewarded trials) during the two-week training period (1st, 2nd, 8th days), the transfer day, and the recording day. A lever lock (waiting) period was imposed for an hour before the start of each daily task session in the second week.
4 Y. Isomura et al. 4 Supplementary Figure 4. Task performance in a novel environment for recording. (a) Recording room where task-trained animals performed the same forelimb movement task during the final electrophysiological experiment. (b) Stereotaxic frame installed with all behavioral and electrophysiological devices. (c) Task performance by a head-restraint rat during the simultaneous recording of neural activity in the left FL area through juxtacellular and multiunit electrodes. (d) Evoked electromyography (EMG) activity was observed selectively in the right upper forelimb (FL), but not in the right upper hindlimb (HL), in response to intracortical microstimulation (ICMS) at the left FL area of the motor cortex under urethane anesthesia (preliminary experiments). (e) Consecutive video pictures before and after the onset (0.000 s) of lever movement (pull). Note that the forelimb begins to move one or two images (about ms) prior to the onset of the lever movement. Supplementary Figure 5. Stable and reliable juxtacellular spike recordings. (a) Round-shape tip of a juxtacellular glass electrode (< 1 µm diameter) observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). (b) Development (traces 1 and 2) and maintenance (3 and 4) of positive spikes (light green) recorded juxtacellularly from a single neuron. (c) Temporal changes in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd principle components (PC1-3) of isolated spikes from the same recorded neuron (light green dots) and the noise detected in the recorded trace (white dots). Juxtacellular spikes of single neurons were isolated off-line using KlustaKwik software with a principle component analysis 25 and refined using Klusters and NeuroScope 37.
5 Y. Isomura et al. 5 Supplementary Figure 6. Several examples of juxtacellularlly recorded neurons. (a) Layer 6 pyramidal cell with steep Pre-movement activity before the onset of pull movement and antagonistic inactivation in the non-preferred (push) direction. Left, neuron morphology (upper) and axons extending into the white matter (lower). Top, task-related firing activity aligned to the onset of pull or push movement (bin, 20 ms). Bottom; spike waveforms (left), traces of spontaneous and evoked (I) spiking (middle), and auto-correlation histogram (right; bin, 1 ms; gray, ongoing firing rate). (b) Layer 3 pyramidal cell with intrinsically bursting activity related to local field potential during slow-wave sleep. This neuron was not involved in task behavior (data not shown). (c) Putative pyramidal cell in the superficial layer (395 µm in depth) showing Movement activity with very few spikes. The neuron fired only one or two spikes every two to four trials, but most spikes were associated with lever movement. (d) Medium spiny neuron in the striatum, which displayed task-related activation in the juxtacellular recording (a preliminary experiment). The neuron expressed mrna for dopamine D1 receptor, as indicated by in situ hybridization (arrowhead).
6 Y. Isomura et al. 6 Supplementary Figure 7. Physiological properties of functionally different groups of pyramidal cells and FS interneurons. (a) Correlation between the physiological depth of juxtacellular recording site and the histological depth of the visualized neuron in a counter-stained section. Thus, physiological depth is a good measure of the cortical position of identified and unidentified neurons. (b) Cortical position (i.e., physiological depth) plotted against ongoing firing rate for identified and putative pyramidal cells (PC) and interneurons (FS) from juxtacellular recordings. Note that some pyramidal cells in superficial layers (above 800 µm) discharged at a very low firing rate. (c) Average firing rate at a baseline level (in lever-holding period) plotted for functionally different groups of RS and FS neurons in multiunit recordings (left) and pyramidal cells and FS interneurons in juxtacellular recordings (right). See Fig. 4 for Symbol legend.
7 Y. Isomura et al. 7 Supplementary Figure 8. Verification for excitatory synaptic connectivity in multiunit data analysis. (a) Original analysis using the entire spike dataset of the same RS (green) and FS (gray) neurons shown in Fig. 6b. Left, spike distribution in a two-dimensional plane out of 17 spike feature parameters 25,37. Middle, auto-correlation histograms (a.c.; bin, 1 ms). Right, cross-correlation histogram (c.c.; bin, 1 ms) between these neurons showing a single, asymmetric peak around +1.5 ms from spiking of a triggering (RS) neuron. The gap at 0 ms is due to the lack of spike-detection within ±0.5 ms from each spike 30. (b) Strict analysis by excluding all overlapping outlier spikes from the same neurons in the two-dimensional plane. The single peaks are almost identical in a and b, suggesting true short-latency interaction between two neurons with completely distinct spike features. (c) Representative raw traces of their spike pairs in each channel (1-4ch; 6 sets). Note that the first spikes (green) are largest in channel 1, while the following spikes (gray) are largest in channel 3, supporting evidence that they are really different neurons. (d) Excitatory synaptic interaction during task performance in the same RS and FS neurons shown in Fig. 6c (upper). A single peak was consistently observed throughout lever-hold and pull periods (analyzed for a duration of 500 ms, starting 1000, 750, 500, and 250 ms before the onset of pull movement). The single peak was completely abolished after shuffling task-trials in a triggering RS neuron (lower).
