Radiation-Induced Cavernomas of the Brain
|
|
|
- Eleanore Barker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
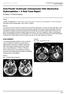
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26: , May 2005 Case Report Radiation-Induced Cavernomas of the Brain Rajan Jain, Patricia L. Robertson, Dheeraj Gandhi, Sachin K. Gujar, Karin M. Muraszko, and Stephen Gebarski Summary: The purpose of this report is to add support to the growing literature that there is a correlation between radiation and cavernomas of the brain, particularly if the radiation is received in childhood, as well as to increase awareness of this correlation in the radiology community. Retrospective review of our experience returned five patients who received radiation therapy while they were children and developed cavernomas in the irradiated tissues 3 41 years later. Cavernomas should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a hemorrhagic lesion in any patient who has received previous CNS radiation, particularly if he or she underwent radiation therapy in childhood. Cavernomas also known as cavernous hemangiomas and cavernous malformations are CNS vascular lesions composed of thin-walled, dilated capillary spaces with no intervening brain tissue (1). Most cavernomas are believed to be of congenital origin, either sporadic or autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance, and have an incidence as high as 0.5% (2). A correlation between radiation therapy and cavernoma has been suspected since 1994 (3). Since that time, additional cases have appeared in the literature (4 10), although only a few reports have been published in the radiology literature (7 9). Findings in Our Five Patients Our institutional review board ruled that this research project was exempt from review. Retrospective review of our experience with cavernomas over the past 3 years returned five patients who developed cavernomas in the treated field after having received prior cranial or craniospinal irradiation (Table). Age range at diagnosis of the cavernomas was 6 57 years (mean, 27 years). Age range at the time of irradiation was 3 16 years (mean, 7.5 years). Latency interval between the time of irradiation and time of detection of the cavernomas was 3 41 years (mean, 19.5 years). The mean latency period was 16 years for the patients irradiated in the 1st decade and 24.5 years for those irradiated in the 2nd decade. All cavernomas were in the irradiated field. Two patients received whole-brain irradiation for posterior fossa medulloblastomas (Fig 1), one received involved field irradiation for a posterior fossa ependymoma Received February 25, 2004; accepted after revision July 30. Presented at the 41st annual meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology, Washington, D.C., April 26 May 2, From the Departments of Radiology (R.J., D.G., S.K.G., S.G.), Neurology (P.L.R.), and Neurosurgery (K.M.M.), University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI. Address correspondence to Rajan Jain, MD, Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology, Henry Ford Health System, 2799 West Grand Boulevard, Detroit, MI American Society of Neuroradiology (Fig 2), one received craniospinal radiation for a suprasellar germinoma (Fig 3), and the fifth patient received cobalt radiation therapy for Cushing disease. Cavernomas were diagnosed incidentally in all five patients on routine surveillance imaging of their tumors or while being evaluated for unrelated problems. Two patients had multiple cavernomas, one with four lesions and the other with at least two lesions detected by use of MR imaging (Table). Progressive hemorrhage with enlargement of one cavernoma was seen on serial images in each of these two patients, although both were asymptomatic for bleeding. These cavernomas were in surgically accessible locations and were resected because of the progressive hemorrhage and in view of their increased risk for further bleeding. Histopathologic results confirmed the diagnosis of cavernoma. At the time of this writing four patients with seven lesions are being followed up with surveillance imaging. Three patients also had other radiation-induced neoplasms, including two patients with meningiomas and one with a scalp juvenile dermatofibrosarcoma, all in the irradiated fields. Three patients also had hypothalamic-pituitary axis dysfunction related to radiation injury. Discussion Many of the deleterious effects of radiation on