IGCSE Biology Revision Answers
|
|
|
- Anis Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IGCSE Biology Revision Answers Test 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms 1. (b), (c) and (e) 2. Nutrition; respiration 3. (b) and (d) 4. T, F, F, F 5. Nutrition; respiration Metabolism; excretion 7. F, T, F, F 8. Movement 9. The supply of petrol nutrition for the car is similar to The release of energy respiration when petrol is burnt in a car is like The release of energy movement from petrol in a car makes the wheels go round. In a living organism this is like A car releases exhaust excretion fumes. In a living organism this is like 10. (b) and (d) Test 2 Classification of Living Organisms 1. Y and Z; genus 2. F, F, T, F 3. (b) and (d) 4. Arachnids 5. The animal is a thin cylinder in shape with rings around its body showing that it is segmented. The animal is a thin cylinder in shape with a dry scaly skin. The animal is a thin cylinder in shape and has a moist, slimy skin. annelid reptile nematode Dicotyledons 7. Mammals; myriapods; molluscs 8. The skin is moist and they have legs. The skin is covered in fur and they have legs. The skin is covered in scales and they have fins. The skin is covered in feathers and they have legs. The skin is covered in scales and they have legs. amphibian mammals fish birds reptiles 9. Mammals 10. (a) and (d) Test 3 Classification of Living Organisms 1. (c) and (e) 2. Vertebrates T, T, F, F 5. (a), (c) and (d) Arthropods 7. Arthropods 8. (a) and (c)
2 9. Rana ibericus 10. Birds Legs covered in scales and body covered in feathers. Amphibians Body covered in moist skin. Reptiles Body covered in dry scales. Mammals Body covered in hair or fur. Test 4 Cell Structure and Function 1. T, F, T, T, F, F 2. A cell membrane 3. F, F, F, T 5. A large surface area root hair cell leaf organ xylem tissue 7. Trachea or oviducts 8. (a) 9. T, T, F, F 10. nucleus controls cell activities cell wall gives the plant cell shape chloroplast produces food cell controls what enters membrane and leaves the cell Test 5 Cell Structure and Function 8. Cell wall 9. Fungi Test 6 Movement in and out of Cells 1. (c) 2. T, T, F, F 3. Diffusion 4. (a) 5. (a) T, F, F, F 7. Down 8. Solute when salt dissolves in water, this is the salt Solution when salt dissolves in water, this is the product Solvent when salt dissolves in water, this is the water 9. T, T, F, F, T 10. Does not need energy Test 7 Cells 1. (c) 2. T, F, F, T 3. Energy; against 4. T, F, T, F 5. (a) and (c) Down; lost; to; 6% 7. (a) 8. T, F, T, F, F 9. Water; high; low; down 10. F, T, T, T, F 1. Cell wall 2. Chloroplast 3. (a) 4. F, F, T, T 5. (b) and (d) T, F, F, T, F, T 7. Contraction
3 Test 8 Enzymes 1. (b) (c) 4. (a) and (b) 5. F, T, F, F, T F, F, T, T 7. (c) 8. F, F, T, T Test 9 Nutrients and Plant Nutrition 1. Amino acids 2. Protein 3. (c) 4. Nitrogen 5. Less carbon dioxide; more oxygen (c) 7. F, F, F, T 9. Mineral ions; chlorophyll 10. F, F, F, T Test 10 Nutrients and Plant Nutrition 1. Water; oxygen 2. (c) 3. T, F, F, T 4. (d) 5. Stoma (b) 7. Glucose; chlorophyll; chloroplast 8. Amino acids/proteins 9. (d) 10. Fat C Carbohydrate B Protein A Test 11 Nutrients and Plant Nutrition 1. Bacteria; lactic acid 2. (a) 3. (d) 4. A wood burner 5. F, T, F, T, F, F Photosynthesis manufactures small carbohydrate molecules. Some of the molecules made in photosynthesis are converted to amino acids. Some molecules made in photosynthesis are converted to starch grains. These are called glucose. These are used for protein synthesis. These are used for storage. 7. Magnesium 8. F, T, F 9. (d) 10. F, F, T, F Test 12 Animal Nutrition 1. (b), (d) and (e) 2. Duodenum 3. Peristalsis 4. Fats Fatty acids and glycerol Proteins Amino acids Carbohydrates Simple sugars 5. Liver Incisor biting and cutting Canine piercing and tearing Molars grinding and chewing 7. F, F, F, T and (d) 9. Pancreas 10. (a) and (b)
4 Test 13 Animal Nutrition 1. Produces digestive juice Transports food from mouth to stomach Absorbs digested food Produces pancreas oesophagus small intestine stomach hydrochloric acid 2. Mouth; stomach 3. (a) and (b) 4. F, T, T, F, T 5. (c) Stomach 7. Amylase 8. (a) 9. (b), (c) and (e) 10. Constipation Test 14 Transport in Plants 1. Xylem vessels; mesophyll cells 2. (d) 3. F, F, F, T 4. Phloem; translocation 5. (b) T, F, T, F 7. Root 8. F, T, F, T Test 15 Transport in Humans 1. Right ventricle 2. T, F, F 3. (a) 4. X and Z 5. (b) (a) 7. Plasma Platelets carrying food substances clotting Red blood cells carrying oxygen White blood defence against cells disease 9. Is fitter 10. Towards the heart Test 16 Transport in Humans 1. (a), (b) and (d) 2. Pulmonary artery; aorta 3. F, T, F, T, F 4. (b) and (d) 5. F, T, F, F A vein B artery C capillaries 7. (b) 8. Left ventricle 9. Carrying oxygen 10. Arteries; capillaries; veins Test 17 Respiration 1. (b), (d) and (e) 2. Tar 3. Lactic acid 4. Carbon monoxide Nicotine Tar stops blood cells carrying oxygen raises blood pressure causes lung cancer 5. T, T, F To make the dough rise 7. (d) 8. Water 9. (a) and (b) 10. C
