Central giant cell lesion (CGCL) and peripheral giant cell lesion (PGCL) are non-neoplastic
|
|
|
- Imogen Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FASN expression, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in central and peripheral giant cell lesions Saulo Gabriel Moreira FALCI 1 1 2, Department of Dentistry, College of Basic Sciences and Health, Federal University of Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri (UFVJM), Diamantina, MG, Brazil. 2- Oral Pathology, School of Dentistry, Fluminense Federal University, Nova Friburgo, RJ, Brazil. 3- Oral Pathology, Department of Stomatology, Public Oral Health and Forensic Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil. 4- Oral Pathology Section, Department of Oral Diagnosis, Piracicaba Dental School, University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Piracicaba, SP, Brazil. Saulo Gabriel Moreira Falci - Tiradentes, Diamantina - MG - Brazil - Postal code: 39100/000 - Phone/Fax: / saulofalci@hotmail.com ABSTRACT Central giant cell lesion (CGCL) and peripheral giant cell lesion (PGCL) are non-neoplastic proliferative processes of the jaws. PGCL is a reactive process induced by irritant local factors and CGCL is an intra-osseous lesion of unknown etiology. Both lesions exhibit similar histologic features showing abundant mononuclear cells, admixed with a large number of multinucleated giant cells and a rich vascularized stroma with extravasated fatty acid synthase (FASN) with angiogenesis. Objective: To evaluate angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis and their relationship with FASN expression in CGCL and PGCL. Material and Methods: Thirteen CGCL and 14 PGCL of the jaws were selected for immunoexpression of FASN; CD34 and CD105 (to assess blood microvessel density [MVD] and microvessel area [MVA]); and D2-40 (to assess lymphatic MVD and MVA). Results: Within PGCL and mononuclear cells were observed. Between PGCL and CGCL, only MVD-CD34 and all MVA positive mononuclear cells in both lesions was observed. Conclusions: Our results show both lesions exhibiting similar levels of FASN expression and neoangiogenesis, suggesting constitutive processes that regulate tissue maintenance. Keywords: Giant cell lesion. Immunohistochemistry. Angiogenesis. Lymphangiogenesis. Fatty acid synthase. INTRODUCTION Giant cell lesion (GCL) of the jaws is a nonneoplastic proliferative process, divided into central giant cell lesion (CGCL) and peripheral giant cell lesion (PGCL). PGCL is considered a reactive process induced by local irritants on the gingiva or alveolar mucosa. CGCL is an intra-osseous lesion of unknown etiology 11. Both CGCL and PGCL exhibit similar histopathological features, and are characterized by the presence of abundant mononuclear stromal cells, admixed with a large number of multinucleated giant cells and a rich vascularized stroma with extravasated erythrocytes, hemosiderin deposition, and blood- In spite of this, these lesions may have different clinical behaviors 11,13,23. Fatty acid synthase (FASN) is the metabolic enzyme responsible for endogenous synthesis of saturated long-chain fatty acid, specifically palmitate, from the precursors acetyl-coa and malonyl-coa 7. FASN is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers affecting breast 19, ovaries 2, prostate 20, and oral cavity 22, whereas FASN is
2 downregulated in most normal human tissues (except in the liver, lactating breast, fetal lung, and adipose tissue) because cells preferentially use circulating dietary fatty acids for the synthesis of new structural lipids 29. In the oral cavity, FASN expression has been shown in squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma 3,22 ; however, its expression in benign neoplasms 3 and/or reactive conditions is little known. Interestingly, some studies have linked FASN expression with endothelial cell proliferation 4,21. Accordingly, the role of FASN expression in angiogenesis must be in GCL of the jaws is unknown. CD34 is a cell surface glycoprotein consistently expressed in the vascular endothelium. Some studies have previously assessed CD34 expression in CGCL in order to compare aggressive and non-aggressive subtypes. They showed increased microvessel density (MVD)-CD34 in aggressive CGCL 10,18,25. Although CD34 is unable to distinguish between pre-existing vessels and neoformed vessels, interestingly, it has been shown that distinguishing neoformed vessels in proliferative tissues is relevant and may have prognostic implications, identifying possible targets for developing anti-angiogenic therapeutic strategies 5,18. CD105 (endoglin) is an angiogenic membrane protein that is highly expressed in neoformed vessels 6. Although CD105 has been assessed in oral vascular malformations and pyogenic granulomas 26, to our knowledge, CD105 expression in GCL of the jaws is unknown. Another unclear and relevant point is the characterization of the lymphatic MVD (LMVD) in GCL, which may be immunohistochemically evaluated through the D2-40 marker 13. Nevertheless, as in the case of CD105, the lymphatic vascular stroma characterization in GCL of the jaws has not been evaluated. As previously mentioned, increased FASN expression in oral malignant tumors has been reported 3,22, and some studies have linked FASN expression with endothelial cell proliferation 4,21. It remains to be determined what happens with such events in oral benign and/or reactive