PREVALENCE OF CANINE EPITHELIAL, MELANOCYTIC AND MESENCHYMAL TUMOURS OF THE SKIN AND SOFT TISSUES: A 10-YEAR STUDY
|
|
|
- Tracey Farmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2011), 14, No 3, PREVALENCE OF CANINE EPITHELIAL, MELANOCYTIC AND MESENCHYMAL TUMOURS OF THE SKIN AND SOFT TISSUES: A 10-YEAR STUDY Summary R. SIMEONOV 1, I. DINEV 1, G. SIMEONOVA 2, N. GORANOV 2, M. PASKALEV 2, S. KRASTEV 2, I. TODOROVA 2, T. CHAPRAZOV 2, R. ROIDEV 2, I. BORISSOV 2, H. HUBENOV 2 & D. DINEV 2 1 Department of General and Clinical Pathology, 2 Department of Veterinary Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Stara Zagora, Bulgaria Simeonov, R., I. Dinev, G. Simeonova, N. Goranov, M. Paskalev, S. Krastev, I. Todorova, Ts. Chaprazov, R. Roidev, I. Borissov, H. Hubenov & D. Dinev, Prevalence of canine epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours of the skin and soft tissues: A 10- year study. Bulg. J. Vet. Med., 14, No 3, А histopathological analysis of 430 specimens of canine skin tumours obtained in the period , was performed at the Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Bulgaria. The tumours were classified according to the last World Health Organization classification. The incidence of benign and malignant neoplasms was 48.14% and 51.86% respectively. Among the total number of skin tumours, 250 cutaneous growths were diagnosed as epithelial and melanocytic tumours and another 78 as mesenchymal skin and soft tissue tumours. The most frequently diagnosed tumours from the skin epithelial and melanocytic group were hepatoid gland adenoma (9.3 %), squamous cell carcinoma (8.6 %), hepatoid gland carcinoma (5.34 %) and basalioma (5.11 %). The most frequently diagnosed canine mesenchymal skin and soft tissue tumours were lipoma (5.58 %), fibrosarcoma (4.41 %), haemangiopericytoma (2.32 %) and haemangioma (2.09 %). Key words: dogs, incidence, melanocytic, mesenchymal, skin epithelial, tumours INTRODUCTION The skin is continuously exposed to a wide variety of chemical and physical insult and other environmental factors, and therefore, is prone to neoplastic proliferation. Tumours of the skin and subcutaneous tissues are the commonest tumours affecting dogs, accounting for approximately one third of all tumours encountered in the species (Brodey, 1970; Finnie & Bostock, 1979; Bostock, 1986; Rothwell et al., 1987). The incidence of cutaneous tumours in dogs is estimated to be 450 cases every years per 100,000 dogs (Priester, 1979; Bostock, 1986). Approximately 20 % to 40 % of primary tumours of the skin and subcutaneous tissues are histologically malignant in the dog, compared to 50 65% in the cat (Brodey, 1970; Bostock, 1986; Carpenter et al., 1987; Kaldrymidou et al., 2002; Mucuratirwa et al., 2005). Epithelial and melanocytic skin tumours appeared in approximately 38% of cases, while mesenchymal skin tumours in 30% of
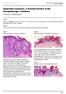
2 Prevalence of canine epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours of the skin and soft tissues cases (Chalita et al., 2001). The age of the dogs with diagnosed skin tumours is reported to range widely between 4 months and 16 years, although the average age is approximately 9 years (Tzvetkov, 1998; Kaldrymidou et al., 2002). One report calculated the odds ratio of the development of malignant cutaneous tumours in dogs based on age and breed (Kaldrymidou, 2002). The researcher found that the risk increased linearly by a factor of 1.1 per year of increasing age and that purebred dogs were twice as likely to develop a malignancy as crossbred dogs. Information on the prevalence and distribution of individual cutaneous tumours helps veterinary practitioners to diagnose them in time, determine an appropriate therapy, and anticipate an adequate prognosis (Vail & Withrow, 2001). The study aims to determine the relative prevalence and distribution of canine skin epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours in bioptic samples, received and analyzed between at the Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Bulgaria. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals and tumours The study was performed between at the Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Bulgaria. Four hundred and thirty samples of spontaneous skin tumour growths in dogs were studied. The study included dogs of all breeds and both sexes (216 male dogs and 214 bitches), aged between 3 months and 15 years. Histopathologic examination For histopathologic examination, the tissues were fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered neutral formalin, routinely processed, parafin embedded, and stained with hematoxyllin and eosin (H&E). Replicate sections of particular cases were also stained with special stains such Giemsa, periodic acid-schiff and toluidine blue whenewer needed to