Microbiology Final. 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea?
|
|
|
- Pearl McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microbiology Final 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea? - EAEC* 2) Ab toxin A is stand for : - active* 3) Differentiate between staphylococcus and streptococcus : - catalase test* 4) Microsporum infect : - hair and skin * 5) All of the following are transmitted by blood except: - HCV - HBV* - HIV - HTLV- 1 6) The following viruses : HAV, HCV, HDV,HEV share the characteristic that : - ssrna* 7) A pathogen that causes disease from eating Pig meat : - Trichinella spiralis* 8) Giardia lamblia, an intestinal flagellate moves by : - flagella* 9) cave disease associated with : - Histoplasma* 10) Taenia Saginata : - Type of tapeworm in beef *
2 11) Which is true about lag phase : - increase in size* 12) No nucleic acid : - prions* 13) Dna virus integrate within bacterial chromosome : - prophage* 14) Not DNA virus : - Papovavirus - Hepadnavirus - Adenoviurs - Enterovirus* 15) Most causes flu infection : - influenza A* 16) plasmodium vivax and p ovale may persist as dormant form as: - hypnozoites* 17) Which is incorrect about Mumps: - human and animal reservoir * 18) SARS cuzd by : - coronaviruses* 19) Ligase: - connect the DNA segment* 20) Sabin vaccine: - oral live attenuated vaccine * 21) process used to Kill all life forms : - Sterilization* 22) What is the symptom: - Non measurable changes* 23) Congenital rubella infection is most likely to happen: - during 1st trimester of pregnancy* 24) fungi can found in the yeast form at 37 C but changes to the mold form at 25 C: - dimorphic* 25) which of the next is not nematode : - Shostosimia
3 26) if yeast is grown and there was no filamentous outgrowth that mean the fungi is not : - candida albicans* 27) Mycotoxins: - are fungal metabolites that are toxic to the human* 28) Vaginal Candidiasis don t cuz : - oral thrush* 29) aspergillosis w candidiasis are : - Opportunistic Fungal pathogens* 30) High stationary phase rate growth equal : - zero* 31) which of these don't happen by the genera dermatophytoses: - candida* 32) Dental caries cuzed by : - sterptococcus mutans* 33) after lap dignoss we found Bacteria gram (+) coccus,catalase + it could be: - s.arues* 34) Athelet's foot caused by : - Tinea pedis* 35) Primary pathogen originates: - in lungs* 36) Not an immune test: - PCR* 37) Hydrophobia,muscle paralysis,fatigue: - symptoms of rabies* 38) Imperfect fungi : - candida * 39) Mononucleosis : - HHV4 * 40) Two disease have the same pathogenic cause : - shingles and chicken box * 41) scotch tape for : - Enterobius vermicularis eggs*
4 42) turbidity on upper part of tube &clean area in the rest of it : - areob* 43) infectious form of Schistosoma is : - Cercariae* 44) Which bacteria move using actin polymerization: - A&b ( Listeria &shigella) * 45) normal flora normally are not found in : - blood* 46) standard for sterilization : - Phenol * 47) Spirochete: - treponma pallidium* 48) Botulism: - flaccid paralysis* 49) Suderophores : - extract iron to use it (bacteria!!) * 50) Gram +, spore forming : - Tetanus* 51) Thermal death point is: - Lowest temperture at which all cells in a culture are killed in 10 min* 52) terminate protein synthesis is : - UAA* 53) bacteriophage move the genome by : - Transduction* 54) safety pin: - Yersinia* 55) some patient with History with swimming : - naegleria meningoencephaliti* 56) tissue infection by helminths is reach with : - Eosinophilia* 57) Wool sorters disease: - pulmonary anthrax* 58) not content of gram(+): - lipid A*
5 59) Which form next is not part of cell envelope: - Gas vacuole* 60) which could rise the resestanat of a pathogen : - miss use of antibacterial drug* 61) Virus lead to accumulation of: - lymphocytes* 62) all are correct about 5th disease exept : (was clear answer) 63) which is not correct regarding to Cytomegalovirus: - Negri bodies* 64) fried egg-shaped culture: - mycoplasma* 65) toxin is: - lipid * - protein - carbohydrate - mineral 66) -bactria rrna consist of : * do not give up the beginning is always the hardest Collected by: Ahmad Osama Al-Masri Good Luck
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE. 1. Type of cell. 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM)
 HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
Pathogens of the Digestive System
 Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester FRIDAY. MICROBIOLOGY Lecture (Head Building) 11:00-12:30
 SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester Lectures -Head Building, Friday 11:00-12:30 Seminars/Practical Lessons-Lab.Room Instutute of Microbiology and Immunology, Friday 13:00-15:30
SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester Lectures -Head Building, Friday 11:00-12:30 Seminars/Practical Lessons-Lab.Room Instutute of Microbiology and Immunology, Friday 13:00-15:30
Chapter 10. Objectives. Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious diseases. Describe how the human body fights diseases.
 Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Objectives Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious diseases. Describe how the human body fights diseases. Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Disease What
Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Objectives Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious diseases. Describe how the human body fights diseases. Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Disease What
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
Bacteriology Virology Mycology Parasitology Immunology Pathology Epidemiology. Microbe alternate terms Germs, microorganisms, pathogens, agents, bugs
 1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
Pathogens!! What are Pathogens? 12/7/14. Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens
 Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE
 2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms. Mutualism both organisms benefit. Commensalism one organisms and the other is not harmed
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms. Mutualism both organisms benefit. Commensalism one organisms and the other is not harmed
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Epidemiology. Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Human Reservoir :
 Lecture ( 3 ) Dr. Ismail I. Daood Epidemiology Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Infectious disease is disease that is caused the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host's
Lecture ( 3 ) Dr. Ismail I. Daood Epidemiology Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Infectious disease is disease that is caused the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host's
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory. 11 April 2013
 Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
Montgomery County Community College BIO 241 Clinical Microbiology II 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 241 Clinical Microbiology II 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course that introduces Immunology, Virology, Mycology, and Parasitology as well as the immunological
Montgomery County Community College BIO 241 Clinical Microbiology II 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course that introduces Immunology, Virology, Mycology, and Parasitology as well as the immunological
MICROBIOLOGY BACTERIOLOGY III semester
 MICROBIOLOGY 2016-17 BACTERIOLOGY III semester 07. 10. 2016. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial properties. Bacterial structures (capsule, cell wall). Pathogenicity and
MICROBIOLOGY 2016-17 BACTERIOLOGY III semester 07. 10. 2016. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial properties. Bacterial structures (capsule, cell wall). Pathogenicity and
Microbiology and Pathogens. Teacher - Peter Mitchell
 Microbiology and Pathogens Teacher - Peter Mitchell BSc (Anatomy & Histology). Dip Health Science (Massage Therapy) Microbiology is the study of organisms not visible to the naked eye. Thus requiring the
Microbiology and Pathogens Teacher - Peter Mitchell BSc (Anatomy & Histology). Dip Health Science (Massage Therapy) Microbiology is the study of organisms not visible to the naked eye. Thus requiring the
18.2 Viruses and Prions
 KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705
![February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705](/thumbs/80/81975511.jpg) February 2009 [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks Answer All questions. I. Essays: (2x15=30) 1. Define hypersensitivity. Classify Hypersensitivity. Discuss in
February 2009 [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks Answer All questions. I. Essays: (2x15=30) 1. Define hypersensitivity. Classify Hypersensitivity. Discuss in
Potential etiologies of infection in these patients are diverse, including common and uncommon opportunistic infections.
 In the name of God Principles of post Tx infections 1: Potential etiologies of infection in these patients are diverse, including common and uncommon opportunistic infections. Infection processes can progress
In the name of God Principles of post Tx infections 1: Potential etiologies of infection in these patients are diverse, including common and uncommon opportunistic infections. Infection processes can progress
19/06/2013. Viruses are not organisms (do not belong to any kingdom). Viruses are not made of cells, have no cytoplasm, and no membranes.
 VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE?
 1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
Virology Introduction. Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment.
 DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
Overview of Microbiology. James D. Dick, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
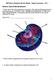 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
1. Virus 2. Capsid 3. Envelope
 VIRUSES BIOLOGY II VOCABULARY- VIRUSES (22 Words) 1. Virus 2. Capsid 3. Envelope 4. Provirus 5. Retrovirus 6. Reverse transcriptase 7. Bacteriophage 8. Lytic Cycle 9. Virulent 10. Lysis 11. Lysogenic Cycle
VIRUSES BIOLOGY II VOCABULARY- VIRUSES (22 Words) 1. Virus 2. Capsid 3. Envelope 4. Provirus 5. Retrovirus 6. Reverse transcriptase 7. Bacteriophage 8. Lytic Cycle 9. Virulent 10. Lysis 11. Lysogenic Cycle
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine)
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity. 2 nd Lecture
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 2 nd Lecture Preferred Portal of Entry Just because a pathogen enters your body it does not mean it s going to cause disease. pathogens - preferred portal of entry
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 2 nd Lecture Preferred Portal of Entry Just because a pathogen enters your body it does not mean it s going to cause disease. pathogens - preferred portal of entry
Microbiology. Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites
 Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Viruses. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 3.5 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.4 Viruses 1. Explain the problem of defining what a virus is - living or non-living? 2. show you
Name: 3.5 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.4 Viruses 1. Explain the problem of defining what a virus is - living or non-living? 2. show you
1/29/2013. Viruses and Bacteria. Infectious Disease. Pathogens cause disease by: Chapters 16 and 17
 Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Rheem Totah, Office H172M, Ph Office hours MWF 11:30 12:20 or by arrangement
 Rheem Totah, Office H172M, Ph 206-543-9481 rtotah@uw.edu Office hours MWF 11:30 12:20 or by arrangement Date/Time Topic Readings Mon March 26 Antifungal agents Foye s Chapter 40 Wed March 28 Antifungal
Rheem Totah, Office H172M, Ph 206-543-9481 rtotah@uw.edu Office hours MWF 11:30 12:20 or by arrangement Date/Time Topic Readings Mon March 26 Antifungal agents Foye s Chapter 40 Wed March 28 Antifungal
Normal Flora. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Normal Flora CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Relationships between Organisms Symbiosis Permanent association between two different organisms. Neutralism Two organisms living together, and neither is affected
Normal Flora CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Relationships between Organisms Symbiosis Permanent association between two different organisms. Neutralism Two organisms living together, and neither is affected
Chapter 17. Infectious Diseases
 Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Microbiology 2: PATHOGENS. Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon
 Microbiology 2: PATHOGENS Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Disease: normal body functions are disrupted Pathogen: any microbe that causes disease Noninfectious disease: can t be spread from person to person Genetic
Microbiology 2: PATHOGENS Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Disease: normal body functions are disrupted Pathogen: any microbe that causes disease Noninfectious disease: can t be spread from person to person Genetic
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
co URSE Medical Microbiology 3 COURSE CODE MMB310S
 @ セ M オセ M セ セ M@ - @ M セ M セ @ -- M --- @ M POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES Department of Health Sciences セ BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES -- ----- - QU ALIFICATION: ALIFICATION
@ セ M オセ M セ セ M@ - @ M セ M セ @ -- M --- @ M POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES Department of Health Sciences セ BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES -- ----- - QU ALIFICATION: ALIFICATION
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Structures of the Digestive System
 Topic: Diseases of the Digestive System 1 Structures of the Digestive System 2 groups Gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) The pathway from the mouth to the anus Most organs of the GI tract protected by a
Topic: Diseases of the Digestive System 1 Structures of the Digestive System 2 groups Gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) The pathway from the mouth to the anus Most organs of the GI tract protected by a
Chapter 17 Reading guide
 Chapter 17 Reading guide 1. Define pathogen, epidemic, pandemic, virulence, direct contact, indirect contact, autoinoculate. 2. Describe several risk factors for disease which you can not control. 3. Describe
