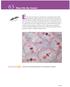
Q1.Figure 1 shows photographs of some animal cells at different stages during the cell cycle. Figure 1
|
|
|
- Kristina Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q1.Figure 1 shows photographs of some animal cells at different stages during the cell cycle. Figure 1 A Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images B Ed Reschke/Oxford Scientific/Getty Images C Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a) Which photograph in Figure 1 shows a cell that is not going through mitosis? Tick one box. A B C Page 2
2 (b) Describe what is happening in photograph A (c) A student wanted to find out more about the cell cycle. The student made a slide of an onion root tip. She counted the number of cells in each stage of the cell cycle in one field of view. The table below shows the results. Stages in the cell cycle Non-dividing cells Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Total Number of cell s Each stage of the cell cycle takes a different amount of time. Which stage is the fastest in the cell cycle? Give a reason for your answer. Stage... Reason... (d) The cell cycle in an onion root tip cell takes 16 hours. Page 3
3 Calculate the length of time Stage 2 lasts in a typical cell. Give your answer to 2 significant figures Time in Stage 2 =... minutes (3) (e) Bacteria such as Escherichia coli undergo cell division similar to mitosis. Figure 2 shows a growth curve for E. coli grown in a nutrient broth. Figure 2 What type of cell division causes the change in number of E. coli cells at P?... Page 4
4 (f) Suggest why the number of cells levels out at Q (Total 11 marks) Page 5
5 Q2. The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth. (a) Name the two types of cell division, A and B, shown in the diagram. Type A... Type B... (b) Name the process in which an egg and sperm join together (c) Cell 1 contains 46 chromosomes. How many chromosomes will there be in: Page 6
6 (i) cell 10;... (ii) cell 14?... (Total 5 marks) Page 7
7 Q3. The diagram shows how an immature egg could be used either to produce cells to treat some human diseases or to produce a baby. Scientists may be allowed to use this technique to produce cells to treat some human diseases, but not to produce babies. Using information from the diagram, suggest an explanation for this (Total 4 marks) Page 8
8 Q4. Meiosis and mitosis are different types of division in human cells. Compare the two processes by referring to where each takes place and the kind of products that are made (Total 6 marks) Page 9
9 Q5. The table shows the number of chromosomes found in each body cell of some different organisms. Animals Species Number of chromosomes in each body cell Plants Species Number of chromosomes in each body cell Fruit fly 8 Tomato 24 Goat 60 Potato 44 Human 46 Rice 24 (a) Nearly every organism on earth has an even number of chromosomes in its body cells. Suggest why (b) Chromosomes contain DNA molecules. Describe the function of DNA (c) Gametes are made in the testes by meiosis. (i) Look at the diagrams. Page 10
10 Which diagram, A, B, C or D, represents how cell division by meiosis produces gametes in the testes? (ii) How many chromosomes will each goat gamete contain? (d) Body cells divide by mitosis. (i) Why is the ability of body cells to divide important? Page 11
11 (ii) When a body cell of a potato plant divides, how many chromosomes will each of the new cells contain? (Total 7 marks) Page 12
12 Q6. Read the information about stem cells. Stem cells are used to treat some human diseases. Stem cells can be collected from early embryos. These stem cells have not begun to differentiate, so they could be used to produce any kind of cell, tissue or organ. The use of embryonic stem cells to treat human diseases is new and, for some diseases, trials on patients are happening now. Stem cells can also be collected from adult bone marrow. The operation is simple but may be painful. Stem cells in bone marrow mainly differentiate to form blood cells. These stem cells have been used successfully for many years to treat some kinds of blood disease. Recently there have been trials of other types of stem cell from bone marrow. These stem cells are used to treat diseases such as heart disease. Evaluate the use of stem cells from embryos or from adult bone marrow for treating human diseases. You should give a conclusion to your evaluation (5) (Total 5 marks) Page 13
13 Q7.The photographs show the flowers of two closely-related species of plant. Species A Species B Images: istock/thinkstock The drawings show chromosomes from one cell in the root of each plant during cell division. Species A Species B One chromosome One chromosome (a) The drawings show that each chromosome has two strands of genetic material. (i) How does a chromosome become two strands? (ii) Explain why each chromosome must become two strands before the cell divides. Page 14
14 (b) For sexual reproduction, the plants produce gametes. (i) Name the type of cell division that produces gametes.... (ii) How many chromosomes would there be in a gamete from each of these two plant species? Species A Species B (iii) It is possible for gametes from Species A to combine with gametes from Species B to produce healthy offspring plants. How many chromosomes would there be in each cell of one of the offspring plants? (c) (i) Look back at the information at the start of the question and the information from part (b). What evidence from these two pieces of information supports the belief that Species A and Species B evolved from a common ancestor? Page 15
