CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS
|
|
|
- Ethel Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
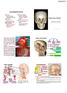
1 CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS Introduction Facial nerve paralysis, whilst not a disease of the ear itself, commonly arises within the ear due to its anatomical course, and often as a result of ear disease. These paralyses therefore require ontological input. It is important to note that facial paralysis is an otological emergency. Ear disease is a leading cause of these problems. Origins in the ear often require same day management for optimal outcomes; this may require experience, specialised equipment and ear cleaning expertise for diagnosis. Conversely, few non-otological origins are of similar urgency. Figure 1: Course of the facial nerve in the temporal bone. Proximity to the middle ear, and its enclosure in rigid bony confines place the nerve at some risk from disease. Anatomy The facial nerve emerges from the brain as a motor root and the nervus intermedius, entering the internal ear canal with the nerves of hearing and balance. The roots fuse at the geniculate ganglion. From here it zig-zags through the middle ear to emerge from the stylomastoid foramen, deep to the tip of the mastoid, then passes into the parotid, as an interconnecting plexus, between the superficial and deep divisions of this gland, fanning out to the facial muscles. For the most part the nerve is encased within a bony canal, but this is often lacking superior to the stapes. The nerve may therefore be damaged by problems within the skull, in the ear, or externally. Functions a) Motor b) Secreto-motor, lacrimation c) Taste d) Tactile
2 Functional plan of the facial nerve in the temporal bone. iam: internal auditory meatus; gspn: greater superficial petrosal nerve; gg: geniculate ganglion; st nerve to stapedius; ct: chorda tympani; smf: stylomastoid foramen. The facial nerve activates the facial muscles during expression, speech and ingestion. It also supplies the muffler and reflex actions of the Stapedius snd the Tensor Tympani within the middle ear itself. In addition to this muscular action, the nerve supplies taste, tear and saliva production via the greater superficial petrosal nerve (to the lacrimal gland, nose and palate), and the chorda tympani (anterior two-thirds of the tongue, submandibular and sublingual glands). It supplies tactile sensation to part of the outer ear canal and conchal bowl. Figure 3: Facial palsy. Severe left loss. Bell s palsy, spontaneous resolution over several weeks. Figure 2: Congenital partial facial palsy, mandibular branch, history of forceps delivery, CT normal. Presentation Strokes not uncommonly affect the nerve. but the results differ from other damage in that only the mid and lower facial muscles are weakened as a result. Other cases of paralysis may arise from viral infections within the nerve itself. Bell s Palsy is a paralysis of uncertain origins, probably viral (herpes simplex), but without known activation causes. The paralysis is frequently of rapid onset without other major symptoms, although pain may be noted. The patient is free of findings related to the problem, and especially the ear appears normal. Prompt treatment with steroid and antiviral agents may be beneficial, but must be started early after onset. Generally, most Bell s palsy cases resolve to a substantial degree, or totally. Severe cases, especially in the older age group, may do less well. Some require complex re-innervation or other surgical methods.
3 Infection of the nerve due to the herpes zoster virus is often severe. Shingles in the ear (Ramsay Hunt syndrome, herpes zoster oticus) may cause severe irreversible paralysis, with nerve deafness and vertigo. The outlook for these is poorer. Figure 5: Acoustic schwannoma, impacting on the brainstem. Removal, whilst sparing a very splayed facial nerve, will be difficult. Figure 4: Herpes zoster oticus. Healing vesicles, facial palsy and viral labyrinthitis. Older patient, poor recovery of facial function and lingering disequilibrium as a result of the inner ear damage. Other forms of facial palsy are more related to its anatomical position in the ear and outer soft tissues. Infection in the middle ear is a major cause of problems. Acute bacterial middle ear infections may invade the nerve causing swelling then paralysis of the nerve fibres in their bony passage as the blood supply is compressed. Prompt treatment with steroids and antibiotics is optimal, plus surgical drainage of the infection to accelerate recovery. Cholesteatoma requires more aggressive action. These sacs of infected debris gradually erode overlying bone, exposing the nerve to chronic infection. Relief, and prevention of longer term paralysis, will require rapid surgical removal of the cause, preferably within 24 hours. Whilst in the internal ear canal, the nerve may be troubled by growth of an acoustic schwannoma. The tumour itself rarely paralyses the nerve, but surgery to remove these is a common cause of a damaged nerve, perhaps totally divided, as the nerve is often splayed into fine strands due to the growth of the tumour. Figuure 6: Attic cholesteatoma. Prompt surgery is required to salvage a recent facial palsy.
