Principles of Cancer. How Can Massage Help?
|
|
|
- Kristina Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Cancer How Can Massage Help?
2 Skilled massage therapy is safe for people with cancer and will not spread the disease. Specific massage adjustments are based on clinical presentations of cancer, not the presence of a cancer diagnosis. --Tracy Walton
3 Cancer A collection of 175+ diseases with one thing in common: normal body cells mutate slightly and begin to replicate uncontrollably First described by Hippocrates ( BC) who named it for a tumor s resemblance to a crab Galen ( AD), a Roman physician, used the word oncos (Greek for swelling) to describe tumors. Although the crab analogy of Hippocrates is still used to describe malignant tumors, Galen s term is now used as a part of the name for cancer specialists oncologists.
4 General types: Carcinoma begins in epithelial cells (solid tumors) Sarcoma begins in muscle or connective tissue (solid tumors) Lymphoma begins in glands, nodes, and organs of the lymphatic system Myeloma begins in plasma cells from bone marrow Leukemia begins in bone marrow, esp. white blood cells ( liquid or blood cancer ) Mixed begins in more than one type of tissue
5 Cancers discussed Elsewhere in Pathology by Ruth Werner Skin Cancer (Chapter 2) Osteosarcoma (Chapter 3) Leukemia and Myeloma (Chapter 5) Lymphoma (Chapter 6) Lung and Laryngeal cancer (Chapter 7) Esophageal, stomach, colorectal, liver, and pancreatic cancer (Chapter 8) Thyroid cancer (Chapter 9) Kidney and Bladder cancer (Chapter 10) Cervical, uterine, breast, ovarian, prostate, and testicular cancer (Chapter 11)
6 Risks of Cancer and Massage? No risk of spreading cancer with massage it s already present in the body Do no harm Guidelines for massage are determined by the circumstances presented in each case, not by the fact that cancer exists
7 Cancer Statistics Bleak yet Hopeful 40% of all men & women in the U.S. will develop some sort of cancer during their life. Diagnosed in 1.5 million people per year 570,000 people die every year of cancer the 2 nd leading cause of death (1 st is heart attack) 12 million people alive in the U.S. have survived cancer.
8 Most common cancers Skin cancers Lung cancer Breast & Ovarian cancer (women) Prostate cancer (men) Cancer of the colon, rectum, and pancreas (both genders) Outside the U.S., lung cancer (smoking) and liver and cervical cancers (Hepatitis B and C, and HPV, respectively)
9 Metastasis Cancer Spreads It s still unclear how a healthy cell changes to a malignant one DNA of a cell mutates The current (very simplified) version of metastasis has 6 stages:
10 Oncogene Activation An oncogene is a gene that initiates malignant characteristics within a cell. When activated, an oncogene begins the changes that cause a cell to become malignant. Oncogenes are usually inhibited by the activity of tumor suppressor genes. A lack of the suppressor genes may be a significant factor in cancer risk. Triggers for oncogene activation are thought to be: Toxic environmental exposures Diet Genetic predisposition Combination of the above
11 Local Invasion As a tumor grows, it must convince the local extracellular matrix to make room for it without stimulating an inflammatory response. Special enzymes secreted by cancer cells are at the center of this process. The enzymes dissolve the surrounding connective tissue, and the process does not trigger the usual inflammatory response. This is why cancer is often silent in the early stages.
12 Proliferation Mutated cells reproduce without control, often piling up into masses called tumors. These tumors secrete enzymes that allow them to survive a normal immune system attack.
13 Angiogenesis Angiogenesis is the growth of blood vessels that supply the tumor. Any growth of more than 1 or 2 cubic centimeters requires a dedicated blood supply; chemical messengers from the tumor command the body to build new capillaries. The more blood vessels a tumor has, the more likely it is to have metastasized.
14 Migration Cell Shedding Cancer cells break off of the primary tumor and travel to new areas. The circulatory or lymphatic systems can be used as a transfer medium, but cancer cells can also spread through direct contact with other organs in the peritoneal fluid.
15 Colonization Cell Planting When the cancer cells land in their new location, the process begins again with proliferation. The first tumor that grows is the primary tumor; other tumors that grow from the metastasis of the primary tumor are called secondary tumors. For example, a tumor that is in the bladder that metastasized from the ovary is not bladder cancer; it is considered to be secondary ovarian cancer in the bladder.
16 Causes of Cancer: Internal and External Factors Internal factors Apoptosis is cell death; however, cancer cells seem to refuse to die Inherited characteristics (a genetic predisposition; Angelina Jolie) Hormonal activity (some hormones seem to stimulate malignant cell division) Immune system problems (reduced ability of the body to recognize and fight off cancer cells)
17 External factors Environmental Carcinogens Hydrocarbons in cigarette smoke Compounds (from amino acids) are created when meat is grilled on high heat Substances found in dyes, inks, and paints Radiation from the sun Radon gas Gamma rays Excessive x-rays Asbestos Benzene Nickel Cadmium Uranium Vinyl chloride
18 Viruses HTLV-1 resembles HIV, a retrovirus that is spread through intimate fluids (lymphocytic leukemia, non-hodgkin lymphoma) HPV human papillomavirus (warts, cancer of the cervix, anus, penis, vagina, vulva, mouth, and throat). Vaccine is available HHV-8 human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi sarcoma, a type of skin cancer associated with repressed immune system) HIV indirectly associated with cancer due to suppressed immune system that would otherwise protect from HPV and HHV-8 EBV Epstein-Barr Virus, another herpesvirus (nasopharyngeal cancer, stomach cancer, etc.) HBV and HCV Hepatitis B & C viruses (liver cancer)
19 Bacteria Helicobacter pylori (stomach cancer) Borrelia burgdorferi (Spirochete for Lyme disease) Campylobacter jejuni Both of the last two have been associated with digestive tract lymphomas Animal parasites Liver flukes (cancer of the bile ducts) spread through consumption of raw or undercooked fish Schistoma haematobium (bladder cancer) Spread through contaminated water; not found much in the U.S.
