Development of an In Vitro Human Liver System for Interrogating Non-Alcoholic. Brian R. Wamhoff, 501 Locust Ave., Charlottesville, VA 22902
|
|
|
- Colleen Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Information Development of an In Vitro Human Liver System for Interrogating Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Ryan Feaver, Banumathi K Cole, Mark J Lawson, Stephen A Hoang, Svetlana Marukian, Robert A Figler, Arun J Sanyal, Brian R Wamhoff, Ajit Dash HemoShear Therapeutics LLC, Charlottesville, VA Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine Richmond, VA Corresponding Author: Brian R Wamhoff, 5 Locust Ave, Charlottesville, VA 9 Wamhoff@HemoShearcom
2 Supplemental Figures and Tables: Supplemental Figure Correlation plot demonstrating the reproducibility of data from different experiments in the lipotoxic system Hepatocyte transcriptomic data of all genes (each gene is an individual dot) from two different experiments (# and #) performed months apart with n=3 and n=4 donors, respectively, is represented in this correlation plot Comparison is healthy vs lipotoxic + ng/ml TNFα milieu for each experiment The scatterplot shows that genes from both experiments exhibit a strong positive correlation in gene response, and thus high reproducibility (Log Fold Change) Experiment # (Log Fold Change) Experiment # LGLI NASH BGA3 Pearson correlation = at a p value <e-6
3 Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Oxaloacetate PC TCA Cycle Fatty Acid Pyruvate ACLY Citrate ACSL3 ACSL ACAS ACACB ACACA Acetyl-CoA MLYCD ACSL4 ACSL5 ACSL6 Malonyl-CoA CPTA FASN Palmitic Acid Acyl-CoA Cytosol Cytosol ELOVL6 Steric Acid SCD Oleic Acid Acetyl-CoA CPTA Long-Chain fatty acid Beta Oxidation ACSL ACSL3 ACSL4 ACSL5 Mitochondrion logfold ACSL6 ACAS Fatty acyl CoA DGAT DGAT Triacylglyceride Synthesis pathway Supplemental Figure Transcriptomic data from hepatocytes exposed to the lipotoxic compared to the healthy milieu is overlaid onto a diagram representing the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway A red-filled box indicates the gene is upregulated while a blue-filled box indicates the gene is downregulated; the intensity of the color corresponds to greater logfoldchanges Boxes with a green perimeter indicate the gene expression logfoldchange is significant (FDR<%) 3
4 Cholesterol Biosynthesis Fatty Acid Degradation Acetyl-CoA HMGCS HMG-CoA Cholesterol HMGCR DHCR7 Mevalonic acid 7-Dehydrocholesterol MVK SC5DL Mevalonic acid-5p Lathosterol PMVK Mevalonic acid 5-pyrophosphate NSDHL SC4MOL CYP5A Dimethylallylpyrophosphate IDI MVD isopentenyl pyrophosphate Lanosterin LSS logfold FDPS (S)-,3-Epoxysqualene Geranyl-PP farnesyl pyrophosphate Squalene SQLE FDPS FDFT Supplemental Figure 3 Transcriptomic data from hepatocytes exposed to the lipotoxic compared to the healthy milieu is overlaid onto a diagram representing the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway A red-filled box indicates the gene is upregulated while a blue-filled box indicates the gene is downregulated; the intensity of the color corresponds to greater logfoldchanges Boxes with a green perimeter indicate the gene expression logfoldchange is significant (FDR<%) 4
5 Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis Glucose SLCA SLCA SLCA3 SLCA4 Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis SLCA5 Glucose HK HK HK3 G6PC GCK Glucose-6P Pentose Phosphate Pathway GPI Glycogen metabolism PFKM PFKL PFKP Fructose 6P Fructose-,6BP FBP FBP ALDOA ALDOB ALDOC Glyceraldehyde 3P Dihydroxyacetone-P Triglyceride synthesis GAPDHS GAPDH TPI,3BP-Glycerate PGK PGK Cytosol 3P-Glycerate PGAM Mitochondrion PGAM P-Glycerate ENO Aspartate Aspartate ENO3 P-enolpyruvate ENO GOT GOT PKM PKM Oxaloacetate Oxaloacetate PKLR PCK MDH PC MDH LDHAL6B Pyruvate Malate Malate logfold LDHA LDHB LDHC Lactate MPC MPC Pyruvate PDHA PDHA PDHB TCA Cycle DLAT DLD PDHX Acetyl-CoA Supplemental Figure 4 Transcriptomic data from hepatocytes exposed to the lipotoxic compared to the healthy milieu is overlaid onto a diagram representing the glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathway A red-filled box indicates the gene is upregulated while a blue-filled box indicates the gene is downregulated; the intensity of the color corresponds to greater logfoldchanges Boxes with a green perimeter indicate the gene expression logfoldchange is significant (FDR<%) 5
6 Count 4 Value Gene Response Heatmap Gene Response Heatmap Gene Gene Response Heatmap Heatmap Gene Response Heatmap Gene Response Heatmap Gene Response Heatmap Count 6 Value Count 4 Value Count Count 6 Value Value Count Value FADD NUMA PTK BID CASP7 SPTAN RIPK TNFRSFB FAS Apoptosis cell CYPA CAT HADHA TXNRD NOX4 HADHB MGST XDH ACADS NQO CASP6 NFKBEC HEALTH ACADM SATB GPX TNFRSFA MAPK4 ECHS CASP MADD NFIX TRADD SOD3 ECI CASP8 UGTA6 APAF CASP MAPK DECR DIABLO GSR CRADD GCLC Oxidative Stress Response DFFA SOD TNFRSFA TOP SP CASP9 TXNRD CASP3 CYBA MAP3K TXN CYCS GAS NFEL DFFB SOD BAX JUNB KRT8 BCLL FOS VIM GPX3 TNFSF HMOX APP MAOA GSN LIMK MTX Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Beta Oxidation Genes (97) comparison MUT ACADL PCCA MCEE PCCB HADH Genes (9) ACADVL Inflammation Genes (9) comparison cell CXCL6 CCR6 CCL6 CXCL TLR4 CXCL CXCL8 TLR CCL TLR STAT ILRB CXCL6 IFNAR CCL5 STAT6 IFNGR STAT5A CSF STAT ILR STAT5B MIF IL5 IFNAR TLR3 TNFRSFB IFNLR IL7 TNFSF3B ILRN CXCR5 IFNGR TLR6 TLR5 STAT3 AIMP CXCL CXCL3 Genes (86) Inflammasome Genes (86) PTGS EDN PTGS comparison cell cell PYCARD PRX7 TXNIP CASP BCLL NFKB APP NFKB TXN RELA PANX HSP9AB SUGT Genes (73) logfold Genes (73) cell EC SMC cell_type i p Responses (NA) Responses (NA) Responses (NA) (NA) Responses (NA) Responses (NA) Responses (NA) HSP9AB CALM HSP9B CAV Supplemental Figure 5 Transcriptomic data from hepatocytes NOS3exposed to the lipotoxic compared to the healthy milieu is presented KLFfor various biological pathways associated with cellular stress and inflammation KLF4 Expression of each gene is represented as logfold-change of lipotoxic vs ARG healthy CCA STATIC milieu CCA STATIC (red=upregulation, ICS CCA ICS CCA CCA STATIC blue=downregulation) CCA STATIC ICS CCA ICS CCA n=6 experiments, 3 donors 6
