Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
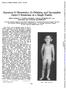
1 Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 417. An Unusual Chromosomal Aberration in a Case of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome BURHAN SAY, ERGUL TUNCBILEK, BEHICE YAMAK, and SEVIM BALCI From the Department of Pediatrics and the Clinical Genetics Laboratory, Hacettepe University, Hacettepe Children's Hospital, Ankara, Turkey Chediak-Higashi syndrome which appears to be a lysosomal disease (Douglas and Fudenberg, 1969; White, 1966) is characterized by partial albinism, photophobia, recurrent infections, hepatosplenomegaly, and a distinctive leucocyte anomaly (Chediak, 1952; Higashi, 1954). Available genetic and fine structural studies suggest that the condition is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait (Sadan et al., 1965; Douglas, Blume, and Wolff, 1969). Chromosome studies have been done in a few cases, but as expected have not shown any significant numerical chromosomal abnormalities (Kritzler et al., 1964; Rosenszajn et al., 1969). The condition does not seem to be confined to a particular population group, since patients with this syndrome have been reported from various parts of the world. The purpose of this communication is to report a case of Chediak-Higashi syndrome from Turkey, in which chromosome studies revealed an unexpected and unusual abnormality in the form of partial monosomy for a G group chromosome (45,XY,G - 46,XY/46,XY,Gr). Case Report A 3-year-old boy was referred to us by his local physician with a history of recurrent infections of unknown aetiology (Fig. 1). His past history revealed that he had had an infection associated with a rash which was diagnosed as scarlet fever approximately one year previously, since when he had been treated for multiple episodes of diarrhoea and tonsillitis. Two weeks before his referral he was found to have enlarged submandibular and cervical glands associated with high fever and weight loss. The mother was 29 and the father 36 years of age, and there was no consanguinity between them. His 3- month-old brother was reported to be in good health. A detailed family history revealed the presence of other members (with and without fair hair) who had photophobia. Received 14 January Physical examination. The patient's height was 92 cm. (10th centile), weight 14-5 kg. (50th centile), and head circumference 49 cm. (75th centile). He was pale, and acutely ill. His hair was light-coloured, in contrast to his parents' dark hair. The skin was dry, with slight desquamation, and there was horizontal nystagmus and photophobia in both eyes, which also had an antimongoloid slant. Other pertinent clinical findings included an enlarged left submandibular lymph node (2 x 1 cm. in size), and multiple slightly enlarged lymph nodes over the axillary and inguinal areas. The liver was palpable 2-5 and the spleen 3 cm. below the costal margins. Chest x-ray revealed pneumonia. Laboratory findings. Routine haematological studies showed the patient's haemoglobin to be 7-8 g./ 100 ml., haematocrit 26%, WBC 8600/cu. mm., and reticulocyte count, 10-2%. Peripheral smears revealed hypochromia, anisocytosis, polychromasia, and poikilocytosis, and there were abundant thrombocytes. The most interesting finding was the presence of discrete FIG. 1. The patient.
2 418 FIG. 2. Peripheral blood. ( x 1250.) azurophilic inclusion bodies of various sizes in the cytoplasm of the lymphocytes as well as the polymorphonuclear leucocytes (Fig. 2). They were frequently round and occasionally irregular in shape. Repeated bonemarrow examinations revealed erythroid hyperplasia and eosinophilia, in addition to the inclusion bodies described above, in the lymphoid and myeloid cells. There were also many young myeloid cells with numerous vacuoles (Fig. 3), and smears obtained by splenic punctures revealed cells with similar inclusion bodies. No Say, Tunqbilek, Yamak, and Balci inclusions could be seen in the blood smears obtained from the parents, two grandparents, or a maternal aunt. Cytogenetic investigations. Chromosome studies of the patient and his parents were made using cultures of peripheral blood, for which a modification of Moorhead et al.'s method (1960) was used. The chromosomes in 102 metaphase plates were counted and analysed, and in 19 of them a small acrocentric chromosome from the G group was missing. In all these latter plates, the Y chromosome could be clearly identified by its well-known morphological characteristics. In a further 17 metaphase plates a minute ring chromosome, replacing a G chromosome, was present (Fig. 4). The remaining 62 plates showed 46 chromosomes, none of which had any structural abnormalities. An additional 4 plates showed inconsistent abnormalities. Chromosome studies of the parents revealed no abnormalities (Table I). Discussion Until recently, inborn autosomal monosomy in man was considered to be incompatible with life. The first case of complete monosomy for TABLE I CHEDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROME: CHROMOSOME STUDIES N R 17 Jan Feb Total (102) ^, 0, -W,',.... ^... J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 December Downloaded from FIG. 3. Bone-marrow. A cell with multiple inclusion bodies. (x 1250.) 9 on 17 November 2018 by guest. Protected by
3 FIG. 4. An Unusual Chromosomal Aberration in a Case of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome 419 ms--, _ p pp,,,p,,l, Karyotypes showing a minute ring chromosome from group (above) and a chromosome missing from the same group (below).
