Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. 3.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions
|
|
|
- Albert Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues 3.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. A) Label A B) Label B C) Label C D) Label D E) Label E Page Ref:
2 2) The illustration of skeletal muscle tissue is. A) Label A B) Label B C) Label C D) Label D E) Label E Answer: E Page Ref: ) The illustration of stratified squamous epithelium is. A) Label A B) Label B C) Label C D) Label D E) Label E Answer: D Page Ref: 91 4) The illustration of simple squamous epithelium is. A) Label A B) Label B C) Label C D) Label D E) Label E Page Ref: 90 5) The illustration of cardiac muscle tissue is. A) Label A B) Label B C) Label C D) Label D E) Label E Page Ref: 98 2
3 6) Cellular material located outside the nucleus yet inside the plasma membrane is the. A) nucleolus B) cytoplasm C) interstitial fluid D) extracellular fluid Page Ref: 64, ) The specialized cellular compartments within the cytosol of the cell are collectively called. A) organelles B) cilia C) flagella D) microvilli Page Ref: 67 8), a type of cell junction, anchor adjacent cells together and prevent cells from being pulled apart. A) Tight junctions B) Gap junctions C) Desmosomes D) Cytoplasm Page Ref: 66 9) The phospholipid tails are, which make the plasma membrane impermeable to water. A) water-loving B) hydrophilic C) polar D) hydrophobic Answer: D Page Ref: 65 10) The organelle responsible for making the majority of ATP in a cell is the. A) Golgi apparatus B) mitochondrion C) rough endoplasmic reticulum D) lysosome Page Ref: 67 3
4 11) The membrane connections that prevent the leaking of fluid between cells are called. A) gap junctions B) tight junctions C) desmosomes D) microvilli Page Ref: 66 12) The is a network of proteins that forms an internal framework for the cell. A) mitochondrion B) cytoskeleton C) rough endoplasmic reticulum D) Golgi apparatus Page Ref: 70 13) The passive process that involves the movement of water through aquaporins is. A) facilitated diffusion B) endocytosis C) solute pumping D) osmosis Answer: D Page Ref: 77 14) The nucleoplasm and cytosol make up the fluid. A) interstitial B) intracellular C) extracellular D) nuclear Page Ref: 76 15) The movement of substances through the cell membrane against their concentration gradient is a type of process. A) active B) passive C) diffusion D) filtration Page Ref: 78 4
5 16) The nucleotides of DNA join in a complementary way in which adenine pairs with while cytosine pairs with. A) adenine; cytosine B) uracil; guanine C) thymine; guanine D) guanine; thymine Page Ref: 82 17) In cell division, the term that refers to division of the cytoplasm is. A) mitosis B) interphase C) cytokinesis D) meiosis Page Ref: 82 18) The period of the cell cycle when the cell grows and performs its metabolic activities is. A) anaphase B) interphase C) metaphase D) telophase Page Ref: 81 19) The purpose of is to produce two genetically identical cells. A) interphase B) cell division C) DNA replication D) protein synthesis Page Ref: 82 5
6 20) The DNA segment that carries information for building one protein or polypeptide chain is called a(n). A) codon B) gene C) anticodon D) amino acid Page Ref: 85 21) The two steps of protein synthesis, in the correct order, are and. A) transcription; translation B) replication; mitosis C) mitosis; cytokinesis D) transcription; replication Page Ref: 85 22) Groups of cells that are similar in both structure and function are known as. A) organs B) organ systems C) tissues D) atoms Page Ref: 87 23) Epithelial tissues have one free surface or edge known as the surface. A) basement B) apical C) matrix D) attached Page Ref: 88 24) The type of tissue consisting of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix is tissue. A) epithelial B) connective C) muscle D) nervous Page Ref: 93 6
7 25) glands possess ducts that transport secretions onto epithelial surfaces. A) Endocrine B) Adrenal C) Thyroid D) Exocrine Answer: D Page Ref: 92 26) The type of epithelial tissue found lining organs of the digestive system such as the small intestines is. A) simple columnar B) simple cuboidal C) pseudostratified columnar D) simple squamous Page Ref: 90 27) The cell type found in nervous tissue is the. A) fibroblast B) osteocyte C) neuron D) chondrocyte Page Ref: 99 28) tissue is commonly called fat. A) Adipose B) Bone C) Reticular D) Dense fibrous Page Ref: 97 29) muscle tissue has no visible striations and has spindle-shaped cells. A) Smooth B) Cardiac C) Skeletal D) Dense regular Page Ref: 99 7
8 30) Many layers of flattened cells should be termed epithelial tissue. A) stratified columnar B) stratified squamous C) pseudostratified columnar D) simple squamous Page Ref: 92 31) The cell shown in Figure 3.2 has been placed into a(n) solution. A) hypertonic B) hypotonic C) isotonic D) equilibrium Page Ref: 84 Bloom's: 3) Application 8
