SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Annabelle Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3) Microvilli 3) 4) Mitochondrion 4) 5) Golgi apparatus 5) Answer: E 1
2 Figure 2.2 Using Figure 2.2, match the following: 6) DNA molecule 6) 7) Chromatid 7) 8) Nucleosomes 8) 9) Histones 9) 10) Metaphase chromosome 10) Answer: E 2
3 Match the following: A. Golgi apparatus B. lysosome C. rough endoplasmic reticulum D. mitochondria E. centrosome 11) This organelle is involved in production of cellular energy. 11) Answer: mitochondria 12) This structure is characterized by folded membranes called cristae. 12) Answer: mitochondria 13) When a cell ingests a foreign cell, the vesicle fuses with this organelle. 13) Answer: lysosome 14) This membranous structure is the site of protein synthesis. 14) Answer: rough endoplasmic reticulum 15) A spherical, nonmembranous structure near the nucleus. 15) Answer: centrosome 16) Cisternae of this structure are continuous with the nuclear envelope. 16) Answer: rough endoplasmic reticulum 17) This structure has both a cis and a trans face. 17) Answer: Golgi apparatus 18) This structure consists of a cloud of proteins surrounding a pair of centrioles. 18) Answer: centrosome 19) These structures are often called the demolition crew of the cell. 19) Answer: lysosome 20) This structure primarily modifies products from the rough ER, and is characterized by a flattened stack of membranes. Answer: Golgi apparatus 20) 21) These structures are primarily sacs of powerful enzymes. 21) Answer: lysosome 22) These structures are defective in the disorder Tay Sachs disease. 22) Answer: lysosome 23) The lysosomes are derived from this structure. 23) Answer: Golgi apparatus 3
4 24) These structures produce ATP. 24) Answer: mitochondria 25) These structures contain their own DNA. 25) Answer: mitochondria TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 26) The smooth ER contains its own molecules of DNA. 26) 27) Clathrin-coated regions of the plasma membrane are locations where exocytosis occurs. 27) 28) Ribosomes consist of two subunits, each surrounded by a membrane. 28) 29) Peroxisomes are important in detoxification of a number of toxic substances, for instance hydrogen peroxide. 29) 30) The majority of the DNA in a cell is found in the nucleolus. 30) 31) Microtubules are composed of actin. 31) 32) Chromatin is composed of DNA wound around proteins known as actin. 32) 33) An example of a type of cell with high rates of mitosis is a cell of the skin. 33) 34) During the G1 phase, cells are characterized by rapid growth. 34) 35) During the S phase, DNA is replicated in the cytoplasm. 35) 36) Smooth and skeletal muscles are characterized by much actin and myosin. 36) 37) Extended chromatin is tightly wound around histones. 37) 38) A mitotic spindle develops during early prophase of mitosis. 38) 4
5 39) During anaphase, the chromosomes are pulled toward the center of the cell. 39) 40) Cytokinesis is the physical division of the cells. 40) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 41) Mitosis refers only to nuclear division. Separation of the entire cell following mitosis is 41) A) meiosis. B) telophase. C) cytokinesis. D) karyokinesis. 42) Phospholipids of the plasma membrane are arranged 42) A) with their nonpolar tails sandwiched between the heads. B) around a central layer of cholesterol. C) in a single layer with polar heads facing outwards. D) with their polar heads sandwiched between the tails. 43) Which of the following cytoskeleton elements are the thinnest? 43) A) intermediate filaments B) centrioles C) microtubules D) microfilaments 44) Which of the following statements about integral proteins in the plasma membrane is false? 44) A) Some attach to the glycocalyx. B) They determine which molecules are transported through the membrane. C) Most extend all the way through the membrane. D) They are more abundant by volume than the membrane phospholipids. 45) Which type of endocytosis engulfs the most specific type of molecule or material? 45) A) receptor-mediated endocytosis B) pinocytosis C) fluid-phase endocytosis D) phagocytosis 46) Products of gland cells are secreted by 46) A) osmosis. B) exocytosis. C) phagocytosis. D) pinocytosis. 47) Of the following, the only organelle that has a double membrane structure is the 47) A) Golgi apparatus. B) endoplasmic reticulum. C) centriole. D) mitochondrion. 48) Functions of the Golgi apparatus include all of the following except 48) A) plasma membrane formation. B) synthesis of lysosomes. C) production of secretory granules. D) DNA replication. 5
6 49) Tay-Sachs disease is a lysosome storage disease, of which there are many types, all characterized by the absence of some functional acid hydrolase. The cells of individuals with a lysosome storage disease have A) abnormally large lysosomes. B) no lysosomes. C) abnormally small lysosomes. D) lysosomes that are structurally normal. 49) 50) Which of the following is not a cytoskeleton element? 50) A) intermediate filaments B) centrioles C) microfilaments D) microtubules 51) Which type of protein is required for exocytosis? 51) A) clathrin B) SNARE C) caveolin D) coatomer proteins 52) In chromatin, the DNA molecule wraps around proteins called 52) A) codons. B) integral protein. C) histones. D) nucleotides. 53) In the cell life cycle, DNA is replicated during 53) A) interphase "G1." B) prophase II. C) prophase I. D) interphase "S." 54) The longest arrays of microtubules that assemble on the centrioles during prophase form filaments called A) kinetochores. B) asters. C) the mitotic spindle. D) the nuclear envelope. 54) 55) During mitosis, contractions of the mitotic spindle serve to 55) A) re-form the nuclear envelope. B) form the aster. C) pull together the replicated chromosomal strands. D) separate the chromatids at the centromere. 56) The face of the Golgi apparatus is to receive spherical vesicles from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. A) trans; concave B) cis; flattened C) trans; convex D) cis; convex 56) 57) Which membranous organelle stores calcium? 57) A) Golgi apparatus B) peroxisomes C) mitochondria D) endoplasmic reticulum 6