5 Test 18 Respiration 1. (b) and (c) 2. Lactic acid 3. Ferment; alcohol 5. F, F, F, T Increases; increases 7. A smaller surface area 8. (c) 9. F, T, F, F 10. (a) Test 19 Transport and Respiration 1. (a) 2. 1 Exposure to damaged tissue 2 Platelets activated 3 Fibrinogen converted to fibrin 4 Red blood cells trapped 3. An infection 4. F, T, T, F 5. (b) Lymphocytes; antibodies 7. (c) 8. Lymph vessels 9. Contract; relax; up and out; increases 10. F, T, F Test 20 Excretion 1. F, T, F, F 2. Excess protein 3. Urine 4. (a), (c) and (d) 5. Urine (b) 7. B 8. (a), (b) and (d) Test 21 Gas Exchange and Excretion 1. 1 External intercostal muscles contract 2 Ribs are raised 3 Volume of the chest increases 4 Pressure inside the chest falls 5 Air enters 2. F, T, F, F 3. Proteins 4. (b) 5. T, F, F, F (b) 7. F, T, F Test 22 Co-ordination and Response 1. (c) 2. F, T, F, F 3. Synapse 4. Plants; gravity; growth 5. (a) 1 Sense organ 2 Sensory neurone 3 Central nervous system 4 Motor neurone 5 Effector 7. Retina 8. Sensory neurone; motor neurone 9. A receptor; a relay; an effector 10. (a) Test 23 Co-ordination and Response 1. Adrenaline 2. (c)
6 3. 1 receptor 2 sensory neurone 3 relay neurone 4 motor neurone 5 effector 4. Thicker; less 5. F, T, T Circular; radial 7. Motor neurone 8. (d) 9. Triceps 10. (b) and (d) Test 24 Co-ordination and Response 1. Homeostasis 2. Evaporation; cooled 3. F, F, F, T 4. (b) and (c) 5. (c) T, T, T, T 7. (c) 8. F, F, T, F Test 25 Co-ordination and Response 1. T, F, F, F 2. (a) and (b) 3. Retina; black-and-white; dim 5. (a) Glycogen; insulin; sugar 7. T, F, T, F, F 8. Glucagon 9. (c) and (d) 10. F, F, F, T Test 26 Reproduction 1. (a), (c) and (d) 2. T, F, F, F 3. Anther and (d) 5. Contracts; dilates; dilates B and C; A and D; C 7. F, F, T, F 8. Pollination; pollen grain; fertilisation 9. (c) 10. F, F, T, T Test 27 Reproduction 1. (b) 2. T, T, F, F 3. Testes 4. (a) 5. Anther; filament F, T, F 7. C; E; B 8. (c) 9. Southwest 10. Ovary forms a fruit Petal drops off Ovule becomes a seed Sepal remains in position, protects the developing fruit Stamen dries up and falls off Test 28 Reproduction Revision mode 1. F, F, T, F 2. (a) 3. Amnion 4. Sperms; vagina 5. T, T, T, F (a) 7. Oviduct; vagina; ovary 9. Menopause 10. (c)
7 Test 29 Reproduction 1. F, F, T, F 2. Decreases; very low levels 3. Testes 4. (b) and (d) 5. F, F, T, F A vasectomy 7. (a) 8. Puberty 9. T, F, T, T 10. (d) Test 30 Reproduction 1. F, F, T, T 2. (a) and (d) 3. T, T, F, F 4. Bacterial; can be treated 5. (a), (c) and (d) F, F, T, T 7. Cutting; oviducts 8. T, F, F, F 2 Food reserves are digested 3 Digested food moves to growing points 4 The radicle grows out of the seed 5 The plumule grows out of the seed Main root; shoot; food reserve 7. (c) and (d) o C; in an oven or incubator; water Test 33 Inheritance 1. Sex; X; X; X; Y 2. (c) 3. F, F, T, F 5. Mitosis; diploid (b), (c) and (e) 7. F, T, F, F, F 8. Diploid; haploid; more 9. (d) Y; 23+Y Test 31 Reproduction 1. (a) and (d) 2. Ovaries 3. F, T, F, F 4. Mammary 5. (a), (b), (c), (e) and (f) Artificial insemination 7. F, F, F, F, T 8. (a) Test 32 Growth and Development 1. F, F, F, T 2. (b) 3. Germination; decreases 4. Water 5. 1 Enzymes in the seed become active Test 34 Inheritance 1. (a) and (c) 2. Haploid; diploid; neither; diploid 3. F, F, F, T 5. M; 0.5M; M (d) 7. An X chromosome Test 35 Inheritance 1. BB and Bb 2. F, T, F, F 3. (b), (c) and (d) 4. Harmful; increased 5. Aidan (d) 7. 1:2:1; 3:1
8 8. 3:1 9. (a) and (c) 10. (b) Test 36 Inheritance T, F, F, T, T, T 3. (a) 4. 25% 5. T, F, F, F, T 50% 7. (b) and (e) 8. T, F, F, T 9. (e) red and 200 white Test 37 Inheritance 1. (b) 2. F, F, F, T 3. An antibiotic; resistant; survive 4. Co-dominance 5. (c) (c) 7. A white forelock; dominant Test 38 Relationships 1. (a) 2. T, T, F, T 3. C 4. (d) 5. Producers (d) 7. F, T, F, F 8. Energy flow 9. Exponential phase 10. C Test 39 Relationships 1. (a) and (c) 2. F, F, F, T 3. Photosynthesis 4. Reproduction; death 5. (b) and (d) Carnivore 7. Light; chemical and (c) 9. T, T, F, T 10. Decomposers Test 40 Relationships 1. F, F, F, T 2. (a) 3. Cause mutations 4. Carbon monoxide 5. F, T, F, F (a) and (c) 7. Nitrates; dissolved oxygen 8. T, F, F, F, T 9. (a) 10. Decreases; light; suspended solids Test 41 Relationships 1. F, F, T, F 2. (c) 3. Increase; oxygen 4. (a) 5. F, T, F, F (c) 7. D 9. F, F, T, F