20 Combining factors increases risk of developing cancers Example: heavy smoking and alcohol consumption is potent for developing cancers of the mouth or upper GI tract It can take years for a cancer to form between the time of exposure and the time of diagnosis; this makes it hard to pin down the exact causes of cancer
21 Signs and Symptoms of Cancer A change in bowel or bladder habits blood in the stool or urine A sore that does not heal, or comes and goes in the same place Change in a wart or mole Uterine bleeding between periods, or post menopause A lump or thickening in the breast or elsewhere A prostate exam that shows enlargement Indigestion or swallowing difficulty Persistent cough or hoarseness, coughing up blood Unexplained weight loss Fatigue, anemia Unexplained fever
22 Cancer Screening 2 Goals To find cancer cells while treatment is most likely to succeed Increase survival rate Screening Tests Mammograms Prostate Exams Colonoscopy/Endoscopy Cervical Cancer Screening Other tests depending on risk factors
23 Not all screening protocols accomplish these goals equally well risks are: Exposure to radiation Perforation of hollow organs False-negative results False-positive results Over diagnosis, which can lead to anxiety and unnecessary interventions (surgery)
24 Biopsy A tissue sample taken after screening to analyze for the presence of malignant cells Often done for skin lesions If the analysis is positive for malignant cells, further examinations of the patient follow to determine how far the cancer has developed.
25 Staging Labeling a cancer to indicate how far it has progressed Based on how cancer grows and how readily certain types of cancer metastasize For more information, go to and search for cancer staging
26 Cancer Treatment Depends on: The stage of the cancer The age, general health and wishes of the patient What kind of cancer is present Different modes of attack may be used to treat the cancer if different types of tumors are present
27 Types of Therapy for Treatment Treatments used before treatment begins Radiation to shrink tumors before surgery Treatments used following the main treatment (surgery, chemo, radiation) to increase the chance for complete success Tamoxifen (oral chemotherapy for breast cancer survivors) Palliative therapy is given to a patient who is not likely to survive the disease Surgery to reduce tumor size might be conducted, not to cure the cancer but to relieve pain
28 Main Treatments for Cancer Surgery to remove tumors and affected lymph nodes (especially sentinel nodes) Radiofrequency thermal ablation (microwave the tumors) Chemotherapy (cytotoxic drugs target fast growing cells) Autologous bone marrow transplant Radiation therapy Hormone therapy
29 Hypothermia (cryotherapy used for skin cancers in the early stage or for cancer of the cervix) Hyperthermia (raising body temperature, makes chemotherapy work better) Biologic (targeted) therapy (strengthens the immune system to fight off the cancer) Stem cell implantation (currently used for leukemia patients)
30 Prevention Stop smoking and tobacco use Avoid known carcinogens Use sunscreen Eat more fruit & veggies, whole grains, and control dietary fat Exercise regularly and control weight Use alcohol moderately Practice safe sex Vaccinate against cancer-causing pathogens Use early cancer screening methods
31 Massage for Cancer WILL NOT spread cancer but it would be inappropriate to rub on a tumor or mobilize joints in the vicinity of a tumor 5 common symptoms patients experience while undergoing treatment for cancer Pain Anxiety Nausea Fatigue Depression Massage helps with ALL these symptoms!
32 Massage also helps with other problems during and after cancer treatment, such as Constipation Altered body image Poor sleep Dry Skin Most important, however, is that massage provides a basic human need: nurturing, caring, and informed touch when many patients feel isolated and dehumanized
33 Massage Risks for Clients with Cancer Complications of cancer & various cancer treatments have serious implications on the choice to bodywork modalities you do. Tumor sites Massage should not disrupt a tumor site close to the surface of the body Bone involvement Cancer that has metastasized to the bone can make the bones brittle; risk of fracture Vital organ involvement Cancer in organs can compromise function of that organ; evaluate risk carefully with medical team Deep vein thrombosis Red flag for massage; danger of moving a clot
34 Massage Risks for Cancer Treatment Surgery Infection Constipation Implanted medical devices (ports, catheters, drains, ostomies) Possible lymphedema Radiation Thin, reddened skin at radiation site Implanted radiation pellets Irritated GI tract (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) Bone marrow suppression Fatigue
35 Chemotherapy Administered orally or via IV drips (ports, arm) Suppress bone marrow activity (anemia, risk of infection, clotting problems) GI irritation, mouth sores, hand-foot syndrome, hair loss, neuropathy, constipation, skin rashes, mood changes, dry skin Wearing gloves is indicated for treatment Some chemotherapy drugs can be expressed through the patient s skin Cuts down the risk of infection because chemotherapy patients are often so immune-compromised
36 Other therapies Hormone treatments may increase blood clots Biologic therapies increase fatigue and flu-like symptoms Cryotherapy can leave irritated places on the skin In all cases it is imperative to communicate with the health care team to provide the best bodywork with minimal risk.