7 58) Which organelle is important in neutralizing free radicals? 58) A) Golgi apparatus B) lysosomes C) peroxisomes D) mitochondria 59) Which of the following is the function of the nuclear envelope? 59) A) protein synthesis B) regulation of passage of substances in and out of the cell membrane C) transcription of DNA D) separation of nucleoplasm and cytoplasm 60) Peroxisomes function to 60) A) produce pigments. B) store cellular free radicals. C) form and degrade hydrogen peroxide. D) regulate membrane permeability. 61) Dyneins and kinesins 61) A) resist pulling forces that are placed on cells. B) push and pull on chromosomes to align them during metaphase of mitosis. C) enable a cell to send out and retract extensions called pseudopods. D) move organelles along microtubules through the cytoplasm. 62) Cell division is analogous to 62) A) a building forming another building by random accumulation of materials. B) two buildings duplicating their parts and fusing. C) a building forming another building through a loss of some of its parts. D) a building duplicating its blueprint and then forming a new building by splitting in two. 63) The plasma membrane is important for all the following reasons except 63) A) it surrounds the cell contents. B) it acts as a site for cell-to-cell interaction and recognition. C) it determines what substances enter and exit the cell. D) it is so thick and rigid, it offers some protection to the cell. 64) The plasma membrane is composed of all of the following except 64) A) glycoproteins. B) phospholipids. C) cholesterol. D) tubulin protein. 65) Materials that are to be exocytosed by cells are packed by the 65) A) nucleosome. B) mitochondrion. C) Golgi apparatus. D) ribosome. 7
8 66) Which of the following does not pass through nuclear pores? 66) A) messenger RNA B) water and electrolytes C) chromatin D) proteins 67) Which of the following is associated with protein synthesis? 67) A) chloroplasts B) ribosomes C) smooth endoplasmic reticulum D) mitochondria 68) Ribosomes may be either free within the cytoplasm or bound to a channeling system known as the 68) A) cytoskeleton. B) microtubule organizing center. C) Golgi apparatus. D) rough endoplasmic reticulum. 69) Which is not part of interphase? 69) A) S B) G1 C) M D) G2 70) In the plasma membrane of cells, cholesterol acts to 70) A) stabilize the membrane. B) make the membrane more resistant to freezing. C) participate in pinocytosis. D) destabilize the membrane, leading to heart attacks. 71) The endocytotic process in which tiny packets of fluid are brought into the cell is called 71) A) exocytosis. B) pinocytosis. C) xenocytosis. D) phagocytosis. 72) The double membrane structure is unique to the 72) A) peroxisome. B) lysosome. C) mitochondrion. D) nucleolus. 73) Mitochondria 73) A) are single-membrane structures involved in the breakdown of ATP. B) are always the same shape. C) synthesize proteins for use outside the cell. D) contain some of the code necessary for their own duplication. 74) The stiffest elements of the cytoskeleton, analogous to the bones of the human body, are 74) A) the cytosol. B) intermediate filaments. C) microtubules. D) microfilaments. 75) The mitotic spindle forms from the 75) A) Golgi apparatus. B) nucleolus. C) nucleus. D) centrioles. 8
9 76) The nuclear envelope is continuous with the rough ER, but it differs from the rough ER in that it 76) A) is not associated with ribosomes. B) consists of two membranes separated by a space. C) has unique pores. D) consists of tubes like the smooth ER. 77) Membrane-bound organelles have the same type of membrane as the plasma membrane except 77) A) they are all covered with ribosomes. B) for the absence of cholesterol. C) for the absence of a glycocalyx. D) the nonpolar tails face outward. 78) In the process of phagocytosis, the organelles whose enzymes break down ingested foreign cells are the A) smooth endoplasmic reticulum. B) lysosomes. C) peroxisomes. D) nucleoli. 78) 79) During mitosis, the kinetochore microtubules of the mitotic spindle 79) A) pull on the chromatids and align them at the metaphase plate. B) push the two poles of the cell apart. C) anchor the centriole to the cell membrane. D) push on the chromatids. 80) The theory that proposes that aging results from the effects of free radicals is primarily a theory of 80) A) cross-linking of glucose. B) wear and tear. C) genetically programmed aging. D) progressive disorder of immunity. 81) The cytoskeletal elements that are analogous to the muscles of the body in that they help generate contractile forces are A) microtubules. B) integral proteins. C) microfilaments. D) intermediate filaments. 81) 82) Transcription of DNA requires the presence of 82) A) histones. B) nucleosomes. C) extended chromatin. D) centrosomes. 83) The process of cellular aging may involve each of the following except 83) A) progressive shortening of telomeres. B) accumulated damage by free radicals. C) excessive metabolic rate. D) decreased production of lysosomes. 84) During what phase of mitosis does the mitotic spindle break down and disappear? 84) A) metaphase B) telophase C) anaphase D) late prophase 9
