ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE
|
|
|
- Justin Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences
2 Background Information This program, made entirely of 3-D computer animation, contains two parts: ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and THE ACTIONS OF NICOTINE, COCAINE, AND MARIJUANA IN THE BRAIN. Each part is approximately 12 minutes and may be presented in 2 different class sessions so that discussion may follow. In part 1, the basic structure of the brain and its principal cells neuro n s a re described. In addition, the communication (electrical and chemical) between neurons is explained. In part 2, the entry of nicotine, cocaine, and marijuana into the brain is shown, and the cellular actions of these drugs are described. The contents described here are scientifically accurate. The material is suitable as an adjunct to biology classes and health classes or in any curriculum that may benefit from a scientific component to drug education/prevention programs. It is not intended that this program, by itself, be used in drug education programs; other forms of education are needed as well. This teacher s guide consists of a set of learning objectives, a glossary of terms used in the video, and additional reference material. The teacher s guide also includes a series of worksheets that students may use for self-testing. Each worksheet includes a representative still frame from the video. A set of worksheets with the answers for the teachers is provided. Learning Objectives After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. Neurons send information to each other using both electrical and chemical signals. Electrical information moves along a neuron, and chemical information moves between neurons. When they work together as a unit, the neurons control the function of a specific brain area. The communication between neurons can be disrupted by drugs; this happens specifically at the synapse, the most important control point in the process of communication. Regardless of their method of intake, drugs of abuse, such as nicotine, cocaine and marijuana, reach the brain through the bloodstream. When drugs are smoked they reach the brain as fast as if they were injected, and even faster than if snorted or taken by mouth. The faster a drug reaches the brain, the more likely it will be abused. Drugs interact with neurons at the synapse. Their targets can be receptors (e.g. for nicotine and marijuana) or uptake pumps (e.g. for cocaine). By acting at the synapse, drugs change the way the brain functions and can affect behavior, thinking and learning, movement and sensations. Sometimes this is beneficial, as in the treatment of a disease, and sometimes this is detrimental, especially when drugs are abused. 2 Copyright 2007 Films for the Humanities & Sciences A Films Media Group Company P.O. Box 2053 Princeton, NJ
3 Vocabulary Acetylcholine--A major neurotransmitter in the brain. Acetylcholine is synthesized in and released from neurons into the synaptic space. It then binds to an acetylcholine receptor. Acetylcholine receptor A protein with five subunits to which acetylcholine binds. Upon binding, the acetylcholine receptor changes shape to open a channel through which sodium ions flow into the neuron, producing a current across the membrane. Acetylcholinesterase The enzyme that destroys acetylcholine by hydrolyzing or cutting it into two parts, choline and acetate. Axon A long portion of the neuron that leaves the cell body (or soma) and carries chemicals and proteins to the terminal. Caudate nucleus An area of the brain involved in voluntary movement, and drug addiction. Cerebral cortex The largest part of the brain. It is subdivided into several parts, including the frontal cortex (motor), parietal cortex (sensory), temporal cortex (hearing) and occipital cortex (vision). The sensory cortex receives sensory information coming from the spinal cord, and the motor cortex sends motor information back down the spinal cord. Cocaine The active ingredient found in the coca plant. It binds to the dopamine uptake pump and prevents the pump from bringing dopamine back into the terminal. It is a central nervous system stimulant. Current The flow of ions (charged atoms such as sodium, potassium, calcium or chloride) across the neuron membrane. Cyclic AMP (Adenosine monophosphate) A nucleotide that is generated by the action of the enzyme, adenyl cyclase. It directs other proteins to regulate the movement of ions into and out of the cell, producing membrane currents. Dendrite A short portion of the neuron that leaves the cell body. Each cell body has many dendrites which are covered with little spines containing receptors to which neurotransmitters bind. Dopamine A neurotransmitter released from neurons in parts of the brain especially involved in drug addiction (i.e. the reward pathway). Electrical Impulse The movement of an ion current along the neuron membrane. It is generated in the cell body and moves along the axon to the terminal. Exocytosis When an impulse arrives at the terminal, the vesicles fuse with the terminal membrane and release the neurotransmitters within them into the synaptic cleft (space). G Proteins Proteins that help receptors such as dopamine or THC receptors to activate or inhibit the enzyme adenyl cyclase and the generation of cyclic AMP. 3
