Brain Microanatomy: Artifacts, Neoplastic Lesions and Utilization of Special Stains
|
|
|
- Archibald Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 Brain Microanatomy: Artifacts, Neoplastic Lesions and Utilization of Special Stains Current Standard for CNS Evaluation in Rodent Toxicity Studies ESTP Congress in Ghent, Belgium 12 September 2013 Robert H. Garman, DVM Consultants In Veterinary Pathology, Inc. Monroeville, PA
3 Neurocytology, Including Cell Types, Cell Reactions and Artifact Cells of Neuroectodermal Origin Neurons Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Ependymocytes Cells of Mesenchymal Origin Microglia (as well as blood vessels, adipose tissue, and meninges) 3
4 Large Motor Neurons 4
5 Large Sensory Neurons 5
6 Mixtures of Large Neurons and Small Neurons (Granule Cells) 6
7 Olfactory Bulb Cochlear Nucleus 7
8 Normal Striatum Striatum (Hemorrhagic Shock) 8
9 Locations of all 7 circumventricular organs in a rat brain (LFB/CV stain) 9
10 6 CVOs from a rat brain a = organum vasculosum of lamina terminalis b = subfornical organ c = mediam eminence d = subcommissural organ e = pineal F = area postrema Garman RH (2011) Histology of the Central Nervous System. Toxicol Pathol, 39:
11 Necrotic neurons versus Artifactual Dark Neurons Red Dead (Eosinophilic) Neuron (left) Dark Neuron - representing a handling artifact - (right) 11
12 Dark neurons tend to cluster 12
13 Dark Neurons Are most often the result of handling. 13
14 Drying Artifact Saline Artifact 14
15 Dark neuron artifact is most apparent in large cytoplasm-rich neurons 15
16 In cresyl violetstained sections, dark neurons are not degenerative! 16
17 Dark Neurons (H&E) Eosinophilic Neurons (H&E) 17
18 Eosinophilic Neurons (H&E) Eosinophilic Neurons (Cresyl Violet) 18
19 Dark Neurons vs. Dead Neurons 1) Dark neurons are monomorphic; eosinophilic neurons are characterized by different stages of degeneration. (The only exception may shortly after a peracute injury.) 2) Eosinophilic neurons are accompanied by additional changes such as secondary cellular reactions and, occasionally, an altered neuropil. 19
20 Unilateral ischemic insult, rat brain 20
21 Eosinophilic neurons in different stages of degeneration 21
22 Swollen neuron, eosinophilic neurons, karyorrhexis and active microglial cell 22
23 Fluoro-Jade Stains for Degenerating Neurons 1) Lower the threshold (magnification) for detection. 2) Allow observation of degenerative neuronal processes as well as cell bodies. 3) Allow for the detection of small-sized degenerating neurons for which it is difficult to detect an eosinophilic cytoplasmic change. 4) Assist in the detection of peracute degenerative processes (prior to development of eosinophilia). 23
24 Retrosplenial cortex (rat) 48 hrs. after MK-801 treatment 24
25 Retrosplenial cortex (rat) 48 hrs. after MK- 801 treatment (H&E- vs. Fluoro- Jade B-stained sections) 25
26 Hippocampal CA1 sector (rat) 24 hrs. after fentanyl treatment (H&E- vs. Fluoro- Jade B-stained sections) 26
27 CA1 sector of a rat hippocampus 48 hours after a drug treatment. H&E vs. Fluoro-Jade B for detecting degeneration in smallsized interneurons. 27
28 Higher magnification images for degenerating small-sized interneurons. 20x 40x 28
29 Peracute injury (due to a one-hour grand mal seizure). 29
30 Adenosine A1 KO mouse killed after a one-hour grand mal seizure. H&E vs. Fluoro-Jade C 30
31 H&E Dark Neurons in H&E and Fluoro- Jade-stained sections Fluoro-Jade 31
32 Fluoro-Jade versus Silver Degeneration Stains 1. Frozen sections are necessary for silver degeneration stains. F-J stains may be used on frozen or paraffin sections. 2. Silver degeneration stains require greater technical skill/may have more artifactual staining. 3. Silver degeneration stains are archivable. (Fluoro- Jade will fade while viewed with fluorescent light, although the shelf life of stained slides is fairly long.) 4. Silver degeneration stains show greater neuronal process detail. 32
33 Fluoro-Jade B, retrosplenial cortex of a rat 48 hours after MK- 801 treatment. Section from the same rat and the same (contralateral) brain level stained with amino cupric silver. 33
34 Unilateral Optic Nerve Atrophy in a rat (H&E, F-J B and cupric silver) 34