15 (ii) For successful gamete production to take place, chromosomes that contain the same genes must pair up. The drawings showing the chromosomes of Species A and of Species B are repeated below. Species A Species B The offspring plants cannot reproduce sexually. Suggest an explanation for this. (Total 10 marks) Page 16
16 Q8.CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family. (a) CADASIL is caused by a dominant allele. (i) What is a dominant allele? (ii) What is the evidence in the diagram that CADASIL is caused by a dominant allele? (iii) Person 7 has CADASIL. Is person 7 homozygous or heterozygous for the CADASIL allele? Give evidence for your answer from the diagram. Page 17
17 (b) Persons 7 and 8 are planning to have another baby. Use a genetic diagram to find the probability that the new baby will develop into a person with CADASIL. Use the following symbols to represent alleles. D = allele for CADASIL d = allele for not having CADASIL Probability =... (4) (c) Scientists are trying to develop a treatment for CADASIL using stem cells. Specially treated stem cells would be injected into the damaged part of the brain. (i) Why do the scientists use stem cells? (ii) Embryonic stem cells can be obtained by removing a few cells from a human embryo. In 2006, scientists in Japan discovered how to change adult skin cells into stem cells. Suggest one advantage of using stem cells from adult skin cells. (Total 10 marks) Page 18
Q1. The photograph shows some cells in the root of an onion plant. By UAF Center for Distance Education [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr
![Q1. The photograph shows some cells in the root of an onion plant. By UAF Center for Distance Education [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr Q1. The photograph shows some cells in the root of an onion plant. By UAF Center for Distance Education [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr](/thumbs/89/99791547.jpg) MITOSIS. STEM CELLS. Thornton College NAME. Q. The photograph shows some cells in the root of an onion plant. By UAF Center for Distance Education [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr (a) Cells X and Y have just been
MITOSIS. STEM CELLS. Thornton College NAME. Q. The photograph shows some cells in the root of an onion plant. By UAF Center for Distance Education [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr (a) Cells X and Y have just been
CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain.
 REPRODUCTION PART II Q1. CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family.
REPRODUCTION PART II Q1. CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family.
Page 2. Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1. Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C
 Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
Unit B2, B2.7. Cell division and inheritance. Stage 1. Ovary. Cell Q. Cell P. Cell R. Cell S. 7 Embryo A B C
 Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 1
 Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 56 minutes 56 marks Page of 25 Q. People have different shaped ear lobes, either hanging or attached. The diagrams show the two shapes of ear lobe. A gene controls
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 56 minutes 56 marks Page of 25 Q. People have different shaped ear lobes, either hanging or attached. The diagrams show the two shapes of ear lobe. A gene controls
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. A B C D ... (1) ... (1)
 1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7
 Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
(i) List these events in the correct order, starting with D.... (1)... (1)... (1)
 Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye
 Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye colour or hair colour Gregor Mendel discovered how traits
Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye colour or hair colour Gregor Mendel discovered how traits
REPRODUCTION. NAME.. Page 1. Q1.Figure 1 shows the stages in the transmission of the malaria parasite by mosquitoes to humans.
 REPRODUCTION. Thornton College NAME.. Q.Figure shows the stages in the transmission of the malaria parasite by mosquitoes to humans. Figure (a) Where in the mosquito does Stage 2 happen? Draw a ring around
REPRODUCTION. Thornton College NAME.. Q.Figure shows the stages in the transmission of the malaria parasite by mosquitoes to humans. Figure (a) Where in the mosquito does Stage 2 happen? Draw a ring around
Cell Division Questions. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS:
 Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
Push down hard on the cover slip, but do not push the cover slip sideways
 Q1.A student investigated mitosis in the tissue from an onion root tip. (a) The student prepared a temporary mount of the onion tissue on a glass slide. She covered the tissue with a cover slip. She was
Q1.A student investigated mitosis in the tissue from an onion root tip. (a) The student prepared a temporary mount of the onion tissue on a glass slide. She covered the tissue with a cover slip. She was
4-6 Inheritance Biology
 4-6 Inheritance Biology.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Circle one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
4-6 Inheritance Biology.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Circle one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next.
 Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction?
 1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction - Genetic information from two cells is combined to produce a new genetically unique organism. Sexual reproduction occurs when
1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction - Genetic information from two cells is combined to produce a new genetically unique organism. Sexual reproduction occurs when
3.1 Meiosis
 3.1 Meiosis Chromosome Number Individuals of the same species have the same number of chromosomes. Meiosis is used to half the number of chromosomes passed to the offspring. What is meiosis Meiosis happens
3.1 Meiosis Chromosome Number Individuals of the same species have the same number of chromosomes. Meiosis is used to half the number of chromosomes passed to the offspring. What is meiosis Meiosis happens
Gregor Mendel. What is Genetics? the study of heredity
 Gregor Mendel What is Genetics? the study of heredity Gregor Mendel s Peas Pollen: plant s sperm Egg Cells: plants reproductive cells Fertilization: joining of pollen + egg cells develops into embryo in
Gregor Mendel What is Genetics? the study of heredity Gregor Mendel s Peas Pollen: plant s sperm Egg Cells: plants reproductive cells Fertilization: joining of pollen + egg cells develops into embryo in
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 4734-1 - Page 1 Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to the viruses stimulating cellular digestion mitotic
Name: 4734-1 - Page 1 Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to the viruses stimulating cellular digestion mitotic
The Experiments of Gregor Mendel
 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Every living thing (plant or animal, microbe or human being) has a set of characteristics inherited from
11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Every living thing (plant or animal, microbe or human being) has a set of characteristics inherited from
4-6 Inheritance Trilogy
 4-6 Inheritance Trilogy.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Choose one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
4-6 Inheritance Trilogy.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Choose one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]
![EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]](/thumbs/87/96059079.jpg) EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents.
 Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
2. Was there a scientific way to predict the outcome of a cross between two parents?
 Name Date Period Heredity WebQuest DNA from the Beginning Mendelian Genetics Go to http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Children resemble their parents Read the text and answer the following
Name Date Period Heredity WebQuest DNA from the Beginning Mendelian Genetics Go to http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Children resemble their parents Read the text and answer the following
VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous chromosome sexual reproduction meiosis
 SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
How do living things Sexually Reproduce?
 How do living things Sexually Reproduce? Besides animals, what other things reproduce sexually? Think of a family that has both biological parents and has 2 or more children #1 Consider what the parents
How do living things Sexually Reproduce? Besides animals, what other things reproduce sexually? Think of a family that has both biological parents and has 2 or more children #1 Consider what the parents
Unit 4 - Reproduction
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually? A) mutation B) replication C) meiosis D) mitosis 2. Which sequence represents the
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually? A) mutation B) replication C) meiosis D) mitosis 2. Which sequence represents the
St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College
 St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College Year 12 Pre Course Tasks: BIOLOGY Student Name GCSE science grade Mark /127 Percentage % This booklet contains 15 GCSE examination questions
St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College Year 12 Pre Course Tasks: BIOLOGY Student Name GCSE science grade Mark /127 Percentage % This booklet contains 15 GCSE examination questions
Unit 11 Test: Genetics Date: /Period:
 Name: 1. Compared to human cells resulting from mitotic cell division, human cells resulting from meiotic cell division would have A) twice as many chromosomes B) the same number of chromosomes C) one-half
Name: 1. Compared to human cells resulting from mitotic cell division, human cells resulting from meiotic cell division would have A) twice as many chromosomes B) the same number of chromosomes C) one-half
TEST NAME:review TEST ID: GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:review TEST ID:1070005 GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom review Page 1 of 18 Student: Class: Date: 1. There are four blood types: A, B, AB,
TEST NAME:review TEST ID:1070005 GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom review Page 1 of 18 Student: Class: Date: 1. There are four blood types: A, B, AB,
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits.
 Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA:
Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA:
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1
 Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
Meiosis. 4. There are multiple alleles for the ABO blood group. Why are there only two of these alleles normally present in any one individual?