4 420 Say, Tunqbilek, Yamak, and Balci TABLE II CASES ASSOCIATED WITH DEFICIENCIES OF G GROUP OF CHROMOSOMES Anti- Pro- Low-set Authors mongoloid minent Micro- Mal- Genito-urinary Mental Chromosomes Slant Nasal gnathia formed System retard. Bridge Ears Lejeune et al. (1964) + _ + + Hypospadias 45,XY,G - /46,XY,Gq - Penrose (1966) ,XX,Gr Thorburn and Johnson (1966) ,XX,G- Reisman et al. (1967) Hypospadias, 0 46,XY,Gq - cryptorchidism Al-Aish et al. (1966) + + _ + 45,XX,G- R. C. Hindle (1969) (personal communication to Challacombe and Taylor, (1969)) Cryptorchidism 45,Xy,G -, ace Challacombe and Taylor (1969) Hypospadias, + 45,XY,G - /46,XY,Gr cryptorchidism, inguinal hernia Endo et al. (1969)? 0 + Hypospadias, inguinal + 45,XY,G - /46,XY,Gqhernia, scrotal dysp. Present case _ + 45,XY,G - /46,XY,Gr, 46,XY Cohen (1966) - _ 0 + Bilateral hydroureters + 45,XY,G - /46,XY Engel et al. (1966) Infantile external + 46,XX,Bp -,Gq - genitalia McIlree et al. (1966) ,XY,Gr Reisman et al. (1967) ,XY,Gq- Weleber et al. (1968) ,XX,Gr Blank and Lorber (1969) ,XX,G - /46,XX,Gr chromosome in peripheral blood cultures was described by Thorburn and Johnson (1966). This was followed by another report by Al-Aish et al. (1967) describing a 4j-year-old girl who had complete monosomy for a G group chromosome, not only in the peripheral blood lymphocytes but also in the bone-marrow and skin fibroblasts. Earlier, Lejeune et al. (1964) published their findings of multiple congenital malformations in a patient whose chromosomes revealed mosaicism for a monosomy chromosome. A large proportion of cells lacked a G group chromosome, while the others showed a deleted chromosome in the form of a ring chromosome. In view of the peculiar downward slant of this patient's eyes, and other findings that were the opposite of those seen in Down's syndrome, the term 'antimongolism' was assigned to this newly discovered entity, and several patients with similar phenotype have since been described (Penrose, 1966; Thorburn and Johnson, 1966; Reisman et al., 1966; Al-Aish et al., 1967; R. C. Hindle, 1969, personal communication to Challacombe and Taylor (1969); Challacombe and Taylor, 1969; Endo et al., 1969). However, there have also been reports of patients whose chromosomes frequently showed incomplete and sometimes complete, inborn monosomy for a G chromosome but without antimongoloid features (Cohen, 1966; Engel et al., 1966; McIlree, Tulloch, and Newsam, 1966; Reisman et al., 1967; Weleber, Hecht, and Giblett, 1968; Blank and Lorber, 1969) (Table II). This prompted Weleber et al. (1968) to suggest that partial or complete absence of a G chromosome may ±, Present; -, Absent; 0, not recorded; ace, acentric. result in at least two different entities. According to these writers, the main distinguishing factor may be the presence or absence of an antimongoloid slant in the eyes. However, a study of the cases reported so far suggests that there may be other differences between these proposed entities with regard to the presence or absence of a prominent nasal bridge, micrognathia, and certain malformations of the genito-urinary system. The varying clinical features associated with a G group chromosome deficiency can easily be explained by the fact that the deficiencies observed may actually involve a different member of the G group of chromosomes. Likewise, even cases with deletions of the same chromosome may differ from one another, since the amount of deleted material, and the part of the chromosome involved, may not be the same. It may also be of interest to note that for the patients with a ring chromosome the possibility exists of a monosomy for some genetic material, while some of the genes are in double dose as a result of the misdivision which is observed in these chromosomes. Some of the clinical features seen in our patient resembled those first described by Lejeune et al. (1964). These include an antimongoloid slant of the eyes, relatively big ears, prominent root of nose, delayed physical growth, and slight mental retardation. The presence of other clinical and laboratory findings typical of the syndrome described by Chediak and Higashi is, of course, of further interest. Since it is generally accepted that this syndrome is inherited as an autosomal recessive
5 An Unusual Chromosomal Aberration in a Case of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome trait, and also that the chromosome studies of these patients have so far revealed no similar abnormalities, it is quite likely that the unusual chromosomal abnormality seen in our case is coincidental, though in a recent study chromatid and chromosomal breakages, elongated chromosomes, and heteropycnotic gaps were found (Rosenzajn et al., 1969). On the other hand, it should be emphasized that only a few cases of Chediak-Higashi syndrome have been investigated for chromosome abnormalities, and detailed reports on leucocyte morphology in patients with antimongolism are lacking. For this reason it is hoped that our paper will prompt other workers to report whether or not any relation exists between the loss of genetic material from a G group chromosome and the clinical and laboratory findings seen in patients with Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Finally it should be remembered that patients with this condition have a high incidence of lymphoreticular malignancy, and acquired monosomy G has been reported in acute myeloblastic leukaemia (Sandberg et al., 1964), in the terminal stage of the Di Guglielmo syndrome (Castoldi et al., 1968), and in a case of refractory sideroblastic anaemia with leukaemic transformation (Silberman and Krmpotic, 1969). This indicates that follow-up of our case would be of interest to see whether or not malignant transformation occurs at an early age. Summary A 3-year-old boy with Chediak-Higashi syndrome is described. Chromosomal analyses interestingly revealed a partial monosomy of the chromosome 21. The possible aetiological significance of this unusual chromosome aberration is discussed. REFEENCES Al-Aish, M. S., de la Cruz, F., Goldsmith, L. A., Volpe, J., Mella, G., and Robinson, J. C. (1967). Autosomal monosomy in man. Complete monosomy G (21-22) in a four-and-one-half-year-old mentally retarded girl. New England Journal of Medicine, 277, Blank, C. E., and Lorber, J. (1969). A patient with 45,XX,G -/ 46,XX,Gr mosaism. Journal of Medical Genetics, 6, Castoldi, G., Yam, L. T., Mitus, W. J.. and Crosby, W. H. (1968). Chromosomal studies in erythroleukemia and chronic erythremic myelosis. Blood, 31, Challacombe, D. N., and Taylor, A. (1969). Monosomy for a G autosome. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 44, Chediak, M. (1952). Nouvelle anomalie leucocytaire de caractere constitutional et familial. Revue d'hematologie, 7, Cohen, M. M. (1966). Chromosomal mosaicism associated with a case of cyclopia. journal of Pediatrics, 69, Douglas, S. D., Blume, R. S., and Wolff, S. M. (1969). Fine structural studies of leukocytes from patients and heterozygotes with the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Blood, 33, , and Fudenberg, H. H. (1969). Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Medical Clinics of North America, 53, Endo, A., Yarnamoto, M., Watanabe, G.-I., Suziki, Y., and Sakai, K. (1969). 'Antimongolism' syndrome. British Medical Journal, 4, Engel, E., Hastings, C. P., Merrill, R. E., McFarland, B. S., and Nance, W. E. (1966). Apparent cri-du-chat and 'antimongolism' in one patient. Lancet, 1, Higashi, 0. (1954). Congenital gigantism of peroxidase granules. The first case ever reported of qualitative abnormity of peroxidase. Tohoku_Journal of Experimental Medicine, 59, Kritzler, R. A., Temer, J. Y., Lindenbaum, J., Magidson, J., Williams, R., Preisig, R., and Phillips, G. B. (1964). Chediak- Higashi syndrome. Cytologic and serum lipid observations in a case and family. American_Journal of Medicine, 36, Lejeune, J., Berger, R., Rethore, M. O., Archambault, L., Jer6me, H., Thieffry, S., Aicardi, J., Broyer, M., Lafourcade, J., Cruveiller, J., and Turpin, R. (1964). Monosomie partielle pour un petit acrocentrique. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l'acadlmie des Sciences, 259, McIlree, M. E., Tulloch, W. S., and Newsam, J. E. (1966). Studies on human meiotic chromosomes from testicular tissue. Lancet, 1, Moorhead, P. S., Nowell, P. C., Mellman, W. J., Battips, D. M., and Hungerford, D. A. (1960). Chromosome preparations of leukocytes from human peripheral blood. Experimental Cell Research, 20, Penrose, L. S. (1966). Anti-mongolism. Lancet, 1, 497. Reisman, L. E., Darnell, A., Murphy, J. W., Hall, B., and Kasahara, S. (1967). A child with partial deletion of a G-group autosome. American Journal of Diseases of Children, 114, , Kasahara, S., Chung, C. Y., Darnell, A., and Hall, B. (1966). Anti-mongolism, studies in an infant with a partial monosomy of the 21 chromosome. Lancet, 1, Rosenszajn, A. L., Radnai, J., Tatarski, A., and Benderlei, A. (1969). Blood cell culture and chromosomal findings in Chediak-Higashi syndrome (Abst.). Israel_Journal of Medical Sciences, 5, Sadan, N., Yaffe, D., Rozenszajn, L., Adar, H., Soroker, B., and Efrati, P. (1965). Cytochemical and genetic studies in four cases of Chediak-Higashi-Steinbrinck syndrome. Acta Haematologica, 34, Sandberg, A. A., Ishihara, T., Kikuchi, Y., and Crosswhite, L. H. (1964). Chromosomal differences among the acute leukemias. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 113, Silberman, S., and Krmpotic, E. (1969). Refractory anemia with leukemic transformation and chromosomal change. A case report. Acta Haematologica, 41, Thorburn, M. J., and Johnson, B. E. (1966). Apparent monosomy of a G autosome in a Jamaican infant. journal of Medical Genetics, 3, Weleber, R. G., Hecht, F., and Giblett, E. R. (1968). Ring-G chromosome, a new G-deletion syndrome? American Journal of Diseases of Children, 115, White, J. G. (1966). The Chediak-Higashi syndrome: a possible lysosomal disease. Blood, 28,
Apparent G-Monosomy, G-Deletion, and Incomplete Down's Syndrome in a Single Family
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1972). 9, 457. Apparent G-Monosomy, G-Deletion, and Incomplete Down's Syndrome in a Single Family RINA SCHMIDT, GEORGE MUNDEL, MALKA ROSENBLATT, and MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON
Journal of Medical Genetics (1972). 9, 457. Apparent G-Monosomy, G-Deletion, and Incomplete Down's Syndrome in a Single Family RINA SCHMIDT, GEORGE MUNDEL, MALKA ROSENBLATT, and MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON
Nails Associated with a Group-G Ring Chromosome A Case Report on Two Unrelated Cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 195. Mental Retardation, Unusual Facies, and Abnormal Nails Associated with a Group-G Ring Chromosome A Case Report on Two Unrelated Cases VICTOR DUBOWITZ, PATRICIA
Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 195. Mental Retardation, Unusual Facies, and Abnormal Nails Associated with a Group-G Ring Chromosome A Case Report on Two Unrelated Cases VICTOR DUBOWITZ, PATRICIA
Cytological and Clinical Interpretation
 110 pericentric inversion and an unbalanced crossover segregation product from the inversion. However, the structurally abnormal chromosome involved is No. 4 and not a D chromosome. Summary A non-satellited,
110 pericentric inversion and an unbalanced crossover segregation product from the inversion. However, the structurally abnormal chromosome involved is No. 4 and not a D chromosome. Summary A non-satellited,
Chromosome Studies in Familial Leukaemia*
 J. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 96. Chromosome Studies in Familial Leukaemia* P. H. FITZGERALD, P. E. CROSSEN, A. C. ADAMS, C. V. SHARMAN, and F. W. GUNZ From the Cytogenetics Unitt, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
J. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 96. Chromosome Studies in Familial Leukaemia* P. H. FITZGERALD, P. E. CROSSEN, A. C. ADAMS, C. V. SHARMAN, and F. W. GUNZ From the Cytogenetics Unitt, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