9 3.2 Multiple Choice Part II Questions 1) The structural and functional unit of all living things is the. A) nucleus B) element C) cytoplasm D) cell E) organelle Answer: D Page Ref: 62 2) Which of the following statements is NOT part of the cell theory? A) The biochemical activities of cells depends on the number of their subcellular structures. B) The human body is composed of 50 to 100 trillion cells. C) Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. D) The activity of an organism depends on its collective cellular activities. E) The continuity of life has a cellular basis. Page Ref: 63 3) What is the arrangement of the phospholipids as a substance passes through the plasma membrane? A) phospholipid head, phospholipid tails, phospholipid head, phospholipid tails B) phospholipid head, phospholipid head, phospholipid tails, phospholipid tails C) phospholipid head, phospholipid tails, phospholipid tails, phospholipid head D) phospholipid tail, phospholipid head, phospholipid tail E) phospholipid tails, phospholipid head, phospholipid head, phospholipid tails Page Ref: 65 4) Which of the following is NOT a structural component of the nucleus? A) nuclear envelope B) nucleolus C) Golgi apparatus D) chromatin E) nuclear pores Page Ref: 64 9
10 5) Nutrients and ions can pass directly from cell to cell through special membrane junctions known as. A) desmosomes B) gap junctions C) inclusions D) microvilli E) tight junctions Page Ref: 66 6) The three major components of the cytoplasm are the. A) cytosol, organelles, and inclusions B) cytosol, inclusions, and nucleoli C) cytosol, organelles, and nucleoli D) organelles, inclusions, and nucleoli E) organelles, inclusions, and ribosomes Page Ref: 67 7) Which of the following is NOT considered a cytoplasmic organelle? A) mitochondrion B) Golgi apparatus C) flagellum D) rough endoplasmic reticulum E) peroxisome Page Ref: 71 8) The preparation of secretory vesicles for export from the cell is the responsibility of the. A) mitochondrion B) Golgi apparatus C) cytoskeleton D) peroxisome E) smooth endoplasmic reticulum Page Ref: 68 10
11 9) The organelle that contains enzymes produced by ribosomes and packaged by the Golgi apparatus is the. A) Golgi apparatus B) lysosome C) peroxisome D) ribosome E) rough endoplasmic reticulum Page Ref: 70 10) The movement of fluid through the cell membrane from a high pressure area to a lower pressure area is called. A) active transport B) bulk transport C) osmosis D) diffusion E) filtration Answer: E Page Ref: 78 11) Passive processes that move substances across membranes. A) utilize ATP B) employ protein pumps C) transport substances against their concentration gradients D) require no ATP E) include exocytosis and endocytosis Answer: D Page Ref: 76 12) Osmosis transports water across membranes using. A) ATP B) solute pumping C) aquaporins D) sodium-potassium pump E) vesicles Page Ref: 77 11
12 13) What assists the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion? A) ATP B) protein carrier or channel C) lysosomes D) aquaporins E) solute pumps Page Ref: 77 14) What is required for diffusion to occur? A) protein carrier or channel B) concentration gradient C) ATP D) solute pump E) ribosomes Page Ref: Bloom's: 4) Analysis 15) Two types of endocytosis are. A) cellular secretion and solute pumping B) solute pumping and active transport C) active transport and phagocytosis D) phagocytosis and pinocytosis E) pinocytosis and passive transport Answer: D Page Ref: 79 16) A solution that contains fewer solutes than the cell is. A) hypotonic B) hypertonic C) intravenous D) isotonic E) Ringer's lactate Page Ref: 84 12
13 17) Which of the following substances must travel across a membrane via facilitated diffusion? A) carbon dioxide B) water C) oxygen D) fat-soluble vitamins E) glucose Answer: E Page Ref: 77 18) Which of the following processes require the use of protein carrier molecules? A) facilitated diffusion and solute pumping B) facilitated diffusion and vesicular transport C) vesicular transport and osmosis D) osmosis and filtration E) filtration and exocytosis Page Ref: ) A cell is isotonic to its 4% dextrose solution. When moved to a 6% dextrose solution, that cell will. A) shrink B) plump C) bloat D) rupture E) lyse Page Ref: 84 Bloom's: 3) Application 20) The portion of the cell's life cycle that does NOT involve cell division is known as. A) interphase B) mitosis C) metaphase D) prophase E) cytokinesis Page Ref: 81 13