4 Hippocampus An area of the brain beneath the cerebral cortex involved in learning and memory. It lies beneath the cerebral cortex. Neuron The major cell type in the brain and spinal cord. It consists of the soma, axon and dendrites. There are billions of neurons in the brain. Neurotransmitter A chemical such as acetylcholine or dopamine that is stored in vesicles within a nerve terminal and released into the synaptic space. It binds to receptors to cause currents to flow in the postsynaptic neuron. Neurotransmitter action is terminated either by enzymes or by the uptake of the neurotransmitter into the terminal. Nicotine The active compound in the tobacco plant. It binds to acetylcholine receptors in the brain and causes the release of many neurotransmitters. Postsynaptic Pertaining to the membrane of the receiving neuron (containing the receptors) at a synapse. Presynaptic Pertaining to the membrane of the axon terminal at a synapse. Receptor A special protein to which neurotransmitters, hormones, and drugs bind. Receptors are found on the membranes of the neuron dendrites, soma, and even the terminal. Reward pathway A specific network of neurons that become activated by pleasurable or rewarding behaviors such as use of cocaine, heroin, nicotine, and alcohol. Many addictive behaviors activate this pathway which originates in the midbrain, and travels through the nucleus accumbens and up to the frontal cortex. Soma The cell body and largest part of the neuron. Proteins are synthesized in the cell body and transported to other parts of the neuron. The electrical impulse is generated in the cell body and travels down the axon. Spinal cord A bundle of long neurons that travel up and down the vertebral column. The neurons form synapses with sensory neurons from the periphery to carry sensory information up to the brain. Neurons leaving the brain travel down the spinal cord and form synapses with neurons that direct muscle movement. Synapse The connection between two neurons; it consists of the terminal of one neuron, the membrane of the neighboring neuron and the space between them (synaptic cleft). It is here that chemical information is passed from one neuron to another. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) A major active compound in the cannabis (marijuana) plant. It binds to THC receptors that are concentrated in areas such as the hippocampus. Uptake pump A special protein to which neurotransmitters such as dopamine bind so that they can be transported back inside the terminal. Drugs such as cocaine bind to dopamine uptake pumps and prevent them from functioning. 4 Vesicles Small sacs found within the axon terminal. They contain neurotransmitters which are released into the synaptic cleft when an impulse arrives at the terminal.
5 Student Worksheets/Self Test The following pages contain a set of worksheets that students can use as a self-test after viewing the video. Sets may be copied for the students as needed. The worksheets are designed to reinforce information already presented in the video and to provide new information not found in the video. Each worksheet contains a representative frame from the video that serves as reference for the questions. A set of worksheets with the answers provided is included for the teacher. 5
6 B C D A 1. Neurons are the major cells in the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system). They have several parts. Indicate the name of the parts that are labeled in the picture by filling in the blanks below: A. B. C. D. Each part of the neuron serves a special function. For each part that you have labeled above, match it to its function in the blanks below. The is the largest part of the cell. It has a nucleus which contains the genetic material to direct the production of proteins. The electrical impulse is formed here. Electrical impulses travel along the toward the nerve. This long structure carries more than just electrical messages; it also carries many nutrients to the, especially those that help make the neurotransmitters. When an electrical impulse reaches the nerve neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic space. A neuron has many that form branches like trees. Each has millions of receptors on its membrane so that many synapses can be formed with other neurons. The more synapses that can transmit chemical information at a time, the more likely the receiving cell will generate the electrical impulse. 6
7 D A C B 2. Electrical information is converted into chemical information at the nerve terminal. The terminal forms a connection with another neuron very nearby. This connection is called a. Inside the terminal are small sacs or vesicles that contain neurotransmitters. Although there are many kinds of neurotransmitters, there is only one kind found in each neuron s terminal. When an electrical impulse reaches the nerve terminal, the vesicles move toward the membrane and fuse to it. Then the neurotransmitters are released into the cleft, or space. This process is called. In the picture shown above, several components of the are marked. Indicate below the name of the components. A. B. C. D. 7
