Original Article CD24 negative lung cancer cells, possessing partial cancer stem cell properties, cannot be considered as cancer stem cells
|
|
|
- Roy Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1): /ISSN: /ajcr Original Article CD24 negative lung cancer cells, possessing partial cancer stem cell properties, cannot be considered as cancer stem cells Haineng Xu 1,2*, Jiasheng Mu 3,4*, Jing Xiao 1*, Xiangsong Wu 3,4, Maolan Li 3,4, Tianrun Liu 5, Xinyuan Liu 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai , China; 2 Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA; 3 Department of General Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, Affiliated to School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai , China; 4 Institute of Biliary Tract Disease, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai , China; 5 Department of Otorinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. * Equal contributors. Received September 27, 2015; Accepted November 24, 2015; Epub December 15, 2015; Published January 1, 2016 Abstract: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) play vital role in lung cancer progression, resistance, metastasis and relapse. Identifying lung CSCs makers for lung CSCs targeting researches are critical for lung cancer therapy. In this study, utilizing previous identified lung CSCs as model, we compared the expression of CD24, CD133 and CD44 between CSCs and non-stem cancer cells. Increased ratio of CD24- cells were found in CSCs. CD24- cells were then sorted by flow cytometry and their proliferative ability, chemo-resistance property and in vivo tumor formation abilities were detected. A549 CD24- cells formed smaller colonies, slower proliferated in comparison to A549 CD24+ cells. Besides, A549 CD24- exhibited stronger resistance to chemotherapy drug. However, A549 CD24- didn t exert any stronger tumor formation ability in vivo, which is the gold standard of CSCs. These results showed that CD24- A549 cells showed some properties of CSCs but not actually CSCs. This study provides evidence that CD24 cannot be considered as lung CSCs marker. Keywords: Lung cancer, cancer stem cells, cancer stem cell marker, biomarker, CD24, CD133, CD44, A549 Introduction Lung cancer is one of the leading cause deathrelated cancers male and female were died due to lung cancer worldwide in Lung cancer ranked the first and second cause of death in male and female respectively in 2008 [1]. The current methods of lung cancer therapy are mostly surgery, chemo-therapy and radio-therapy. However, some of the patients have already got tumors metastasized, making it unresectable. Moreover, lung tumors usually showed resistance to chemo-therapy and radio-therapy [2, 3]. Thus it is urgent to obtain an efficient approach for lung cancer therapy. In the recent years, it is found that a subpopulation cancer cells are more origin of cancer relapse. They also play critical role in cancer progression, metastasis and resistance. This type of cells are called cancer stem cells (CSCs). CSCs was firstly mentioned in 1937 and attracted researchers attention since Dick s finding of lymphoma CD34+CD38- CSCs [4]. Clake et al. isolated the first CSCs, CD44+CD24-/low breast CSCs, in solid tumor. CSCs were then reported in glioma, liver cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer and other cancers [5-10]. Eradiating CSCs will make the tumors loss of their self-renew ability and finally got shrinked [11]. Thus identifying and targeting CSCs is critical important in cancer therapy. For targeting CSCs researches, isolating and identifying CSCs are the premise. Currently, CSCs are majorly isolated by three types of methods: sphere formation, isolation by flow
2 cytometry based on surface markers or isolating side population [9, 12-14]. Of these, surface markers are always the most welcome method for CSCs identification and isolation. It possesses several advantages in comparison with the other methods. It can be used to isolate CSCs, evaluate CSCs targeting efficiency and trace the CSCs in vivo. There are several reports about lung CSCs markers. CD133, CD44, ALDH, side population have ever been reported as lung CSCs markers [6, 15-17]. However, till now, there is no clear lung CSCs marker. There are even some opposite reports about the lung CSCs markers. One reports CD133+ as lung CSCs marker but another one demonstrated it not as lung CSCs marker [6, 18]. Thus it is important to find lung CSCs markers for CSCs targeting. In this study, we used sphere formation assay to accumulated lung CSCs from lung cancer cell line A549 cells. We demonstrated them as CSCs in vitro and in vivo in our previous study [19]. We compared the expression of CD133, CD44 and CD24, three mostly used CSCs markers, between these accumulated CSCs and normally cultured A549 cells. We found dramatically alteration of the ratio of CD24- cells. We further isolated the CD24- cells and tested their CSCs properties in vitro and in vivo. This study used identified lung CSCs for biomarkers search, providing a novel approach for looking for lung CSCs markers. It also provided the information that CD24 is not a lung CSCs marker. Materials and methods Cell culture Lung cancer cell lines, A549, H460, H1299 and colon cancer cells HCT116, HT29 were from Cell Bank of Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). A549 cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS). H460, H1299, HCT116 and HT29 cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS. All the cells were incubated in the humidified atmosphere at 37 C with 5% CO 2. Sphere formation assay To accumulate cancer stem cells, A549, H460 or H1299 cells were trypsined into single cells, washed with PBS. All the cells were cultured in serum free DMEM/F12 (Hyclone Beijing, China) medium with 20 ng/ml EGF (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA), 20 ng/ml bfgf (PeproTech) and 20 ng/ml IGF1 (PeproTech). All the cells were split into ultralow attachment 6-well dishes (Corning). Growth factors EGF, bfgf, IGF1 (20 ng/ml) were added every day. The cells were collected three days later for further experiments. For secondary spheroid bodies formation, the A549 spheres were trypsined into single cells and split into ultralow attachment 6-well dishes with the same culture medium described above. Flow cytometry Regular cultured cancer cells or cells cultured in sphere status were trypsined into single cells, stained with PE conjugated CD24 antibody (Miltenyi, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) or FITC conjugated CD44 antibody (Biolegend) in 0.1% BSA/PBS for 30 min at 4 C, then subjected to flow cytometry for expression detection. For CD133 staining, A549 cells, A549 sphere cells, HCT116 or HT29 cells were stained with mouse anti-cd133 (Miltenyi) antibody for 30 min, then stained with FITC conjugated goat anti-mouse (Jackson ImmunoResearch) for 30 min and subjected to flow cytometry for analysis. Fluorescence activated cell sorting A549 or H460 cells were stained with PE conjugated CD24 antibody (Miltenyi) for 30 min, washed with PBS and subjected to Aria II (BD Biosciences) for cell sorting. CD24+ and CD24- cells were collected for further experiments. Chemo-resistance and cell proliferation detection CD24+ and CD24- cells from A549 cells were sorted by Flow cytometry. The cells were split into 96 well dishes at cells/well and treated with 5-FU at 0, 1, 10, 50, 200 µg/ml for 48 hrs. Cell viability were then detected by MTT assay describe previously [19]. Colony formation assay The A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells were split into 6-well dishes at cells/well. 8 days later, the colonies were observed under micro- 52 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