14 21) The molecule that carries an amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into a protein is. A) ATP B) messenger RNA (mrna) C) ribosomal RNA (rrna) D) DNA E) transfer RNA (trna) Answer: E Page Ref: 85 22) The correct order of phases of the mitosis is. A) prophase, interphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase B) prophase, anaphase, telophase, metaphase C) metaphase, anaphase, prophase, telophase D) telophase, metaphase, anaphase, prophase E) prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase Answer: E Page Ref: ) The process of transcription. A) produces ATP from glucose and oxygen B) transfers information from DNA into mrna C) occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell D) creates proteins from mrna E) translates nucleic acids into amino acids Page Ref: 85 24) Sequences of three bases found in messenger RNA (mrna) are called. A) anticodons B) deoxyribose sugars C) codons D) ribosomes E) amino acids Page Ref: 85 14
15 25) The two major phases of protein synthesis are. A) transcription and replication B) mitosis and interphase C) replication and translation D) transcription and translation E) synthesis and cytokinesis Answer: D Page Ref: 85 26) Which of the following represents a segment of RNA? A) AUGUCA B) ATGCTA C) TGCGTT D) CTGTGG E) GTCATA Page Ref: 85, 87 27) DNA replication takes place during. A) interphase B) prophase C) metaphase D) anaphase E) telophase Page Ref: 81 28) During transcription, which base pairs with adenine of DNA in the newly formed molecule of RNA? A) thymine B) adenine C) uracil D) cytosine E) guanine Page Ref:
16 29) If the sequence of nitrogenous bases in one strand of DNA is GTA-GCA, the sequence of bases on its complementary DNA strand would be. A) CAU-CGU B) CAT-CGT C) GAU-GCU D) GAT-GCT E) ACG-ATT Page Ref: 82 30) A tissue constructed of a single layer of flattened cells is known as. A) simple squamous epithelium B) simple columnar epithelium C) simple cuboidal epithelium D) stratified squamous epithelium E) transitional epithelium Page Ref: 88 31) Which type of tissue conducts electrochemical impulses? A) epithelial tissue B) muscle tissue C) nervous tissue D) connective tissue E) dense tissue Page Ref: ) Which of the following is NOT classified as a connective tissue? A) bone B) cartilage C) blood D) skeletal muscle E) adipose Answer: D Page Ref: 93 Bloom's: 3) Application 16
17 33) Which type of tissue is situated in the lining of the urinary bladder and urethra where stretching occurs? A) simple cuboidal epithelium B) stratified squamous epithelium C) simple squamous epithelium D) pseudostratified columnar epithelium E) transitional epithelium Answer: E Page Ref: 89, 91, 92 34) The tissue that is usually well vascularized and has an extensive extracellular matrix is called. A) epithelial tissue B) connective tissue C) nervous tissue D) muscle tissue E) brain tissue Page Ref: 93 35) Which of the following epithelial tissues is composed of many layers of cells? A) pseudostratified columnar epithelium B) simple squamous epithelium C) simple columnar epithelium D) simple cuboidal epithelium E) stratified squamous epithelium Answer: E Page Ref: 92 36) Bone is best described as. A) dense connective tissue B) epithelial tissue C) adipose tissue D) areolar tissue E) osseous tissue Answer: E Page Ref: 93 17
18 37) Identify the type of connective tissue that is found in lymph nodes, the spleen, and bone marrow. A) adipose tissue B) dense connective tissue C) areolar tissue D) reticular connective tissue E) osseous tissue Answer: D Page Ref: 96, 97 38) Glands, such as the thyroid, that secrete their products directly into the blood rather than through ducts are classified as. A) exocrine B) endocrine C) sebaceous D) ceruminous E) sudoriferous Page Ref: 92 39) Which of these characteristics best describes cardiac muscle tissue? A) movement is involuntary and cells possess striations B) attached to the skeleton C) movement is voluntary and cells possess striations D) single nucleus and spindle-shaped cells E) multinucleate and long, cylindrical cells Page Ref: 99 40) The type of muscle found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the stomach, and in the walls of blood vessels is. A) cardiac muscle B) skeletal muscle C) smooth muscle D) both smooth muscle and skeletal muscle E) both cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle Page Ref: 99 18
19 41) The presence of chondrocytes indicates that a tissue is. A) adipose B) cartilage C) bone D) blood E) areolar Page Ref: 93 42) Damaged tissues that are repaired by the same kind of cells experience a replacement process known as. A) inflammation B) regeneration C) fibrosis D) scarring E) clotting Page Ref: ) Intercalated discs found in cardiac muscle tissue are. A) tight junctions B) phagocytes C) gap junctions D) signet ring cells E) desmosomes Page Ref: 99 44) Jacinda tore her Achilles (calcaneal) tendon during a recent track meet. She has injured. A) muscle tissue B) loose connective tissue C) epithelial tissue D) dense connective tissue E) nervous tissue Answer: D Page Ref: 96 Bloom's: 3) Application 19