lesions. Thus, the aim of the current study was to assess angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, as well as establishing their relationship with FASN expression in CGCL and PGCL of the jaws. MATERIAL AND METHODS This retrospective study examined the records and tissues of patients diagnosed and treated for GCL of the jaws. None of the patients had received any treatment with a therapeutic agent prior to paraffin-embedded tissue blocks of 13 CGCL (8 males, 5 females; mean age 18.5 years; 8 mandible, 5 maxilla) and 14 PGCL (9 males, 5 females; mean age 38.9 years; 11 mandibular gingiva, 3 maxillary gingiva) were selected from our laboratory archives. According to their clinical characteristics, such as painful symptoms, growth pattern rate, root resorption, cortical bone perforation and recurrence, the CGCL cases of the 8. All lesions were reviewed through hematoxylineosin stained slides and the diagnosis was from the study were GCL cases which presented inadequate clinical description, cases diagnosed as aneurysmal bone cyst, cherubism and brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism (confirmed by establishing elevated serum parathyroid hormone for histological analysis. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (Process 042/2011). Immunohistochemical methods For each antibody (FASN, CD34, CD105 and D2- glass slides were used. All tissue specimens were and cut into parallel consecutive sections. For the immunohistochemical (IHC) reactions, the slides were hydrated and treated with hydrogen peroxide (3%). Primary antibodies, dilutions and antigen retrieval are shown in Table 1. The tissue sections were then washed three times in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution and exposed to secondary antibody using the LSAB+Kit (Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA). Peroxidase activity was visualized by using the chromogen diaminobenzidine (DAB) Table 1- Antibodies used for immunohistochemical analysis of central and peripheral giant cell lesions Clone Manufacturer Dilution FASN 23/ Becton Dickinson Transduction 1:200 TRIS/EDTA (ph 9.0) Laboratories 1 CD34 QBEnd10 Dako# jan/ 1:50 Citric acid (ph 6.0) CD105 SN6h Dako jan/ 1:30 Proteinase K D2-40 D2-40 Dako 1:100 Citric acid (ph 6.0) 1 Lexington, KY, USA. # Carpinteria, CA, USA
3 (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, USA). Finally, the tissue sections were counterstained with Carrazi s hematoxylin for 5 minutes. Thereafter, the sections were dehydrated in a series of graded ethanol solutions, diaphanized and mounted in Canada balsam under cover glasses. Sections of oral Kaposi s sarcomas were included in all reactions as positive control for CD34, CD105 and D2-40, while prostate carcinomas were used for FASN. Negative controls of reactions were performed by omitting the primary antibody. The slides were scanned and photographed using the Aperio Scanscope CS Slide Scanner (Aperio Technologies, Vista, CA, USA). Immunostaining assessment and statistical analysis MVD and microvessel area (MVA), assessed through CD34 and CD105 expression, as well as lymphatic MVD (LMVD) and MVA (LMVA), assessed through D2-40 expression, were established identifying the most vascularized areas within the lesions ( hot spots ), which were chosen at low magnification (100x) and subsequently 14. The images were made using the Aperio Scan Scope software, which depicted 2. area, respectively, of positive microvessels stained MVD and MVA. The MVA measurement was done by means of vascular contour tracing using the Image J software, which automatically measured 2 ). Single endothelial cells or clusters of endothelial cells, with or without a lumen, were considered to be individual vessels. To assess FASN expression, similar to angiogenic markers, the area containing a high number of positive mononuclear cells and multinucleated giant cells in both lesions were counted in each high-power field using the software Image J (Scion Corporation, USA), and then the average percentages of the immunostained cells were calculated in each case. The data collected were recorded and organized in a database using Statistical Package for Social Science (version 17.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Normal distribution was tested using the Shapiro Wilk test. In samples with a normal distribution, the Student t-test and Pearson correlation were applied. In samples that presented non-normal distributions, the Mann Whitney U test and Spearman correlation were applied. A P<0.05 probability value was RESULTS All vascular structures in all cases were highlighted by CD34. By comparing the MVD within CD105-positive vessels than CD34-positive vessels (P<0.001) was observed (Table 2). In addition, a Table 2- Comparison between PGCL and CGCL in relation to (L)MVD, (L)MVA, and percentage of FASN-positive multinucleated giant cells and mononuclear cells n p n p PGCL CGCL MVD-CD34 14 MVD-CD34 13 MVD-CD MVD-CD MVD-CD34 14 MVD-CD LMVD-D LMVD-D MVD-CD MVD-CD LMVD-D LMVD-D FASN+ MGC FASN+ MGC FASN+ MC 14 FASN+ MC 13 MVA-CD34 14 MVA-CD34 13 MVA-CD MVA-CD MVA-CD34 14 MVA-CD34 13 LMVA-D LMVA-D MVA-CD MVA-CD LMVA-D LMVA-D