3 Figure 1. CD24- cells enriched in A549 sphere cells. A. Morphology of A549 cells and A549 sphere cells. Scale bar: 200 µm. B. CD44 expression detection in A549 and A549 sphere cells. A549 and A549 sphere cells without CD44 staining were used as negative control. C. CD133 expression detection in A549 and A549 sphere cells. A549 and A549 sphere cells without CD133 staining were used as negative control. HT29 and HCT116 stained with CD133 were used as positive control. D. CD24 expression detection in A549 and A549 sphere cells. A549 and A549 sphere cells without CD24 staining were used as negative control. 53 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
4 Figure 2. Chemo-drug accumulated CD24- A549 cells. A. Morphology of H460 cells and H460 sphere cells, H1299 cells and H1299 sphere cells. B. CD24 expression detection in H1299 and H1299 sphere cells. H1299 and H1299 sphere cells without CD24 staining were used as negative control. C. CD24 expression detection in H460 and H460 sphere cells. H460 and H460 sphere cells without CD24 staining were used as negative control. D. CD24 expression detection in A549 cells, cisplatin treated A549 cells and 5-FU treated A549 cells. Cisplatin: 50 µg/ml, 5-FU: 100 µg/ml. Cells without CD24 staining were used as negative control. scope and been taken pictures. Stained the cells with 2% crystal violet in 20% methanol for 1 hour, washed with water, photographed them after they are dry. 54 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
5 Figure 3. CD24- A549 cells proliferated slower and showed chemoresistance. A. Isolating CD24+ and CD24- A549 cells by fluorescence activated cell sorting. B. Morphology of formed colonies by CD24+ and CD24- A549 cells. Photos were taken 8 days post culture. C. Colony formation of CD24+ and CD24- A549 cells. Colonies were stained with crystal violet 8 days post culture. D. Proliferation curve of A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells. Cells were split in 96 well dishes at cells/well. ***means P< E. Chemo-sensitivity of A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells. Cells were treated with indicated doses of 5-FU for 48 hrs. **means P<0.01. Animal experiments All the animal experiments were conducted according to the U.S. Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and the Use of Laboratory Animals. All are approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Four-week old female BALB/c nude mice were purchased from SLAC (Shanghai, China) and raised in the SPF animal facilities. 55 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
6 Table 1. A549 CD24+, CD24- occurrence time in nude mice Occurence Latency A549 CD24+ 3/3 13, 16, 28 A549 CD24-3/3 13, 13, A549 CD24+ 3/3 13, 16, 21 A549 CD24-3/3 13, 16, A549 CD24+ 3/3 28, 28, 28 A549 CD24-3/3 28, 34, A549 CD24+ 3/3 34, 34, 34 A549 CD24-2/3 34, 51 For A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells tumor formation, cells were mixed with Matrigel at 8:5 and subcutaneous injected into rear parts of mice. A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells were injected at the right and left parts respectively , , , cells per side of mouse were injected. The tumor occurrence was observed twice every week since injection. The tumor size was measured at the end of the experiment. The volume of tumor was calculated as length width width/2. For NOD/SCID mice experiments, or A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells were subcutaneously injected into the mice similarly as nude mice. For H460 CD24+ and CD24- cells tumor formation, cells were mixed with Matrigel 2:1 and injected at the right or left rear parts of nude mice , , , cells were injected respectively. The tumor size was measured twice every week. Statistical analysis All the data in the manuscript were analyzed by Student s t.test with R software. P<0.05 is considered as significant difference between two groups. Results CD24- cells enriched in A549 sphere cells To obtain lung cancer stem cells (CSCs), we cultured A549 cells in serum free medium with growth factors to form spheroid bodies (Figure 1A). The A549 sphere cells were demonstrated as CSCs in our previous study [19]. A549 spheres formed at day 3, day 7 and day 14 showed similar morphology. The A549 sphere cell was able to be passaged and formed similar secondary spheroid bodies (Supplementary Figure 1). To look for the lung CSCs markers, we detected the expression CD44, CD133 and CD24 in A549 sphere cells and A549 cells. These three surface proteins are reported CSCs markers in other cancers. Both of A549 sphere cells and A549 cells showed almost CD44+ and CD133-. No alteration on CD44 or CD133 expression was found in A549 sphere cells in comparing to A549 cells. HCT116 and HT29 cells were used as positive control of CD133 staining (Figure 1B and 1C). In CD24 expression detection, in comparison to normally cultured A549 cells, A549 sphere cells showed dramatically increased proportion of CD24- cells (Figure 1D). To confirm the increase of CD24- cells in spheroid bodies, we cultured other two lung cancer cell lines, H460 and H1299, in serum free medium. They formed good spheres (Figure 2A). In H460 cells, proportion of CD24- cells increased from 53.5% to 94.4% after formed spheres. H1299 were originally almost CD24- cells at regular culture medium and kept at high level of CD24- cells in H1299 spheres (Figure 2B). These demonstrated that lung CSCs possess more CD24- cells. Chemotherapy drugs accumulated CD24- A549 cells Previous studies reported that chemo-drugs or radiation could accumulate the CSCs. To further confirm the accumulation of CD24- cells in lung CSCs, we treated the A549 cells with chemotherapy drugs, 5-FU or cisplatin. Both 5-FU and cisplatin treatment increased CD24- subpopulation cells in A549 cells (Figure 2C). CD24- A549 cells proliferated slower and showed chemoresistance To test whether the CD24- cells are lung CSCs, we sorted the CD24- cells by flow cytometry (Figure 3A). In sorted A549 cells, CD24- cells formed smaller colonies (Figure 3B and 3C). They proliferated much slower than CD24+ cells (Figure 3D). This indicated that the CD24- cells are more quiescent. A549 CD24- cells showed stronger drug resistance to 5-FU treatment further supported they are more quiescent (Figure 3E). Quiescence is a critical prop- 56 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