10 85) The cytoskeletal elements that form a ring to "squeeze" the two daughter cells apart during cytokinesis are A) microfilaments. B) the microtrabecular lattice. C) intermediate filaments. D) microtubules. 85) 86) During what phase of mitosis is the DNA duplicated? 86) A) interphase B) prophase C) metaphase D) anaphase 87) The plasma membrane is 87) A) a single-layered membrane enclosing the plasma. B) a single-layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus of the cell. C) a membrane composed of tiny shelves or cristae. D) the membrane surrounding the cell. 88) Which of the following cellular phenomena would not be affected by the absence of microtubules? 88) A) the arrangement of organelles B) cell shape C) cell division D) energy production (ATP manufacture) 89) Lysosomes originate from 89) A) smooth endoplasmic reticulum. B) the Golgi apparatus. C) the plasma membrane. D) cholesterol. 90) Which of the following is an inclusion, not an organelle? 90) A) mitochondrion B) microtubule C) glycogen D) lysosome SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 91) This phase is the physical division of two cells during mitosis. 91) Answer: cytokinesis 92) These structures give scientists clues about cellular senescence. 92) Answer: telomeres 93) Cell aging may be related to production of what chemicals produced by the mitochondria? 93) Answer: radicals (free radicals) 94) This is the collective name for short carbohydrates on the extracellular surface of integral proteins, which help cells recognize each other. Answer: glycocalyx 94) 95) This is the name of a cluster of DNA wrapped around a group of eight histones. 95) Answer: nucleosome 10
11 96) This is the phase in which a cell grows and carries on all its usual activities except for division. Answer: interphase 96) 97) These are the smallest living units in the body. 97) Answer: cells 98) This is the outer physical boundary of a human cell. 98) Answer: plasma membrane (plasmalemma) 99) This is the name for the currently held theory describing the plasma membrane. 99) Answer: fluid mosaic model 100) The plasma membrane is primarily composed of this type of fat molecule. 100) Answer: phospholipid 101) This type of membrane protein is attached to only one side of the plasma membrane. 101) Answer: peripheral protein 102) This is the mechanism by which large particles enter a cell. 102) Answer: endocytosis 103) Coated pits are covered with this molecule. 103) Answer: clathrin 104) This is the type of protein involved in transport mechanisms across the plasma membrane. 104) Answer: integral proteins 105) This is a genetic disease that leads to very high cholesterol in the blood. 105) Answer: familial hypercholesterolemia ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 106) Differentiate between phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Answer: In phagocytosis, the cell extends pseudopods and engulfs the particle. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, the cell membrane forms inpocketings called caveolae lined with the protein clathrin, and binds to membrane receptors, causing it to be enveloped. 107) Describe the action of exocytosis and the SNAREs. Answer: Exocytosis is the process by which a cell expels materials. These molecules are within a lipid bound secretory vesicle with a vesicle SNARE, which binds to the plasma membrane SNARE, causing the vesicle phospholipid molecules to fuse with the plasma membrane phospholipid molecules, and the molecules are expelled from the cell. 108) Describe the two checkpoints that occur during interphase. Answer: The first checkpoint, G1, ensures that the cell has grown enough and replicated the necessary organelles and other structures to synthesize DNA. The second checkpoint, G2, checks to see whether errors occurred during DNA synthesis. 11
12 109) Describe the mitochondria. Answer: These are long and thin organelles, contain their own DNA involved in their own replication, and move within the cell to sites where they are needed. They produce ATP molecules, which are the equivalent of cellular energy. They are bound by two membranes, the inner one is highly folded into ristae, where many of the critical molecules involved in energy production are imbedded. 110) Describe the three major types of cytoskeletal elements. Answer: Microtubules are the largest and are formed by the protein tubulin. They are stiff, but bendable. Microfilaments are the thinnest, and are strands of the protein actin, and are contractile, and are typically very labile. Intermediate filaments are of intermediate diameter, and are very stabile and permanent, functioning as support structures, as well as holding cells together. 12
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
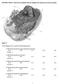 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
Goals. Cells. Cells: The Living Units. By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe.
