Neonatal Brain Tumors: A Review. Shaam Bodeliwala, Vikas Kumar, Daljit Singh*
|
|
|
- Oswin Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Neonatal Surgery 2017; 6:30 Doi: /jns.v6i2.579 REVIEW ARTICLE Neonatal Brain Tumors: A Review Shaam Bodeliwala, Vikas Kumar, Daljit Singh* Department of Neurosurgery, G. B. Pant Institute of Postgraduate Education and Research (GIPMER), New Delhi. How to cite: Bodeliwala S, Kumar V, Singh D. Neonatal brain tumors: A review. J Neonat Surg. 2017;6:30. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Brain tumors in neonatal age group is uncommon comparing with older children and adults. In older children brain tumors are commonly infratentorial, where as in neonates, they are supratentorial. Though extracranial tumors are commoner in neonates, brain tumors cause 5-20% deaths approximately. We are presenting a review on brain tumors in neonates. Key words: Tumors; Brain; Neonate Incidence Central nervous system malignancy is the third most common pediatric malignancy in India [1,2]. Fortunately, incidence of neonatal brain tumors (NBT) is very low comprising <1% of pediatric CNS malignancy[1], the exact incidence of NBT is not known in India due to lack of complete registration and data collection. Classifications Histological types of common neonatal brain tumors are different from older children and adults. Types of NBTs are teratomas, astrocytomas, embryonal tumors, choroid plexus tumors, craniopharyngiomas, gangliogliomas, ependymal and meningeal tumors and other miscellaneous tumors. Among them teratoma is being the commonest tumor comprising of almost one third of cases[1]. Indian neonatal brain tumor incidence in different types is not specified, but astrocytoma (34.7%) being the most common pediatric brain tumor followed by medulloblastoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors (22.4%)[3]. Another single center study from southern India mentioned incidence of the most common pediatric brain tumor as astrocytoma 47.3% followed by medulloblastoma 11.4% and craniopharyngioma 9.7%[4]. Clinical features NBTs are mainly classified into three groups according to presentation: prenatal, perinatal and postnatal. Since last two decades, use of advanced technology in antenatal imaging has increased incidence of prenatal diagnosis of NBTs. Antenatal ultrasonography is the main stay of diagnosis. Increased head size, large for gestational age uterus, polyhydramnios, hydrops, and hydrocephalus are initial presenting findings in antenatal ultrasonography. Ultrasonography also finds macrocephaly, hydrocephalus, an abnormal intracranial echogenicity or features suggestive of intracranial mass. Nowadays, use of fetal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in suspicious cases has increased specificity in the diagnosis of brain tumors. Others can present with obstructed labor or dystocia due to cephalo-pelvic disproportion owing to large head. It may cause stillbirth or premature labor. Postnatally, neonates present with large head, symptoms of raised intracranial pressure, bulging fontanels, irritability, drowsiness, morning vomiting, failure to thrive, apnoeic episodes, neurological deficits or seizures [1,5]. Volpe [6] divided NBTs in four groups: (1) severe macrocrania caused by gigantic tumors leading to cephalo-pelvic disporportion, dystocia, stillbirth, or premature labor; (2) hydrocephalus with a large head and Correspondence*: Dr. Daljit Singh, Professor and Head, Department of Neurosurgery, G. B. Pant Institute of Postgraduate Education and Research (GIPMER), New Delhi. E mail: drdaljit@hotmail.com 2017, Journal of Neonatal Surgery Submitted: Accepted: Conflict of interest: Nil Source of Support: Nil
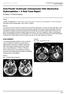
2 bulging fontanel; (3) specific neurologic findings according to the type and site of the lesion (e.g. hemiparesis, or quadri-paresis, seizures, cranial nerve abnormalities, and increased intracranial pressure); (4) sudden intracranial hemorrhage (8-18%). Large head size or macrocephaly ( %) [1,7] is the commonest finding in such neonates, while hydrocephalus (17.3%) [1] is the second most common. Macrocephaly can be due to tumor itself or hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus commonly occurs with compression of ventricles by tumor or hemorrhage from the tumor or hypersecretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in case of choroid plexus tumors. Seizure is the rare presentation but may be present in some cases (10 15%) [5]. Intra-ventricular hemorrhage is rare but has been reported in few cases of astrocytoma [3]. create drop metastasis [5]. Some radiological features of common neonatal brain tumors are summarized in table 1. Disadvantage of MRI is that it takes several minutes and neonates are required to stay still. Often neonates are subjected to general anesthesia if sedatives do not serve the purpose. MRI delineates anatomy of surrounding structures and extent of the tumor very well but does not show calcification present in tumors, which is helpful to differentiate subtypes of glioma-oligodendroglioma or ganglioglioma. Computed tomography shows calcification better but uses high dose of ionizing radiation. Ultrasonography has the limited role in postnatal period. For the tumors in the pineal region, biomarkers like alpha-feto protein (AFP), human beta-chorionic gonadotropin (hcg) levels are of help in diagnosis, as they are raised in germ cell tumors, choriocarcinoma and yolk cell tumors. Figure1: figures, computed tomography (A) and contrast T1- weighted magnetic resonance image (B) of a 4 months old child showing a tumor in suprachiasmatic region extending into third ventricle, which is homogeneously contrast enhancing. These radiological features are suggestive of optico-chiasmatic glioma. Figure 3: figures, contrast T1-weighted axial (A) and sagittal (B) magnetic resonance images of a child showing an intraventricular contrast enhancing lesion with hydrocephalus, features compatible with of choroid plexus papilloma. Figure 2: figures, contrast T1-weighted (A) and T2-weighted (B) magnetic resonance images of 2 months old child showing a heterogeneously enhancing solid-cystic mass extending from suprachiasmtic region to third ventricle. Histopathological diagnosis was pilocytic astrocytoma. Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the choice of investigation (Fig.1-4). Screening of the entire neuraxis is necessary as germ cell tumours, embryonal tumors and occasionally pilocytic (benign) lesions have a propensity to metastasise through CSF and Figure 4: Non-contrast (A) and contrast enhanced (B)T1-weighted magnetic resonance images of a patient showing solid-cystic mass with heterogeneous contrast enhancement and intensity suggestive of medulloblastoma. Antenatal diagnosis of congenital brain tumors is possible by antenatal ultrasonography and fetal MRI. Fetal MRI can delineate tumor and surrounding anatomy but it is indicated after ultrasound in third trimester. Safety of MRI has not been established in second or first trimester. Gadolinium MRI contrast is
3 not recommended during pregnancy. A fast T2- weighted single-shot technique on a 1.5-Tesla machine is recommended for fetal anatomy assessment to minimize the fetal movement artifacts [8]. Caution should be taken while using a 3-Tesla machine in indicated cases. Table 1: radiological features of common neonatal brain tumors [21, 22] Tumor type Location Radiological appearance Teratoma Choroid plexus papilloma Astrocytoma Supratentorial (common), Infratentorial (less often) Supratentorial Supratentorial (optic nerve, and hypothalamic/chiasmatic region), Infratentorial (less often) Large, solid/cystic, heterogeneous signal intensity on T1- and T2- weighted images, mixed-density lesion in CT, hypodense fatty components, coarse calcification, sometimes reflect the presence of bone and teeth Intraventricular mass with homogeneous contrast enhancement, Homogeneous intermediate T1 signal and high T2 signal, Hydrocephalus (common) Pilocytic astrocytoma (solid component) shows hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2 but higher grade may show heterogenous intensity. Medulloblastoma (embryonal tumors) Infratentorial Heterogeneous signal intensity on T1- and T2- weighted images, Curvilinear/sparse calcification Ganglioglioma Supratentorial Microscopic calcification, Diffusion restriction not seen Glioblastoma Supratentorial Isointense to the brain or slightly hyperintense on T1- weighted images and isointense on T2-weighted images, Diffusion restriction seen Management Treatment of neonatal brain tumors have two aspects: surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy. Radiotherapy is contraindicated in children less than three years of age due to its exaggerated long term side effects in neonates like developmental retardation, neuro-endocrine abnormalities, the risk of secondary neoplasms in the CNS and premature death [5]. Radiotherapy can be postponed up to three years of age as chemotherapy can buy time. Surgical resection is the primary treatment of NBTs. It decreases the tumor burden as provides tissue for histological diagnosis. Gross total resection (GTR) is independently correlated with improved survival even in pediatric population [9,10]. Surgical resection can be done by open or endoscopic approach. Endoscopic approach is suitable for intra-ventricular tumors, particularly small tumors. Large tumors or parenchymal tumors are better approached through open surgery as per our experience. Additionally, it can be combined with endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) in patients with obstructive hydrocephalus. Major hurdle of open surgery in NBTs, particularly for large tumors, is blood loss. Blood loss and tumor location in eloquent area preclude gross total resection [5]. Poor outcome in neonates is due to subtotal resection, high-grade tumor histology and avoidance of radiotherapy [5]. Review of literature did not show relevance of mortality with tumor size in NBTs. Many patients present with symptomatic hydrocephalus, they require CSF diversion in form of ventriculo-peritoneal shunt, ETV or external ventricular drainage. Such patients can be underwent CSF diversion procedure in emergency followed by planned surgical tumor resection. Some patients may require a CSF diversion in postoperative period. One study from southern India mentioned that short history, Evan s index at the time of presentation and need of intraoperative ventricular drainage are positively associated with requirement of CSF shunt following posterior fossa tumor resection in pediatric patients [11]. Adjuvant chemotherapy is the second aspect of treatment of NBTs. Multi-agent chemotherapy had been tried with or without delayed radiotherapy after surgical resection. A German study involving children less than 3 years of anaplastic ependymoma suggested that delaying radiotherapy decreases the survival even after intensive chemotherapy [12]. The prospective multicenter trial HIT 2000 proposed