8 3. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter in the brain. It is synthesized in neurons and released from the terminals. Once in the synaptic space, acetylcholine binds to. Once acetylcholine binds to its, several things happen. Below is a list of the steps that take place. Arrange the steps in order by placing a number in the space provided. An electrical current flows across the membrane. Sodium ions (Na+) flow into the cell through the ion channel. The electrical current stops flowing across the membrane. Acetylcholine molecules come off of the. The changes its shape to open a channel within its structure. The changes its shape to close the ion channel. 8
9 4. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that binds to a dopamine receptor. In order for dopamine to produce its effect, it requires a series of events. Below, put these events in order by placing a number in the blank. The G protein activates an enzyme (adenylate cyclase) to generate cyclic AMP. Dopamine binds to its receptor. As cyclic AMP builds up inside the cell, it causes a change in the membrane currents to increase neuron firing. When dopamine is bound to its receptor, the helper G protein becomes activated. 9
10 A A A B B B 5. T h e re are two basic ways that the actions of neurotransmitters are terminated. Once they come off of their receptors, neurotransmitters can be inactivated by enzymes or taken back up into nerve terminals by uptake pumps. Consider the two neuro t r a n s m i t t e r s, acetylcholine and dopamine. Below, fill in the blanks to indicate the termination pro c e s s for each neurotransmitter; then name the labeled structures in each picture above. Acetylcholine Dopamine A: B: 10
11 11 6. Nicotine and bind to the same. The drug and the neurotransmitter compete for the same binding site. When a person smokes a cigarette, the wins the competition because there are more molecules compared to molecules present in the synaptic space.
12 7. Drugs such as nicotine, cocaine and THC have special chemical properties that allow them to diffuse across biological membranes very easily (this is called passive diffusion). If they are smoked, the drugs enter the bloodstream by diffusing through membranes in the lungs. Cocaine, which is also snorted, enters the bloodstream by diffusing through membranes in the nose. Once in the bloodstream, these drugs travel to the heart and then to the brain. There is a special arrangement of capillary cells in the brain itself called the blood-brain-barrier. This barrier excludes from the brain many compounds that are potentially harmful to the brain. But the chemical structure of nicotine, cocaine, and THC allows them to diff u s e easily across the that are part of the blood-brain-barrier, and then they enter the brain itself. 12
13 8. In many cases, scientists have discovered receptors to which drugs bind before they have discovered the natural substance in the body that binds to the receptors. Some examples include opiate receptors (to which opiates such as morphine bind) and THC receptors. We now know that endorphins and enkephalins found in our central nervous system bind to opiate receptors to help alleviate pain. Most recently, scientists have found chemicals made in our bodies that bind to THC receptors. One of these, called anandamide (from the Sanskrit word meaning bliss), has received much attention. Now that it has been identified, scientists can determine its function within the brain. THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the active ingredient in the plant. Once it binds to a THC receptor, a series of events takes place inside the cell. Number the blanks below to put the series of events in order. When THC binds to its receptor, it signals the helper G protein to become inactive. THC binds to a cannabinoid receptor. Nerve impulses in the hippocampus are reduced, causing a loss in short-term memory. The loss of cyclic AMP inside the cell causes a change in membrane currents to decrease neuron firing. Cyclic AMP, which is normally generated inside cells, is no longer generated. 13
14 re w a rd p a t h w a y 9. There is a pathway in the brain that is activated by addictive drugs. This is called the reward pathway because anything that activates the pathway produces rewarding feelings that may lead to a repetitive behavior. For example, food, water and sex are natural rewards that activate this pathway. Without these, our species would not survive. When drugs activate this pathway, the user often finds more reward in the drugs than in natural rewards. The powerful control that drugs exert on this pathway produces addictive behavior. Which of the following drugs activate the reward pathway? (Write either yes or no.) cocaine heroin THC (in marijuana) nicotine aspirin LSD alcohol penicillin 14 Dopamine is the major neurotransmitter released by the neurons in the reward pathway. Addictive drugs all increase neurotransmission at dopamine synapses within the reward pathway in a variety of different ways. For example, cocaine increases dopamine in the synaptic space by blocking on the terminals of dopamine neurons. Nicotine binds to receptors that are located on dopamine neurons and increases dopamine release from those neurons. The ability of these drugs to increase dopamine neurotransmission within the reward pathway explains their liability.