35 Different levels of midbrain (and different time points) showing axonal injury with retraction ball formation. Garman RH et al. (2011) Blast exposure in rats with body shielding is characterized primarily by diffuse axonal injury. J Neurotrauma, 28(6)
36 For Axonal Injury Silver degeneration stains (e.g. amino cupric silver) are the stains of choice if you can use frozen sections. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) stains are O.K. for peracute axonal injury if you are limited to doing IH on paraffin sections. Non-degenerative silver stains such as Bodian s, Bielschowsky s, Gallyas are also good for axonal injury. 36
37 Non-degenerative silver stain for internal neuronal structure (Bielschowsky s) 37
38 Astrocytes 1. Provide nutritional support of neurons and maintenance of extracellular electrolyte & neurotransmitter levels. Crucial for neuron function and survival. 2. Signal other astrocytes via gap junctions. 3. Have neurotransmitter receptors similar to those of neurons. 4. Are an important component of the BBB & also regulate blood flow. 5. Principle marker = GFAP. 38
39 Normal-appearing astrocytes, H&Estained section of cerebral cortex. 39
40 Examples of reactive and gemistocytic cytoplasm-rich astrocytes. 40
41 Normal GFAP-stained astrocytes ( star cells ), cerebral cortex.41
42 Reactive astrocytes have thickened cytoplasmic processes. 42
43 Hippocampal sclerosis, CA1 sector H&E Hippocampal sclerosis, CA1 sector (GFAP) 43
44 Multiple brain sections from a clinically normal rat!!! 44
45 Vacuoles: Artifact or a Peracute Alteration? 45
46 Cerebellar Vacuoles; H&E, GFAP and Fluoro-Jade B. 46
47 One Example of Good Artifact Dog cerebral cortex, H&E stain. Alzheimer type II astrocyte change due to experimentallyinduced hyperammonemia. Images courtesy of Dr. Michael D. Norrenberg 47
48 Are these changes also examples of good artifact? 48
49 Two Types of Brain Edema Francesca & Rezzani (2010). Aquaporin and blood brain barrier Curr Neuropharm 8:
50 GFAP (Green) vs. Aquaporin 4 (Red) Simard M et al (2003). Signaling at the gliovascular interface, JNS, 23(27): ,
51 Astrocytes and Aquaporins in the Pathogenesis of Cytotoxic Brain Edema and/or in Postmortem Swelling of Astrocytes 1) Astrocyte nuclear or cytoplasmic swelling may occur in certain metabolic diseases. 2) Astrocyte swelling (especially cytoplasmic) also represents a very common postmortem artifact. 3) This swelling may be enhanced by certain pharmacologic agents. 51
52 Oligodendrocytes 1. Myelin-forming cells of the CNS. 2. One oligodendrocyte myelinates multiple axons (as many as 50 or more). 3. Para-neuronal oligodendrocytes are often referred to as satellite cells. 52
53 Left: Classic Artifactual Fried Egg Appearance of Oligodendrocytes Right: Normal Oligodendrocytes in a Perfusion-fixed Brain 53
54 Left side micrograph: Within the brain s fiber tracts, oligodendrocytes are typically arranged in rows. Right side micrograph: Some cranial nerves show an extra-axial transition between a central (right) to a peripheral (left) pattern of myelination. 54
55 Examples of Neoplastic Satellitosis 55
56 Microglia 1. Are the inflammatory cells of the CNS comparable to the blood monocytes and tissue histiocytes. 2. Constitute 5 20% of the brain cells. 3. Function in both pro-inflammatory ( classical activation and reparative ( alternative activation ) modalities. 4. Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1) is often used to stain reactive microglia. 56
57 Find the single microglial cell in this section of normal cortex. H&E 57
58 Neuronophagia by activated microglial cells 58
59 Progression of neuronophagia by microglial cells 59
60 Microglia reacting to necrotic neurons CA1 sector of hippocampus 60
61 Iba1 Stain, cerebral cortex Reactive microglial cell, cerebral cortex 61
62 Ventricular fibrillation/cardiac arrest model, rat (14-days prior to death) H&E Iba1 62
63 Principal Histologic Artifacts in Brain Sections 1) Dark Neurons 2) Vacuolation of neurons, neuropil or myelin 63
64 Good (left) versus suboptimal preservation of DRG by perfusion fixation 64
65 Prominent vacuoles found sporadically in sensory ganglia of rats 65
66 Buscaino bodies ( Mucocytes ) An artifact of myelin. H&E 66
67 Contrasting Two Patterns of Intramyelinic edema 67
68 Buscaino bodies are occasionally refractile under polarized light. 68