confirm the diagnosis. All tumour diagnoses were histopathologically confirmed according to WHO International Histological Classification of Tumours of Domestic Animals (Goldschmidt et al., 1998). The criteria for histopathological classification of investigated tumours included cellular and nuclear pleomorphism, number of nucleoli, frequency of mitosis, discreteness of cellular borders, presence of necrosis and stromal tissue. RESULTS Based on the final diagnosis, 223 (51.86%) out of 430 cutaneous neoplasms were malignant, while 207 (48.14 %) were benign. Among the biopsy specimens, 250 cases were diagnosed as skin epithelial and melanocytic tumours and 78 cases as mesenchymal tumours of skin and soft tissues (Table 1). The most frequently diagnosed epithelial and melanocytic tumours were hepatoid adenoma (9.3%), squamous cell carcinoma (8.6%), hepatoid carcinoma (5.34%) and basal cell tumour (5.11%). The other neoplastic types varied between 0.23 % and 4.18 %. Hepatoid gland adenoma is a benign tumour of the modified sebaceous gland developing on the skin of the anal and paranal region, as well as on the tail, hind limbs, laterally on the preputium, on the back and other locations. Of all 40 cases, 172 BJVM, 14, No 3
3 Simeonov, R., I. Dinev, G. Simeonova, N. Goranov, M. Paskalev, S. Krastev, I. Todorova Table 1. Incidence of canine skin epithelial, melanocytic and mesencymal tumours diagnosed at the Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Stara Zagora from 2000 to Tumour diagnosis Number (%)* Skin epithelial and melanocytic tumours Hepatoid gland adenoma 40 (9.30) Squamous cell carcinoma 37 (8.60) Hepatoid carcinoma 23 (5.34) Basalioma 22 (5.11) Malignant melanoma 18 (4.18) Anal sac carcinoma 12 (2.79) Apocrine adenoma 12 (2.79) Anal sac adenoma 10 (2.32) Apocrine carcinoma 10 (2.32) Sebaceous adenoma 8 (1.86) Sebaceous carcinoma 8 (1.86) Ceruminous adenoma 8 (1.86) Ceruminous carcinoma 8 (1.86) Benign melanoma 7 (1.62) Papilloma 6 (1.39) Meibomian adenoma 6 (1.39) Trichoepithelioma 2 (0.46) Meibomian carcinoma 1 (0.23) Pilomatricoma 1 (0.23) Total 250 (58.13) Mesenchymal tumours of skin and soft tissues Lipoma 24 (5.58) Fibrosarcoma 19 (4.41) Haemangioma 9 (2.09) Liposarcoma 8 (1.86) Canine 10 (2.32) haemangipericytoma Fibroma 4 (0.93) Myxoma 2 (0.46) Myxosarcoma 1 (0.23) Schvannoma 1 (0.23) Total 78 (18.14) * of all cutaneous tumours. 28 were observed in male dogs aged approximately 11 years. Histologically, the neoplastic parenchyma was composed of cells with well-defined borders and pale eosinophilic cytoplasm, whose structure looked like liver trabeculae. The cells were polyhedral and had centrally located large, ovoid nuclei with a central small nucleolus, abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and distinct cell borders. Basaloid reserve cells, usually one layer thick, with small hyperchromatic nuclei and little cytoplasm were observed at the periphery of the lobules (Fig. 1). Fig. 1. Hepatoid gland adenoma. Note the hepatoid appearance of neoplastic tissue. H/E, bar=20 μm. Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant tumour which most frequently develops on the skin of limbs, trunk, head and neck, as well as on poorly pigmented skin areas. The average age of affected dogs was 8 years, varying from 6 to 10 years. No sex predilection was noted. Histologically, extending to the dermis, associated or not to the overlying epidermis, were islands, strands, and trabeculae of neoplastic epithelial cells showing a variable degree of squamous differentiation. The amount of keratin, seen as intracytoplasmic, eosinophilic fibrillar material (keratin tonofibres), produced by the neoplastic cells was quite variable: there was an extensive keratinization, and in well-differentiated tumours formation of distinct keratin pearls (Fig. 2). BJVM, 14, No 3 173
4 Prevalence of canine epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours of the skin and soft tissues Fig. 2. Squamous cell carcinoma. Formation of a distinct keratin pearl (arrow). H/E, bar= 20 μm. Fig. 3. Hepatoid gland carcinoma. The hepatoid cells have a vacuolated cytoplasm and large nuclei with several prominent nucleoli. The neoplastic cells show nuclear pleomorphism (arrow). H/E, bar=20 μm. Hepatoid gland carcinomas generally appear as nodular lesions affecting the perianal region. The average age of affected dogs was 11 years, varying from 7 to 15 years. Histologically, the tumour could consist of a single cell type; these cells were undifferentiated, with hyperchromatic nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and little cytoplasm. Only individual cells within the sheets and lobules of tumour cells showed differentiation to hepatoid cells. Other tumours may consist of reserve cells and hepatoid cells: the reserve cells showed pleomorphism of their nuclei and abundant mitotic