15 Answers 1) A = axon B = dendrite C = soma D = terminal soma or cell body axon; terminal; terminal terminal dendrites; dendrite 2) synapse synaptic; exocytosis synapse A = synaptic space B = receptors C = neurotransmitters D = axon terminal 3) acetylcholine receptors receptor 3; 2; 6; 4, receptor; 1, receptor; 5, receptor 4) 3; 1; 4; 2 5) enzyme inactivation reuptake into terminal A = acetylcholine (in orange) B = dopamine (in blue) 6) acetylcholine; receptor; nicotine; nicotine; acetylcholine 7) capillary; capillary; capillaries 8) marijuana 2; 1; 5; 4; 3 9) yes,; yes; maybe; yes; no; no; yes; no; uptake pumps; acetylcholine; addictive 15
16 Additional Resources National Institute on Drug Abuse for Teens: The Science Behind Drug Abuse BrainSource.com (click on Brain on Drugs ) National Families in Action (click on NFIA s Guide to Drugs and the Brain ) NCADI: US Dept of Health and Human Services and SAMHSA s National Clearinghouse for Alcohol and Drug Information The Partnership for a Drug-Free America How Stuff Works: How Your Brain Works Live Science: Your Brain Works Like the Internet ThinkQuest: Library (type brain into search engine) Additional Resources at Available from Films Media Group Drugs and the Brain Preview clip online Close captioned 5-part series, 51 minutes each DVD/VHS Order #36364 This is your brain on drugs, may be an effective sound bite, but the reality of drug use and abuse is more complicated. As this five-part series shows, the brain can be affected by drugs and alcohol in many diff e rent ways, depending on the substance consumed. The effects of stimulants, painkillers, tobacco and alcohol, cannabis, and hallucinogens are analyzed in detail, using the latest re s e a rch and computer graphics. Each program demonstrates the elaborate and f requently dangerous ways in which various drugs alter brain chemistry. Scientific histories and case studies are clearly illustrated in each program. The series includes Stimulants: The Mechanics of Pleasure; Painkillers: Numbing the Mind; Legal Drugs: Still Addictive, Still Deadly; Cannabis: Satanic Herb or Healing Potion?; Designer Drugs: Uncertain Borders
17 Messing with Heads: Marijuana and Mental Illness Preview clip online Close captioned DVD/VHS/Digital On-Demand Correlates to educational standards Order #34954 For decades, heavy marijuana use has been linked to impaired judgment and mental ability. This program explores new research into another link this time between marijuana and mental illnesses, specifically schizophrenia and paranoid psychosis. Citing a wealth of clinical evidence and observations by neurologists, psychiatrists, and psychologists, the program delves into the frightening effects of THC on young brains: psychotic delusions and behavior that may not appear until years after drug abuse has ended. This program is essential viewing in any anti-drug education campaign. (46 minutes) Drugs: Uses and Abuses Preview clip online Close captioned 8-part series, minutes each DVD/VHS/Digital On-Demand Correlates to educational standards Attention-grabbing, informative programs. School Library Journal Well-paced to keep teens interest. Good overview. The Book Report Recommended by Today s Librarian. Order #9286 A veritable encyclopedia of pharmacological facts, this outstanding series thoroughly examines the therapeutic uses and dangerous abuses of drugs. Moving beyond the Just Say No mentality, each program gives a general overview of a particular class of drugs, then moves on to closely examine specific drugs in that group. These programs promote discussion, explore myths, and provide information delivered in accessible language by a wide range of concern e d p rofessionals and recovering users. Review questions are provided with each program to test viewers knowledge, along with provocative discussion questions that address some of the sensitive issues concerning the use and abuse of drugs. A Cambridge Educational Pro d u c t i o n. The series includes Sedatives; Narcotics; Stimulants; Psychedelics and Hallucinogens; Inhalants; THC; PCP and Ketamine; Stero i d s The Addicted Brain Preview clip online DVD/VHS/Digital On-Demand Correlates to educational standards CINE Golden Eagle, this fascinating production mounts its case with stunning cinemicrography, three-dimensional models, expert interviews, and live-action sequences. Booklist Order #1363 This documentary takes viewers on a tour of the world s most prolific manufacturer and user of drugs the human brain. The biochemistry of the brain is responsible for joggers highs, for the compulsion of some people to seek thrills, for certain kinds of obsessive-compulsive behavior, even for the drive to achieve power and dominance. The program explores developments in the biochemistry of addiction and addictive behavior. (26 minutes) 1987.