the CNS are well known. These include early effects that can occur within a few weeks of the radiation therapy, such as vasogenic edema due to increased capillary permeability and vasodilation (10) and delayed effects that can occur months to years after the irradiation. The latter include cerebral atrophy, white matter necrosis, demyelination, gliosis, and induction of neoplasm (10). Delayed radiation injury, however, can also manifest as vasculopathy with hyalinization and fibrinoid necrosis of vascular walls, resulting in occlusion and infarction as well as vascular proliferative lesions such as capillary telangiectasia and cavernoma (4, 11 13). Capillary telangiectasias, thin-walled ectatic capillaries with intervening normal brain parenchyma, which distinguishes them from cavernomas, usually occur 3 9 months after irradiation (12, 13). Cavernomas take a longer time to develop after radiation. Reported latency periods for radiation-induced cavernomas range from 1 to 26 years (4). It is interesting to note that capillary telangiectasias and cavernomas may be sequential variations of the same pathologic process (5, 14). Cavernomas have been hypothesized to result from a proliferative vasculopathy that begins with the development of capillary telangiectasias triggered by radiation injury to the cerebral microcirculation (5). Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been demonstrated in an animal model of radiation-in- 1158
2 AJNR: 26, May 2005 RADIATION-INDUCED CAVERNOMAS OF THE BRAIN 1159 Case Material Case No. Age*/ Sex Primary CNS Neoplasm Or Disease Age at RT (years) RT and Dose Latency Interval (years) Clinical Presentation Location of CM s Number of CM s Treatment of CM s Associated Findings 1 18/F Posterior fossa Medulloblastoma 2 6/M Posterior fossa Ependymoma 3 34/M Posterior fossa Medulloblastoma 4 21/M Supra-sellar Germinoma 3 Craniospinal RT 54 Gy (T) 3 Involved field RT 50.4 Gy 3 Craniospinal RT 54 Gy (T) 13 Craniospinal RT 50.4 Gy (T) 15 Incidental Lt temporal lobe/ Intraventricular 3 Incidental (Subsequent asymptomatic Hemorrhage) Rt cerebellum 1 Observation Lt cerebellum Rt cerebellum Rt temporal lobe 1 Observation Meningioma Scalp DFS Panhypopitutarism Surgery Observation Observation TH & GH Deficiency 31 Incidental Lt frontal lobe 1 Observation Meningioma 8 Incidental (Subsequent asymptomatic hemorrhage) Rt fronto-parietal lobe 1 Surgery /F Cushing s Disease 16 Cobalt RT 41 Incidental Rt frontal lobe 1 Observation Panhypopitutarism Unknown dose Note. Age* indicates Age at the time of diagnosis of cavernomas; RT, Radiation therapy; T, Total Dose; CS, Craniospinal Dose; CM s, cavernous malformations; DFS, Dermatofibrosarcoma; TH, Thyroid hormones; GH, Growth hormone.
3 1160 JAIN AJNR: 26, May 2005 FIG 1. Case 1. A, Axial T2-weighted MR image obtained 12 years after craniospinal radiation therapy at 3 years of age for a posterior fossa medulloblastoma showing no lesion in the left temporal lobe/temporal horn. B, Axial T1-weighted and, C, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MR images obtained 15 years after the radiation therapy, showing a lobulated area of mixed signal intensity with peripheral hypointense rim (white arrow) in left medial temporal lobe/temporal horn, typical popcorn MR appearance of a cavernous angioma. duced spinal injury. VEGF, along with other possible vasculogenic factors, could initiate such neoangiogenesis, inducing the formation of capillary telangiectasia that eventually develops into cavernomas (15). An alternative explanation is that radiation may cause direct DNA damage, which leads to formation of cavernomas. DNA mutations at multiple foci have been linked to the autosomal dominant form of cavernoma development (3, 16). Ciricillo et al (3) first reported cavernomas as a possible result of prior CNS irradiation in Gaensler et al (8) described the appearance of hemorrhagic foci on MR images following CNS irradiation; these foci were similar to the cryptic vascular malformations described as radiation-induced telangiectasia. Koike et al (9) concluded that radiationinduced telangiectasia appeared to occur in at least 20% of children who undergo cranial irradiation; however, higher radiation dose was not significantly associated with higher frequency of telangiectasia, although there was a trend in this direction. From one of the recent analysis of 40 patients reported in the literature through 2002, a conclusion was made that, not only are cavernomas