Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers. EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3
|
|
|
- Robert Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3
2
3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring bioluminescent bacteria. The fish uses the light to attract prey and to signal potential mates. The bacteria receive nutrients from the fish.
4 Prokaryotes impacts on humans Harmful Illness Beneficial Essential tools in agriculture and industry
5 Pathogenic Prokaryotes
6 Exo and Endotoxins Poisons Exotoxins are proteins secreted by prokaryotes Endotoxins are lipopolysaccharide components of the outer membrane of gram negative bacteria
7 Bioremediation
8 a tentative phylogeny of some of the major taxa of prokaryotes based on molecular systematics
9 Structure of the Bacterial Cell
10 EUKARYOTES PROKARYOTES BACTERIA ARCHAEA
11 Prokaryotes (Bacteria) Eubacter "True" bacteria human pathogens clinical or environmental one kingdom Archaea Environmental organisms second kingdom
12 Eukaryotes Other cell-based life e.g. plants animals fungi
13 Prokaryotic Cell (versus Eukaryotic Cell) Not compartmentalized Cell membranes lack sterols (e.g. cholesterol) Single circular chromosome Ribosomal are 70S - subunits 30S 50S
14 A prokaryotic chromosome. The thin, tangled loops surrounding this ruptured E. coli cell are parts of a single ring of DNA (colorized TEM).
15 Bacteria versus Archaebacteria Eubacteria peptidoglycan (murein) muramic acid Archaebacteria pseudomurein no muramic acid
16 Shape
17
18
19 Basic components of a bacterial cell
20 Flagella: long filamentous appendages with filament, hook and basal body Used in movement Can present taxis Negative Positive Monotrichous Peritrichous Flagellar H protein acts as an antigen E.c O157:H7 Flagellin
21 Flagella Arrangement Figure 4.7
22 Fimbriae/pili Shorter and less complex than flagella Helps adhere to surfaces Used for sex and communication
23
24 Gram Positives have large cell wall and Teichoic acids
25 Gram negative cells have lipopolysaccharide
26 Typical Prokaryotic cell types Cell membrane Nucleoid Flagellum Cell wall Gram +ve cell Gram ve cell Pili Capsule Granule Cell (inner) membrane Outer membrane Ribosomes Cell wall
27 Lipoteichoic acid GRAM POSITIVE Peptidoglycan-teichoic acid Cytoplasmic membrane Cytoplasm GRAM NEGATIVE Porin Lipopolysaccharide Periplasmic space Outer Membrane Inner (cytoplasmic) membrane Braun lipoprotein Cytoplasm
28 Gram-Negative Outer Membrane Figure 4.13c
29 How the gram stain works to differentiate between G+ and G-
30
31 Plasma Membrane Phospholipid bilayer Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Transmembrane proteins Figure 4.14b
32
33 Membrane is as viscous as olive oil. Proteins move to function Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids rotate and move laterally Figure 4.14b
34 Ribosomes Figure 4.6a
35 Ribosomes Figure 4.19
36 Endospores Resting and waiting stage Resistant to drying and other harsh conditions
37
38 The Cell Envelope Gram Positive Gram Negative
39
40 Oxidative phosphorylation occurs at cell membrane (since there are no mitochondria). Cell Wall Cytoplasm Cell membrane The cell wall is outside of cell membrane rigid, protecting cell from osmotic lysis.