4 Paralysis outside the skull frequently has more sinister overtones, arising from tumours of the salivary gland in the cheek, e.g. squamous cell carcinoma, or other sites nearby. The nerve may be cut during removal of these problems. Also, the branch of the nerve to the lower lip muscle is at risk during surgery beneath the line of the jaw. Figure 8: Schirmer s test. Litmus paper is hooked onto the lower eyelids and lacrimation is stimulated. If a facial nerve paresis is located at the geniculate ganglion or above, lacrimation on the affected side will be significantly depressed. Figure 7: Facial palsy due to a squamous cell carcinoma of the parotid. Excision required sacrifice of the nerve. Acoustic reflex testing may show hypofunction of the stapedial reflex if a nerve block is medial to the stapedius. Investigation Detection of the level of the paralysis may be judged by testing the other functions of the nerve; in turn, middle ear reflexes, taste, or lacrimation, which are sequentially affected depending on the site, as one moves from outside inwards along the nerve. Schirmer s test places the site of paralysis at the geniculate ganglion, or medially This reduces greater superficial petrosal stimulus of ipsilateral lacrimation. Electrogustomery, using an electrode on the tongue, may indicate paresis that originates medial to the chorda. Tests of motor function are useful to gauge severity and progress: a) Nerve excitability testing utilises an electrode over the stylomastoid foramen to stimulate facial action, compared to the contralateral (normal) function. b) Electromyography records muscle function from a needle electrode placed into facial muscles: i. Volitional motor potentials: if these are present on stimulation, degeneration has not occurred. ii. Denervation potentials/fibrillations appear about ten days after the onset of palsies as a result of axon degeneration. Their absence is a positive sign.
5 iii. Polyphasic motor unit potentials appear during reinnervation of muscle whose motor supply has degenerated, appearing 2-3 months after the onset of a palsy. c) Electroneuronography (ENoG) provides the best assessment of neuronal function and is valuable in assessing clinical progress of degeneration after a complete palsy. A bipolar electrode stimulates the facial trunk just anterior to the mastoid and action potentials are read by an electrode over the nasolabial fold. The affected and the normal sides are compared; degeneration is detected by diminishing potentials on successive tests. varying results. Alternatively, redirection of other muscle (motor) nerves may be possible. Failure to close the eye is a frequent concern in palsy cases, causing drying, irritation and potential corneal ulceration. Partial closure of the eye (tarsorrahpy) or a weight implant in the upper eyelid may be considered. Prognosis Four features help to assess the likelihood of recovery. a) Age: As a rule, the elderly fare worse than the young. b) Speed on onset: rapid progression seems a poorer outlook c) Severity of the palsy: Complete loss of function is ominous. d) Pain at the onset mat indicate a worse prospect. Management The treatment of the paralysis for which there is no overt cause (Bell s Palsy) is controversial. Steroid and antiviral treatment evidently must be prompt for optimal effect. In a minority of pressing circumstances, the surgeon may consider relieving pressure on the nerve by removal of overlying bone (decompression). If a nerve has been completely severed, a sensory nerve from elsewhere may be used to repair the site, but with
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Facial Paralysis: Objectives: Discuss the anatomy of the facial nerve. Look at common patterns of facial nerve palsy
 Facial Paralysis: Objectives: Discuss the anatomy of the facial nerve Look at common patterns of facial nerve palsy Discuss imaging appearance of lesions that lead to facial paralysis. Lindell R. Gentry,
Facial Paralysis: Objectives: Discuss the anatomy of the facial nerve Look at common patterns of facial nerve palsy Discuss imaging appearance of lesions that lead to facial paralysis. Lindell R. Gentry,
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
The Seventh Cranial Nerve The Facial By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Seventh Cranial Nerve The Facial By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Functional Components: SVE: Fibers originate from nucleus of facial nerve, and supply facial muscles GVE: Fibers derived from superior
The Seventh Cranial Nerve The Facial By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Functional Components: SVE: Fibers originate from nucleus of facial nerve, and supply facial muscles GVE: Fibers derived from superior
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY. Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan
 ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan FACIAL PARALYSIS - ETIOLOGY Bells Palsy Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Infection (Acute/Chronic)
ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan FACIAL PARALYSIS - ETIOLOGY Bells Palsy Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Infection (Acute/Chronic)
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II. Nerves covered in other lectures. A reminder about embryology. Prof. Stuart Bunt
 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
4/30/2009 FN PARALYSIS HEMIFACIAL SPASM
 FN PARALYSIS HEMIFACIAL SPASM 1 Hemifacial spasm (Involuntary twitches) Etiology: Vascular loop compressing the FN at the root exit zone in the CPA = Neuro-vascular conflict Diagnosis: CT & MRI, Electrophysiology
FN PARALYSIS HEMIFACIAL SPASM 1 Hemifacial spasm (Involuntary twitches) Etiology: Vascular loop compressing the FN at the root exit zone in the CPA = Neuro-vascular conflict Diagnosis: CT & MRI, Electrophysiology
14, 2007 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
 TITLE: Bell s Palsy SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: February 14, 2007 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Ki-Hong Kevin Ho, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Shawn D. Newlands, MD, PhD, MBA
TITLE: Bell s Palsy SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: February 14, 2007 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Ki-Hong Kevin Ho, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Shawn D. Newlands, MD, PhD, MBA
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
CNS CRANIAL NERVES STEPS OF EXAMINATION
 CNS CRANIAL NERVES STEPS OF EXAMINATION (1) APPROACH THE PATIENT Read the instructions carefully for clues Approach the right hand side of the patient, shake hands, introduce yourself Ask permission to
CNS CRANIAL NERVES STEPS OF EXAMINATION (1) APPROACH THE PATIENT Read the instructions carefully for clues Approach the right hand side of the patient, shake hands, introduce yourself Ask permission to
Facial nerve, more than any other cranial nerves, Intratemporal Facial Nerve Paralysis- A Three Year Study. Case Series
 Case Series Intratemporal Facial Nerve Paralysis- A Three Year Study Anirban Ghosh, 1 Sankar Prasad Bera, 2 Somnath Saha 3 ABSTRACT Introduction This study on intratemporal facial paralysis is an attempt
Case Series Intratemporal Facial Nerve Paralysis- A Three Year Study Anirban Ghosh, 1 Sankar Prasad Bera, 2 Somnath Saha 3 ABSTRACT Introduction This study on intratemporal facial paralysis is an attempt
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
VII NERVE PALSY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT
 VII NERVE PALSY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT The eye cannot close and constantly weeps. The mouth dribbles, the speech is interfered with and mastication impaired. The delicate shades of continence are lost.
VII NERVE PALSY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT The eye cannot close and constantly weeps. The mouth dribbles, the speech is interfered with and mastication impaired. The delicate shades of continence are lost.
Imaging of facial paralysis
 Imaging of facial paralysis Poster No.: C-2151 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Martinez Molina, L. Aleman Romero, L. A. Sanchez Alonso, A. Puerta Sales, V. Garcia Medina; Murcia/ES
Imaging of facial paralysis Poster No.: C-2151 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Martinez Molina, L. Aleman Romero, L. A. Sanchez Alonso, A. Puerta Sales, V. Garcia Medina; Murcia/ES
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
DIZZINESS Varieties. : Fainting, hypotension : Rotatory, spinning. : Muscular incoordination : Collapse without LOC: ELH : Disturbed awareness
 DIZZINESS Varieties head Syncope Vertigo Dysequilibrium Ataxia Drop attacks Confusion Panic Attacks Non-organic : Fainting, hypotension : Rotatory, spinning : Unsteadiness on moving : Muscular incoordination
DIZZINESS Varieties head Syncope Vertigo Dysequilibrium Ataxia Drop attacks Confusion Panic Attacks Non-organic : Fainting, hypotension : Rotatory, spinning : Unsteadiness on moving : Muscular incoordination
POST TRAUMATIC FACIAL PARALYSIS - A REVIEW
 POST TRAUMATIC FACIAL PARALYSIS - A REVIEW Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Naresh K. Panda, Y. N. Mehra, S.B.S. Mann, Satish K. Mehta ( Deptt. of Otolaryngology, Postgraduate Institute of
POST TRAUMATIC FACIAL PARALYSIS - A REVIEW Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Naresh K. Panda, Y. N. Mehra, S.B.S. Mann, Satish K. Mehta ( Deptt. of Otolaryngology, Postgraduate Institute of
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Anatomy of the ear: Lymphatics
 Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
K. J. Lee: Essential Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery (IIIrd Ed) Chapter 10: Facial Nerve Paralysis. Evaluation