induced by radiation, but also that this occurs at a significantly higher rate when patients are irradiated as children (4). In that study, a significant preponderance of cavernomas was found in patients who were irradiated as children, even when the analysis was controlled for possible selection bias of their potentially longer survival times and the relatively high incidence of sporadic and familial cavernoma. Our series, in which all five patients were children at the time they received radiation therapy, supports this conclusion. A possible explanation for this relationship is that some of the angiogenic factors hypothesized to be involved in the development of cavernomas after irradiation are expressed at the highest levels in children (17, 18). Analysis of previously reported radiation-associated cavernomas found a correlation between a radiation dose 30 Gy and a shorter latency to development of cavernomas (4). This could not be assessed in our series because all four patients for whom the radiation dose was known received a total dose 30 Gy to the field in which the cavernoma was found. We found a mean latency of 16 years for our patients, who received radiation when they were 10 years old. This is significantly longer than the 4.75-year mean latency reported in the literature for such patients (4). The reason for this difference is not certain but could reflect that all of our patients were asymptomatic from their cavernomas. Accordingly, the cavernomas in our patients may have been present long before they were detected. Our finding of 100% asymptomatic patients matches one of the most recent studies about asymptomatic radiation-induced telangiectasias (9) although in another study 50% of the 40 reported patients had signs or symptoms referable to their cavernomas (4). Two of our five patients showed recent asymptomatic hemorrhage associated with their cavernomas. Cavernomas are associated with hemorrhage, but the estimated risk is only % per year (19, 20). Radiation-induced cavernomas may, however, have increased risk of hemorrhage (5). The appearance of a new brain lesion or hemorrhage in a patient who has undergone radiation therapy for a CNS neoplasm always raises the possibility of neoplastic recurrence or metastases. Ordinarily, it is not difficult to differentiate a cavernoma from other neoplasms, because most cavernomas have a distinctive appearance of their nidus with little or no surrounding edema. Acute hemorrhage can complicate the appearance and result in blurring of the nidus and reactive edema, but differentiation is still usually possible on the basis of the CT and MR imaging character of the nidus (6). MR imaging usu-
4 AJNR: 26, May 2005 RADIATION-INDUCED CAVERNOMAS OF THE BRAIN 1161 FIG 2. Case 2. A, Axial T2- and, B, T1-weighted MR images obtained 3 years after involved field radiation therapy at 3 years of age for a posterior fossa ependymoma showing a large hemorrhagic, lobulated lesion of mixed signal intensity (white arrow) in left cerebellar hemisphere and vermis. Two more small cavernomas (black arrowheads) are seen in the right cerebellum. Postoperative changes (black arrow) are noted in the right cerebellum. C, Axial T2*-weighted MR image shows an area of blooming due to another small cavernoma (black arrow) in the right temporooccipital region. FIG 3. Case 4. A, Axial T2-weighted MR image obtained 6 years after craniospinal radiation therapy at age 13 years for a suprasellar germinoma showing no lesion in right frontoparietal region. B, Axial T2-weighted and, C, FLAIR MR images obtained 8 years after the radiation therapy showing interval appearance a round lesion of mixed signal intensity with a fluid-fluid level and peripheral hypointense rim (black arrow) in right frontoparietal region. ally shows a reticulated core of heterogeneous signal intensity with a dark peripheral rim of hemosiderin, giving a typical popcorn appearance (14). CT usually shows ring-like calcification with core reticulation of variable attenuation. Conclusion In light of the fairly well established correlation between radiation and cavernoma formation, it is prudent to consider cavernoma in the differential diagnosis of a hemorrhagic lesion in any patient who has received previous CNS radiation, particularly if he or she underwent radiation therapy in childhood. References 1. Russel DS, Rubinstein LJ. Pathology of Tumors of the Nervous System. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins;1989: Rigamonti D, Hadley MN, Drayer BP, et al. Cerebral cavernous malformations: incidence and familial occurrence. N Engl J Med 1988;319: Ciricillo SF, Cogen PH, Edwards MS. Pediatric cryptic vascular malformations: presentation, diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Neurosurg 1994;20: Heckl S, Aschoff A, Kunze S. Radiation-induced cavernous hemangiomas of the brain: a late effect predominantly in children. Cancer 2002;94: Larson JJ, Ball WS, Bove KE, et al. Formation of intracerebral cavernous malformations after radiation treatment for central nervous system neoplasia in children. J Neurosurg 1998;88: Olivero WC, Deshmukh P, Gujrati M. Radiation-induced cavern-
5 1162 JAIN AJNR: 26, May 2005 ous angioma mimicking metastatic disease. Br J Neurosurg 2000;14: Maeder P, Gudinchet F, Meuli R, et al. Development of a cavernous malformation of the brain. Am J Neuroradiol 1998;19: Gaensler EH, Dillon WP, Edwards MS, et al. Radiation-induced telangiectasia in the brain simulates cryptic vascular malformations at MR imaging. Radiology 1994;193: Koike S, Aida N, Hata M, et al. Asymptomatic radiation-induced telangiectasia in children after cranial irradiation: frequency, latency, and dose relation. Radiology 2004;230:93 99 [Epub November 26, 2003] 10. Valk PE, Dillon WP. Radiation injury of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991;12: Poussaint TY, Siffert J, Barnes PD, et al. Hemorrhagic vasculopathy after treatment of central nervous system neoplasia in childhood: diagnosis and follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16: Hassler O, Movin A. Microangiographic studies on changes in the cerebral vessels after irradiation. 1. Lesions in the rabbit produced by 60Co gamma-rays, 195kV and 34MV roentgen rays. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol 1966;4: Reinhold HS, Hopewell JW. Late changes in the architecture of blood vessels of the rat brain after irradiation. Br J Radiol 1980;53: Rigamonti D, Drayer BP, Johnson PC, et al. The MRI appearance of cavernous malformations (angiomas). J Neurosurg 1987; 67: Tsao MN, Li YQ, Lu G, et al. Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with radiation-induced blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1999;58: Gunel M, Awad IA, Finberg K, et al. Genetic heterogeneity of inherited cerebral cavernous malformation. Neurosurgery 1996;38: Rivard A, Berthou-Soulie L, Principe N, et al. Age-dependent defect in vascular endothelial growth-factor expression is associated with reduced hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity. J Biol Chem 2000;275: Malamitsi-Puchner A, Tziotis J, Tsonou A, et al. Changes in serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in males and females throughout life. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2000;7: Del Curling O Jr, Kelly DL Jr, Elster AD, Craven TE. An analysis of the natural history of cavernous angiomas. J Neurosurg 1991;75: Robinson JR, Awad IA, Little JR. Natural history of the cavernous angioma. J Neurosurg 1991;75:
There are clear indications that gliomas and meningiomas can. Radiation-Induced Cavernous Hemangiomas of the Brain
 3285 Radiation-Induced Cavernous Hemangiomas of the Brain A Late Effect Predominantly in Children Stefan Heckl, M.D. 1 Alfred Aschoff, M.D. 2 Stefan Kunze, M.D. 2 1 Department of Oncological Diagnostics
3285 Radiation-Induced Cavernous Hemangiomas of the Brain A Late Effect Predominantly in Children Stefan Heckl, M.D. 1 Alfred Aschoff, M.D. 2 Stefan Kunze, M.D. 2 1 Department of Oncological Diagnostics
Neurosurg Focus 3 (3):Clinical Pearl, 1997
 Neurosurg Focus 3 (3):Clinical Pearl, 1997 De novo formation of a central nervous system cavernous malformation: implications for predicting risk of hemorrhage Case report and review of the literature
Neurosurg Focus 3 (3):Clinical Pearl, 1997 De novo formation of a central nervous system cavernous malformation: implications for predicting risk of hemorrhage Case report and review of the literature
Incidence of cavernoma development in children after radiotherapy for brain tumors
 J Neurosurg (5 Suppl Pediatrics) 106:379 383, 2007 Incidence of cavernoma development in children after radiotherapy for brain tumors SASHA BURN, F.R.C.S.(SN), 1 ROXANA GUNNY, F.R.C.R., 2 KIM PHIPPS, B.SC.
J Neurosurg (5 Suppl Pediatrics) 106:379 383, 2007 Incidence of cavernoma development in children after radiotherapy for brain tumors SASHA BURN, F.R.C.S.(SN), 1 ROXANA GUNNY, F.R.C.R., 2 KIM PHIPPS, B.SC.