41 GRAM NEGATIVE CELL ENVELOPE Outer Membrane (Major permeability barrier) Porin Lipopolysaccharide Braun lipoprotein Periplasmic space Degradative enzyme Inner (cytoplasmic) membrane Periplasmic binding protein Permease Cytoplasm
42 GRAM POSITIVE CELL Degradative enzyme ENVELOPE Lipoteichoic acid Peptidoglycan-teichoic acid Cytoplasmic membrane Cytoplasm
43 FLAGELLA Some bacteria are motile Locomotory organelles- flagella Taste environment Respond to food/poison chemotaxis
44
45
46
47
48 Axial filaments similar function to flagella run lengthwise along cell snake-like movement
49
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles
 Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Bacterial Structures. Capsule or Glycocalyx TYPES OF FLAGELLA FLAGELLA. Average size: µm 2-8 µm Basic shapes:
 PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
Ch 4. Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Microbiology. Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism. Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi
 Microbiology Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi Microbiology: the study of organisms too small to be seen without magnification. Micro - too small to be seen
Microbiology Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi Microbiology: the study of organisms too small to be seen without magnification. Micro - too small to be seen
Cell Structure. Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell. Cytoplasmic Membrane 4/6/2011. Chapter 3. Cytoplasmic membrane
 Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Fig. LPS in Gram negative bacteria
 Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Structure of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
 Structure of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Review of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus vs nucleoid DNA : circular vs linear, presence of histones Membranous organelles Cell wall-peptidoglycan Cell
Structure of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Review of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus vs nucleoid DNA : circular vs linear, presence of histones Membranous organelles Cell wall-peptidoglycan Cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3)
 Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Classification of Infectious Agents. Dr W. D. Colby
 Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi
 number Done by Corrected by 46 2017/9/20 Doctor Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 2 nd year Medical Students JU Bacterial Structure and
number Done by Corrected by 46 2017/9/20 Doctor Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 2 nd year Medical Students JU Bacterial Structure and
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Characteristics DNA not enclosed in membrane. No histone proteins associated with DNA. Lack membrane-bound organelles
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Characteristics DNA not enclosed in membrane. No histone proteins associated with DNA. Lack membrane-bound organelles
ILOs. 10/10/2016 Maha Fathy 2
 ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
Chapter 4 M I C R O B I O L O G Y. The Anatomy of the Cell. a n i n t r o d u c t i o n
 ninth edition TORTORA FUNKE CASE M I C R O B I O L O G Y a n i n t r o d u c t i o n Chapter 4 The Anatomy of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case! Copyright 2006
ninth edition TORTORA FUNKE CASE M I C R O B I O L O G Y a n i n t r o d u c t i o n Chapter 4 The Anatomy of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case! Copyright 2006
Chapter 4. Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells. Comparing Prokaryotic and. Eukaryotic cells.
 Chapter 4 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No nucleus No organelles Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce asexually via binary fission
Chapter 4 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No nucleus No organelles Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce asexually via binary fission
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 4.1 What is a Cell? Each cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells) or a nucleoid (in prokaryotic cells) 1 Nucleoid concentrated DNA
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 4.1 What is a Cell? Each cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells) or a nucleoid (in prokaryotic cells) 1 Nucleoid concentrated DNA
Bacterial Structure and Function
 Bacterial Structure and Function Charles Okolie, PhD. Room 311 (on level 4), First College Building, Landmark University okolie.charles@lmu.edu.ng Tel: Ext: Mobile: 08060241166 Structure of Bacteria The
Bacterial Structure and Function Charles Okolie, PhD. Room 311 (on level 4), First College Building, Landmark University okolie.charles@lmu.edu.ng Tel: Ext: Mobile: 08060241166 Structure of Bacteria The
