ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Getachew Assefa, Fathia Omar, Hagos Biluts, Mersha Abebe. Ethiop Med J, 2016, Vol 54, No.3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
|
|
|
- Julia Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 135 Getachew Assefa, Fathia Omar, Hagos Biluts, Mersha Abebe. Ethiop Med J, 2016, Vol 54, No.3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE REVIEW OF THE CLINICAL, COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SCAN AND/OR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FINDINGS OF INTRACRANIAL TUBERCULOMA IN AN ETHIOPIAN TEACHING HOSPITAL Getachew Assefa, MD, 1* Fathia Omar, MD, 1 Hagos Biluts, MD, 2 Mersha Abebe, MD 2 ABSTRACT Background: Ethiopia is one of the countries that has high burden of all forms of tuberculosis and there is no published report on computerized tomography scan and/or magnetic resonance imaging of intracranial tuberculomas. Objective : to review the clinical, computerized tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial tuberculoma Methods: A retrospective review of patient s medical records of patients operated for intracranial mass that had computerized tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging brain scans and had histopathological diagnoses, at Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital between January 2009 and June Results: Of 222 operated cases of intracranial mass subjected to histopathological test 29 (14.6%) were found to have tuberculomas, 28 (14.1%) had caseous necrosis and one was a tuberculous abscess, in 25 cases imaging was available for review and were included in the study. There were 15 males and 10 females with age range being 2 to 65 years and with the Median age being 13 years. Twenty patients had computerized tomography and five patients had magnetic resonance imaging. Seizure 15/25 (60%) and headache 11/25 (44%) were the commonest presentation. Solitary or confluent large lesions were seen in 12/25 (48%) of patients. 14/25 (56%) of the lesions had their size between 2 cm and 5 cm. Majority of the lesions 15/25 (60%) were in the frontal and parietal lobes. The lesions were isodense on CT in 18/25 (72%) of the pre-contrast studies and 21/25 (84%) showed ring or rim enhancement after intravenous administration of the contrast medium. Conclusion: Tuberculoma, more frequently, presented with non-specific clinical findings and chronic seizure disorder and comonly occurred in young patients and often seen infratentorialy. It is often complicated with hydrocephalus in the pediatric age group. Computerized tomography scan and/or magnetic resonance imaging features are not different from reports from other countries. Key Words: Intracranial Tuberculoma, computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, Ethiopia INTRODUCTION Central nervous system (CNS) tuberculosis is the most important form of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis that caries serious consequences and accounts for 10% of all cases of tuberculosis (1). Despite effective anti-tuberculous therapy, it associated with high case fatality rates and neurological deficits. The pandemic of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) has resulted in an increased incidence of CNS tuberculosis (TB) worldwide (2) According to the Ethiopian Federal Ministry of Health s report based on health facility data, tuberculosis is the leading cause of morbidity, the third cause of hospital admission, and the second cause of death in Ethiopia, only surpassed by malaria. Ethiopia ranks seventh among the 22 countries with high TB burden, and third only to South Africa and Nigeria in Africa, with an estimated incidence of all forms of TB at 378/100,000 in 2009 (3). Even though tuberculosis is very common in Ethiopia, introduction of cross-sectional imaging, computerized tomography Scan (CT scan) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is very recent and not widely available during 1 Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Addis Ababa University 2 Department of surgery, School of Medicine, Addis Ababa University * Corresponding author: g_asefa@yahoo.com
2 the study period, there is no radiological descriptive study done on histopathologically proven tuberculoma of the brain. Therefore this study aimed to identify the commonly affected age group, clinical presentation, common brain location and CT/MRI appearance of tuberculoma, observations that will assist in making decisions on early medical treatment, avoid unnecessary surgery, and associated morbidity and mortality. MATERIALS AND METHODS A retrospective review of imaging, CT and/or MRI when available, and medical record of patients who had hitopathological diagnosis of Tuberculoma between January 2009 and June 2013 in Tikur Anbessa Hospital, teaching, a tertiary referral hospital, was made.. Ethical clearance was obtained from the Department of Neurosurgery and Radiology Department Ethics Committee. Clinical presentations and demographic data of patients were filled into a preprepared data entry format. Hard and/or soft copy images, when available for patients who had it done outside the teaching hospitals were re-read by senior consultant neuroradiologiest. The size, number, locations and CT and or MRI desnsity and signal patterns, respectively, of the lesion were entered into the data format. 