4 short intensive induction chemotherapy using carboplatin and etoposide followed by tandem-high dose chemotherapy (HDCT) in young children with CNS- PNET/pineoblastomas increased survival benefits [13]. In one American study, second look surgery was done in enrolled patients to achieve the GTR after multi-agent chemotherapy and found induction chemotherapy resulted in devascularization of tumors with volume regression in the majority and subsequently facilitated resection with acceptable intraoperative blood loss. GTR achieved in second look surgery added survival benefit. This concluded that a GTR of infantile brain tumors is one of the most important predictors of outcome [10]. Many studies indicated that tandem HDCT with autologous stem cell transplantation (SCT) may improve survival in young children in malignant brain tumors with an acceptable risk [14,15]. But elaborative studies are required for further implementation. Prognosis Survival in neonatal brain tumors is poor due to less aggressive tumor resection, high grade pathology and avoidance of radiotherapy. Location of the tumor is also an important factor as in eloquent areas surgical resection is difficult, for example brain stem glioma. Median survival in pediatric brain stem glioma is 10 months [16]. Mortality was more than 90% in neonatal brain tumors within 5 years of age [17]. Isaacs reported 15% overall survival in a review of 154 cases (54 were stillborn) diagnosed prenatally [18]. High-grade tumors like medulloblastomas, embryonal tumors (primitive neuroectodermal tumors), glioblastoma have poorer prognosis than low-grade astrocytomas, gangliogliomas and meningeal tumors. One study mentioned that survival was 48.1±9.6% for patients with medulloblastoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors; 83.3±6.2% for low-grade astrocytoma; 56.6±16.6% for ependymoma, while 0% at 72 months for high-grade glioma [19]. Literature reveals that there is very high incidence of endocrine, neurologic, and cognitive deficits in survivors [20,5]. So it is at far most important that parents should be consented and counseled regarding treatment and prognosis. Conclusion Neonatal brain tumors are fortunately rare but with very high mortality and morbidity. Most of the survivors suffer from endocrinological, neurological or cognitive deficits. Parents should be informed and consented for the treatment and prognosis of the children. Cumulative approach by pediatricians, neurosurgeons should be taken in highly specialized centers with long term follow up. REFERENCES 1. Isaacs H. I. Perinatal brain tumors: a review of 250 cases. Pediatr Neurol. 2002;27: Satyanarayana L, Asthana S, Preeti Labani S. Childhood cancer incidence in India: A review of population-based cancer registries. Indian Pediatr. 2014;51: Sarkar C, Jain A, Sharma M, Suri V, Kale S, Mahapatra A, et al. Spectrum of pediatric brain tumors in India: A multi-institutional study. Neurol India. 2011;59: Asirvatham J, Deepti A, Chyne R, Prasad M, Chacko A, Rajshekhar V, et al. Pediatric tumors of the central nervous system: a retrospective study of 1,043 cases from a tertiary care center in South India. Child's Nervous System. 2011;27(8): Magdum S. Neonatal brain tumours-a review. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86: Volpe JJ. Brain tumors and vein malformations. In: Volpe JJ (ed.) Neurology of the newborn, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1995; pp Wilne S, Collier J, Kennedy C, Koller K, Grundy R, Walker D. Presentation of childhood CNS tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(: Wataganara T, Ebrashy A, Aliyu L, Moreira de Sa R, Pooh R, Kurjak A, et al. Fetal magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound. J Perinat Med. 2016;44: Adams H, Adams H, Jackson C, Rincon-Torroella J, Jallo G, Quiñones-Hinojosa A. Evaluating extent of resection in pediatric glioblastoma: a multiple propensity scoreadjusted population-based analysis. Child's Nerv Syst. 2016;32: Van Poppel M, Klimo P, Dewire M, Sanford R, Boop F, Broniscer A, et al. Resection of infantile brain tumors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: the St. Jude experience. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2011;8: Gopalakrishnan C, Dhakoji A, Menon G, Nair S. Factors predicting the need for cerebrospinal fluid diversion following posterior fossa tumor surgery in children. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2012;48: Timmermann B, Kortmann R, Kühl J, Rutkowski S, Dieckmann K, Meisner C, et al. Role of radiotherapy in anaplastic ependymoma in children under age of 3 years: Results of the prospective German brain tumor trials HIT-SKK 87 and 92. Radiother Oncol. 2005;77: Friedrich C, von Bueren A, von Hoff K, Gerber N, Ottensmeier H, Deinlein F, et al. Treatment of young children with CNS-primitive neuroectodermal tumors/pineoblastomas in the prospective multicenter trial HIT 2000 using different chemotherapy regimens and radiotherapy. Neuro-Oncol. 2012;15: Lee J, Lim D, Sung K, Lee H, Yi E, Yoo K, et al. Tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for high-grade gliomas in children and adolescents. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32: Sung K, Lim D, Lee S, Yoo K, Koo H, Kim J, et al. Tandem high-dose chemotherapy and auto-sct for malignant brain tumors in children under 3 years of age. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013; 48: Jansen M, Veldhuijzen van Zanten S, Sanchez Aliaga E, Heymans M, Warmuth-Metz M, Hargrave D, et al. Survival prediction model of children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma based on clinical and radiological criteria. Neuro-Oncol. 2014; 17: Armstrong G, Liu Q, Yasui Y, Huang S, Ness K, Leisenring W, et al. Long-term outcomes among adult survivors of childhood central nervous system malignancies in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:
5 18. Isaacs H. Fetal Brain Tumors: A Review of 154 Cases. Am J Perinatol. 2009;26: Pogorzala M, Styczynski J, Wysocki M. Survival and prognostic factors in children with brain tumors: longterm follow-up single center study in Poland. Anticancer Res. 2014;34: Qaddoumi I, Carey S, Conklin H, Jenkins J, Sabin N, Boop F et al. Characterization, treatment, and outcome of intracranial neoplasms in the first 120 days of life. J Child Neurol. 2011;26: Buetow P, Smirniotopoulos J, Done S. Congenital brain tumors: a review of 45 cases. Am J Roentgenol. 1990;155: Parmar H, Pruthi S, Ibrahim M, Gandhi D. Imaging of congenital brain tumors. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI. 2011;32:
