Movimento volontario dell'arto superiore analisi, perturbazione, ottimizzazione
|
|
|
- Amy Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Movimento volontario dell'arto superiore analisi, perturbazione, ottimizzazione Antonio Currà UOS Neurologia Universitaria, Osp. A. Fiorini, Terracina UOC Neuroriabilitazione ICOT, Latina, Dir. Prof. F. Pierelli
2 Voluntary movement voluntary recruitment of skeletal motor units to generate torque or displacement
3 To produce a voluntary movement the human nervous system must solve two problems the first is to prepare the movement the second is to execute it
4 During the motor preparation phase the nervous system has to plan the movement and code the motor programs
5 During movement execution it transforms the motor commands into action
6 Central voluntary motor command takes place at various levels, i.e. higher, middle, lower
7 The higher level can be subdivided into two functional units
8 The first unit provides the spatial and temporal representation or guidance of the movement it generates the kinematic parameters of the movement required spatial location of origin and end of movement kinematic profile including acceleration, speed, and course
9 This unit corresponds to activities termed motor imagination, mental representation, movement rehearsal, or spatiotemporal concept Hanakawa et al, 2003
10 The mental representation of movement is assumed to involve various cortical areas posterior parietal and lateral frontal premotor areas for sensorybased, i.e., externally triggered functions
11 The mental representation of movement is assumed to involve various cortical areas inferior parietal and prefrontal circuits for well learned skilled actions or internally-based functions, i.e., automatic movements
12 Patients with lesions of the posterior parietal or lateral prefrontal cortex may show apraxia and deficits in motor memory clinical impression of excessive motor hesitation with a sense of ineluctable inaccuracy during the performance of voluntary movement, and intense patient frustration. These patients are not paretic
13 The second unit of the higher level of motor command generates the voluntary drive, or motivation to move involves specific limbic pathways, particularly the medial frontalsubcortical (anterior cingulate) circuits, which could interface between deep limbic and neocortical functions Winterer et al, 2002
14 Anterior cingulate cortex activity is associated with a gain in reaction speed, at the expense of spatial accuracy subjects with short reaction times showed significantly more ACC activation (Brodmann Area 24) and an increased error rate this finding suggests that increased ACC activity is associated with a gain in reaction speed at the expense of correctness Mulert et al, 2005
15 Patients with lesions of the mesial prefrontal cortex show slow motor performance and reduced MRPs but are not paretic Wiese et al, 2004
16 The middle level of motor command corresponds to the planning and preparation of the movement the actual programming in time and space of the various muscle contractions and relaxations required to accomplish the movement intended by the higher level s mental representation
17 Important distinction is made between - the geometry of a movement (kinematics) - the forces needed to generate the movement (dynamics)
18 Parameters include timing, rapidity of onset, and intensity and duration of each muscle contraction
19 This level of motor preparation involves the rsma which has reciprocal connections with the prefrontal cortex and the basal ganglia it also involves the cerebellum, which adds this preparatory role to its involvement in monitoring the movement during its execution and in motor learning
20 Patients with disturbances of movement preparation typically exhibit acceleration deficits patients with disturbances of movement preparation are not paretic
21 The lower level of central voluntary motor command is the execution of the movement itself motor commands take the complex viscoelastic and inertial properties of multijointed limbs into account so that the appropriate force is applied to generate the desired motion
22 Refined motor command starts from the primary motor cortex
23 ... through the centrum semiovale they descend in the internal capsule...