37 Massage Benefits for Cancer Patients Improves sleep Increases appetite Relieves constipation Improves mood Reduces anxiety Decreases depression Alleviates pain Improves quality of life
38 The Massage Therapy Pressure Scale Tracy Walton %20Pressure%20Scale%20Descriptions %20Table%202-1%20Medical %20Conditions%20and%20Massage %20Therapy.pdf
39 The Massage Therapy Pressure Scale Level 1 Light Lotioning (as if applying lotion). For clients who are fragile. Note: Slow speed is required to monitor this pressure. Use full hand contact, even though pressure is light. Hand contact should be full and contoured relax the whole palm, fingers, and fingertips onto the skin s surface. Resist the impulse to pull back. Strokes: Light effleurage, holding, light touch Tissue displacement: Either no skin movement or movement of skin only. Therapist body use: Use just arms and hands. No leaning body mechanics required.
40 Level 2 Heavy Lotioning (as if rubbing in lotion). For clients who are ill or elderly. Note: this is less careful than light lotioning. Do not need slow speed to monitor this pressure. Similar to applying sun block or lotion on a child. Strokes: Effleurage, light friction, gentle trembling, vibration, holding, touch Tissue displacement: Some movement of the superficial muscles and adipose tissue. Therapist body use: Little hand strength is needed, just for contouring. Use arms and hands. No leaning body mechanics required.
41 Training Available Tracy Walton Oncology Massage Training at TLC (November) 4 full days Includes a hands-on clinic with people with cancer or in remission Register Early at TLC MD Anderson Oncology Massage training 3 full days at MD Anderson in Houston (July 18, 2014) Lectures from doctors and LMTs, a panel discussion with cancer patients currently in treatment, hands on experience Other Hands-on Training Available in various courses all over the country Required for S4OM (Society for Oncology Massage) membership. Tracy Walton, Gail MacDonald, others teach this type of course Infusion Room Training Greet the Day (California based) offers a specific protocol in massage techniques for patients while they are receiving chemotherapy
42 Volunteer A great way to practice is to volunteer your massage services right here in Austin Oncology Massage Alliance (OMA) provides free massages in the infusion rooms at Texas Oncology Basic training provided
43 By touching a body, we touch every event it has experienced. For a few brief moments we hold all of a client's stories in our hands. We witness someone's experience of their own flesh, through some of the most powerful means possible: the contact of our hands, the acceptance of the body without judgment, and the occasional listening ear. With these gestures we reach across the isolation of the human experience and hold another person's legend. In massage therapy, we show up and ask, in so many ways, what it is like to be another human being. In doing so, we build a bridge that may heal us both. --Tracy Walton, "The Health History of a Human Being," Massage Therapy Journal, Winter 1999.
Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points The survival rate for many types of cancer has improved in recent years; however, cancer is still the second leading cause of death in the United States (see paragraph
Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points The survival rate for many types of cancer has improved in recent years; however, cancer is still the second leading cause of death in the United States (see paragraph
Chapter 3. Neoplasms. Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 3 Neoplasms Terminology Related to Neoplasms and Tumors Neoplasm New growth Tumor Swelling or neoplasm Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow Hematoma Bruise or contusion Classification of Neoplasms
Chapter 3 Neoplasms Terminology Related to Neoplasms and Tumors Neoplasm New growth Tumor Swelling or neoplasm Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow Hematoma Bruise or contusion Classification of Neoplasms
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer. Chapter 31 Lesson 2
 Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
guide to living with cancer Brought to you by Alliance Health.
 guide to living with cancer Brought to you by Alliance Health. The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice
guide to living with cancer Brought to you by Alliance Health. The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice
Cell Death and Cancer. SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou
 Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Cancer. University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing
 Cancer University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants will be better able to: 1. Develop a basic understanding of cancer 2. Describe
Cancer University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants will be better able to: 1. Develop a basic understanding of cancer 2. Describe
Why is Crab ( ) The Symbol of Cancer?
 2017 What is Cancer? A REVOLT OF CELLS Cancer is the uncontrolled growth and spread of cells. The growth often invade surrounding tissue and can metastasize to distant sites. Normally when old cell die,
2017 What is Cancer? A REVOLT OF CELLS Cancer is the uncontrolled growth and spread of cells. The growth often invade surrounding tissue and can metastasize to distant sites. Normally when old cell die,
Chapter 20 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 20 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 20 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Information. about cancer
 1 Information about cancer This chapter may help you answer simple questions about what cancer is and how it is treated. There are more than 200 different types of cancer and a range of treatments. Being
1 Information about cancer This chapter may help you answer simple questions about what cancer is and how it is treated. There are more than 200 different types of cancer and a range of treatments. Being
Cancer Fundamentals. Julie Randolph-Habecker, Ph.D. Director, Experimental Histopathology Shared Resource
 Cancer Fundamentals Julie Randolph-Habecker, Ph.D. Director, Experimental Histopathology Shared Resource Cancer Overview Leading cause of death in US 1.2 million diagnosed each year More common after age
Cancer Fundamentals Julie Randolph-Habecker, Ph.D. Director, Experimental Histopathology Shared Resource Cancer Overview Leading cause of death in US 1.2 million diagnosed each year More common after age
CANCER = Malignant Tumor = Malignant Neoplasm
 CANCER = Malignant Tumor = Malignant Neoplasm A tissue growth: Not necessary for body s development or repair Invading healthy tissues Spreading to other sites of the body (metastasizing) Lethal because
CANCER = Malignant Tumor = Malignant Neoplasm A tissue growth: Not necessary for body s development or repair Invading healthy tissues Spreading to other sites of the body (metastasizing) Lethal because
Cancer arises from the mutation of a normal gene. A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen.
 Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Cancer 101 Spring Family Cancer Retreat 4/18/15. Amish Shah, M.D. New Mexico Cancer Center
 Cancer 101 Spring Family Cancer Retreat 4/18/15 Amish Shah, M.D. New Mexico Cancer Center Topics to cover What is Cancer? Screening Diagnosis/Staging Treatment Basics Clinical Trials Surveillance What
Cancer 101 Spring Family Cancer Retreat 4/18/15 Amish Shah, M.D. New Mexico Cancer Center Topics to cover What is Cancer? Screening Diagnosis/Staging Treatment Basics Clinical Trials Surveillance What
Noncommunicable Diseases:
 Noncommunicable Diseases: Chapter 14 Lesson 1 What Are Noncommunicable Diseases? An allergy is an example of a noncommunicable disease. noncommunicable disease A disease that cannot be spread from person
Noncommunicable Diseases: Chapter 14 Lesson 1 What Are Noncommunicable Diseases? An allergy is an example of a noncommunicable disease. noncommunicable disease A disease that cannot be spread from person
CELL AGING. Process of getting older. Losing hair, wrinkled skin Fingernails- the new cells push out the old cells
 CELL AGING & CANCER CELL AGING What is aging? Process of getting older. Losing hair, wrinkled skin Fingernails- the new cells push out the old cells As a person ages, mitosis slows down CELL AGING COMPARISON
CELL AGING & CANCER CELL AGING What is aging? Process of getting older. Losing hair, wrinkled skin Fingernails- the new cells push out the old cells As a person ages, mitosis slows down CELL AGING COMPARISON
Chapter 6.1. pages Prayer Next Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapter 6.1 pages 108-110 Prayer Next Prayer Attendance Homework Terms Cancer A disease that begins when a single cell makes copies of itself when it should not. Cell division A process where a parent
Chapter 6.1 pages 108-110 Prayer Next Prayer Attendance Homework Terms Cancer A disease that begins when a single cell makes copies of itself when it should not. Cell division A process where a parent
Cancer Awareness Talk ICPAK 2014
 Cancer Awareness Talk ICPAK 2014 F. Chite Asirwa, MB ChB. MD. MSc. Internist. Medical Oncologist & Hematologist Asst. Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology/Oncology Indiana University Email: fasirwa@iu.edu
Cancer Awareness Talk ICPAK 2014 F. Chite Asirwa, MB ChB. MD. MSc. Internist. Medical Oncologist & Hematologist Asst. Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology/Oncology Indiana University Email: fasirwa@iu.edu
Care of the Patient with Cancer
 Chapter 17 Care of the Patient with Cancer 1 Slide 1 Slide 2 Oncology Branch of medicine that deals with the study of tumors Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related related death in both men
Chapter 17 Care of the Patient with Cancer 1 Slide 1 Slide 2 Oncology Branch of medicine that deals with the study of tumors Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related related death in both men
Figure 1. Comparison of Cancer Incidence Rates 1 of Individual Census Tracts with Louisiana, All Cancers Combined,
 Figure. Comparison of Cancer Incidence Rates of Individual Census Tracts with Louisiana, All Cancers Combined, 006-04 The rate is statistically significantly lower than Louisiana The rate is not statistically
Figure. Comparison of Cancer Incidence Rates of Individual Census Tracts with Louisiana, All Cancers Combined, 006-04 The rate is statistically significantly lower than Louisiana The rate is not statistically
What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
 Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
 Page 1 of 10 PATIENT EDUCATION Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Introduction Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer of the lymphocytes (a kind of white blood cell). It is also referred
Page 1 of 10 PATIENT EDUCATION Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Introduction Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer of the lymphocytes (a kind of white blood cell). It is also referred
CANCER. Mrs. Davis Health Education
 CANCER Mrs. Davis Health Education Cancer Terms: Tumors: Masses of useless tissue Benign: Non-cancerous Malignant: Cancerous Metastasis: Spread of cancer from the point where it originated to other parts
CANCER Mrs. Davis Health Education Cancer Terms: Tumors: Masses of useless tissue Benign: Non-cancerous Malignant: Cancerous Metastasis: Spread of cancer from the point where it originated to other parts
Philippine Cancer Society Forum: Cancer can be cured!
 Philippine Cancer Society Forum: Cancer can be cured! Throughout history, doctors and scientists have extensively studied Their researchers have not only yielded a wealth of information on the disease,
Philippine Cancer Society Forum: Cancer can be cured! Throughout history, doctors and scientists have extensively studied Their researchers have not only yielded a wealth of information on the disease,
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
DRUGS FOR NEOPLASIA. Chapter 37
 DRUGS FOR NEOPLASIA Chapter 37 Keywords- You tell Me! Cancer dz characterized by abnormal, uncontrolled cell division Tumor swelling, abnormal enlargement or mass of tissue Carcinogen any substance or
DRUGS FOR NEOPLASIA Chapter 37 Keywords- You tell Me! Cancer dz characterized by abnormal, uncontrolled cell division Tumor swelling, abnormal enlargement or mass of tissue Carcinogen any substance or
*It can appear almost anywhere in the body. *The tumor can invade adjoining parts of the body and metastasize to other organs.
