Circular RNA functions as an oncogene through direct binding to mir p and mir-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer
|
|
|
- Curtis O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Circular RNA functions as an oncogene through direct binding to mir p and mir-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer Lijian Chen 1,2, Aruo Nan 2, Nan Zhang 2, Yangyang Jia 2, Xin Li 2, Yihui Ling 2, Jiabin Dai 2, Shaozhu Zhang 2, Qiaoyuan Yang 2, Yanni Yi 2 and Yiguo Jiang 1,2* Open Access Abstract Circular RNAs are widely expressed in eukaryotic cells and associated with cancer. However, limited studies to date have focused on the potential role of circrnas in progression of lung cancer. Data from the current investigation showed that circrna is highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines and the chemically induced malignant transformed bronchial cell line, 16HBE-T, as well as 40 paired tissue samples of NSCLC. Suppression of circrna inhibited the proliferation and invasion of cells and promoted apoptosis. Furthermore, circrna could interact with splicing factors and bind mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p to regulate multiple downstream mrnas. Our collective findings support a role of circrna in the development of NSCLC and further demonstrate endogenous competition among circrna , SF3B3 and mirnas, providing novel insights into the mechanisms underlying nonsmallcelllungcancer. Keywords: circrna, NSCLC, Splicing factor, microrna Main text Non-small cell lung cancer accounts for up to 85% of all lung cancer cases and is the leading cause of lung cancer-associated mortality [1]. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to improve patient survival. However, the mechanisms underlying lung cancer progression are not yet to be fully elucidated. Recent progress in RNA research has led to the identification of non-coding RNAs (ncrnas) involved in a variety of biological processes [2]. Previous studies have revealed critical roles of mirnas and lncrnas in lung cancer development, in particular, regulation of proliferation, apoptosis and invasion [3, 4]. In-depth analysis of ncrnas should thus aid in further clarifying cancer-associated mechanisms at the epigenetic level. * Correspondence: jiangyiguo@vip.163.com; jiangyiguo@gzhmu.edu.cn Lijian Chen and Aruo Nan contributed equally to this work. 1 State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou , People s Republic of China 2 Institute for Chemical Carcinogenesis, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, People s Republic of China Circular RNAs (circrnas) are a class of newly discovered RNAs extensively expressed in eukaryotic cells. In recent years, the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics has significantly improved our understanding of circrnas. The majority of currently reported circrnas are non-coding, with some have been reported to encode polypeptides or proteins [5]. CircRNAs are formed by non-canonical splicing and relatively resistant to exonuclease degradation [6]. CircRNAs are closely associated with the development of various disorders, particularly with cancer [7, 8]. However, our understanding of the specific roles of circrnas in NSCLC remains limited and requires further exploration. In the current study, we examined the biological function of circrna (also known as hsa_circ_ in the circbase) and underlying molecular mechanisms in the development of NSCLC from multiple viewpoints. Our findings provide novel clues for the identification of biomarkers for NSCLC. The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
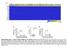
2 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Page 2 of 8 Results and discussion Screening and expression of circrna in NSCLC cells and tissues We employed the immortalized normal human bronchial epithelial cell line, 16HBE, and the malignantly transformed cell line, 16HBE-T, for circrna microarray analysis (Additional file 1). Differentially expressed circrnas were displayed through fold change filtering (Fig. 1a, Additional file 2). Specific primers were designed and qrt-pcr was employed to detect the top six upregulated circrnas (Additional file 3: Table S1) expression in 16HBE and 16HBE-T cells. Compared with 16HBE, the expressions of circrna , circrna , circrna and circrna were significantly higher expression in 16HBE-T cells by 2.58 ± 0.50, 5.12 ± 0.19, 3.49 ± 0.32 and 7.64 ± 0.55-fold, with circrna displaying the greatest increase (Fig. 1b). CircRNA is formed by the head-to-tail splicing of exon 5 and exon 6 of EIF3I, with a predicted length of 278 bp (Fig. 1c). To validate the formation of circrna , we designed convergent primers to amplify linear mrna, as well as divergent primers to amplify circrna. By using cdna and gdna as templates, only circrna could be amplified by divergent primers in cdna, and no other products were observed in the gdna groups (Additional file 