Arrested DNA Synthesis in Erythroleukaemia
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 95. Chromosomal Abnormality, Megaloblastosis, and Arrested DNA Synthesis in Erythroleukaemia P. E. CROSSEN, P. H. FITZGERALD, R. C. MENZIES, and L. A. BREHAUT From Cytogenetics
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 95. Chromosomal Abnormality, Megaloblastosis, and Arrested DNA Synthesis in Erythroleukaemia P. E. CROSSEN, P. H. FITZGERALD, R. C. MENZIES, and L. A. BREHAUT From Cytogenetics
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle
 CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
ISSN CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR
 J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKAEMIA IN CHILDREN
 Vol. 9, No. I SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 39 March, 1968 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKAEMIA IN CHILDREN By Tan Kwang Hob, M.B., B.S., M.R.C.P.E., D.C.H. and Tan Sim Keng, M.B., B.S. (Paediatric Unit (East), General
Vol. 9, No. I SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 39 March, 1968 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKAEMIA IN CHILDREN By Tan Kwang Hob, M.B., B.S., M.R.C.P.E., D.C.H. and Tan Sim Keng, M.B., B.S. (Paediatric Unit (East), General
Testicular hypoplasia in a horned goat with 61, XXY/60, XY karyotype
 Jpn. J. Genet. (1986) 61, pp. 177-181 SHORT PAPER Testicular hypoplasia in a horned goat with 61, XXY/60, XY karyotype BY Sandra S. G. TAKEBAYASHI and Wilham JORGE Department of Genetics, State University
Jpn. J. Genet. (1986) 61, pp. 177-181 SHORT PAPER Testicular hypoplasia in a horned goat with 61, XXY/60, XY karyotype BY Sandra S. G. TAKEBAYASHI and Wilham JORGE Department of Genetics, State University
A CHROMOSOME STUDY IN 20 SEXUALLY ABNORMAL PATIENTS>> WOSAMU MARUYAMA, HACHIRO SHIMBA AND SET-ICHI KOHNO
 JAPAN. J. GENETICS Vol. 43, No. 4: 289-298 (1968) A CHROMOSOME STUDY IN 20 SEXUALLY ABNORMAL PATIENTS>> WOSAMU MARUYAMA, HACHIRO SHIMBA AND SET-ICHI KOHNO Received May 9, 1968 Zoological Institute, Hokkaido
JAPAN. J. GENETICS Vol. 43, No. 4: 289-298 (1968) A CHROMOSOME STUDY IN 20 SEXUALLY ABNORMAL PATIENTS>> WOSAMU MARUYAMA, HACHIRO SHIMBA AND SET-ICHI KOHNO Received May 9, 1968 Zoological Institute, Hokkaido
CHAPTER:4 LEUKEMIA. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY 8/12/2009
 LEUKEMIA CHAPTER:4 1 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Leukemia A group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of
LEUKEMIA CHAPTER:4 1 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Leukemia A group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Terri Boyer 17 th October 2006 Overview Disease information: Aetiology of ALL proposed theory, contributing factors Symptoms Complications Diagnostic approaches - morphology
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Terri Boyer 17 th October 2006 Overview Disease information: Aetiology of ALL proposed theory, contributing factors Symptoms Complications Diagnostic approaches - morphology
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia
 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 46-50 Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality J. HARVEY, C. JUDGE, and S. WIENER From St. Nicholas Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Auistralia
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 46-50 Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality J. HARVEY, C. JUDGE, and S. WIENER From St. Nicholas Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Auistralia
r). SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER nnmlbih UNIVERSITY Sophia Blaauw INSTRUCTIONS FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
 r). nnmlbih UNIVERSITY OF SCIEFICE nnd TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
r). nnmlbih UNIVERSITY OF SCIEFICE nnd TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 159. XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism also Showing Features of Klinefelter's Syndrome D. A. SPENCER, JULIE W. EYLES, and M. K. MASON From Westwood Hospital, Bradford 6, and
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 159. XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism also Showing Features of Klinefelter's Syndrome D. A. SPENCER, JULIE W. EYLES, and M. K. MASON From Westwood Hospital, Bradford 6, and
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (PAEDIATRICS) EXAMINATION - JULY/AUGUST 2012' PAPER I STRUCTURED ESSAY QUESTIONS
 CO POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (PAEDIATRICS) EXAMINATION - JULY/AUGUST 2012' Date 16 th July 2012 Time :- 9.00 a.m. - 12.00 noon PAPER I STRUCTURED ESSAY QUESTIONS Answer
CO POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (PAEDIATRICS) EXAMINATION - JULY/AUGUST 2012' Date 16 th July 2012 Time :- 9.00 a.m. - 12.00 noon PAPER I STRUCTURED ESSAY QUESTIONS Answer
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and
 Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
If unqualified, Complete remission is considered to be Haematological complete remission
 Scroll right to see the database codes for Disease status and Response Diagnosis it refers to Disease status or response to treatment AML ALL CML CLL MDS or MD/MPN or acute leukaemia secondary to previous
Scroll right to see the database codes for Disease status and Response Diagnosis it refers to Disease status or response to treatment AML ALL CML CLL MDS or MD/MPN or acute leukaemia secondary to previous
CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 199 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS t The rapid development of human genetics during the past couple of decades and the discovery of numerous cytogenetic abnormalities have
CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 199 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS t The rapid development of human genetics during the past couple of decades and the discovery of numerous cytogenetic abnormalities have
