Clinical profile of lesions of brain
|
|
|
- Eileen Shavonne Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
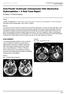
1 Research Article Clinical profile of lesions of brain Pradeep Vaijinathrao Benjarge 1*, Anant Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Government Medical College, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, INDIA. 2 Consultant Physician, Krishna Hospital and ICU, Jalna Road, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, INDIA. drpradeep777@gmail.com Abstract This study is a study of ICSOL admitted in department of medicine GMCH Aurangabad.. In this study detail clinical examination of all cases done with contrast CT in each cases. As per the clinical and radiological criterion they were divided into different SOLS. As neurosurgery was not possible at that time to have the histopathological diagnosis so the radiological suspicion is taken as final diagnosis of the SOL. After studying 80 cases in sequence of ICSOL we come to the conclusion that the commonest occurrence is tuberculoma followed by glioma. The comment presenting symptom was convulsions followed by headache. The commonest CT finding was Ring enhancing region in brain followed by diffuse intracerebral lesions. Anatomically multiple lobes were involved in 40% of cases followed by parietal lobe. Key Word: brain, intracranial space. * Address for Correspondence: Dr Pradeep Vaijnathrao Benjarge, 38, Rokdiya hanuman Colony Jalna Road, Aurangabad , Maharashtra,, INDIA. drpradeep777@gmail.com Received Date: 10/06/2014 Accepted Date: 20/06/2014 Quick Response Code: Access this article online Website: DOI: 20 June 2014 INTRODUCTION Space occupying lesions of cranium are those lesions which occupy the space, which is normally occupied by the brain. It includes vascular, neoplastic and inflammatory lesions. The clinical features of ICSOL relate to the site of lesion and its rate of expansion. The following mechanisms produce the signs and symptoms. 1. local effects on adjacent cerebral tissue 2. raised intracranial pressure 3. seizures 4. False localizing signs. To know the details what were the clinical presentation we noted the main functions of each part/lobe of brain. Frontal lobe: personality, emotional response, social behavior Parital lobe (Dominant): calculation, language, planning movement, appreciation of size and shape. Parietal lobe (Non Dominant)): constructional skills, spatial orientation. intracranial space occupying Occipital lobe: analysis of vision. When there is lesion in the particular area these functions are hampered. MATERIALS AND METHODS This prospective study was carried out in the Department of Medicine Govt Medical Collage and Hospital Aurangabad from Jan 1998 to Jan In this study 80 cases of ICSOL were studied in detail at the time of first presentation. In all cases after routine investigations, Plain and Contrast CT was done in all cases. Etiological diagnosis can be reasonably made on the basis of CT findings and clinical correlation. OBSERVATIONS AND RESULT The age rang was between 12 to 81 years. The maximum no of cases were in the 3rd decade i.e. 29 cases (36.25%). There was a male dominance with 43 male: 37 female cases. The commonest presentation was convulsions followed by headache. Seizures were seen in 71%, headache in 68%, vomiting in 47% and motor weakness in!7% of cases studied. In the present study 71% patients had convulsions out of whichh 88% had generalized convulsions. The commonest type of headache observed was compressive type of headache followed by tension type headache. CT scan diagnosis of ICSOL were tuberculoma 34 cases (42.5%),glioma 13 cases (16.25%), neurocystecerecosis 10 cases(12.5%), secondaries in brain 6 cases (7.5%), astrocytoma 5 cases(6.25%), meningioma 5 cases (6.25%), brain abscesses in 3 cases(3.75%).thus tuberculoma forming the majority of How to site this article: Pradeep Vaijinathrao Benjarge, Anant Kulkarni. Clinical profile of intracranial space occupying lesions of brain. MedPulse International Medical Journal June 2014; 1(6): (accessed 21 June 2014).