Cumulative incidence of radiation-induced cavernomas in long-term survivors of medulloblastoma
 J Neurosurg (2 Suppl Pediatrics) 104:103 107, 2006 Cumulative incidence of radiation-induced cavernomas in long-term survivors of medulloblastoma SEAN M. LEW, M.D., JOSEPH N. MORGAN, M.D., ESTEE PSATY,
J Neurosurg (2 Suppl Pediatrics) 104:103 107, 2006 Cumulative incidence of radiation-induced cavernomas in long-term survivors of medulloblastoma SEAN M. LEW, M.D., JOSEPH N. MORGAN, M.D., ESTEE PSATY,
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
CCMs and DVAs are both low-flow vascular malformations
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.A. Petersen L.A. Morrison R.M. Schrader B.L. Hart Familial versus Sporadic Cavernous Malformations: Differences in Developmental Venous Anomaly Association and Lesion Phenotype BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.A. Petersen L.A. Morrison R.M. Schrader B.L. Hart Familial versus Sporadic Cavernous Malformations: Differences in Developmental Venous Anomaly Association and Lesion Phenotype BACKGROUND
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) comprise
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS. Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University
 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University Introduction Brain and spinal cord vascular malformations can be separated into five main categories: 1) Arteriovenous malformation,
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University Introduction Brain and spinal cord vascular malformations can be separated into five main categories: 1) Arteriovenous malformation,
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
Radiological Appearance of Extra-axial CNS Hemangioma
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 183-190 183 Radiological Appearance of Extra-axial CNS Hemangioma MING-SHIANG YANG CLAYTON CHI-CHANG CHEN WEN-HSIEN CHEN HAO-CHUN HUNG SAN-KAN LEE Department of Radiology, Taichung
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 183-190 183 Radiological Appearance of Extra-axial CNS Hemangioma MING-SHIANG YANG CLAYTON CHI-CHANG CHEN WEN-HSIEN CHEN HAO-CHUN HUNG SAN-KAN LEE Department of Radiology, Taichung
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Pathological Evaluation of Radiation-Induced Vascular Lesions of the Brain: Distinct from De Novo Cavernous Hemangioma
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 2015 Nov;56(6):1714-1720 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Pathological Evaluation of Radiation-Induced Vascular Lesions of the Brain: Distinct from De Novo Cavernous Hemangioma
Original Article Yonsei Med J 2015 Nov;56(6):1714-1720 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Pathological Evaluation of Radiation-Induced Vascular Lesions of the Brain: Distinct from De Novo Cavernous Hemangioma
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Imaging The Turkish Saddle. Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Common and uncommon differential diagnosis of cerebral microhemorrhages
 Common and uncommon differential diagnosis of cerebral microhemorrhages Poster No.: C-0261 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. C. Rodrigues 1, S. B. Bergamaschi 1, C. F. R. B. Milito
Common and uncommon differential diagnosis of cerebral microhemorrhages Poster No.: C-0261 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. C. Rodrigues 1, S. B. Bergamaschi 1, C. F. R. B. Milito
The Use of Early Postoperative MR in Detecting Residual Juvenile Cerebellar Pilocytic Astrocytoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:151 156, January 1998 The Use of Early Postoperative MR in Detecting Residual Juvenile Cerebellar Pilocytic Astrocytoma Nancy K. Rollins, Perry Nisen, and Kenneth N. Shapiro PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:151 156, January 1998 The Use of Early Postoperative MR in Detecting Residual Juvenile Cerebellar Pilocytic Astrocytoma Nancy K. Rollins, Perry Nisen, and Kenneth N. Shapiro PURPOSE:
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Arvinder Singh 1,*, Poonam Ohri 1, Manjeet Kaur 2 and Sohan Singh 1. Keywords: Unusual Cerebral Cavernoma, Imaging Modalities, Disease Outcome.