7 IL8 (pg/ml) MCP(pg/ml) CULTURE: MILIEU: < INTERACTION: < Y Y H H + TNF CULTURE: < MILIEU: < INTERACTION: 8 IL6 (fg/ml) p= p=3 YKL4 (pg/ml) CULTURE: < MILIEU: < INTERACTION: TNF CULTURE: < MILIEU: < INTERACTION: 76 CXCL (pg/ml) VEGF (pg/ml) CULTURE: 53 MILIEU: < INTERACTION: TNF CULTURE: 4 MILIEU: 8 INTERACTION: 4 Mono-culture Multi-culture 8 64 Y Y H H + TNF + TNF + TNF Supplemental Figure 6 The presence of non-parenchymal cells (NPCs) in the in vitro human liver system significantly impacts its inflammatory profile Secreted analytes were measured in the media effluent from devices at day The lipotoxic milieu for these experiments is composed of 65µM oleic acid and ng/ml TNFα n=4 experiments, donor Triangles indicate samples were below lower limit of quantification Tables above charts provide overall significance from -way ANOVA for cell culture and milieu treatment conditions and the interaction p-value Multiple comparison were performed as indicated with p<5, p<, -way ANOVA, Tukey 7
8 Mono-culture Milieu Mono-culture Milieu 5 Mono-culture PC PC Multi-culture Milieu Milieu 5 Multi-culture Milieu Multi-culture Milieu 5 5 PC PC Supplemental Figure 7 The presence of non-parenchymal cells (NPCs) in the in vitro human liver system significantly impacts the transcriptomic profile of hepatocytes Transcriptomic data was acquired from hepatocytes exposed for days to a lipotoxic milieu composed of 65µM oleic acid and ng/ml TNFα in the presence or absence of NPCs n=3-6 experiments, donor Gene expression profile reveals that the hepatocytes from healthy and lipotoxic treatments separate along principle component, and these further separate along principle component if co-cultured with NPCs 8
9 CE CER DAG DCER FFA HCER LCER LPC (OCA) (VEH) logfold LPE PC PE PI RSI SM TAG 4 4 logfold (VEH) (VEH) Supplemental Figure 8 OCA treatment in the lipotoxic milieu promotes a change in lipid profile towards the healthy controls Lipids from hepatocytes from device exposed to the healthy or lipotoxic milieu with 5µM OCA or vehicle control were measured by metabolomics Scatterplot representation of differentially expressed lipids in these hepatocytes are shown as logfold-change and colored by RSI n=4 experiments, donors Each lipid species is represented in an individual plot: CE (cholesterol ester), CER (ceramide), DAG (diacylglycerol), DCER (dihydroceramide), FFA (free fatty acid), HCER (hexosylceramide), LCER (lactosylceramide), LPC (lysophosphatidylcholine), LPE (lysophosphatidylethanolamine), PC (phosphatidylcholine), PE (phosphatidylethanolamine), PI (phosphatidylinositol), SM (sphingomyelin), TAG (triacylglycerol) 9
10 p= Total Intracellular Cholesterol (Fold VEH) 8 Veh OCA ATOR Supplemental Figure 9 Obeticholic acid (OCA) increases total intracellular cholesterol levels Total intracellular cholesterol was measured from hepatocytes from the device exposed to vehicle control, 5µM OCA, or 3nM atorvastatin (ator) in the lipotoxic milieu for days and represented as fold change relative to vehicle controls Atorvastatin serves as a positive control as it inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme of the cholesterolproducing mevalonate pathway n=4 experiments, 4 donors p<5, student s -tailed t-test
11 In Vitro References / Figure/Table Model Reviews Steatosis / Lipogenesis Yes Fig -3 Hypertriglycermia Yes Table -5 Increased Cholesterol Yes Table -5 Increased Glucose Output Yes Fig 3A,3 6 Insulin Resistance Yes Fig 3-3,6,7 Cell Stress / Elevated ALT Yes Fig 4-3,7,8 Inflammatory Signaling Yes Fig 4,3,7,8 Increased Apoptosis Yes Fig 4,3,7-9 Histological Features (eg ballooning) NA -3 Early Fibrosis Yes Fig 5,3,7, Advanced Fibrosis Fig 5,3, Cirrhosis NA,3, Oncogenesis NA,3 Supplemental Table Pathological features of NAFLD in the in vitro human liver lipotoxic system
12 Donor Donor ID Age Gender BMI Vendor HC5-3 Male 5 XenoTech QHuf44 55 Female 9 QPS 3 QHuf58 58 Female QPS 4 HC3-3 4 Female 3 XenoTech 5 QHu Male 3 QPS Supplemental Table Hepatic donors used in this study with their sourcing details and demographic information