BRAIN TUMORS IN INFANTS
 BRAIN TUMORS IN INFANTS Dr Sergio Valenzuela M.D-( ISPN-ESPN-FLANC)&cols. Head Pediatric Neurosurgery Unit I Instituto de NeurocirugiaAsenjo Santiago CHILE RATE OF MENINGEAL,BRAIN AND OTHER CNS MALIGNANT
BRAIN TUMORS IN INFANTS Dr Sergio Valenzuela M.D-( ISPN-ESPN-FLANC)&cols. Head Pediatric Neurosurgery Unit I Instituto de NeurocirugiaAsenjo Santiago CHILE RATE OF MENINGEAL,BRAIN AND OTHER CNS MALIGNANT
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
A Rare Aggressive Fetal Intracranial Tumor
 J. Fetal Med. (June 2015) 2:91 95 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0046-y BRIEF COMMUNICATION A Rare Aggressive Fetal Intracranial Tumor Ravi Kapoor 1 Ashutosh Bansal 1 Aakriti Kapoor Aggarwal 2 Abhinav Aggarwal
J. Fetal Med. (June 2015) 2:91 95 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0046-y BRIEF COMMUNICATION A Rare Aggressive Fetal Intracranial Tumor Ravi Kapoor 1 Ashutosh Bansal 1 Aakriti Kapoor Aggarwal 2 Abhinav Aggarwal
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors
 Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management. Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP
 Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS BACKGROUND: Incidence: Third most common pediatric tumor type (leukemia, neuroblastoma,
Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS BACKGROUND: Incidence: Third most common pediatric tumor type (leukemia, neuroblastoma,
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care
 Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care Writer Classroom Rishi R. Lulla, MD MS Objectives Introduce the common pediatric brain tumors Discuss current treatment strategies for pediatric brain
Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care Writer Classroom Rishi R. Lulla, MD MS Objectives Introduce the common pediatric brain tumors Discuss current treatment strategies for pediatric brain
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity
 Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours. Colin Kennedy March 2015
 Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Clinical, radiological, and histopathological features and prognostic factors of brain tumors in children
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Clinical, radiological, and histopathological features and prognostic factors of brain tumors in children To cite this article: M H Siregar et al
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Clinical, radiological, and histopathological features and prognostic factors of brain tumors in children To cite this article: M H Siregar et al
Pediatric Oncology. Vlad Radulescu, MD
 Pediatric Oncology Vlad Radulescu, MD Objectives Review the epidemiology of childhood cancer Discuss the presenting signs and symptoms, general treatment principles and overall prognosis of the most common
Pediatric Oncology Vlad Radulescu, MD Objectives Review the epidemiology of childhood cancer Discuss the presenting signs and symptoms, general treatment principles and overall prognosis of the most common
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Financial Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose. Templar Eye Foundation Oppenheimer Family Foundation
 Financial Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose. Templar Eye Foundation Oppenheimer Family Foundation 2 Case 7 year old girl Initially parents noticed photophobia Then started to complain
Financial Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose. Templar Eye Foundation Oppenheimer Family Foundation 2 Case 7 year old girl Initially parents noticed photophobia Then started to complain
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
Childhood Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors Treatment Overview (PDQ )
 1 di 14 27/11/2016 17.42 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 14 27/11/2016 17.42 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
Neurosurgical Management of Brain Tumours. Nicholas Little Neurosurgeon RNSH
 Neurosurgical Management of Brain Tumours Nicholas Little Neurosurgeon RNSH General Most common tumours are metastatic 10x more common than primary Incidence of primary neoplasms is 20 per 100000 per year
Neurosurgical Management of Brain Tumours Nicholas Little Neurosurgeon RNSH General Most common tumours are metastatic 10x more common than primary Incidence of primary neoplasms is 20 per 100000 per year
Nature and Science 2017;15(7) Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus
 Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Protocol for management of patients with pineal region tumours v1
 Protocol for management of patients with pineal region tumours v1 West Midlands Cancer Alliance Coversheet for Cancer Alliance Expert Advisory Group Agreed Documentation This sheet is to accompany all
Protocol for management of patients with pineal region tumours v1 West Midlands Cancer Alliance Coversheet for Cancer Alliance Expert Advisory Group Agreed Documentation This sheet is to accompany all
Department of Neurosurgery, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, United Kingdom
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:563 573, 2018 Surgical decision-making in the management of childhood tumors of the CNS disseminated at presentation Matthew A. Kirkman, MEd, MRCS, Richard Hayward,
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:563 573, 2018 Surgical decision-making in the management of childhood tumors of the CNS disseminated at presentation Matthew A. Kirkman, MEd, MRCS, Richard Hayward,
Ependymomas: Prognostic Factors and Outcome Analysis in a Retrospective Series of 33 Patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 2017;5(2):70-76 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.2.70 Ependymomas: Prognostic Factors and Outcome Analysis in a Retrospective