69 Brain Microanatomy: Neoplastic Glial Lesions in Rodents Current Standard for CNS Evaluation in Rodent Toxicity Studies ESTP Congress in Ghent, Belgium 12 September 2013 Important Reference: Kaufmann, W et al (2012): Proliferative and non-proliferative lesions of the rat and mouse central and peripheral nervous system Toxicol Pathol. 40:
70 Classification of Proliferative Lesions Neuronal Medulloblastoma Neuromyoblastoma Glial/Schwann Cell Astrocytoma Glioma Oligodendroglioma Schwannoma Choroid plexus Papilloma Carcinoma Ependyma Ependymoma Meninges Granular cell aggregates Granular cell tumour Meningioangiomatosis Meningioma Other cell lineages Lipomatous hamartoma Malignant reticulosis Lymphoma 70
71 Historical Control Data* for Brain from the NTP F344 RATS Brain Tumor Incidence (M) Incidence (F) ASTROCYTOMA, High grade (aka. Malignant) 3/1248 0/1200 EPENDYMOMA, benign 1/1248 0/1200 EPENDYMOMA, malignant 0/1248 1/1200 GLIOMA**, low grade (aka. Benign) 0/1248 1/1200 GLIOMA**, high grade (aka. Malignant) 0/1248 2/1200 OLIGODENDROGLIOMA, low grade (aka. Benign) 1/1248 0/1200 OLIGODENDROGLIOMA, high grade (aka. Malignant) 1/1248 3/1200 GRANULAR CELL TUMOUR, BENIGN 2/1248 0/1200 SCHWANNOMA, MALIGNANT 1/1248 0/1200 Publically available at ** Has been used for glioma, mixed or astrocytoma 71
72 Historical Control Data* for Brain from the NTP B6C3F1 MICE Brain Tumour Incidence (M) Incidence (F) MENINGIOMA, benign 1/1150 0/1197 MENINGIOMA, malignant 1/1150 0/1197 OLIGODENDROGLIOMA, high grade (aka. Mal) 1/1150 0/1197 SCHWANNOMA, malignant 0/1150 2/1197 * Publically available at 72
73 Glial Cell Neoplasms in Rodents 1) Astrocytomas are the most common glial tumor in rats, followed by oligodendroglioma and mixed glioma 2) Primarily seen in older-aged rats (15 months +) 3) Immunohistochemistry suggests a histiocytic cell lineage for astrocytomas in rats, so the new terms that have been recommended are malignant microglial tumor or microglioma. 73
74 Astrocytoma: malignant, high grade Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 74
75 Astrocytoma: H&E, protoplasmic morphology Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 75
76 Astrocytoma: fibrillary morphology Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 76
77 Astrocytoma: neuronal satellitosis Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 77
78 Astrocytoma: extension into meninges Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 78
79 Astrocytoma: necrosis and palisading Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 79
80 Astrocytoma: cellular atypia Photo courtesy of Dr. James Morrison. 80
81 Oligodendroglioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 81
82 Oligodendroglioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 82
83 Oligodendroglioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 83
84 Oligodendroglioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 84
85 Oligodendroglioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 85
86 Mixed Glioma: Photos courtesy of the NTP 86
87 Mixed Glioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 87
88 Mixed Glioma: Photo courtesy of the NTP 88
89 Immunohistochemical Staining of Rat Glial Cell Neoplasms 1) Astrocytoma 2) Oligodendroglioma 3) Mixed gliomas (oligo + astrocytoma) 89
90 IHC on Rat Astrocytomas GFAP IHC Photos courtesy of Dr. James Morrison Iba-1 IHC 90
91 IHC on Rat Oligodendrogliomas Anti-Olig2 IHC Anti-GFAP IHC Images from: Kolenda-Roberts HM et al. (2013) Immunohistochemical characterization of spontaneous and acrylonitrile-induced brain tumors in the rat. Toxicol Pathol 41:98-108Pathology ` Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology 91
92 IHC staining of mixed gliomas Staining for GFAP and for nestin (a marker of astrocyte precursors) Images from: Nagatani M et al (2013): GFAP-positive neoplastic astrocytes in spontaneous oligodendrogliomas and mixed gliomas of rats. Toxicol Pathol; 41:
93 Summary Comments Glial Neoplasms in Rats - Glial cell neoplasms are very uncommon in rats and are rare in mice; these neoplasms are primarily found in old rats. The most frequent glial cell neoplasm in the rat is the astrocytoma, but IHC has shown the tumor cells to stain for monocyte markers such as Iba1. The diagnostic terms microglioma or malignant microglial cell tumor may, therefore, be more appropriate. Oligodendrogliomas show IHC markers for oligodendrocytes. Some mixed gliomas have been shown to contain both neoplastic oligodendrocytes and GFAP + neoplastic astrocytes or nestin + cells. (Nestin is expressed in proliferating neuroepithelial cells, including astrocyte precursors.) 93