Chapter 17 Reading guide 1. Define pathogen, epidemic, pandemic, virulence, direct contact, indirect contact, autoinoculate. 2. Describe several risk factors for disease which you can not control. 3. Describe
PHAR 6724: Introduction to the Immune System and Infectious Disease
 PHAR 6724: Introduction to the Immune System and Infectious Disease Course Syllabus Spring 2018 3.1 Credits This course adheres to the items listed in the College of Pharmacy Central Syllabus: https://docs.google.com/a/umn.edu/document/d/1artq5e1rbzxe8letwo7be8k8snzaegmmz_qcw8yj-ii/edit?pli=1
PHAR 6724: Introduction to the Immune System and Infectious Disease Course Syllabus Spring 2018 3.1 Credits This course adheres to the items listed in the College of Pharmacy Central Syllabus: https://docs.google.com/a/umn.edu/document/d/1artq5e1rbzxe8letwo7be8k8snzaegmmz_qcw8yj-ii/edit?pli=1
الحترمونا من خري الدعاء
 الحترمونا من خري الدعاء Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could be true or
الحترمونا من خري الدعاء Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could be true or
Health Sciences 1110 Module 5-Microbiology
 Laboratory Activities Health Sciences 1110 Module 5-Microbiology Watch Raw Terror: E. coli Bacteria video o Answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet. View the images listed below in WebPath and
Laboratory Activities Health Sciences 1110 Module 5-Microbiology Watch Raw Terror: E. coli Bacteria video o Answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet. View the images listed below in WebPath and
All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction
 Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics. AP Biology
 Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
The prokaryotic domains
 Diversity of Bacteria, Archaea, and Viruses Chapter 19 The prokaryotic domains Bacteria Three types of structure Spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral Archaea Many are extremophilic Prefer to live in very
Diversity of Bacteria, Archaea, and Viruses Chapter 19 The prokaryotic domains Bacteria Three types of structure Spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral Archaea Many are extremophilic Prefer to live in very
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
 The Microbial Size The Viruses Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Electron Micrograph Images of Viruses Influenza virus (RNA virus) Rotavirus (RNA virus) Adenovirus, showing
The Microbial Size The Viruses Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Electron Micrograph Images of Viruses Influenza virus (RNA virus) Rotavirus (RNA virus) Adenovirus, showing
1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution. 2) know the mechanisms of host immune responses to viral infections
 VIROLOGY A The course aims to provide the student with the cognitive and methodological tools necessary to: 1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution 2) know the
VIROLOGY A The course aims to provide the student with the cognitive and methodological tools necessary to: 1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution 2) know the
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
DRUGS TO FIGHT AGAINST MICROORGANISMS. Fungi, Viruses, Protozoa, & Helminths Chapter s 42 & 43
 DRUGS TO FIGHT AGAINST MICROORGANISMS Fungi, Viruses, Protozoa, & Helminths Chapter s 42 & 43 FUNGI Simple, plant like, lack green pigment, like dark, damp environments Molds- fuzzy, filamentous (mushrooms,
DRUGS TO FIGHT AGAINST MICROORGANISMS Fungi, Viruses, Protozoa, & Helminths Chapter s 42 & 43 FUNGI Simple, plant like, lack green pigment, like dark, damp environments Molds- fuzzy, filamentous (mushrooms,
namibia UniVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY
 namibia UniVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACUL TV OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBMES LEVEL: 7 COURSE
namibia UniVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACUL TV OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBMES LEVEL: 7 COURSE
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the
 Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
for a germ-free environment
 for a germ-free environment the universal ecological germ-killer Effectivity 99,999% not chemical not toxic effective for a routine and targeted disinfection at home, in the gastronomy and food market
for a germ-free environment the universal ecological germ-killer Effectivity 99,999% not chemical not toxic effective for a routine and targeted disinfection at home, in the gastronomy and food market
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES. 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES I. CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES A. General Characteristics 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells 2. Contain a single
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES I. CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES A. General Characteristics 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells 2. Contain a single
Part I. Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents.
 Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Name Class Date. Infection in which a virus inserts its nucleic acid into the DNA of the host cell and is duplicated with the cell s DNA
 Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
& VIRAL EYE PATHOGENS
 FUNGAL, MYCOBACTERIAL, & VIRAL EYE PATHOGENS Dr. WILLIAM J. BENJAMIN Eye Physiology & Ocular Prosthetics Laboratory University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Optometry Presented at the UAB School of
FUNGAL, MYCOBACTERIAL, & VIRAL EYE PATHOGENS Dr. WILLIAM J. BENJAMIN Eye Physiology & Ocular Prosthetics Laboratory University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Optometry Presented at the UAB School of
Date. Student Name. Prompt: This passage is called Characteristics of Viruses. It is about viruses.
 Student Name Characteristics of Viruses--Part I Level High School - Science Date _ Prompt: This passage is called Characteristics of Viruses. It is about viruses. Similarities and Differences Between Viruses
Student Name Characteristics of Viruses--Part I Level High School - Science Date _ Prompt: This passage is called Characteristics of Viruses. It is about viruses. Similarities and Differences Between Viruses
History of Virology. Russian Bacteriologist Dimitri Iwanowski TMD tobacco mosaic disease TMV isolated and purified
 Viruses & Prions Viruses Virus miniscule, acellular, infectious agent having one or several pieces of either DNA or RNA No cytoplasmic membrane, cytosol, organelles Cannot carry out any metabolic pathway
Viruses & Prions Viruses Virus miniscule, acellular, infectious agent having one or several pieces of either DNA or RNA No cytoplasmic membrane, cytosol, organelles Cannot carry out any metabolic pathway
Boston MRC Introduction to Biological Hazards Response
 Boston MRC Introduction to Biological Hazards Response Julien Farland MS, RBP Director of Biological Safety Boston Public Health Commission March 25, 2015 Objectives Describe the types and classes of biological
Boston MRC Introduction to Biological Hazards Response Julien Farland MS, RBP Director of Biological Safety Boston Public Health Commission March 25, 2015 Objectives Describe the types and classes of biological
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS
 COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
Viral Genetics. BIT 220 Chapter 16
 Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
SECTION 25-1 REVIEW STRUCTURE. 1. The diameter of viruses ranges from about a. 1 to 2 nm. b. 20 to 250 nm. c. 1 to 2 µm. d. 20 to 250 µm.
 SECTION 25-1 REVIEW STRUCTURE VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. virus 2. capsid 3. retrovirus 4. viroid 5. prion MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The diameter of
SECTION 25-1 REVIEW STRUCTURE VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. virus 2. capsid 3. retrovirus 4. viroid 5. prion MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The diameter of
Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio
 Labquality EQAS Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio Clinically relevant external quality assessment program for microbiology Bacterial serology Bacteriology Mycology Parasitology Preanalytics Virology Labquality
Labquality EQAS Microbiology EQA Product Portfolio Clinically relevant external quality assessment program for microbiology Bacterial serology Bacteriology Mycology Parasitology Preanalytics Virology Labquality
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Chapter 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens
 Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
MICROBIOLOGICAL PROFILE
 Evans Vanodine International plc G L O B A L H Y G I E N E S O L U T I O N S HANDSAN MICROBIOLOGICAL PROFILE 2 INTRODUCTION HANDSAN is a ready to use, quick acting and highly effective, alcohol based hygienic
Evans Vanodine International plc G L O B A L H Y G I E N E S O L U T I O N S HANDSAN MICROBIOLOGICAL PROFILE 2 INTRODUCTION HANDSAN is a ready to use, quick acting and highly effective, alcohol based hygienic
Do Viruses Play a Role in Childhood Leukaemia?