136 Surgical Procedures: Surgical decompression, nine suboccipital craniotomy/craniectomy, 15 supratentorial craniotomies and one burrhole were performed to remove posterior fossa, supratentorial massess. Iindications for surgery were signs of mass effect with impending herniation and, neurologic detrrioration or deficit in 14 cases, old masses with thick capsule not responding to anti tubercuous therapy in two, and uncontrolled seizure in four, and uncertainty of diagnosis in five patients. Total removal was done when the lesion was solitary and big with significant mass effect; and a biopsy was taken when the lesions were multiple, and the most neurosurgicaly accessible lesion was biopsied. Hematoxillin/eiosin stained histological sections were made for diagnosis of tuberculosis. Ziel Neelson stain for detection of acid fast bacilli and culture were not done because of resource limitation. Collected data was edited and entered into the computer and descriptive analysis made using SPSS statistical software. RESULTS Demographic and clinical: During the study period specimens of 222 operated cases of intra cranial mass were submitted to the department of pathology and out of these 199 had definitive diagnosis of which 29 cases were found to be tuberculomas 28(14.1%) most of which had caseous necrosis and one was a tuberculous abscess. Out of 29 cases 25 of the patients had imaging available for review and were included in the study and out of these 15/25 (60%) were male and 10/25 (40%) patients were female. Twenty percent of the patients were pediatric and below five years of age and 18/25 (72%) of the patients were young adults between the age of years, two of the patients were pregnant mothers. The age range is from 2 to 65 years with the mean and median age of presentation 18 and 13 years respectively (Table1) Table 1: age and sex destribution of patients with CNS tuberculoma, January 2009-June 2013, Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia Description N (%) Sex Male 15(60) Female 10(40) Total 25 (100) Age in <5 5(20) years (36) (24) (12) >45 2(8) Total 25 (100) Median 13
3 137 The main clinical presentations (Table 2.) described at admission were seizure recorded in 15/25 (60%) patients, visual disturbance 9/25 (36%), headache 11/25 (44%), focal neurological defecit 6/25 (24%), change in mentation and gait disturbance in 3/25 (12%). The duration of symptoms before diagnosis ranged one month to eight years, with the mean duration of presentation 11 months. Table 2: Clinical presentation of patients with central nervous system tuberculoma, January June 2013, Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia Clinical presentation Number and perecentage frequency Seizure 15 (60) Headache 11 (44) Visual disturbance 9 (36) Focal neurological deficet 6 (24) Change in mentation 3 (12) Gait abnormality (ataxia) 3 (12 ) Total 25 (100%) Concomitant and chest x-ray suggestive of pulmonary TB was found in 28% of the patients, 2/25 (8%) had previous history of TB, and 4/25 (16%) has contact with active TB patient. Radiological findings: Hard copies and soft copies, when available, were reviewed and 20 patients had CT scans and five patients had an MRI (Table 3). CT demonstrated 18/25 (72%) iso-dense, 4/25 (16%) hypo-dense lesions and calcification was seen in 7/25 (28%) of the cases. Solitary lesion were common finding (Figure 1) accounting for 12/25 (48%), 5/25 (20%) had more than five lesions (Figure 2). Fiftysix percent of the tuberculomas had sizes ranging between 2 cm and 5 cm (Figure 3). Overall, post contrast enhancement was seen in the majority of the lesions except in two which have dense calcification. Twenty-one patients of 25 (84%) demonstrated ring enhancement, 3/25 (12%) solid enhancement, 5/25 (20%) had target lesion. None of the lesion showed heterogeneous enhancement or appearance. Pathological basal meningeal enhancement was seen in 10/25 (40%) of the patient and three of them had basal exudative meningitis. Twelve patients of 25 (48%) had hydrocephalus, and hydrocephalus was more common in the pediatric age group (Figure 4). Table 3: Pre- and post-contrast computerized tomography scans appearance of patients with central nervous system tuberculoma, January June Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia CT Appearance Density Number (%) (n=25) Pre-contrast Iso-dense 18 (72) density Hypo-dense 4 (16) Calcification 7 (28) Post contrast Ring enhancement 21 (84) Target lesion 5 (20) Solid enhancement 3 (12) No enhancement 2 (8) MRI Signal Number (n= 25) T1W hyperintense 1 T1W isointense 4 T2W hypointense 2 T2W intermediate/ isointens 3 T1W contrast enhancement 4 Supra tentoral 16 (64%) location location 9 (36%) Bihemispheric cerebral meningial enhancement 8 (32%) 10 (40%)
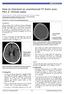
