Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: on November 16, 2018 jcb.rupress.org Downloaded from
|
|
|
- Ashley Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 16, 2018 B~IEF NOrmS 799 Permanganate--A New Fixative for Electron Microscopy.* BY Jo~N H. Lu~'T.;~ (From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) During the early phases of tissue sectioning for electron microscopy, virtually all of the standard cytological fixatives were tried. Of these, osmium tetroxide appeared to give the best preservation, and this was further improved by buffering the fixative solution at a slightly alkaline ph (Palade (1)). A variant developed by Dalton (2) contains Os04 in a chromate-dichromate system. Formalin has been used for special purposes for electron microscopy, and a fixative without OsO4 has been described by Low (3), consisting of a chromic acid-formaldehyde mixture. Potassium permanganate, or more specifically the permanganate ion, has occasionally been used as a fixative or stain in light microscopy (4). It provides remarkable preservation of many cell components at the electron microscope level, as the following plates illustrate. The tissue fine structure looks similar to that following osmium treatment, thus rendering less likely the criticism that electron microscopists are merely seeing artifacts of osmium fixation. Besides preserving fine structure, permanganate fixation enhances tissue density * This work was initiated in the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, under a National Research Council Fellowship in the Medical Sciences, for which funds were provided by The Rockefeller Foundation. It was completed while the author was a Visiting Investigator at The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research. Present address: Department of Anatomy, University of Washington, Seattle. Received for publication, A~gust 2!), and contrast. This feature is of interest because of the low atomic weight of manganese (54.9) in comparison to the high atomic weight of osmium (190.8). It would seem that explanations of tissue contrast must consider other factors besides the atomic weight or number of the fixative components. Permanganate appears to fix membrane systems first, (within 15 to 30 minutes), allowing the remaining cellular components either to leach out during dehydration, or to be volatilized in the electron beam as reported by Morgan et al. (5). Longer fixation (1 to 12 hours) retains other structures such as nuclear chromatin, the nucleolus, and the matrix of mitochondria. One hour fixation retains enough nuclear material to give a moderate Feulgen reaction in sections 2# thick. Sodium permanganate appears to offer no advantage over the potassium salt, nor does the addition of OsO4 to the permanganate. The actual details of the method are as follows: A stock solution of reagent grade potassium permanganate (KMnO~) is made up in distilled water to 1.2 per cent w/v and stored in the refrigerator. It is best to keep the stock solution in a well filled, glass-stoppered bottle since KMnO4 solutions are slowly reduced on contact with air. This solution replaces the 2 per cent Os04 stock solution used to prepare the usual 1 per cent buffered OsO4 (Palade (1)). For use, equal volumes of the permanganate stock solution are mixed with the veronal-acetate buffer, giving a final concentration of 0.6 per cent KMnO4 at the ph selected--generally ph Within the range tested, namely from 0.5 to
2 800 BRIEF NOTES 1.2 per cent, the concentration of KMnO4 does not appear to be critical. The buffered KMnO4 solution is cooled in cracked ice, and 1 or 2 mm. cubes of tissue are fixed at O C. for 15 minutes to 12 hours. Tissue fixed in this manner but at room temperature seems to be badly damaged; the effect of intermediate temperatures has not been established. At the end of fixation, the tissue is rinsed for several minutes in cold (0-5 C.) 25 per cent ethanol, and allowed to warm to room temperature in fresh 25 per cent ethanol, (15 to 20 minutes). The blocks are then dehydrated through graded alcohols as usual, and taken into n-butyl methacrylate in