 CHILDREN with LEUKAEMIA, 6 September 2004 Do Viruses Play a Role in Childhood Leukaemia? Robin A. Weiss Natural Bioweapons of Mass Destruction A Richter Scale of Viruses and Global Mortality HIV HBV +
CHILDREN with LEUKAEMIA, 6 September 2004 Do Viruses Play a Role in Childhood Leukaemia? Robin A. Weiss Natural Bioweapons of Mass Destruction A Richter Scale of Viruses and Global Mortality HIV HBV +
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 15 / Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 Chapter 15 / Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 1 2 The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms? a. Clostridium tetani b. Escherichia coli c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Streptococcus mutans e. Clostridium botulinum 3
1 2 The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms? a. Clostridium tetani b. Escherichia coli c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Streptococcus mutans e. Clostridium botulinum 3
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
INFECTIOUS DISEASE. Page 2
 Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Microbiology - Problem Drill 21: Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 21: Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following organs is not part of the gastrointestinal tract (GI)? (A) Esophagus (B) Small intestine
Microbiology - Problem Drill 21: Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following organs is not part of the gastrointestinal tract (GI)? (A) Esophagus (B) Small intestine
PATHOGEN DETECTION WITH THE FILMARRAY
 PATHOGEN DETECTION WITH THE FILMARRAY The System Sample-to-Answer in an Hour Single sample Multiple samples The FilmArray integrates sample preparation, amplification, detection, and analysis all into
PATHOGEN DETECTION WITH THE FILMARRAY The System Sample-to-Answer in an Hour Single sample Multiple samples The FilmArray integrates sample preparation, amplification, detection, and analysis all into
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L AA
 OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
Multiple Choice Questions - Paper 1
 Multiple Choice Questions - Paper 1 Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could
Multiple Choice Questions - Paper 1 Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could
Professor Diane Hilker
 Professor Diane Hilker I. Exp. 19: Water Analysis for Fecal Contamination II. Exp. 20: Quantitative Analysis of H 2 O Purpose: To learn & perform the 3 stage standard H 2 O analysis test for fecal contamination
Professor Diane Hilker I. Exp. 19: Water Analysis for Fecal Contamination II. Exp. 20: Quantitative Analysis of H 2 O Purpose: To learn & perform the 3 stage standard H 2 O analysis test for fecal contamination
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 307 308 Actinomycetes, 307 308 Actinomycosis, in oral cavity, 288 290 Aggregatibacter, 308 309 Amoxicillin, in odontogenic infections,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 307 308 Actinomycetes, 307 308 Actinomycosis, in oral cavity, 288 290 Aggregatibacter, 308 309 Amoxicillin, in odontogenic infections,
Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner
 SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner Description Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner is an effective economical 4 ounce per gallon disinfectant, specifically designed for hospitals,
SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner Description Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner is an effective economical 4 ounce per gallon disinfectant, specifically designed for hospitals,
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
MICROORGANISM NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS
 MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity -Pathogenicity - ability of pathogen to cause disease by overcoming the defenses of the host -Virulence - degree of pathogenicity
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity -Pathogenicity - ability of pathogen to cause disease by overcoming the defenses of the host -Virulence - degree of pathogenicity
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease
 The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY
 LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY 1. General characteristics of piogenic cocci. 2. Staphylococcus, staphylococcus species, differentiation signs of staphylococci. Factor
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR MODULE 2 and 3 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY 1. General characteristics of piogenic cocci. 2. Staphylococcus, staphylococcus species, differentiation signs of staphylococci. Factor
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology
 NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
Viruses. Properties. Some viruses contain other ingredients (e.g., lipids, carbohydrates), but these are derived from their host cells.
 Viruses Properties They are obligate intracellular parasites. Probably there are no cells in nature that escape infection by one or more kinds of viruses. (Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.)
Viruses Properties They are obligate intracellular parasites. Probably there are no cells in nature that escape infection by one or more kinds of viruses. (Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.)
Infection Control. Infection Control. Infection Control. Disease. Infection
 Disease Any deviation or interruption of the normal structure or function of any part, organ, or system of the body Caused by microbes Absence of health HCPs need to understand infectious diseases and
Disease Any deviation or interruption of the normal structure or function of any part, organ, or system of the body Caused by microbes Absence of health HCPs need to understand infectious diseases and