 CANCER Cancer is an uncontrollable process of growth and cell dissemination. It can appear almost anywhere in the body. The tumor can invade adjoining parts of the body and metastasize to other organs.
CANCER Cancer is an uncontrollable process of growth and cell dissemination. It can appear almost anywhere in the body. The tumor can invade adjoining parts of the body and metastasize to other organs.
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CANCER.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers
 Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Asexual Reproduction & Cancer
 Asexual Reproduction & Cancer Asexual Reproduction Only one individual needed No new genetic material added = organism clones itself Reproduction is fast and produces many individuals Gene pool is shallow
Asexual Reproduction & Cancer Asexual Reproduction Only one individual needed No new genetic material added = organism clones itself Reproduction is fast and produces many individuals Gene pool is shallow
- A cancer is an uncontrolled, independent proliferation of robust, healthy cells.
 1 Cancer A. What is it? - A cancer is an uncontrolled, independent proliferation of robust, healthy cells. * In some the rate is fast; in others, slow; but in all cancers the cells never stop dividing.
1 Cancer A. What is it? - A cancer is an uncontrolled, independent proliferation of robust, healthy cells. * In some the rate is fast; in others, slow; but in all cancers the cells never stop dividing.
Cancer Facts for People Over 50
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Cancer Facts for People Over 50 Cancer strikes people of all ages, but you are more likely to get cancer as you get older, even if no one in your family has ever had
National Institute on Aging AgePage Cancer Facts for People Over 50 Cancer strikes people of all ages, but you are more likely to get cancer as you get older, even if no one in your family has ever had
The Future of Cancer. Lawrence Tsui Global Risk Products Actuary Swiss Reinsurance Company Hong Kong. Session Number: WBR8
 Lawrence Tsui Global Risk Products Actuary Swiss Reinsurance Company Hong Kong Session Number: WBR8 Agenda Cancer the basics Cancer past and present Cancer the future CANCER THE BASICS Cancer the basics
Lawrence Tsui Global Risk Products Actuary Swiss Reinsurance Company Hong Kong Session Number: WBR8 Agenda Cancer the basics Cancer past and present Cancer the future CANCER THE BASICS Cancer the basics
Common Questions about Cancer
 6 What is cancer? Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. The cancer cells form tumors that destroy normal tissue. If cancer cells break away from
6 What is cancer? Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. The cancer cells form tumors that destroy normal tissue. If cancer cells break away from
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
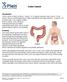 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
MEDICAL DATA SHEET For Patients 18 years of age and older
 MEDICAL DATA SHEET For Patients 18 years of age and older NAME: DATE: / / AGE: DOB: / / 1. What is the main reason you are seeking a physician s advice? 2. Please list all allergies: Drug Allergies: Other
MEDICAL DATA SHEET For Patients 18 years of age and older NAME: DATE: / / AGE: DOB: / / 1. What is the main reason you are seeking a physician s advice? 2. Please list all allergies: Drug Allergies: Other
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General
 Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended chemotherapy for your breast cancer. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended chemotherapy for your breast cancer. Chemotherapy
HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH
 HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH W H O THEME FOR 2017 D E P R E S S I O N : L E T S TA L K WHAT IS DEPRESSION? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness, and loss of interest in activities that
HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH W H O THEME FOR 2017 D E P R E S S I O N : L E T S TA L K WHAT IS DEPRESSION? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness, and loss of interest in activities that
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN VIRUS-ASSOCIATED HUMAN CANCERS
 ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN VIRUS-ASSOCIATED HUMAN CANCERS Joint Graduate Seminar Depar tment of Microbiology The Chinese University of Hong Kong PhD Candidate: Zhang Chuqing Super visor: Professor Paul Chan
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN VIRUS-ASSOCIATED HUMAN CANCERS Joint Graduate Seminar Depar tment of Microbiology The Chinese University of Hong Kong PhD Candidate: Zhang Chuqing Super visor: Professor Paul Chan
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
Cancer in Women. Lung cancer. Breast cancer
 Cancer in Women You can get cancer at any age, but it is more likely as you get older. The types of cancer people get and the risk of dying from cancer are not the same for all ethnic groups. Here are
Cancer in Women You can get cancer at any age, but it is more likely as you get older. The types of cancer people get and the risk of dying from cancer are not the same for all ethnic groups. Here are
Lecture 29 Epidemiology of Cancer
 Babylon University College Of Medicine Department of Community Medicine Lectures in Community Medicine For 4 th Stage Students By Dr. Hassan Baiee 2010 2011 Lecture 29 Epidemiology of Cancer Tumors are
Babylon University College Of Medicine Department of Community Medicine Lectures in Community Medicine For 4 th Stage Students By Dr. Hassan Baiee 2010 2011 Lecture 29 Epidemiology of Cancer Tumors are
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
Cancer Epidemiology, Manifestations, and Treatment
 Cancer Epidemiology, Manifestations, and Treatment Chapter 10 Environmental Risk Factors Tobacco Ø Multipotent carcinogenic mixture Ø Linked to cancers of the lung, lower urinary tract, digestive tract,
Cancer Epidemiology, Manifestations, and Treatment Chapter 10 Environmental Risk Factors Tobacco Ø Multipotent carcinogenic mixture Ø Linked to cancers of the lung, lower urinary tract, digestive tract,
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis. Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval
 Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
American Society of Clinical Oncology PATIENT EDUCATION MATERIALS CATALOG.