 K. J. Lee: Essential Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery (IIIrd Ed) Chapter 10: Facial Nerve Paralysis Evaluation Evaluation of patients with facial nerve paralysis must be a careful process including
K. J. Lee: Essential Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery (IIIrd Ed) Chapter 10: Facial Nerve Paralysis Evaluation Evaluation of patients with facial nerve paralysis must be a careful process including
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Facial Nerve Palsy in Three HIV/AIDS Patients
 Facial Nerve Palsy in Three HIV/AIDS Patients By A.I. Shugaba, R.M. Mathew, C. B. Uzokwe, F.Shinku, Y.M. Usman B. M. Mohammed, A. M. Rabiu, I. M. Gambo and M.B.T. Umar ISSN 0970-4973 (Print) ISSN 2319-3077
Facial Nerve Palsy in Three HIV/AIDS Patients By A.I. Shugaba, R.M. Mathew, C. B. Uzokwe, F.Shinku, Y.M. Usman B. M. Mohammed, A. M. Rabiu, I. M. Gambo and M.B.T. Umar ISSN 0970-4973 (Print) ISSN 2319-3077
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
 Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
UC SF. Safe Surgery Rule #1. Cholesteatoma. It s hard to have a surgical complication when you are not operating
 UC SF Cholesteatoma Chronic Ear Surgery: Staying Out of Trouble! Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Department of Oto-HNS University of California San Francisco Ligaments and folds Spaces NU Epitympanic Cholesteatoma
UC SF Cholesteatoma Chronic Ear Surgery: Staying Out of Trouble! Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Department of Oto-HNS University of California San Francisco Ligaments and folds Spaces NU Epitympanic Cholesteatoma
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德
 Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Neoplasms that present as a swelling in the neck may be either
 Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
STUDY OF VARIOUS CAUSES OF FACIAL PALSY AND ITS MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL
 STUDY OF VARIOUS CAUSES OF FACIAL PALSY AND ITS MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL S. Venkataramana Rao 1, V. S. Sharma 2, M. V. Subba Rao 3, B. J. Prasad 4, Kalyan 5, Pravin Tez 6, Vijay Kumar 7, G. S. Keerthi 8 1Professor,
STUDY OF VARIOUS CAUSES OF FACIAL PALSY AND ITS MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL S. Venkataramana Rao 1, V. S. Sharma 2, M. V. Subba Rao 3, B. J. Prasad 4, Kalyan 5, Pravin Tez 6, Vijay Kumar 7, G. S. Keerthi 8 1Professor,
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Ramsay Hunt syndrome a case report and review of literature
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan January 1, 2013 Ramsay Hunt syndrome a case report and review of literature Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/27/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan January 1, 2013 Ramsay Hunt syndrome a case report and review of literature Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/27/
Trigeminal nerve. Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me
 Trigeminal nerve Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me Hala nsour 2/26/2018 P a g e 1 this lecture contain two topics
Trigeminal nerve Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me Hala nsour 2/26/2018 P a g e 1 this lecture contain two topics
The ear: some applied basic science
 Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY
 MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY This information leaflet is to support your decision with your Specialist. This leaflet will explain about the ear are and what surgery can be offered
MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY This information leaflet is to support your decision with your Specialist. This leaflet will explain about the ear are and what surgery can be offered
Neurological Assessment Part 1
 Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Refresher Course EAR TUMOR. Sasikarn Chamchod, MD Chulabhorn Hospital
 Refresher Course EAR TUMOR Sasikarn Chamchod, MD Chulabhorn Hospital Reference: Perez and Brady s Principles and Practice of radiation oncology sixth edition Outlines Anatomy Epidemiology Clinical presentations
Refresher Course EAR TUMOR Sasikarn Chamchod, MD Chulabhorn Hospital Reference: Perez and Brady s Principles and Practice of radiation oncology sixth edition Outlines Anatomy Epidemiology Clinical presentations
Anatomy of External and Middle ear. Dr Sai Manohar
 Anatomy of External and Middle ear. Dr Sai Manohar 1 Human Ear For Anatomical description, Ear is divided into Auricle (or pinna) The external auditory canal The Middle Ear and its derivatives The Inner
Anatomy of External and Middle ear. Dr Sai Manohar 1 Human Ear For Anatomical description, Ear is divided into Auricle (or pinna) The external auditory canal The Middle Ear and its derivatives The Inner