 26 Journal of Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging, 2014, 2, 26-31 Unusual Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Mimicking Intracranial Malignancy: Role of Computed Tomography, Conventional MR Sequences and Susceptibility
26 Journal of Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging, 2014, 2, 26-31 Unusual Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Mimicking Intracranial Malignancy: Role of Computed Tomography, Conventional MR Sequences and Susceptibility
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care
 Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care Writer Classroom Rishi R. Lulla, MD MS Objectives Introduce the common pediatric brain tumors Discuss current treatment strategies for pediatric brain
Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care Writer Classroom Rishi R. Lulla, MD MS Objectives Introduce the common pediatric brain tumors Discuss current treatment strategies for pediatric brain
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports
 Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Dumbbell Shaped Thoracic Spine Cavernous Hemangioma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 3 Number 1 Dumbbell Shaped Thoracic Spine Cavernous Hemangioma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature J Gonzalez-Cruz, A Nanda Citation J Gonzalez-Cruz,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 3 Number 1 Dumbbell Shaped Thoracic Spine Cavernous Hemangioma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature J Gonzalez-Cruz, A Nanda Citation J Gonzalez-Cruz,
Accuracy of intra-operative rapid diagnosis by Squash smear in CNS lesions An early institutional experience. KK Bansal,
 Accuracy of intra-operative rapid diagnosis by Squash smear in CNS lesions An early institutional experience. KK Bansal, Monika Bansal, Sanjeev Kishore, Anuradha K, Meena H, Dushyant G. Department of Neurosurgery
Accuracy of intra-operative rapid diagnosis by Squash smear in CNS lesions An early institutional experience. KK Bansal, Monika Bansal, Sanjeev Kishore, Anuradha K, Meena H, Dushyant G. Department of Neurosurgery
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Sports/activities and ALD
 Sports/activities and ALD Gerald Raymond, MD Penn State Children s Hospital 15:00 Dr Gerald Raymond- Sports and ALD 1 Can Head Injury Influence the site of Demyelination in Adrenoleukodystrophy? Wilkinson
Sports/activities and ALD Gerald Raymond, MD Penn State Children s Hospital 15:00 Dr Gerald Raymond- Sports and ALD 1 Can Head Injury Influence the site of Demyelination in Adrenoleukodystrophy? Wilkinson
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
A Rare Cause of Cerebellar Ataxia Syndrome: Superficial Siderosis of Central Nervous System
 257 Rare Cause of Cerebellar taxia Syndrome: Superficial Siderosis of Central Nervous System Simon Kang Seng Ting, MRCP, Kumar M Prakash, FRCP bstract- Purpose: To describe and emphasize importance of
257 Rare Cause of Cerebellar taxia Syndrome: Superficial Siderosis of Central Nervous System Simon Kang Seng Ting, MRCP, Kumar M Prakash, FRCP bstract- Purpose: To describe and emphasize importance of
TABLES. Table 1: Imaging. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Author (Year) Description of Study Classification Process / Evidence Class
 TABLES Table 1: Imaging Kremer et al (2002) 2 Study Design: Prospective followed case series. Patient Population: Fifty adult patients with NFPA Study Description: Patients underwent MRI before surgery,
TABLES Table 1: Imaging Kremer et al (2002) 2 Study Design: Prospective followed case series. Patient Population: Fifty adult patients with NFPA Study Description: Patients underwent MRI before surgery,
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Overview of Cerebrovascular Malformations
 Overview of Cerebrovascular Malformations Pursuit of Neurovascular Excellence 8 th annual Barbara Albani, MD Chief, Neurointerventional Surgery Christiana Care Health Systems Newark, DE Financial Disclosures
Overview of Cerebrovascular Malformations Pursuit of Neurovascular Excellence 8 th annual Barbara Albani, MD Chief, Neurointerventional Surgery Christiana Care Health Systems Newark, DE Financial Disclosures
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution
 Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Surgery of Angiomas in the Brainstem With a Stress on the Presence of Telangiectasia