 American Society of Clinical Oncology PATIENT EDUCATION MATERIALS CATALOG www.cancer.net www.cancer.net Tell your patients about the ASCO doctor-approved PATIENT INFORMATION WEBSITE Cancer.Net brings the
American Society of Clinical Oncology PATIENT EDUCATION MATERIALS CATALOG www.cancer.net www.cancer.net Tell your patients about the ASCO doctor-approved PATIENT INFORMATION WEBSITE Cancer.Net brings the
Colon Cancer Surgery
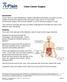 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Cancer is the single name assigned to more than 100 diseases that can occur in any part of body
 Cancer is the single name assigned to more than 100 diseases that can occur in any part of body It s actually the result of abnormal cells that multiply and spread out of control, damaging healthy cells
Cancer is the single name assigned to more than 100 diseases that can occur in any part of body It s actually the result of abnormal cells that multiply and spread out of control, damaging healthy cells
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
CANCER Uncontrolled Cell Division
 CANCER Uncontrolled Cell Division What is cancer? Why does it occur? Where does it occur? Benign vs. Malignant? Types of Cancer (3 main groups) There are over 200 different types of cancer 1) Carcinomas
CANCER Uncontrolled Cell Division What is cancer? Why does it occur? Where does it occur? Benign vs. Malignant? Types of Cancer (3 main groups) There are over 200 different types of cancer 1) Carcinomas
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA non - Hodgkin lymphoma This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand. Please consult your doctor on specific questions and details about your
NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA non - Hodgkin lymphoma This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand. Please consult your doctor on specific questions and details about your
THERE IS A TON OF STUFF ON THE SITE & NOT ENOUGH TIME TO LOOK AT IT ALL
 https://nccih.nih.gov/health/cancer THERE IS A TON OF STUFF ON THE SITE & NOT ENOUGH TIME TO LOOK AT IT ALL FNP Opinion & Commentary 03-26-17 CANCER & CAM Malignant Mesothelioma Possibly Due To Asbestos
https://nccih.nih.gov/health/cancer THERE IS A TON OF STUFF ON THE SITE & NOT ENOUGH TIME TO LOOK AT IT ALL FNP Opinion & Commentary 03-26-17 CANCER & CAM Malignant Mesothelioma Possibly Due To Asbestos
3/9/2017. Chapter 56. Care of the Patient with Cancer. Cancer Rates in the US. Carcinogenesis
 Chapter 56 Care of the Patient with Cancer All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Cancer Rates in the US 1 in 2 men and 1 in 3 women
Chapter 56 Care of the Patient with Cancer All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Cancer Rates in the US 1 in 2 men and 1 in 3 women
Cancer Facts for Women
 Cancer Facts for Women Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to
Cancer Facts for Women Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to
Leader Lesson Family and Consumer Education (FCE) Breast & Cervical Cancer Teaming Up and Taking Control!
 Leader Lesson Family and Consumer Education (FCE) Breast & Cervical Cancer Teaming Up and Taking Control! Goal Protect the health and well-being of FCE members by teaching cancer prevention techniques
Leader Lesson Family and Consumer Education (FCE) Breast & Cervical Cancer Teaming Up and Taking Control! Goal Protect the health and well-being of FCE members by teaching cancer prevention techniques
Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Bone Marrow Transplantation Introduction Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside all of your bones, including your hip and thigh bones. The bone marrow is like a factory that makes different types of blood
Bone Marrow Transplantation Introduction Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside all of your bones, including your hip and thigh bones. The bone marrow is like a factory that makes different types of blood
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center
 LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
Leukemia. There are different types of leukemia and several treatment options for each type.
 Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Welcome to About Women by Women
 Welcome to About Women by Women Today s Date New Patient Questionnaire Name: Birth Date: / / Home Phone: Address: Cell Phone: Work Phone: Occupation: Employer: Marital Status: Married Living w/ Partner
Welcome to About Women by Women Today s Date New Patient Questionnaire Name: Birth Date: / / Home Phone: Address: Cell Phone: Work Phone: Occupation: Employer: Marital Status: Married Living w/ Partner
Scrub In. Lymphocytes are a type of what?
 Scrub In Lymphocytes are a type of what? a. WBC s b. RBC s c. Thrombocytes d. Plasma The nurse received an injection for immediate immunity following exposure to a patient with an infectious disease. What
Scrub In Lymphocytes are a type of what? a. WBC s b. RBC s c. Thrombocytes d. Plasma The nurse received an injection for immediate immunity following exposure to a patient with an infectious disease. What
Cancer Treatment: Radiation. Combination of treatments: ü
 Combination of treatments: ü Cancer Treatment: External radiation: The radiation comes from a large machine outside the body. Radiation ü Internal radiation (implant radiation or brachytherapy): The radiation
Combination of treatments: ü Cancer Treatment: External radiation: The radiation comes from a large machine outside the body. Radiation ü Internal radiation (implant radiation or brachytherapy): The radiation
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases that are characterized by uncontrolled cellular growth,
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases that are characterized by uncontrolled cellular growth,
*
 Introduction Cancer is complex, can have many possible causes, and is increasingly common. For the U.S. population, 1 in 2 males and 1 in 3 females is at risk of developing cancer in their lifetime. The
Introduction Cancer is complex, can have many possible causes, and is increasingly common. For the U.S. population, 1 in 2 males and 1 in 3 females is at risk of developing cancer in their lifetime. The
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
American Society of Clinical Oncology PATIENT EDUCATION MATERIALS CATALOG.