2 MedPulse International Medical Journal, ISSN: , EISSN: , Volume 1, Issue 6, June 2014 pp ICSOL followed by glioma as second largest cause for ICSOL. The commonest CT finding was ring enhancing lesion in 44 cases (55%) followed by diffuse lesions 36 cases (45%) and calcifications 11 cases (13.75%). Out of 80 cases of ICSOL studied, in 48 cases ( i.e. 60%) the lesions were more than 20 mm. In 19 cases (i.e %) the lesion were between 10 mm and 20 mm. The incidence of affection of multiple lobes was the commonest i.e %.The commonest single lobe affected was parietal lobe in 22 cases i.e. 27.5%.the least affected lobe was temporal lobe.the commonest affected lobe in tuberculoma was the parietal lobe in 11 cases (32.35%) and the least affected lobe was the temporal lobe in 1 cases (2.9%). The localizing signs were present in four patients only and out of these 4 patients three patients were of parietal lobe tuberculoma and 1 patient were of neurocysticercosis. In the present study NCC was seen in 10 cases i.e. 12.5% and commonly affecting parietal lobe. DISCUSSION The term ICSOL is generally used to identify any lesion whether neoplastic or inflammatory in origin which increases the volume of intra cranial contents and leads to a rise in intra cranial tension (ICT).In general rapidly expanding lesions produce more profound neurological disturbances and increase in ICT, while slowly growing lesions may reach a large size without a profound deficit. The presentation of ICSOL had changed radically with increased availability of modern imaging techniques like CT SCAN and MRI. The computerized tomography is a non invasive reproducible and highly accurate method which demonstrates the size, location, extent of the SOL and its relation with surrounding structures. The consistency of the mass whether solid or cystic can be identified with CT SCAN and the exact density can be compared with cerebrospinal fluid or brain tissue. Its relation to ventricles can also be easily studied. The CT csan examination can also be identifying the calcific component of the lesion. The CT evaluation of ICSOL gives valuable information s about the lesion if contrast CT is done. Age and Sex The age range of cases of ICSOL in present study was from yrs.the peak incidence of ICSOL was in 3 rd decade (36.25%) followed by 4 th decade (22.5%).There was a slight male predominance in present study,with male to female ratio was 1.16 : 1. A. Mukherjee et al in 1993 observed peak incidence of ICSOL in 4 th and 3 rd decade. In Minnesota study the incidence of ICSOL was seen in middle age group, also ICSOL were common in males. Walker et al did similar observation in 1985, during the national survey of intracranial neoplasms. Incidence In present study the incidence of different lesions were as follows. Tuberculosis 34 cases 42.5% Glioma 13 cases 16.25% NCC 10 cases 12.5% Secondaries 6 cases 7.5% Astrocytoma 5 cases 6.25% Meningioma 5 cases 6.25% Abscess 3 cases 3.75% Also one case each of (1.25%) each of epidermoid cyst, arachnoid cyst, acoustic neuroma and toxoplasmosis were seen. The above finding of incidence are comparable to the previous study of Courviell et al, except for a lower incidence of brain secondaries and a higher incidence of tuberculoma in the present study.the low incidence of brain secondaries is comparable with study of Walker et al in 1985, showing 8.3 per 1 lakh population. There is higher incidence of tuberculoma in the present study. Similar incidence was also reported by Ramamurthi in 1978 (12-20%). The incidence of neurocysticercosishe is comparable with that of Lt. Col. P.C.Sanchetee et al in 1993 (14.5)Russel in 1989, also the incidence of meningioma(1 9.5%) astrocytoma (3.48%) is comparable. In the study by Hiller in 1980, glioma was noted in 34.17% of cases. This is higher than the incidence found in our study. Lowry et al had mentioned the incidence of glioma as 82%. Also in the study of A. Early Walker in 1985 given the incidence of glioma as 57%. Tuberculoma is the most common inflammatory ICSOL in the present study accounting for 42.5% of ICSOL. The incidence of tuberculoma observed in other studies was 9.6% by Maiti in 1967, 21.5% by Dastur et al in 1968 and 20% by A. Bagga et al in Also Ramamurti B. had found the incidence of tuberculoma as 20-30% in different parts of India, being more common in southern India. The incidence of Madras and Bombay were shown as 20-30% but that of Delhi and Calcutta were 5-10%. The variation in incidence of tuberculoma in India could be due to the difference in geographical pattern (A Bagga et al 1988). Since out protocol did not include follow-up and no follow-up CT scan were done we cannot comment whether the ring enhancing lesions which we saw initially could have disappeared without specific treatment. We relied on the radiologists opinion and treated all these cases as tuberculomas or NCC in correlation with the clinical presentation. It has also been mentioned by Garg et al (JAP) update article 1997 vol 45. No.5 page No ) that in all such patients antituberculous treatment is justified. The second commonest ICSOL, seen in the present study was neurocysticercosis. Cysticecosis is the most frequent Copyright 2014, Statperson Publications, MedPulse International Medical Journal, ISSN: , EISSN: , Volume 1, Issue 6 June 2014