8 Y. Isomura et al. 8 (e) A summary diagram of putative excitatory connections between functionally different neurons. Arrows and numbers indicate the delay direction and strength (peak amplitude normalized by baseline activity in the cross-correlation histogram) of individual excitatory synaptic interactions, respectively. Effective excitatory response during task performance ( 1 to s) was also confirmed in 12 neuron pairs (bold numbers). Supplementary Videos (Legends) Supplementary Video 1. Initial behavior of an untrained rat in the training box. This beginner rat entered the body-supporting cylinder by himself, because he had become accustomed to a dummy cylinder (see Supplementary Figure 1c). After his head-attachment was fastened to the stereotaxic frame, the rat grasped the lever naturally and tried to move it with his right forelimb without struggling. Supplementary Video 2. Efficient task-training of six rats in separate training boxes. Up to six rats were simultaneously and separately trained in our multi-rat task-training system to perform the voluntary forelimb movement task in the head-restraint condition. The rat in the lower right box (no. 6) was a beginner in the forelimb movement task. Supplementary Video 3. Pre-movement spiking activity during task performance (with sound). Pre-movement activity was recorded juxtacellularly from the layer 6 pyramidal cell shown in Supplementary Figure 6a while the rat was moving the lever. The sound represents the spiking of this neuron.
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5)
 Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Introduction to Electrophysiology
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001
 Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11239 Introduction The first Supplementary Figure shows additional regions of fmri activation evoked by the task. The second, sixth, and eighth shows an alternative way of analyzing reaction
doi:10.1038/nature11239 Introduction The first Supplementary Figure shows additional regions of fmri activation evoked by the task. The second, sixth, and eighth shows an alternative way of analyzing reaction
Thalamic control of cortical states
 Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites Supplementary Table 2. Quantitative features of EC neuron axons 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Layer distribution
Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites Supplementary Table 2. Quantitative features of EC neuron axons 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Layer distribution
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings. Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014
 Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Rewiring of hindlimb corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury
 Rewiring of hindlimb corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury Arko Ghosh, Florent Haiss, Esther Sydekum, Regula Schneider, Miriam Gullo, Matthias T. Wyss, Thomas Mueggler, Christof Baltes, Markus
Rewiring of hindlimb corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury Arko Ghosh, Florent Haiss, Esther Sydekum, Regula Schneider, Miriam Gullo, Matthias T. Wyss, Thomas Mueggler, Christof Baltes, Markus
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience
 How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in primary visual cortex
 *Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript revised.docx Click here to view linked Referenc Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in
*Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript revised.docx Click here to view linked Referenc Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in
Summary of behavioral performances for mice in imaging experiments.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of behavioral performances for mice in imaging experiments. (a) Task performance for mice during M2 imaging experiments. Open triangles, individual experiments. Filled triangles,
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of behavioral performances for mice in imaging experiments. (a) Task performance for mice during M2 imaging experiments. Open triangles, individual experiments. Filled triangles,
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Thalamo-Cortical Relationships Ultrastructure of Thalamic Synaptic Glomerulus
 Central Visual Pathways V1/2 NEUR 3001 dvanced Visual Neuroscience The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus () is more than a relay station LP SC Professor Tom Salt UCL Institute of Ophthalmology Retina t.salt@ucl.ac.uk
Central Visual Pathways V1/2 NEUR 3001 dvanced Visual Neuroscience The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus () is more than a relay station LP SC Professor Tom Salt UCL Institute of Ophthalmology Retina t.salt@ucl.ac.uk
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity
 An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity Naiyan Chen, Hiroki Sugihara, & Mriganka Sur Nature America, nc. All rights reserved. Cholinergic modulation of cortex
An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity Naiyan Chen, Hiroki Sugihara, & Mriganka Sur Nature America, nc. All rights reserved. Cholinergic modulation of cortex
The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition. Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT
 Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
brain valuation & behavior
 brain valuation & behavior 9 Rangel, A, et al. (2008) Nature Neuroscience Reviews Vol 9 Stages in decision making process Problem is represented in the brain Brain evaluates the options Action is selected