20 45) Looking into a microscope, you notice cells swimming, propelled by a long tail. What cell structure must these cells have in order to be mobile? A) ribosomes B) smooth ER C) flagella D) peroxisomes E) cytoplasm Page Ref: 71 Bloom's: 3) Application 46) Which of the following tissues is constructed of many collagen fibers? A) blood B) scar tissue C) transitional epithelium D) pseudostratified columnar epithelium E) simple cuboidal epithelium Page Ref: ) Which type of connective tissue is avascular? A) adipose B) bone C) cartilage D) areolar E) reticular Page Ref: 93 48) A cancer drug interferes with the development of mitotic spindle fibers during cell division. Which phase is directly affected? A) prophase B) telophase C) anaphase D) metaphase E) interphase Page Ref: 82 Bloom's: 3) Application 20
21 49) Neurons and neuroglia are components of. A) epithelial tissue B) connective tissue C) nervous tissue D) muscle tissue E) granulation tissue Page Ref: ) Which tissue performs peristalsis to move substances, such as food, through the hollow organs of the body? A) skeletal muscle tissue B) transitional epithelium C) cardiac muscle tissue D) nervous tissue E) smooth muscle tissue Answer: E Page Ref: 99 51) The tissue shown in Figure 3.3 most likely. A) contracts to produce movement B) transmits electrochemical impulses C) covers and lines body surfaces D) stores fat E) contains a matrix Page Ref: 74, 88, 91 21
22 3.3 True/False Questions 1) Chromatin and chromosomes are both composed of DNA. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 64 2) Phospholipid tails are hydrophilic and are attracted to water. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 65 3) Protein synthesis occurs on lysosomes in the cell. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 67 4) The process of facilitated diffusion requires energy. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: ) Osmosis is the process of water moving down the concentration gradient. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 77 6) Peroxisomes detoxify harmful or poisonous substances, such as alcohol. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 70 7) Sperm are the only cells in the human body to possess cilia. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 71 8) Mitotic spindles guide the separation of chromosomes during mitosis. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 82 9) Anaphase is the stage of cell division when the cleavage furrow first appears. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 83 22
23 10) Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm, whereas mitosis is the division of the nucleus. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 82 11) Translation is the stage of protein synthesis during which a complementary mrna molecule is synthesized from a DNA template. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 85 12) Stratified epithelium consists of one layer of epithelial cells. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 88 13) Epithelial tissues are often well vascularized and contain an extracellular matrix. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 88 14) The matrix of hyaline cartilage consists of abundant collagen fibers hidden in a rubbery matrix. Answer: TRUE Page Ref: 93 15) Muscle tissue is located in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Answer: FALSE Page Ref: 99,
24 3.4 Matching Questions Match the following: A) site of protein synthesis B) synthesizes cholesterol and fat C) cylindrical structures made of tubulin proteins D) cellular extensions that move substances along the cell surface E) internal framework composed of a network of protein structures F) packages substances for release from cell G) site of ATP synthesis H) genetic control center of the cell I) increases surface area of plasma membrane for absorption J) site of intracellular digestion 1) Cilia Page Ref: 71 2) Mitochondria Page Ref: 67 3) Ribosomes Page Ref: 67 4) Microtubules Page Ref: 70 5) Cytoskeleton Page Ref: 70 6) Golgi apparatus Page Ref: 68 7) Nucleus Page Ref: 64 8) Microvilli Page Ref: 71 24
25 9) Smooth ER Page Ref: 68 10) Lysosomes Page Ref: 70 Answers: 1) D 2) G 3) A 4) C 5) E 6) F 7) H 8) I 9) B 10) J 25
26 Match the following: A) prophase B) anaphase C) metaphase D) telophase 11) Cytokinesis is completed Page Ref: 83 12) Centrioles separate and move toward opposite sides of the cell Page Ref: 83 13) Chromosomes cluster and align at the center of the spindle Page Ref: ) Nucleoli appear in each daughter cell Page Ref: 83 15) Chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell Page Ref: 83 16) Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate Page Ref: ) Spindle breaks down and disappears Page Ref: 83 18) Nuclear envelope and nucleoli break down and disappear Page Ref: 82 19) Cleavage furrow squeezes the cell into two parts Page Ref: 83 Answers: 11) D 12) A 13) C 14) D 15) B 16) C 17) D 18) A 19) D 26