4 than CD105-positive vessels in PGCL (P and CGCL (P percentage indicates that 31% and 13% of the vessels in PGCLs, and 33% and 8% of the vessels in CGCLs were positive for CD105 and D2-40, respectively. The number of CD34-positive vessels was P (Figures 1a, 1b; Figure 2a). However, no statistical difference regarding the number of CD105- and D2-40-positive vessels was found when comparing both lesions (Figures 1c, 1d; Figure 2a; Figures 3a, 3b). greater MVA for all vascular markers used in 2b). Moreover, when comparing the MVA within of CD105-positive vessels than CD34-positive vessels (P<0.001) was observed. In addition, it D2-40-positive vessels than CD105-positive vessels in both lesions (P<0.001) (Table 2). Moreover, through consecutive section analysis, we found focal areas showing vessels stained with Immunoexpression of CD34 in CGCL (a, 400x) and PGCL (b, 400x), almost all vessels were CD34-positive in lesser number of CD105-positive vessels was observed in CGCL than in PGCL Comparison between PGCL and CGCL in relation to MVD and LMVD (a), MVA and LMVA (b) and percentage of FASN-positive MGC and MC (c)
5 Immunoexpression of D2-40 in CGCL (a, 400x) and PGCL (b, 400x), notice that the lymphatic vessels are of larger diameter in PGCL than in CGCL. This case of CGCL on parallel consecutive sections presented vessels positive for both CD105 (c, 400x) and D2-40 (d, 400x), suggesting neolymphangiogenesis Immunoexpression of FASN in CGCL (a, 400x) and PGCL (b, 400x), note immunopositivity for FASN in the multinucleated giant cells and mononuclear cells in both lesions CD105 and D2-40 in both lesions (Figures 3c, 3d), supporting the idea that some CD105-stained vessels represent newly formed lymphatic vessels. All cases present FASN-positive multinucleated giant cells (PGCL, mean 39%; CGCL, mean 36%) and mononuclear cells (PGCL, mean 7%; CGCL, mean 10%) (Figure 2c; Figures 4a, 4b), without both lesions (P P We also observed focal areas showing weak FASN immunoexpression on endothelial cells in 46% and 21% of the CGCL and PGCL cases, respectively. found between MVA-CD105 with FASN-positive DISCUSSION Both CGCL and PGCL of the jaws exhibit similar histopathological features, being characterized by numerous ovoid and spindle-shaped mononuclear cells, admixed with multinucleated giant cell, within a rich vascularized stroma 11,16. Despite this, it is well known that these lesions may have different clinical behaviors 23. In the current study, without all cases presented FASN-positive multinucleated giant cells and mononuclear cells. Nevertheless, we observed a higher number of multinucleated giant cells than mononuclear cells (ratio 4:1) presenting FASN immunoreactivity. It is probable that cell may help to explain our results. Moreover, as a multinucleated giant cells and mononuclear cells 16 is most probably associated with angiogenesis in GCL, on the other hand the lack of correlation between FASN-positive multinucleated giant cells with vascular markers observed in the current study can suggest maintenance and/or remodeling role for FASN expression in multinucleated giant cells. Angiogenesis, which is the formation of new vessels from pre-existing vessels, is thought to be of crucial importance to the growth and maintenance of proliferative tissues 24. In the oral cavity, it has been shown that the number and size of blood vessels increase from normal oral epithelium through dysplastic epithelium to reach a maximum in invasive carcinoma 1, while no significant difference seems to occur between normal mucosa, hyperplasia, and dysplasia for LMVD. Conversely, invasive carcinomas presented higher LMVD
6 than normal mucosa and precancerous lesions 17. Regarding benign and reactive oral lesions, several studies have been performed to quantify MVD by using CD34 and CD105 9,10,12,18,25-27, but none of them have assessed GCL considering both markers. In addition, although D2-40 expression has been demonstrated in normal odontogenic tissues as well as in cystic and tumor odontogenic lesions 30, it is noteworthy that in GCL a stromal lymphatic vessel characterization has not been performed. Like CD105, D2-40 expression in GCL is unknown. In the current study, we have observed uniform positivity for CD34 in all vascular structures in both lesions. Almost all our cases (93% and 92% of the PGCL and CGCL, respectively) exhibited CD105-positive vessels (about 32%, in relation to CD34-positive vessels), while only 78% and 69% of the PGCL and CGCL, respectively, showed D2-40-positive vessels (about 10%, in relation to CD34-positive vessels). Thus, the constitutive expression of CD105 in GCL supports angiogenic activity and tissue remodeling. This is further supported by FASN expression in endothelial cells, detected focally in about 46% and 21% of CGCL and PGCL cases, respectively. Moreover, the expression of endothelial markers in GCL is consistent with the presence of various angiogenic factors and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), transforming growth (b-fgf), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and MMP-9 15,16,28. Since it has been shown that aggressive rather than nonaggressive subtypes of CGCL present higher MVD-CD34 10,18,25, further studies are needed in order to compare whether there are CD105 expression differences between aggressive and nonaggressive subtypes of CGCL. In relation to stromal lymphatic vessel characterization, it is interesting that lymphangiogenesis in reactive or benign oral lesions have been little studied. In the current study, we have shown that about 8% and 13% of the vessels in CGCL and PGCL group, respectively, were immunoreactive for is suggested that the higher number of lymphatic vessels