24 enter the cerebral peduncle at the base of the midbrain
25 run through the base of the pons where they are scattered among the transverse pontine fibers and nuclei of the pontine gray matter
26 coalescing again on the ventral surface of the medulla
27 to enter various fascicles of the spinal cord
28 .. where they reach the lower motor neurons
29 and through the neuromuscular junction activate the effector
30 Motor cortex activity signals not only lower level movement parameters (muscle forces) but also higher level parameters related to the trajectory of the hand during reaching
31 A simplified account of these areas of the motor system would probably state that Rothwell, 2012
32 Primary motor cortex is a common output path through which a large proportion of the motor command is funnelled to reach the spinal cord Rothwell, 2012
33 Dorsal premotor cortex is involved in performing movements triggered by arbitrary cues in the environment such as visual shapes, or auditory tones Rothwell, 2012
34 Ventral premotor cortex is involved in controlling (particularly hand) movements that relate to real objects in the environment within reach of the body Rothwell, 2012
35 Supplementary motor area is involved in performance of sequences of movement particularly if they have to be made in the absence of any external cues Rothwell, 2012
36 The modern laboratory can study voluntary movements by analyzing the ongoing electromyographic (EMG) activity and various kinematic variables including reaction time (RT), movement time, velocity and acceleration of the moving limb Prof. Mark Hallett and his fellows at NIH
37 According to the complexity of motor action or trajectory a voluntary movement can be classified as simple
38 or complex sequential, simultaneous Benecke et al, 1986 and 1987; Agostino et al, 1992
39 According to the number of joints activated single or multijoint Benecke et al, 1986 and 1987
40 According to the speed and accuracy requirements fast and slow
41 According to the modality of execution self initiated (internally guided) or externally triggered (sensory based)
42 According to the modality of execution self initiated (internally guided) or externally triggered (sensory based)
43 According to the modality of execution self initiated (internally guided) or externally triggered (sensory based)
44 According to the modality of execution self initiated (internally guided) or externally triggered (sensory based)
45 The usual way of investigating initiation for a voluntary movement is to study the reaction time
46 Brain processing during the simple reaction time
47 Sequential simple reaction time paradigm Modality of execution Subject initiates the movement in response to an external signal or cue visual, acoustic, somatosensory Subject initiates the movement at will Currà et al, 2000a and 2000b
48 Delayed sequential responses in dystonia with predominant impairment of SI sequences
49 Delayed sequential responses in chorea with similar slowing of SI and ET
50 Reaction time paradigm may be complex
51 Brain processing during choice reaction time A = stimulus identification B = stimulus response mapping C = response selection D = response programming E = response initiation
52 Sequential choice reaction time paradigm Knowledge of the path or modality of execution? Subjects move faster when they know the sequence path in advance Currà et al, 1997
53 Predominant impairment of known sequences in PD correspond to self-initiated sequeces
54 The usual way of investigating execution is to study the movement time Wacholder and Altenburger, 1926
55 Straight paths and bell-shaped velocity profiles also found during the execution of multi-joint movements Morasso, 1981
56 Reaching trajectories involving one or more joints consistently having invariant kinematic characteristics
57 This suggest reaching trajectories are planned in advance without initial need to take account of limb dynamics
58 Perturbation
59 Perturbing voluntary movements by delivering electrical or magnetic stimuli
60 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
61 Suprathreshold sptms lengthens RT more marked with stimuli applied closer to the expected onset of EMG Day et al. 1989; Rothwell et al. 1989; Pascual-Leone et al. 1992; Priori et al. 1993; Berardelli et al. 1994; Romaiguere et al. 1997; Ziemann et al. 1997; Leocani et al. 2000; Burle et al. 2002
62 Sub- or slightly suprathreshold sptms shortens RT when applied together with Go or at a short interval afterward Hallett et al. 1991; Pascual-Leone et al. 1992, 1994; Romaiguere et al. 1997; Terao et al. 1997; Ziemann et al. 1997; Leocani et al. 2000; Molinuevo et al. 2000; Burle et al. 2002; Hashimoto et al. 2004
63 The inhibitory aspect of motor preparation has received relatively less attention Decrease of SICI precedes increase of cortical excitability in Simple RT paradigm Reynolds and Ashby, 1999
64 Inhibition in the human motor cortex is reduced just before a voluntary contraction releasing the brakes before pressing the gas pedal Floeter and Rothwell, 1999
65 At all stimulation time points, both simple and choice reaction time is shorter with pptms than with sptms Difference in SICI during the early phase of srt and crt suggest that inhibitory circuits other than SICI are responsible for setting the level of cortical excitability at earlier parts of the reaction time period
66 Voluntary movement may be perturbed by interfering with the function of distinct motor areas Schluter et al, 1998
67 PMC stimulation alone disrupts an early stage of movement selection M1 stimulation disrupts the movements at a later stage of execution Schluter et al, 1998
68 PMC is important for selecting movements and the left hemisphere is dominant for the rapid selection of action
69 Optimization
70 Motor learning
71
72 Short practise
73 Long practise
74
75 transcranial Direct Current stimulation
76 Small electric field crosses the skull and influences the human brain as behavioral changes are recorded
77 Reversed effects for the two hands anodal stimulation improved RH > LH performance cathodal stimulation improved LH > RH performance