 C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units
 Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Cells: The Living Units
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 2 Part 1 Cells: The Living Units Introduction to Cells Several important scientists made discoveries
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 2 Part 1 Cells: The Living Units Introduction to Cells Several important scientists made discoveries
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
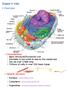 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Cell Theory. Passive Transport
 Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Chapter 2: Introduction to Cells. Introduction to Cells. Cells have three main components. Several important scientists made discoveries about cells
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Cells Several important scientists made discoveries about cells Robert Hooke Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow Cells the smallest living units in our bodies
Chapter 2: Introduction to Cells Several important scientists made discoveries about cells Robert Hooke Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow Cells the smallest living units in our bodies
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cell Structure and Function
 C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Chapter 2: The Cell. Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College
 Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells
 Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
1.3 - Cells. Chapter 3 - Cells
 1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY
 BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Cell. ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange
 Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
3UNIT. Photosynthesis and. Cellular Respiration. Unit PreQuiz? General Outcomes. Unit 3 Contents. Focussing Questions
 3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells
 Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Cell Structure & Interactions
 Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Cells. Introduction: Composite Cell: Bi100 Chapter 3
 Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Cytology. Cell Anatomy. Cell Theory - A good place to start! The generalized cell contains: Cell membrane Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytosol Organelles
 Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
6 functions of membrane proteins integral & peripheral proteins Membrane Junctions
 Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS
 CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells
 Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/human-anatomy-5th-edition-saladin-test-bank/ Chapter 02 - Cytology - The Study of Cells Chapter 02 Cytology -
Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/human-anatomy-5th-edition-saladin-test-bank/ Chapter 02 - Cytology - The Study of Cells Chapter 02 Cytology -
Cell Structure Animal/Human
 Cell Structure Animal/Human cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional if its alive, must contain at least a single cell the function of an organism is the summation of functions of its
Cell Structure Animal/Human cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional if its alive, must contain at least a single cell the function of an organism is the summation of functions of its
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE
 LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 7
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
Cell Structure. Present in animal cell. Present in plant cell. Organelle. Function. strength, resist pressure created when water enters
 Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Chapter 3: The Living Units
 Chapter 3: The Living Units Objectives: 1. Define cell. 2. List the three major regions of a generalized cell and indicate the function of each. 3. Describe the chemical composition of the plasma membrane
Chapter 3: The Living Units Objectives: 1. Define cell. 2. List the three major regions of a generalized cell and indicate the function of each. 3. Describe the chemical composition of the plasma membrane
Structure of a Generalized Cell
 A Quick Tour Through A Cell BIO130 Lab 2 Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy Structure of a Generalized Cell -plasma membrane -cytoplasm: cytosol organelles -nucleus Play TourOfAnimalCell.mpg Plasma membrane
A Quick Tour Through A Cell BIO130 Lab 2 Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy Structure of a Generalized Cell -plasma membrane -cytoplasm: cytosol organelles -nucleus Play TourOfAnimalCell.mpg Plasma membrane
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Cell Organelles and their Functions. Chapter 4 Section 2
 Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
PARTS OF A CELL. The cell is divided into three main parts: 1. Plasma membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Nucleus.
 Cell Overview PARTS OF A CELL The cell is divided into three main parts: 1. Plasma membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Nucleus. Cell Overview (Light Microscope) The initial information in histology was gained by
Cell Overview PARTS OF A CELL The cell is divided into three main parts: 1. Plasma membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Nucleus. Cell Overview (Light Microscope) The initial information in histology was gained by
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
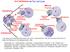 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
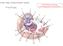 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