detected in PGCL (Figure 2) seems to be influenced by anatomical location, since a be observed at the periphery of the lesions in close association with the lamina propria. Furthermore, through consecutive section analysis, we found focal areas showing vessels stained with CD105 and D2-40, in both lesions. In order to validate CD105 and D2-40 in oral GCL should be compared neolymphangiogenesis in these lesions. greater MVA than CGCL for all vascular markers used. Similar results were shown 27, which favored a reactive nature for PGCL. It is likely that, in addition to the anatomical location of these lesions, differences in the expression pattern of angiogenic growth factors 1,16 may help to explain the differences found in our study. It has been shown that FASN inhibition by orlistat may reduce endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis 4. As previously commented, to our knowledge, the FASN immunoexpression in giant cell lesions is unknown. However, in our study, different from FASN-positive multinucleated giant cells, it is between FASN-positive mononuclear cells and MVA- is suggested that FASN-positive mononuclear cells may contribute with new vessel formation. Future determinate possible interactions between FASN expression and angiogenic proteins in GCL. CONCLUSION In summary, our results suggest that greater MVD-CD34, and greater MVA-CD34, CD105 and D2-40, in PGCL rather than in CGCL, might be associated with a reactive inflammatory process. Moreover, similar levels of FASN expression, neoangiogenesis (MVD-CD105), and lymphangiogenesis (LMVD-D2-40) between PGCL and CGCL indicate constitutive processes to regulate tissue maintenance and remodeling in both lesions. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank the University of Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri for the master s scholarship; Victor Toral Rizo for training in applied methodology; Patrícia Correia Faria for helping with graphics; Piracicaba Dental School, Oral Diagnosis Department, for performing the immunohistochemistry; São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP / ). CONFLICTS OF INTEREST of interest in this manuscript. REFERENCES 1- Abbas NF, Labib El-Sharkawy S, Abbas EA, Abdel Monem El- Shaer M. Immunohistochemical study of p53 and angiogenesis in benign and preneoplastic oral lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103(3):
7 2- Alò PL, Visca P, Framarino ML, Botti C, Monaco S, Sebastiani V, et al. Immunohistochemical study of fatty acid synthase in ovarian neoplasms. Oncol Rep. 2000;7(6): Andrade BA, León JE, Carlos R, Delgado-Azañero W, Mosqueda- Taylor A, Graner E, et al. Expression of fatty acid synthase (FASN) in oral nevi and melanoma. Oral Dis. 2011;17(8): Browne CD, Hindmarsh EJ, Smith JW. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis by orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor. FASEB J. 2006;20(12): Cardoso SV, Souza KC, Faria PR, Eisenberg AL, Dias FL, Loyola AM. Assessment of angiogenesis by CD105 antigen in epithelial salivary gland neoplasms with diverse metastatic behavior. BMC Cancer. 2009;9: Cheifetz S, Bellón T, Calés C, Vera S, Bernabeu C, Massagué J, et al. Endoglin is a component of the transforming growth factorbeta receptor system in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(27): Chirala SS, Wakil SJ. Structure and function of animal fatty acid synthase. Lipids. 2004;39(11): Chuong R, Kaban LB, Kozakewich H, Perez-Atayde A. Central giant cell lesions of the jaws: a clinicopathologic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986;44(9): Davey KJ, Perrier S, Ohe G, Gilbert AD, Bankfalvi A, Saunders WP, et al. Assessment of vascularity as an index of angiogenesis in periradicular granulomas: comparison with oral carcinomas and normal tissue counterparts. Int Endod J. 2008;41(11): Dewsnup NC, Susarla SM, Abulikemu M, Faguin WC, Kaban LB, August M. Immunohistochemical evaluation of giant cell tumors of the jaws using CD34 density analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(5): Flórez-Moreno GA, Henao-Ruiz M, Santa-Sáenz DM, Castañeda-Peláez DA, Tobón-Arroyave SI. Cytomorphometric and immunohistochemical comparison between central and peripheral giant cell lesions of the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105(5): Gadbail AR, Hande A, Chaudhary M, Nikam A, Gawande M, Patil S, et al. Tumor angiogenesis in keratocystic odontogenic tumor assessed by using CD-105 antigen. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(3): Kahn HJ, Marks A. A new monoclonal antibody, D2-40, for detection of lymphatic invasion in primary tumors. Lab Invest. 2002;82(9): Lima SC, Rizo VH, Silva-Sousa YT, Almeida LY, Almeida OP, León JE, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of angiogenesis Endod. 2011;37(12): Matos FR, Moraes M, Nonaka CF, Souza LB, Almeida Freitas R. Immunoexpression of TNF-α giant cell lesions of the jaws. J Oral Pathol Med. 2012;41(2): Matos FR, Nonaka CF, Miguel MC, Galvão HC, Souza LB, Freitas RA. Immunoexpression of MMP-9, VEGF, and vwf in central and peripheral giant cell lesions of the jaws. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(4): Palomba A, Gallo O, Brahimi A, Franchi A. Evaluation of lymphangiogenesis in premalignant conditions of the head and neck mucosa. Head Neck 2010;32(12): Peacock ZS, Jordan RC, Schimidt BL. Giant cell lesion of the jaws: does the level of vascularity and angiogenesis correlate with 19- Pizer ES, Jackisch C, Wood FD, Pasternack GR, Davidson NE, Kuhajda FP. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis induces programmed cell death in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1996;56(12): Rossi S, Graner E, Febbo P, Weinstein L, Bhattacharya N, Onody signatures in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1(1): Seguin F, Carvalho MA, Bastos DC, Agostini M, Zecchin KG, Alvarez-Flores MP, et al. The fatty acid synthase inhibitor orlistat reduces experimental metastases and angiogenesis in B16-F10 melanomas. Br J Cancer. 2012;107(6): Silva SD, Cunha IW, Nishimoto IN, Soares FA, Carraro DM, ErbB2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2009;45(10):e Souza PE, Mesquita RA, Gomez RS. Evaluation of p53, PCNA, Ki-67, MDM2 and AgNOR in oral peripheral and central giant cell lesions. Oral Dis. 2000;6(1): Spiegelaere W, Casteleyn C, Van den Broeck W, Plendl J, Bahramsoltani M, Simoens P, et al. Intussusceptive angiogenesis: a biologically relevant form of angiogenesis. J Vasc Res. 2012;49(5): Susarla SM, August M, Dewsnup N, Faquin WC, Kaban LB, Dodson TB. CD34 staining density predicts giant cell tumor clinical behavior. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(5): Vasconcelos MG, Alves PM, Vasconcelos RG, Silveira EJ, Medeiros AM, Queiroz LM. Expression of CD34 and CD105 as markers for angiogenesis in oral vascular malformations and pyogenic granulomas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;268(8): Vassilopoulos SI, Tosios KI, Panis VG, Vrostsos JA. Endothelial cells of oral pyogenic granulomas express enos and CD105/ endoglin: an immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(4): Vered M, Buchner A, Dayan D. Giant cell granuloma of the growth factor. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006;35(10): Weiss L, Hoffmann GE, Schreiber R, Andres H, Fuchs E, Körber E, et al. Fatty-acid biosynthesis in man, a pathway of organ distribution of fatty-acid synthase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986;367(9): Zustin J, Scheuer HA, Friedrich RE. Podoplanin expression in human tooth germ tissues and cystic odontogenic lesions: an immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010;39(1):
Are CD68 and Factor VIII-RA Expression Different in Central and Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw: An Immunohistochemical Comparative Study
 Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2017.01401 Are CD68 and Factor VIII-RA Expression Different in Central and Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw: An Immunohistochemical Comparative Study Soudabeh
Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2017.01401 Are CD68 and Factor VIII-RA Expression Different in Central and Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw: An Immunohistochemical Comparative Study Soudabeh
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Seyed Mohammad Razavi, Roya Yahyaabadi* Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2279 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2279 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with
Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
 Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Assessment of VEGF, CD-31 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical Markers in Oral Pyogenic Granuloma: A Comparison with Hemangioma and Inflammatory Gingivitis
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 14, No. 2 Mar-Apr 2011, 185-189 Received: Mar 15, 2010; Accepted: Oct 25, 2010 Short communication Assessment of VEGF, CD-31 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 14, No. 2 Mar-Apr 2011, 185-189 Received: Mar 15, 2010; Accepted: Oct 25, 2010 Short communication Assessment of VEGF, CD-31 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
JCDP ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 JCDP Omar Kujan et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1629 Immunohistochemical Comparison of p53, Ki-67, CD68, Vimentin, α-smooth Muscle Actin and Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin in Oral Peripheral
JCDP Omar Kujan et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1629 Immunohistochemical Comparison of p53, Ki-67, CD68, Vimentin, α-smooth Muscle Actin and Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin in Oral Peripheral
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
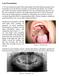 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child: A Case Report
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Expression of CD34 and CD105 as markers for angiogenesis in oral vascular malformations and pyogenic granulomas
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2011) 268:1213 1217 DOI 10.1007/s00405-010-1472-z HEAD AND NECK Expression of CD34 and CD105 as markers for angiogenesis in oral vascular malformations and pyogenic granulomas
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2011) 268:1213 1217 DOI 10.1007/s00405-010-1472-z HEAD AND NECK Expression of CD34 and CD105 as markers for angiogenesis in oral vascular malformations and pyogenic granulomas
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minichromosome maintenance-2 (MCM2) expression differentiates oral squamous cell carcinoma from pre-cancerous lesions
 Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 253 258 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minichromosome maintenance-2 (MCM2) expression differentiates oral squamous cell carcinoma from pre-cancerous lesions Seyed Mohammad RAZAVI, Maryam
Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 253 258 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minichromosome maintenance-2 (MCM2) expression differentiates oral squamous cell carcinoma from pre-cancerous lesions Seyed Mohammad RAZAVI, Maryam
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Hébel Cavalcanti Galvão, Manuel Antonio Gordón-Núñez 1, Rivadávio Fernandes Batista de Amorim 2, Roseana de Almeida Freitas, Lélia Batista de Souza
 Original Research Immunohistochemical expression of protein 53, murine double minute 2, B cell lymphoma 2, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in odontogenic cysts and keratocystic odontogenic tumor
Original Research Immunohistochemical expression of protein 53, murine double minute 2, B cell lymphoma 2, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in odontogenic cysts and keratocystic odontogenic tumor
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Anam Ali 1 *, Muhammad Asif 2, Bismah Ahmad 2, Shahid Jamal 3, Iram Ali 4, Muhammad Tahir Khadim 1. Abstract.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:08/20/2018 Acceptance:12/30/2018 Stromal Expression of CD10 by Immunohistochemistry in Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Dentigerous and Radicular Cysts and Its
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:08/20/2018 Acceptance:12/30/2018 Stromal Expression of CD10 by Immunohistochemistry in Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Dentigerous and Radicular Cysts and Its
RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian cancer
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
A Study of D2-40 Immunohistochemical Expression in Colorectal Carcinomas
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1122 A Study of D2-40 Immunohistochemical Expression in Colorectal Carcinomas Sarvek Bajaj*, Gururajaprasad. C and Suchitha S Department of Pathology, JSS Medical college,
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1122 A Study of D2-40 Immunohistochemical Expression in Colorectal Carcinomas Sarvek Bajaj*, Gururajaprasad. C and Suchitha S Department of Pathology, JSS Medical college,
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization with Colorectal Carcinoma: A Pilot Study
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Case Report Malignant Transformation of an Odontogenic Cyst in aperiodof10years
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 762969, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/762969 Case Report Malignant Transformation of an Odontogenic Cyst in aperiodof10years Juliane Pirágine Araújo, 1 Luiz
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 762969, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/762969 Case Report Malignant Transformation of an Odontogenic Cyst in aperiodof10years Juliane Pirágine Araújo, 1 Luiz
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in Peripheral and Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives in Cancer Research Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in Peripheral and Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws Radien HM El-Attar
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives in Cancer Research Expression of Ki67, CD31, CD68 and P53 in Peripheral and Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws Radien HM El-Attar
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
VEGF/VEGFR2 Axis in Periodontal Disease Progression and Angiogenesis: Basic Approach for a New Therapeutic Strategy
 VEGF/VEGFR2 Axis in Periodontal Disease Progression and Angiogenesis: Basic Approach for a New Therapeutic Strategy MIRCEA VLADAU 1, ANCA MARIA CIMPEAN 2, RALUCA AMALIA BALICA 2, ANDREEA ADRIANA JITARIU
VEGF/VEGFR2 Axis in Periodontal Disease Progression and Angiogenesis: Basic Approach for a New Therapeutic Strategy MIRCEA VLADAU 1, ANCA MARIA CIMPEAN 2, RALUCA AMALIA BALICA 2, ANDREEA ADRIANA JITARIU
Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study)
 GIANT THE IRAQI CELL POSTGRADUATE GRANULOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study) Omar
GIANT THE IRAQI CELL POSTGRADUATE GRANULOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study) Omar
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 19/May 12, 2014 Page 5307
 PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
Comparison of CD10 expression in stroma of epithelial and mesenchymal tumors of the breast
 Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Comparison of -catenin Expression in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor, Dentigerous Cyst and Ameloblastoma
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 109-114 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of -catenin Expression in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor, Dentigerous Cyst and Ameloblastoma Sepideh Vosoughhosseini
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 109-114 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of -catenin Expression in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor, Dentigerous Cyst and Ameloblastoma Sepideh Vosoughhosseini
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
CD15 and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland
 Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis
 Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Applications of IHC. Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
 Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
A Comparative Study of PCNA and Ki-67 Expression in Dental Follicle, Dentigerous Cyst, Unicystic Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastoma
 IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article A Comparative Study of PCNA and Ki-67 Expression in Dental Follicle, Dentigerous Cyst, Unicystic Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastoma Shima Nafarzadeh 1,2, Maryam
IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article A Comparative Study of PCNA and Ki-67 Expression in Dental Follicle, Dentigerous Cyst, Unicystic Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastoma Shima Nafarzadeh 1,2, Maryam
Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Brief Formalin Fixation and Rapid Tissue Processing Do Not Affect the Sensitivity of ER Immunohistochemistry of Breast Core Biopsies
 Brief Formalin Fixation and Rapid Tissue Processing Do Not Affect the Sensitivity of ER Immunohistochemistry of Breast Core Biopsies Victoria Sujoy, MD, Mehrdad Nadji, MD, and Azorides R. Morales, MD From
Brief Formalin Fixation and Rapid Tissue Processing Do Not Affect the Sensitivity of ER Immunohistochemistry of Breast Core Biopsies Victoria Sujoy, MD, Mehrdad Nadji, MD, and Azorides R. Morales, MD From
Saudi Journal of Pathology and Microbiology. DOI: /sjpm ISSN (Print)
 DOI:10.21276/sjpm.2016.1.3.1 Saudi Journal of Pathology and Microbiology Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3362 (Print) ISSN 2518-3370
DOI:10.21276/sjpm.2016.1.3.1 Saudi Journal of Pathology and Microbiology Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3362 (Print) ISSN 2518-3370
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic Adenocarcinoma to Body Fluids
 Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas
 Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Immunohistochemical comparison of cyclin D1 expression in amelobelastoma, odontogenic keratocyst and radicular cyst
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN CHEMISTRY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES (p-issn: 2348-5213: e-issn: 2348-5221) www.ijcrcps.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrcps Coden: IJCROO(USA) Volume 3, Issue 9-2016
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN CHEMISTRY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES (p-issn: 2348-5213: e-issn: 2348-5221) www.ijcrcps.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrcps Coden: IJCROO(USA) Volume 3, Issue 9-2016
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature
 Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test
 753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Središnja medicinska knjižnica
 Središnja medicinska knjižnica Ulamec M., Džombeta T., Čupić H., Leniček T., Tomas D., Krušlin B. (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting and d2-40 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathology Oncology
Središnja medicinska knjižnica Ulamec M., Džombeta T., Čupić H., Leniček T., Tomas D., Krušlin B. (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting and d2-40 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathology Oncology
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Determines Neoangiogenesis in Gallbladder Carcinomas
 & Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Determines Neoangiogenesis in Gallbladder Carcinomas Mateja Legan¹*, Boštjan Luzar², Vera Ferlan-Marolt², Andrej Cör¹ 1. Institute of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of
& Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Determines Neoangiogenesis in Gallbladder Carcinomas Mateja Legan¹*, Boštjan Luzar², Vera Ferlan-Marolt², Andrej Cör¹ 1. Institute of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Immunohistochemical Maspin Expression in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 (2):103-109 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 (2):103-109 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY The histopathological and immunohistochemical study of oral squamous carcinomas PhD Student: DRAGOMIR LUCIAN PAUL Scientific Coordinator:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY The histopathological and immunohistochemical study of oral squamous carcinomas PhD Student: DRAGOMIR LUCIAN PAUL Scientific Coordinator:
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Case 18. M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Immunohistochemical Phenotypes of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 151-6 Immunohistochemical Phenotypes of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast Joo Yeon Song Hye-Kyoung Yoon Department of Pathology, Pusan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine,
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 151-6 Immunohistochemical Phenotypes of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast Joo Yeon Song Hye-Kyoung Yoon Department of Pathology, Pusan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine,
Breast cancer: IHC classification. Mogens Vyberg Professor of Clinical Pathology Director of NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital, Aalborg, Denmark
 Breast cancer: IHC classification Mogens Vyberg Professor of Clinical Pathology Director of NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital, Aalborg, Denmark http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/1a/breast.svg