4: Figure S1a). Then, the RT-PCR product of circrna was confirmed by Sanger sequencing (Additional file 4: Figure S1b). We further predicted the involvement of circrna in cellular processes and pathways, and found its involvement in multiple pathways, particularly pathway in cancer (Fig. 1d). Subsequently, circrna expression was detected in lung cancer cell lines A549, H446, H1299, 95-D and H460. Compared with 16HBE, the expression of circrna was significantly up-regulated in H1299, 95-D and H460 cells and displayed 5.80 ± 0.41-fold increase in H460 cells (Fig. 1e). We also examined circrna expression in 40 pairs of matched NSCLC cancer and adjacent tissue samples. Compared with paracancerous tissues, circrna was highly expressed in cancer tissue (p < 0.05, Fig. 1f) and upregulated in 26 cases (Additional file 4: Figure S1c). Abnormal expression of circrna was associated with pathological classification and differentiation grade of lung cancer (Additional file 3: TableS2).We next investigated whether circrna expression could serve as a biomarker for distinguishing cancerous tissue from adjacent non-cancerous lung tissue. ROC curve analysis was employed to evaluate the diagnostic value of circrna Results showed that the area under the curve (AUC) was (95% CI: ), and the sensitivity and specificity were and 0.575, respectively (Fig. 1g). Suppression of circrna expression inhibits cancer cell proliferation, invasion and promotes apoptosis in vitro To investigate specific function of circrna , we designed and synthesized three specific small interfering RNAs and examined interference efficiency. Overall, sirna1 and sirna2 showed the relative higher interference efficiency (p < 0.01; Additional file 4: Figure S2a, S2b). Notably, interference with circrna did not affect the expression of its parental gene, EIF3I (Additional file 4: Figure S2c). Following 48 h transfection of 16HBE-T and H460 cells with sirnas, cell proliferation and apoptosis were examined by 5-Ethynyl-2 -deoxyuridine (EdU) and flow cytometry (FCM) assays. Proliferation of 16HBE-T and H460 cells was significantly decreased after knockdown of circrna , compared with the sirna NC group (p < 0.05, Fig. 2a-2c). FCM data revealed a marked increase in the apoptotic rates of 16HBE-T and H460 (p <0.01,Fig.2d, 2e). The effects of circrna on invasion and migration of cancer cells were further examined via transwell, wound healing and cell adhesion assays. After transfection with sirna1 and sirna2, average invasion rates were (16.91 ± 0.75%) and (16.56 ± 0.85%) for 16HBE-T and (7.96 ± 0.44%) and (8.34 ± 0.79%) for H460 respectively. Compared with the control group, invasion rates were significantly reduced (p < 0.01; Additional file 4: Figure S2d, S2e). The wound healing assay revealed that knockdown of circrna inhibits migration of cancer cells (p < 0.01; Additional file 4:FigureS2f,S2 g), analogous to data obtained with the cell adhesion assay (p < 0.01, Additional file 4:FigureS2h). Suppression of circrna 100,146 expression inhibits subcutaneous tumor growth in vivo We constructed stably transfected H460 cells with knockdown of circrna circrna expression in H460-sh circrna cells was depleted by 50%, compared with that in the H460-empty vector group (p < 0.01) (Additional file 4: Figure S2i, S2j). The relative expression of EIF3I was detected in H460-sh circrna and H460-empty vector group, results showed that no statistical difference was found between the two groups (Additional file 4: Figure S2k). Xenograft nude mouse model was subsequently established using transfected H460 cells. After 21 days follow-up, growth of tumors in the sh-circrna group was slower and tumor volumes were significantly reduced. Furthermore, we used a small animal live imaging system to obtain fluorescence images of nude mice at 1, 3, 5, 7, 14 and 21d after inoculation (Fig. 2f, 2g). Tumors in nude mice gradually grew larger and fluorescence intensity was increased with time. However, fluorescence intensity in the sh-circrna group consistently remained weaker than that in the control group (Fig. 2h, Additional file 3: Table S3). Hematoxylin-eosin staining and immunohistochemical
3 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Page 3 of 8 Fig. 1 Screening and expression of circrna in NSCLC cells and tissues. a Differential expression circrnas in 16HBE and 16HBE-T cells. The values plotted on X and Y axes in the Scatter-Plot are the normalized signal values of the samples (log2 scaled). The green lines are Fold Change Lines. The circrnas above the top green line and below the bottom green line indicated circrnas > 2.0-fold change between the two samples. b Six circrnas that were mostly upregulated were detected via qrt-pcr. Data are presented as means ± s.d., n =3,pairedt-test, *p < 0.05, **p < c Genomic scheme of circrna TMEM234 and MTMR9LP are genes upstream and downstream of EIF3I, the parental gene of circrna d Pathways and cellular processes analysis were applied