which they are embedded. The tissue seems to be more difficult to cut with glass knives than equivalent osmium-fixed material. It is unlikely that KMnO4 will replace OsO4 as a general purpose fixative. Tissue structure shows a somewhat granular texture, the 150 A cytoplasmic granules which have a high RNA content are absent, and mitochondria appear swollen. Membranes, however, are remarkably distinct. Plasma membranes of cells are exceptionally well defined, for example in the brush border of renal convoluted tubular epithelium (Fig. 2) and the C fibers of peripheral nerve (Fig. 3). The paired membranes surrounding mitochondria, and the cristae projecting from the inner membrane are readily apparent in Figs. 1 and 2. The high contrast of the membranes reveals nuclear pores in oblique sections of nuclear envelope (Fig. 1). The layers of the myelin sheath of peripheral nerve are well preserved, including the middle layer (Fig. 4). The vesicles characteristic of synapses are similarly clearly differentiated after permanganate fixation (Fig. 5). Granules in liver, which are probably glycogen, are preserved better than with osmium, and take the form of cytoplasmic rosettes or clusters, composed of small (100 to 150 A) globular elements (Fig. 1). Permanganate destroys the myofilaments of striated muscle, but the sarcoplasmic reticulum is clearly revealed in the interfibrillar spaces where it appears regularly disposed in relation to the A and I bands of the myofibril (Fig. 8). In the pancreas the delicate membrane surrounding the zymogen granules, and the conspicuous parallel array of endoplasmic reticulum are also well defined (Fig. 6). High resolution micrographs reveal a lace-like or reticular structure to these membranes (Fig. 7), in contrast to the homogeneous membranes seen after osmium fixation. Permanganate fixation seems to demonstrate membrane systems with special clarity. It seems almost specific for the endoplasmic reticulum in its broad aspects (Porter (6)). It reveals a reticular structure in these membranes, which may be artifact, or may have some basis in reality. Permanganate is insoluble in oils and fats, in contrast to the high solubility and reactivity of OsO4 in these materials. This feature may contribute to the further understanding of tissue fine structure in terms of the distribution of lipides and proteins. The author is grateful to Dr. K. R. Porter and Dr. G. E. Palade for their suggestions and comments concerning this project. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Palade, G. E., Y. Exp. Med., 1952, 95, Dalton, A. J., Anat. Rec., 1955, 19.1, Low, F. N., Anat. Rec., 1955, 121, Schmidt, W. J., Z. Zellforsch. u. mikr. Anat., 1936, 23, 261.
3 BRIEF NOTES Morgan, C., Moore, D. H., and Rose, H. M., Y. Biophysic. and Biochem. Cytol., 1956, 2, No. 4., suppl., Porter, K. R., The submicroscopic morphology of protoplasm, Harvey Lectures, , 51, in press.
4 802 BRIEF NOTES EXPLANATION OF :PLATES The solid line represents one micron, unless otherwise noted. P~AT~ 223 FIG. 1. Electron microgr~ph of a portion of a mouse liver cell fixed 12 hours at 0 C. in 0.5 per cent KMnO4 at ph 7.4. Mitochondria are present at m, and membranous and vesicular elements of the endoplasmic reticulum at er. A small portion of the nucleus is visible at n. The nuclear membrane is cut obliquely and reveals many nuclear pores (np). Material which probably is glycogen (g/) is apparent as rosettes and clusters of smaller particles which measure about 100 to 150 A in diameter. Taken with Siemens Elmiskop 1, total magnification 54,000. FIG. 2. Electron micrograph of frog kidney illustrating the brush border of the epithelium of the proximal convoluted tubules. The tissue was fixed 1~ hours at 0 C. in 0.6 per cent KMnO4 at ph 7.5. Mitochondria with cristae are present at m, and a portion of the nucleus at n. The brush border (bb) is composed of numerous projections from the cell surface extending into the lumen of the tubule at 1. Vesicular and tubular elements of the endoplasmic reticulum (er) are present throughout the cytoplasm. Micrograph taken with RCA-EMU-2E, total magnification 12,000.