 II-4. Spinal and Vascular Malformation Other than AVM Surgery of Angiomas in the Brainstem With a Stress on the Presence of Telangiectasia Masashi FUKUI, Toshio MATSUSHIMA, Kiyonobu IKEZAKI, Yoshihiro
II-4. Spinal and Vascular Malformation Other than AVM Surgery of Angiomas in the Brainstem With a Stress on the Presence of Telangiectasia Masashi FUKUI, Toshio MATSUSHIMA, Kiyonobu IKEZAKI, Yoshihiro
Thursday, January 24, 2019
 Thursday, January 24, 2019 6:45am 7:30am 7:30am 7:45am 7:45am 9:45am 9:45am 10:00am 10:00am- 12:00pm 12:00pm 12:30pm 12:30pm 1:30pm 1:30pm 3:30pm 3:30pm-3:45pm 3:45pm - 4:45pm 4:45pm 5:45pm Registrations:
Thursday, January 24, 2019 6:45am 7:30am 7:30am 7:45am 7:45am 9:45am 9:45am 10:00am 10:00am- 12:00pm 12:00pm 12:30pm 12:30pm 1:30pm 1:30pm 3:30pm 3:30pm-3:45pm 3:45pm - 4:45pm 4:45pm 5:45pm Registrations:
RECURRENT ADRENAL DISEASE. Megan Applewhite Endorama 2/19/2015 SR , SC
 RECURRENT ADRENAL DISEASE Megan Applewhite Endorama 2/19/2015 SR 2412318, SC 3421561 Category: Adrenal Attendings: Angelos & Grogan PATIENT #1 36yo woman with a hx of Cushing s Syndrome and right adrenalectomy
RECURRENT ADRENAL DISEASE Megan Applewhite Endorama 2/19/2015 SR 2412318, SC 3421561 Category: Adrenal Attendings: Angelos & Grogan PATIENT #1 36yo woman with a hx of Cushing s Syndrome and right adrenalectomy
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
CNS, Neuroradiology brain, Radiation physics, MR, Complications, Neoplasia /ecr2014/C-0010
 Cerebral radionecrosis: imaging features, differential diagnosis and developmental characteristics. Experience in our center, pictorial essay and literature rewiew. Poster No.: C-0010 Congress: ECR 2014
Cerebral radionecrosis: imaging features, differential diagnosis and developmental characteristics. Experience in our center, pictorial essay and literature rewiew. Poster No.: C-0010 Congress: ECR 2014
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0027 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0027 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
INTRACRANIAL CAVERNOMA
 INTRACRANIAL CAVERNOMA INTRODUCTION CEREBRAL CAVERNOUS MALFORMATION (CCM), CAVERNOUS HEMANGIOMA, CAVERNOUS ANGIOMA, CRYPTIC VASCULAR MALFORMATION,OCCULT VASCULAR MALFORMATION, HEMORRHOID OF BRAIN. Developmental
INTRACRANIAL CAVERNOMA INTRODUCTION CEREBRAL CAVERNOUS MALFORMATION (CCM), CAVERNOUS HEMANGIOMA, CAVERNOUS ANGIOMA, CRYPTIC VASCULAR MALFORMATION,OCCULT VASCULAR MALFORMATION, HEMORRHOID OF BRAIN. Developmental
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MEDULLOBLASTOMA AND PNET CNS Site Group Medulloblastoma and PNET Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MEDULLOBLASTOMA AND PNET CNS Site Group Medulloblastoma and PNET Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
Where Has My Vision Gone? Evaluation of Sellar Lesions. Caleb Stowell,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD November 2008
 Where Has My Vision Gone? Evaluation of Sellar Lesions Caleb Stowell,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD November 2008 Objectives Present a case highlighting the clinical presentation and evaluation of a sellar
Where Has My Vision Gone? Evaluation of Sellar Lesions Caleb Stowell,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD November 2008 Objectives Present a case highlighting the clinical presentation and evaluation of a sellar
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Acavernous angioma, also known as a cavernous malformation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.J. Yun D.G. Na B.J. Kwon H.G. Rho S.-H. Park Y.-L. Suh K.-H. Chang A T1 Hyperintense Perilesional Signal Aids in the Differentiation of a Cavernous Angioma from Other Hemorrhagic Masses
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.J. Yun D.G. Na B.J. Kwon H.G. Rho S.-H. Park Y.-L. Suh K.-H. Chang A T1 Hyperintense Perilesional Signal Aids in the Differentiation of a Cavernous Angioma from Other Hemorrhagic Masses
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Neurosurgery Review. Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008
 Neurosurgery Review Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008 Dr. Mudit Sharma, Neurosurgeon Manassas, Fredericksburg, Virginia http://www.virginiaspinespecialists.com Phone: 1-855-SPINE FIX (774-6334) Fundamentals