figures. The hepatoid cells had a vacuolated cytoplasm and large nuclei with several prominent nucleoli (Fig. 3). The basal cell tumour is an epithelial tumour without epithelial or adnexal differentiation. The neoplasms were mainly localized on the skin of the head and neck. Affected dogs were 7.8-years old on the average. The individual tumour cells were small and round to polyhedral in morphology (Fig. 4). The nuclei were ovoid, nucleoli were inconspicuous, and few mitotic figures were found. A small amount of cytoplasm was present. Melanocytes could be found interspersed between the basal cells, with transfer of melanin to the neoplastic cells. The most frequently diagnosed canine skin mesenchymal tumours were lipoma (5.58%), fibrosarcoma (4.41%), haemangiopericytoma (2.32 %) and haemangioma (2.09%). The incidence of the other neoplastic types varied between 0.23% and 1.86%. Fig. 4. Basal cell tumour. The nuclei of the neoplastic cells are ovoid, nucleoli are inconspicuous, and few mitotic figures are found. A small amount of cytoplasm is present. H/E, bar=40 μm. Lipomas were well circumscribed, unencapsulated, soft to yellow masses, indistinguishable from normal fat. Most were freely moveable over the underlyning deeper tissues and could be easily shelled out. The average age of affected 174 BJVM, 14, No 3
5 Simeonov, R., I. Dinev, G. Simeonova, N. Goranov, M. Paskalev, S. Krastev, I. Todorova dogs was 6.5 years, varying from 3 to 11 years. Out of all 24 cases, 17 (70.84%) were observed in female dogs. Histologically, the cells of lipomas were identical to those of normal adipose tissue. Large clear vacuoles replaced the cytoplasm, with peripheralization and compression of nuclei (Fig. 5). Some tumours had regions of necrosis, inflammation, and/or fibrosis. Fig. 5. Lipoma. H/E, bar=20 μm. Fig. 6. Fibrosarcoma. Cellular and nuclear pleomorphism. H/E, bar=20 μm. Fibrosarcomas were most commonly seen in adult dogs (mean age of 10 years). No breed or sex predisposition has been noted. The tumour could be circumscribed or infiltrative. Capsules were usually not seen. Histologically, the neoplastic cells were arranged in interwoven or herringbone patterns (Fig. 6). Cytoplasm was scant, and nuclei were elongated to oval with inconspicuous nucleoli. The more anaplastic tumours were with marked cellular pleomorphism. The number of mitotic figures varied widely. Peripheral aggregates of lymphocytes were occasionally seen. Hemangiopericytomas had variable gross appearances: white/gray to red, soft to firm, rubbery to fatty. The average age of affected dogs was 7 years, varying from 5 to 10 years. No breed or sex predisposition was observed. Histologically, the hallmark of this neoplasm was the presence of perivascular whorls of fusiform cells (Fig. 7). Although this feature could be present in other sarcomas, it is usually dominant in hemangiopericytomas. The neoplastic cells could range, sometimes within the same tumour, from thin to thick, spindle shaped to almost piriform, and they were separated by variable amounts of collagenous stroma. Hemangiomas are benign tumours of the vascular endothelium. They appeared as well demarcated, encapsulated masses which range from bright red to dark brown. The average age of affected dogs was 6 years, varying from 4 to 8 years, without breed or sex predisposition. Histologically, most growths were well circumscribed and composed of variably sized vascular spaces filled with erythrocytes and lined by a single layer of uniform endothelial cells (Fig. 8). Organized thrombi were often found in tumours, with foci of haemosiderosis. The gross appearance of liposarcoma, the malignant counterpart to the lipoma, varied depending of the amount of produced lipid. The average age of affected dogs was 9 years, varying from 7 to 11 years. No breed or sex predisposition was present. Histologically, most tumours were composed of round to polygonal cells arranged in sheets, with little or no collagenous stroma. In the well-differentiated variant, the majority of cells resembled normal adipocytes, with a single clear fat vacuole and a peripheral BJVM, 14, No 3 175