5 THE JOURNAL OF BIOPHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL CYTOLOGY PLATE 223 VOL. 2 (Luft: Permanganate as a new fixative)
6 PLATE 224 FIG. 3. Electron micrograph of a cross-section of a bundle of C fibers in mouse sciatic nerve. Tissue was fixed 45 minutes at 0 C. in 0.6 per cent KMnO4, at ph 7.4. The numerous nerve fibers (n) are embedded at the surface of the cytoplasm of the Schwann cell (sc). It is possible to trace the invaginated Schwann cell membrane partially (1) or almost completely (2) surrounding the axoplasm with its complete cell membrane. Swollen mitochondria (re) and vesicular components of the endoplasmic reticulum (er) are present in the neural elements. Myelin layers of two accompanying A fibers are seen at A. Micrograph taken with RCA-EMU-2A, total magnification 24,000. FIG. 4. Electron micrograph of the myelin sheath of the A fibers in the same section as Fig. 3. The layers of the sheath are well preserved, spaced 115 A apart. These dense layers (dl) appear to be about 20 A wide, whereas the less dense middle layer (ml) between these appears to be about twice this thickness in many places; Taken with the Elmiskop 1 at a total magnification of 170,000. FIG. 5. Electron micrograph of electric tissue of the electric eel, showing a nerve (n) making synaptic contact with the electroplaque (e/). Tissue fixed 11/~ hours at 0 C. in 0.5 per cent KMnO4 at pit 7.3. Synaptic vesicles (sv) are seen in the nerve cytoplasm and near the site of synaptic contact (x). Micrograph taken with Elmiskop 1, total magnification 24,000.
7 THE JOURNAL OF BIOPHYSIC~ AND B~CHEMIC~ CYTOLOGY PLATE 224 VOL. 2 (Luft : Permanganate as a new fixative)
8 PLATE 225 FIG. 6. Electron micrograph of a part of a cell from the exocrine pancreas of a mouse. Tissue fixed 45 minutes at 0 C. in 0.6 per cent KMnO4, ph 7.4. A portion of the nucleus is present at n, and mitochondria at m. The endoplasmic reticulum is present in the familiar parallel cisternae at x, and as the tubular and vesicular forms of the Golgi apparatus at y. Zymogen granules (z) possess a delicate membrane enclosing them. Micrograph taken with RCA-EMU-2A, total magnification 18,700. FIc. 7. Electron micrograph of the parallel sheets of endoplasmic reticulum of pancreas similar to Fig. 6, but fixed 60 minutes. Self-supporting thin section over holes in a carbon film. The granular or reticular appearance of the membranes is apparent. At the thinnest points, (presumably in cross-sectlon), the membranes measure about 30 A in thickness. The 150 A, RNA-rich granules are absent. Taken with Elmiskop 1, total magnification 170,000. FIG. 8. Electron micrograph of striated muscle from mouse diaphragm. Tissue fixed 1 hour at 0 C. in 0.6 per cent KMnO4 at ph 7.4. The myofibrils run vertically with A bands and I bands labelled as such. Z bands are absent, and the continuity of myofilaments is lost. The sarcoplasmic reticulum (sr), however, is clearly present in its usual form, but is much more apparent because of the accentuated contrast. Micrograph taken with Elmiskop 1 at 23,000 total magnification.
9 THE JOURNAL OF BIOPHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL CYTOLOGY PLATE 225 VOL. 2 (Luft: Permanganate as a new fixative)
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
(From the Department of Pathology and Oncology, University of Kansas Medical School, Kansas City, Kansas)
 Published Online: 25 July, 1955 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.1.4.271 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 3, 2018 THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF ADULT VERTEBRATE PERIPHERAL MYELINATED NERVE FIBERS
Published Online: 25 July, 1955 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.1.4.271 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 3, 2018 THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF ADULT VERTEBRATE PERIPHERAL MYELINATED NERVE FIBERS
IT has been shown (Chou, 1957 a, b) that there are three kinds of lipid
 279 The Ultra-fine Structure of Lipid Globules in the Neurones of Helix aspersa By J. T. Y. CHOU and G. A. MEEK (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology; and Department of Human Anatomy,
279 The Ultra-fine Structure of Lipid Globules in the Neurones of Helix aspersa By J. T. Y. CHOU and G. A. MEEK (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology; and Department of Human Anatomy,
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
ON THE THICKNESS OF THE UNIT MEMBRANE
 Published Online: 1 May, 1963 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.17.2.413 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 1, 2018 ON THE THICKNESS OF THE UNIT MEMBRANE TOSHIYUKI YAMAMOTO, M.D. From the
Published Online: 1 May, 1963 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.17.2.413 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 1, 2018 ON THE THICKNESS OF THE UNIT MEMBRANE TOSHIYUKI YAMAMOTO, M.D. From the
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Staining of Tissue Sections for Electron Microscopy with Heavy Metals*
 Published Online: 25 July, 1958 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.4.4.475 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on May 14, 2018 Staining of Tissue Sections for Electron Microscopy with Heavy Metals* BY MICHAEL
Published Online: 25 July, 1958 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.4.4.475 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on May 14, 2018 Staining of Tissue Sections for Electron Microscopy with Heavy Metals* BY MICHAEL
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
The Extracellular Nature of Enamel in the Rat*
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.489 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 1, 2018 The Extracellular Nature of Enamel in the Rat* By MICHAEL L. WATSON, Ph.D.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.489 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 1, 2018 The Extracellular Nature of Enamel in the Rat* By MICHAEL L. WATSON, Ph.D.
