3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Overview of Cell Structures
|
|
|
- Ann Daniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
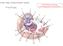
1 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and other organelles. List special structures of plant cells, and state what they do. Explain how cells are organized in living things. Vocabulary ATP cell wall central vacuole chloroplast cytoskeleton endoplasmic reticulum endosymbiotic theory Golgi apparatus mitochondria phospholipid bilayer vacuole vesicle Introduction Your body is made up of trillions of cells, but all of them perform the same basic life functions. They all obtain and use energy, respond to the environment, and reproduce. How do your cells carry out these basic functions and keep themselves and you alive? To answer these questions, you need to know more about the structures that make up cells. Overview of Cell Structures In some ways, a cell resembles a plastic bag full of Jell-O. Its basic structure is a plasma membrane filled with cytoplasm. Like Jell-O containing mixed fruit, the cytoplasm of the cell also contains various structures, such as a nucleus and other organelles. Figure 3.9 shows the structures inside a typical eukaryotic cell, in this case the cell of an animal. Refer to the figure as you read about the structures below. You can also explore the structures of an interactive animal cell at this link:
2 FIGURE 3.9 Animal Cell. This animal cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a plasma membrane. The cytoplasm contains many different organelles. The Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane forms a barrier between the cytoplasm inside the cell and the environment outside the cell. It protects and supports the cell and also controls everything that enters and leaves the cell. It allows only certain substances to pass through, while keeping others in or out. The ability to allow only certain molecules in or out of the cell is referred to as selective permeability or semipermeability. To understand how the plasma membrane controls what crosses into or out of the cell, you need to know its composition. The plasma membrane is discussed at (6:16). The cell wall (see below) is also discussed in this video. The Phospholipid Bilayer The plasma membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fatty acids and alcohol. The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer. As shown in Figure 3.10, each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The head loves water (hydrophilic) and the tails hate water (hydrophobic). The water-hating tails are on the interior of the membrane, whereas the water-loving heads point outwards, toward either the cytoplasm or the fluid that surrounds the cell. Molecules that are hydrophobic can easily pass through the plasma membrane, if they are small enough, because they are water-hating like the interior of the membrane. Molecules that are hydrophilic, on the other hand, cannot pass through the plasma membrane at least not without help because they are water-loving like the exterior of the membrane. Other Molecules in the Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane also contains other molecules, primarily other lipids and proteins. The green molecules in Figure 3.10, for example, are the lipid cholesterol. Molecules of cholesterol help the plasma membrane keep its shape. Many of the proteins in the plasma membrane assist other substances in crossing the membrane. Extensions of the Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane may have extensions, such as whip-like flagella or brush-like cilia. In single-celled organisms, like those shown in Figure 3.11, the membrane extensions may help the organisms move. In multicellular organisms,
3 FIGURE 3.10 Phospholipid Bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer consists of two layers of phospholipids, with a hydrophobic, or water-hating, interior and a hydrophilic, or water-loving, exterior. The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in the single phospholipid molecule. The polar head group and fatty acid chains are attached by a 3-carbon glycerol unit. the extensions have other functions. For example, the cilia on human lung cells sweep foreign particles and mucus toward the mouth and nose. FIGURE 3.11 Flagella (left) and cilia (right). Flagella and cilia are extensions of the plasma membrane of many cells.
4 Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton The cytoplasm consists of everything inside the plasma membrane of the cell. It includes the watery, gel-like material called cytosol, as well as various structures. The water in the cytoplasm makes up about two thirds of the cell s weight and gives the cell many of its properties. Functions of the Cytoplasm The cytoplasm has several important functions, including 1. suspending cell organelles 2. pushing against the plasma membrane to help the cell keep its shape 3. providing a site for many of the biochemical reactions of the cell Cytoskeleton Crisscrossing the cytoplasm is a structure called the cytoskeleton, which consists of thread-like filaments and tubules. You can see these filaments and tubules in the cells in Figure As its name suggests, the cytoskeleton is like a cellular skeleton. It helps the cell maintain its shape and also holds cell organelles in place within the cytoplasm. FIGURE 3.12 Cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton gives the cell an internal structure, like the frame of a house. In this photograph, filaments and tubules of the cytoskeleton are green and red, respectively. The blue dots are cell nuclei. The cytoskeleton is discussed in the following video (4:50). The Nucleus and Other Organelles Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and several other types of organelles. These structures are involved in many vital cell functions. The Nucleus The nucleus is the largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell and is often considered to be the cell s control center. This is because the nucleus controls which proteins the cell makes. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell contains most of the cell s DNA, which makes up chromosomes and is encoded with genetic instructions for making proteins.