Breast cancer: IHC classification Mogens Vyberg Professor of Clinical Pathology Director of NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital, Aalborg, Denmark http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/1a/breast.svg
Senior of Histopathology Department at Khartoum, Radiation and Isotopes Center
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
Immunohistochemical Assessment of Ki-67 Expression in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 10, No. 2, Summer 2007, 84-89 Received: 9 Sep 2006, Accepted: 26 Jun 2007 Immunohistochemical Assessment of Ki-67 Expression in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 10, No. 2, Summer 2007, 84-89 Received: 9 Sep 2006, Accepted: 26 Jun 2007 Immunohistochemical Assessment of Ki-67 Expression in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Results you can trust
 PRODUCT I NF OR MAT ION pharmdx Results you can trust The first and only FDA-approved PD-L1 test to assess the magnitude of treatment effect on progression-free survival in melanoma patients from OPDIVO
PRODUCT I NF OR MAT ION pharmdx Results you can trust The first and only FDA-approved PD-L1 test to assess the magnitude of treatment effect on progression-free survival in melanoma patients from OPDIVO
4Ps LUMPS AND BUMPS B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS. Most Common BUMP in the oral cavity Fibroma INTERDENTAL PAPILLAE LESIONS
 B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
GLUT-1: an extra diagnostic tool to differentiate between haemangiomas and vascular malformations q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2005) 58, 348 352 GLUT-1: an extra diagnostic tool to differentiate between haemangiomas and vascular malformations q J. Leon-Villapalos a, K. Wolfe b, L. Kangesu
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2005) 58, 348 352 GLUT-1: an extra diagnostic tool to differentiate between haemangiomas and vascular malformations q J. Leon-Villapalos a, K. Wolfe b, L. Kangesu
Gingival and alveolar hyperplastic reactive lesions: clinicopathological study of 90 cases
 Braz J Oral Sci. JulySeptember 26 Vol. 5 Number 8 Pryscilla Giglio Peralles Ana Paula Borges Viana André Luiz da Rocha Azevedo 2 Fábio Ramôa Pires 3 DDS; formerly undergraduating students; School of Dentistry,
Braz J Oral Sci. JulySeptember 26 Vol. 5 Number 8 Pryscilla Giglio Peralles Ana Paula Borges Viana André Luiz da Rocha Azevedo 2 Fábio Ramôa Pires 3 DDS; formerly undergraduating students; School of Dentistry,
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(7):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 586-591 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.065
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 586-591 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.065
Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on
 Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
ONCOLOGY. Csaba Bödör. Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research november 19., ÁOK, III.
 ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
 Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma T.J. Zhou 1, X.H. Huang 1, L. Gong 1 and L. Xiang 2 1 Department of Pathology, the Affiliated Hospital
Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma T.J. Zhou 1, X.H. Huang 1, L. Gong 1 and L. Xiang 2 1 Department of Pathology, the Affiliated Hospital
Catechin s anti-angiogenic effects in epithelial ovarian cancer
 Catechin s anti-angiogenic effects in epithelial ovarian cancer Brian Krug Background Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is a common and lethal malignancy of the female reproductive tract (2). Often detected
Catechin s anti-angiogenic effects in epithelial ovarian cancer Brian Krug Background Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is a common and lethal malignancy of the female reproductive tract (2). Often detected
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas
 Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Comparison of immunohistochemical markers between adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
 509 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 4, 509-514, 2009 Original Comparison of immunohistochemical markers between adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma Nasrollah Saghravanian
509 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 4, 509-514, 2009 Original Comparison of immunohistochemical markers between adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma Nasrollah Saghravanian
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Cancer cells in vitro
 Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
A SURVEY OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL BIOPSIES IN CHILDREN. A SINGLE-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 20 YEARS IN PELOTAS-BRAZIL
 www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;6(6):97-402 A SURVEY OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL BIOPSIES IN CHILDREN. A SINGLE-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Giana da Silveira LIMA, Silvia Terra
www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;6(6):97-402 A SURVEY OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL BIOPSIES IN CHILDREN. A SINGLE-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Giana da Silveira LIMA, Silvia Terra