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS*
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Cell Structure. Present in animal cell. Present in plant cell. Organelle. Function. strength, resist pressure created when water enters
 Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
R,;habdomyosarcoma, the most common
 Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
ARANEUS SERICATUS CHANGES IN FINE STRUCTURE DURING SILK PROTEIN PRODUCTION IN THE AMPULLATE GLAND OF THE SPIDER. ALLEN L. BELL and DAVID B.
 Published Online: 1 July, 1969 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.42.1.284 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 18, 2018 CHANGES IN FINE STRUCTURE DURING SILK PROTEIN PRODUCTION IN THE AMPULLATE
Published Online: 1 July, 1969 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.42.1.284 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 18, 2018 CHANGES IN FINE STRUCTURE DURING SILK PROTEIN PRODUCTION IN THE AMPULLATE
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Physiology
 Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Acid phosphatase activity in the neutral red granules of mouse exocrine pancreas cells
 343 Acid phosphatase activity in the neutral red granules of mouse exocrine pancreas cells By JENNIFER M. BYRNE (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) With
343 Acid phosphatase activity in the neutral red granules of mouse exocrine pancreas cells By JENNIFER M. BYRNE (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) With
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Electron Microscope Observations on the Root Hair Cell of Azolla imbricata Nakai
 12 Cytologia 28 Electron Microscope Observations on the Root Hair Cell of Azolla imbricata Nakai Sigenobu Kawamatu Biological Institute, Aichi Gakugei University, Okazaki, Japan Received May 7, 1962 Recently
12 Cytologia 28 Electron Microscope Observations on the Root Hair Cell of Azolla imbricata Nakai Sigenobu Kawamatu Biological Institute, Aichi Gakugei University, Okazaki, Japan Received May 7, 1962 Recently
Department of Applied Physiology (Prof. T. Suzuki), Tohoku University School of Medicine, Sendai
 Tohoku 3. exp. Med., 1967, 91, 299-313 Electron Microscopic Study on the Cellular Interrela tionships in the Smooth Muscle Junichiro Nagasawa and Taizo Suzuki Department of Applied Physiology (Prof. T.
Tohoku 3. exp. Med., 1967, 91, 299-313 Electron Microscopic Study on the Cellular Interrela tionships in the Smooth Muscle Junichiro Nagasawa and Taizo Suzuki Department of Applied Physiology (Prof. T.
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
STAINED PECTIN AS SEEN IN THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. PETER ALBERSHEIM, Ph.D., K. M[J'HLETHALER, D.Se., and A. FREY-WYSSLING, D.Sc.