5 Mitochondria The mitochondrion (plural, mitochondria) is an organelle that makes energy available to the cell. This is why mitochondria are sometimes referred to as the power plants of the cell. They use energy from organic compounds such as glucose to make molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), an energy-carrying molecule that is used almost universally inside cells for energy. Scientists think that mitochondria were once free-living organisms because they contain their own DNA. They theorize that ancient prokaryotes infected (or were engulfed by) larger prokaryotic cells, and the two organisms evolved a symbiotic relationship that benefited both of them. The larger cells provided the smaller prokaryotes with a place to live. In return, the larger cells got extra energy from the smaller prokaryotes. Eventually, the prokaryotes became permanent guests of the larger cells, as organelles inside them. This theory is called the endosymbiotic theory, and it is widely accepted by biologists today Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle that helps make and transport proteins and lipids. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Both types are shown in Figure RER looks rough because it is studded with ribosomes. It provides a framework for the ribosomes, which make proteins. Bits of its membrane pinch off to form tiny sacs called vesicles, which carry proteins away from the ER. SER looks smooth because it does not have ribosomes. SER also makes lipids, stores substances, and plays other roles. Ribosomes Ribosomes are small organelles where proteins are made. They contain the nucleic acid RNA, which assembles and joins amino acids to make proteins. Ribosomes can be found alone or in groups within the cytoplasm as well as on the RER. Golgi Apparatus The Golgi apparatus is a large organelle that processes proteins and prepares them for use both inside and outside the cell. It is shown in Figure The Golgi apparatus is somewhat like a post office. It receives items (proteins from the ER), packages and labels them, and then sends them on to their destinations (to different parts of the cell or to the cell membrane for transport out of the cell). The Golgi apparatus is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell. At the link below, you can watch an animation showing how the Golgi apparatus does all these jobs. Vesicles and Vacuoles Both vesicles and vacuoles are sac-like organelles that store and transport materials in the cell. Vesicles are much smaller than vacuoles and have a variety of functions. The vesicles that pinch off from the membranes of the ER and Golgi apparatus (see Figure 3.13) store and transport protein and lipid molecules. Some vesicles are used as chambers for biochemical reactions. Other vesicles include: Lysosomes, which use enzymes to break down foreign matter and dead cells. Peroxisomes, which use oxygen to break down poisons.
6 FIGURE 3.13 This drawing includes the nucleus, RER, SER, and Golgi apparatus. From the drawing, you can see how all these organelles work together to make and transport proteins. Centrioles Centrioles are organelles involved in cell division. They help organize the chromosomes before cell division so that each daughter cell has the correct number of chromosomes after the cell divides. Centrioles are found only in animal cells and are located near the nucleus (see Figure 3.9). Special Structures in Plant Cells Plant cells have several structures that are not found in animal cells, including a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and organelles called plastids. You can see each of these structures in Figure You can also view them in an interactive plant cell at the link below. Cell Wall The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of a plant cell. It supports and protects the cell. Tiny holes, or pores, in the cell wall allow water, nutrients, and other substances to move into and out of the cell. The cell wall is made up mainly of complex carbohydrates, including cellulose. Central Vacuole Most mature plant cells have a large central vacuole. This vacuole can make up as much as 90% of the cell s volume. The central vacuole has a number of functions, including storing substances such as water, enzymes, and salts. It also helps plant tissues, such as stems and leaves, stay rigid and hold their shape. It even helps give flowers, like the ones in Figure 3.15, their beautiful colors.
7 FIGURE 3.14 Plant Cell. In addition to the organelles and other structures found inside animal cells, plant cells also have a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids such as chloroplasts. Can you find each of these structures in the figure? Plastids Plastids are organelles in plant cells that carry out a variety of different functions. The main types of plastids and their functions are described below. Chloroplasts are plastids that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. They capture light energy from the sun and use it to make food. A chloroplast is shown in Figure Chromoplasts are plastids that make and store other pigments. The red pigment that colors the flower petals in Figure 3.15 was made by chromoplasts. Leucoplasts are plastids that store substances such as starch or make small molecules such as amino acids. Like mitochondria, plastids contain their own DNA. Therefore, according to endosymbiotic theory, plastids may also have evolved from ancient, free-living prokaryotes that invaded larger prokaryotic cells. If so, they allowed early eukaryotes to make food and produce oxygen.