18 Young Addicts: Drugs, Alcohol, and America s Future Preview clip online Close captioned 3-part series, minutes each DVD/VHS/Digital On-Demand Correlates to educational standards Recommended by The New York Times, The Boston Globe, Washington Post, New York Magazine, Booklist, Video Librarian, and JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association) Order #36282 Drug and alcohol addiction is stronger than ever among America s teens and young adults. This t h ree-part series of ABC News programs investigates disturbing new trends: teenage methamphetamine abuse, binge drinking among college-age women, and the alarmingly open access that many underage Americans now have to prescription drugs. For vital information about the dangers facing an emerging generation, this is a must-see group of programs. The series includes Hooked: America on Meth; Women and Alcohol; Pharm Country Close to Home: Moyers on Addiction Preview clip online Close captioned 5-part series, minutes each DVD/VHS/Digital On-Demand Correlates to educational standards Recommended by The New York Times, The Boston Globe, Washington Post, New York Magazine, Booklist, Video Librarian, and JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association) Order #7679 In this critically acclaimed five-part series, Bill Moyers puts a human face on an American public health crisis: drug and alcohol addiction. Each program takes on a diff e rent facet of addiction and re c o v e r y f rom studies of brain pathology and genetic risk, to various prevention and tre a t- ment approaches, to a look at our public policy. The intimate experience of addiction is share d by the addicts themselves, their parents, children, and those helping them toward recovery. The DVD version of this series also includes a special video introduction by Mr. Moyers. 5-part series, minutes each. The DVD version can be viewed using a DVD player or computer DVD-ROM drive.the series includes Portrait of Addiction; The Hijacked Brain; Changing Lives; The Next Generation; The Politics of Addiction
19 Created by Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom, PhD and Gayle Gross de Núñez,, PhD SAVANTES Durham, NC 1998 SAVANTES and Gayle Gross de Núñez,, PhD Films for the Humanities & Sciences A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. PO Box 2053, Princeton, NJ CALL FAX
The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Section I: Introduction
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Section I: Introduction
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs. CHM 108 Lab. Spring Dr. Angela King
 Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs CHM 18 Lab Spring 28 Dr. Angela King Part A: How does the brain communicate? The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and
Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs CHM 18 Lab Spring 28 Dr. Angela King Part A: How does the brain communicate? The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and
BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES
 Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse
 SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body
SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body
Nervous System Notes
 Nervous System Notes The nervous system consists of a network of nerve cells or neurons. I. A nervous system is an important part of a cell s (or an organism s) ability to respond to the environment. A.
Nervous System Notes The nervous system consists of a network of nerve cells or neurons. I. A nervous system is an important part of a cell s (or an organism s) ability to respond to the environment. A.
Addiction in the Brain - Latest Research. Gary M. Henschen, MD, LFAPA Chief Behavioral Health Officer Magellan Healthcare, Inc.