 Published Online: 1 October, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.8.2.501 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 10, 2018 STAINED PECTIN AS SEEN IN THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE PETER ALBERSHEIM,
Published Online: 1 October, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.8.2.501 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 10, 2018 STAINED PECTIN AS SEEN IN THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE PETER ALBERSHEIM,
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Published May 25, 1956
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE OBSERVATIONS ON SYNAPTIC VESI- CLES IN SYNAPSES OF THE RETINAL RODS AND CONES* BY EDUARDO DE ROBERTIS, M.D., AND CARLOS NI. FRANCHI (From Departamenlo de Ultraestructura Celular, Instituto
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE OBSERVATIONS ON SYNAPTIC VESI- CLES IN SYNAPSES OF THE RETINAL RODS AND CONES* BY EDUARDO DE ROBERTIS, M.D., AND CARLOS NI. FRANCHI (From Departamenlo de Ultraestructura Celular, Instituto
Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials are separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. Complex structure Also
 Dr. Gugale Pritesh Ramanlal M.Sc., Ph.D., B.Ed., D.M.L.T. Email id - pritesh.gugale09@gmail.com Contact numbernumber- 8446475310 Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials
Dr. Gugale Pritesh Ramanlal M.Sc., Ph.D., B.Ed., D.M.L.T. Email id - pritesh.gugale09@gmail.com Contact numbernumber- 8446475310 Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE
 TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
t'za~zs 85 ~o 90 (Received for publication, July 5, 1955)
 THE ROLE OF THE GOLGI COMPLEX IN FAT ABSORPTION AS STUDIED WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE WITH OBSERVATIONS ON THE CYTOLOGY OF DUODENAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS BY JULES M. WEISS,* M.D. WrrH THE TECHmC.~ ASSISTANCE
THE ROLE OF THE GOLGI COMPLEX IN FAT ABSORPTION AS STUDIED WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE WITH OBSERVATIONS ON THE CYTOLOGY OF DUODENAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS BY JULES M. WEISS,* M.D. WrrH THE TECHmC.~ ASSISTANCE
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus
 244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 7
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Electron Microscope Studies of the Human Epidermis The Clear Cell of Masson (Dendritic Cell or Melanocyte)*
 Published Online: 25 November, 1958 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.4.6.679 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 1, 2018 Electron Microscope Studies of the Human Epidermis The Clear Cell of Masson
Published Online: 25 November, 1958 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.4.6.679 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 1, 2018 Electron Microscope Studies of the Human Epidermis The Clear Cell of Masson
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Preliminary and Short Report
 Tuz JOURNAL OF INvRSrIOATIVE DERMATOLOOT Copyright 1965 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 45, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report ULTRASTRUCTTJRE OF BLASTOSPORES OF CANDIDA ALBICANS AFTER
Tuz JOURNAL OF INvRSrIOATIVE DERMATOLOOT Copyright 1965 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 45, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report ULTRASTRUCTTJRE OF BLASTOSPORES OF CANDIDA ALBICANS AFTER
(From the Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle)
 THE CONCEPTS OF MEMBRANE FLOW AND MEMBRANE VESICULATION AS MECHANISMS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND ION PUMPING BY H. STANLEY BENNETT, M.D. (From the Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, University of
THE CONCEPTS OF MEMBRANE FLOW AND MEMBRANE VESICULATION AS MECHANISMS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND ION PUMPING BY H. STANLEY BENNETT, M.D. (From the Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, University of
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA
 J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
THE QUESTION OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GOLGI VESICLES AND SYNAPTIC VESICLES IN OCTOPUS NEURONS
 J. Cell Set. 7, 89- (97) Printed in Great Britain THE QUESTION OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GOLGI VESICLES AND SYNAPTIC VESICLES IN OCTOPUS NEURONS E. G. GRAY Department of Anatomy, University College London,
J. Cell Set. 7, 89- (97) Printed in Great Britain THE QUESTION OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GOLGI VESICLES AND SYNAPTIC VESICLES IN OCTOPUS NEURONS E. G. GRAY Department of Anatomy, University College London,
(From the Departments of Pathology and Anatomy, and the Beaumont-May Institute of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine, St.
 Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.2.6.777 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on August 24, 2018 FORMATION OF MYELIN IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF MICE AND RATS,
Published Online: 25 November, 1956 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.2.6.777 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on August 24, 2018 FORMATION OF MYELIN IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF MICE AND RATS,
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle cells have unique characteristics which allow for body movement.
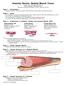 Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
8.2. Types of Neurons
 Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE TISSUE MAST CELL* (From the Dioision of Biological and Medical Research, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, Illinois)
 Published Online: 25 January, 1957 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.3.1.9 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on December 18, 2018 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE TISSUE MAST CELL* BY DOUGLAS E. SMITH, Pa.D.,
Published Online: 25 January, 1957 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.3.1.9 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on December 18, 2018 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE TISSUE MAST CELL* BY DOUGLAS E. SMITH, Pa.D.,
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology
 3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Ultrastructural studies of human cutaneous nerve
 J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 188 Ultrastructural studies of human cutaneous nerve with special reference to lamellated cell inclusions and vacuole-containing cells MARJORE J. EVANS, J. B. FNEAN, AND A. L.