brain valuation & behavior 9 Rangel, A, et al. (2008) Nature Neuroscience Reviews Vol 9 Stages in decision making process Problem is represented in the brain Brain evaluates the options Action is selected
CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 CELLULAR COMPOSITION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX THE CEREBRAL CORTEX CONSISTS OF THE ARCHICORTEX (HIPPOCAMPAL FORMA- TION), PALEOCORTEX
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 CELLULAR COMPOSITION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX THE CEREBRAL CORTEX CONSISTS OF THE ARCHICORTEX (HIPPOCAMPAL FORMA- TION), PALEOCORTEX
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
TEMPORAL PRECISION OF SENSORY RESPONSES Berry and Meister, 1998
 TEMPORAL PRECISION OF SENSORY RESPONSES Berry and Meister, 1998 Today: (1) how can we measure temporal precision? (2) what mechanisms enable/limit precision? A. 0.1 pa WHY SHOULD YOU CARE? average rod
TEMPORAL PRECISION OF SENSORY RESPONSES Berry and Meister, 1998 Today: (1) how can we measure temporal precision? (2) what mechanisms enable/limit precision? A. 0.1 pa WHY SHOULD YOU CARE? average rod
Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey
 3.6.QH Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey Versnel, Huib; Zwiers, Marcel; Van Opstal, John Department of Biophysics University of Nijmegen Geert Grooteplein 655
3.6.QH Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey Versnel, Huib; Zwiers, Marcel; Van Opstal, John Department of Biophysics University of Nijmegen Geert Grooteplein 655
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neural Recording Methods
 Neural Recording Methods Types of neural recording 1. evoked potentials 2. extracellular, one neuron at a time 3. extracellular, many neurons at a time 4. intracellular (sharp or patch), one neuron at
Neural Recording Methods Types of neural recording 1. evoked potentials 2. extracellular, one neuron at a time 3. extracellular, many neurons at a time 4. intracellular (sharp or patch), one neuron at
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
Supplementary Information for Correlated input reveals coexisting coding schemes in a sensory cortex
 Supplementary Information for Correlated input reveals coexisting coding schemes in a sensory cortex Luc Estebanez 1,2 *, Sami El Boustani 1 *, Alain Destexhe 1, Daniel E. Shulz 1 1 Unité de Neurosciences,
Supplementary Information for Correlated input reveals coexisting coding schemes in a sensory cortex Luc Estebanez 1,2 *, Sami El Boustani 1 *, Alain Destexhe 1, Daniel E. Shulz 1 1 Unité de Neurosciences,
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
INTRACELLULAR RECORDING AND STAINING IN THE ACUTE IN VIVO RAT USING SHARP ELECTRODES
 www.kopfinstruments.com INTRACELLULAR RECORDING AND STAINING IN THE ACUTE IN VIVO RAT USING SHARP ELECTRODES BRIAN H. BLAND, Ph.D. JAN KONOPACKI, Ph.D. DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE
www.kopfinstruments.com INTRACELLULAR RECORDING AND STAINING IN THE ACUTE IN VIVO RAT USING SHARP ELECTRODES BRIAN H. BLAND, Ph.D. JAN KONOPACKI, Ph.D. DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE
Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris
 ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Book 3: Lab Procedures Book 3: Ch. 1: The Hypothesis and Overview
 Book 3: Lab Procedures Book 3: Ch. 1: The Hypothesis and Overview 13 Introduction This experiment will investigate how cocaine acts on dopamine neurons in the brain. Cocaine is a drug of abuse that increases
Book 3: Lab Procedures Book 3: Ch. 1: The Hypothesis and Overview 13 Introduction This experiment will investigate how cocaine acts on dopamine neurons in the brain. Cocaine is a drug of abuse that increases
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in. primate lateral prefrontal cortex
 Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Predictive Features of Persistent Activity Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons
 Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons Kyriaki Sidiropoulou, Panayiota Poirazi* Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons Kyriaki Sidiropoulou, Panayiota Poirazi* Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous inhibitory networks
 Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development
 Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Nov versus Fam. Fam 1 versus. Fam 2. Supplementary figure 1
 a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
Synaptic and Network Mechanisms of Sparse and Reliable Visual Cortical Activity during Nonclassical Receptive Field Stimulation
 Article Synaptic and Network Mechanisms of Sparse and Reliable Visual Cortical Activity during Nonclassical Receptive Field Stimulation Bilal Haider, 1 Matthew R. Krause, 1 Alvaro Duque, 1 Yuguo Yu, 1
Article Synaptic and Network Mechanisms of Sparse and Reliable Visual Cortical Activity during Nonclassical Receptive Field Stimulation Bilal Haider, 1 Matthew R. Krause, 1 Alvaro Duque, 1 Yuguo Yu, 1
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs)
 Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
Supplemental Information. Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking. Activity in Early Visual Cortex. Supplemental Information Inventory:
 Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
2Lesson. Outline 3.2. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 3.2: How do our neurons communicate with each other? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to introduce students to the process of synaptic transmission, which is how one neuron communicates with another neuron. Using the pain pathway as a