27 Match the following: A) Solute pumping B) Osmosis C) Endocytosis D) Diffusion 20) Type of active transport in which sodium and potassium are pumped across a membrane using ATP Page Ref: 78 21) Type of passive process in which water is moved through aquaporins Page Ref: 77 22) Type of passive process in which molecules move across the plasma membrane down a concentration gradient Page Ref: ) Type of active process in which the cell engulfs extracellular substances by phagocytosis or pinocytosis Page Ref: Answers: 20) A 21) B 22) D 23) C 27
28 Match the following: A) connective tissue B) nervous tissue C) muscle tissue D) epithelial tissue 24) Type of tissue that has an apical surface and a basement membrane Page Ref: 88 25) Type of tissue that consists of living cells surrounded by an extracellular matrix Page Ref: 93 26) Type of tissue that is specialized to contract and produce movement Page Ref: 97 27) Type of tissue that can be simple or stratified Page Ref: 88 28) Type of tissue that is found in the brain and spinal cord Page Ref: 99 29) Type of tissue that can be described as voluntary or involuntary Page Ref: 97, 99 30) Type of tissue that contains collagen, elastic, or reticular fibers Page Ref: 93 31) Type of tissue that is common in glands and their ducts Page Ref: 89, 92 32) Type of tissue that supports, protects, and binds tissues together Page Ref: 93 33) Type of tissue that can be classified as loose or dense Page Ref: 93 28
29 34) Type of tissue whose two functional characteristics are irritability and conductivity Page Ref: 99 Answers: 24) D 25) A 26) C 27) D 28) B 29) C 30) A 31) D 32) A 33) A 34) B 3.5 Essay Questions 1) Drinking too much water over a short period of time can disrupt the electrolyte balance in the body (called water intoxication or hypotonic hydration). Explain how cells respond to an environment with less solutes than their intracellular fluid. Answer: This solution is hypotonic to the cells since it contains less solutes than the body's cells. In these solutions, cells rapidly swell and fill with water in an attempt to reach equilibrium. Cells may also burst, or lyse. Page Ref: 84 Bloom's: 3) Application 2) List the three main regions of the cells in the human body. Describe the main functions of each region. Answer: 1. Nucleus. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and houses the genetic material of the cell called DNA. DNA also has the instructions for building proteins. 2. Plasma membrane. The plasma membrane is a barrier around the cell's contents and separates it from the surrounding environment. Most of the proteins embedded in the plasma membrane function in the transport of substances across the membrane. 3. Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a semi-fluid medium that includes the cytosol, organelles, and inclusions. Each organelle performs a specific function for the cell. Page Ref: ) Explain the difference between filtration and osmosis. Answer: Filtration is the process by which water and solutes are forced through a membrane by fluid (hydrostatic pressure). Hydrostatic pressure is exerted by the blood. By contrast, osmosis is a type of diffusion in which water moves across a membrane through aquaporins. During osmosis, water moves down its concentration gradient to achieve equilibrium. Page Ref: ) Distinguish between the roles of the ribosome, found freely floating in the cytoplasm, and the ribosomes found attached to membranes, such as the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Answer: Ribosomes function in protein synthesis. Freely floating ribosomes make proteins for use in the cytoplasm of a cell while ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) make proteins that are transported out of the cell. Proteins travel through the membranes of the rough ER in preparation for export in transport vesicles released by the Golgi apparatus. Page Ref: 67 Bloom's: 4) Analysis 29
30 5) List the three different types of RNA and identify their functions. Answer: 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) carries the "message" containing instructions for protein synthesis from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Ribosomal RNA (rrna) forms part of the "ribosomal" structure and helps coordinate the protein building process. 3. Transfer RNA (trna) transports an amino acid to the ribosomal site and recognizes the mrna codons. Page Ref: 85 6) Discuss the three steps in protein synthesis. Answer: 1. Uncoiling of DNA the DNA segment or gene that specifies one polypeptide or protein uncoils. 2. Transcription (DNA-directed synthesis of mrna) one strand of DNA acts as a template for the synthesis of the complementary mrna molecule, and there is a transfer of information from the DNA's base sequence (cod.einto the complementary base sequence of mrna (codon). 