7 Figure 4. A549 CD24- cells didn t show enhanced in vivo tumor formation ability. (A) Volume of A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells formed tumors in nude mice. Seeded cells: cells, cells, cells or cells. (B) Morphology of A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells formed tumors in nude mice. Left: CD24- cells, Right: CD24+ cells. Seeded cells: cells or cells. (C) Correspondent tumors isolated from nude mice in (B). Upper: cells, lower: cells. (D) Weight of A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells formed tumors in nude mice. (E) Volume of A549 CD24+ and CD24- cells formed tumors in NOD/SCID mice. Seeded cells: cells, cells. (F) Volume of H460 CD24+ and CD24- cells formed tumors in nude mice. erty of CSCs. This suggested A549 CD24- cells possess CSCs properties in vitro. A549 CD24- cells didn t show enhanced in vivo tumor formation ability To further test the CSCs properties of A549 CD24- cells, we compared the tumor formation ability of A549 CD24- cells and A549 CD24+ cells in vivo. Stronger tumor formation ability is the gold standard of CSCs. We isolate CD24+ and CD24- cells from A549 cells and injected into the right or left part of nude mice. A549 CD24- cells showed similar tumor occurrence time, but not shorter, in comparison with A549 CD24+ cells (Table 1). A549 CD24- cells even 57 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
8 Table 2. H460 CD24+, CD24- occurrence time in nude mice Occurence Latency H460 CD24+ 3/3 6, 6, 13 H460 CD24-3/3 6, 6, H460 CD24+ 3/3 13, 13, 13 H460 CD24-3/3 13, 13, H460 CD24+ 3/3 18, 18, 18 H460 CD24-3/3 13, 18, H460 CD24+ 3/3 25, 31, 31 H460 CD24-3/3 21, 25, 31 grew smaller tumors than the A549 CD24+ cells at the end of the experiment (Figure 4A-C). Weight of the tumors formed by A549 CD24- cells are also smaller than those formed by A549 CD24+ cells (Figure 4D). NOD/SCID mice are a better model for CSCs tumor formation detection. Subcutaneous injection of A549 CD24+ cells and CD24- cells into NOD/SCID mice also showed that A549 CD24- cells formed smaller tumors (Figure 4E). To further test the tumor formation abilty of CD24- cells, CD24- cells and CD24+ cells from H460 cells were isolated and injected into the nude mice. CD24- cells showed weaker (1 10 5, ), similar ( ) or stronger ( ) tumor formation ability in comparison to CD24+ cells (Figure 4F). No difference in the tumor occurrence time was found (Table 2). All of these results suggested that CD24- cells in A549 cells or H460 cells didn t show any stronger tumor formation ability than CD24+ cells. Discussion Lung cancer is one of the leading cause of death in cancer worldwide. Lung cancer stem cells (CSCs) play vital role in cancer progression, relapse, chemo- and radio-therapy resistance, making it urgent to develop a novel drug to target lung CSCs. Currently, cancer stem cells are majorly be targeted on self-renew pathway, anti-apoptotic proteins, or by oncolytic viruses lysis and small molecular drug screen [20-22]. Developing drugs targeting Notch, Wnt, Akt, hedgehog and other self-renew related pathways showed potently anti-cscs ability [21, 23, 24]. Oncolytic viruses with therapeutic genes showed dramatically anti-cscs ability. Small molecule screen or RNAi screen got efficient drugs to target CSCs and found important genes in CSCs [22, 25]. No matter what kind of methods used for CSCs targeting researches, isolating CSCs is the premise. Accumulating CSCs by sphere formation, side population isolation and flow cytometry sorting based on the surface markers are three majors approaches to obtain CSCs. For in vitro cell lines experiments, sphere formation and side population assays are absolutely qualified. However, for cells from patients tissues or in vivo tracking of CSCs, cell surface markers isolation is the most convenient method. Therefore, investigating the surface markers of CSCs is quite important for lung CSCs mechanism studies and targeting therapies. Several cell surface markers, like CD133, CD44, have ever been reported as lung CSCs markers. ALDH, side population were also reported as lung CSCs biomarkers. However, due to difference of patients samples and difference in cell lines, lung CSCs don t have any well recognized surface markers. Even in some reports, the results are not consistent. In 2009, CD133+ cells were found in lung cancer patients. These populations were decreased when cells were cultured in vitro. Cisplatin treatment could increase the accumulation of CD133+ cells. CD133+ cells were considered as lung CSCs [6]. However, another study published in 2009 as well showed that CD133+ and CD133- cells in lung cancer cell lines A549, H446 cells both possess CSCs populations [18]. To identify the lung CSCs markers, we utilized lung cancer cell lines, A549, H460 and HT29 as models. A549 cells formed spheres in serum free medium with growth factors. A549 sphere were demonstrated as CSCs in our previous published paper [19]. We compared the expression panel of A549 sphere cells and A549 cells. Most famous CSCs markers in other cancers, CD133, CD44, CD24, were tested in the cells. Robust alteration of CD24- population was observed in A549 sphere cells (Figure 1). This increase was also found in other lung cancer cell lines (Figure 2). Chemo-therapy drugs also could increase this population (Figure 2). To further elucidate whether CD24 is the marker of lung CSCs, CD24- and CD24+ cells were isolated. The CSCs properties in these cells were 58 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
9 compared in vitro and in vivo. A549 CD24- cells showed slower proliferative rate and enhanced chemo-resistance (Figure 3), and these are the characters of CSCs. However, A549 CD24- cells didn t show enhanced tumor formation ability (Figure 4), which is the gold standard of CSCs. H460 CD24- cells also showed no greater tumor generation ability than CD24+ cells. These suggested that CD24 is not a lung CSCs marker. In our study, we utilized identified CSCs for lung CSCs surface markers identification. This can help to improve the efficiency of looking for the CSCs markers. Further high throughput surface markers screen may help to get the different expression panel of identified CSCs and nonstem cancer cells. In our work, CD24- cells were found accumulated in identified lung CSCs, possess some properties of CSCs, but actually are not CSCs. These suggest that, in the identification of CSCs marker, we need take advantages of several methods to identify CSCs markers to make sure its accuracy. This study provided that CD24 is not a lung CSCs marker, and should not be used for lung CSCs isolation or identification in the future. Acknowledgements We thank the staff at Cell Center of Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology for their assistance in the experiments. This study was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2010CB529901, 2011CB510100). Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Haineng Xu, State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 320 Yue-Yang Road, Shanghai , China. xuhaineng123@163.com; Dr. Tianrun Liu, Department of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, The Sixth Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou , China. dortianr@163.com; Dr. Xinyuan Liu, State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Institute of Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 320 Yue- Yang Road, Shanghai, , China. xyliu@ sibcb.ac.cn References [1] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E and Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: [2] Baik CS, Chamberlain MC and Chow LQ. Targeted Therapy for Brain Metastases in EGFR- Mutated and ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2015; 10: [3] Chan BA and Hughes BG. Targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: current standards and the promise of the future. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2015; 4: [4] Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med 1997; 7: 8. [5] Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, Morrison SJ and Clarke MF. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100: [6] Bertolini G, Roz L, Perego P, Tortoreto M, Fontanella E, Gatti L, Pratesi G, Fabbri A, Andriani F, Tinelli S, Roz E, Caserini R, Lo Vullo S, Camerini T, Mariani L, Delia D, Calabro E, Pastorino U and Sozzi G. Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: [7] Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ and Maitland NJ. Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: [8] Lee TK, Castilho A, Cheung VC, Tang KH, Ma S and Ng IO. CD24(+) liver tumor-initiating cells drive self-renewal and tumor initiation through STAT3-mediated NANOG regulation. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 9: [9] Qiang L, Yang Y, Ma YJ, Chen FH, Zhang LB, Liu W, Qi Q, Lu N, Tao L, Wang XT, You QD and Guo QL. Isolation and characterization of cancer stem like cells in human glioblastoma cell lines. Cancer Lett 2009; 279: [10] Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E, Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007; 445: [11] Dalerba P, Cho RW and Clarke MF. Cancer stem cells: models and concepts. Annu Rev Med 2007; 58: [12] Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 2003; 63: [13] Fukuda K, Saikawa Y, Ohashi M, Kumagai K, Kitajima M, Okano H, Matsuzaki Y and Kitagawa Y. Tumor initiating potential of side popula- 59 Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
10 tion cells in human gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 2009; 34: [14] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS, Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y and Wang TC. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells 2009; 27: [15] Ho MM, Ng AV, Lam S and Hung JY. Side population in human lung cancer cell lines and tumors is enriched with stem-like cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: [16] Roudi R, Madjd Z, Korourian A, Mehrazma M, Molanae S, Sabet MN and Shariftabrizi A. Clinical significance of putative cancer stem cell marker CD44 in different histological subtypes of lung cancer. Cancer Biomark 2014; 14: [17] Shao C, Sullivan JP, Girard L, Augustyn A, Yenerall P, Rodriguez-Canales J, Liu H, Behrens C, Shay JW, Wistuba II and Minna JD. Essential role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3 for the maintenance of non-small cell lung cancer stem cells is associated with the STAT3 pathway. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: [18] Meng X, Li M, Wang X, Wang Y and Ma D. Both CD133+ and CD133- subpopulations of A549 and H446 cells contain cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Sci 2009; 100: [19] Yang Y, Xu H, Huang W, Ding M, Xiao J, Yang D, Li H, Liu XY and Chu L. Targeting lung cancer stem-like cells with TRAIL gene armed oncolytic adenovirus. J Cell Mol Med 2015; 19: [20] Jiang H, Gomez-Manzano C, Aoki H, Alonso MM, Kondo S, McCormick F, Xu J, Kondo Y, Bekele BN, Colman H, Lang FF and Fueyo J. Examination of the therapeutic potential of Delta-24-RGD in brain tumor stem cells: role of autophagic cell death. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007; 99: [21] Purow B. Notch inhibition as a promising new approach to cancer therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012; 727: [22] Sachlos E, Risueno RM, Laronde S, Shapovalova Z, Lee JH, Russell J, Malig M, McNicol JD, Fiebig-Comyn A, Graham M, Levadoux-Martin M, Lee JB, Giacomelli AO, Hassell JA, Fischer- Russell D, Trus MR, Foley R, Leber B, Xenocostas A, Brown ED, Collins TJ and Bhatia M. Identification of drugs including a dopamine receptor antagonist that selectively target cancer stem cells. Cell 2012; 149: [23] Korkaya H, Paulson A, Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Brown M, Dutcher J, Clouthier SG and Wicha MS. Regulation of mammary stem/progenitor cells by PTEN/Akt/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e [24] Rudin CM, Hann CL, Laterra J, Yauch RL, Callahan CA, Fu L, Holcomb T, Stinson J, Gould SE, Coleman B, LoRusso PM, Von Hoff DD, de Sauvage FJ and Low JA. Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC N Engl J Med 2009; 361: [25] Goidts V, Bageritz J, Puccio L, Nakata S, Zapatka M, Barbus S, Toedt G, Campos B, Korshunov A, Momma S, Van Schaftingen E, Reifenberger G, Herold-Mende C, Lichter P and Radlwimmer B. RNAi screening in glioma stemlike cells identifies PFKFB4 as a key molecule important for cancer cell survival. Oncogene 2012; 31: Am J Cancer Res 2016;6(1):51-60
11 Supplementary Figure 1. Morphology of A549 spheres cultured for indicated days. From left to right: 3 days, 7 days, 14 days. The last one are the secondary spheres cultured for 3 days. 1
Research Article Targeting Lung Cancer Stem Cells with Antipsychological Drug Thioridazine
 BioMed Research International Volume 216, Article ID 679828, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/679828 Research Article Targeting Lung Cancer Stem Cells with Antipsychological Drug Thioridazine Haiying
BioMed Research International Volume 216, Article ID 679828, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/679828 Research Article Targeting Lung Cancer Stem Cells with Antipsychological Drug Thioridazine Haiying
Targeting colon cancer stem cells with novel blood cholesterol drug pitavastatin
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 1226-1233 Targeting colon cancer stem cells with novel blood cholesterol drug pitavastatin Z.-Y. ZHANG 1, S.-H. ZHENG 2, W.-G. YANG 3,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 1226-1233 Targeting colon cancer stem cells with novel blood cholesterol drug pitavastatin Z.-Y. ZHANG 1, S.-H. ZHENG 2, W.-G. YANG 3,
A subpopulation of CD24 + cells in colon cancer cell lines possess stem cell characteristics
 282 Neoplasma 59, 3, 2012 doi:10.4149/neo_2012_036 A subpopulation of CD24 + cells in colon cancer cell lines possess stem cell characteristics J. KE, X. WU, X. WU, X. HE, L. LIAN, Y. ZOU, X. HE, H. WANG,
282 Neoplasma 59, 3, 2012 doi:10.4149/neo_2012_036 A subpopulation of CD24 + cells in colon cancer cell lines possess stem cell characteristics J. KE, X. WU, X. WU, X. HE, L. LIAN, Y. ZOU, X. HE, H. WANG,
Material and Methods. Flow Cytometry Analyses:
 Material and Methods Flow Cytometry Analyses: Immunostaining of breast cancer cells for HER2 was performed by incubating cells with anti- HER2/neu APC (Biosciences, Cat# 340554), anti-her2/neu PE (Biosciences,
Material and Methods Flow Cytometry Analyses: Immunostaining of breast cancer cells for HER2 was performed by incubating cells with anti- HER2/neu APC (Biosciences, Cat# 340554), anti-her2/neu PE (Biosciences,
PRODUCTS FOR CANCER RESEARCH
 PRODUCTS FOR CANCER RESEARCH TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 6 10 11 12 Introduction ALDEFLUOR A Powerful Tool to Study Cancer Stem Cells Culture Media for Cancer Research Culture Media Products for Breast Cancer