4 138 The majority of the lesions were supratentorial, frontal and parietal, some of which showing also transcallosal spread (Figure 5) mimicking lymphoma or Glioblastoma multiformis and accounted for 59 % of cases. Nine lesions (36%) were infratentorial, rare sites of location included brain stem (Figure 6), and basal ganglia. Most of the patients who had infratentorial lesion were children (out of nine, eight were below 18 years of age). Peri-lesional edema and mass effect was observed in 90 % of the patients. MRI was available for only five patients. Signal intensity was intermediate in four on T1W images and 1 patient showed slightly hyper-intense lesion. On T2W noncontrast enhanced sequence two of the patient had hypointense nodular signal at the center (figure 2) and three had intermediate signal. On post contrast T1W rim enhancement was noticed in three. Solid enhancement was seen in one patient and no enhancement was seen in another one patient. Figure 3. A 8yrs old male child presented with visual loss and seizure and CT scan of the brain showed ring enhancing bilateral partial lobes lesions, bigger on the right, with adjacent satellite lesion and sylvian fissure enhancement suggesting meningial involvement as well. Figure 1. A 14 years male patient presented with visual loss of 1month duration. On pre-contrast CT (left axial image), there is iso-dense frontal mass with hyperdense margin, significant mass effect perilesional edema & obstructive hydrocephalus. Post contrast images (right image) showed smooth ring enhancement. Figure 4. A 2 year old male child presented with seizure, visual loss and change in mentation. CT showed calcified and ring enhancing right parietooccipital and midline cerebellar and left posterior hemisphere calcified mass (left image) with obstructive hydrocephalus. Right frontoparietal sub dural hygroma was also noted as a complication of VP shunt seen on the left and middle images. Figure 2. A 26 years old male presented with visual loss of seven months. MRI of the brain showed intermediate intensity on T1W (left) image, Hypo-intense on T2W image (middle image) with perilesional edema. Conglomerate ring enhancing multiple lesions (right image) with significant peri-lesional edema are noted on T1W post contrast image. Figure 5. A 20 yrs male with of seizure disorder and visual loss of seven months duration. Axial CT pre (Left image) and post contrast images (middle and far right images) shows frontal & trans-callosal ring enhancing mass with adjacent falx meningial enhancment and significant perilesional vasogenic edema & mass effect.
5 139 Figure 6. A 4year old presented with gait disturbance. T1W pre contrast showed edema & mass effect on 4th ventricle( left axial image) and axial T1W post contrast study (right axial image) shows conglomerate ring enhancing lesions at the pons and right middle cerebellar peduncle. DISCUSSION Intra cranial tuberculomas are space occupying granulomatus mass lesions that result from hematogeneous spread from distant focus of tuberculous infection commonly from the lung. Tuberculomas account for 5-8% of operated Intra cranial masses in endemic and resource limited countries (4) and which is more higher in our series (14%). Tuberculomas origionate as conglomerate of small tubercles that joint to form a mature tuberculoma simulating as any other space occupying CNS mass lesion that may vary in size between 2 cm-10 cm(1), which is less in our series ranging between 2-5cm and accounting for 56% of the tuberculomas. According to the original description by Rich, a two stage development of CNS tuberculosis - first tuberculous lesion (Rich s focus) develop in the brain during the stage of bacteremia or shortly afterward and later the rupture or growth of one or more of these lesions results in the development of CNS tuberculosis (5). The initial Rich focus may occur in the meninges, the subpial or subependymal surface of the brain, and may remain dormant for many years(5). The diagnosis of Tuberculoma is histopathological, and clinical and radiological diagnosis, although there are non-specific looking for other laboratory findings like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis and history of past tuberculosis and current chest screening are helpful and prior history of tuberculosis infection is present in 50% of children and in 10% of adults (6,7). In our series, concomittant chest x-ray finding suggestive of pulmonary TB was seen in xx/ xx (28%) of the patients, 2/25 (8%) had past history of pulmonary TB treatment and 4/25 (16%) had past history of contact with TB patients. Although CNS involvement is seen in all age groups in our series a predilections for younger age group where 14/25 (56%) of the patients were below the age of 19 years and their median age being 13, which is a little bit lower compared to the reported frequency of 60-70% cases in younger than 20 years (8). and only 2/25 (8%) of the patients were above 45 years, Clinical findings of Tuberculomas are non-specific and are different depending on the size and the location of the pathology, our patients presented with non specific signs and symptoms such as seizure (60%) and headache (40%), visual disturbance (36%), focal neurological deficits (24%) and few of them presented with change of