6 Prevalence of canine epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours of the skin and soft tissues lipid droplets. The diagnosis could be difficult in anaplastic and myxoid variants. The other canine epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours of skin and soft tissues observed in this survey did not differ from the classical appearance. DISCUSSION Fig. 7. Hemangiopericytoma. Its hallmark is the presence of perivascular whorls of fusiform cells (arrows). H/E, bar=20 μm. Fig. 8. Haemangioma. Variably sized vascular spaces filled with erythrocytes and lined by a single layer of uniform endothelial cells. H/E, bar=20 μm. Fig. 9. Liposarcoma. Cellular and nuclear pleomorphism. H/E, bar=10 μm. nucleus (Fig. 9). Other cells had variably sized round to oval nuclei and abundant cytoplasm that contains variably sized The skin is permanently exposed to the influence of physical, chemical and other environmental factors and is readily accessible to clinical examinations. These are some reasons for more frequent diagnostics of cutaneous neoplasms (Bostock, 1986; Sanja et al., 2005). Out of the total number of tumours examinated for the period , skin tumours are the second most frequent group of neoplasms with an incidence of 33%, coming after mammary gland tumours (35%), which is consistent with the findings of others authors (Finnie & Bostock, 1979; Benjamin et al., 1999; Moulton, 1990; Dinev, 2002; Sanja et al., 2005). According to the final diagnosis, out of all 430 canine cutaneous tumours 223 were malignant, while 207 were benign. This is in agreement with the finding of Sanja et al. (2005). However, based on the findings of Kaldrymidou et al. (2002) malignant cutaneous neoplasms accounted for 46.6% vs 53.4% for benign. Bostock et al. (1975) reported an incidence of malignant cutaneous neoplasms of approximately 40%. The results of Pakhrin et al. (2007) are similar. There was not any significant sex predilection of investigated tumours, but males were more affected by hepatoid gland adenoma. Hepatoid gland tumours are associated with androgen sex hormones; hence, are reported more frequently in male dogs (Kaldrymidou et al., 176 BJVM, 14, No 3
7 Simeonov, R., I. Dinev, G. Simeonova, N. Goranov, M. Paskalev, S. Krastev, I. Todorova 2002; Sanja et al., 2007). The age-related incidence in our survey is very close to that reported from most researchers (Finnie & Bostock, 1979; Benjamin et al., 1999; Kaldrymidou et al., 2002; Dinev, 2002; Pakhrin et al., 2007; Sanja et al., 2007). They confirmed the fact that the highest incidence of canine skin tumours is observed by the age of 10 years. The localization of tumour growth in the regions of the head, neck and limbs is also analogous to what is already reported (Finnie & Bostock, 1979; Benjamin et al., 1999; Kaldrymidou et al., 2002; Dinev, 2002; Pakhrin et al., 2007; Sanja et al., 2007). Our study revealed that canine skin tumours that are prevalent in other parts of the world are also found among dogs in Bulgaria. It is important to provide detailed information as well as proper bioptic specimens when submitting samples for diagnosis (Pakhrin et al., 2007). Clinical history and gross morphology are important and integral components of diagnosis. This should include the duration and rate of tumour growth, change in appearance over time, size shape, colour, consistency, tissue of origin, and the presence or absence of attachment with the underlying tissues (Vail & Withrow, 2001). According to our investigation it may be concluded that canine cutaneous tumours are increasingly frequent and are an important problem in the pathology of this animal species. Information on frequency and appearance of individual cutaneous tumours helps the clinicians to recognize them in time, to perform appropriate sampling and on the basis of histopathological analysis to provide a correct prognosis and a therapy as effective as possible. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Thanks to my colleagues from the Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Stara Zagora and from private pet clinics from the country which provided a considerable part of cutaneous lesion specimens for histological study. REFERENCES Benjamin, S., A. Lee & W. Saunders, Classification and behaviour of canine mammary neoplasms based on life-span observation in beagles. Veterinary Pathology, 36, Bostock, D., Neoplasms of the skin and subcutaneous tissues in dogs and cats. British Vetereinary Journal, 142, Brodey, R., Canine and feline neoplasia. Advances in Veterinary Sciences & Comparative Medicine, 14, Carpenter, J., L. Andrews & J. Horzworth, Tumors and tumor-like lesions. In: Diseases of the Cat: Medicine and Surgery, ed. A. Horzworth, W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp Chalita, M., J. Matera, M. Alves & A. Longatto Filho, Nonaspiration fineneedle cytology and its histologic correlation in canine skin and soft tissue tumours. Analitycal and Quantitative Cytology and Histology, 23, Dinev, I., Incidence of canine neoplasms a retrospective histopathological study. II. Tumours of the skin and associated structures. Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 5, Finnie, J. & D. Bostock, Skin neoplasia in dogs. Australian Veterinary Journal, 55, Goldschmidt, M., R. Dunstan, A. Stannard, C. von Tscharner, E. Walder & J. Yager, Histological classification of epithelial and melanocytic tumors of the skin of domestic animals, World Health Organization International Classification of Tumors in Domestic Animals, 2 nd BJVM, 14, No 3 177