3 Pradeep Vaijinathrao Benjarge, Anant Kulkarni parasitosis of the nervous system. Its incidence in endemic area is between 2-4% in general population as shown by B. Maiti in 1955 and R.K. Garg in In the present setup patients belonged to low socio-economic status, with poor personal hygiene, poor sanitation, lack of proper water supply and sewage system, which might made them more susceptible to be infected. (Mukherjee et al (1993) and Garg (1994) Acoustic neuroma was observed in one case i.e. 1.25% only which is slightly lower than that observed by Lalitha and Dasture in Clinical features of ICSOL In the present study the commonest symptom was convulsions, observed in 57 patients i.e %. The similar observation was seen in study of Burger et al in The incidence of seizures in ICSOL, mentioned by Arseni et al in 1972 and Steplen in 1962 was in the range of 22-94%. Similarly, the Bahita and Tandon in 1988 reported the incidence of seizures as 80%. Out of 57 cases having convulsions, 50(87.80%) had generalized seizures, 4 (7%) had partial seizures and 3 (5.2%) had complex partial seizures. Arseni and Cresescu had reported the incidence of generalized convulsions as 45%, focal convulsions as 24% and mixed convulsions as 31%. Most series from India mention generalized seizures to be more common, than partial seizures mentioned by Dinkar et al in 1970, Ramamurthi in 1970 and Mani et al in The second commonest symptom was headache observed in 55 patients (68.75%). In the study by Barone et al in 1970 headache was seen in 80% of cases whereas Ludwing et al in 1986 shown occurrence of headache in 38-86% of cases. In the present study out of 55 cases of headache 32 (58.3%) had generalized headache, 18 (32.7%) had frontal headache and only 5 (9%) had occipital headache. In the present study the duration of headache was less than 1 month in 19(33%) cases and more than 12 months in 13 (23.60%) cases. In the available references no one has mentioned about the type of headache and the duration of headache. Vomiting was the third commonest symptom observed in 37 patients (46.25%). In the study of Barone et al in 1970 vomitings were seen in 52% cases. Weakness was observed in 14 cases (17.5^), loss of consciousness in 13 cases (16.25%) and visual symptoms in 12 cases (15%). The visual symptoms were in the form of diplopia in 4 (33.33%), black outs in 8(66.66%) and diminished vision in 2 patients (16.66%) in the present study. Lowry et al in 1998, observed hemiplegia in 11.3% cases. In the present study hemiplegia was seen in 14 cases (17.5%). The other symptoms seen in the present study were loss of consciousness in 13 (16.25%) cases, abnormal behavior in 7(8.75%) cases, auditory symptoms in 5(6%) cases. Giddiness was in 4 (5%) cases, fever and speech difficulty in 2 (2.5%) each and walking difficulty in 1 (1.25%) case. In the present study aphasia was seen in 3% of cases where as Lowry et al 1998, found in 7% cases. In the present study extensor plantars and papilloedema were seen in 35% and 18% cases respectively. The incidence of papilloedema was 89% in the study of A. Asenjo et al 1951, 93% by Dastur H. M. et al 1965 and % by Sibley et al Tuberculomas In the present study 31 out of 34 (91.17%) cases were seen in cerebral hemisphere, with commonest being a parietal lobe 32.35%. Cerebellum and mid brain were also involved in 5.8% and 2.9% cases respectively. B.Rammurthi (1978), found that tuberculomas may occur in any part of the brain including the base of the brain and the brain stem. Commonly they occur in cerebral hemispheres, cerebellar lobes, cerebellopontine angle and along the base of the brain. Bhatia and Tandon (1988) have reported the incidence of seizures in 80% of cases. They also reported that the focal convulsions were seen in 80% of these patients and generalized convulsions in 20% cases only. This findings is in contract to our present study where the incidence of convulsions is 57% and generalized convulsions were seen in 87.8% of cases. In only 4 (7%) cases, partial seizures were seen. Hiller et al in 1980 have reported the incidence of tuberculoma as nil. Also most of the studies from developed countries have reported low incidence of tuberculoma and high incidence of glioma. Lowry et al has reported the incidence of tuberculoma as 1% whereas, the incidence of tuberculoma in the present study is 42.5%. Anderson J. M. et al 1976, found the incidence of hemisparesis in tuberculoma to be 38% Sibley et al 1956 found the incidence of papilloedema to be 42-55%. Neurocysticercosis In the present study neurocysticercosis was seen commonly affecting the multiple lobes, 50% cases, with extensor plantars, motor weakness and cranial nerve involvement being the commoner signs in 80%, 50%, and 20% cases respectively. Byrd et al (1982) found that the clinical presentation of cysticercosis was not related to the age of the patient, but it does depend on the size, number and location of the cyst and the host response to the cyst. The patients with completely calcified lesions presented with seizure. Those with homogenously enhancing lesions presented with seizures and signs of a solitary brain mass. Seizures were the most common presentation and initial symptom of NCC. NCC has been described as an important cause of epilepsy in India. The incidence of seizures in NCC has been variably mentioned as between 22-94%. In our study the incidence of NCC was 12.5%. Such wide variation is probably due to different criteria used by different authors (A. MedPulse International Medical Journal, ISSN: , EISSN: , Volume 1, Issue 6, June 2014 Page 290
4 MedPulse International Medical Journal, ISSN: , EISSN: , Volume 1, Issue 6, June 2014 pp Mukherjee 1991). In India NCC should be entertained as a first possible cause in all cases of adult onset epilepsy (B. Maiti 1995). Primary brain tumours In the present study out of 80 cases studied, 23 (28.75%) cases were of primary brain tumors. Out of these 13 (56.52%) were of glioma. Similarly Stephan and Israeli had reported the incidence of glioma between 55-60%. Our study also coincides with the study of Israeli. Meningioma was seen in 5 (21.7%) cases in our study. In the Minnesota cohort study headache was seen in 21% of cases, in our study it was seen in 54% of cases. Jennet K. Lowry in 1998 have reported the incidence of headache in 40%. In our study hemiparesis was seen in 5 (38.46) cases, cranial nerve involvement in 3 (23.07%) and hemiplegia in 5 (38.46%) cases. The histopathological diagnosis was possible in only case, which was astrocytoma grade II, in other cases due to unavailability of neurosurgical facility in our hospital it was not possible. Most of these patients were referred to higher centre for further operative management. Brain abscess Brain abscess presented with fever, headache, focal neurological deficit, altered sensorium and vomiting in all cases. Other clinical features like seizures, neck rigidity, ear discharge were also present. In our study 3 cases of brain abscess were noted. These cases presented mainly for altered level of consciousness. The presentation of brain abscess