78 In the motor system, anodal tdcs enhances cortical excitability and cathodal tdcs diminishes it eighteen publications of motor studies 15 publications evaluated the effect of both anodal and cathodal over the target motor areas 3 evaluated the effect of anodal only Lang et al, 2004; Fregni et al, 2006; Furubayashi et al, 2008; Jefferson et al, 2009; Jeffery et al, 2007; Csifcsak et al, 2009; Kirimoto et al, 2009; Stagg et al, 2009
79 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation epidural recordings
80 Low-frequency rtms (1-Hz) decreases the amplitude of the later I-waves with the amplitude of the I1-wave staying relatively constant intracortical circuitry modulated by 1-Hz rtms, and pyramidal cells are not directly modulated intracortical inhibitory activity, and therefore later I-waves, generated in superficial layers of motor cortex play a role in the early stages of skill acquisition rtms reduces cortical excitability, likely through its facilitation of GABA interneuron activity
81 High-frequency rtms ( 5Hz) increases D-wave amplitude and induces an additional I-wave modulates motor cortex excitability with differing neural mechanisms depending on the frequency and composition of the magnetic pulse trains continuous 5-Hz rtms increases D-wave amplitude and induces an additional I-wave I1-wave amplitude was not changed
82 Theta Burst stimulation (TBS) TBS consists of a train of pulse triplets delivered at 50 Hz, with sets of triplets delivered at 5 Hz TBS can be delivered as continuoustbs or intermittent TBS itbs uses triplets at the same frequency as ctbs but in bursts every 200 ms ctbs decreases MEP amplitude by decreasing the amplitude of I1- waves itbs increases MEP amplitude by increasing the amplitude of later I- waves [43].
83 rtms influences both distal
84 and proximal sequential limb movements
85 Paoloni, Di Lorenzo et al, 2012
86 rtms over cm1 influences both motor initiation and motor execution of a ET known, ET unknown, and SI simple upper limb movement Paoloni, Dilorenzo et al, submitted
87 Grazie
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
Paired-Pulse TMS to one Brain Region. Joyce Gomes-Osman Research Fellow Berenson-Allen Center for Non-Invasive Stimulation LEASE DO NOT COPY
 Paired-Pulse TMS to one Brain Region Joyce Gomes-Osman Research Fellow Berenson-Allen Center for Non-Invasive Stimulation Paired-Pulse Paradigms Sequential pulses applied to the same cortical region Variable
Paired-Pulse TMS to one Brain Region Joyce Gomes-Osman Research Fellow Berenson-Allen Center for Non-Invasive Stimulation Paired-Pulse Paradigms Sequential pulses applied to the same cortical region Variable
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
The Motor Systems. What s the motor system? Plan
 The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
Degree of freedom problem
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Water immersion modulates sensory and motor cortical excitability
 Water immersion modulates sensory and motor cortical excitability Daisuke Sato, PhD Department of Health and Sports Niigata University of Health and Welfare Topics Neurophysiological changes during water
Water immersion modulates sensory and motor cortical excitability Daisuke Sato, PhD Department of Health and Sports Niigata University of Health and Welfare Topics Neurophysiological changes during water
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Circuits & Behavior. Daniel Huber
 Circuits & Behavior Daniel Huber How to study circuits? Anatomy (boundaries, tracers, viral tools) Inactivations (lesions, optogenetic, pharma, accidents) Activations (electrodes, magnets, optogenetic)
Circuits & Behavior Daniel Huber How to study circuits? Anatomy (boundaries, tracers, viral tools) Inactivations (lesions, optogenetic, pharma, accidents) Activations (electrodes, magnets, optogenetic)
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Mechanosensation. Central Representation of Touch. Wilder Penfield. Somatotopic Organization
 Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
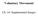 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization
 Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE
 TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE Angel Lago-Rodriguez 1, Binith Cheeran 2 and Miguel Fernández-Del-Olmo 3 1. Prism Lab, Behavioural Brain Sciences, School of
TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE Angel Lago-Rodriguez 1, Binith Cheeran 2 and Miguel Fernández-Del-Olmo 3 1. Prism Lab, Behavioural Brain Sciences, School of
Voluntary Movements. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Outline. Organization of the motor cortex (somatotopic) Corticospinal projection
 Voluntary Movements Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Organization of the motor cortex (somatotopic) Corticospinal projection Physiology of motor neurons Direction representation, population coding
Voluntary Movements Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Organization of the motor cortex (somatotopic) Corticospinal projection Physiology of motor neurons Direction representation, population coding
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
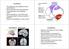 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Neural Basis of Motor Control. Chapter 4
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Big Ideas. (e.g. puberty, immune function (autoimmune disorders)) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves
 CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1 As with sensory input, motor output is organized in central nervous system Peripheral Nervous system divides efferent signals somatotopically
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1 As with sensory input, motor output is organized in central nervous system Peripheral Nervous system divides efferent signals somatotopically
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Cortical Organization. Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:.
 Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:. 2. Secondary cortex: located immediately adjacent to primary cortical areas,
Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:. 2. Secondary cortex: located immediately adjacent to primary cortical areas,
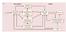 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control
 Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control How Your Brain Works - Week 10 Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net The Story So Far In the first few lectures we introduced you to some
Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control How Your Brain Works - Week 10 Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net The Story So Far In the first few lectures we introduced you to some
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector
 At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector Normal condition, using fingers and wrist Using elbow as folcrum Using shoulder as folcrum (outstretched
At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector Normal condition, using fingers and wrist Using elbow as folcrum Using shoulder as folcrum (outstretched
Neurophysiological Basis of TMS Workshop
 Neurophysiological Basis of TMS Workshop Programme 31st March - 3rd April 2017 Sobell Department Institute of Neurology University College London 33 Queen Square London WC1N 3BG Brought to you by 31 March
Neurophysiological Basis of TMS Workshop Programme 31st March - 3rd April 2017 Sobell Department Institute of Neurology University College London 33 Queen Square London WC1N 3BG Brought to you by 31 March
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura Avanzino
 Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
THE PREFRONTAL CORTEX. Connections. Dorsolateral FrontalCortex (DFPC) Inputs
 THE PREFRONTAL CORTEX Connections Dorsolateral FrontalCortex (DFPC) Inputs The DPFC receives inputs predominantly from somatosensory, visual and auditory cortical association areas in the parietal, occipital
THE PREFRONTAL CORTEX Connections Dorsolateral FrontalCortex (DFPC) Inputs The DPFC receives inputs predominantly from somatosensory, visual and auditory cortical association areas in the parietal, occipital
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Session 4 Virtual Lesion Approach I Alexandra Reichenbach MPI for Biological Cybernetics Tübingen, Germany Today s Schedule Virtual Lesion Approach : Study Design Rationale
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Session 4 Virtual Lesion Approach I Alexandra Reichenbach MPI for Biological Cybernetics Tübingen, Germany Today s Schedule Virtual Lesion Approach : Study Design Rationale
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions
 Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Summary of my talk. Cerebellum means little brain but a huge neural resource. Studying the cerebellum in. Chris Miall
 Studying the cerebellum in sensory motor control Chris Miall Behavioural Brain Sciences School of Psychology University of Birmingham Summary of my talk Cerebellum means little brain but a huge neural
Studying the cerebellum in sensory motor control Chris Miall Behavioural Brain Sciences School of Psychology University of Birmingham Summary of my talk Cerebellum means little brain but a huge neural
Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes
 Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes Jessica Matthes, Ph.D., ABN Barrow TBI Symposium March 23, 2019 jessica.matthes@dignityhealth.org Outline TBI Mechanisms of Injury Types
Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes Jessica Matthes, Ph.D., ABN Barrow TBI Symposium March 23, 2019 jessica.matthes@dignityhealth.org Outline TBI Mechanisms of Injury Types
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Seventh Edition. The Nervous System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Notes: Organization. Anatomy of the Nervous System. Cerebral cortex. Cortical layers. PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall Professor Claffey
 PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Organization Version: 10/30/12 - original version Anatomy of the Nervous System Content covered in Hans's lecture: CNS & PNS Directions/Planes
PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Organization Version: 10/30/12 - original version Anatomy of the Nervous System Content covered in Hans's lecture: CNS & PNS Directions/Planes
-Zeina Assaf. -Omar Odeh. - Maha Beltagy
 -3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
-3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions
 Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Cortex and Mind Chapter 6
 Cortex and Mind Chapter 6 There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system. It has
Cortex and Mind Chapter 6 There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system. It has
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Exam 1 PSYC Fall 1998
 Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