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
7. Anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. Harmonic and disharmonic vestibular syndrome.
 7. Anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. Harmonic and disharmonic vestibular syndrome. 8. Fundamental examination tools of otoneurology. 20. Ménière s syndrome and Ménière s disease. Therapeutic
7. Anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. Harmonic and disharmonic vestibular syndrome. 8. Fundamental examination tools of otoneurology. 20. Ménière s syndrome and Ménière s disease. Therapeutic
Acyclovir for ear infections
 Acyclovir for ear infections The Borg System is 100 % Acyclovir for ear infections User feedback about Acyclovir side effects covering chicken pox, fatigue, shingles, hair loss, HSV2, dosage, anemia, ear
Acyclovir for ear infections The Borg System is 100 % Acyclovir for ear infections User feedback about Acyclovir side effects covering chicken pox, fatigue, shingles, hair loss, HSV2, dosage, anemia, ear
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Contents. Facial nerve re- animation techniques Conclusions. Microsurgical resection Radiosurgery
 Contents Introduction Anatomy of facial nerve Imaging Intra- op landmarks and intra- op nerve monitoring Grading of facial palsy Factors associated with preservation of facial nerve Microsurgical resection
Contents Introduction Anatomy of facial nerve Imaging Intra- op landmarks and intra- op nerve monitoring Grading of facial palsy Factors associated with preservation of facial nerve Microsurgical resection
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Perineural Tumor Spread (PNS) Perineural Tumor Spread (PNS) PNS Anatomic Considerations. Perineural Tumor Spread-Imaging
 Imaging of Perineural Tumor Spread in Head and Neck Cancer Lawrence E. Ginsberg, MD Departments of Diagnostic Radiology and Head and Neck Surgery University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston,
Imaging of Perineural Tumor Spread in Head and Neck Cancer Lawrence E. Ginsberg, MD Departments of Diagnostic Radiology and Head and Neck Surgery University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston,
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Facial Nerve Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-110 BOOK Facial Nerve Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:09 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Michigan Ear Institute Facial Nerve Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-110 BOOK Facial Nerve Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:09 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
This is the largest of the three major glands. It lies partly in the front of the lower half of the ear and partly below the earlobe.
 Parotid Gland Lumps The lining of the mouth contains many small saliva glands. In addition there are three major glands on each side of the face, the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands. The Parotid
Parotid Gland Lumps The lining of the mouth contains many small saliva glands. In addition there are three major glands on each side of the face, the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands. The Parotid
Both the major and minor glands have ducts, which are the channels down which the saliva travels on its way to the mouth.
 What and where are salivary glands? make the saliva in your mouth, which is very important for the health of your mouth and teeth (eg it stops your mouth drying out) - and also for the first stages of
What and where are salivary glands? make the saliva in your mouth, which is very important for the health of your mouth and teeth (eg it stops your mouth drying out) - and also for the first stages of
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
HBA THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014
 HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
Corticosteroids: Still a Cornerstone in Treatment of Bell s Palsy - A Case Report
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2015;2(1):94-98 January-March All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Corticosteroids: Still a Cornerstone in Treatment of Bell s Palsy
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2015;2(1):94-98 January-March All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Corticosteroids: Still a Cornerstone in Treatment of Bell s Palsy
CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS. Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD
 CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD The facial nerve innervates a total of 23 paired muscles and the orbicularis oris muscle. The majority of muscles innervated by the
CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD The facial nerve innervates a total of 23 paired muscles and the orbicularis oris muscle. The majority of muscles innervated by the
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
INTRATYMPANIC GENTAMICIN PERFUSIONS. ENDOLYMPHATIC HYDROPS (ELH, Meniere s disease)
 INTRATYMPANIC GENTAMICIN PERFUSIONS ENDOLYMPHATIC HYDROPS (ELH, Meniere s disease) Risks, Complications and Post-operative Instructions The inner ear comprises a bony casing (the otic capsule), containing
INTRATYMPANIC GENTAMICIN PERFUSIONS ENDOLYMPHATIC HYDROPS (ELH, Meniere s disease) Risks, Complications and Post-operative Instructions The inner ear comprises a bony casing (the otic capsule), containing
Cranial Nerve VII : The Facial Nerve and Taste
 62 Cranial Nerve VII : The Facial Nerve and Taste H. KENNETH WALKER Definition The motor portion, or the facial nerve proper, supplies all the facial musculature. The principal muscles are the frontalis,
62 Cranial Nerve VII : The Facial Nerve and Taste H. KENNETH WALKER Definition The motor portion, or the facial nerve proper, supplies all the facial musculature. The principal muscles are the frontalis,
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