Late-replicating X Chromosome
 J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, I07. The Relative Length and Arm Ratio of the Human Late-replicating X Chromosome AUDREY BISHOP, MARGARET LEESE, and C. E. BLANK From the Centre for Human Genetics, United Sheffield
J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, I07. The Relative Length and Arm Ratio of the Human Late-replicating X Chromosome AUDREY BISHOP, MARGARET LEESE, and C. E. BLANK From the Centre for Human Genetics, United Sheffield
If unqualified, Complete remission is considered to be Haematological complete remission
 Scroll right to see the database codes for Disease status and Response Diagnosis it refers to Disease status or response to treatment AML ALL CML CLL MDS or MD/MPN or acute leukaemia secondary to previous
Scroll right to see the database codes for Disease status and Response Diagnosis it refers to Disease status or response to treatment AML ALL CML CLL MDS or MD/MPN or acute leukaemia secondary to previous
176 N. TAKAGI, S. MAKINO, S. TAKAI, and M. HIKITA [Vol. 41,
 No. 2] 175 39. A Phenotypical XXYY Human Male with Notes on Two Regular Kline f elter Cases*' By Nobuo TAKAGI, Sajiro MAKINO, Shudo TAKAI, **~ and Masahiro HIKITA**) (Comm. by Yoshimaro TANAKA, M.J.A.,
No. 2] 175 39. A Phenotypical XXYY Human Male with Notes on Two Regular Kline f elter Cases*' By Nobuo TAKAGI, Sajiro MAKINO, Shudo TAKAI, **~ and Masahiro HIKITA**) (Comm. by Yoshimaro TANAKA, M.J.A.,
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab
 Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
Title. Author(s)IKEUCHI, Tatsuro; MITANI, Muneo; TAMURA, Takeo. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Chromosome Studies in 2 Patients with Suspected Cri Author(s)IKEUCHI, Tatsuro; MITANI, Muneo; TAMURA, Takeo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 15(4): 706-711 Issue
Title Chromosome Studies in 2 Patients with Suspected Cri Author(s)IKEUCHI, Tatsuro; MITANI, Muneo; TAMURA, Takeo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 15(4): 706-711 Issue
manifestations are uncommon. Initial descriptions of the disease (Rosai and Dorfman, 1969) specifically
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Ch. 15 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 Ch. 15 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Nov 12 12:58 PM 1 Essential Question: Are chromosomes the basis of inheritance? Nov 12 1:00 PM 2 1902 Walter S. Sutton, Theodor Boveri, et al Chromosome Theory
Ch. 15 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Nov 12 12:58 PM 1 Essential Question: Are chromosomes the basis of inheritance? Nov 12 1:00 PM 2 1902 Walter S. Sutton, Theodor Boveri, et al Chromosome Theory
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS Chediak-Higashi Syndrome H.N. Usha Preetha D. Prabhu M. Sridevi Kishore Baindur C.M. Balakrishnan The Chediak Higashi Syndrome (CHS) is a rare autosomal recessive disease characterized
INDIAN PEDIATRICS Chediak-Higashi Syndrome H.N. Usha Preetha D. Prabhu M. Sridevi Kishore Baindur C.M. Balakrishnan The Chediak Higashi Syndrome (CHS) is a rare autosomal recessive disease characterized
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
 Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA. April 16, 2008
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study
 Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA IN HODGKIN'S DISEASE ASSOCIATED
 98 HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA IN HODGKIN'S DISEASE ASSOCIATED WITH IMMUNOGLOBULIN DEFICIENCIES B. I. HOFFBRAND From the University College Hospital, Gower Street, London, W.C.1 Received for publication January
98 HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA IN HODGKIN'S DISEASE ASSOCIATED WITH IMMUNOGLOBULIN DEFICIENCIES B. I. HOFFBRAND From the University College Hospital, Gower Street, London, W.C.1 Received for publication January
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE
 CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
Acute myeloid leukemia. M. Kaźmierczak 2016
 Acute myeloid leukemia M. Kaźmierczak 2016 Acute myeloid leukemia Malignant clonal disorder of immature hematopoietic cells characterized by clonal proliferation of abnormal blast cells and impaired production
Acute myeloid leukemia M. Kaźmierczak 2016 Acute myeloid leukemia Malignant clonal disorder of immature hematopoietic cells characterized by clonal proliferation of abnormal blast cells and impaired production
LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES Identify etiology and epidemiology for leukemia and lymphoma. Discuss common types of leukemia. Distinguish
LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES Identify etiology and epidemiology for leukemia and lymphoma. Discuss common types of leukemia. Distinguish
Genetic Studies on Hypospadias in Males
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 153. Genetic Studies on Hypospadias in Males YOU C. CHEN and PAUL V. WOOLLEY Jr From the Variety Club Growth and Development Center and Cytogenetic Laboratory, Children's
Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 153. Genetic Studies on Hypospadias in Males YOU C. CHEN and PAUL V. WOOLLEY Jr From the Variety Club Growth and Development Center and Cytogenetic Laboratory, Children's
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Chromosome Abnormalities
 Chromosome Abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities vs. molecular mutations Simply a matter of size Chromosomal abnormalities are big errors Two types of abnormalities 1. Constitutional problem present
Chromosome Abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities vs. molecular mutations Simply a matter of size Chromosomal abnormalities are big errors Two types of abnormalities 1. Constitutional problem present
A rare thing may be just like any other but it is also paradoxically nothing like any of them.