chapter one: the history of microbiology
 chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 8/29/2016 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 8/29/2016 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
Bacterial Cell Structures. Stijn van der Veen
 Bacterial Cell Structures Stijn van der Veen How do I know what bacterium makes my patient ill? Bacterial species can be differentiated by: Morphology (shape) Composition (cell envelope and other structures)
Bacterial Cell Structures Stijn van der Veen How do I know what bacterium makes my patient ill? Bacterial species can be differentiated by: Morphology (shape) Composition (cell envelope and other structures)
! gives mechanical strength to the cell and protects it from exploding due to osmotic lysis (shape and strength due to the peptidoglycan)
 Cell Wall! The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the bacterial cell just outside of the plasma membrane Functions to:! gives the bacterium its shape! gives mechanical strength to the cell and
Cell Wall! The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the bacterial cell just outside of the plasma membrane Functions to:! gives the bacterium its shape! gives mechanical strength to the cell and
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college
 A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
Introduction. Microbiology. Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Lecture 2
 Introduction to Microbiology Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Lecture 2 Cell structure / Eukaryotes 1. Nucleolus 2. Nucleus 3. Ribosome (80S) 4. Vesicle 5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum 6. Golgi apparatus (or
Introduction to Microbiology Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Lecture 2 Cell structure / Eukaryotes 1. Nucleolus 2. Nucleus 3. Ribosome (80S) 4. Vesicle 5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum 6. Golgi apparatus (or
What s in a Cell? From Ch. 4
 What s in a Cell? From Ch. 4 Plant cell walls Amit1b.files.wordpress.com genomebiology.com Figure 4.1 Arrangements of cocci. Plane of division Diplococci Streptococci Tetrad Sarcinae Staphylococci. Figure
What s in a Cell? From Ch. 4 Plant cell walls Amit1b.files.wordpress.com genomebiology.com Figure 4.1 Arrangements of cocci. Plane of division Diplococci Streptococci Tetrad Sarcinae Staphylococci. Figure
Chapter 3: Cellular Structure
 Chapter 3: Cellular Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2. Eukaryotic Cell Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure A. Cell Shape B. External Structures C. Internal (Cytoplasmic) Structures A. Cell
Chapter 3: Cellular Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2. Eukaryotic Cell Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure A. Cell Shape B. External Structures C. Internal (Cytoplasmic) Structures A. Cell
it selectively allows some molecules to pass into the organism
 Multiple Choice Quiz Procaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Choose the best answer 1. The significance of the plasma membrane is that it selectively allows some
Multiple Choice Quiz Procaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Choose the best answer 1. The significance of the plasma membrane is that it selectively allows some
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 02 Glimpses of Microbial World-Bacteria. Good morning students. (Refer Slide Time: 00:29)
 Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of Agricultural and Food Engineering Assistant Prof. Dr. Saikat Chakraborty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of Agricultural and Food Engineering Assistant Prof. Dr. Saikat Chakraborty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Chapter 3 The Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 The Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function 1 Does Size Matter? for a sphere: surface area = 4πr 2 ; volume = 4/3πr 3 if r = 1 µm; then surface area = 12.6 and vol. = 4.2 if r = 2 µm; then surface
Chapter 3 The Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function 1 Does Size Matter? for a sphere: surface area = 4πr 2 ; volume = 4/3πr 3 if r = 1 µm; then surface area = 12.6 and vol. = 4.2 if r = 2 µm; then surface
Review from Biology A
 Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE/FUNCTION. 2. The uses the visible light to illuminate cell. 3. How is the magnification of a compound microscope calculated?
 CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE/FUNCTION 1. Define magnification and the term resolution. 2. The uses the visible light to illuminate cell. 3. How is the magnification of a compound microscope calculated? 4.
CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE/FUNCTION 1. Define magnification and the term resolution. 2. The uses the visible light to illuminate cell. 3. How is the magnification of a compound microscope calculated? 4.