9 10. 1 Screening to remove plastics and rubber for recycling 2 Sedimentation to allow solids to collect 3 Sludge digestion to kill parasite eggs and break down organic matter 4 Liquid filtration to remove particles in suspension Test 42 Relationships 1. (a), (d) and (f) 2. T, F, T, T, F, F 3. Plastic 4. T, T, F, F 5. (a), (d) and (e) Not biodegradable 7. (c) 8. T, F, T, T, F
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
Multicellular Organisms Homework
 Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/01. Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2003
 MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2003 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser
MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2003 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark
www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2004 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2004 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
2014 Secondary Three Biology Curriculum Outline
 Week 1 Theory Week 2 2.1 Cell structure and Organization. Identify from prepared slides or from fresh preparations using appropriate temporary staining technique or on diagrams or photomicrographs, the
Week 1 Theory Week 2 2.1 Cell structure and Organization. Identify from prepared slides or from fresh preparations using appropriate temporary staining technique or on diagrams or photomicrographs, the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2006 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2006 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2015 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2015 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0610 BIOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2005 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2005 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
c Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology Part 1
 c ngel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 iology Grade 11 uration: 03 hours Part 1 Index No:- 1 The cell wall of a plant cell is removed using an enzyme. What would happen
c ngel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 iology Grade 11 uration: 03 hours Part 1 Index No:- 1 The cell wall of a plant cell is removed using an enzyme. What would happen
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 www.xtremepapers.com International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice OTOER/NOVEMER SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials:
www.xtremepapers.com International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice OTOER/NOVEMER SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials:
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL
 Write your Examination Number here 2007. M. 43 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 12 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00
Write your Examination Number here 2007. M. 43 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 12 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *3725898241* IOLOGY 61/1 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 27 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *3725898241* IOLOGY 61/1 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 27 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/31
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/31
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/21 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
Soft clean eraser Soft pencil (type B or HB is recommended)
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level *7097859728* IOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2016 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS FIRST Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level *7097859728* IOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2016 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS FIRST Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
UR Revision Guide. igcse Biology. Page 1
 UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *1478016376* IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2008 dditional Materials: RE THESE
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *1478016376* IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2008 dditional Materials: RE THESE
* * Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level. BIOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2014.