PRODUCTS FOR CANCER RESEARCH TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 6 10 11 12 Introduction ALDEFLUOR A Powerful Tool to Study Cancer Stem Cells Culture Media for Cancer Research Culture Media Products for Breast Cancer
TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
 Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Original Article Study on like-stem characteristics of tumor sphere cells in human gastric cancer line HGC-27
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19717-19724 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012612 Original Article Study on like-stem characteristics of tumor sphere cells in human gastric cancer line HGC-27 Wei-Hong
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19717-19724 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012612 Original Article Study on like-stem characteristics of tumor sphere cells in human gastric cancer line HGC-27 Wei-Hong
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
A modified method by differential adhesion for enrichment of bladder cancer stem cells
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (4): 817-824, July - August, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0409 A modified method by differential adhesion for enrichment of bladder cancer stem cells Yong-tong Zhu 1,2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (4): 817-824, July - August, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0409 A modified method by differential adhesion for enrichment of bladder cancer stem cells Yong-tong Zhu 1,2,
Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery & VP Integrated Health Services University of Saskatchewan & Saskatoon Health Region
 Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Effects of curcumin on stem-like cells in human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines
 Almanaa et al. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012, 12:195 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effects of curcumin on stem-like cells in human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines Taghreed N Almanaa
Almanaa et al. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012, 12:195 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effects of curcumin on stem-like cells in human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines Taghreed N Almanaa
Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT
 Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Getting to the root of Cancer
 Cancer Stem Cells: Getting to the root of Cancer Dominique Bonnet, Ph.D Senior Group Leader, Haematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute Venice, Sept 2009 Overview
Cancer Stem Cells: Getting to the root of Cancer Dominique Bonnet, Ph.D Senior Group Leader, Haematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute Venice, Sept 2009 Overview
Dopamine receptor D2 is correlated with gastric cancer prognosis
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 13: 1223-1227, 2017 Dopamine receptor D2 is correlated with gastric cancer prognosis JIASHENG MU 1,2*, WEIDAN HUANG 3*, ZHUJUN TAN 1,2, MAOLAN LI 1,2, LIN ZHANG 1,2, QICHEN DING 1,2, XIANGSONG
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 13: 1223-1227, 2017 Dopamine receptor D2 is correlated with gastric cancer prognosis JIASHENG MU 1,2*, WEIDAN HUANG 3*, ZHUJUN TAN 1,2, MAOLAN LI 1,2, LIN ZHANG 1,2, QICHEN DING 1,2, XIANGSONG
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0618 TITLE: Are Breast Tumor Stem Cells Responsible for Metastasis and Angiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Quintin Pan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0618 TITLE: Are Breast Tumor Stem Cells Responsible for Metastasis and Angiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Quintin Pan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant molecular mechanism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Cancer Stem Cells: A Step Toward the Cure
 VOLUME 26 NUMBER 17 JUNE 10 2008 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O V E R V I E W Cancer Stem Cells: A Step Toward the Cure Bruce M. Boman, Helen F. Graham Cancer Center, Newark, DE; Thomas Jefferson University,
VOLUME 26 NUMBER 17 JUNE 10 2008 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O V E R V I E W Cancer Stem Cells: A Step Toward the Cure Bruce M. Boman, Helen F. Graham Cancer Center, Newark, DE; Thomas Jefferson University,
Head and neck cancer is a common malignancy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SINGLE-MARKER IDENTIFICATION OF HEAD AND NECK SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA CANCER STEM CELLS WITH ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE Matthew R. Clay, BSc, 1 Mark Tabor, MD, 2 John Henry Owen, BSc, 3 Thomas
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SINGLE-MARKER IDENTIFICATION OF HEAD AND NECK SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA CANCER STEM CELLS WITH ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE Matthew R. Clay, BSc, 1 Mark Tabor, MD, 2 John Henry Owen, BSc, 3 Thomas
Autophagy regulates chemoresistance of gastric cancer stem cells via the Notch signaling pathway
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3402-3407 Autophagy regulates chemoresistance of gastric cancer stem cells via the Notch signaling pathway L.-Q. LI, D. PAN, S.-W. ZHANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3402-3407 Autophagy regulates chemoresistance of gastric cancer stem cells via the Notch signaling pathway L.-Q. LI, D. PAN, S.-W. ZHANG,
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0337 TITLE: Molecular Innovations Toward Theranostics of Aggressive Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hsieh, Jer-Tsong CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Southwestern
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0337 TITLE: Molecular Innovations Toward Theranostics of Aggressive Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hsieh, Jer-Tsong CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Southwestern
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
5-hydroxymethylcytosine loss is associated with poor prognosis for
 5-hydroxymethylcytosine loss is associated with poor prognosis for patients with WHO grade II diffuse astrocytomas Feng Zhang 1,*, Yifan Liu 2, Zhiwen Zhang 1, Jie Li 1, Yi Wan 3, Liying Zhang 1, Yangmei
5-hydroxymethylcytosine loss is associated with poor prognosis for patients with WHO grade II diffuse astrocytomas Feng Zhang 1,*, Yifan Liu 2, Zhiwen Zhang 1, Jie Li 1, Yi Wan 3, Liying Zhang 1, Yangmei
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs)
 GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma
 CSU ID: 2558414 Name: Sonal Patel Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma Cancer is one of the most common disease in the US with more than a million people affected every
CSU ID: 2558414 Name: Sonal Patel Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma Cancer is one of the most common disease in the US with more than a million people affected every
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT
 CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Department of General Surgery, The Third People s Hospital of Dalian, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China,
 JBUON 2018; 23(2): 340-345 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Boswellic acid exerts potent anticancer effects in HCT-116 human colon
JBUON 2018; 23(2): 340-345 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Boswellic acid exerts potent anticancer effects in HCT-116 human colon
Significance of CD133 as a cancer stem cell markers focusing on the tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer cell lines
 J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:263-270 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.4.263 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Significance of CD133 as a
J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:263-270 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.4.263 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Significance of CD133 as a
Stem cells and Cancer. John Glod. December 2, 2009
 Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Clinical significance of stem cell marker CD133 expression in colorectal cancer
 Histol Histopathol (2016) 31: 299-306 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology From Cell Biology to Tissue Engineering Clinical significance of stem cell marker CD133 expression in colorectal cancer
Histol Histopathol (2016) 31: 299-306 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology From Cell Biology to Tissue Engineering Clinical significance of stem cell marker CD133 expression in colorectal cancer
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
Jung Sun Lee 1, Woo Gyeong Kim 2. Introduction
 Case Report Page 1 of 5 Cutaneous metastases of breast cancer during adjuvant chemotherapy correlates with increasing CD44 + /CD24 and ALDH-1 expression: a case report and literature review Jung Sun Lee
Case Report Page 1 of 5 Cutaneous metastases of breast cancer during adjuvant chemotherapy correlates with increasing CD44 + /CD24 and ALDH-1 expression: a case report and literature review Jung Sun Lee
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information. Targeting BRK-positive Breast Cancer with Small
 Supplementary Information Targeting BRK-positive Breast Cancer with Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Jie Jiang 1#, Fu Gui 1#, Zhixiang He 1#, Li Li 1, Yunzhan Li 1, Shunying Li 2, Xinrui Wu 1, Zhou Deng
Supplementary Information Targeting BRK-positive Breast Cancer with Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Jie Jiang 1#, Fu Gui 1#, Zhixiang He 1#, Li Li 1, Yunzhan Li 1, Shunying Li 2, Xinrui Wu 1, Zhou Deng
LGR5 is required for the maintenance of spheroid-derived colon cancer stem cells
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: 35-42, 2014 LGR5 is required for the maintenance of spheroid-derived colon cancer stem cells XIANG CHEN 1*, BO WEI 1*, XIAOYAN HAN 2*, ZONGHENG ZHENG 1,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: 35-42, 2014 LGR5 is required for the maintenance of spheroid-derived colon cancer stem cells XIANG CHEN 1*, BO WEI 1*, XIAOYAN HAN 2*, ZONGHENG ZHENG 1,
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression correlates with the invasion of breast cancer
 Pan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2015) 10:66 DOI 10.1186/s13000-015-0301-5 RESEARCH Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression correlates with the invasion of breast cancer Open Access Hong Pan 1, Naping Wu 1,2,
Pan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2015) 10:66 DOI 10.1186/s13000-015-0301-5 RESEARCH Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression correlates with the invasion of breast cancer Open Access Hong Pan 1, Naping Wu 1,2,
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Enrichment of colorectal cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via CDH1 knockdown
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 6: 507-512, 2012 Enrichment of colorectal cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via CDH1 knockdown JUN YE *, DANG WU *, JINWEN SHEN, PIN WU, CHAO NI, JING
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 6: 507-512, 2012 Enrichment of colorectal cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via CDH1 knockdown JUN YE *, DANG WU *, JINWEN SHEN, PIN WU, CHAO NI, JING
Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Systemic Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 with PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Systemic Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 with PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles for
CD44 AND CD24 CANNOT ACT AS CANCER STEM CELL MARKERS IN HUMAN LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA CELL LINE A549
 CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received: 02 June 2013 Volume 19 (2014) pp 23-36 Final form accepted: 13 December 2013 DOI: 10.2478/s11658-013-0112-1 Published online: December
CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received: 02 June 2013 Volume 19 (2014) pp 23-36 Final form accepted: 13 December 2013 DOI: 10.2478/s11658-013-0112-1 Published online: December
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Effect of lncrna LET on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1609-1614 Effect of lncrna LET on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells G. KONG 1, X.-J. QI 2, J.-F. WANG 3 1 Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1609-1614 Effect of lncrna LET on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells G. KONG 1, X.-J. QI 2, J.-F. WANG 3 1 Department of
Concise Review: Emerging Concepts in Clinical Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells
 CANCER STEM CELLS Concise Review: Emerging Concepts in Clinical Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells ZESHAAN A. RASHEED, a JEANNE KOWALSKI, b B. DOUGLAS SMITH, a WILLIAM MATSUI a a The Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive
CANCER STEM CELLS Concise Review: Emerging Concepts in Clinical Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells ZESHAAN A. RASHEED, a JEANNE KOWALSKI, b B. DOUGLAS SMITH, a WILLIAM MATSUI a a The Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive
Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1: A specific cancer stem cell marker for human colorectal carcinoma
 3894 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 3894-3899, 2015 Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1: A specific cancer stem cell marker for human colorectal carcinoma FEI ZHOU 1, YIN DONG MU 2, JUN LIANG 2, ZHI XIN LIU 2, DAN
3894 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 3894-3899, 2015 Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1: A specific cancer stem cell marker for human colorectal carcinoma FEI ZHOU 1, YIN DONG MU 2, JUN LIANG 2, ZHI XIN LIU 2, DAN
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
St. Gallen 2011 Symposium Highlights in China
 May 2011 Shanghai St. Gallen 2011 Symposium Highlights in China Chang Hai Hospital of Shanghai Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center Guangzhou Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Beijing 307 Hospital