Outline OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to introduce students to the process of synaptic transmission, which is how one neuron communicates with another neuron. Using the pain pathway as a
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment
 Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Supplementary Figure 2. Inter discharge intervals are consistent across electrophysiological scales and are related to seizure stage.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Progression of seizure activity recorded from a microelectrode array that was not recruited into the ictal core. (a) Raw LFP traces recorded from a single microelectrode during
Supplementary Figure 1. Progression of seizure activity recorded from a microelectrode array that was not recruited into the ictal core. (a) Raw LFP traces recorded from a single microelectrode during
FORWARD ELEVATION. Stretches inferior and anterior-inferior capsule
 FORWARD ELEVATION Stretches inferior and anterior-inferior capsule Lie down on a flat surface Use your good arm to grasp the arm of your stiff shoulder at the level of the elbow Raise the stiff arm above
FORWARD ELEVATION Stretches inferior and anterior-inferior capsule Lie down on a flat surface Use your good arm to grasp the arm of your stiff shoulder at the level of the elbow Raise the stiff arm above
Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man
 Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man D. GRAHAM SLAUGHTER, M.D., BLAINE S. NASHOLD, Jn., M.D., AND GEORGE G. SOMJEN, M.D. The Division of Neurosurgery, and the
Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man D. GRAHAM SLAUGHTER, M.D., BLAINE S. NASHOLD, Jn., M.D., AND GEORGE G. SOMJEN, M.D. The Division of Neurosurgery, and the
A Brain Computer Interface System For Auto Piloting Wheelchair
 A Brain Computer Interface System For Auto Piloting Wheelchair Reshmi G, N. Kumaravel & M. Sasikala Centre for Medical Electronics, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, College of Engineering,
A Brain Computer Interface System For Auto Piloting Wheelchair Reshmi G, N. Kumaravel & M. Sasikala Centre for Medical Electronics, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, College of Engineering,
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c
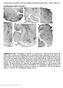 Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Popescu, Popa, Pare SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c LG LP LD R LA BL OT BM HF V HF VP RE VP CL PC d PU e 2 mm R f CP HF 2 mm GP
Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Popescu, Popa, Pare SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c LG LP LD R LA BL OT BM HF V HF VP RE VP CL PC d PU e 2 mm R f CP HF 2 mm GP
Supplementary Information. Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels. in cell attached patch clamp recordings
 Supplementary Information Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels in cell attached patch clamp recordings Stephen R. Williams 1,2 and Christian Wozny 2 1 Queensland Brain Institute,
Supplementary Information Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels in cell attached patch clamp recordings Stephen R. Williams 1,2 and Christian Wozny 2 1 Queensland Brain Institute,
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
THE SIGMOID NONLINEARITY IN PREPYRIFORM CORTEX. Frank H. Eeckman University of California, Berkeley, CA ABSlRACT
 242 THE SIGMOID NONLINEARITY IN PREPYRIFORM CORTEX Frank H. Eeckman University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 ABSlRACT We report a study on the relationship between EEG amplitude values and unit spike
242 THE SIGMOID NONLINEARITY IN PREPYRIFORM CORTEX Frank H. Eeckman University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 ABSlRACT We report a study on the relationship between EEG amplitude values and unit spike
CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS
 Neuroscience 147 (2007) 272 276 RAPID REPORT CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS Y. CISSÉ, 1,2 D. A. NITA, 2 M. STERIADE AND I. TIMOFEEV* Department of
Neuroscience 147 (2007) 272 276 RAPID REPORT CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS Y. CISSÉ, 1,2 D. A. NITA, 2 M. STERIADE AND I. TIMOFEEV* Department of
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary table and figures
 3D single molecule tracking with multifocal plane microscopy reveals rapid intercellular transferrin transport at epithelial cell barriers Sripad Ram, Dongyoung Kim, Raimund J. Ober and E. Sally Ward Supplementary
3D single molecule tracking with multifocal plane microscopy reveals rapid intercellular transferrin transport at epithelial cell barriers Sripad Ram, Dongyoung Kim, Raimund J. Ober and E. Sally Ward Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control Authors: Iñaki Iturrate 1,2, Ricardo Chavarriaga 2, Luis Montesano 1, Javier Minguez 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control Authors: Iñaki Iturrate 1,2, Ricardo Chavarriaga 2, Luis Montesano 1, Javier Minguez 1,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
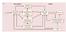 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
The Brain & Homeostasis. The Brain & Technology. CAT, PET, and MRI Scans
 The Brain & Homeostasis Today, scientists have a lot of information about what happens in the different parts of the brain; however they are still trying to understand how the brain functions. We know
The Brain & Homeostasis Today, scientists have a lot of information about what happens in the different parts of the brain; however they are still trying to understand how the brain functions. We know