mentation and ataxia. Bihemispheric and transcallosal lesions were seen in 8/25 (32%) and 2/25 (8%) of the patients respectively. The transcallosal lesion may mimick lymphoma and Glioblastoma multiformis and bihemispheric location may pause the differential diagnosis of metastasis. Other associated findings like meningial enhancement and hydrocephalus (48%) were seen in our study subjects and most of them were below young adults (<18) and pediatric age which is similar to Indian reports (9,10). The imaging features (CT, MRI) particularly that of its MRI feature is much more specific and sensitive in picking meningeal involvement is been shown to correlate with the histology and n maturity of the tuberculoma, wether the granuloma is having caseous or non casous central necrosis or abscess formations and wether its surrounding capsule contains fibroblasts, epitheloid cells, Langhans giant cells and lymphocytes (11,12) and tuberculoma has been shown to be usually isointense relative to grey matter on both T1W and T2W weighted images and appear as a conglomerated ring-enhancing mass on gadolinium enhanced T1 weighted images and layers of different signal intensities and the shortcoming of our study is that despite most of the histopathology report were caseouss necrosis it lacks direct and one to one correlation of the histology with that of the imaging which could have been coordinated between the pathologist and radiologists in the prior design of the study. Nevertheless the non-specific findings of smooth ring and solid enhancement with perilesional edema, smaller satellite and target and conglomerated lesions and associated meningial enhancement were seen in both CT and MRI, and on MRI T2W hypointense rim and central hyperintensty, T1W isointense rim,
6 140 CT hyperdensity and isodensity and calcification were seen in agreement to the description of most of the radiological and particularly MRI histologically correlated and non correlated cross-sectional studies (13-15) with due consideration of sampling errors and coexisting different pathologies, which could be a potential bias to the study. Conclusion and recommendation Tuberculoma is common in our set up and accounts for significant proportion of operated space occupying CNS lesions and commonly seen in young and pediatric patients, and though the imaging features are non-specific additional findings of meningeal involvement and past or present history of TB, the endemicity of the TB, young age of the patient and conglomerated and multiple lesions are invaluable coexisting findings for the differential diagnosis. Imaging and histopathology correlated prospective well designed study is recommended so that timely diagnosis by the radiologists and treating physicians could be made for prompt early medical treatment and avoid unnecessary neurosurgical intervention unless and otherwise complicated. Surgical intervention for intracranial tuberculomas is generally not recommended because prolonged pharmacologic therapy combined with corticosteroides is usually effective in treating these lesions,. However, surgery may be warranted if immediate decompression is necessary for patients with raised intracranial pressure secondary to the lesion or if biopsy is required for definitive diagnosis. In the current study, indications for surgery were similar to the reports made in low-income countries (16,17) REFERENCE 1. Chatterjee S: Brain tuberculomas,tubercular meningitis, and post-tuberular hydrocephalus in children. J Pediatric Neurosci (Sppl 1): S96-S Kent SJ, Crowe SM, Yung A, Lucas CR, Mijch AM. Tuberculous1meningitis: a 30-year review. Clin Infect Dis 1993; 17: Global and national burden of tuberculosis WHO report Bouchama A, al-kawi MZ, Kanaan I, Coates R, Jallu A, Rahm B, Siquera EB. Brain biopsy in tuberculoma: the risks and benefits. Neurosurgery Mar;28(3): Rich AR, McCordock HA. The pathogenesis of tuberculous meningitis. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1933;52: Garg RK. Tuberculosis of the central nervous system. Postgrad Med J. 1999;75: Sultas PN, Unal A, Forta H, Senol S, Kirbas D. Tuberculous meningitis in adults: Review of 61 cases. Infection.2003;31: Curless RG, Mitchell CD. Central nervous system tuberculosis in children. Pediatr Neurol 1991; 7: Ravindra Kumar Garg. Diagnosis of intracranial Tuberculoma. Ind. J. Tub., 1996; 43: Gupta RK, Jena A, Sharma A, et al. MR imaging of intracranial tuberculomas. J Comput Assist Tomogr1988; 12(2): Gupta RK, Lufkin RB. MR imaging and spectroscopy of central nervous system infection. In Tuberculosis and other non-tuberculous bacterial granulomatous infection. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York; p Gupta RK, Pandey R, Khan EM, Mittal P, Gujral RB, Chhabra DK. Intracranial tuberculomas: MRI signal intensity correlation with histopathology and localized proton spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging 1993; 11: Mohammed W., Bhojo A. Kheleani, Mahesh K. Moolani et al: Brain CT and MRI findings in 100 consecutive patients with intracranial tuberculoma. Journal of Neuroimaging. 07, 2003, 13(3): Tae Kyoung Kim, Kee Hyun Chang, Chong Jai Kim et al. Intra cranial Tuberculoma: comparison of MR with pathological Findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16: , October Benaerts A, Vanhoenaker FM, Parizel PM, Van Goethen JW, Van Altena R, Laridon A, et al. Tubeculosis Of the central nervous system: Overview of neuroradiological findings. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13: Tuberculosis of the central nervous system. Postgrad Med J 1999:75: doi: /pgm Kumar, R.,C.K. Pandey,N. Bose, and S. Sahay Tuberculosis brain abscess: clinical presentation, pathophysiology and treatment (in Children). Childs Nerv. Syst. 18:
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Case Report Multiple Dural Tuberculomas Presenting as Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 581230, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/581230 Case Report Multiple Dural Tuberculomas Presenting as Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Hasan Kocaeli,
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 581230, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/581230 Case Report Multiple Dural Tuberculomas Presenting as Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Hasan Kocaeli,
Thalamic Tuberculoma Mimicking a Malignant Brain Tumor
 122 CASE REPORT Thalamic Tuberculoma Mimicking a Malignant Brain Tumor Hung-Lin Lin, Jung-Tsung Chen, Yu-Fang Liu 1, Der-Yang Cho Department of Neurosurgery, 1 Department of Anesthesia, China Medical University
122 CASE REPORT Thalamic Tuberculoma Mimicking a Malignant Brain Tumor Hung-Lin Lin, Jung-Tsung Chen, Yu-Fang Liu 1, Der-Yang Cho Department of Neurosurgery, 1 Department of Anesthesia, China Medical University
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study
 Original Paper Med Principles Pract 2001;10:135 139 Received: October 8, 2000 Revised: July 4, 2001 Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study Salwa Ramadan Aduh Prosper
Original Paper Med Principles Pract 2001;10:135 139 Received: October 8, 2000 Revised: July 4, 2001 Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study Salwa Ramadan Aduh Prosper
Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
A Clinical Study of Miliary Brain Tuberculomas in China
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 69, 231 235, 2016 Original Article A Clinical Study of Miliary Brain Tuberculomas in China Ming Yang, Jia-Tang Zhang*, Yan Yao, Qing-Che Tan, Ting Gao, Cheng-Lin Tian, Xusheng Huang,
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 69, 231 235, 2016 Original Article A Clinical Study of Miliary Brain Tuberculomas in China Ming Yang, Jia-Tang Zhang*, Yan Yao, Qing-Che Tan, Ting Gao, Cheng-Lin Tian, Xusheng Huang,
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2011; 52(2) 124
 Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2011; 52(2) 124 CME Article Manifestations of cerebral tuberculosis Bathla G, Khandelwal G, Mailer V G, Gupta A ABSTRACT ntracranial tuberculosis continues to be a serious
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2011; 52(2) 124 CME Article Manifestations of cerebral tuberculosis Bathla G, Khandelwal G, Mailer V G, Gupta A ABSTRACT ntracranial tuberculosis continues to be a serious
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES. Background:
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.890719 Received: 2014.03.19 Accepted: 2014.05.15 Published: 2014.09.02 Multi-Slice Computed Tomography 5-Minute Delayed Scan is Superior to Immediate Scan after Contrast
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.890719 Received: 2014.03.19 Accepted: 2014.05.15 Published: 2014.09.02 Multi-Slice Computed Tomography 5-Minute Delayed Scan is Superior to Immediate Scan after Contrast
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment
 Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Role of in Correlation with Mr Spectroscopy R. Archana 1, P. Sunil Kumar 2, Anurudh Kishore 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Post Graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis:
Original Research Article Role of in Correlation with Mr Spectroscopy R. Archana 1, P. Sunil Kumar 2, Anurudh Kishore 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Post Graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis:
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
Primary Intracranial CNS Lymphoma: MR Manifestations
 725 Primary Intracranial CNS Lymphoma: MR Manifestations Bernhard W. Schwaighofer 1 John R. Hesselink 1 Gary A. Press 1 Ronald L. Wolf 1 Mark E. Healy 2 Dean P. Berthoty1 We reviewed MR scans of 10 patients
725 Primary Intracranial CNS Lymphoma: MR Manifestations Bernhard W. Schwaighofer 1 John R. Hesselink 1 Gary A. Press 1 Ronald L. Wolf 1 Mark E. Healy 2 Dean P. Berthoty1 We reviewed MR scans of 10 patients
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
Brain Pain Infections of the CNS
 FRIDAY, OCTOBER 28, 2016 Brain Pain Infections of the CNS Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC Assistant Professor of Radiology & Neurosurgery Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine
FRIDAY, OCTOBER 28, 2016 Brain Pain Infections of the CNS Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC Assistant Professor of Radiology & Neurosurgery Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis
 Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175)
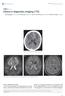 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2:59 514, March 1999 MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis William K. Erly, Richard J. Bellon, Joachim F. Seeger, and Raymond F. Carmody BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2:59 514, March 1999 MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis William K. Erly, Richard J. Bellon, Joachim F. Seeger, and Raymond F. Carmody BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 08 Page August 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i8.19 Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i8.19 Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation
Cystic Meningioma in the Inter-Hemisferic Space Location
 Case Cystic Meningioma in the Inter-Hemisferic Space Location Muhammad Zafrullah Arifin, Firman Priguna Tjahjono, Agung Budi Sutiono, Ahmad Faried Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas
Case Cystic Meningioma in the Inter-Hemisferic Space Location Muhammad Zafrullah Arifin, Firman Priguna Tjahjono, Agung Budi Sutiono, Ahmad Faried Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas
MR neuroimaging of HIV infected patients : A pictorial review
 MR neuroimaging of HIV infected patients : A pictorial review Poster No.: R-0198 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. F. Kwan, R. Thomas, A. Dixon; SOUTH YARRA/AU Keywords: Neuroradiology
MR neuroimaging of HIV infected patients : A pictorial review Poster No.: R-0198 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. F. Kwan, R. Thomas, A. Dixon; SOUTH YARRA/AU Keywords: Neuroradiology
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: Available online at: Case Study
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
Isolated Aspergillosis of the Brain in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report
 Isolated Aspergillosis of the Brain in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report Jihe Lim 1, Tae-Sub Chung 1, Hyunki Kim 2, Jung Yong Ahn 3, Sang Hyun Suh 1 Brain aspergillosis has been increasing remarkably.
Isolated Aspergillosis of the Brain in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report Jihe Lim 1, Tae-Sub Chung 1, Hyunki Kim 2, Jung Yong Ahn 3, Sang Hyun Suh 1 Brain aspergillosis has been increasing remarkably.
Metastasis. 57 year old with progressive Headache and Right Sided Visual Loss
 Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
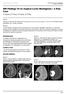 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging in CNS Tuberculosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:867 875, May 1999 Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging in CNS Tuberculosis Rakesh K. Gupta, Manoj K. Kathuria, and Sunil Pradhan BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: CNS tuberculosis may simulate
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:867 875, May 1999 Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging in CNS Tuberculosis Rakesh K. Gupta, Manoj K. Kathuria, and Sunil Pradhan BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: CNS tuberculosis may simulate
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases
 Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
CT and MRI Findings of Intracranial Lymphoma
 Neuroradiology- Slone et al. CT and MRI of Intracranial Lymphoma Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.233 on 02/10/18 from IP address 37.44.204.233. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all
Neuroradiology- Slone et al. CT and MRI of Intracranial Lymphoma Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.233 on 02/10/18 from IP address 37.44.204.233. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma in the Cerebellum: Case Report
 Case Report Neuroimaging and Head and Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.151 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):151-155 Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma
Case Report Neuroimaging and Head and Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.151 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):151-155 Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma
FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT in HIV PATIENTS -a case based approach. Dr Jency Maria Koshy, CMC, Ludhiana
 FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT in HIV PATIENTS -a case based approach Dr Jency Maria Koshy, CMC, Ludhiana Case 1 Middle aged gentleman Diagnosed to have HIV 5 months prior to admission CD4 at the time of detection-132
FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT in HIV PATIENTS -a case based approach Dr Jency Maria Koshy, CMC, Ludhiana Case 1 Middle aged gentleman Diagnosed to have HIV 5 months prior to admission CD4 at the time of detection-132
Miliary Tuberculosis Mimicking Brain Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma
 CASE REPORT J Neurocrit Care 2018;11(1):47-53 eissn 2508-1349 Miliary Tuberculosis Mimicking Brain Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma Yousang Ko, MD 1, Eun-Kyung Mo, MD, PhD 1, Yong Bum Park, MD 1, Mi-Ri
CASE REPORT J Neurocrit Care 2018;11(1):47-53 eissn 2508-1349 Miliary Tuberculosis Mimicking Brain Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma Yousang Ko, MD 1, Eun-Kyung Mo, MD, PhD 1, Yong Bum Park, MD 1, Mi-Ri
Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center. 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Guerbet Outline Indications for imaging CNS infections
Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Guerbet Outline Indications for imaging CNS infections
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist
 Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist Poster No.: C-0679 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gargallo Vaamonde, M. Iridoy Zulet, I. Rubio
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist Poster No.: C-0679 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gargallo Vaamonde, M. Iridoy Zulet, I. Rubio
MRI imaging in meningeal diseases
 Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist,
Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist,
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report
 Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/523 Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study Bulabai Karpagam 1, V Vadanika 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/523 Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study Bulabai Karpagam 1, V Vadanika 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Falx cerebri tuberculoma mimicking en plaque meningioma case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 2: 209-213 209 Falx cerebri tuberculoma mimicking en plaque meningioma case report A.I. Cucu 1, Dana Mihaela Turliuc 1,2, Anca Sava 1,2, Gabriela Florența Dumitrescu 1,
Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 2: 209-213 209 Falx cerebri tuberculoma mimicking en plaque meningioma case report A.I. Cucu 1, Dana Mihaela Turliuc 1,2, Anca Sava 1,2, Gabriela Florența Dumitrescu 1,
Role of imaging (images) in my practice. Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases
 Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity
 Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
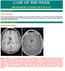 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE 26 years old male patient presented clinically with a grand male fit, confusion, fever, headache, and nausea. Examination showed bilateral papilledema and left sided extensor
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE 26 years old male patient presented clinically with a grand male fit, confusion, fever, headache, and nausea. Examination showed bilateral papilledema and left sided extensor
EVALUATION OF CHRONIC HEADACHE BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
 EVALUATION OF CHRONIC HEADACHE BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Abstract: Anish Subedee Objective: To find out the proportion of intracranial abnormalities in patients with chronic headache
EVALUATION OF CHRONIC HEADACHE BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Abstract: Anish Subedee Objective: To find out the proportion of intracranial abnormalities in patients with chronic headache
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits
 An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
Intracranial Ganglioglioma: MR, CT,
 109 Intracranial Ganglioglioma: MR, CT, and Clinical Findings in 18 Patients Mauricio Castillo 1 Patricia C. Davis 1 Yoshii Takei 2 James C. Hoffman, Jr. 1 Eighteen cases of pathologically proved intracranial
109 Intracranial Ganglioglioma: MR, CT, and Clinical Findings in 18 Patients Mauricio Castillo 1 Patricia C. Davis 1 Yoshii Takei 2 James C. Hoffman, Jr. 1 Eighteen cases of pathologically proved intracranial
Stereotactic Brain Biopsies in AIDS Patients - Early Local Experience
 Singapore Med J 2000 Vol 41(4) : 161-166 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Stereotactic Brain Biopsies in AIDS Patients - Early Local Experience K K Yeo, T T Yeo, C Y Chan, Y Y Sitoh, J Teo, S Y Wong ABSTRACT
Singapore Med J 2000 Vol 41(4) : 161-166 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Stereotactic Brain Biopsies in AIDS Patients - Early Local Experience K K Yeo, T T Yeo, C Y Chan, Y Y Sitoh, J Teo, S Y Wong ABSTRACT
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
PRIMARY MUSCULOSKELETAL HYDATID CYST DISEASE. Radiology Department, Military Hospital Mohamed V. Rabat Morocco
 PRIMARY MUSCULOSKELETAL HYDATID CYST DISEASE. A. El Kharras S. Semlali A. Darbi S. Akjouj J. El Fenni A. Hanine M. Benameur D. Bassou Radiology Department, Military Hospital Mohamed V. Rabat Morocco Introduction
PRIMARY MUSCULOSKELETAL HYDATID CYST DISEASE. A. El Kharras S. Semlali A. Darbi S. Akjouj J. El Fenni A. Hanine M. Benameur D. Bassou Radiology Department, Military Hospital Mohamed V. Rabat Morocco Introduction
3.1. Uniform research case definition criteria differentiate tuberculous and bacterial meningitis in children. R.S. Solomons M. Wessels D.H.