Prokaryotic Profiles The Bacteria and Archaea. Chapter 3
 Prokaryotic Profiles The Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 3 Prokaryotic Form and Function Prokaryotes can be distinguished from eukaryotes by: the way their DNA is packaged (lack of nucleus and histones) the
Prokaryotic Profiles The Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 3 Prokaryotic Form and Function Prokaryotes can be distinguished from eukaryotes by: the way their DNA is packaged (lack of nucleus and histones) the
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
done by: mohammad haitham
 done by: mohammad haitham "Anatomy" and Function of Prokaryotes: The pictures are very important, go back to the slide2! Last lecture we talked about the shape of the bacteria. Now the shape of the bacteria
done by: mohammad haitham "Anatomy" and Function of Prokaryotes: The pictures are very important, go back to the slide2! Last lecture we talked about the shape of the bacteria. Now the shape of the bacteria
Made by :aseel al-waked corrected by : sarah awaisheh
 Microbiology sheet (2) Made by :aseel al-waked corrected by : sarah awaisheh DATE :25-9-2016 "Anatomy" and Function of Prokaryotes: Last lecture we talked about the shape of the bacteria. Now the shape
Microbiology sheet (2) Made by :aseel al-waked corrected by : sarah awaisheh DATE :25-9-2016 "Anatomy" and Function of Prokaryotes: Last lecture we talked about the shape of the bacteria. Now the shape
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells. Dr. Carmen Rexach Mt San Antonio College Microbiology
 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells By Dr. Carmen Rexach Mt San Antonio College Microbiology Eukaryotes = true nucleus DNA in linear arrangement = chromosomes DNA associated with histone & nonhistone proteins
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells By Dr. Carmen Rexach Mt San Antonio College Microbiology Eukaryotes = true nucleus DNA in linear arrangement = chromosomes DNA associated with histone & nonhistone proteins
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
BABS1202 APPLIED BIOMOLECULAR SCIENCES
 BABS1202 APPLIED BIOMOLECULAR SCIENCES CELL STRUCTURE BINARY FISSION VS. MITOSIS Bacteria and archaea have no nucleus and no centromeres Binary fission cannot be divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase
BABS1202 APPLIED BIOMOLECULAR SCIENCES CELL STRUCTURE BINARY FISSION VS. MITOSIS Bacteria and archaea have no nucleus and no centromeres Binary fission cannot be divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function
 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
Mahon: Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 4 th Edition
 Mahon: Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 4 th Edition Chapter 01: Bacterial Cell Structure, Physiology, Metabolism, and Genetics Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. To survive, microbial inhabitants have learned
Mahon: Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 4 th Edition Chapter 01: Bacterial Cell Structure, Physiology, Metabolism, and Genetics Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. To survive, microbial inhabitants have learned
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Prokaryotic structure and function 1
 - 1 - Prokaryotic structure and function 1 Morphology, size and other features to distinguish Size Bacteria 1-6!m length, 0.2-1.5!m wide/thick = prokaryote no nuclear membrane, mitochondria, golgi bodies,
- 1 - Prokaryotic structure and function 1 Morphology, size and other features to distinguish Size Bacteria 1-6!m length, 0.2-1.5!m wide/thick = prokaryote no nuclear membrane, mitochondria, golgi bodies,
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Structure of Prokaryotes
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege There are many differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, all cells have four common structures: the plasma membrane, which functions as a barrier for the cell
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege There are many differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, all cells have four common structures: the plasma membrane, which functions as a barrier for the cell
Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
I. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells
 科目 : 生命科學概論教材單元 : A Tour of the Cell 共 8 頁第 1 頁 I. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells 1. A were first isolated from mold in 1928 2. The widespread use of a drastically
科目 : 生命科學概論教材單元 : A Tour of the Cell 共 8 頁第 1 頁 I. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells 1. A were first isolated from mold in 1928 2. The widespread use of a drastically
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. RPTSE Biology Fall 2015, Dr. Jong B. Lee 1. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Microbiology 微生物学 Spring-Summer
 Microbiology 微生物学 2017 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Microbiology 微生物学 2017 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Cell Biology 1.2- Ultrastructure of Cells
 Essential idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure than prokaryotes. Cell Biology 1.2- Ultrastructure of Cells Nature of science: Developments in scientific research follow improvements
Essential idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure than prokaryotes. Cell Biology 1.2- Ultrastructure of Cells Nature of science: Developments in scientific research follow improvements
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
All bacteria are Prokaryotes
 All bacteria are Prokaryotes Chapter 4: Prokaryote cell biology Chapter 6: Gram Stain Dr. Amy Rogers Fall 2006 Lectures: MW Noon Office Hours: Wednesdays 9 AM Most Mondays No nucleus or other membrane-bound
All bacteria are Prokaryotes Chapter 4: Prokaryote cell biology Chapter 6: Gram Stain Dr. Amy Rogers Fall 2006 Lectures: MW Noon Office Hours: Wednesdays 9 AM Most Mondays No nucleus or other membrane-bound
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
Important Chemical Components of Surface Structures
 Structure Milton R.J. Salton Kwang-Shin Kim General Concepts Gross Morphology Bacteria have characteristic shapes (cocci, rods, spirals, etc.) and often occur in characteristic aggregates (pairs, chains,
Structure Milton R.J. Salton Kwang-Shin Kim General Concepts Gross Morphology Bacteria have characteristic shapes (cocci, rods, spirals, etc.) and often occur in characteristic aggregates (pairs, chains,
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Medical Microbiology. Microscopic Techniques :
 ! Lecture 2 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Microscopic Techniques : Several types of microscopes are used in study of microbiology one of the most important tools for studying microorganisms
! Lecture 2 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Microscopic Techniques : Several types of microscopes are used in study of microbiology one of the most important tools for studying microorganisms
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222
 Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collec=on of ma>er that can live Cell structure is correlated to cellular
Ch. 6 A Tour of the Cell BIOL 222 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collec=on of ma>er that can live Cell structure is correlated to cellular
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
ii. cellular organization: prokaryotes have no membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotes have membranebound organelles, including a nucleus.