with headache and vomiting were accordance with the observation made by John Walton in Metastases In the present study metastases were seen in 6 (7.5%) of cases. Out of these 6 cases, 4 (66.66%) were having primary tumor in lung and 1 case was diagnosed to have carcinoma endometrium. In 1 case primary tumor localization was not possible. These tumors prescribed mainly for headache in 4 (66.66%) cases and projectile vomiting in 3 (50%) cases. Investigations in cases of ICSOL Investigations done were either for the confirmation of diagnosis or for detection of primary disease elsewhere. CT Profile in cases of ICSOL In the present study, ring enhancing lesions were the commonest presentations on the CT scan seen in 44 (55%) cases, followed by diffuse lesions in 36(45%) cases and calcifications in 11(13.75%) cases. Multiple lesions on CT were commonly seen in the tuberculoma cases, followed by secondary s in brain. Other Investigations As it is mentioned, the investigations done were either for the confirmation of diagnosis or for the detection of primary disease elsewhere. Accordingly, out of 34 tuberculoma cases 28 (82.4%) underwent chest X ray out of which 4 (11.8%) cases were having primary pulmonary tuberculosis. In only one case the brain biopsy was done which was proved to be astrocyptoma grade II. In other cases brain biopsy was not possible because of lack of neurosurgical back up in our institution. In the only case of tosoplasmosis, antibody titer for toxoplasma was found positive, the same case was also positive for HIV. Cranial nerve involvement in ICSOL In the present study cranial nerve involvement was seen in 12 (15%) cases. Out of these 12 cases tuberculoma was the cause in 5 (41.66%) cases. Out of these 5 cases 4 (80%) were having VI nerve and 1 case was having VII nerve involvement. In 2 (16.66%) cases NCC was the cause and brain abscess, toxoplasmosis was seen in 1 (8.33%) case each. All the VII nerve affections were supramuclear and VI nerve lesion was lower motor neuron type. In cases of tuberculoma the cranial nerve involvement was associated with hemiplegia in 3 (60%) cases. In 1 case of NCC it was associated with hemiplegia. Details of Hemiplegia cases In the present study hemiplegia was seen in 14 (17.5%) cases. Out of these 14 cases, 5 (35%) cases were diagnosed as tuberculoma and 5 brain tumors and 1 (7.1%) case each of NCC secondaries, brain abscess, toxoplasmosis was seen. In 1 case with left hemiplegia, aphasia was seen. In the study by Jennet K. Lowry in 1998, hemiplegia was seen in 10.5% patients. Lis M. de Angeles have given the incidence of hemiplegia as 13%. Details of Abnormal cortical sensations In three cases abnormal cortical sensations were seen and all these cases were of tuberculoma. In the present study all the three cases of abnormal cortical sensation were seen in tuberculomas and anatomically located to right parietal lobe. Abnormal cortial sensations like two point discriminations, agraphasthesia, tactile localization, tactile discrimination and tactile extinction were seen in all cases. None of these cases were associated with cranial nerve involvement, motor weakness or seizures. SUMMARY The present prospective study on clinical and CT evaluation of cases of ICSOL was carried out in 80 cases of ICSOL suspected clinically, and confirmed on CT scan examination, in the Department of Medicine, Governemtn College and Hospital, Aurangabad. A detailed history was taken and was followed by complete neurological Copyright 2014, Statperson Publications, MedPulse International Medical Journal, ISSN: , EISSN: , Volume 1, Issue 6 June 2014
5 Pradeep Vaijinathrao Benjarge, Anant Kulkarni examination. All cases were subjected to investigations of CT scan brain. Significant clinical and radiological findings were recorded and analyzed. Incidence The commonest ICSOL in the present study was tuberculoma accounting for 42% of cases. The relative percentage of other ICSOL were neurocysticerosis 12.5%, abscess 3.75%, secondaries 7.5%, astrocytoma 6.25%, glioma 16.25%, meningioma 6.25%, epidermoid cyst 1.25%, arachnoid cyst 1.25%, acoustic neuroma 1.25%, toxoplasmosis 1.25%. Age and Sex The maximum number of cases were distributed in 3 rd and 4 th decade (The age distribution varied from years) Slight male preponderance was noted in the present study. There were 53 males and 37 females. The average sex ratio for male to female 1.16:1 Clinical Features The commonest presenting features were signs and symptoms of raised intracranial tension, such as convulsions (71%), headache (55%) of vomiting (47%). The other common presentations were motor weakness (17.5%), loss of consciousness (16.25%), visual symptoms (15%), abnormal behavior (8.75%), auditory symptoms (6.25%), fever (2.5%) and sensory symptoms (2.5%). Investigation CT scan Brain The presentation, prognosis and treatment of ICSOL has changed radically with the increased availability of modern imaging techniques (computerized tomography).the computerized tomography is a noninvasive, reproducible and highly accurate method which demonstrates the size, location, configuration, extent and relationship with surrounding structure. It is possible in judge the consistency of the mass whether cystic or solid with the CT scan and also the exact density comparable to cerebrospinal fluid or brain tissue. Ventricular relationship is also easily studied. In CT evaluation of ICSOL valuable information may be gained when the scans are performed before and after admniistrration of contrast material. With contrast enhancement the diagnostic yield of CT scanning increase. CONCLUSION Thus, in the 80 cases of ICSOL studied in the present study, the age group commonly affected was between years. The common ICSOL found was tuberculoma in 42.50% cases, followed by glioma in 16.25%, NCC in 12.5% and secondaries in 7.5% cases. Biopsy could be obtained in only one case which was diagnosed to have astrocytoma grade-ii. Toxoplasmosis was seen in one case. The common symptoms found were seizures (71.25%), headache (68.75%) and vomiting (46.25%). The common signs found were extensor plantars (30%), exaggerated DTR (21.25%) and motor weakness (18.75%). REFERENCES 1. A. Bagga, V. Kaira, O