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram shown represents a cell that will undergo mitosis. Which diagrams below best illustrate the nuclei of the daughter cells that result from a normal mitotic cell division of the
Name: ate: 1. The diagram shown represents a cell that will undergo mitosis. Which diagrams below best illustrate the nuclei of the daughter cells that result from a normal mitotic cell division of the
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
14.1 Human Chromosomes pg
 14.1 Human Chromosomes pg. 392-397 Lesson Objectives Identify the types of human chromosomes in a karotype. Describe the patterns of the inheritance of human traits. Explain how pedigrees are used to study
14.1 Human Chromosomes pg. 392-397 Lesson Objectives Identify the types of human chromosomes in a karotype. Describe the patterns of the inheritance of human traits. Explain how pedigrees are used to study
A man is albino. His wife is heterozygous for the melanin-producing allele. The fertilised egg cell produced by the couple divides to form two cells.
 REPRODUCTION PART 4 Q1. The black pigment in human skin and eyes is called melanin. Production of melanin is controlled by a single pair of genes. A person who is homozygous for a recessive allele of the
REPRODUCTION PART 4 Q1. The black pigment in human skin and eyes is called melanin. Production of melanin is controlled by a single pair of genes. A person who is homozygous for a recessive allele of the
Individual Feedback Report for: St#: Test: GENETICS UNIT TEST 2score Grade: 3 Score: % (20.00 of 35.00)
 Individual Feedback Report for: St#: 703709 Test: GENETICS UNIT TEST 2score Grade: 3 Score: 57.14 % (20.00 of 35.00) 26. T F The cell wall controls the transfer of nutrients into animal cells. 27. Mitosis
Individual Feedback Report for: St#: 703709 Test: GENETICS UNIT TEST 2score Grade: 3 Score: 57.14 % (20.00 of 35.00) 26. T F The cell wall controls the transfer of nutrients into animal cells. 27. Mitosis
You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism.
 Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS
 REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS TEKS 7.14A Define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next generation 7.14B Compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring from sexual
REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS TEKS 7.14A Define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next generation 7.14B Compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring from sexual
Genetics Unit Outcomes
 Genetics Unit Outcomes In the cell division unit, you learned that chromosomes come in pairs and that humans have 46 chromosomes in each of their body cells. You receive one of each chromosome from dad
Genetics Unit Outcomes In the cell division unit, you learned that chromosomes come in pairs and that humans have 46 chromosomes in each of their body cells. You receive one of each chromosome from dad
Darwin s dilemma 8/14/2014. Meiosis & Inheritance Lecture 18 Summer Mitosis & Meiosis. The Modern Synthesis
 Darwin s dilemma 1 Meiosis & Inheritance Lecture 18 Summer 2014 How do organisms pass heritable traits to their offspring? The Modern Synthesis 2 Mitosis & Meiosis 3 1844 - Darwin essay on Natural Selection
Darwin s dilemma 1 Meiosis & Inheritance Lecture 18 Summer 2014 How do organisms pass heritable traits to their offspring? The Modern Synthesis 2 Mitosis & Meiosis 3 1844 - Darwin essay on Natural Selection
Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked.
 AQA GCSE Biology H SET A Paper 2 Higher Tier Author: Mike Smith Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Information Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Answer all questions
AQA GCSE Biology H SET A Paper 2 Higher Tier Author: Mike Smith Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Information Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Answer all questions
Gallery Walk. Fundamentals of Genetics
 Gallery Walk Fundamentals of Genetics Question 1 Hitchhiker's thumb (H) is dominant to no hitchhiker's thumb (h). A woman who does not have hitchhiker's thumb marries a man who is heterozygous for hitchhiker's
Gallery Walk Fundamentals of Genetics Question 1 Hitchhiker's thumb (H) is dominant to no hitchhiker's thumb (h). A woman who does not have hitchhiker's thumb marries a man who is heterozygous for hitchhiker's
The Work of Gregor Mendel. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Work of Gregor Mendel
 Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel GENETICS Genetics: The scientific study of heredity Genetics is the key to understanding what makes each organism unique. THINK ABOUT IT What is an inheritance?
Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel GENETICS Genetics: The scientific study of heredity Genetics is the key to understanding what makes each organism unique. THINK ABOUT IT What is an inheritance?