J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 188 Ultrastructural studies of human cutaneous nerve with special reference to lamellated cell inclusions and vacuole-containing cells MARJORE J. EVANS, J. B. FNEAN, AND A. L.
The ultrastructure of the egg and
 The ultrastructure of the egg and central cell of Petunia J.L. van Went Botanisch Laboratorium, Universiteit, Nijmegen SUMMARY The egg and central cell of Petunia hybrida undergo a number of changes and
The ultrastructure of the egg and central cell of Petunia J.L. van Went Botanisch Laboratorium, Universiteit, Nijmegen SUMMARY The egg and central cell of Petunia hybrida undergo a number of changes and
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
MUSCLE DUGESIA TIGRINA. From the Department of Anatomy, University of Illinois, College of Medicine, Chicago
 OBSERVATIONS ON THE FINE STRUCTURE OF PHARYNGEAL MUSCLE IN THE PLANARIAN DUGESIA TIGRINA EDITH KRUGELIS MAcRAE, Ph.D. From the Department of Anatomy, University of Illinois, College of Medicine, Chicago
OBSERVATIONS ON THE FINE STRUCTURE OF PHARYNGEAL MUSCLE IN THE PLANARIAN DUGESIA TIGRINA EDITH KRUGELIS MAcRAE, Ph.D. From the Department of Anatomy, University of Illinois, College of Medicine, Chicago
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Structure of the Rete Mirabile in the Kidney of the Rat as Seen with the Electron Microscope
 Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.1.103 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 2, 2018 Structure of the Rete Mirabile in the Kidney of the Rat as Seen with
Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.1.103 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 2, 2018 Structure of the Rete Mirabile in the Kidney of the Rat as Seen with
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Trigeminal Ganglion. Fine Structure of Nerve-Cell Bodies and Satellite Cells in the
 Fine Structure of Nerve-Cell Bodies and Satellite Cells in the Trigeminal Ganglion ANDREW D. DIXON* Department of Anatomy, Medical School, University of Manchester, England A solution to some of the major
Fine Structure of Nerve-Cell Bodies and Satellite Cells in the Trigeminal Ganglion ANDREW D. DIXON* Department of Anatomy, Medical School, University of Manchester, England A solution to some of the major
Cytology II Study of Cells
 Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
Muscle Tissue. Xie Fenfen. Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Anhui Medical University
 Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Looking Inside Cells
 Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
THE FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN THE ERYTHROCYTES OF THE COD, GADUS CALLARIAS
 J. Cell Set. 8, 407-412 (1971) 407 Printed in Great Britain THE FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN THE ERYTHROCYTES OF THE COD, GADUS CALLARIAS N.W.THOMAS Department of Anatomy, Marischal College, Aberdeen, Scotland
J. Cell Set. 8, 407-412 (1971) 407 Printed in Great Britain THE FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN THE ERYTHROCYTES OF THE COD, GADUS CALLARIAS N.W.THOMAS Department of Anatomy, Marischal College, Aberdeen, Scotland
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION*
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
:1c.c :& Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* structure with rounded ends and a striated lamella
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
DURING the past ten years it has been suggested that the classical form
 163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
10 The Golgi Apparatus: The First 100 Years
 2 Structure With no cell compartment or organelle has morphology served such a pivotal role in its discovery and investigation as with the apparatus of Golgi. The original description of the apparato reticulo
2 Structure With no cell compartment or organelle has morphology served such a pivotal role in its discovery and investigation as with the apparatus of Golgi. The original description of the apparato reticulo
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 8, 339-346 (1984) C by Japan Society for Cell Biology Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice Ikuo Yamaoka, Sumie Katsuta and Yoshimi
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 8, 339-346 (1984) C by Japan Society for Cell Biology Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice Ikuo Yamaoka, Sumie Katsuta and Yoshimi
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