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 2017;5(2):70-76 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.2.70 Ependymomas: Prognostic Factors and Outcome Analysis in a Retrospective
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome
 Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome SAN The Sudanese association of neurosurgeons By Dr. Abubakr Darrag Salim Ahmed Dr. Mohammed Awad Elzain Khartoum Sudan Pediatric
Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome SAN The Sudanese association of neurosurgeons By Dr. Abubakr Darrag Salim Ahmed Dr. Mohammed Awad Elzain Khartoum Sudan Pediatric
Brain tumors: tumor types
 Brain tumors: tumor types Tumor types There are more than 120 types of brain tumors. Today, most medical institutions use the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system to identify brain tumors.
Brain tumors: tumor types Tumor types There are more than 120 types of brain tumors. Today, most medical institutions use the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system to identify brain tumors.
Early Human Development
 Early Human Development 86 (2010) 627 631 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Early Human Development journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/earlhumdev Neonatal brain tumours A review Shailendra
Early Human Development 86 (2010) 627 631 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Early Human Development journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/earlhumdev Neonatal brain tumours A review Shailendra
Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma With Surgical Correlation
 Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma With Surgical Correlation Ali Mahmood, M.D., and Nadia F. Mahmood, M.D. Citation: Mahmood A, Mahmood NF. Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal
Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma With Surgical Correlation Ali Mahmood, M.D., and Nadia F. Mahmood, M.D. Citation: Mahmood A, Mahmood NF. Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal
THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION. Mustafa Rashid Issa
 THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION Mustafa Rashid Issa ABSTRACT: Illustrate malignant tumors that form either in the brain or in the nerves originating in the brain.
THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION Mustafa Rashid Issa ABSTRACT: Illustrate malignant tumors that form either in the brain or in the nerves originating in the brain.
Aria Fallah MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Aria Fallah MD, MSc, FRCSC Department of Neurosurgery David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pineal Region Tumors Brain Tumor Symposium August 22, 2015 Disclosures None Pineal Gland Arises from an invagination
Aria Fallah MD, MSc, FRCSC Department of Neurosurgery David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pineal Region Tumors Brain Tumor Symposium August 22, 2015 Disclosures None Pineal Gland Arises from an invagination
Case Report Tackling a Recurrent Pinealoblastoma
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 135435, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/135435 Case Report Tackling a Recurrent Pinealoblastoma Siddanna Palled, 1 Sruthi Kalavagunta, 1 Jaipal Beerappa
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 135435, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/135435 Case Report Tackling a Recurrent Pinealoblastoma Siddanna Palled, 1 Sruthi Kalavagunta, 1 Jaipal Beerappa
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CNS Embryonal Tumors File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_cns_embryonal_tumors
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CNS Embryonal Tumors File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_cns_embryonal_tumors
Small and Big Operations: New Tools of the Trade for Brain Tumors. Disclosure. Incidence of Childhood Cancer
 Small and Big Operations: New Tools of the Trade for Brain Tumors Nalin Gupta MD PhD Chief, Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Departments of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of California San Francisco
Small and Big Operations: New Tools of the Trade for Brain Tumors Nalin Gupta MD PhD Chief, Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Departments of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of California San Francisco
A rare case of large fetal intracranial tumor: Teratoma
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS A rare case of large fetal intracranial tumor: Teratoma Chiranjeev Kumar Gathwal, Devender Kaur, Kulvinder Singh, Jyotsana Sen, Monika B. Gathwal,
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS A rare case of large fetal intracranial tumor: Teratoma Chiranjeev Kumar Gathwal, Devender Kaur, Kulvinder Singh, Jyotsana Sen, Monika B. Gathwal,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Dr.Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University
 Dr.Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University Brain tumors are the second commonest malignancy in children Infratentorial tumors are more common As a general rule they do not metastasize out of the CNS, but
Dr.Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University Brain tumors are the second commonest malignancy in children Infratentorial tumors are more common As a general rule they do not metastasize out of the CNS, but
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits
 An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
CHAPTER 11 Tumors Originating in the Brain Medulloblastomas, PNETs and Ependymomas