Genetics. Genetics. True or False. Genetics Vocabulary. Chapter 5. Objectives. Heredity
 Genetics True or False Genes are things you wear on your legs. A priest raising peas in his garden was one of the first to discover how genetics works. Plants can be purebred just like dogs. Dominate alleles
Genetics True or False Genes are things you wear on your legs. A priest raising peas in his garden was one of the first to discover how genetics works. Plants can be purebred just like dogs. Dominate alleles
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel
 THINK ABOUT IT What is an inheritance? Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel It is something we each receive from our parents a contribution that determines our blood type, the color of our hair,
THINK ABOUT IT What is an inheritance? Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel It is something we each receive from our parents a contribution that determines our blood type, the color of our hair,
Lesson Overview. The Work of Gregor Mendel. Lesson Overview The Work of Gregor Mendel
 Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Where does an organism get its unique characteristics? An individual s characteristics are determined by factors that are
Lesson Overview 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Where does an organism get its unique characteristics? An individual s characteristics are determined by factors that are
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages
 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
biology Slide 1 of 32
 biology 1 of 32 11-1 The Work of Gregor 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel Mendel 2 of 32 Gregor Mendel s Peas Gregor Mendel s Peas Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian
biology 1 of 32 11-1 The Work of Gregor 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel Mendel 2 of 32 Gregor Mendel s Peas Gregor Mendel s Peas Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 3 (LEARNER NOTES)
 TOPIC 1: MENDEL S 1 ST LAW, SEX AND BLOOD GROUP DETERMINATION Learner Note: Mendel s Laws are very important and you must understand the basic concepts of Genetics. You must understand the concepts of
TOPIC 1: MENDEL S 1 ST LAW, SEX AND BLOOD GROUP DETERMINATION Learner Note: Mendel s Laws are very important and you must understand the basic concepts of Genetics. You must understand the concepts of
Genetics & Heredity 11/16/2017
 Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
c. Relate Mendelian principles to modern-day practice of plant and animal breeding.
 Course: Biology Agricultural Science & Technology Unit: Genetics in Agriculture STATE STANDARD IV: Students will understand that genetic information coded in DNA is passed from parents to offspring by
Course: Biology Agricultural Science & Technology Unit: Genetics in Agriculture STATE STANDARD IV: Students will understand that genetic information coded in DNA is passed from parents to offspring by
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel
 Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
2017 Version. Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948
 2017 Version Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Linking DNA, Alleles and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. DNA is a large molecule that is coiled into a double helix
2017 Version Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Linking DNA, Alleles and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. DNA is a large molecule that is coiled into a double helix
Asexual Reproduction
 Asexual Reproduction Only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. The offspring inherits all of its traits from one parent. Therefore, the
Asexual Reproduction Only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. The offspring inherits all of its traits from one parent. Therefore, the
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares
 Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Notes: Mendelian Genetics
 Notes: Mendelian Genetics Heredity is passing characteristics from one generation to the next. Genetics is the study of heredity. Who was Gregor Mendel? Gregor Mendel is the Father of Modern Genetics.
Notes: Mendelian Genetics Heredity is passing characteristics from one generation to the next. Genetics is the study of heredity. Who was Gregor Mendel? Gregor Mendel is the Father of Modern Genetics.
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment. Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment Student name: Author: Megan Kitchens School: SHAW HIGH SCHOOL Printed: Monday January 30, 2017 1 In fruit flies, the gray body color (G) is dominant
Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment Student name: Author: Megan Kitchens School: SHAW HIGH SCHOOL Printed: Monday January 30, 2017 1 In fruit flies, the gray body color (G) is dominant
Collated questions Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to genetic variation DNA STRUCTURE
 Collated questions Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to genetic variation DNA STRUCTURE THE ROLE OF DNA IN INHERITANCE (2013:2) Use the diagram above to help you explain the relationship
Collated questions Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to genetic variation DNA STRUCTURE THE ROLE OF DNA IN INHERITANCE (2013:2) Use the diagram above to help you explain the relationship
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity
 Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Genetics Review. Alleles. The Punnett Square. Genotype and Phenotype. Codominance. Incomplete Dominance
 Genetics Review Alleles These two different versions of gene A create a condition known as heterozygous. Only the dominant allele (A) will be expressed. When both chromosomes have identical copies of the
Genetics Review Alleles These two different versions of gene A create a condition known as heterozygous. Only the dominant allele (A) will be expressed. When both chromosomes have identical copies of the
2. Circle the genotypes in the table that are homozygous. Explain how the two different homozygous genotypes result in different phenotypes.