94 Neuropathology Overview 1. The brain is a highly heterogeneous organ. 2. Many neuroanatomic regions have unique sensitivities to physical or chemical insult. 3. Adequate evaluation for neurotoxic endpoints requires: a) Proper tissue preparation (to avoid artifact) b) Relatively extensive sampling c) Application of a variety of stains, when appropriate d) Pathologist s time and experience The regulatory agencies need to know which brain regions were examined.
95 Acquiring new scientific knowledge can be a pleasing experience. Un-retouched electron micrograph of normal mitochondria within a small myelinated axon. From : Haines, DE; Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications, 3 rd Ed. Elsevier, 2006
96 96
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Classification of spontaneous brain tumors in rats
 Classification of spontaneous brain tumors in rats Central Nervous System Neoplasms in the Rat (Solleveld HA, et al., 1991) 1. Tumors of Neuroepithelial Tissue A. Astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors
Classification of spontaneous brain tumors in rats Central Nervous System Neoplasms in the Rat (Solleveld HA, et al., 1991) 1. Tumors of Neuroepithelial Tissue A. Astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors
Histology of the Central Nervous System
 Toxicologic Pathology, 39: 22-35, 2011 Copyright # 2011 by The Author(s) ISSN: 0192-6233 print / 1533-1601 online DOI: 10.1177/0192623310389621 Histology of the Central Nervous System ROBERT H. GARMAN
Toxicologic Pathology, 39: 22-35, 2011 Copyright # 2011 by The Author(s) ISSN: 0192-6233 print / 1533-1601 online DOI: 10.1177/0192623310389621 Histology of the Central Nervous System ROBERT H. GARMAN
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA
 THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
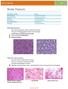 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019. Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 1: an introduction: Nervous system cells and their response to injury.
 CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 1: an introduction: Nervous system cells and their response to injury. CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 1: an introduction: Nervous system cells and their response to injury. CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors
 Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Contents 1 Normal Histology and Commonly Used Stains 2 Basic Pathologic Reactions
 Contents 1 Normal Histology and Commonly Used Stains.... 1 1.1 Cells of the Nervous System... 1 1.1.1 Neurons... 1 1.1.2 Astrocytes.... 2 1.1.3 Oligodendrocytes... 5 1.1.4 Schwann Cells... 5 1.1.5 Ependyma....
Contents 1 Normal Histology and Commonly Used Stains.... 1 1.1 Cells of the Nervous System... 1 1.1.1 Neurons... 1 1.1.2 Astrocytes.... 2 1.1.3 Oligodendrocytes... 5 1.1.4 Schwann Cells... 5 1.1.5 Ependyma....
Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Understanding general brain tumor pathology, Part I: The basics. Craig Horbinski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology University of Kentucky
 Understanding general brain tumor pathology, Part I: The basics Craig Horbinski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology University of Kentucky plan of attack what IS a pathologist, anyway? what s so special
Understanding general brain tumor pathology, Part I: The basics Craig Horbinski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology University of Kentucky plan of attack what IS a pathologist, anyway? what s so special
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
Five Most Common Problems in Surgical Neuropathology
 Five Most Common Problems in Surgical Neuropathology If the brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn t Emerson Pugh What is your greatest difficulty in neuropathology?
Five Most Common Problems in Surgical Neuropathology If the brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn t Emerson Pugh What is your greatest difficulty in neuropathology?