for prediction of circrna We used KEGG database to analyze circrna and its target genes for signal pathway enrichment, and to calculated the hypergeometric distribution between differentially expressed genes and pathways, then analyzed the enrichment of these genes in different pathways, and finally screened out pathways that these genes involved based on the p value. The left Y axis represents p value and right Y axis represents the number of target genes associated with circrna. e Relative expression of circrna in five lung cancer cell lines. Data are expressed as means ± s.d., n =3,unpairedt-test, *p < 0.05, **p < f The scatter plot shows circrna expression in 40 paired NSCLC cancer and paracancerous tissues (2^-ΔCt, which was normalized according to GAPDH expression level), n = 40, ANOVA, *p <0.05.g ROC curve analysis to evaluate the diagnostic value of circrna The area under the curve (AUC) was (95% CI: , *p = 0.028)
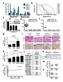
4 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Page 4 of 8 Fig. 2 Suppression of circrna expresssion inhibits cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in vitro and inhibits subcutaneous tumor growth in vivo. a, b After knockdown of circrna , proliferation of 16HBE-T (a) and H460 cells (b) was detected with the EdU assay. Blue fluorescence represents DAPI-stained nuclei and red fluorescence represents EdU-labeled proliferative cells (magnification 200). c The histogram shows the relative proportions of EdU-positive 16HBE-T and H460 cells. Cells were counted using Image-pro-plus software. d Apoptosis of cancer cells was detected using flow cytometry. Upper left quadrant (UL) represents necrotic cells, lower left quadrant (LL) living cells, right upper quadrant (UR) late apoptotic and necrotic cells, lower right quadrant (LR) early apoptotic cells. e Percentage of apoptotic cells (sum of LR and UR) in the negative control and interference groups. f, g H460-empty vector(f) and H460-sh-circRNA(g) were injected subcutaneously in nude mice. Subcutaneous tumor fluorescence intensities were determined in vivo by using an small animal imaging system at 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, and 21d. There is a fluorescence value coordinate on the right side of the displayed picture, and the darker of the red, the higher of the fluorescence value. h Changes in subcutaneous fluorescence intensity in the empty vector and experimental groups at different time-points were analyzed. i Immunohistochemical detection of expression of PCNA, Caspase-9, E-cadherin and p53 in H460-empty vector and H460 sh-circrna groups (magnification 400). c,e Data are presented as means±s.d., n = 3, unpaired t-tests; compared with the sirna NC group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
5 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Fig. 3 (See legend on next page.) Page 5 of 8
6 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Page 6 of 8 (See figure on previous page.) Fig. 3 CircRNA binding to mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p indirectly affecting multiple downstream mrnas expression. a Subcellular localization of circrna detected by FISH. Images were obtained under a confocal fluorescence microscope. Green fluorescence represents 6-FAM-labeled circrna probes while blue fluorescence represents DAPI-stained nuclei. b Sequence alignments between mir-361-3p, mir-615-5p or mir-330-3p, and the seed sequence of circrna WT and Mut represent wild-type and mutant sequences of circrna. c Results of the dual-luciferase reporter gene assay in HEK-293 T cells. d, f Western blot of NFAT5, COL1A1, TRAF3 and MEF2C in 16HBE-T (d) and H460 (f) following interference with circrna expression. e Gray value analysis of the protein bands in (d). g Gray value analysis of the protein bands in (f). h Sequence alignments between mirnas and seed sequence of the 3 -UTR of SF3B3. i Results of the dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. j Expression of SF3B3 in subcutaneous tumors tissues detected using immunohistochemistry. c, i Data are presented as means ± s.d, n = 3, unpaired t-test, compared with the mimic NC + WT group, *p < 0.05, **p < e, g Data are presented as means ± s.d, n = 3, unpaired t-test, Compared with sirna NC group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 analysis of removed tumors disclosed decreased PCNA and p53 and increased caspase-9 and E-cadherin levels in the sh-circrna group (Additional file 4: Figure S2i and Fig. 2i), clearly suggesting that proliferation and invasion of tumor cells are suppressed while apoptosis is enhanced. CircRNA binds subtypes of splicing factor SF3 family To clarify circrna expression at the subcellular level, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed in 16HBE, 16HBE-T and H460 cells. The overlay images showed expression of circrna was mainly in the cytoplasm (Fig. 3a). Moreover, nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA was extracted from cells and circrna relative expression was detected by qrt-pcr and results also showed circrna was predominantly expressed in the cytoplasm (Additional file 4: Figure S3a). To determine the possible mechanisms underlying the effects of circrna on general transcription, we designed specific circrna protein-pull-down probe and isolated the interacting proteins in H460 cells (Additional file 4: Figure S3b). Protein mass spectrometry facilitated the identification of 657 proteins in total. Gene ontology analysis further disclosed that nucleic acid binding proteins accounted for 31.2% of all the identified proteins (Additional file 4: Figure S3c and Additional file 5). Upon ranking of the proteins according to score (high to low), we observed that the splicing factor SF3 family was the most closely associated with gene transcription among the top 100 proteins, including SF3B3, SF3B2 and SF3A1 (Additional file 4: Figure S3d). Our findings indicate that circrna bind to multiple subtypes of splicing factor family SF3. CircRNA direct binding to mir-361-3p and mir p Several studies have reported circrnas can act as mirna sponge affecting mirna activity [9]. We further explored regulatory functions of circrna at post-transcriptional level. Except for bioinformatics analysis, we also performed an RNA antisense purification experiment (Additional file 4: Figure S4a) and sequenced the products to accurately identify interacting mirnas. Overall, mirnas accounted for 7.26% of the total non-coding RNAs (Additional file 4: Figure S4b). Based on bioinformatics, sequencing and literature reviews, mir-330-3p, mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p that directly bind to circrna were selected for further analyses (Additional file 4: Figure S4c). Furthermore, dual luciferase reporter assays were used to detect direct interactions between circrna and three mirnas. Co-transfection cells with circrna wild-type vector and mir-361-3p or mir-615-5p mimics led to significantly reduced relative luciferase activity while co-transfection with mir-330-3p mimics induced non-significant differences (Fig. 3b, 3c), clearly suggesting that circrna interacts directly with mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p. Moreover, FISH experiments showed that circrna , mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p are co-expressed in the cytoplasm at the subcellular level (Additional file 4: Figure S4d). Our results support that circrna direct binding to mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p to regulating their activity. In view of the association of two mirnas with NSCLC development, we propose that circrna affects tumor progression via regulation of mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p. CircRNA indirectly affects multiple downstream mrnas through regulating mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p We used mirdb and TargetScan to predict the target mrnas of mir-361-3p or mir-615-5p. Combination of sequence matching, functional analyses and correlations with cancer led to the identification of 21 mrnas. Twelve of these were targeted by mir-361-3p and 9 by mir-615-5p (Additional file 3: Table S4). Upon knockdown of circrna or overexpression of mir-361-3p or mir-615-5p in 16HBE-T and H460, some mrnas were significantly downregulated, including NFAT5, COL1A1, TRAF3 and MEF2C (Additional file 4: Figure S4e-S4 h). Bioinformatics analyses suggested that TRAF3, NFAT5 and COL1A1 are likely to be the direct targets of mir-361-3p and MEF2C the direct target of mir-615-5p. Following suppression of circrna , we detected endogenous proteins expression of NFAT5, COL1A1, MEF2C and TRAF3 via western blot. Result showed NFAT5, COL1A1 and MEF2C proteins were
7 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Page 7 of 8 downregulated and TRAF3 protein upregulated in16hbe-t cells (Fig. 3d, 3e). Endogenous proteins were expressed to a similar extent in H460 cells (Fig. 3f, 3g). In summary, changes of circrna expression affected multiple downstream genes through regulating mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p. Splicing factor, SF3B3, is predicted to be a common target of mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p (Additional file 4: Figure S4i). Upon overexpression of mir-361-3p or mir-615-5p, SF3B3 expression was decreased (p < 0.01, Additional file 4: Figure S4j). We further conducted dual luciferase reporter gene assay with plasmids expressing wild-type and mutant SF3B3 3 UTR (Fig. 3h). Data showed that mir-361-3p directly binds to the 3 UTR region of SF3B3 whereas only one of the two predicted sites of mir-615-5p binds directly to this region (Fig. 3i). Western blot showed SF3B3 protein are reduced upon overexpression of mir-361-3p or mir-615-5p in H460 cells (Additional file 4: Figure S4k, S4l). The relative expression of SF3B3 was detected in H460-sh circrna and H460-empty vector, results show that that SF3B3 