P Ghai : clinical Tuberculoma. Clinical Pediatrics, October 1998; 47: A David Mendelow : Brains Diseases of the nervous system- Levingeston Publication, Editor Walton, 199; Chapter 4, A. Earl Walker, Mortoan Robins Frederic, D. Weinfeld : epediology og brain tumors. The nation surey of Intracranial neoplasms. Neurology, 1985; 35, Arseni C : two hundred and one cases of intracranial tuberculoma treated surgically, Journal of neurology, neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 1958; 21: Bajaj Sarita, S P Barthwal, N C Dwiredi: contrast computered tomographyin epilepsy with special reference to Intracranial Ring or Disc Enhancing Lesions : JAPI,1991;39, Bhargav S, Tandon P N : Intracranial Tuberculoma- A CT study; British journal of Radiology; 1980;53(643), Bhatia S and Tondon P N : solitary microlesions in CT,a clinical study and follow up; Neurology India:1988;36, Brown W J, Voge M: Cysticercosis- A modern day plague: Pediatric Clinic of North Am. 1985;32, Campbell M : Cerebral Diseases in cyanotic conegenital heart diseases: lancet 1957, Castano s, Botero D. Treatment of Neurocysticercosis with Praziquental in Columbia. Progress in clinical Neurosisences; 1985: Cohen M M : The central nervous system in CHD : Neurology 1960; Dinkar J, Mathai KV and Chandi j: cysticercosis in brain : arch. Neurology: 1970; 18, Evans W: the pathology and etiology of abscess. Lancet :1931; 1231 and Garg R K, Agrawal A. : Epilepsy : A common manifestation of Neurocysticercosis its diagnosis and management. JAPI 1992; 42, Garg R K, Agrawal A, Verma M: CT spectrum of NCC JAPI 1991, 49, Garg R K, Chakrawarti P: Disappearing CT lesions in patients of epilepsy, JAPI 1997: 45, 5, Goulatia R F, Verma A, Mishra M : Disappearing Ct lesions in epilepsy. Epilepsia 1987: 28, Grainer R G and Allison D J : Diagnostic Radiology 2 nd edition, 1992: 3, Kumar N, Narayanswami, singh K : ring enhancing CT lesions- a diagnostic dilemma. JAPI 1995, vol 43, 6, Maiti B : Neurocysticercosis An Update : JAPI, 1995, 43, Weisberg L A, Nice C and Kartz M : Cerebral CT A text atlas by Saunders, Philadelphia : Source of Support: None Declared Conflict of Interest: None Declared MedPulse International Medical Journal, ISSN: , EISSN: , Volume 1, Issue 6, June 2014 Page 292
T HIS paper is based upon experience
 DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOMAS OF THE BRAIN CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION* B. RAMAMURTHI, M.D., AND M. G. VARADARAJAN, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Madras Medical College, Madras, India (Received
DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOMAS OF THE BRAIN CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION* B. RAMAMURTHI, M.D., AND M. G. VARADARAJAN, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Madras Medical College, Madras, India (Received
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Ocular Manifestations of Intracranial Space Occupying Lesions A Clinical Study
 248 Kerala Journal of Ophthalmology Vol. XXI, No. 3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ocular Manifestations of Intracranial Space Occupying Lesions A Clinical Study Dr.Sandhya somasundaran.ms, Dr. K.V.Raju.MS Abstract
248 Kerala Journal of Ophthalmology Vol. XXI, No. 3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ocular Manifestations of Intracranial Space Occupying Lesions A Clinical Study Dr.Sandhya somasundaran.ms, Dr. K.V.Raju.MS Abstract
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Accuracy of intra-operative rapid diagnosis by Squash smear in CNS lesions An early institutional experience. KK Bansal,
 Accuracy of intra-operative rapid diagnosis by Squash smear in CNS lesions An early institutional experience. KK Bansal, Monika Bansal, Sanjeev Kishore, Anuradha K, Meena H, Dushyant G. Department of Neurosurgery
Accuracy of intra-operative rapid diagnosis by Squash smear in CNS lesions An early institutional experience. KK Bansal, Monika Bansal, Sanjeev Kishore, Anuradha K, Meena H, Dushyant G. Department of Neurosurgery
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers
 Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors
 Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Posterior Fossa Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Posterior Fossa Lesions Gupta MK 1, Rauniyar RK 1, Bhatta N 2, Raja S 3, Ahmad K 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis & Imaging, 2 Department of Internal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Posterior Fossa Lesions Gupta MK 1, Rauniyar RK 1, Bhatta N 2, Raja S 3, Ahmad K 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis & Imaging, 2 Department of Internal
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs
 Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs Professor Peter Sandercock University of Edinburgh EAN teaching course Burkina Faso 8 th November 2017 Clinical diagnosis is important to Ensure stroke
Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs Professor Peter Sandercock University of Edinburgh EAN teaching course Burkina Faso 8 th November 2017 Clinical diagnosis is important to Ensure stroke
Neurosurgery Review. Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008
 Neurosurgery Review Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008 Dr. Mudit Sharma, Neurosurgeon Manassas, Fredericksburg, Virginia http://www.virginiaspinespecialists.com Phone: 1-855-SPINE FIX (774-6334) Fundamentals
Neurosurgery Review Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008 Dr. Mudit Sharma, Neurosurgeon Manassas, Fredericksburg, Virginia http://www.virginiaspinespecialists.com Phone: 1-855-SPINE FIX (774-6334) Fundamentals
Late Onset Shake-Etiology At Stake - A Prospective Study
 Original Article Late Onset Shake-Etiology At Stake - A Prospective Study G Sendil 1, Arun N Kumar 1, Mohan V Kumar 2 1 Senior Resident, ESIC PGIMSR & MH, Bangalore, 2 Consultant Physician Columbia Asia
Original Article Late Onset Shake-Etiology At Stake - A Prospective Study G Sendil 1, Arun N Kumar 1, Mohan V Kumar 2 1 Senior Resident, ESIC PGIMSR & MH, Bangalore, 2 Consultant Physician Columbia Asia
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Epilepsy after two different neurosurgical approaches