May 2011 Shanghai St. Gallen 2011 Symposium Highlights in China Chang Hai Hospital of Shanghai Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center Guangzhou Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Beijing 307 Hospital
The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells
 The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells Yi Liu, Lunhui Zhang, Liang Xu * ABSTRACT This paper aims at analyzing the
The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells Yi Liu, Lunhui Zhang, Liang Xu * ABSTRACT This paper aims at analyzing the
Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Antiestrogen Resistance. Creighton University Omaha, NE
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0497 TITLE: Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Antiestrogen Resistance PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhaoyi Wang, Ph.D. Hao Deng, Ph.D. XinTian Zhang, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Creighton
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0497 TITLE: Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Antiestrogen Resistance PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhaoyi Wang, Ph.D. Hao Deng, Ph.D. XinTian Zhang, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Creighton
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Ginsenoside-Rh2 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Side Population Cells
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ginsenoside-Rh2 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Side Population Cells Jun Qian 1& *, Jing Li 1&, Jian-Guang Jia 1, Xin Jin 1, Da-Jun Yu 1,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Ginsenoside-Rh2 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Side Population Cells Jun Qian 1& *, Jing Li 1&, Jian-Guang Jia 1, Xin Jin 1, Da-Jun Yu 1,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Clinical Development for Patients with Cancer
 OMP 59R5: a Novel Therapeutic Antibody in Clinical Development for Patients with Cancer Jakob Dupont, MD, MA Chief Medical Officer and Senior Vice President OncoMed Pharmaceuticals Inc. Adjunct Clinical
OMP 59R5: a Novel Therapeutic Antibody in Clinical Development for Patients with Cancer Jakob Dupont, MD, MA Chief Medical Officer and Senior Vice President OncoMed Pharmaceuticals Inc. Adjunct Clinical
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber
 Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354480, 354481 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200 (U.S.) CLSTechServ@Corning.com www.corning.com/lifesciences
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354480, 354481 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200 (U.S.) CLSTechServ@Corning.com www.corning.com/lifesciences
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells
 Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
The Cancer Stem Cell Concept in Progression of Head and Neck Cancer
 The Cancer Stem Cell Concept in Progression of Head and Neck Cancer Georgia Chen, Emory University Journal Title: Journal of Oncology Volume: Volume 2009, Number 2009 Publisher: 2009-12-03, Pages 1-8 Type
The Cancer Stem Cell Concept in Progression of Head and Neck Cancer Georgia Chen, Emory University Journal Title: Journal of Oncology Volume: Volume 2009, Number 2009 Publisher: 2009-12-03, Pages 1-8 Type
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or
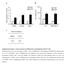 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Original Article TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma cells
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):4951-4958 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002516 Original Article TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):4951-4958 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002516 Original Article TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth
 210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
Isolation and characterization of CD133+ cell population within human primary and metastatic colon cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2009; 13(Suppl 1): 55-62 Isolation and characterization of CD133+ cell population within human primary and metastatic colon cancer M.A. PUGLISI
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2009; 13(Suppl 1): 55-62 Isolation and characterization of CD133+ cell population within human primary and metastatic colon cancer M.A. PUGLISI
IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF CANCER STEM CELLS IN PRIMARY COLORECTAL CANCER MODELS
 IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF CANCER STEM CELLS IN PRIMARY COLORECTAL CANCER MODELS An Internship Report Presented to the Faculty of the Biology Program California State University Channel Islands
IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF CANCER STEM CELLS IN PRIMARY COLORECTAL CANCER MODELS An Internship Report Presented to the Faculty of the Biology Program California State University Channel Islands
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Expression of programmed death ligand-1 on tumor cells varies pre and post
 Expression of programmed death ligand-1 on tumor cells varies pre and post chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Jin Sheng 1,2,3,*, Wenfeng Fang 1,2,3,*, Juan Yu 3, Yunpeng Yang 1,2,3, Yuxiang Ma
Expression of programmed death ligand-1 on tumor cells varies pre and post chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Jin Sheng 1,2,3,*, Wenfeng Fang 1,2,3,*, Juan Yu 3, Yunpeng Yang 1,2,3, Yuxiang Ma
The Side Population in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line NCI-H460 Is Enriched in Stem-Like Cancer Cells
 The Side Population in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line NCI-H460 Is Enriched in Stem-Like Cancer Cells Yang Shi 1, Xuelian Fu 1, Yong Hua 2, Yang Han 1, Ying Lu 2, Junchen Wang 1,3 * 1 Department of Pathology,
The Side Population in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line NCI-H460 Is Enriched in Stem-Like Cancer Cells Yang Shi 1, Xuelian Fu 1, Yong Hua 2, Yang Han 1, Ying Lu 2, Junchen Wang 1,3 * 1 Department of Pathology,
A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor for treating lung cancer
 698358TUB1.1177/11428317698358Tumor BiologyXia et al. research-article217 Original Article A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor for treating lung cancer Tumor Biology April 217: 1 5 The Author(s)
698358TUB1.1177/11428317698358Tumor BiologyXia et al. research-article217 Original Article A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor for treating lung cancer Tumor Biology April 217: 1 5 The Author(s)
LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and predicts poor survival of glioma patients
 Zhang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:225 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0864-6 RESEARCH Open Access LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT
Zhang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:225 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0864-6 RESEARCH Open Access LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT
Backgrounder. 1. What are targeted therapies? 2. How do targeted therapies work?