8 Prevalence of canine epithelial, melanocytic and mesenchymal tumours of the skin and soft tissues Series, Vol III. Washington DC, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, American Registry of Pathology, pp Guzman, E., J. Langowski & L. Owen- Schaub, Mad dogs, Englishmen and apoptosis: The role of cell death in UVinduced skin cancer. Apoptosis, 4, Kaldrymidou, H., L. Leontides, A. Coutinas, M. N. Saridomichelakis & M. Karayannopoulou, Prevalence, distribution and factors associated with the presence and potential for malignancy of cutaneous neoplasms in in 174 dogs admitted to a clinic in northern Greece. Journal of Veterinary Medicine A, Physiology, Pathology, Clinical Medicine, 49, Miller, M., S. Nelson & J. Turk, Cutaneous neoplasia in 340 cats. Veterinary Pathology, 28, Moulton, J, Tumours of the skin and soft tissue. In: Tumours in Domestic Animals, 3rd edn, University of California Press, Ltd. London, pp Mukaratirwa, S., J. Chipunza, S. Chitanga, M. Chimonyo & E. Bhebhe, Canine cutaneous neoplasms: prevalence and influence of age, sex, and site of the presence and potential malignancy of citaneous neoplasms in Zimbabwe. Journal of the South African Veterinary Association, 76, Pakhrin, B., M. Kang, I. Bae, M. Park, H. Jee, M. You, J. Kim, B. Yoon, Y. Choi & Dae-Young Kim, Retrospective study of canine cutaneous tumours in Korea. Journal of Veterinary Sciences, 8, Priester, W., Skin tumors in domestic animals: data from 12 United States and Canadian colleges of veterinary medicine. Journal of National Cancer Institute, 50, Rothwell, T., C. Howlett, D. Middleton, D. A. Griffits & B. C. Duff, Skin neoplasms of dogs in Sidney. Australian Veterinary Journal, 64, Sanja, A., V. Kukolj, D. Marincovic & M. Knezevic, Retrospective study of canine epithelial and melanocytic tumours. Acta Veterinaria (Beograd), 55 (4), Tzvetkov, Y., Pathomorphological studies and some epizootological properties at the tumours in dogs. PhD thesis, Central Laboratory of Biology and Game Diseases with Small Animal Clinics, Sofia, pp Vail, D. & S. Withrow, Tumours of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. In: Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 3 rd edn, eds Withrow, S. & E. MacEwen, Saunders, Philadelphia, pp Paper received ; accepted for publication Correspondence: Dr. Radostin Simeonov Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Student's Campus, 6000 Stara Zagora, Bulgaria rsimeonov@uni-sz.bg 178 BJVM, 14, No 3
Science & Technologies A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE SKIN ROUND CELL TUMOURS
 A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE SKIN ROUND CELL TUMOURS Radostin Simeonov Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Stara Zagora, Bulgaria, e-mail:
A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE SKIN ROUND CELL TUMOURS Radostin Simeonov Department of General and Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Stara Zagora, Bulgaria, e-mail:
NUCLEAR MORPHOMETRY IN RELATION TO METASTASES IN CANINE SPONTANEOUS CUTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp 74-78, 2010 Copyright 2009 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp 74-78, 2010 Copyright 2009 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
XX. Tumours of the nasal cavity *
 XX. Tumours of the nasal cavity * H. STONZI 1 & B. HAUSER2 Tumours of the nasal cavity are rare in domestic animals, most cases occurring in the dog. Epithelial tumours are the most common type in carnivores
XX. Tumours of the nasal cavity * H. STONZI 1 & B. HAUSER2 Tumours of the nasal cavity are rare in domestic animals, most cases occurring in the dog. Epithelial tumours are the most common type in carnivores
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Cytology of NeoPlasia
 PEEr reviewed Cytology of NeoPlasia An Essential Component of Diagnosis Anne Barger, DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVP Cytology is a quick, easy, and inexpensive diagnostic tool. It is commonly used for the diagnosis
PEEr reviewed Cytology of NeoPlasia An Essential Component of Diagnosis Anne Barger, DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVP Cytology is a quick, easy, and inexpensive diagnostic tool. It is commonly used for the diagnosis
OVERVIEW OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL TUMORS IN DOG
 OVERVIEW OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL TUMORS IN DOG Georgeta Dinescu, Elvira Condruţ, Virginia Şerbănică, A. Feghiu Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,
OVERVIEW OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL TUMORS IN DOG Georgeta Dinescu, Elvira Condruţ, Virginia Şerbănică, A. Feghiu Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,
Submission of samples. Cytology of Lumps and Bumps. Evaluation of samples. Use caution interpreting. Criteria of malignancy.