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 1052-1056 Epilepsy after two different neurosurgical approaches to the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysm R. J. CABRAL, T. T. KING,
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 1052-1056 Epilepsy after two different neurosurgical approaches to the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysm R. J. CABRAL, T. T. KING,
Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis
 Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis Neurologic Diagnosis History Physical & Neurological Examination Ancillary Procedures 3 Questions Asked Focal neurologic deficits Increased intracranial pressure Signs
Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis Neurologic Diagnosis History Physical & Neurological Examination Ancillary Procedures 3 Questions Asked Focal neurologic deficits Increased intracranial pressure Signs
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Men think epilepsy divine, merely because they do not understand it. But if they called everything divine which they do not understand, why, there would be no end to divine things.
Chapter 1 Introduction Men think epilepsy divine, merely because they do not understand it. But if they called everything divine which they do not understand, why, there would be no end to divine things.
Page 21. occurring in the society may be much more, since many people cannot afford to come to this only institution of the
 ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Nervous System Task Exploration
 Nervous System Task Exploration Read It! Directions: Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the task questions. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from the
Nervous System Task Exploration Read It! Directions: Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the task questions. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from the
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis
 Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis Schwannomas (also called neurinomas or neurilemmomas) constitute the most common primary cranial nerve tumors. They are benign slow-growing
Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis Schwannomas (also called neurinomas or neurilemmomas) constitute the most common primary cranial nerve tumors. They are benign slow-growing
Nervous System Task Exploration
 Nervous System Task Exploration Read It! Directions: Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the task questions. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from the
Nervous System Task Exploration Read It! Directions: Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the task questions. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from the
Diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis: Some modifications are needed for Indian patients
 Review Article Diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis: Some modifications are needed for Indian patients Ravindra Kumar Garg Department of Neurology, King George's Medical University, Lucknow, India.
Review Article Diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis: Some modifications are needed for Indian patients Ravindra Kumar Garg Department of Neurology, King George's Medical University, Lucknow, India.
Epidemiology of primary tumours of the brain and
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 290-296 Epidemiology of primary tumours of the brain and spinal cord: a regional survey in southern England D. J. P. BARKER, R. 0. WELLER,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 290-296 Epidemiology of primary tumours of the brain and spinal cord: a regional survey in southern England D. J. P. BARKER, R. 0. WELLER,
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator. Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol
 NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Neurocysticercosis an uncommon intra-cerebral infection in Malaysia-
 Neurocysticercosis an uncommon intra-cerebral infection in Malaysia- A review of 3 cases. Kalai Arasu M. M.S (Malaya), Khairul Anuar FACTM *, Waran V. FRCS(SN). Division of Neurosurgery, Department of
Neurocysticercosis an uncommon intra-cerebral infection in Malaysia- A review of 3 cases. Kalai Arasu M. M.S (Malaya), Khairul Anuar FACTM *, Waran V. FRCS(SN). Division of Neurosurgery, Department of
Relationship between Histopathological Subtypes of Intracranial Astrocytoma Patients
 Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience 2011; Vol. 27 (2) : 87-93 Relationship between Histopathological Subtypes of Intracranial Astrocytoma Patients FAZLE MAHMUD 1, HARADHAN DEB NATH 2, KANAK KANTI BARUA
Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience 2011; Vol. 27 (2) : 87-93 Relationship between Histopathological Subtypes of Intracranial Astrocytoma Patients FAZLE MAHMUD 1, HARADHAN DEB NATH 2, KANAK KANTI BARUA
Study of radiological response to albendazole therapy in neurocysticercosis patients
 Original Article Study of radiological response to albendazole therapy in neurocysticercosis patients Haroon Salaria 1, Shazia Hamid d 2* 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Neurosurgery, 2 Department
Original Article Study of radiological response to albendazole therapy in neurocysticercosis patients Haroon Salaria 1, Shazia Hamid d 2* 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Neurosurgery, 2 Department
A Study on Demographic & Radiological Profile of Children with Seizure Disorder Admitted in the Pediatric Emergency Ward of a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Research A Study on Demographic & Radiological Profile of Children with Seizure Disorder Admitted in the Pediatric Emergency Ward of a Tertiary Care Centre Taraknath Ghosh*, Mrinalkanti Ghosh#,
Original Research A Study on Demographic & Radiological Profile of Children with Seizure Disorder Admitted in the Pediatric Emergency Ward of a Tertiary Care Centre Taraknath Ghosh*, Mrinalkanti Ghosh#,
Vascular Pattern in Tumours