 Tumors Originating in the Brain Medulloblastomas, PNETs and Ependymomas Foolishly, I waited 7 months before I joined this (or any) group. By that time, my son had radiation, chemo, and a recurrence of
Tumors Originating in the Brain Medulloblastomas, PNETs and Ependymomas Foolishly, I waited 7 months before I joined this (or any) group. By that time, my son had radiation, chemo, and a recurrence of
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution
 Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
MALIGNANT GLIOMAS: TREATMENT AND CHALLENGES
 MALIGNANT GLIOMAS: TREATMENT AND CHALLENGES DISCLOSURE No conflicts of interest to disclose Patricia Bruns APRN, CNS Givens Brain Tumor Center Abbott Northwestern Hospital October 12, 2018 OBJECTIVES THEN
MALIGNANT GLIOMAS: TREATMENT AND CHALLENGES DISCLOSURE No conflicts of interest to disclose Patricia Bruns APRN, CNS Givens Brain Tumor Center Abbott Northwestern Hospital October 12, 2018 OBJECTIVES THEN
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors
 Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt
 Bangladesh Medical Journal 2011 Vol. 0 No. 1 Orginal Article Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt MR Islam 1, KMT Islam 2, M Hossain, MH Rashid,
Bangladesh Medical Journal 2011 Vol. 0 No. 1 Orginal Article Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt MR Islam 1, KMT Islam 2, M Hossain, MH Rashid,
An Updated Nationwide Epidemiology of Primary Brain Tumors in Republic of Korea, 2013
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 217;5(1):16-23 / pissn 2288-245 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/1.14791/btrt.217.5.1.16 An Updated Nationwide Epidemiology of Primary Brain Tumors in Republic of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 217;5(1):16-23 / pissn 2288-245 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/1.14791/btrt.217.5.1.16 An Updated Nationwide Epidemiology of Primary Brain Tumors in Republic of
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules MALIGNANT CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways
Original Article Clinical Outcome after Transcortical Approach for Lateral Ventricular Neoplasms
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 2 / April - June 2014 19-24 Original Article Clinical Outcome after Transcortical Approach for Lateral Ventricular Neoplasms ARTICLE INFO Received: 1 March
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 2 / April - June 2014 19-24 Original Article Clinical Outcome after Transcortical Approach for Lateral Ventricular Neoplasms ARTICLE INFO Received: 1 March
Case Based Fetal Lung Masses
 Case Based Fetal Lung Masses Advances in Fetal and Neonatal Imaging Course Orlando, Florida, January 28, 2017 Leann E. Linam, MD Associate Professor Radiology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences/
Case Based Fetal Lung Masses Advances in Fetal and Neonatal Imaging Course Orlando, Florida, January 28, 2017 Leann E. Linam, MD Associate Professor Radiology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences/
Histopathological Spectrum of Central Nervous System Tumors: A Single Centre Study of 100 Cases
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/408 Histopathological Spectrum of Central Nervous System Tumors: A Single Centre Study of 100 Cases Sarita Nibhoria 1, Kanwardeep Kaur Tiwana 1, Richa Phutela 2,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/408 Histopathological Spectrum of Central Nervous System Tumors: A Single Centre Study of 100 Cases Sarita Nibhoria 1, Kanwardeep Kaur Tiwana 1, Richa Phutela 2,
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad
 Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal macrocephaly: cerebral PNET or neuroblastoma. cause
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal macrocephaly: cerebral PNET or neuroblastoma as an infrequent cause May 2006 2 Kaczala G, Poskitt K, Steinbok P, Hendson G, Phang M, Solimano A, British Columbia Children
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal macrocephaly: cerebral PNET or neuroblastoma as an infrequent cause May 2006 2 Kaczala G, Poskitt K, Steinbok P, Hendson G, Phang M, Solimano A, British Columbia Children
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM GERM CELL TUMOURS CNS Site Group Germ Cell Tumours Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM GERM CELL TUMOURS CNS Site Group Germ Cell Tumours Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Intrinsic brainstem tumors may be a challenge to the
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:598 603, 2014 AANS, 2014 Neurosurgical treatment of pediatric low-grade midbrain tumors: a single consecutive institutional series of 15 patients Clinical article Tryggve Lundar,
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:598 603, 2014 AANS, 2014 Neurosurgical treatment of pediatric low-grade midbrain tumors: a single consecutive institutional series of 15 patients Clinical article Tryggve Lundar,
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Adult Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors
 Adult Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors An adult central nervous system (CNS) tumor is a disease in which abnormal cells form in the tissues of the brain and or the spinal cord. Major Parts of the Brain Anatomy
Adult Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors An adult central nervous system (CNS) tumor is a disease in which abnormal cells form in the tissues of the brain and or the spinal cord. Major Parts of the Brain Anatomy
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
Anatomy, Histology and general pathology of the Pineal gland. Uri Shiri 1 st year, Int. medicine B
 Anatomy, Histology and general pathology of the Pineal gland Uri Shiri 1 st year, Int. medicine B The Pineal gland A small, ~8mm sized Endocrine gland. The Pineal gland A small, ~8mm sized Endocrine gland.