 Submission of samples Cytology of Lumps and Bumps Paul Avery VMD, PhD, DACVP paul.avery@colostate.edu Air dry only No wet fixation using formalin or ethanol Stain 1-2 on-site to evaluate quality Send all
Submission of samples Cytology of Lumps and Bumps Paul Avery VMD, PhD, DACVP paul.avery@colostate.edu Air dry only No wet fixation using formalin or ethanol Stain 1-2 on-site to evaluate quality Send all
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1
 A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS. Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology
 SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS
 NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Abstract: The primary as well as metastatic tumours of the skin can be diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology
NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Abstract: The primary as well as metastatic tumours of the skin can be diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF THE MOST COMMON CANINE SKIN AND MAMMARY TUMOURS
 PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF THE MOST COMMON CANINE SKIN AND MAMMARY TUMOURS Donatas Šimkus 1,2, Alius Pockevičius 2, Petras Mačiulskis 1,2, Virginija Šimkienė 1, Ligita Zorgevica-Pockeviča 2 1 National
PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF THE MOST COMMON CANINE SKIN AND MAMMARY TUMOURS Donatas Šimkus 1,2, Alius Pockevičius 2, Petras Mačiulskis 1,2, Virginija Šimkienė 1, Ligita Zorgevica-Pockeviča 2 1 National
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
A Canine Case of Complex Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland with Metastasis to the Axillary Lymph Node
 A Canine Case of Complex Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland with Metastasis to the Axillary Lymph Node Kenjiro Hashimoto 1), Atsushi Kawabata 1), Tamio Ohmuro 2), Kinji Shirota 1, 3) * 1) Research Institute
A Canine Case of Complex Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland with Metastasis to the Axillary Lymph Node Kenjiro Hashimoto 1), Atsushi Kawabata 1), Tamio Ohmuro 2), Kinji Shirota 1, 3) * 1) Research Institute
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR )
 ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Histopathological Spectrum at a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (VI) No (I) January-June 2017 Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Histopathological Spectrum at a Tertiary Care Hospital Neeraja Barve*, Hansa Goswami**, Urvi Parikh *** Abstract
Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (VI) No (I) January-June 2017 Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Histopathological Spectrum at a Tertiary Care Hospital Neeraja Barve*, Hansa Goswami**, Urvi Parikh *** Abstract
PROGNOSTIC TESTING INTO FELINE CUTANEOUS MAST CELL TUMOURS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk PROGNOSTIC TESTING INTO FELINE CUTANEOUS MAST CELL TUMOURS Author : Melanie Dobromylskyj Categories : Vets Date : October
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk PROGNOSTIC TESTING INTO FELINE CUTANEOUS MAST CELL TUMOURS Author : Melanie Dobromylskyj Categories : Vets Date : October
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
Histogenesis of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
 J. clin. Path., (1966), 19, 114 E. D. WILLIAMS1 From the Institute ofpathology, The London Hospital SYNOPSIS Thirty-one dog thyroid tumours and 28 spontaneous rat thyroid tumours were studied histologically
J. clin. Path., (1966), 19, 114 E. D. WILLIAMS1 From the Institute ofpathology, The London Hospital SYNOPSIS Thirty-one dog thyroid tumours and 28 spontaneous rat thyroid tumours were studied histologically
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
LOCALIZATION AND ACTIVITY OF TISSUE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FELINE PROSTATE GLAND
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2010), 13, No 1, 13 17 LOCALIZATION AND ACTIVITY OF TISSUE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FELINE PROSTATE GLAND Summary R. DIMITROV, P. YONKOVA, K. STAMATOVA, D. YOVCHEV
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2010), 13, No 1, 13 17 LOCALIZATION AND ACTIVITY OF TISSUE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FELINE PROSTATE GLAND Summary R. DIMITROV, P. YONKOVA, K. STAMATOVA, D. YOVCHEV
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
In the third part of the present study tumours which previous were described as basal cell tumours but now have been reclassified as trichoblastomas
 170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
Charalampos Attipa, Rachel Hampel, Simon L. Priestnall, Kate English Pathobiology and Population Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, UK
 SUBCUTANEOUS MASS OVER THE SCAPULA IN A CAT Charalampos Attipa, Rachel Hampel, Simon L. Priestnall, Kate English Pathobiology and Population Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, UK Signalment:
SUBCUTANEOUS MASS OVER THE SCAPULA IN A CAT Charalampos Attipa, Rachel Hampel, Simon L. Priestnall, Kate English Pathobiology and Population Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, UK Signalment:
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
A neoplasm is defined as "an abnormal tissue proliferation, which exceeds that of adjacent normal tissue. This proliferation continues even after
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
UNUSUAL OCULAR HODGKINʼS-LIKE LYMPHOMA IN A DOG
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2019 ONLINE FIRST ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.2241 Case report UNUSUL OCULR HODGKINʼS-LIKE LYMPHOM IN DOG Summary M. KHORDDMEHR 1, S. JROLMSJED 2, J. SHRFI-HELN
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2019 ONLINE FIRST ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.2241 Case report UNUSUL OCULR HODGKINʼS-LIKE LYMPHOM IN DOG Summary M. KHORDDMEHR 1, S. JROLMSJED 2, J. SHRFI-HELN
CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY FOR TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY IN INDIA (STPI) OCTOBER 29-31, 2010 The Atria Hotel, # 1, Palace Road, Bangalore - 560 001
CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY FOR TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY IN INDIA (STPI) OCTOBER 29-31, 2010 The Atria Hotel, # 1, Palace Road, Bangalore - 560 001
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER. Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D.
 NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
Principles of Surgical Oncology. Winnie Achilles Tierklinik Hollabrunn Lastenstrasse Hollabrunn
 Principles of Surgical Oncology Winnie Achilles Tierklinik Hollabrunn Lastenstrasse 2 2020 Hollabrunn boexi@gmx.de The first surgery provides the best chance for a cure in an animal with a tumor Clinical
Principles of Surgical Oncology Winnie Achilles Tierklinik Hollabrunn Lastenstrasse 2 2020 Hollabrunn boexi@gmx.de The first surgery provides the best chance for a cure in an animal with a tumor Clinical
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A. Pathological Case Report
 Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Cytology of Neoplasms that Occur on the Limbs Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP
 Cytology of Neoplasms that Occur on the Limbs Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP I. Introduction The purpose of this material is to provide information that may be useful in the identification of tumors
Cytology of Neoplasms that Occur on the Limbs Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP I. Introduction The purpose of this material is to provide information that may be useful in the identification of tumors
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types. Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed
 External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE EPITHELIAL AND MELANOCYTIC TUMORS. ALEKSI]-KOVA^EVI] SANJA, KUKOLJ V, MARINKOVI] D and MILIJANA
![RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE EPITHELIAL AND MELANOCYTIC TUMORS. ALEKSI]-KOVA^EVI] SANJA, KUKOLJ V, MARINKOVI] D and MILIJANA RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE EPITHELIAL AND MELANOCYTIC TUMORS. ALEKSI]-KOVA^EVI] SANJA, KUKOLJ V, MARINKOVI] D and MILIJANA](/thumbs/76/74107602.jpg) Acta Veterinaria (Beograd), Vol. 55, No. 4, 319-326, 2005. UDK 619:616-006.8:636.7 RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE EPITHELIAL AND MELANOCYTIC TUMORS ALEKSI]-KOVA^EVI] SANJA, KUKOLJ V, MARINKOVI] D and KNE@EVI]
Acta Veterinaria (Beograd), Vol. 55, No. 4, 319-326, 2005. UDK 619:616-006.8:636.7 RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF CANINE EPITHELIAL AND MELANOCYTIC TUMORS ALEKSI]-KOVA^EVI] SANJA, KUKOLJ V, MARINKOVI] D and KNE@EVI]
Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms
 Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pleomorphic adenoma of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari
 of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms
 My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP)
 Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Brief Report. Shivanand Gundalli 1, Smita Kadadavar 1, Somil Singhania 1, Rutuja Kolekar 2 INTRODUCTION. Melanocytic Nevus
 Our Dermatology Online Histopathological spectrum of benign melanocytic nevi our experience in a tertiary care centre Shivanand Gundalli 1, Smita Kadadavar 1, Somil Singhania 1, Rutuja Kolekar 2 1 Department
Our Dermatology Online Histopathological spectrum of benign melanocytic nevi our experience in a tertiary care centre Shivanand Gundalli 1, Smita Kadadavar 1, Somil Singhania 1, Rutuja Kolekar 2 1 Department
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Tumors of Adipose Tissue Tumors Epidemiology Clinical Features. Morphology. Mature Adipocytes Separated by delicate fibrous septa
 Tumors of Adipose Tissue Lipoma Liposarcoma Most commonly happens in female The most common soft tissue tumor o Originates from matured Adipocytes Most commonly happes at the 4 th and 5 th decade of life
Tumors of Adipose Tissue Lipoma Liposarcoma Most commonly happens in female The most common soft tissue tumor o Originates from matured Adipocytes Most commonly happes at the 4 th and 5 th decade of life
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Cytology in Veterinary Practice: Sample Collection, Slide Preparation and Interpretation Guidelines
 Cytology in Veterinary Practice: Sample Collection, Slide Preparation and Interpretation Guidelines ASPIRATION OF A MASS A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP Lighthouse Veterinary Consultants, LLC Gainesville,
Cytology in Veterinary Practice: Sample Collection, Slide Preparation and Interpretation Guidelines ASPIRATION OF A MASS A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP Lighthouse Veterinary Consultants, LLC Gainesville,
Histopathology of Melanoma
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
Egypt. J. Comp. Path. & Clinic. Path. Vol. 21 No. 4 (December) 2008;
 Clinicopathological Aspects of Canine Skin Neoplasms in Egypt By Abuseida, A.M. *; Sherein, S.A El Gayed** and Abd-El-Hady, A.A.*** * Dept. of Surgery, Anesthesiology & Radiology, Fac. of Vet. Med., Cairo
Clinicopathological Aspects of Canine Skin Neoplasms in Egypt By Abuseida, A.M. *; Sherein, S.A El Gayed** and Abd-El-Hady, A.A.*** * Dept. of Surgery, Anesthesiology & Radiology, Fac. of Vet. Med., Cairo