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Vascular Pattern in Tumours To cite this article: (1957) Vascular Pattern in Tumours, Acta Radiologica,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Vascular Pattern in Tumours To cite this article: (1957) Vascular Pattern in Tumours, Acta Radiologica,
A clinical study of neurological manifestations in HIV positive patients in a tertiary care hospital of Telangana, India
 Original Research Article A clinical study of neurological manifestations in HIV positive patients in a tertiary care hospital of Telangana, India Kamera Sateesh Kumar 1*, Veena Narisetty 2, P. Chandra
Original Research Article A clinical study of neurological manifestations in HIV positive patients in a tertiary care hospital of Telangana, India Kamera Sateesh Kumar 1*, Veena Narisetty 2, P. Chandra
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution
 Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Symptoms of a brain tumour in adults
 Symptoms of a brain tumour in adults A tumour is an abnormal growth caused by cells dividing in an uncontrolled manner. Approximately 9,300 people are diagnosed with a primary brain tumour each year. (Primary
Symptoms of a brain tumour in adults A tumour is an abnormal growth caused by cells dividing in an uncontrolled manner. Approximately 9,300 people are diagnosed with a primary brain tumour each year. (Primary
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Nervous System Test Bank
 Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Nervous System Test Bank Objective 4.01 Describe the basic functions of the nervous system. 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of nervous system? a. Sensation b. Protection
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Nervous System Test Bank Objective 4.01 Describe the basic functions of the nervous system. 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of nervous system? a. Sensation b. Protection
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Outcome and Prognosis of Metastatic Brain Tumour: A Study of 35 Cases
 Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience 2008; Vol. 24 (1) : 17-23 Outcome and Prognosis of Metastatic Brain Tumour: A Study of 35 Cases HARADHAN DEB NATH 1, KANAK KANTI BARUA 2, MOHAMMAD AFZAL HOSSAIN 3, MD
Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience 2008; Vol. 24 (1) : 17-23 Outcome and Prognosis of Metastatic Brain Tumour: A Study of 35 Cases HARADHAN DEB NATH 1, KANAK KANTI BARUA 2, MOHAMMAD AFZAL HOSSAIN 3, MD
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Nervous System Test Bank
 Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Nervous System Test Bank Objective 4.01 Describe the basic functions of the nervous system. 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of nervous system? a. Sensation b. Protection
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Nervous System Test Bank Objective 4.01 Describe the basic functions of the nervous system. 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of nervous system? a. Sensation b. Protection
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM
 TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT in HIV PATIENTS -a case based approach. Dr Jency Maria Koshy, CMC, Ludhiana
 FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT in HIV PATIENTS -a case based approach Dr Jency Maria Koshy, CMC, Ludhiana Case 1 Middle aged gentleman Diagnosed to have HIV 5 months prior to admission CD4 at the time of detection-132
FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT in HIV PATIENTS -a case based approach Dr Jency Maria Koshy, CMC, Ludhiana Case 1 Middle aged gentleman Diagnosed to have HIV 5 months prior to admission CD4 at the time of detection-132
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine
 Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Chapter 14, Part 2! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial Nerves! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3
 SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors
 Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Dr Eddie Mee. Neurosurgeon Auckland City Hospital, Ascot Integrated Hospital, MercyAscot Hospitals, Auckland
 Dr Eddie Mee Neurosurgeon Auckland City Hospital, Ascot Integrated Hospital, MercyAscot Hospitals, Auckland 16:30-17:25 WS #48: Current Management of Brain Bleeds and Tumours 17:35-18:30 WS #58: Current
Dr Eddie Mee Neurosurgeon Auckland City Hospital, Ascot Integrated Hospital, MercyAscot Hospitals, Auckland 16:30-17:25 WS #48: Current Management of Brain Bleeds and Tumours 17:35-18:30 WS #58: Current
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Selected radiosurgery cases from the Rotating Gamma Institute Debrecen, Hungary
 Selected radiosurgery cases from the Rotating Gamma Institute Debrecen, Hungary László Bognár M.D., Ph.D., József G. Dobai M.D., Gábor Csiky and Imre Fedorcsák M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Medical
Selected radiosurgery cases from the Rotating Gamma Institute Debrecen, Hungary László Bognár M.D., Ph.D., József G. Dobai M.D., Gábor Csiky and Imre Fedorcsák M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Medical
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Seventh Edition. The Nervous System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Stroke in the ED. Dr. William Whiteley. Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian
 Stroke in the ED Dr. William Whiteley Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian 2016 RCP Guideline for Stroke RCP guidelines for acute ischaemic stroke
Stroke in the ED Dr. William Whiteley Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian 2016 RCP Guideline for Stroke RCP guidelines for acute ischaemic stroke
P1: OTA/XYZ P2: ABC c01 BLBK231-Ginsberg December 23, :43 Printer Name: Yet to Come. Part 1. The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Clinical characteristics, seizure spread patterns and prognosis of seizures associated with a single small cerebral calcific CT lesion
 Seizure 1998; 7:153-157 Clinical characteristics, seizure spread patterns and prognosis of seizures associated with a single small cerebral calcific CT lesion J. M. K. MURTHY & V. SREENIVAS REDDY Department