Anatomy, Histology and general pathology of the Pineal gland Uri Shiri 1 st year, Int. medicine B The Pineal gland A small, ~8mm sized Endocrine gland. The Pineal gland A small, ~8mm sized Endocrine gland.
Building a Neuro-Oncology Program and Epidemiological Profiling of Pediatric Brain Tumors in a Tertiary Cancer Care Center in India
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; July 2018; 9(3): 228-234 Building a Neuro-Oncology Program and Epidemiological Profiling of Pediatric Brain Tumors in a Tertiary Cancer Care Center in India
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; July 2018; 9(3): 228-234 Building a Neuro-Oncology Program and Epidemiological Profiling of Pediatric Brain Tumors in a Tertiary Cancer Care Center in India
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms
 New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
Pediatric low-grade glioma
 J Radiat Oncol (2013) 2:129 133 DOI 10.1007/s13566-012-0078-z REVIEW Pediatric low-grade glioma Anita Mahajan Received: 21 October 2012 / Accepted: 6 November 2012 / Published online: 19 November 2012
J Radiat Oncol (2013) 2:129 133 DOI 10.1007/s13566-012-0078-z REVIEW Pediatric low-grade glioma Anita Mahajan Received: 21 October 2012 / Accepted: 6 November 2012 / Published online: 19 November 2012
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC CANCERS
 WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC CANCERS INTRODUCTION Childhood cancers are RARE 0.5% of all cancers in the West Overall risk that a child will develop cancer during first 15 years of life is 1 in 450 and 1 in 600
WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC CANCERS INTRODUCTION Childhood cancers are RARE 0.5% of all cancers in the West Overall risk that a child will develop cancer during first 15 years of life is 1 in 450 and 1 in 600
Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CNS Embryonal Tumors and Ependymoma
 Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CNS Embryonal Tumors and Ependymoma Policy Number: 8.01.28 Last Review: 7/2014 Origination: 7/2002 Next Review: 7/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CNS Embryonal Tumors and Ependymoma Policy Number: 8.01.28 Last Review: 7/2014 Origination: 7/2002 Next Review: 7/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Symtomatic Subependymoma Of The Lateral Ventricle: A Rare Entity A Case report and review of literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Symtomatic Subependymoma Of The Lateral Ventricle: A Rare Entity A Case report and review of M Sharma, V Velho, P Ghodgaonkar, D Palande
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Symtomatic Subependymoma Of The Lateral Ventricle: A Rare Entity A Case report and review of M Sharma, V Velho, P Ghodgaonkar, D Palande
Adult Central Nervous System Tumors Treatment (PDQ )
 1 di 20 28/06/2016 11.18 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 20 28/06/2016 11.18 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 08 Page August 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i8.19 Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i8.19 Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation
Risk factors for Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in children with posterior fossa tumor
 Risk factors for Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in children with posterior fossa tumor Raed M Aljubour, MD *, Ahmed K Alomari, MD*, Awni F Musharbash, MD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To investigate the Predictors
Risk factors for Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in children with posterior fossa tumor Raed M Aljubour, MD *, Ahmed K Alomari, MD*, Awni F Musharbash, MD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To investigate the Predictors
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
Adult intramedullary astrocytomas of the spinal cord
 J Neurosurg 77:355-359, 1992 Adult intramedullary astrocytomas of the spinal cord FRED J. EPSTEIN, M.D., JEAN-PIERRE FARMER, M.D., F.R.C.S., AND DIANA FREED Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery, Department
J Neurosurg 77:355-359, 1992 Adult intramedullary astrocytomas of the spinal cord FRED J. EPSTEIN, M.D., JEAN-PIERRE FARMER, M.D., F.R.C.S., AND DIANA FREED Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery, Department
Childhood Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors Treatment Overview (PDQ )
 1 di 8 04/03/2017 07.31 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 8 04/03/2017 07.31 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
Case Report Papillary Tumor of the Pineal Region: MR Signal Intensity Correlated to Histopathology
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 315095, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/315095 Case Report Papillary Tumor of the Pineal Region: MR Signal Intensity Correlated to Histopathology
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 315095, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/315095 Case Report Papillary Tumor of the Pineal Region: MR Signal Intensity Correlated to Histopathology
Childhood Central Nervous System Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Treatment (PDQ )
 1 di 10 27/06/2016 08.16 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 10 27/06/2016 08.16 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM LOW GRADE GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Low Grade Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM LOW GRADE GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Low Grade Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING
SOLID TUMOURS IN CHILDHOOD
 SOLID TUMOURS IN CHILDHOOD Fareed Omar Paediatric Oncology Steve Biko Academic hospital Introduction 1 Introduction Lymphomas and Leukemias make up about 40% of all childhood Cancers (Systemic cancers)
SOLID TUMOURS IN CHILDHOOD Fareed Omar Paediatric Oncology Steve Biko Academic hospital Introduction 1 Introduction Lymphomas and Leukemias make up about 40% of all childhood Cancers (Systemic cancers)
Brain tumors in infants (defined as children younger. Resection of infantile brain tumors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: the St.