1. Infectious or non infectious granulomatous / pyogranulomatous dermatitis
 7-year-old, male, Persian cat with multiple nodules on face and right earpiece. Which of the following is the most likely disease? 1. Infectious or non infectious granulomatous / pyogranulomatous dermatitis
7-year-old, male, Persian cat with multiple nodules on face and right earpiece. Which of the following is the most likely disease? 1. Infectious or non infectious granulomatous / pyogranulomatous dermatitis
Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng
 ADS Dermatopathology Meeting 2014 Selected Adnexal Tumors Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology (Dermatology) University of Colorado School
ADS Dermatopathology Meeting 2014 Selected Adnexal Tumors Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology (Dermatology) University of Colorado School
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CUTANEOUS ROUND CELL TUMORS DIAGNOSED USING ASPIRATIVE CYTOLOGY IN DOGS
 Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (1) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 Abstract EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (1) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 Abstract EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
A retrospective Study of Canine Tumors in Grenada, West Indies
 Research Article A retrospective Study of Canine Tumors in Grenada, West Indies Muhammed Iqbal Bhaiyat 1, Alfred Chikweto 1, Keshaw Prasad Tiwari 1, Claude DeAllie 1, Rajveer Singh Pawaiya 3, Allison Inga
Research Article A retrospective Study of Canine Tumors in Grenada, West Indies Muhammed Iqbal Bhaiyat 1, Alfred Chikweto 1, Keshaw Prasad Tiwari 1, Claude DeAllie 1, Rajveer Singh Pawaiya 3, Allison Inga
A 5 Year Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors at a Tertiary Care Hospital
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VII (Apr. 2015), PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org A 5 Year Histopathological Study of Skin
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VII (Apr. 2015), PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org A 5 Year Histopathological Study of Skin
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF CANINE EPITHELIAL TUMOURS
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF CANINE EPITHELIAL TUMOURS * Chandravathi T. 1, Anjaneyulu Y. 2, Anand Kumar A. 3, Narasimha Reddy Y. 4 and Samatha V. 1 1 Department of Pathology, N.T.R
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF CANINE EPITHELIAL TUMOURS * Chandravathi T. 1, Anjaneyulu Y. 2, Anand Kumar A. 3, Narasimha Reddy Y. 4 and Samatha V. 1 1 Department of Pathology, N.T.R
Canine Cutaneous Melanoma
 Canine Cutaneous Melanoma By Elizabeth Downing Clinical Advisor: Dr. Angharad Waite, VMD Basic Science Advisor: Dr. Cheryl Balkman, DVM, DACVIM Senior Seminar Paper Cornell University College of Veterinary
Canine Cutaneous Melanoma By Elizabeth Downing Clinical Advisor: Dr. Angharad Waite, VMD Basic Science Advisor: Dr. Cheryl Balkman, DVM, DACVIM Senior Seminar Paper Cornell University College of Veterinary
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
BSD 2015 Case 19. Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is:
 BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS
 7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
Special slide seminar
 Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumours Institutional Study in South India
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 543756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/543756 Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumours Institutional Study in South India Ankit Sharma, 1 Deepak
Skin Cancer, Article ID 543756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/543756 Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumours Institutional Study in South India Ankit Sharma, 1 Deepak
Classification and Grading of Canine Mammary Tumors
 Classification and Grading of Canine Mammary Tumors Veterinary Pathology 48(1) 117-131 ª The American College of Veterinary Pathologists 2011 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Classification and Grading of Canine Mammary Tumors Veterinary Pathology 48(1) 117-131 ª The American College of Veterinary Pathologists 2011 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Tinh hoàn
 Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Pedunculated Leiomyoma of Breast: A Common Lesion at An Uncommon Location.
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 8 (2015) pp:01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Pedunculated Leiomyoma
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 8 (2015) pp:01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Pedunculated Leiomyoma
Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update 5/29/2009
 Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