expression was decreased in H460-sh circrna group (p < 0.01, Additional file 4: Figure S4 m). Immuno-histochemical analysis of SF3B3 expression in subcutaneously transplanted tumors revealed significantly decreased in the sh-circrna group (Fig. 3j). Based on this, we propose that circrna may affect SF3B3 expression through regulating mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p. Conclusions We have demonstrated an oncogenic role of circrna in the progession of NSCLC for the first time. The endogenous competitive relationships among circrna , SF3B3 and mirnas has been elaborated. Our data provide a platform for further elucidating mechanisms underlying the NSCLC and identifying diagnostic or therapeutic targets. Additional files Additional file 1: Supplementary materials and methods. (DOCX 149 kb) Additional file 2: Microarray analysis of up-regulated circrnas. (XLS 765 kb) Additional file 3: Supplementary tables (Table S1-S11.) (DOCX 45 kb) Additional file 4: Figure S1. Identification of circrna and its expression in lung cancer tissues. Figure S2. Suppression of circrna expresssion inhibits cancer cell invasion and migration in vitro. Figure S3. circrna binds subtypes of splicing factor SF3 family. Figure S4. circrna binding to mir-361-3p and mir-615-5p indirectly affecting multiple downstream mrnas expression. (DOCX 4346 kb) Additional file 5: Excel document with protein mass spectrum of pull down experiment. (XLS 6165 kb) Abbreviations Circular RNA: CircRNA; COL1A1: Collagen type I alpha 1 chain; EdU: 5-Ethynyl- 2 -deoxyuridine; FCM: Flow Cytometry; FISH: Fuorescence in situ hybridization; HBE: Human Bronchial Epithelial; MEF2C: Myocyte enhancer factor 2C; NFAT5: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; RAP: RNA antisense purification; SF3B3: Splicing factor 3b subunit 3; TRAF3: TNF receptor associated factor 3 Acknowledgements We thank Dr. Yueting Shao for her assistance with language editing, and comments that improve the final version of the manuscript. Funding This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( , , to J.Y.), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou ( to J.Y.), University Chief Scientist Program of Guangzhou ( to J.Y.), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2018B to J.Y.). Availability of data and materials All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its additional information files. Authors contributions YJ, LC and AN conceived and designed the project. LC and AN completed the majority of experiments and analyzed the data. NZ, YYJ, XL, YL and YY performed some of the experiments. JD, SZ and QY collected tissue samples. LC and YJ wrote the manuscript. YJ is responsible for research supervision and funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was conducted in compliance with the declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. The ethics approval statements for human subjects were provided by the Ethnic Committee of the General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command of PLA. The ethics approval statements for animal work were provided by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Guangzhou Medical University. Consent for publication All authors agreed on the manuscript. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Received: 22 August 2018 Accepted: 9 January 2019 References 1. Reck M, Popat S, Reinmuth N, De Ruysscher D, Kerr KM, Peters S. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 3):i Cech TR, Steitz JA. The noncoding RNA revolution trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157(1): Li X, Wu J, Zheng J, Li Y, Yang T, Hu G, Dai J, Yang Q, Dai L, Jiang Y. Altered mirna expression profiles and mir-1a associated with urethane-induced pulmonary carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci. 2013;135(1): Nie W, Ge HJ, Yang XQ, Sun X, Huang H, Tao X, Chen WS, Li B. LncRNA- UCA1 exerts oncogenic functions in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting mir-193a-3p. Cancer Lett. 2016;371(1): Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, Hanan M, Wyler E, Perez-Hernandez D, Ramberger E, Shenzis S, Samson M, Dittmar G, Landthaler M, Chekulaeva M, Rajewsky N, Kadener S. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell. 2017;66(1): Suzuki H, Tsukahara T. A view of pre-mrna splicing from RNase R resistant RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(6): Li P, Chen H, Chen S, Mo X, Li T, Xiao B, Yu R, Guo J. Circular RNA affects cell growth and migration in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2017;116(5):
8 Chen et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:13 Page 8 of 8 8. Qin M, Liu G, Huo X, Tao X, Sun X, Ge Z, Yang J, Fan J, Liu L, Qin W. Hsa_ circ_ : a circular RNA and potential novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2016;16(1): Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microrna sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384 8.