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Lesson Overview 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles
 THINK ABOUT IT Nothing in life is certain. Lesson Overview 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles If a parent carries two different alleles for a certain gene, we can t be sure which of those alleles will be
THINK ABOUT IT Nothing in life is certain. Lesson Overview 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles If a parent carries two different alleles for a certain gene, we can t be sure which of those alleles will be
HEREDITY BASKETBALL CHALLENGE!!!! WHO IS UP FOR A LITTLE COMPETITION!!??!?
 October 18, 2013 HEREDITY BASKETBALL CHALLENGE!!!! WHO IS UP FOR A LITTLE COMPETITION!!??!? James Brady Instructions for Editing Create a new Text box for the answer to the question. Click the basketball
October 18, 2013 HEREDITY BASKETBALL CHALLENGE!!!! WHO IS UP FOR A LITTLE COMPETITION!!??!? James Brady Instructions for Editing Create a new Text box for the answer to the question. Click the basketball
Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes. Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Reproduction and Heredity
 Reproduction and Heredity Pretest Edit File Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. One trait that differs in pea plants involves the placement of the flowers. In some plants, flowers grow along the stem
Reproduction and Heredity Pretest Edit File Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. One trait that differs in pea plants involves the placement of the flowers. In some plants, flowers grow along the stem
Chapter 12 Multiple Choice
 Chapter 12 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Gregor Mendel do to study different characteristics in his genetics experiments? a.
Chapter 12 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Gregor Mendel do to study different characteristics in his genetics experiments? a.
Patterns of Inheritance
 1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
GCSE Biology Flying Start
 GCSE Biology Flying Start 1. Figure 1 shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure 1 Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D 1.1 Into
GCSE Biology Flying Start 1. Figure 1 shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure 1 Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D 1.1 Into
Normal enzyme makes melanin (dark pigment in skin and hair) Defective enzyme does not make melanin
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Guided Reading and Study. Definition a. The scientific study of heredity. b. Physical characteristics
 Genetics: The Science of Heredity Mendel's Work Guided Reading and Study This section describes how Gregor Mendel identified the method by which characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring.
Genetics: The Science of Heredity Mendel's Work Guided Reading and Study This section describes how Gregor Mendel identified the method by which characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring.
3.0 DNA is the Inherited Material Responsible for Variation
 2.2 Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Homework: p. 29 #1-3 p. 36 #1-6 Create a table that looks like this: Read pages 35-36 and fill in your table. Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Advantages Disadvantages
2.2 Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Homework: p. 29 #1-3 p. 36 #1-6 Create a table that looks like this: Read pages 35-36 and fill in your table. Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Advantages Disadvantages
Name Class Date. Review Guide. Genetics. The fundamental principles of genetics were first discovered by. What type of plant did he breed?.
 Name Class Date Review Guide Genetics The fundamental principles of genetics were first discovered by. What type of plant did he breed?. True-breeding parental plants are called the generation. Their hybrid
Name Class Date Review Guide Genetics The fundamental principles of genetics were first discovered by. What type of plant did he breed?. True-breeding parental plants are called the generation. Their hybrid
The Living Environment
 Name: Class: 1. Asexual reproduction primarily involves the process of 1) pollination 3) spermatogenesis 2) mitosis 4) ovulation The Living Environment Ms. Fazio Base your answers to questions 4 and 5
Name: Class: 1. Asexual reproduction primarily involves the process of 1) pollination 3) spermatogenesis 2) mitosis 4) ovulation The Living Environment Ms. Fazio Base your answers to questions 4 and 5
biology Slide 1 of 32 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 32 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel 2 of 32 Gregor Mendel s Peas Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk. His work was important to the understanding
biology 1 of 32 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel 2 of 32 Gregor Mendel s Peas Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk. His work was important to the understanding
Mrs. Fanek Asexual/Sexual Reproduction Date
 Name Period Mrs. Fanek Asexual/Sexual Reproduction Date 1. An organism that reproduces asexually will have offspring that have A) the same as both of its parents B) different from either of its parents
Name Period Mrs. Fanek Asexual/Sexual Reproduction Date 1. An organism that reproduces asexually will have offspring that have A) the same as both of its parents B) different from either of its parents
Mendelian Genetics. Activity. Part I: Introduction. Instructions
 Activity Part I: Introduction Some of your traits are inherited and cannot be changed, while others can be influenced by the environment around you. There has been ongoing research in the causes of cancer.
Activity Part I: Introduction Some of your traits are inherited and cannot be changed, while others can be influenced by the environment around you. There has been ongoing research in the causes of cancer.