13 Supplemental References: () Sass DA, Chang P, Chopra KB Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical review Dig Dis Sci 5;5:7-8 () Paschos P, Paletas K Non alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome Hippokratia 9;3:9-9 (3) Marra F, Lotersztajn S Pathophysiology of NASH: perspectives for a targeted treatment Curr Pharm Des 3;9: (4) Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ, Jessurun J, Boldt, MD, Parks EJ Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease J Clin Invest 5;5: (5) Puri P, Baillie RA, Wiest MM, Mirshahi F, Choudhury J, Cheung O, et al A lipidomic analysis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Hepatology 7;46:8-9 (6) Chitturi S, Abeygunasekera S, Farrell GC, Holmes-Walker J, Hui, JM, Fung C, et al NASH and insulin resistance: Insulin hypersecretion and specific association with the insulin resistance syndrome Hepatology ;35: (7) Basaranoglu M, Basaranoglu G, Senturk H From fatty liver to fibrosis: a tale of "second hit" World J Gastroenterol 3;9:58-65 (8) Takaki A, Kawai D, Yamamoto K Multiple hits, including oxidative stress, as pathogenesis and treatment target in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) Int J Mol Sci 3;4:
14 (9) Wieckowska A, Zein NN, Yerian LM, Lopez AR, McCullough AJ, Feldstein AE In vivo assessment of liver cell apoptosis as a novel biomarker of disease severity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Hepatology 6;44:7-33 () Friedman SL Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver Physiol Rev 8;88;5-7 4
SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc1,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD,!! Sébastien!M.!
 SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD, SébastienM.Labbé,,MathildeMouchiroud,,AlexandreCaron,,BlandineSecco,, Elizaveta
SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD, SébastienM.Labbé,,MathildeMouchiroud,,AlexandreCaron,,BlandineSecco,, Elizaveta
Lipid and Bile Acids as NAFLD- Related Biomarkers
 Lipid and Bile Acids as NAFLD- Related Biomarkers Puneet Puri, MBBS, MD Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 1st International Workshop
Lipid and Bile Acids as NAFLD- Related Biomarkers Puneet Puri, MBBS, MD Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 1st International Workshop
Development of an in vitro human liver system for interrogating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
 Downloaded from http:// on December 8, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90954 Development of an in vitro human liver system for interrogating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Ryan E. Feaver, 1 Banumathi
Downloaded from http:// on December 8, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90954 Development of an in vitro human liver system for interrogating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Ryan E. Feaver, 1 Banumathi
Supplementary Materials Modeling cholesterol metabolism by gene expression profiling in the hippocampus
 Supplementary Materials Modeling cholesterol metabolism by gene expression profiling in the hippocampus Christopher M. Valdez 1, Clyde F. Phelix 1, Mark A. Smith 3, George Perry 1,2, and Fidel Santamaria
Supplementary Materials Modeling cholesterol metabolism by gene expression profiling in the hippocampus Christopher M. Valdez 1, Clyde F. Phelix 1, Mark A. Smith 3, George Perry 1,2, and Fidel Santamaria
Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC. Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC
 Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Poly-unsaturated phospholipids WE (FA18:1) A B C D OAHFA 18:1/24:0 OAHFA 18:1/30:2 PS 38:4 C18:1C23:0 OAHFA 18:1/25:0 OAHFA 18:1/30:1
 Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Correlation scatter plots illustrating individual lipid species from various classes that exhibited statistically significant correlations to age. (A-B) Various species
Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Correlation scatter plots illustrating individual lipid species from various classes that exhibited statistically significant correlations to age. (A-B) Various species
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Metabolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients
 Metaolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients Franck Chiappini, Audrey Coilly, Hanane Kadar, Philippe Gual, Alert Tran, Christophe Desterke, Didier
Metaolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients Franck Chiappini, Audrey Coilly, Hanane Kadar, Philippe Gual, Alert Tran, Christophe Desterke, Didier
Lecture 16. Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III
 Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma Lipids
 Application Note omics LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma s Authors Tomas Cajka and Oliver Fiehn West Coast Metabolomics Center, University of California Davis, 451 Health Sciences Drive,
Application Note omics LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma s Authors Tomas Cajka and Oliver Fiehn West Coast Metabolomics Center, University of California Davis, 451 Health Sciences Drive,
Lecture 16. Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III
 Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
NASH Bench to Bedside
 NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
LIPID METABOLISM
 LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
Assessed Molecular Mechanism of Action of Milagro de la Selva
 Assessed Molecular Mechanism of Action of Milagro de la Selva Results A report prepared by Connexios Life Sciences Bangalore 1. Muscle - C2C12 cells. 1.1. Glucose uptake, Glycolysis and Tricarboxylic acid
Assessed Molecular Mechanism of Action of Milagro de la Selva Results A report prepared by Connexios Life Sciences Bangalore 1. Muscle - C2C12 cells. 1.1. Glucose uptake, Glycolysis and Tricarboxylic acid
Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells.
 Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
How To Use SubpathwayGMir
 How To Use SubpathwayGMir Li Feng, Chunquan Li and Xia Li May 20, 2015 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 The experimentally verified mirna-target interactions 2 3 Reconstruct KEGG metabolic pathways 2 3.1 Embed
How To Use SubpathwayGMir Li Feng, Chunquan Li and Xia Li May 20, 2015 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 The experimentally verified mirna-target interactions 2 3 Reconstruct KEGG metabolic pathways 2 3.1 Embed
Lipid Metabolism. Catabolism Overview
 Lipid Metabolism Pratt & Cornely, Chapter 17 Catabolism Overview Lipids as a fuel source from diet Beta oxidation Mechanism ATP production Ketone bodies as fuel 1 High energy More reduced Little water
Lipid Metabolism Pratt & Cornely, Chapter 17 Catabolism Overview Lipids as a fuel source from diet Beta oxidation Mechanism ATP production Ketone bodies as fuel 1 High energy More reduced Little water
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Table S1. Genes in each pathway selected for analysis.
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Genes in each pathway selected for analysis. Gene Chr Start End bp Pathway 1 AKR1C1 10 5000044 5022159 22115 COX 2 AKR1C2 10 5029967 5060207 30240 COX 3 AKR1C3 10 5077549 5149878
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Genes in each pathway selected for analysis. Gene Chr Start End bp Pathway 1 AKR1C1 10 5000044 5022159 22115 COX 2 AKR1C2 10 5029967 5060207 30240 COX 3 AKR1C3 10 5077549 5149878
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
glucose glucose 6-phospho fructose 6-phosphate fructose 1,6-bisphosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
 Cells glucose glucose glucose 6-phospho glycogen pentose phosphate T 1-phosphate 6-phosphate gluconate CC T CC+PD-1 pathway Isobar: fructose 1,6-diphosphate; glucose 1,6-diphosphate DHAP lactate fructose
Cells glucose glucose glucose 6-phospho glycogen pentose phosphate T 1-phosphate 6-phosphate gluconate CC T CC+PD-1 pathway Isobar: fructose 1,6-diphosphate; glucose 1,6-diphosphate DHAP lactate fructose
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol
 Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Lippincott s Chapter 16 Fatty Acid Synthesis Mainly in the Liver Requires Carbon Source: Acetyl CoA Reducing Power: NADPH 8 CH 3 COO C 15 H 33 COO Energy Input:
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Lippincott s Chapter 16 Fatty Acid Synthesis Mainly in the Liver Requires Carbon Source: Acetyl CoA Reducing Power: NADPH 8 CH 3 COO C 15 H 33 COO Energy Input:
ALT (U/L) (Relative expression) HDL (mm) (Relative expression) ALT (U/L) (Relative expression)
 a DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.96 P =. DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.99 P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.9 DMT mrna () BMI (kg/m ) 8 6 r =.7 P =.966 DMT mrna () 8 ALT (U/L) 8 6 r = -.66 P =.76 DMT
a DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.96 P =. DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.99 P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.9 DMT mrna () BMI (kg/m ) 8 6 r =.7 P =.966 DMT mrna () 8 ALT (U/L) 8 6 r = -.66 P =.76 DMT
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Modifications of Pyruvate Handling in Health and Disease Prof. Mary Sugden
 Modifications of Handling Modifications of Handling Centre for Diabetes and Metabolic Medicine Institute of Cell and Molecular Science Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry 1 Potential
Modifications of Handling Modifications of Handling Centre for Diabetes and Metabolic Medicine Institute of Cell and Molecular Science Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry 1 Potential
number Done by Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb
 number 23 Done by A. Rawajbeh Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are used by the peripheral tissues like the skeletal and cardiac muscles, where they are the preferred source
number 23 Done by A. Rawajbeh Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are used by the peripheral tissues like the skeletal and cardiac muscles, where they are the preferred source
METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM HCV
 METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE HCV Steatosis Insulin resistance Arun J Sanyal M.D. Chairman, Div. of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE HCV Steatosis Insulin resistance Arun J Sanyal M.D. Chairman, Div. of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Glycolysis Part 2. BCH 340 lecture 4
 Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
Fatty liver as a consequence and cause of insulin resistance: Lessons from type 2 diabetic liver
 Endocrine Journal 2012, 59 (9), 745-763 Re v i e w Fatty liver as a consequence and cause of insulin resistance: Lessons from type 2 diabetic liver Toshinari Takamura, Hirofumi Misu, Tsuguhito Ota and
Endocrine Journal 2012, 59 (9), 745-763 Re v i e w Fatty liver as a consequence and cause of insulin resistance: Lessons from type 2 diabetic liver Toshinari Takamura, Hirofumi Misu, Tsuguhito Ota and
Points 1. Following is the overall reaction catalyzed by the Calvin-Benson cycle:
 BCH 4054 February 22, 2002 HOUR TEST 2 NAME_ Points 1. Following is the overall reaction catalyzed by the Calvin-Benson cycle: CO 2 + 3ATP + 2NADPH 1/3 glyceraldehyde-3-p + 3ADP + 2NADP + Give the structures
BCH 4054 February 22, 2002 HOUR TEST 2 NAME_ Points 1. Following is the overall reaction catalyzed by the Calvin-Benson cycle: CO 2 + 3ATP + 2NADPH 1/3 glyceraldehyde-3-p + 3ADP + 2NADP + Give the structures
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Triacylglycerol and Fatty Acid Metabolism
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM II. Triacylglycerol synthesis A. Overall pathway Glycerol-3-phosphate + 3 Fatty acyl-coa à Triacylglycerol + 3 CoASH B. Enzymes 1. Acyl-CoA synthase 2. Glycerol-phosphate
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM II. Triacylglycerol synthesis A. Overall pathway Glycerol-3-phosphate + 3 Fatty acyl-coa à Triacylglycerol + 3 CoASH B. Enzymes 1. Acyl-CoA synthase 2. Glycerol-phosphate
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol
 Fatty Acid Synthesis Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Requires Carbon Source: Reducing Power: NADPH Energy Input: ATP Why Energy? Why Energy? Fatty Acid Fatty Acid + n(atp) ΔG o : -ve Fatty
Fatty Acid Synthesis Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Requires Carbon Source: Reducing Power: NADPH Energy Input: ATP Why Energy? Why Energy? Fatty Acid Fatty Acid + n(atp) ΔG o : -ve Fatty
Companion to Biosynthesis of Ketones & Cholesterols, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Lecture Notes
 Companion to Biosynthesis of Ketones & Cholesterols, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Lecture Notes The major site of acetoacetate and 3-hydorxybutyrate production is in the liver. 3-hydorxybutyrate is the
Companion to Biosynthesis of Ketones & Cholesterols, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Lecture Notes The major site of acetoacetate and 3-hydorxybutyrate production is in the liver. 3-hydorxybutyrate is the
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Information transmission
 1-3-3 Case studies in Systems Biology Goutham Vemuri goutham@chalmers.se Information transmission Fluxome Metabolome flux 1 flux flux 3 Proteome metabolite1 metabolite metabolite3 protein 1 protein protein
1-3-3 Case studies in Systems Biology Goutham Vemuri goutham@chalmers.se Information transmission Fluxome Metabolome flux 1 flux flux 3 Proteome metabolite1 metabolite metabolite3 protein 1 protein protein
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Typical and Atypical
 Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Typical and Atypical Disclosure Naim Alkhouri, MD discloses the following relationships with commercial companies: Membership in the Speakers Bureau for Alexion
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Typical and Atypical Disclosure Naim Alkhouri, MD discloses the following relationships with commercial companies: Membership in the Speakers Bureau for Alexion
Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
 Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1249 1254 Cytokeratin 18 Fragment Levels as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Bariatric Surgery Patients DIMA L. DIAB,* LISA YERIAN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1249 1254 Cytokeratin 18 Fragment Levels as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Bariatric Surgery Patients DIMA L. DIAB,* LISA YERIAN,
How do we retain emphasis on function?