 3.1 Uniform research case definition criteria differentiate tuberculous and bacterial meningitis in children R.S. Solomons M. Wessels D.H. Visser P.R. Donald B.J. Marais J.F. Schoeman A.M. van Furth Clin
3.1 Uniform research case definition criteria differentiate tuberculous and bacterial meningitis in children R.S. Solomons M. Wessels D.H. Visser P.R. Donald B.J. Marais J.F. Schoeman A.M. van Furth Clin
Solitary Skull Metastasis as Initial Manifestation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Case Report
 Solitary Skull Metastasis as Initial Manifestation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Case Report Ellyda MN a and Mohd Shafie A b a Department of Radiology, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuantan,
Solitary Skull Metastasis as Initial Manifestation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Case Report Ellyda MN a and Mohd Shafie A b a Department of Radiology, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuantan,
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1994
 Neuroradiology (1994) 36:39M3 Neuro-- radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1994 MRI in intraspinal tuberculosis R.K. Gupta ~, S. Gupta 1, S.Kumar ~, A.Kohli 2, U.K.Misra 2, R.B. Gujral 1 1 Department of Radiology,
Neuroradiology (1994) 36:39M3 Neuro-- radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1994 MRI in intraspinal tuberculosis R.K. Gupta ~, S. Gupta 1, S.Kumar ~, A.Kohli 2, U.K.Misra 2, R.B. Gujral 1 1 Department of Radiology,
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies
 Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hssine, N. Mallat, M. Limeme, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, H. Amara, D. Bakir,
Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hssine, N. Mallat, M. Limeme, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, H. Amara, D. Bakir,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Magn Reson Imaging. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 June 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 June ; 31(6): 1469 1472. doi:10.1002/jmri.22192. Eccentric Target Sign in Cerebral Toxoplasmosis neuropathological
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 June ; 31(6): 1469 1472. doi:10.1002/jmri.22192. Eccentric Target Sign in Cerebral Toxoplasmosis neuropathological
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated.
 Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated. Poster No.: C-1092 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Ospina Moreno, I. Montejo
Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated. Poster No.: C-1092 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Ospina Moreno, I. Montejo
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
The Variable MR Appearance of Primary Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System: Comparison with Histopathologic Features
 The Variable MR Appearance of Primary Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System: Comparison with Histopathologic Features Blake A. Johnson, Evan K. Fram, Peter C. Johnson, and Ronald Jacobowitz PURPOSE: To
The Variable MR Appearance of Primary Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System: Comparison with Histopathologic Features Blake A. Johnson, Evan K. Fram, Peter C. Johnson, and Ronald Jacobowitz PURPOSE: To
Brain is one of the common sites of distant metastasis as
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnetic Resonance (MR) Patterns of Brain Metastasis in Lung Cancer Patients Correlation of Imaging Findings with Symptom Amarnath Jena, DNB (NM),* Sangeeta Taneja, DNB (Radiodiagnosis),*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnetic Resonance (MR) Patterns of Brain Metastasis in Lung Cancer Patients Correlation of Imaging Findings with Symptom Amarnath Jena, DNB (NM),* Sangeeta Taneja, DNB (Radiodiagnosis),*
Fourth Ventricular Lesions in Metastatic Gliomas: A Rare Predilection?
 CASE REPORT Brain Tumor Res Treat 2017;5(1):24-29 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.1.24 Fourth Ventricular Lesions in Metastatic Gliomas: A Rare Predilection? Mohammed
CASE REPORT Brain Tumor Res Treat 2017;5(1):24-29 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.1.24 Fourth Ventricular Lesions in Metastatic Gliomas: A Rare Predilection? Mohammed
Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report
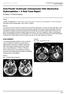 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
Predictors of Mortality in Brain Abscess
 Predictors of Mortality in Brain Abscess H. U. Qureshi,A. A. Siddiqui ( Sections of Neurosurgery, Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan University, Karachi. ) A. A. Habib,T. Mozaffar ( Sections of Neurology,
Predictors of Mortality in Brain Abscess H. U. Qureshi,A. A. Siddiqui ( Sections of Neurosurgery, Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan University, Karachi. ) A. A. Habib,T. Mozaffar ( Sections of Neurology,
Guerbet Update India
 www.guerbet.co.in Guerbet Update India Imaging News & Activities Edition #3 Nov 2011-Jan 2012 Edition #3 Nov 2011 - Jan 2012 Clinical Cases CEMRI in Children by Dr. Bharat Gala, Dr. Bipin Shah, Dr. Kirit
www.guerbet.co.in Guerbet Update India Imaging News & Activities Edition #3 Nov 2011-Jan 2012 Edition #3 Nov 2011 - Jan 2012 Clinical Cases CEMRI in Children by Dr. Bharat Gala, Dr. Bipin Shah, Dr. Kirit
Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2012, Article ID 718651, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/718651 Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum Jesús Vaquero, 1,
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2012, Article ID 718651, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/718651 Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum Jesús Vaquero, 1,
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Features in Tubercular Meningoencephalitis Diagnosis: 18 Childhood Cases
 American Journal of Infectious Diseases 4 (3): 187-192, 2008 ISSN 1553-6203 2008 Science Publications Features in Tubercular Meningoencephalitis Diagnosis: 18 Childhood Cases 1 P. Di Carlo, 2 D. Cabibi,
American Journal of Infectious Diseases 4 (3): 187-192, 2008 ISSN 1553-6203 2008 Science Publications Features in Tubercular Meningoencephalitis Diagnosis: 18 Childhood Cases 1 P. Di Carlo, 2 D. Cabibi,