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating mirna-487a
 Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
CircFAT1 sponges mir-375 to promote the expression of Yes-associated protein 1 in osteosarcoma cells
 Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:170 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0917-7 RESEARCH Open Access CircFAT1 sponges mir-375 to promote the expression of Yes-associated protein 1 in osteosarcoma cells
Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:170 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0917-7 RESEARCH Open Access CircFAT1 sponges mir-375 to promote the expression of Yes-associated protein 1 in osteosarcoma cells
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging mir-424-5p and regulating LATS1 expression
 Zhang et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:151 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0719-3 RESEARCH Open Access Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging mir-424-5p and regulating
Zhang et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:151 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0719-3 RESEARCH Open Access Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging mir-424-5p and regulating
Marta Puerto Plasencia. microrna sponges
 Marta Puerto Plasencia microrna sponges Introduction microrna CircularRNA Publications Conclusions The most well-studied regions in the human genome belong to proteincoding genes. Coding exons are 1.5%
Marta Puerto Plasencia microrna sponges Introduction microrna CircularRNA Publications Conclusions The most well-studied regions in the human genome belong to proteincoding genes. Coding exons are 1.5%
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Original Article Circ-PAX2 promotes proliferation and metastasis by absorbing mir-186 in lung cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3793-3801 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0078547 Original Article Circ-PAX2 promotes proliferation and metastasis by absorbing mir-186 in lung cancer cells Lei Wang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3793-3801 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0078547 Original Article Circ-PAX2 promotes proliferation and metastasis by absorbing mir-186 in lung cancer cells Lei Wang
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
CircPSMC3 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by acting as a competitive endogenous RNA through sponging mir-296-5p
 Rong et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:25 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0958-6 RESEARCH CircPSMC3 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by acting as a competitive endogenous
Rong et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:25 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0958-6 RESEARCH CircPSMC3 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by acting as a competitive endogenous
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
MIR-708 promotes phagocytosis to eradicate T-ALL cells by targeting CD47
 Huang et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:12 DOI 10.1186/s12943-018-0768-2 LETTER TO THE EDITOR MIR-708 promotes phagocytosis to eradicate T-ALL cells by targeting CD47 Wei Huang 1, Wen-Tao Wang 1, Ke Fang
Huang et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:12 DOI 10.1186/s12943-018-0768-2 LETTER TO THE EDITOR MIR-708 promotes phagocytosis to eradicate T-ALL cells by targeting CD47 Wei Huang 1, Wen-Tao Wang 1, Ke Fang
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Negative correlation between mir-375 and its predicted target genes, as demonstrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). 1 The correlation between
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Negative correlation between mir-375 and its predicted target genes, as demonstrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). 1 The correlation between
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
Circular RNA circtada2a promotes osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by sponging mir-203a-3p and regulating CREB3 expression
 Wu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:73 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1007-1 RESEARCH Open Access Circular RNA circtada2a promotes osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by sponging mir-203a-3p and
Wu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:73 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1007-1 RESEARCH Open Access Circular RNA circtada2a promotes osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by sponging mir-203a-3p and
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation
 MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Title: LATS2 is De-methylated and Overexpressed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Predicts Poor Prognosis of the Patients
 Author's response to reviews Title: LATS2 is De-methylated and Overexpressed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Predicts Poor Prognosis of the Patients Authors: Yan Zhang (zhangy2@sysucc.org.cn) Chun-Fang
Author's response to reviews Title: LATS2 is De-methylated and Overexpressed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Predicts Poor Prognosis of the Patients Authors: Yan Zhang (zhangy2@sysucc.org.cn) Chun-Fang
CircMTO1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8203-8209 CircMTO1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer Z. GE,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8203-8209 CircMTO1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer Z. GE,
mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1
 Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Expanded View Figures
 Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
mir-132 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4
 Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung
 Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
LncRNA TUG1 promoted KIAA1199 expression via mir-600 to accelerate cell metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer
 Sun et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:106 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0771-x RESEARCH Open Access LncRNA TUG1 promoted KIAA1199 expression via mir-600 to accelerate
Sun et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:106 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0771-x RESEARCH Open Access LncRNA TUG1 promoted KIAA1199 expression via mir-600 to accelerate
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 1977-1984, 2017 mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9 Hua Liang, Ruoyu Luo, Xiaoqi Chen, Yuzi Zhao and Aili Tan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 1977-1984, 2017 mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9 Hua Liang, Ruoyu Luo, Xiaoqi Chen, Yuzi Zhao and Aili Tan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, MS 39216
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0201 TITLE: Role of long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yin-Yuan Mo CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0201 TITLE: Role of long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yin-Yuan Mo CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson,
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Identification of the tumor suppressive function of circular RNA FOXO3 in non small cell lung cancer through sponging mir 155
 7692 Identification of the tumor suppressive function of circular RNA FOXO3 in non small cell lung cancer through sponging mir 155 YANNI ZHANG 1, HUI ZHAO 2 and LICHUAN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Emergency
7692 Identification of the tumor suppressive function of circular RNA FOXO3 in non small cell lung cancer through sponging mir 155 YANNI ZHANG 1, HUI ZHAO 2 and LICHUAN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Emergency
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Circ_ /PHDLA1 suppresses gastric cancer progression by sponging mir 101 3p.1
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-018-0252-0 Cell & Bioscience RESEARCH Open Access Circ_0027599/PHDLA1 suppresses gastric cancer progression by sponging mir 101 3p.1 Liang Wang *, Jingyan Shen and Yushan
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-018-0252-0 Cell & Bioscience RESEARCH Open Access Circ_0027599/PHDLA1 suppresses gastric cancer progression by sponging mir 101 3p.1 Liang Wang *, Jingyan Shen and Yushan
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
The pro-metastasis effect of circanks1b in breast cancer
 Zeng et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:160 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0914-x RESEARCH Open Access The pro-metastasis effect of circanks1b in breast cancer Kaixuan Zeng 1,2, Bangshun He 1, Burton
Zeng et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:160 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0914-x RESEARCH Open Access The pro-metastasis effect of circanks1b in breast cancer Kaixuan Zeng 1,2, Bangshun He 1, Burton
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Temozolomide suppresses MYC via activation of TAp63 to inhibit progression of human glioblastoma Tomohiro Yamaki, Yusuke Suenaga, Toshihiko Iuchi, Jennifer Alagu, Atsushi Takatori,
Supplementary Information Temozolomide suppresses MYC via activation of TAp63 to inhibit progression of human glioblastoma Tomohiro Yamaki, Yusuke Suenaga, Toshihiko Iuchi, Jennifer Alagu, Atsushi Takatori,
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-1-1-176 TITLE: Suppression of BRCA2 by Mutant Mitochondrial DNA in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hsieh, Jer-Tsong CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Southwestern
AD Award Number: W81XWH-1-1-176 TITLE: Suppression of BRCA2 by Mutant Mitochondrial DNA in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hsieh, Jer-Tsong CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Southwestern
Long non-coding RNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell growth and metastasis in cervical cancer via acting AS a sponge for mir-324-5p
 Jiang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:169 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0846-8 RESEARCH Open Access Long non-coding RNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell growth and metastasis
Jiang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:169 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0846-8 RESEARCH Open Access Long non-coding RNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell growth and metastasis
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by sponging microrna-575 to modulate ST7L expression
 Yan et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:214 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0853-9 RESEARCH Open Access Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation
Yan et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:214 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0853-9 RESEARCH Open Access Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation
LncSNHG14 promotes the development and progression of bladder cancer by targeting mirna-150-5p
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 1022-1029 LncSNHG14 promotes the development and progression of bladder cancer by targeting mirna-150-5p J. LI 1,2, A.-S. WANG 2, S. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 1022-1029 LncSNHG14 promotes the development and progression of bladder cancer by targeting mirna-150-5p J. LI 1,2, A.-S. WANG 2, S. WANG
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL-
 Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