 Bacteriology Exam 1 Name 1/31/06 1. (3 pts) What are 3 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Explain each difference. i. size: prokaryotes are typically from 1 to 10 μm in diameter, whereas eukaryotes
Bacteriology Exam 1 Name 1/31/06 1. (3 pts) What are 3 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Explain each difference. i. size: prokaryotes are typically from 1 to 10 μm in diameter, whereas eukaryotes
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Prokaryotic Profiles: The Bacteria and Archaea
 Prokaryotic Profiles: The Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 3 To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please note:
Prokaryotic Profiles: The Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 3 To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please note:
Bacteria. Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles)
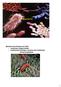 Bacteria Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles) 1 Grouped by their need for oxygen obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen
Bacteria Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles) 1 Grouped by their need for oxygen obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
j. Project outward from plasma membranes of
 10. fluid [p, 56] c. Reflects the mixed composition of cell membranes concentrated 9. mosaic [p.56] the channel to the other side where they are more b. Channels across a membrane; solutes diffuse through
10. fluid [p, 56] c. Reflects the mixed composition of cell membranes concentrated 9. mosaic [p.56] the channel to the other side where they are more b. Channels across a membrane; solutes diffuse through
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Microbiology 微生物学 Spring-Summer
 Microbiology 微生物学 2016 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Microbiology 微生物学 2016 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
The Basic Principle of Microbiology
 The Basic Principle of Microbiology Chapter 1 The Basic Character of Bacterium Section 1 Bacterial Morphology I. Size of bacteria Measure unit ----- μm (micrometer) 大 中 小 炭疽芽胞杆菌 3-10 μm 大肠埃希菌 2-3 μm 布鲁菌
The Basic Principle of Microbiology Chapter 1 The Basic Character of Bacterium Section 1 Bacterial Morphology I. Size of bacteria Measure unit ----- μm (micrometer) 大 中 小 炭疽芽胞杆菌 3-10 μm 大肠埃希菌 2-3 μm 布鲁菌
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
1/18/2018. BIO 1101 Lecture 4 Chapters 4 & 5: Cells & The Working Cell. What is a Cell?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BIO 1101 Lecture 4 Chapters 4 & 5: Cells & The Working Cell What is a Cell? The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life. All organisms are made of cells
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BIO 1101 Lecture 4 Chapters 4 & 5: Cells & The Working Cell What is a Cell? The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life. All organisms are made of cells
2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope. nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, ribosomes
 Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
UNIT 10: Classification and Ecology DAYSHEET 106: Introduction to Kingdoms of Life
 UNIT 10: Classification and Ecology DAYSHEET 106: Introduction to Kingdoms of Life Name Biology I Date: Catalyst/Bellringer: Use the passage below to answer the following questions. Be sure to use your
UNIT 10: Classification and Ecology DAYSHEET 106: Introduction to Kingdoms of Life Name Biology I Date: Catalyst/Bellringer: Use the passage below to answer the following questions. Be sure to use your
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