 A rare thing may be just like any other but it is also paradoxically nothing like any of them. A RARE ANEMIA WHERE THERE IS PAUCITY AMIDST PLENTY. Dr.Rena, DNB Pediatrics Resident, Dr.Mehta s Children
A rare thing may be just like any other but it is also paradoxically nothing like any of them. A RARE ANEMIA WHERE THERE IS PAUCITY AMIDST PLENTY. Dr.Rena, DNB Pediatrics Resident, Dr.Mehta s Children
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
 chapter 7 Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease involving both T- and B-lymphocytes. In addition, the blood cells that help control bleeding, called platelets
chapter 7 Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease involving both T- and B-lymphocytes. In addition, the blood cells that help control bleeding, called platelets
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN
 LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D.
 Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D. SUPPLEMENTAL READING Nussbaum, RL, McInnes, RR, and Willard HF (2007) Thompson and Thompson Genetics in Medicine, 7th edition. Saunders: Philadelphia.
Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D. SUPPLEMENTAL READING Nussbaum, RL, McInnes, RR, and Willard HF (2007) Thompson and Thompson Genetics in Medicine, 7th edition. Saunders: Philadelphia.
Leukocyte Disorders. Dr Alauldeen Mudhafar Zubair
 Leukocyte Disorders Dr Alauldeen Mudhafar Zubair Composition of blood Specialized connective tissue Blood cells (formed elements) suspended in plasma Blood volume: 5-6 liters (approx 1.5 gal) in males
Leukocyte Disorders Dr Alauldeen Mudhafar Zubair Composition of blood Specialized connective tissue Blood cells (formed elements) suspended in plasma Blood volume: 5-6 liters (approx 1.5 gal) in males
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD. Part 1
 HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 1 NONNEOPLASTIC DISEASES OF THE WHITE BLOOD CELLS There are five major types of WBCs in the blood: neutrophils,
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 1 NONNEOPLASTIC DISEASES OF THE WHITE BLOOD CELLS There are five major types of WBCs in the blood: neutrophils,
Heterochromatic polymorphism in spontaneous abortions
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1979, 16, 358-362 Heterochromatic polymorphism in spontaneous abortions LORRINE HEMMING ND CM BURNS From the Cytogenetics Department, Mater Misericordiae Public Hospitals,
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1979, 16, 358-362 Heterochromatic polymorphism in spontaneous abortions LORRINE HEMMING ND CM BURNS From the Cytogenetics Department, Mater Misericordiae Public Hospitals,
Karyology. Preparation and study of karyotypes is part of Cytogenetics.
 Chromosomal Karyotyping Karyology Karyotyping - process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual's chromosomes. Karyotypes describe
Chromosomal Karyotyping Karyology Karyotyping - process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual's chromosomes. Karyotypes describe
Chromosome pathology
 Chromosome pathology S. Dahoun Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital of Geneva Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome
Chromosome pathology S. Dahoun Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital of Geneva Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome
Class XII Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Biology
 Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring. He selected
Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring. He selected
Human Genetic Mutations
 Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis. (Sections 11-3,11-4;)
 MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome*
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 322. Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome* MIRIAM G. WILSONt, JOHN MELNYK, and JOSEPH W. TOWNER Fronm University of Southern California School of Medicine, Los Angeles
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 322. Retinoblastoma and Deletion D (14) Syndrome* MIRIAM G. WILSONt, JOHN MELNYK, and JOSEPH W. TOWNER Fronm University of Southern California School of Medicine, Los Angeles
REGISTRATION PATIENT DETAILS
 PATIENT DETAILS Person completing form: (please print) FOR REGIONAL REFERRAL CENTER USE ONLY Registration: Approved Date: / / Not approved RRC telephone contact with primary MD: Date: / / Reviewers Signature:
PATIENT DETAILS Person completing form: (please print) FOR REGIONAL REFERRAL CENTER USE ONLY Registration: Approved Date: / / Not approved RRC telephone contact with primary MD: Date: / / Reviewers Signature:
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
Further Chromosomal Studies on Irradiated Human
 Jap. Jour. Genet. Vol. 38, No. 2, 106-112 (1963) Further Chromosomal Studies on Irradiated Human Leukocytes in vitrol) Akio AWA, Yasushi OHNUKI, and C. M. POMERAT Zoological Institute, Hokkaido University,
Jap. Jour. Genet. Vol. 38, No. 2, 106-112 (1963) Further Chromosomal Studies on Irradiated Human Leukocytes in vitrol) Akio AWA, Yasushi OHNUKI, and C. M. POMERAT Zoological Institute, Hokkaido University,
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Answer Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of
Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Answer Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of
HYPER IgM SYNDROME This booklet is intended for use by patients and their families and should not replace advice from a clinical immunologist.