 American Society of Clinical Oncology PATIENT EDUCATION MATERIALS CATALOG www.cancer.net www.cancer.net Tell your patients about the doctor-approved PATIENT INFORMATION WEBSITE FROM ASCO Cancer.Net brings
American Society of Clinical Oncology PATIENT EDUCATION MATERIALS CATALOG www.cancer.net www.cancer.net Tell your patients about the doctor-approved PATIENT INFORMATION WEBSITE FROM ASCO Cancer.Net brings
For the Patient: Cyclosporine injection Other names: SANDIMMUNE I.V.
 For the Patient: Cyclosporine injection Other names: SANDIMMUNE I.V. Cyclosporine (sye kloe spor een) is a drug that may be used to treat certain types of cancer. It may also be used to suppress your immune
For the Patient: Cyclosporine injection Other names: SANDIMMUNE I.V. Cyclosporine (sye kloe spor een) is a drug that may be used to treat certain types of cancer. It may also be used to suppress your immune
DR. RAMESH U2 L4 MITOSIS AND CANCER
 DR. RAMESH U2 L4 MITOSIS AND CANCER Objective! The student will (TSW) identify the relationship between cancer and mitosis. Benchmark/Standard LS-H-B2: Compare mitosis and meiosis Why are we learning this?!
DR. RAMESH U2 L4 MITOSIS AND CANCER Objective! The student will (TSW) identify the relationship between cancer and mitosis. Benchmark/Standard LS-H-B2: Compare mitosis and meiosis Why are we learning this?!
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Name: Date: Referring Provider: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary).
 Name: Date: Referring Provider: Age: D.O.B. Race/ ethnicity: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary). We are interested in learning
Name: Date: Referring Provider: Age: D.O.B. Race/ ethnicity: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical problem (use the other side if necessary). We are interested in learning
Published on The Well Project ( Home > Cancers. Cancers [1] Submitted on Jul 9, 2017
![Published on The Well Project ( Home > Cancers. Cancers [1] Submitted on Jul 9, 2017 Published on The Well Project ( Home > Cancers. Cancers [1] Submitted on Jul 9, 2017](/thumbs/85/92441827.jpg) Published on The Well Project (https://www.thewellproject.org) Home > Cancers Cancers [1] Submitted on Jul 9, 2017 Table of Contents What Is Cancer? Kaposi's Sarcoma (KS) Lymphoma Cervical Cancer Anal
Published on The Well Project (https://www.thewellproject.org) Home > Cancers Cancers [1] Submitted on Jul 9, 2017 Table of Contents What Is Cancer? Kaposi's Sarcoma (KS) Lymphoma Cervical Cancer Anal
Lecture 2. [Pathophysiology]
![Lecture 2. [Pathophysiology] Lecture 2. [Pathophysiology]](/thumbs/83/88432253.jpg) II. Rate of Growth Most benign tumors grow slowly, and most cancers (malignant tumors) grow much faster. However, there are some exceptions to this generalization e.g., the rate of growth of leiomyomas
II. Rate of Growth Most benign tumors grow slowly, and most cancers (malignant tumors) grow much faster. However, there are some exceptions to this generalization e.g., the rate of growth of leiomyomas
What is Liver Cancer? About the Liver
 Your liver is important and it has many functions. The top three are that it cleans your blood of toxins, gives you energy and produces bile for digestion. What is Liver Cancer? Cancer starts when cells
Your liver is important and it has many functions. The top three are that it cleans your blood of toxins, gives you energy and produces bile for digestion. What is Liver Cancer? Cancer starts when cells
number Done by Corrected by Doctor مها شوماف
 number 15 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Waseem Alhaj Doctor مها شوماف 1 P a g e Epidemiology Epidemiology is the study of the incidence of a disease. It can give us information about the possible causes
number 15 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Waseem Alhaj Doctor مها شوماف 1 P a g e Epidemiology Epidemiology is the study of the incidence of a disease. It can give us information about the possible causes
Wellness Along the Cancer Journey: Health Habits and Cancer Screening Revised October 20, 2015
 Wellness Along the Cancer Journey: Health Habits and Cancer Screening Revised October 20, 2015 Healthy Habits and Cancer Screening Rev. 10.20.15 Page 164 WELLNESS ALONG THE CANCER JOURNEY: HEALTHY HABITS
Wellness Along the Cancer Journey: Health Habits and Cancer Screening Revised October 20, 2015 Healthy Habits and Cancer Screening Rev. 10.20.15 Page 164 WELLNESS ALONG THE CANCER JOURNEY: HEALTHY HABITS
Health Questionnaire
 Patient Name Date of Birth Thank you for choosing Southern Cancer Center for your care. To help us best prepare for your appointment, please complete this form and bring it to your appointment. If you
Patient Name Date of Birth Thank you for choosing Southern Cancer Center for your care. To help us best prepare for your appointment, please complete this form and bring it to your appointment. If you
41a Pathology: Reproductive System
 41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Cancer, Massage, and the Myth of Metastasis Why Skilled Massage Won t Spread Cancer
 Cancer, Massage, and the Myth of Metastasis Why Skilled Massage Won t Spread Cancer Prep for 4-Day Intensive, Oncology Massage Therapy With Tracy Walton & Associates, LLC Were you Taught that Massage Could
Cancer, Massage, and the Myth of Metastasis Why Skilled Massage Won t Spread Cancer Prep for 4-Day Intensive, Oncology Massage Therapy With Tracy Walton & Associates, LLC Were you Taught that Massage Could
AllinaHealthSystems 1
 Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Cancer Causes Preventions Treatments Presentation By Dr. Bhavani Nair. MBBS;DGO;FRCP(C) Retired Radiation Oncologist University of Ottawa
 Cancer Causes Preventions Treatments Presentation By Dr. Bhavani Nair. MBBS;DGO;FRCP(C) Retired Radiation Oncologist University of Ottawa In Ontario, someone is diagnosed with cancer every eight minutes