 Systems Biology Systems biology studies biological systems by systematically perturbing them (biologically, genetically, or chemically); monitoring the gene, protein, and informational pathway responses;
Systems Biology Systems biology studies biological systems by systematically perturbing them (biologically, genetically, or chemically); monitoring the gene, protein, and informational pathway responses;
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids. By Dr.QUTAIBA A. QASIM
 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids By Dr.QUTAIBA A. QASIM Fatty Acids Definition Fatty acids are comprised of hydrocarbon chains terminating with carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids and their associated derivatives
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids By Dr.QUTAIBA A. QASIM Fatty Acids Definition Fatty acids are comprised of hydrocarbon chains terminating with carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids and their associated derivatives
Summary of fatty acid synthesis
 Lipid Metabolism, part 2 1 Summary of fatty acid synthesis 8 acetyl CoA + 14 NADPH + 14 H+ + 7 ATP palmitic acid (16:0) + 8 CoA + 14 NADP + + 7 ADP + 7 Pi + 7 H20 1. The major suppliers of NADPH for fatty
Lipid Metabolism, part 2 1 Summary of fatty acid synthesis 8 acetyl CoA + 14 NADPH + 14 H+ + 7 ATP palmitic acid (16:0) + 8 CoA + 14 NADP + + 7 ADP + 7 Pi + 7 H20 1. The major suppliers of NADPH for fatty
Yun-Jung Choi, Jiangao Song, Jeff D. Johnson, Charles McWherter. NASH-TAG Conference Park City, Utah January 4, 2019
 Combination Therapy of Seladelpar and Liraglutide Attenuates Obesity, Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis in a Diet-induced and Biopsy-confirmed Mouse Model of NASH Yun-Jung Choi, Jiangao Song, Jeff D. Johnson,
Combination Therapy of Seladelpar and Liraglutide Attenuates Obesity, Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis in a Diet-induced and Biopsy-confirmed Mouse Model of NASH Yun-Jung Choi, Jiangao Song, Jeff D. Johnson,
Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004
 Name Write your name on the back of the exam Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004 This examination consists of forty-four questions, each having 2 points. The remaining
Name Write your name on the back of the exam Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004 This examination consists of forty-four questions, each having 2 points. The remaining
Comprehensive Lipid Profiling of Human Liver Tissue Extracts of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 Comprehensive Lipid Profiling of Human Liver Tissue Extracts of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Multiplexed Precursor Ion Scanning and LipidView Software Brigitte Simons 1 and Bianca Arendt 2 1 AB SCIEX,
Comprehensive Lipid Profiling of Human Liver Tissue Extracts of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Multiplexed Precursor Ion Scanning and LipidView Software Brigitte Simons 1 and Bianca Arendt 2 1 AB SCIEX,
Lipid metabolism. Degradation and biosynthesis of fatty acids Ketone bodies
 Lipid metabolism Degradation and biosynthesis of fatty acids Ketone bodies Fatty acids (FA) primary fuel molecules in the fat category main use is for long-term energy storage high level of energy storage:
Lipid metabolism Degradation and biosynthesis of fatty acids Ketone bodies Fatty acids (FA) primary fuel molecules in the fat category main use is for long-term energy storage high level of energy storage:
Unit 2: Metabolic Processes
 How is energy obtained biologically? Recall: Red Ox Reactions Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Oxidation Is the chief mechanism by which chemical potential energy is released This energy comes from reduced
How is energy obtained biologically? Recall: Red Ox Reactions Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Oxidation Is the chief mechanism by which chemical potential energy is released This energy comes from reduced
Supplementary figures legends
 Supplementary Information to Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome fibroblasts and ipscs: cellular models for uncovering diseaseassociated signaling pathways and establishing a screening platform for anti-oxidants
Supplementary Information to Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome fibroblasts and ipscs: cellular models for uncovering diseaseassociated signaling pathways and establishing a screening platform for anti-oxidants
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe
 number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
Transcriptomic analysis of hepatic responses to testosterone deficiency in miniature pigs fed a high-cholesterol diet
 Cai et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:59 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1283-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Transcriptomic analysis of hepatic responses to testosterone deficiency in miniature pigs fed a high-cholesterol
Cai et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:59 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1283-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Transcriptomic analysis of hepatic responses to testosterone deficiency in miniature pigs fed a high-cholesterol
Simvastatin Modulates the Alzheimer s Disease-Related Gene seladin-1
 Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 28 (2012) 1 5 IOS Press 1 Supplementary Data Simvastatin Modulates the Alzheimer s Disease-Related Gene seladin-1 Maria C. Ramos, Saleta Sierra, Carlos Ramirez, Javier Velasco
Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 28 (2012) 1 5 IOS Press 1 Supplementary Data Simvastatin Modulates the Alzheimer s Disease-Related Gene seladin-1 Maria C. Ramos, Saleta Sierra, Carlos Ramirez, Javier Velasco
Review of Carbohydrate Digestion
 Review of Carbohydrate Digestion Glycolysis Glycolysis is a nine step biochemical pathway that oxidizes glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid. During this process, energy is released and some of it
Review of Carbohydrate Digestion Glycolysis Glycolysis is a nine step biochemical pathway that oxidizes glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid. During this process, energy is released and some of it
METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI 1 METABOLISM Process of how cells acquire, transform, store and use energy Study of the chemistry, regulation and energetics
METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI 1 METABOLISM Process of how cells acquire, transform, store and use energy Study of the chemistry, regulation and energetics
Biochemistry Sheet 27 Fatty Acid Synthesis Dr. Faisal Khatib
 Page1 بسم رلاهللا On Thursday, we discussed the synthesis of fatty acids and its regulation. We also went on to talk about the synthesis of Triacylglycerol (TAG). Last time, we started talking about the
Page1 بسم رلاهللا On Thursday, we discussed the synthesis of fatty acids and its regulation. We also went on to talk about the synthesis of Triacylglycerol (TAG). Last time, we started talking about the
6. How Are Fatty Acids Produced? 7. How Are Acylglycerols and Compound Lipids Produced? 8. How Is Cholesterol Produced?
 Lipid Metabolism Learning bjectives 1 How Are Lipids Involved in the Generationand Storage of Energy? 2 How Are Lipids Catabolized? 3 What Is the Energy Yield from the xidation of Fatty Acids? 4 How Are
Lipid Metabolism Learning bjectives 1 How Are Lipids Involved in the Generationand Storage of Energy? 2 How Are Lipids Catabolized? 3 What Is the Energy Yield from the xidation of Fatty Acids? 4 How Are
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids
 Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and
 Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Lipid Metabolism. Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals
 Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Cholesterol and Sphingolipids in Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease.