 *9130719436* ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level IOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft
*9130719436* ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level IOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *575642182* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 61/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 215 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
*575642182* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 61/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 215 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
Year 10 IGCSE Biology Revision Checklist
 Year 10 IGCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 10 Biology examinations. This is the work that you will have covered by the end of
Year 10 IGCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 10 Biology examinations. This is the work that you will have covered by the end of
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Biology Notes. Homeostasis
 Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 45 minutes *8205284412* dditional Materials:
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 45 minutes *8205284412* dditional Materials:
 *3305766201* www.onlineexamhelp.com ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level IOLOGY 5090/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet
*3305766201* www.onlineexamhelp.com ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level IOLOGY 5090/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *7539978956* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 Multiple hoice (Extended) May/June 2018 dditional Materials: Multiple
*7539978956* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 Multiple hoice (Extended) May/June 2018 dditional Materials: Multiple
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level *4900384293* IOLOGY 5090/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 dditional Materials:
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level *4900384293* IOLOGY 5090/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 dditional Materials:
17. What are lipids made from? Fatty acids and glycerol 18. What are proteins used in the body for? (What is their function?) Growth and repair 19.
 100 Facts Biology 1. What is a eukaryote? A plant or animal cell that have a membrane and a nucleus 2. What five things do most animal cells contain? Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria
100 Facts Biology 1. What is a eukaryote? A plant or animal cell that have a membrane and a nucleus 2. What five things do most animal cells contain? Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria
5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2005 question paper 0610 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2005 question paper 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/02 Paper 2 (Core Theory),
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2005 question paper 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/02 Paper 2 (Core Theory),
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *0369736826* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 Multiple hoice (Extended) May/June 2017 dditional Materials: Multiple
*0369736826* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 Multiple hoice (Extended) May/June 2017 dditional Materials: Multiple
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
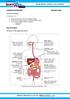 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Human Biology *P41558A0128* P41558A. Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01. Edexcel International GCSE. Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided
 GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June 2015 Time 1. 30 hours S 3 MOT II Name class/no INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided ANSWERS
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June 2015 Time 1. 30 hours S 3 MOT II Name class/no INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided ANSWERS
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *8747337823* IOLOGY 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2010 dditional Materials: RE THESE
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *8747337823* IOLOGY 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2010 dditional Materials: RE THESE
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSIT OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *5868903410* IOLOG 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
UNIVERSIT OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *5868903410* IOLOG 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSIT OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *1041307990* IOLOG 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
UNIVERSIT OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *1041307990* IOLOG 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement
 B7.1 Peak performance movement and exercise 1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement 2. understand that muscles can only move bones at a joint by contraction,
B7.1 Peak performance movement and exercise 1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement 2. understand that muscles can only move bones at a joint by contraction,
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *1276425606* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) May/June 2018 dditional Materials: Multiple
*1276425606* ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) May/June 2018 dditional Materials: Multiple
Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED
 Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED This is a summary of everything you need to know for the Biology part of your Combined science GCSE for your exam on 8 th March 2019. 9 Cells and Simple Cell Transport
Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED This is a summary of everything you need to know for the Biology part of your Combined science GCSE for your exam on 8 th March 2019. 9 Cells and Simple Cell Transport
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education *3567300897* IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: RE THESE
ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education *3567300897* IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: RE THESE
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *4543376409* UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
*4543376409* UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the March 2016 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core), maximum raw mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the March 2016 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core), maximum raw mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *4625240491* IOLOGY 0610/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *4625240491* IOLOGY 0610/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Grade 10 IGCSE_ Biology Term 1 Final Exam _ Study Guide. The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include:
 The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include: multiple Choice questions short-answers questions Alternative to practical Chapter 14 Coordination and response, P: 161-174 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe
The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include: multiple Choice questions short-answers questions Alternative to practical Chapter 14 Coordination and response, P: 161-174 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
0610 BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 32 (Extended Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 00 BIOLOGY 00/ Paper
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 00 BIOLOGY 00/ Paper