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 8:000 000, 8:251 256, 2011 Resection of infantile brain tumors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: the St. Jude experience Clinical article Mark Van Poppel, M.D., 1 Paul Klimo Jr., M.D.,
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 8:000 000, 8:251 256, 2011 Resection of infantile brain tumors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: the St. Jude experience Clinical article Mark Van Poppel, M.D., 1 Paul Klimo Jr., M.D.,
Protocol Abstract and Schema
 Protocol Abstract and Schema A Phase I Trial of p28 (NSC745104), a Non-HDM2 mediated peptide inhibitor of p53 ubiquitination in pediatric patients with recurrent or progressive CNS tumors Description and
Protocol Abstract and Schema A Phase I Trial of p28 (NSC745104), a Non-HDM2 mediated peptide inhibitor of p53 ubiquitination in pediatric patients with recurrent or progressive CNS tumors Description and
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Neuro-oncology Update Andrew Kokkino, MD Medical Director, The Neurosciences Institute at Sacred Heart at Riverbend May 20, 2013
 Neuro-oncology Update 2013 Andrew Kokkino, MD Medical Director, The Neurosciences Institute at Sacred Heart at Riverbend May 20, 2013 Case 1 58 year old man with recent facial droop and HA s Thin, cachectic
Neuro-oncology Update 2013 Andrew Kokkino, MD Medical Director, The Neurosciences Institute at Sacred Heart at Riverbend May 20, 2013 Case 1 58 year old man with recent facial droop and HA s Thin, cachectic
Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2012, Article ID 718651, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/718651 Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum Jesús Vaquero, 1,
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2012, Article ID 718651, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/718651 Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum Jesús Vaquero, 1,
Leukaemia 35% Lymphoma 14%
 Distribution ib ti of Cancers in Children under 15 years Leukaemia 35% Lymphoma 14% Neuroblastoma 9% Other 5% Liver 1% Retinoblastoma 3% Bone and STS 15% CNS 20% Wilms' 8% 30-40% Mortality Germ Cell Tumours
Distribution ib ti of Cancers in Children under 15 years Leukaemia 35% Lymphoma 14% Neuroblastoma 9% Other 5% Liver 1% Retinoblastoma 3% Bone and STS 15% CNS 20% Wilms' 8% 30-40% Mortality Germ Cell Tumours
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_in_the_treatment_of_germ_cell_tumor
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Germ File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_in_the_treatment_of_germ_cell_tumor
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Surgical experience with a huge supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumour in a 3 years old boy
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol.09 No.3 Jul 10 Case Report Surgical experience with a huge supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumour in a 3 years old boy Islam MJ 1, Saha SK 2, Khan AM
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol.09 No.3 Jul 10 Case Report Surgical experience with a huge supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumour in a 3 years old boy Islam MJ 1, Saha SK 2, Khan AM
EANS Training Course Moscow, 5 th 8 th May 2019 Tumours
 EANS Training Course Moscow, 5 th 8 th May 2019 Tumours SUNDAY, MAY 5 th, 2019 09:00 09:10 Welcome 09:15 10:30 Tumours Chair: Meling 09:15 09:30 Molecular biology of brain tumours Reinert 09:30 09:45 Imaging
EANS Training Course Moscow, 5 th 8 th May 2019 Tumours SUNDAY, MAY 5 th, 2019 09:00 09:10 Welcome 09:15 10:30 Tumours Chair: Meling 09:15 09:30 Molecular biology of brain tumours Reinert 09:30 09:45 Imaging
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM ANAPLASTIC GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Anaplastic Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM ANAPLASTIC GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Anaplastic Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
What is Brain Cancer? What is the brain?
 What is Brain Cancer? The brain and spinal column make up the central nervous system (CNS), where all vital functions of the body are controlled. When tumors arise in the central nervous system, they are
What is Brain Cancer? The brain and spinal column make up the central nervous system (CNS), where all vital functions of the body are controlled. When tumors arise in the central nervous system, they are