 Cholesterol and Sphingolipids in Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease. José C. Fernández-Checa Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic CIBEK and IDIBAPS Instituto Investigaciones Biomédicas Barcelona Consejo Superior
Cholesterol and Sphingolipids in Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease. José C. Fernández-Checa Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic CIBEK and IDIBAPS Instituto Investigaciones Biomédicas Barcelona Consejo Superior
METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways
 METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways Metabolism Metabolism involves : Catabolic reactions that break down large, complex molecules to provide energy and smaller molecules. Anabolic reactions that use ATP energy
METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways Metabolism Metabolism involves : Catabolic reactions that break down large, complex molecules to provide energy and smaller molecules. Anabolic reactions that use ATP energy
Conflicts of Interest in the last 12 months
 STEATOHEPATITIS Richard K. Sterling, MD, MSc, FACP, FACG VCU Hepatology Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, VA Conflicts of Interest in the last
STEATOHEPATITIS Richard K. Sterling, MD, MSc, FACP, FACG VCU Hepatology Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, VA Conflicts of Interest in the last
Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: Da. m/z. hrmif ( Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ Da. m/z.
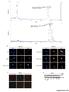 Intensity % Intensity % A Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: 12428.31 Da m/z hrmif (12428.31 Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ 12715.21 Da m/z B HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3 Merge HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3
Intensity % Intensity % A Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: 12428.31 Da m/z hrmif (12428.31 Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ 12715.21 Da m/z B HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3 Merge HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3
Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR
 Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR BCAA, SAMe and ACAT Carolyn Ledowsky Overview of This Presentation 1. Fat Metabolism and MTHFR 2. SAMe and Fat Metabolism 3. Acetyl Co A and Fat Metabolism 4. How to Maintain
Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR BCAA, SAMe and ACAT Carolyn Ledowsky Overview of This Presentation 1. Fat Metabolism and MTHFR 2. SAMe and Fat Metabolism 3. Acetyl Co A and Fat Metabolism 4. How to Maintain
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY. BI 28 Second Midterm Examination April 3, 2007
 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm Examination April 3, 2007 Name SIS # Make sure that your name or SIS # is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with your exam after
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm Examination April 3, 2007 Name SIS # Make sure that your name or SIS # is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with your exam after
Fatty Liver- how important is it? Jeremy F.L. Cobbold MA PhD MRCP Clinical Lecturer in Hepatology Imperial College London
 Fatty Liver- how important is it? Jeremy F.L. Cobbold MA PhD MRCP Clinical Lecturer in Hepatology Imperial College London Fatty liver- how important is it? Importance in terms of: Prevalence Pathogenesis
Fatty Liver- how important is it? Jeremy F.L. Cobbold MA PhD MRCP Clinical Lecturer in Hepatology Imperial College London Fatty liver- how important is it? Importance in terms of: Prevalence Pathogenesis
Early life determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and NASH DR JULIANA MUIVA-GITOBU KENYA PAEDIATRIC ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE APRIL 2016.
 Early life determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and NASH DR JULIANA MUIVA-GITOBU KENYA PAEDIATRIC ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE APRIL 2016. Outline Definition NAFLD and NASH Magnitude of the problem
Early life determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and NASH DR JULIANA MUIVA-GITOBU KENYA PAEDIATRIC ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE APRIL 2016. Outline Definition NAFLD and NASH Magnitude of the problem
Biomarkers of NAFLD progression an omics approach to an epidemic
 Biomarkers of NAFLD progression an omics approach to an epidemic D. Lee Gorden 1,2, David S. Myers 3, Pavlina T. Ivanova 3, Eoin Fahy 4, Mano R. Maurya 4, Shakti Gupta 4, Jun Min 4, Nathanael J. Spann
Biomarkers of NAFLD progression an omics approach to an epidemic D. Lee Gorden 1,2, David S. Myers 3, Pavlina T. Ivanova 3, Eoin Fahy 4, Mano R. Maurya 4, Shakti Gupta 4, Jun Min 4, Nathanael J. Spann
METABOLISM CATABOLIC Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
 Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages)
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages) READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages) READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Ahn_Supp. Fig. 1 * * * * BSA Oleate. Triglyceride SBI-477 ( M) Veh Veh TriC DGATi 1.5. Normalized FA Uptake
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Ahn_Supp. Fig. 1 A Triglyceride ( g/mg protein) 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 BSA Oleate B Normalized FA Uptake 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 Veh Veh 0.3 1.0 3.0 10.0 30.0 TriC DGATi 0.0 Veh SBI-477 SBI-477 (
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Ahn_Supp. Fig. 1 A Triglyceride ( g/mg protein) 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 BSA Oleate B Normalized FA Uptake 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 Veh Veh 0.3 1.0 3.0 10.0 30.0 TriC DGATi 0.0 Veh SBI-477 SBI-477 (
The lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans
 Research article The lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans Fadila Benhamed, 1,2,3 Pierre-Damien Denechaud, 1,2,3 Maud Lemoine, 4,5,6
Research article The lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans Fadila Benhamed, 1,2,3 Pierre-Damien Denechaud, 1,2,3 Maud Lemoine, 4,5,6
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
 NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD, MSc Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Terminology Pathogenesis
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD, MSc Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Terminology Pathogenesis
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 mir 26a mir 26b Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of mir-26a is higher than mir-26b in the mouse liver. Dot blot analysis of mir-26a/b expression in the livers of wild-type mice fed
Supplemental Figure 1 mir 26a mir 26b Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of mir-26a is higher than mir-26b in the mouse liver. Dot blot analysis of mir-26a/b expression in the livers of wild-type mice fed
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination
 AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
Lecture 36. Key Concepts. Overview of lipid metabolism. Reactions of fatty acid oxidation. Energy yield from fatty acid oxidation
 Lecture 36 Lipid Metabolism 1 Fatty Acid Oxidation Ketone Bodies Key Concepts Overview of lipid metabolism Reactions of fatty acid oxidation Energy yield from fatty acid oxidation Formation of ketone bodies
Lecture 36 Lipid Metabolism 1 Fatty Acid Oxidation Ketone Bodies Key Concepts Overview of lipid metabolism Reactions of fatty acid oxidation Energy yield from fatty acid oxidation Formation of ketone bodies
Integration Of Metabolism
 Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
WHAT THE EXPERIMENTAL MODELS CAN TEACH US IN NAFLD/NASH? Claudio Tiribelli, MD PhD Scientific Director FIF
 WHAT THE EXPERIMENTAL MODELS CAN TEACH US IN NAFLD/NASH? Claudio Tiribelli, MD PhD Scientific Director FIF ctliver@fegato.it Worldwide estimated prevalence of NAFLD distribution of PNPLA3 genotypes 2017-Younussi
WHAT THE EXPERIMENTAL MODELS CAN TEACH US IN NAFLD/NASH? Claudio Tiribelli, MD PhD Scientific Director FIF ctliver@fegato.it Worldwide estimated prevalence of NAFLD distribution of PNPLA3 genotypes 2017-Younussi
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Supplementary Information. Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis.
 Supplementary Information Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Phillip J. White, Philippe St-Pierre, Alexandre Charbonneau, Patricia Mitchell,
Supplementary Information Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Phillip J. White, Philippe St-Pierre, Alexandre Charbonneau, Patricia Mitchell,
NAME KEY ID # EXAM 3a BIOC 460. Wednesday April 10, Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided!
 EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
MITOCW watch?v=ddt1kusdoog
 MITOCW watch?v=ddt1kusdoog The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=ddt1kusdoog The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin
 Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Supporting Information. Supporting Tables. S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Product size. Gene Primer pairs
 Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-3. (Note that you are not allowed to use any calculator)
 Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-3 (Note that you are not allowed to use any calculator) 1. In the non-cyclic pathway, electron pathway is. Select the most accurate one. a. PSII PC Cyt b 6 f PC PSI Fd-NADP
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-3 (Note that you are not allowed to use any calculator) 1. In the non-cyclic pathway, electron pathway is. Select the most accurate one. a. PSII PC Cyt b 6 f PC PSI Fd-NADP
Moh Tarek. Razi Kittaneh. Jaqen H ghar
 14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
Chapter 22, Fatty Acid Metabolism CH 3 (CH 2 ) 14 CO 2 R C C O2 CH 2 OH O R. Lipase + 3 H 2 O
 hapter 22, Fatty Acid Metabolism Pages: 603-613 I. Introduction - Fatty acids have 4 major physiological roles: - omponents of phospholipids and glycolipids (membranes) - Attachment to Proteins targets
hapter 22, Fatty Acid Metabolism Pages: 603-613 I. Introduction - Fatty acids have 4 major physiological roles: - omponents of phospholipids and glycolipids (membranes) - Attachment to Proteins targets
Energy metabolism - the overview
 Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Metabolism of cardiac muscle. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013
 Metabolism of cardiac muscle Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed., p. 890-891 Hand-out Why is this topic important? Heart failure
Metabolism of cardiac muscle Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed., p. 890-891 Hand-out Why is this topic important? Heart failure
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Multiple choice: Circle the best answer on this exam. There are 12 multiple choice questions, each question is worth 3 points.
 CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
Improving Access to Quality Medical Care Webinar Series
 Improving Access to Quality Medical Care Webinar Series Presented by The Arizona Telemedicine Program and the Southwest Telehealth Resource Center 2015 UA Board of Regents Welcome AZ, UT, CO, NM & NV FLEX
Improving Access to Quality Medical Care Webinar Series Presented by The Arizona Telemedicine Program and the Southwest Telehealth Resource Center 2015 UA Board of Regents Welcome AZ, UT, CO, NM & NV FLEX
23.1 Lipid Metabolism in Animals. Chapter 23. Micelles Lipid Metabolism in. Animals. Overview of Digestion Lipid Metabolism in
 Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies
 Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