8 FIGURE 3.15 These flowers are red because of red pigment molecules in the central vacuoles of their cells. The bright colors are an important adaptation. They help the flowers attract pollinators such as hummingbirds so the plants can reproduce. Organization of Cells Cells can exist as individual cells or as groups of cells. Cells in groups can be organized at several levels. From One Cell to Many The simplest level of cell organization is a single-celled organism, and the most complex level is a multicellular organism. In between these two levels are biofilms and colonies. A single-celled organism floats freely and lives independently. Its single cell is able to carry out all the processes of life without any help from other cells. A biofilm is a thin layer of bacteria that sticks to a surface. Cells in a biofilm are all alike, but they may play different roles, such as taking in nutrients or making the glue that sticks the biofilm to the surface. The sticky plaque that forms on teeth is a biofilm of bacterial cells. Some single-celled organisms, such as algae, live in colonies. A colony is an organized structure composed of many cells, like the Volvox sphere in Figure Volvox are algae that live in colonies of hundreds of cells. All of the cells in the colony live and work cooperatively. For example, they can coordinate the movement of their flagella, allowing them to swim together through the water as though they were part of a single organism. A multicellular organism consists of many cells and has different types of cells that are specialized for various functions. All the cells work together and depend on each other to carry out the life processes of the organism. Individual cells are unable to survive on their own. Levels of Organization in Multicellular Organisms Scientists think that multicellular organisms evolved when many single-celled organisms of the same species started to work together and benefited from the relationship. The oldest known multicellular organisms are algae that lived 1.2 billion years ago. As multicellular organisms continued to evolve, they developed increasingly complex levels of organization. Today there are multicellular organisms at all levels of organization, from the simplest, cell level of organization to the most complex, organ-system level of organization. Consider these examples:
9 FIGURE 3.16 Volvox Colony. Volvox cells live in a colony shaped like a hollow ball. The cells of the colony may be connected by strands of cytoplasm and can function together. For example, the whole colony can swim from one place to another as one. Sponges have cell-level organization, in which different cells are specialized for different functions, but each cell works alone. For example, some cells digest food, while other cells let water pass through the sponge. Jellyfish have tissue-level organization, in which groups of cells of the same kind that do the same job form tissues. For example, jellyfish have some tissues that digest food and other tissues that sense the environment. Roundworms have organ-level organization, in which two or more types of tissues work together to perform a particular function as an organ. For example, a roundworm has a primitive brain that controls how the organism responds to the environment. Human beings have organ system-level organization, in which groups of organs work together to do a certain job, with each organ doing part of the overall task. An example is the human digestive system. Each digestive system organ from the mouth to the small intestine does part of the overall task of breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. Lesson Summary The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that supports and protects a cell and controls what enters and leaves it. The cytoplasm consists of everything inside the plasma membrane, including watery cytosol and organelles. The cytoplasm suspends the organelles and does other jobs. The cytoskeleton crisscrosses the cytoplasm and gives the cell an internal framework. The nucleus is the largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell and contains most of the cell s DNA. Other organelles in eukaryotic cells include the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles, and centrioles (in animal cells only). Each type of organelle has important functions in the cell. Plant cells have special structures that are not found in animal cells, including a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and organelles called plastids. Cells can exist independently as single-celled organisms or with other cells as multicellular organisms. Cells of a multicellular organism can be organized at the level of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.
10 Lesson Review Questions Recall 1. Describe the composition of the plasma membrane. 2. List functions of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. 3. What is the role of the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell? 4. List three structures that are found in plant cells but not in animal cells. 5. Outline the levels of organization of cells in living things, starting with the simplest level, that of single-celled organisms. Apply Concepts 6. Create a diagram to show how the cells of multicellular organisms may be organized at different levels, from the level of the cell to the level of the organ system. Give an example of a multicellular organism at each level of organization. Think Critically 7. Explain why hydrophobic ( water-hating ) molecules can easily cross the plasma membrane, while hydrophilic ( water-loving ) molecules cannot. 8. What is endosymbiotic theory? How does it explain the presence of certain organelles in eukaryotic cells? 9. Explain how the following organelles ensure that a cell has the proteins it needs: nucleus, rough and smooth ER, vesicles, and Golgi apparatus. Points to Consider Cells carry out all the functions of life, and they use nutrients and oxygen and produce wastes. These substances must cross the plasma membrane. How do you think substances cross the plasma membrane to enter or leave the cell? Does the membrane have tiny holes in it like a sieve? What if the substances are large? Protein molecules, for example, are very large. How do they enter or leave the cell?
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson 3.2: True or False. Lesson 3.2: Critical Reading
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson 3.2: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. The water-hating hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer face the outside
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson 3.2: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. The water-hating hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer face the outside
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
Draw and Complete the Chart.
 Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
BIOLOGY FIRST QUARTER UNIT 2. The Chemistry of Life Matter and Organic Compounds 2.1 Biochemical Reactions 2.2
 BIOLOGY FIRST QUARTER UNIT 2 The Chemistry of Life Matter and Organic Compounds 2.1 Biochemical Reactions 2.2 Cellular Structure and Function Introduction to Cells 3.1 Cell Structure 3.2 Cell Transport
BIOLOGY FIRST QUARTER UNIT 2 The Chemistry of Life Matter and Organic Compounds 2.1 Biochemical Reactions 2.2 Cellular Structure and Function Introduction to Cells 3.1 Cell Structure 3.2 Cell Transport
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Vocabulary. Cell Wall. Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell.
 Bellringer Objectives Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Plant cells and animal cells have many cell parts in common. But they also
Bellringer Objectives Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Plant cells and animal cells have many cell parts in common. But they also
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Cellular Boundaries. Cell Organelles. The Nucleus and Cell Control. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall. Nucleus 10/11/2012. Cell Membrane Cell Wall
 Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Cellular Structure and Function
 7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
BIOSC 041. v Today s lecture. v Today s lab. v Note- Monday is a holiday good time to do some reading!
 BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells.
 CELL ORGANELLES - NOTES CELL THEORY Cells are the basic unit of life. The Cell Theory states that: 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells. 2) All cells carry
CELL ORGANELLES - NOTES CELL THEORY Cells are the basic unit of life. The Cell Theory states that: 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells. 2) All cells carry
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key. Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions
 Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Chapter 3. Cell Structure
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Objectives. To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles.
 Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Parts (organelles) of the Cell
 Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 11. Mr. Gandha
 WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 11 Mr. Gandha TOPICS OF BIOLOGY 11 Chemicals of life Cells Evolution Taxonomy Microbio Plants Animals BIOLOGY THIS SEMESTER Review of Biology and Processes Adaptation and Evolution:
WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 11 Mr. Gandha TOPICS OF BIOLOGY 11 Chemicals of life Cells Evolution Taxonomy Microbio Plants Animals BIOLOGY THIS SEMESTER Review of Biology and Processes Adaptation and Evolution:
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
7.2 Cell Structure. Sunday, December 16, :13 PM. Chapter 7 Cell Strucutre and Function Page 1
 7.2 Cell Structure Sunday, December 16, 2012 5:13 PM Vocabulary: Cytoplasm: in eukaryotic cells, all cellular contents outside the nucleus; in prokaryotic cells, all of the cells' contents Organelle: specialized
7.2 Cell Structure Sunday, December 16, 2012 5:13 PM Vocabulary: Cytoplasm: in eukaryotic cells, all cellular contents outside the nucleus; in prokaryotic cells, all of the cells' contents Organelle: specialized
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
NUCLEOLUS CELL MEMBRANE MITOCHONDRIA CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST NUCLEAR MEMBRANE VACOULE NUCLEUS ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD
 CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY
 BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
Cells 2/2/2019. Cell Theory. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Life on Earth. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Bacterial Cell. Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cells Structure and Function All living things are made of cells New cells come from pre-existing cells NO Spontaneous Generation Francesco Redi Italian 17 th century Louis Pasteur French 19
Cell Theory Cells Structure and Function All living things are made of cells New cells come from pre-existing cells NO Spontaneous Generation Francesco Redi Italian 17 th century Louis Pasteur French 19
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function
 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cells. Cells are the best!
 Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems. Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
 IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
Cells. A typical animal cell THE CELL MEMBRANE FIRST STOP
 WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
Structure Characteristics Function. Double layer of phospholipid molecules studded with proteins
 CELL BOOKLETS: Instructions for creating the pages Take 4 pieces of white computer type paper. Cut them so that you have 4 slips from each page that measure 8-1/2 x 2-3/4 inches. You will have 8 slips
CELL BOOKLETS: Instructions for creating the pages Take 4 pieces of white computer type paper. Cut them so that you have 4 slips from each page that measure 8-1/2 x 2-3/4 inches. You will have 8 slips
Cell Organelles and their Functions. Chapter 4 Section 2
 Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
A Tour of the Cell Period
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
10/5/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope. nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, ribosomes
 Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Cell Structure. Cells. Why are cells so small? 9/15/2016. Schleiden and Schwann proposed Cell Theory in
 Cell Structure Cells Cells are sacs of fluid that are reinforced by proteins and surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float organelles. Organelles: structures inside the cell that are used for metabolic
Cell Structure Cells Cells are sacs of fluid that are reinforced by proteins and surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float organelles. Organelles: structures inside the cell that are used for metabolic
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