Seizure 1998; 7:153-157 Clinical characteristics, seizure spread patterns and prognosis of seizures associated with a single small cerebral calcific CT lesion J. M. K. MURTHY & V. SREENIVAS REDDY Department
Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 131962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/131962 Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report F. Koech,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 131962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/131962 Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report F. Koech,
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Understand Your Disease: Brain Metastases
 Understand Your Disease: Brain Metastases Princess Margaret For patients and families coping with brain metastases Read this resource to know: What brain metastases are Common symptoms of brain metastases
Understand Your Disease: Brain Metastases Princess Margaret For patients and families coping with brain metastases Read this resource to know: What brain metastases are Common symptoms of brain metastases
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex
 Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The following information provides criteria for the evaluation of permanent impairment resulting from dysfunction brain, spinal cord and cranial nerves and certain peripheral
IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The following information provides criteria for the evaluation of permanent impairment resulting from dysfunction brain, spinal cord and cranial nerves and certain peripheral
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 with contrast material(s) 70470
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 with contrast material(s) 70470
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Diagnosis of Unusual Case of Cystecercal Meningoencephalitis Anita Kumari, Gaurav Mukhija, Ajeet Pratap Singh Journal of Pediatric
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Diagnosis of Unusual Case of Cystecercal Meningoencephalitis Anita Kumari, Gaurav Mukhija, Ajeet Pratap Singh Journal of Pediatric
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study
 Original Paper Med Principles Pract 2001;10:135 139 Received: October 8, 2000 Revised: July 4, 2001 Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study Salwa Ramadan Aduh Prosper
Original Paper Med Principles Pract 2001;10:135 139 Received: October 8, 2000 Revised: July 4, 2001 Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study Salwa Ramadan Aduh Prosper
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Prospective Study of Adult Onset Seizure
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 46-50 www.iosrjournals.org Prospective Study of Adult Onset Seizure
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 46-50 www.iosrjournals.org Prospective Study of Adult Onset Seizure
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
Health Learning Partnership 13 th September Neuroimaging. Headache Dementia Incidentalomas DR MARCUS BRADLEY CONSULTANT NEURORADIOLOGIST
 Health Learning Partnership 13 th September 2017 Neuroimaging DR MARCUS BRADLEY CONSULTANT NEURORADIOLOGIST Headache Dementia Incidentalomas Dr Marcus Bradley Consultant Neuroradiologist Interventional
Health Learning Partnership 13 th September 2017 Neuroimaging DR MARCUS BRADLEY CONSULTANT NEURORADIOLOGIST Headache Dementia Incidentalomas Dr Marcus Bradley Consultant Neuroradiologist Interventional
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults P. S. V. Ramana Murthy Associate Professor, Department of General
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults P. S. V. Ramana Murthy Associate Professor, Department of General
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Clinico-pathological study of intradural extramedullary spinal tumors
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Venugopal G et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2795-2799 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150685
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Venugopal G et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2795-2799 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150685
Surgery for Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy
 Surgery for Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy Seth F Oliveria, MD PhD The Oregon Clinic Neurosurgery Director of Functional Neurosurgery: Providence Brain and Spine Institute Portland, OR Providence
Surgery for Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy Seth F Oliveria, MD PhD The Oregon Clinic Neurosurgery Director of Functional Neurosurgery: Providence Brain and Spine Institute Portland, OR Providence
NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP. Neurology for MRCP Downloaded from The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2 and PACES
 NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2 and PACES This page intentionally left blank MRCP NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2
NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2 and PACES This page intentionally left blank MRCP NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2
The Nervous System. Nerves, nerves everywhere!
 The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome
 Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome SAN The Sudanese association of neurosurgeons By Dr. Abubakr Darrag Salim Ahmed Dr. Mohammed Awad Elzain Khartoum Sudan Pediatric
Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome SAN The Sudanese association of neurosurgeons By Dr. Abubakr Darrag Salim Ahmed Dr. Mohammed Awad Elzain Khartoum Sudan Pediatric
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Value of a Chest CT in the Evaluation of a Newly Detected Brain Tumor
 Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Senior Research Projects Southern Scholars 1999 The Value of a Chest CT in the Evaluation of a Newly Detected Brain Tumor Jennifer L. White John
Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Senior Research Projects Southern Scholars 1999 The Value of a Chest CT in the Evaluation of a Newly Detected Brain Tumor Jennifer L. White John
Dating Neurological Injury
 Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