 Addiction in the Brain - Latest Research Gary M. Henschen, MD, LFAPA Chief Behavioral Health Officer Magellan Healthcare, Inc. The Neurobiology of Addiction About the speaker Gary M. Henschen, M.D. is
Addiction in the Brain - Latest Research Gary M. Henschen, MD, LFAPA Chief Behavioral Health Officer Magellan Healthcare, Inc. The Neurobiology of Addiction About the speaker Gary M. Henschen, M.D. is
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
AP Biology Unit 6. The Nervous System
 AP Biology Unit 6 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading
AP Biology Unit 6 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading
35-2 The Nervous System Slide 1 of 38
 1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
Branches of the Nervous System
 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Module 1 An Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System
 Module 1 An Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System Overview Summary This introductory module of the Brain Power! Challenge Program is designed to help students learn about the parts of the brain,
Module 1 An Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System Overview Summary This introductory module of the Brain Power! Challenge Program is designed to help students learn about the parts of the brain,
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
9neurotransmission: Content lessons
 Making the leap part 2 Making the leap station Cards (Laminate for re-use) Making the Leap Station 1 Neuron Structure and Function The nervous system is like an electrical network. It relays information
Making the leap part 2 Making the leap station Cards (Laminate for re-use) Making the Leap Station 1 Neuron Structure and Function The nervous system is like an electrical network. It relays information
Nervous System Communication. Nervous System Communication. The First Nerve Cells 1/2/11
 Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Module 4 Weeding Out the Grass
 Module 4 Weeding Out the Grass Overview Summary Marijuana is the most commonly abused illegal drug in the United States. Nearly half of all high school students have used marijuana. Many children and adolescents,
Module 4 Weeding Out the Grass Overview Summary Marijuana is the most commonly abused illegal drug in the United States. Nearly half of all high school students have used marijuana. Many children and adolescents,
General Functions (3) 1.Sensory gathers information 2.Integrative information is brought together 3.Motor responds to signals, homeostasis
 Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Notes are online at The Neuron
 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Physical and Physiological Aspects of Drug Use and Abuse
 Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain
 Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets
 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
2Lesson. Outline 3.2. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 3.2: How do our neurons communicate with each other? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to introduce students to the process of synaptic transmission, which is how one neuron communicates with another neuron. Using the pain pathway as a
Outline OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to introduce students to the process of synaptic transmission, which is how one neuron communicates with another neuron. Using the pain pathway as a
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Chapter 22. The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets. 561
 Chapter 22 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets (Opening image copyright by Sebastian Kaulitzki, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 22.1: The Nervous System Lesson 22.2: The
Chapter 22 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets (Opening image copyright by Sebastian Kaulitzki, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 22.1: The Nervous System Lesson 22.2: The
Nervous System Review
 Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Drugs, addiction, and the brain
 Drugs, addiction, and the brain Topics to cover: What is addiction? How is addiction studied in the lab? The neuroscience of addiction. Caffeine Cocaine Marijuana (THC) What are the properties of addiction?
Drugs, addiction, and the brain Topics to cover: What is addiction? How is addiction studied in the lab? The neuroscience of addiction. Caffeine Cocaine Marijuana (THC) What are the properties of addiction?
Fig Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs
 Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs Core Concept: Addictive drugs affect signaling at the synapses in the reward pathway of the brain. Class time required: Approximately 40-60 minutes Teacher Provides: For
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs Core Concept: Addictive drugs affect signaling at the synapses in the reward pathway of the brain. Class time required: Approximately 40-60 minutes Teacher Provides: For
Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior
 Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA)
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Section I Section II
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Section I Section II
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
 6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology SL Part 1 - Nerves Outcomes Part 1 6.5.1State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology SL Part 1 - Nerves Outcomes Part 1 6.5.1State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling. Chapter 48
 Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Cocaine and Dopamine. Script for the Virtual Cocaine Lab Tutorial. Page 1. Introduction
 Page 1 Script for the Virtual Cocaine Lab Tutorial Cocaine and Dopamine http://www.mind.ilstu.edu Introduction This tutorial is for The Virtual Neuroscience Lab #1: Cocaine Study, a free virtual lab available
Page 1 Script for the Virtual Cocaine Lab Tutorial Cocaine and Dopamine http://www.mind.ilstu.edu Introduction This tutorial is for The Virtual Neuroscience Lab #1: Cocaine Study, a free virtual lab available
Activity 1: Connections
 Neurobiology: Activity 1 Page 1 of 2 Activity 1: Connections Based on video content 15 minutes (10 minutes before and 5 minutes after the video) Setup Neurobiology is all about connections. So, to begin
Neurobiology: Activity 1 Page 1 of 2 Activity 1: Connections Based on video content 15 minutes (10 minutes before and 5 minutes after the video) Setup Neurobiology is all about connections. So, to begin
Name Date Class. In your textbook, read about neurons basic units of the nervous system.