3. Translation (RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide or protein) involves five steps. First, mrna leaves the nucleus and attaches to ribosomes. Second, trna (anticodon) transports an amino acid to the mrna strand and recognizes a mrna molecule (codon). Third, the codon and the anticodon bind. Fourth, the ribosome moves the mrna strand along as each codon is read sequentially. Finally, as each amino acid is bound to the next by a polypeptide bond, its trna is released. The polypeptide or protein chain is released when the termination (stop) codon is read. Page Ref: 85 7) Discuss the four stages of mitosis. Answer: 1. Prophase chromatin threads coil and shorten so that visible bar-like bodies, called chromosomes, appear. Each chromosome is made up of two strands, called chromatids, which are held together by a centromere. Additionally, the centrioles separate and move toward opposite sides of the cell, directing the assembly of the mitotic spindle (composed of microtubules) between them as they move. 2. Metaphase the chromosomes cluster and align in the center of the spindle, midway between the centrioles, forming a straight line of chromosomes. 3. Anaphase the centromeres split and the chromosomes move slowly apart toward opposite ends of the cell. A cleavage furrow appears over the midline of the spindle and eventually pinches the cytoplasmic mass into two parts in a process called cytokinesis. 4. Telophase the chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell and their movement ends, and they then uncoil and become chromatin again. A nuclear membrane then forms around each chromatin mass, the spindle breaks down and disappears, and nucleoli re-appear in each of the daughter nuclei. Finally, cytokinesis produces two separate daughter cells. Page Ref:
31 8) A fat-soluble vitamin, vitamin A, is moving down its concentration gradient into a cell. What type of membrane transport is responsible for its movement? Describe this process. Answer: Vitamin A is moving via simple diffusion, a type of passive transport. Passive transport requires no energy input from the cell. Vitamin A is moving from an area where it is more concentrated to an area where it is less concentrated. This vitamin is moving without assistance through the plasma membrane. Page Ref: 77 Bloom's: 3) Application 9) Some cancer drugs, such as vincristine, interfere with the creation of mitotic spindle fibers of a cell. Explain how this drug affects mitosis. Answer: The mitotic spindle is formed during prophase by centrioles. This spindle guides the movement of chromosomes later as mitosis progresses. By late prophase, the spindle has attached to the centromere of each chromosome. Without the creation of the spindle fibers, chromosomes cannot successfully be separated as mitosis progresses through anaphase. Page Ref: Bloom's: 4) Analysis 10) Stranded on an island, you have two sources of water to drink: salty ocean water and contaminated fresh water. Explain your choice of drinking water and indicate why your selection is the best choice. Answer: The contaminated fresh water is the better choice to drink, because this water is hypotonic to our cells. Our cells will become rehydrated and bloat with the fluid when we drink. The salty ocean water is hypertonic to our cells and will cause our cells to dehydrate and shrivel as water leaves the cell. Page Ref: 84 11) Describe the naming scheme for epithelial tissues. Answer: Epithelial tissues are named based on two features: the number of cell layers and the predominant cell shape. If the epithelial tissue has one layer, it is called a simple tissue. Two or more layers qualifies the tissue as stratified. Cells can be flat in shape (squamous), cube-shaped (cuboidal), or brick-shaped (columnar). The viewer should look toward the apical surface for the most mature cells in the tissue for the cell shape. When naming the epithelial tissue, place the number of cell layers first (such as simple) followed by the cell shape (such as squamous). Page Ref: 88 31
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Plasma membrane The Nucleus Control center of the cell Contains genetic material (DNA) Three regions Nuclear envelope (membrane) Nucleolus
 Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy
Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
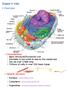 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things
 Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure
Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Unit 3 - Cells and Tissues 1
 Unit 3 - Cells and Tissues 1 I. Unit 3: Cells and Tissues A. Cells and Tissues 1. Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life 2. Cells are the building blocks of all living things 3. Tissues
Unit 3 - Cells and Tissues 1 I. Unit 3: Cells and Tissues A. Cells and Tissues 1. Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life 2. Cells are the building blocks of all living things 3. Tissues
Cell. ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange
 Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
1.3 - Cells. Chapter 3 - Cells
 1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Cell Structure and Function