 HYPER IgM SYNDROME This booklet is intended for use by patients and their families and should not replace advice from a clinical immunologist. 1 HYPER IgM SYNDROME Also available : COMMON VARIABLE IMMUNODEFICIENCY
HYPER IgM SYNDROME This booklet is intended for use by patients and their families and should not replace advice from a clinical immunologist. 1 HYPER IgM SYNDROME Also available : COMMON VARIABLE IMMUNODEFICIENCY
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Classifications of genetic disorders disorders
 Classifications of genetic disorders Dr. Liqaa M. Sharifi Human diseases in general can roughly be classified in to: 1-Those that are genetically determined. 2-Those that are almost entirely environmentally
Classifications of genetic disorders Dr. Liqaa M. Sharifi Human diseases in general can roughly be classified in to: 1-Those that are genetically determined. 2-Those that are almost entirely environmentally
Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function. Ch. 8
 Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism
 Kamla-Raj 2006 Int J Hum Genet, 6(4): 291-295 (2006) Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism Cyril Cyrus 1, Teena K. 2, Solomon F.D.Paul 2, Chandra N.
Kamla-Raj 2006 Int J Hum Genet, 6(4): 291-295 (2006) Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism Cyril Cyrus 1, Teena K. 2, Solomon F.D.Paul 2, Chandra N.
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Calico cats are female because 1) A) the Y chromosome has a gene blocking orange coloration.
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Calico cats are female because 1) A) the Y chromosome has a gene blocking orange coloration.
Human inherited diseases
 Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
Meiosis and Introduction to Inheritance
 Meiosis and Introduction to Inheritance Instructions Activity 1. Getting Started: Build a Pair of Bead Chromosomes Materials bag labeled diploid human genome (male) bag labeled diploid human genome (female)
Meiosis and Introduction to Inheritance Instructions Activity 1. Getting Started: Build a Pair of Bead Chromosomes Materials bag labeled diploid human genome (male) bag labeled diploid human genome (female)
Dr.P.Subramani II year Postgraduate SRMC. Dr.Latha Ravichandran Professor Department of pediatrics
 Dr.Latha Ravichandran Professor Department of pediatrics Dr.Julius Xavier Scott Professor Department of pediatric hematooncology Sri Ramachandra University, Porur. Dr.P.Subramani II year Postgraduate SRMC
Dr.Latha Ravichandran Professor Department of pediatrics Dr.Julius Xavier Scott Professor Department of pediatric hematooncology Sri Ramachandra University, Porur. Dr.P.Subramani II year Postgraduate SRMC
Chapter 15 Notes 15.1: Mendelian inheritance chromosome theory of inheritance wild type 15.2: Sex-linked genes
 Chapter 15 Notes The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Mendel s hereditary factors were genes, though this wasn t known at the time Now we know that genes are located on The location of a particular gene
Chapter 15 Notes The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Mendel s hereditary factors were genes, though this wasn t known at the time Now we know that genes are located on The location of a particular gene
GENETICS NOTES. Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16
 GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
The Chromosomal Basis Of Inheritance
 The Chromosomal Basis Of Inheritance Chapter 15 Objectives Explain the chromosomal theory of inheritance and its discovery. Explain why sex-linked diseases are more common in human males than females.
The Chromosomal Basis Of Inheritance Chapter 15 Objectives Explain the chromosomal theory of inheritance and its discovery. Explain why sex-linked diseases are more common in human males than females.
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Differences in the satellite association pattern in- the human population
 Hrrriliras 66: 21 3 (197) Differences in the satellite association pattern in- the human population ALF HANSSON Institute of Genetics, University of Lund, Sweden (Received July 16, 197) The incidence and
Hrrriliras 66: 21 3 (197) Differences in the satellite association pattern in- the human population ALF HANSSON Institute of Genetics, University of Lund, Sweden (Received July 16, 197) The incidence and
Canadian College of Medical Geneticists (CCMG) Cytogenetics Examination. May 4, 2010
 Canadian College of Medical Geneticists (CCMG) Cytogenetics Examination May 4, 2010 Examination Length = 3 hours Total Marks = 100 (7 questions) Total Pages = 8 (including cover sheet and 2 pages of prints)
Canadian College of Medical Geneticists (CCMG) Cytogenetics Examination May 4, 2010 Examination Length = 3 hours Total Marks = 100 (7 questions) Total Pages = 8 (including cover sheet and 2 pages of prints)
Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype.
 UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #34: Chromosomes and Phenotype Objective: Explain how the chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. Take a moment to look at the variety of treats
UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #34: Chromosomes and Phenotype Objective: Explain how the chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. Take a moment to look at the variety of treats
Hths 2231 Laboratory 3 Genetics
 Watch Movie: Cystic Fibrosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-5 Activity #1: Under Lab 3 Click on activity 1 Click on Tour of the Basics Do all 6 What is exercises Activity
Watch Movie: Cystic Fibrosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-5 Activity #1: Under Lab 3 Click on activity 1 Click on Tour of the Basics Do all 6 What is exercises Activity
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms
 Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) A multipotent stem cell that can differentiate into any of the myeloid lineage cells (RBCs, granulocytes, megakaryocytes)
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) A multipotent stem cell that can differentiate into any of the myeloid lineage cells (RBCs, granulocytes, megakaryocytes)
Structural Chromosome Aberrations
 Structural Chromosome Aberrations 2 Structural chromosome aberrations or chromosome mutations represent apart from aneuploidies the most frequent pathologic findings in applied chromosome diagnostics.
Structural Chromosome Aberrations 2 Structural chromosome aberrations or chromosome mutations represent apart from aneuploidies the most frequent pathologic findings in applied chromosome diagnostics.
Case 1B. 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21)
 Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Syndrome Associated with a Deficiency of Part of
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 140. Syndrome Associated with a Deficiency of Part of the Long Arm of Chromosome No. 18* J. INSLEY From the Institute of Child Health, Francis Road, Birmingham 16 In 1964
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 140. Syndrome Associated with a Deficiency of Part of the Long Arm of Chromosome No. 18* J. INSLEY From the Institute of Child Health, Francis Road, Birmingham 16 In 1964
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM
 STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
Six Year Experience of 116 Leukaemic Children at Shaikh Zayed Hospital Lahore Pakistan.
 Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.l vol: 14(1) 2000, pp. 13-17. Six Year Experience of 116 Leukaemic Children at Shaikh Zayed Hospital Lahore Pakistan. M. Akbar Malik, Muhammad Javed Asif, Zafar Iqbal, Sajid Maqbool
Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.l vol: 14(1) 2000, pp. 13-17. Six Year Experience of 116 Leukaemic Children at Shaikh Zayed Hospital Lahore Pakistan. M. Akbar Malik, Muhammad Javed Asif, Zafar Iqbal, Sajid Maqbool
Diseases Of The Blood
 Diseases Of The Blood DR. Associate Professor Of Pathology Faculty Of Medicine Ain Shams University Red Blood Cells and Anemia RBC=4-6 million/mm 2 Hb=12-18 g/dl Oxygen Carrying Molecule Hemoglobin Tetramer:
Diseases Of The Blood DR. Associate Professor Of Pathology Faculty Of Medicine Ain Shams University Red Blood Cells and Anemia RBC=4-6 million/mm 2 Hb=12-18 g/dl Oxygen Carrying Molecule Hemoglobin Tetramer:
CYTOGENETICAL AND DERMATOGLYPHIC STUDIES IN PATIENTS AFFECTED BY STEENERT'S MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY
 CYTOGENETICAL AND DERMATOGLYPHIC STUDIES IN PATIENTS AFFECTED BY STEENERT'S MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY R. B. LEVISKY * M. SCAFF ** J. A. LEVY.** E. LUSVARGHI ** C. P. SERRANO*** Steinert's myotonic dystrophy is
CYTOGENETICAL AND DERMATOGLYPHIC STUDIES IN PATIENTS AFFECTED BY STEENERT'S MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY R. B. LEVISKY * M. SCAFF ** J. A. LEVY.** E. LUSVARGHI ** C. P. SERRANO*** Steinert's myotonic dystrophy is
Extramedullary precursor T-lymphoblastic transformation of CML at presentation
 Extramedullary precursor T-lymphoblastic transformation of CML at presentation Neerja Vajpayee, Constance Stein, Bernard Poeisz & Robert E. Hutchison Clinical History 30 year old man presented to the emergency
Extramedullary precursor T-lymphoblastic transformation of CML at presentation Neerja Vajpayee, Constance Stein, Bernard Poeisz & Robert E. Hutchison Clinical History 30 year old man presented to the emergency
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 15 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Locating Genes on Chromosomes A century
Chapter 15 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Locating Genes on Chromosomes A century
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias
 Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Pedigree Analysis. Genetic disorders. Dominant inheritance. Recessive inheritance. Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits. X-linked recessive inheritance
 Genetic disorders 4.2 Errors During Meiosis 5.3 Following Patterns of Human nheritance Pedigree Analysis 2005 Lee Bardwell Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits Autosomal traits are caused by genes on autosomes
Genetic disorders 4.2 Errors During Meiosis 5.3 Following Patterns of Human nheritance Pedigree Analysis 2005 Lee Bardwell Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits Autosomal traits are caused by genes on autosomes
Chromosomal Abnormalities and Karyotypes Creating a Karyotype
 Chromosomal Abnormalities and Karyotypes Creating a Karyotype The Normal Human Karyotype The normal human karyotype is composed of SEVEN groups of chromosomes A G plus the sex chromosomes X and Y. The
Chromosomal Abnormalities and Karyotypes Creating a Karyotype The Normal Human Karyotype The normal human karyotype is composed of SEVEN groups of chromosomes A G plus the sex chromosomes X and Y. The
- Aya Alomoush. - Talal Al-Zabin. - Belal Azab. 1 P a g e
 24 - Aya Alomoush - Talal Al-Zabin - Belal Azab 1 P a g e 1) Features of autosomal dominant inheritance: A) Vertical transmission: direct transmission from grandparent to parent to child without skipping
24 - Aya Alomoush - Talal Al-Zabin - Belal Azab 1 P a g e 1) Features of autosomal dominant inheritance: A) Vertical transmission: direct transmission from grandparent to parent to child without skipping
Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