 The Nervous System Reinforcement and Study Guide Section.1 The Nervous System In your textbook, read about neurons basic units of the nervous system. Complete the table by filling in the missing information
The Nervous System Reinforcement and Study Guide Section.1 The Nervous System In your textbook, read about neurons basic units of the nervous system. Complete the table by filling in the missing information
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
3 Basic Nerve Cells. Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON
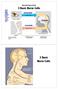 Senses TASTE SMELL VISION HEARING TOUCH Pressure Temp. Stretch Pain Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON Muscles and Glands typically react to motor output
Senses TASTE SMELL VISION HEARING TOUCH Pressure Temp. Stretch Pain Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON Muscles and Glands typically react to motor output
Learning Intention. Name and describe the components of a neuron
 c) Neural Pathways Learning Intention Name and describe the components of a neuron Cells of the Nervous System The nervous system consists of a complex network of nerve cells called neurons which receive
c) Neural Pathways Learning Intention Name and describe the components of a neuron Cells of the Nervous System The nervous system consists of a complex network of nerve cells called neurons which receive
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior
 Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE
 1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses Toxins prevent the release of acetylcholine ex. Clostridium botulinum (botulism: muscle paralysis)/ Clostridium tetani (tetanus: a disease characterized
Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses Toxins prevent the release of acetylcholine ex. Clostridium botulinum (botulism: muscle paralysis)/ Clostridium tetani (tetanus: a disease characterized
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Substance Prevention
 First Name Last Name Period Substance Prevention POINTS ASSIGNMENT /75 pts Worksheet Total /10 pts Book Activity Page /10 pts Group Discussion on Substance Use in Teenagers /10 pts Teenage Drinking Brain
First Name Last Name Period Substance Prevention POINTS ASSIGNMENT /75 pts Worksheet Total /10 pts Book Activity Page /10 pts Group Discussion on Substance Use in Teenagers /10 pts Teenage Drinking Brain
Objectives. ! Describe the major structures of the nervous system. ! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.
 Objectives! Describe the major structures of the nervous system.! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.! Distinguish between the functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.! Identify
Objectives! Describe the major structures of the nervous system.! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.! Distinguish between the functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.! Identify
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
2. When a neuron receives signals, an abrupt, temporary the inside becomes more positive in the polarity is generated (an action potential).
 Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
The Nervous System. Nerves, nerves everywhere!
 The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Understanding Drug Abuse and Addiction: What Science Says
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Understanding Drug Abuse and Addiction: What Science Says Last Updated February 2016 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents Understanding Drug Abuse and Addiction:
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Understanding Drug Abuse and Addiction: What Science Says Last Updated February 2016 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents Understanding Drug Abuse and Addiction:
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Overview of Neurons. Psychology 470. Introduction to Chemical Additions. Neurons2. Axons and Related Structures. Structures
 Soma Collateral Overview of Neurons Psychology 470 Axon Hillock Teleodendria Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Node of Ranvier Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides
Soma Collateral Overview of Neurons Psychology 470 Axon Hillock Teleodendria Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Node of Ranvier Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
2Lesson. Outline 3.3. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 3.3 Why does applying pressure relieve pain? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson introduces students to inhibitory synapses. To review synaptic transmission, the class involves a student model pathway to act out synaptic transmission.
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson introduces students to inhibitory synapses. To review synaptic transmission, the class involves a student model pathway to act out synaptic transmission.
Introduction and Background
 Introduction and Background The brain consists of several large regions, each responsible for some of the activities vital for living. These include the brainstem, cerebellum, limbic system, diencephalon,
Introduction and Background The brain consists of several large regions, each responsible for some of the activities vital for living. These include the brainstem, cerebellum, limbic system, diencephalon,
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Assignment 3: Drugs Change Our Behavior Via Actions on Neurons.
 Assignment 3: Drugs Change Our Behavior Via Actions on Neurons. In order for us to be able to understand how drugs and diseases affect the brain and our behavior we need to have a basic understanding of
Assignment 3: Drugs Change Our Behavior Via Actions on Neurons. In order for us to be able to understand how drugs and diseases affect the brain and our behavior we need to have a basic understanding of
Nervous System. 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands. 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data
 Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD
 Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
The Nervous System II Neurons
 The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
 BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
15-1: How the Nervous System Works. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
How We Grow & Change
 How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