Neurosurgery Review Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008 Dr. Mudit Sharma, Neurosurgeon Manassas, Fredericksburg, Virginia http://www.virginiaspinespecialists.com Phone: 1-855-SPINE FIX (774-6334) Fundamentals
Laurie A. Loevner, MD
 Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Paraspinal Venous Malformation Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Paraspinal Venous Malformation Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 06/04/2010 History 2 year old with history of fall. Rule out spinal injury. Diagnosis Paraspinal Venous Malformation Additional Clinical CT of the
Paraspinal Venous Malformation Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 06/04/2010 History 2 year old with history of fall. Rule out spinal injury. Diagnosis Paraspinal Venous Malformation Additional Clinical CT of the
Visual pathways in the chiasm
 Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
X-ray Corner. Imaging of The Pancreas. Pantongrag-Brown L
 X-ray Corner 125 Imaging of The Pancreas Modern imaging modalities commonly used in pancreas include ultrasound (US), CT, and MRI. Pancreas is a retroperitoneal organ which makes it difficult to visualize
X-ray Corner 125 Imaging of The Pancreas Modern imaging modalities commonly used in pancreas include ultrasound (US), CT, and MRI. Pancreas is a retroperitoneal organ which makes it difficult to visualize
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Diffuse Proliferative Cerebral Angiopathy: A case report and review of the literature
 Diffuse Proliferative Cerebral Angiopathy: A case report and review of the literature Rohit 1*, Poh Sun Goh 1 1. Department of Radiology, National University hospital, Singapore * Correspondence: Dr. Rohit,
Diffuse Proliferative Cerebral Angiopathy: A case report and review of the literature Rohit 1*, Poh Sun Goh 1 1. Department of Radiology, National University hospital, Singapore * Correspondence: Dr. Rohit,
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Uncommon Symptomatic Cerebral Vascular Malformations
 Uncommon Symptomatic Cerebral Vascular Malformations Mauro Bergui and Gianni Boris Bradac Summary: We describe three cases of unusual vascular malformations in which the most relevant angiographic findings
Uncommon Symptomatic Cerebral Vascular Malformations Mauro Bergui and Gianni Boris Bradac Summary: We describe three cases of unusual vascular malformations in which the most relevant angiographic findings
Delayed Cerebral Metastases from Completely Resected Cardiac Myxoma: Case Report and Review of Literature
 Delayed Cerebral Metastases from Completely Resected Cardiac Myxoma: Case Report and Review of Literature Ah Hyun Kim 2, Jae-Wook Lee 1, Mi-Kyung Lee 3, Pyeong Ho Yoon 1, Min Jung Kim 2 Cardiac myxoma
Delayed Cerebral Metastases from Completely Resected Cardiac Myxoma: Case Report and Review of Literature Ah Hyun Kim 2, Jae-Wook Lee 1, Mi-Kyung Lee 3, Pyeong Ho Yoon 1, Min Jung Kim 2 Cardiac myxoma
Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of 27 Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
General Data. Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30
 General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
Spinal cord tumours Luc van den Hauwe et al.
 overview spinal cord tumours L. van den Hauwe 1,2, D. Balériaux 3, J.W. Van Goethem 2, C. Venstermans 2, F. De Belder 2, P.M. Parizel 2 introduction imaging spinal tumour classification spinal cord tumours
overview spinal cord tumours L. van den Hauwe 1,2, D. Balériaux 3, J.W. Van Goethem 2, C. Venstermans 2, F. De Belder 2, P.M. Parizel 2 introduction imaging spinal tumour classification spinal cord tumours
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM..
 Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
Journal of Radiology Case Reports
 Pediatric Holohemispheric Developmental Venous Anomaly: Definitive characterization by 3D Susceptibility Weighted Magnetic Resonance Angiography Michael A. Casey 1, Sourabh Lahoti 2, Ajeet Gordhan 2* 1.
Pediatric Holohemispheric Developmental Venous Anomaly: Definitive characterization by 3D Susceptibility Weighted Magnetic Resonance Angiography Michael A. Casey 1, Sourabh Lahoti 2, Ajeet Gordhan 2* 1.
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
In some patients with pituitary macroadenoma, visual acuity
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