 C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
4. A phospholipid is an example of organization at the level.
 1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
Cell Theory. Passive Transport
 Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units
 Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Connexons: hollow connective tubes
 Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
Cell Structure and Function
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 3 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3 Learning Outcomes 3-1 3-2 3-3 3-4 3-5 List the main points of the cell
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 3 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3 Learning Outcomes 3-1 3-2 3-3 3-4 3-5 List the main points of the cell
Cells. I. Introduction to the Cell. II. Composite Cell
 I. Introduction to the Cell Cells A. 75 trillion cells in the human adult. B. Size 1. Large enough for organelles 2. Limited by the cell s surface to volume ratio I. Introduction to the Cell C. Shape 1.
I. Introduction to the Cell Cells A. 75 trillion cells in the human adult. B. Size 1. Large enough for organelles 2. Limited by the cell s surface to volume ratio I. Introduction to the Cell C. Shape 1.
CHAPTER 3. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK ACTIVE LEARNING
 CHAPTER 3 QUICK CHECK Page 52 1. Two layers of phosphate-containing fat molecules called phospholipids form a fluid framework for the plasma membrane. Cholesterol is a component of the plasma membrane.
CHAPTER 3 QUICK CHECK Page 52 1. Two layers of phosphate-containing fat molecules called phospholipids form a fluid framework for the plasma membrane. Cholesterol is a component of the plasma membrane.
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Cytology. Cell Anatomy. Cell Theory - A good place to start! The generalized cell contains: Cell membrane Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytosol Organelles
 Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology
 A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology Form A Name Lab 1. Pinocytosis would allow the intake of a. solid b. gas c. liquids d. all of these answers are true 2. Which of the following
A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology Form A Name Lab 1. Pinocytosis would allow the intake of a. solid b. gas c. liquids d. all of these answers are true 2. Which of the following
Chapter 3: The Living Units
 Chapter 3: The Living Units Objectives: 1. Define cell. 2. List the three major regions of a generalized cell and indicate the function of each. 3. Describe the chemical composition of the plasma membrane
Chapter 3: The Living Units Objectives: 1. Define cell. 2. List the three major regions of a generalized cell and indicate the function of each. 3. Describe the chemical composition of the plasma membrane
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
 Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION It is within the cell where the functions of the body occur. We are going to look at structure, function and reproduction of cells in this chapter. Cytology
Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION It is within the cell where the functions of the body occur. We are going to look at structure, function and reproduction of cells in this chapter. Cytology
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells
 Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
6 functions of membrane proteins integral & peripheral proteins Membrane Junctions
 Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells and Tissues Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Define cell, organelle, and inclusion. 2. Identify the three major cell regions nucleus,
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells and Tissues Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Define cell, organelle, and inclusion. 2. Identify the three major cell regions nucleus,
Tissues. groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types. epithelium connective muscle nervous
 Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224. Lama Alzamil 3 rd floor/ office #119
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office #119 Lecture 2: Cells, Tissues, and body fluids (Chapter 3) 1. Anatomy and physiology of a generalized cell.
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office #119 Lecture 2: Cells, Tissues, and body fluids (Chapter 3) 1. Anatomy and physiology of a generalized cell.
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Anatomy & Physiology 1 st Semester Exam Review Academy High School 2016 Ch. 1: Human Body Orientation
 Ch. 1: Human Body Orientation Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Identify the cavity that houses the spinal cord. Page Ref: 19 2) Label A points to the cavity. A) thoracic B) pelvic C) cranial
Ch. 1: Human Body Orientation Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Identify the cavity that houses the spinal cord. Page Ref: 19 2) Label A points to the cavity. A) thoracic B) pelvic C) cranial
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements II. Atoms III. Matter Matter
 REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements Cannot be broken down by chemical means and still retain the same chemical and physical characteristics
REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements Cannot be broken down by chemical means and still retain the same chemical and physical characteristics
1. Adaptation 2. Reproduce 3. Growth 4. Organization 5. Metabolism 6. Irritability 7. Contractility. List the seven activities of all living cells
 List the seven activities of all living cells 1. Adaptation 2. Reproduce 3. Growth 4. Organization 5. Metabolism 6. Irritability 7. Contractility What is anabolism? Joining small molecules (amino acids)
List the seven activities of all living cells 1. Adaptation 2. Reproduce 3. Growth 4. Organization 5. Metabolism 6. Irritability 7. Contractility What is anabolism? Joining small molecules (amino acids)
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Cells. Introduction: Composite Cell: Bi100 Chapter 3
 Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
Epithelial Tissue. Simple Cuboidal Function: secretion and absorption. Simple Squamous
 Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS
 CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells
 Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Mitosis Models 3-5. Chromosome. #1 Prophase. #2 Prophase. 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids. 2n = 4
 MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
Exam 2 spring 2016 Page 1
 xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells
 Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/human-anatomy-5th-edition-saladin-test-bank/ Chapter 02 - Cytology - The Study of Cells Chapter 02 Cytology -
Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/human-anatomy-5th-edition-saladin-test-bank/ Chapter 02 - Cytology - The Study of Cells Chapter 02 Cytology -
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
1. Which of the following functions or capabilities must be performed by a transmembranal/intrinsic protein in the plasma membrane?