Cancer Causes Preventions Treatments Presentation By Dr. Bhavani Nair. MBBS;DGO;FRCP(C) Retired Radiation Oncologist University of Ottawa In Ontario, someone is diagnosed with cancer every eight minutes
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Wellness Along the Cancer Journey: Cancer Types Revised October 2015 Chapter 1: Module Overview
 Wellness Along the Cancer Journey: Cancer Types Revised October 2015 Chapter 1: Module Overview Cancer Types Rev. 10.20.15 Page 5 Module Overview Cancer is the leading cause of death among American Indians
Wellness Along the Cancer Journey: Cancer Types Revised October 2015 Chapter 1: Module Overview Cancer Types Rev. 10.20.15 Page 5 Module Overview Cancer is the leading cause of death among American Indians
MEDICAL DATA SHEET For Patients 18 years of age and older
 MEDICAL DATA SHEET For Patients 18 years of age and older NAME: DATE: / / AGE: DOB: / / 1. What is the main reason you are seeking a physician s advice? 2. Please list all allergies: Drug Allergies: Other
MEDICAL DATA SHEET For Patients 18 years of age and older NAME: DATE: / / AGE: DOB: / / 1. What is the main reason you are seeking a physician s advice? 2. Please list all allergies: Drug Allergies: Other
Introduction to Basic Oncology
 Introduction to Basic Oncology Cancer Cell AHS 102 Med Term Dr. Susie Turner 1/3/13 General Oncology Study of Tumors Neoplasms/Tumors Abnormal growth of new tissue Are either; Benign or Malignant Onc/o
Introduction to Basic Oncology Cancer Cell AHS 102 Med Term Dr. Susie Turner 1/3/13 General Oncology Study of Tumors Neoplasms/Tumors Abnormal growth of new tissue Are either; Benign or Malignant Onc/o
Cancer Key facts The problem Cancer causes
 Cancer Key facts Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 7.6 million deaths (around 13% of all deaths) in 2008 (1). Lung, stomach, liver, colon and breast cancer cause the most cancer
Cancer Key facts Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 7.6 million deaths (around 13% of all deaths) in 2008 (1). Lung, stomach, liver, colon and breast cancer cause the most cancer
Liver Cancer And Tumours
 Liver Cancer And Tumours What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood from all parts of the body, cancer cells from elsewhere can
Liver Cancer And Tumours What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood from all parts of the body, cancer cells from elsewhere can
The table below presents the summary of observed geographic variation for incidence and survival by type of cancer and gender.
 Results and Maps Overview When disparities in cancer incidence and survival are evident, there are a number of potential explanations, including but not restricted to differences in environmental risk
Results and Maps Overview When disparities in cancer incidence and survival are evident, there are a number of potential explanations, including but not restricted to differences in environmental risk
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Tumour Structure and Nomenclature. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 Tumour Structure and Nomenclature Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Malignant Metastasis Core idea of cancer Normal Cell Slightly
Tumour Structure and Nomenclature Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Malignant Metastasis Core idea of cancer Normal Cell Slightly
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Viruses and cancer: Should we be more afraid?
 Viruses and cancer: Should we be more afraid? Viruses and cancer: Should we be more afraid? During the past 30 years it has become exceedingly clear that several viruses play significant roles in the development
Viruses and cancer: Should we be more afraid? Viruses and cancer: Should we be more afraid? During the past 30 years it has become exceedingly clear that several viruses play significant roles in the development
Address Street Address City State Zip Code. Address Street Address City State Zip Code
 Male Initial Visit Intake Form PATIENT INFORMATION Today s Date Last Name Mid Initial First Name Date of Birth Address Home Phone Social Security Number Street Address City State Zip Code Cell Phone E-mail
Male Initial Visit Intake Form PATIENT INFORMATION Today s Date Last Name Mid Initial First Name Date of Birth Address Home Phone Social Security Number Street Address City State Zip Code Cell Phone E-mail
This information explains the advice about suspected cancer that is set out in NICE guideline NG12.
 Recognising, investigating and referring people with symptoms of suspected cancer Information for the public Published: 25 June 2015 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on
Recognising, investigating and referring people with symptoms of suspected cancer Information for the public Published: 25 June 2015 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on
New Patient Information Form
 New Patient Information Form Patient Label Dear Patient: Please take a few minutes to complete this form. Your answers will help the doctors and staff plan and provide your care. If you are unsure of any
New Patient Information Form Patient Label Dear Patient: Please take a few minutes to complete this form. Your answers will help the doctors and staff plan and provide your care. If you are unsure of any
PATIENT HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE Radiation Oncology
 REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Yes No Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: Yes No If YES, please list medication allergies:
REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Yes No Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: Yes No If YES, please list medication allergies:
PATIENT HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE Radiation Oncology
 REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: If YES, please list medication allergies: Do you have
REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: If YES, please list medication allergies: Do you have