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
CNS third year med students Summary of midterm material H Awad
 CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
The New WHO Classification and the Role of Integrated Molecular Profiling in the Diagnosis of Malignant Gliomas
 The New WHO Classification and the Role of Integrated Molecular Profiling in the Diagnosis of Malignant Gliomas Stefan Prokop, MD Neuropathology Fellow Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Background
The New WHO Classification and the Role of Integrated Molecular Profiling in the Diagnosis of Malignant Gliomas Stefan Prokop, MD Neuropathology Fellow Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Background
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
10.1: Introduction. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites.
 10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
Nervous Tissue. Prof. Zhou Li Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Nervous Tissue Prof. Zhou Li Dept. of Histology and Embryology Organization: neurons (nerve cells) neuroglial cells Function: Ⅰ Neurons 1. structure of neuron soma neurite a. dendrite b. axon 1.1 soma
Nervous Tissue Prof. Zhou Li Dept. of Histology and Embryology Organization: neurons (nerve cells) neuroglial cells Function: Ⅰ Neurons 1. structure of neuron soma neurite a. dendrite b. axon 1.1 soma
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are important for your clinical years and your work as
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are important for your clinical years and your work as
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
monotonous, stippled, round, smoothcontoured nuclei and scanty acidophilic or
 monotonous, stippled, round, smoothcontoured nuclei and scanty acidophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm. The cells are surrounded by a loose fibrillary stroma that is traversed by delicate capillaries. Ill
monotonous, stippled, round, smoothcontoured nuclei and scanty acidophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm. The cells are surrounded by a loose fibrillary stroma that is traversed by delicate capillaries. Ill
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
features of CNS pathology
 سالي ابو رمان Characteristic features of CNS pathology Important notes : - In this sheet I arranged slides within what the doctor said plus what is written in the book, hopefully it will be helpful and
سالي ابو رمان Characteristic features of CNS pathology Important notes : - In this sheet I arranged slides within what the doctor said plus what is written in the book, hopefully it will be helpful and
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad
 Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Classification of Diffuse Gliomas: Progress, Pearls and Pitfalls. Rob Macaulay Neuropathologist, MCC October 21, 2017
 Classification of Diffuse Gliomas: Progress, Pearls and Pitfalls Rob Macaulay Neuropathologist, MCC October 21, 2017 Objectives Explain why the designation high grade glioma is preferable to GBM for intraoperative
Classification of Diffuse Gliomas: Progress, Pearls and Pitfalls Rob Macaulay Neuropathologist, MCC October 21, 2017 Objectives Explain why the designation high grade glioma is preferable to GBM for intraoperative
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue. Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells. The Nervous System. The Nervous System 21/12/2010
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms
 Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium
 NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
HISTOLOGY د.عبد الجبار فالح الربيعي
 Nervous System The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Anatomically
Nervous System The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Anatomically
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0027 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0027 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Overview of the Nervous System A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Irene Yu, class of 2019
 Irene Yu, class of 2019 Nerve Cells and Glia Overview What is the brain made of - types of cells What do neurons do; How are they specialized to do it? CONCEPTS communication via signalling changeability
Irene Yu, class of 2019 Nerve Cells and Glia Overview What is the brain made of - types of cells What do neurons do; How are they specialized to do it? CONCEPTS communication via signalling changeability
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
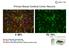 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat
 Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
What we will talk about
 Surgical Neuropathology: Avoiding pitfalls at frozen section and Immunochemistry that really helps Arizona Society of Pathologists Fall 2013 Stephen W. Coons MD Barrow Neurological Institute Beauregard
Surgical Neuropathology: Avoiding pitfalls at frozen section and Immunochemistry that really helps Arizona Society of Pathologists Fall 2013 Stephen W. Coons MD Barrow Neurological Institute Beauregard
Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more
 Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
The Nervous System 7PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
Advances In Orbital Neuropathology
 Advances In Orbital Neuropathology Charles G. Eberhart, MD PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, Ophthalmology and Oncology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Overview Non-neoplastic lesions Microphthalmos/pseudoglioma
Advances In Orbital Neuropathology Charles G. Eberhart, MD PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, Ophthalmology and Oncology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Overview Non-neoplastic lesions Microphthalmos/pseudoglioma
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS OF GLIOMAS
 MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS OF GLIOMAS Arie Perry, M.D. Director, Neuropathology Division DIFFUSE GLIOMAS Cell types Astrocytomas (A) Oligodendrogliomas (O) Mixed oligoastrocytoma (MOA) Three WHO grades: II,
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS OF GLIOMAS Arie Perry, M.D. Director, Neuropathology Division DIFFUSE GLIOMAS Cell types Astrocytomas (A) Oligodendrogliomas (O) Mixed oligoastrocytoma (MOA) Three WHO grades: II,
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
1 NORMAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY
 1 NORMAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY OF THE CNS Anatomy 1 Histology 4 ANATOMY Knowledge of nervous system anatomy is essential for success in surgical neuropathology. Familiarity with native cellular elements
1 NORMAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY OF THE CNS Anatomy 1 Histology 4 ANATOMY Knowledge of nervous system anatomy is essential for success in surgical neuropathology. Familiarity with native cellular elements
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Neurons vs. glia. Traditionally, glia have been viewed as passive cells that help to maintain the function of neurons.
 GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
Chapter 7. The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
Cellular components of CNS
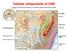 Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Neurons and Glial Cells *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44747 1 Neurons and Glial Cells * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m44747 1 Neurons and Glial Cells * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Nervous system. 1. Neurons :
 Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
USCAP Neuropathology. Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC
 USCAP Neuropathology Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC Clinical history The patient is a 9 year-old boy who has had seizures since age 2, at which time
USCAP Neuropathology Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC Clinical history The patient is a 9 year-old boy who has had seizures since age 2, at which time
BAH1 - Primary Glioblastoma
 BAH1 - Primary Glioblastoma R frontal tumour for frozen section. No known primary. Contrast enhancing lesion. Cholecystectomy. FROZEN SECTION REPORT Right frontal tumour: The specimen consists of multiple
BAH1 - Primary Glioblastoma R frontal tumour for frozen section. No known primary. Contrast enhancing lesion. Cholecystectomy. FROZEN SECTION REPORT Right frontal tumour: The specimen consists of multiple
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei
 Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Functions of the Nervous System. Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue
 Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Overview Structure cell types & structures Neurophysiology membrane potential Synapse, neurotransmitters & receptors Functions of the Nervous System
Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Overview Structure cell types & structures Neurophysiology membrane potential Synapse, neurotransmitters & receptors Functions of the Nervous System
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Unit Three. I. General Functions of the Nervous System. I. General Functions of the Nervous System
 10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
Man and his environment
 Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Nervous Tissue. OpenStax College. 1 Neurons
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46509 1 Nervous Tissue OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46509 1 Nervous Tissue OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3
 SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
Intraoperative Cytology of CNS Lesions
 1 Intraoperative Cytology of CNS Lesions Matthew A Zarka, M.D. Director of Cytopathology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona Gregory S. Moes, M.D. Department
1 Intraoperative Cytology of CNS Lesions Matthew A Zarka, M.D. Director of Cytopathology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona Gregory S. Moes, M.D. Department
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Epidemiology and Outcome of Brain Disorders & Damage Across the Life Span: Some Notes. Vincent W. Hevern, SJ, Ph.D. 2016
 Epidemiology and Outcome of Brain Disorders & Damage Across the Life Span: Some Notes Cerebrovascular Disease or Stroke Vincent W. Hevern, SJ, Ph.D. 2016 A. Epidemiology of Brain Disorders & Damage Number
Epidemiology and Outcome of Brain Disorders & Damage Across the Life Span: Some Notes Cerebrovascular Disease or Stroke Vincent W. Hevern, SJ, Ph.D. 2016 A. Epidemiology of Brain Disorders & Damage Number
STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
USCAP Neuropathology night panel CASE 4
 USCAP Neuropathology night panel CASE 4 B.K. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters MD University of Colorado Denver Denver, Colorado Sheep Mountain, Telluride, Colorado Clinical History The patient is a 46 year old male
USCAP Neuropathology night panel CASE 4 B.K. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters MD University of Colorado Denver Denver, Colorado Sheep Mountain, Telluride, Colorado Clinical History The patient is a 46 year old male
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Data Mining for Research and Diagnostics
 UCL DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY UCL INSTITUTE OF NEUROLOGY Data Mining for Research and Diagnostics Sebastian Brandner, UCL Institute of Neurology, London Data mining for Research and Diagnostics Our setup
UCL DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY UCL INSTITUTE OF NEUROLOGY Data Mining for Research and Diagnostics Sebastian Brandner, UCL Institute of Neurology, London Data mining for Research and Diagnostics Our setup