Sexual Reproduction & Inheritance
 Sexual Reproduction & Sexual Reproduction & Overview Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Meiosis Genetic Diversity Mendel & The Laws of Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes
Sexual Reproduction & Sexual Reproduction & Overview Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Meiosis Genetic Diversity Mendel & The Laws of Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes
In the mid-20th century the structure of DNA was discovered. What is a section of DNA which codes for one specific protein called?
 Q1.Our understanding of genetics and inheritance has improved due to the work of many scientists. (a) Draw one line from each scientist to the description of their significant work. Scientist Description
Q1.Our understanding of genetics and inheritance has improved due to the work of many scientists. (a) Draw one line from each scientist to the description of their significant work. Scientist Description
Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs:
 Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs: Which of these adult bears do you think is most likely to be the parent of the bear cubs shown in the photograph on the right? How did you
Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs: Which of these adult bears do you think is most likely to be the parent of the bear cubs shown in the photograph on the right? How did you
Science 10- Course Review Unit 2-Biology
 Science 10 Science 10- Course Review Unit 2-Biology The Science 10 Biology Unit covers: Chapter 14-The Microscope Chapter 15-The Cell Chapter 16-Reproduction Chapter 17-Heredity Name Date Date due You
Science 10 Science 10- Course Review Unit 2-Biology The Science 10 Biology Unit covers: Chapter 14-The Microscope Chapter 15-The Cell Chapter 16-Reproduction Chapter 17-Heredity Name Date Date due You
Unit 1 Biological Diversity Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15
 Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15 Variation to the MAX! Biologists have identified over species of animals and over species of plants. The most successful life form is What is Biodiversity? The
Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15 Variation to the MAX! Biologists have identified over species of animals and over species of plants. The most successful life form is What is Biodiversity? The
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s,
 63 Show Me the Genes! The History of the Germ Theory of Disease Activity 37 r e a d i n g Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male
63 Show Me the Genes! The History of the Germ Theory of Disease Activity 37 r e a d i n g Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male
Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses:
 Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses: 2.5 Genetics Objectives 2.5.6 Genetic Inheritance 2.5.10.H Origin of the Science of genetics 2.5.11 H Law of segregation 2.5.12 H Law of independent assortment 2.5.13.H Dihybrid
Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses: 2.5 Genetics Objectives 2.5.6 Genetic Inheritance 2.5.10.H Origin of the Science of genetics 2.5.11 H Law of segregation 2.5.12 H Law of independent assortment 2.5.13.H Dihybrid
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis. (Sections 11-3,11-4;)
 MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
Genetics Practice Questions
 Name: ate: 1. If Jessica has light eyes (bb) and both of her parents have dark eyes (b) which statement is true?. Jessica inherited both genes from her father.. Jessica inherited both genes from her mother..
Name: ate: 1. If Jessica has light eyes (bb) and both of her parents have dark eyes (b) which statement is true?. Jessica inherited both genes from her father.. Jessica inherited both genes from her mother..
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0091861388* BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2017 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0091861388* BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2017 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials
NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948
 NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Achievement Criteria Biological ideas relating to genetic variation are limited to concepts and processes connected with: the continuity of life based on the
NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Achievement Criteria Biological ideas relating to genetic variation are limited to concepts and processes connected with: the continuity of life based on the
Unit 2 Reproduction & Genetics Grade 9 Science SCI 10F Mr. Morris
 Unit 2 Reproduction & Genetics Grade 9 Science SCI 10F Mr. Morris This booklet belongs to: Lesson 1 Cells and Organelles Lesson 1 SCI10F A short list of Organelles (little organs): Nucleus Cytoplasm Chromosome
Unit 2 Reproduction & Genetics Grade 9 Science SCI 10F Mr. Morris This booklet belongs to: Lesson 1 Cells and Organelles Lesson 1 SCI10F A short list of Organelles (little organs): Nucleus Cytoplasm Chromosome
12.1 X-linked Inheritance in Humans. Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12. X-linked Inheritance. X-linked Inheritance
 Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12 12.1 in Humans X-chromosomes also have non genderspecific genes Called X-linked genes Vision Blood-clotting X-linked conditions Conditions caused by
Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12 12.1 in Humans X-chromosomes also have non genderspecific genes Called X-linked genes Vision Blood-clotting X-linked conditions Conditions caused by
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