 (3.45 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer
(3.45 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Euakryotic cells are generally one to one hundred times bigger than prokaryotic cells
 Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Structure of a Generalized Cell
 A Quick Tour Through A Cell BIO130 Lab 2 Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy Structure of a Generalized Cell -plasma membrane -cytoplasm: cytosol organelles -nucleus Play TourOfAnimalCell.mpg Plasma membrane
A Quick Tour Through A Cell BIO130 Lab 2 Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy Structure of a Generalized Cell -plasma membrane -cytoplasm: cytosol organelles -nucleus Play TourOfAnimalCell.mpg Plasma membrane
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cytology and Histology Practice Test
 Cytology and Histology Practice Test 1. Which of the following manufactures proteins: A. lysosomes B. chromosomes C. ribosomes D. golgi apparatus 2. Which of the following contain digestive enzymes: A.
Cytology and Histology Practice Test 1. Which of the following manufactures proteins: A. lysosomes B. chromosomes C. ribosomes D. golgi apparatus 2. Which of the following contain digestive enzymes: A.
human cell Mader s Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapters 1, 3 and 4
 1 The human cell INTRODUCTION All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing
1 The human cell INTRODUCTION All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing
Tissues. Group of cells that are similar in structure and function. 4 primary types. Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control)
 Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
The Cell Study Guide, Chapter 2
 Part I. Clinical Applications Name: The Cell Study Guide, Chapter 2 Lab Time: 1 1. Johnny lacerated his arm and rushed home to Mom so she could fix it. His mother poured hydrogen peroxide over the area,
Part I. Clinical Applications Name: The Cell Study Guide, Chapter 2 Lab Time: 1 1. Johnny lacerated his arm and rushed home to Mom so she could fix it. His mother poured hydrogen peroxide over the area,
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Exam 2 fall 2015 Page 1
 xam 2 fall 2015 Page 1 Name: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium for
xam 2 fall 2015 Page 1 Name: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium for
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 3
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 3 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 3 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Basrah University Pharmacy College. Human Biology. Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Basrah University Pharmacy College Human Biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cells: The Basic Units of Life All organisms are composed of one (e.g. bacteria) or more cells (e.g. human body contains
Basrah University Pharmacy College Human Biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cells: The Basic Units of Life All organisms are composed of one (e.g. bacteria) or more cells (e.g. human body contains
Lecture 3: Cells and Tissues. Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross
 Lecture 3: Cells and Tissues Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cell Physiology Cell Physiology Brief review of organelles Should be mostly review Cell surrounded by plasma membrane Lipid bilayer Also surrounds organelles
Lecture 3: Cells and Tissues Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cell Physiology Cell Physiology Brief review of organelles Should be mostly review Cell surrounded by plasma membrane Lipid bilayer Also surrounds organelles
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Sample Questions BSC1010C Chapters 5-7
 Sample Questions BSC1010C Chapters 5-7 1. Which type of lipid is most important in biological membranes? a. oils b. fats c. wax d. phospholipids e. triglycerides 2. Which type of interaction stabilizes
Sample Questions BSC1010C Chapters 5-7 1. Which type of lipid is most important in biological membranes? a. oils b. fats c. wax d. phospholipids e. triglycerides 2. Which type of interaction stabilizes
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Tissues and Membranes
 I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
3UNIT. Photosynthesis and. Cellular Respiration. Unit PreQuiz? General Outcomes. Unit 3 Contents. Focussing Questions
 3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