 Backgrounder TARGETED THERAPIES FOR CANCER 1. What are targeted therapies? 2. How do targeted therapies work? 3. What are some of the different types of targeted therapy? 4. What are the potential benefits
Backgrounder TARGETED THERAPIES FOR CANCER 1. What are targeted therapies? 2. How do targeted therapies work? 3. What are some of the different types of targeted therapy? 4. What are the potential benefits
A NOVEL CANCER STEM CELL (CSC) DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM. Collaborative Opportunity
 A NOVEL CANCER STEM CELL (CSC) DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM Collaborative Opportunity March 2014 PURPOSE Cancer Research UK funded Investigators have established in vitro and in vivo models of CSCs for use
A NOVEL CANCER STEM CELL (CSC) DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM Collaborative Opportunity March 2014 PURPOSE Cancer Research UK funded Investigators have established in vitro and in vivo models of CSCs for use
Supporting information. Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers
 Supporting information Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers Yulei Chang 1, Xiaodan Li 1,3, Li zhang 1,3, Lu Xia 1, Xiaomin
Supporting information Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers Yulei Chang 1, Xiaodan Li 1,3, Li zhang 1,3, Lu Xia 1, Xiaomin
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
Targeting the Notch Pathway: Killing Cancer Stem Cells
 Targeting the Notch Pathway: Killing Cancer Stem Cells 1 Celeste Alverez Frontiers of Chemistry January 2, 2016 Outline 2 Background Cancer Stem Cells The Notch Pathway Targeting agents Drugs Antibodies
Targeting the Notch Pathway: Killing Cancer Stem Cells 1 Celeste Alverez Frontiers of Chemistry January 2, 2016 Outline 2 Background Cancer Stem Cells The Notch Pathway Targeting agents Drugs Antibodies
Exon 19 L747P mutation presented as a primary resistance to EGFR-TKI: a case report
 Case Report Exon 19 L747P mutation presented as a primary resistance to EGFR-TKI: a case report Yu-Ting Wang, Wei-Wei Ning, Jing Li, Jian-n Huang Department of Respiratory Medicine, the First ffiliated
Case Report Exon 19 L747P mutation presented as a primary resistance to EGFR-TKI: a case report Yu-Ting Wang, Wei-Wei Ning, Jing Li, Jian-n Huang Department of Respiratory Medicine, the First ffiliated
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features
 Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Cytokine-induced killer cells efficiently kill stem-like cancer cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the NKG2D-ligands recognition
 Cytokine-induced killer cells efficiently kill stem-like cancer cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the NKG2D-ligands recognition The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Cytokine-induced killer cells efficiently kill stem-like cancer cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the NKG2D-ligands recognition The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
ELUCIDATION OF ANTICANCER MECHANSIMS OF ISOLATED PHYTO- CONSTITUENTS
 7 CHAPTER SEVEN ELUCIDATION OF ANTICANCER MECHANSIMS OF ISOLATED PHYTO- CONSTITUENTS 136 7.1 INTRODUCTION Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death in women (Stephens et al., 2012). Several chemotherapeutic
7 CHAPTER SEVEN ELUCIDATION OF ANTICANCER MECHANSIMS OF ISOLATED PHYTO- CONSTITUENTS 136 7.1 INTRODUCTION Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death in women (Stephens et al., 2012). Several chemotherapeutic
Cancer Cell Research 14 (2017)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Ping Xu, Hongmei Li*, Xiaoyan Zhang Department of
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Ping Xu, Hongmei Li*, Xiaoyan Zhang Department of
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Gene Vaccine Expressing PSMA
 6 Clin Oncol Cancer Res () 7: 6-5 DOI.7/s85--5-7 Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Gene Vaccine Expressing PSMA Xiao-ling YANG Jing LV Yue-hong ZHANG Bo NIU, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Shanxi Bo ai Hospital,
6 Clin Oncol Cancer Res () 7: 6-5 DOI.7/s85--5-7 Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Gene Vaccine Expressing PSMA Xiao-ling YANG Jing LV Yue-hong ZHANG Bo NIU, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Shanxi Bo ai Hospital,
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
Casticin inhibits self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells from the MHCC97 cell line
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 7: 2023-2028, 2014 Casticin inhibits self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells from the MHCC97 cell line GUICHENG HE 1*, XIAOCHENG CAO 2*, MENG HE 1, XIFENG SHENG 2, YOUHUA WU 1 and XIAOHONG
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 7: 2023-2028, 2014 Casticin inhibits self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells from the MHCC97 cell line GUICHENG HE 1*, XIAOCHENG CAO 2*, MENG HE 1, XIFENG SHENG 2, YOUHUA WU 1 and XIAOHONG
The expression of ALDH1 in cervical carcinoma
 PMID: 21804471 WWW.MEDSCIMONIT.COM Hypothesis HY Received: 2010.07.22 Accepted: 2011.02.08 Published: 2011.08.01 The expression of ALDH1 in cervical carcinoma Tingting Yao 1,2, Qing Chen 1, Bingzhong Zhang
PMID: 21804471 WWW.MEDSCIMONIT.COM Hypothesis HY Received: 2010.07.22 Accepted: 2011.02.08 Published: 2011.08.01 The expression of ALDH1 in cervical carcinoma Tingting Yao 1,2, Qing Chen 1, Bingzhong Zhang
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Screening of Monacolin K-high-yielding Monascus strain by combinative mutation treatment
 264507~5162007 Mycosystema 1 550002 2 100039 3 550002 4 550000 Monascus purpureus 45s 1.0 Monacolin K Monascus purpureus ZT32 5 Monacolin K 219.9µg/mL 2 Monacolin K 8.33mg/g 3.3 Q939.5 A 1672-6472200704-0507-0516
264507~5162007 Mycosystema 1 550002 2 100039 3 550002 4 550000 Monascus purpureus 45s 1.0 Monacolin K Monascus purpureus ZT32 5 Monacolin K 219.9µg/mL 2 Monacolin K 8.33mg/g 3.3 Q939.5 A 1672-6472200704-0507-0516
Inhibitory Effect of D-chiro-inositol on Both Growth and Recurrence of Breast Tumor from MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cells
 Natural Product Sciences 23(1) : 35-39 (2017) https://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2017.23.1.35 Inhibitory Effect of D-chiro-inositol on Both Growth and Recurrence of Breast Tumor from MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cells
Natural Product Sciences 23(1) : 35-39 (2017) https://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2017.23.1.35 Inhibitory Effect of D-chiro-inositol on Both Growth and Recurrence of Breast Tumor from MDA-MB-231 Cancer Cells
