The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所
|
|
|
- Lucy Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1
2 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會
3 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule
4 The Cardiovascular System 1. The first major system to function 2. The primordial heart and vascular system appear in the middle of the third week 3. The heart starts to function at the beginning of the fourth week 4
5 The cardiovascular system is derived mainly from: Splanchnic mesoderm Paraxial and lateral mesoderm Neural crest cells 5
6 Early development of the heart Heart primordium Angioblastic cord 18 days Angioblastic cord 6
7 Fusion of endocardial heart tubes Ventral views 7
8 Fusion of endocardial heart tubes Pericardial coelom 20-day Dorsal mesocardium Epicardium Cardiac jelly Primordial myocardium (from splanchnic mesoderm) 22-day 8
9 U-shaped bulboventricular loop Primordial atrium 有不同命名方式 Truncus arteriosus Sinus venosus Bulbus cordis Primordial ventricle 24 days 9
10 Circulation through primordial heart 6 Sinus venosus End of 4th week: unidirectional flow 4 10
11 Partitioning of primordial heart begins around middle of the 4th week. is completed by the end of the 8th week. includes partitioning of: Atrioventricular canal Primordial atrium Primordial ventricle 11
12 Partitioning of Atrioventricular Canal 5th week Fused endocardial cushions End of 4th week Endocardial cushions (from cardiac jelly) Left AV canal Transformed endocardial cushions also contribute to the formation of valves and membranous septa of the heart. 12
13 AV endocardial cushions Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP2) the primordia of the valves and membranous septa 13
14 Partitioning of primordial atrium begins at the end of the 4th week. is divided into right and left atria by: Septum primum Septum secundum 14
15 Septum primum Septum primum Endocardial cushion Septum secundum Foramen secundum (Ostium secundum) Foramen primum (Ostium primum) 15
16 Septum primum Septum primum Foramum primum Foramum primum Foramum secundum Foramum primum Septum secundum Foramum secundum Septum primum 16
17 Septum secundum Septum secundum (upper limb) 5th~6th week Foramen secundum Oval foramen Valve of oval foramen (from septum primum) Oval foramen Valve (from septum primum) 17
18 Valve of oval foramen Septum primum Oval foramen (open) Valve of oval foramen Septum secundum 18
19 Oval fossa is a remnant of oval foramen Before birth After birth Septum secundum Oval foramen Septum primum (valve of oval foramen) Oval fossa 19
20 Development of sinus venosus Left horn of sinus venosus Opening of sinus venosus into primordial atrium Right horn of sinus venosus Left Right Dorsal view (4 th week) 20
21 Progressive enlargement of the right horn results from two left-to-right shunts of blood Left Right Dorsal view (7 weeks) 21
22 Doral view Primordial atrium 26 days Right horn of sinus venosus Left horn of sinus venosus 8 weeks Sinus venarum of right atrium Coronary sinus Left Right 22
23 Right sinuatrial valve Crista terminalis Valve of IVC Valve of coronary sinus Left sinuatrial valve fused with septum secundum Interatrial septum Crista terminalis Valve of coronary sinus Right Left Valve of inferior vena cava 23
24 Absorption of pulmonary vein into left atrium 5 weeks 6 weeks Primordial pulmonary vein Primordial left atrium Smooth-walled part of left atrium Left auricle Right 8 weeks Left 24
25 The role of pulmonary veins in atrial fibrillation (Pharmacol Ther Nov;124(2): ) Pulmonary vein ablation 心房顫動 (atrial fibrillation) myocardial sleeves of pulmonary veins Cardiovasc Res (2002) 54 (2):
26 Bulbus cordis incorporates into the walls of ventricles Conus arteriosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule 26
27 Partitioning of primordial ventricle Fused endocardial cushions 5th week Interventricular foramen Interventricular septum (muscular part) Expansion Right Left 27
28 Membranous part of IV septum Membranous septum Aortic vestibule
29 Closure of the interventricular foramen Membranous part of IV septum Right bulbar ridge Left bulbar ridge Fused endocardial cushions 7 weeks 29
30 Cavitation of the ventricular walls forms a sponge-work of muscular bundles trabeculae carneae 5 weeks 6 weeks 20 weeks 7 weeks Chordae tendinae Right Trabeculae carneae Left Papillary muscle 30
31 Partitioning of Bulbus Cordis and Truncus Arteriosus Truncus arteriosus Truncal ridge Bulbus cordis 5 weeks Bulbar ridge Aorta Pulmonary trunk Aorticopulmonary septum 6 weeks 31
32 Spiral form of Aorticopulmonary Septum 32
33 Development of cardiac valves (semilunar valves) Swellings of subendothelial tissue Dorsal valve swelling Bulbar ridges Ventral valve swelling 33
34 Hollowing and thinning of valve swellings Valve swelling 34
35 Cardiac conduction system Sinus venosus Sinuatrial (SA) node (5 th week) Atrioventricular (AV) node Right Left Atrioventricular bundle Branches of AV bundle 35
36 Fetal circulation Ductus arteriosus Foramen ovale Ductus venosus Sphincter 36
37 Transitional Neonatal Circulation 1. Alteration of the lungs Fall in pulmonary vascular resistance Increase pulmonary blood flow Thinning of walls of pulmonary arteries 2. The oval foramen closes. Higher left atrium pressure Thicker left ventricular wall by the end of 1st month 3. The ductus arteriosus constricts. Close: Oxygen, bradykinin, indomethacin (PGE 2 inhibitor) Open: Hypoxia, PGE 2, prostacyclin (PGI2) 4. The umbilical arteries constrict. 37
38 Adult Derivatives of fetal vascular structures Ligamentum arteriosum (Ductus arteriosus) Oval fossa (Foramen ovale) Ligamentum venosum (ductus venosus) Ligamentum teres (umbilical vein) Superior vesical artery (umbilical artery, proximal) Medial umbilical ligament (umbilical artery, distal) 38
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the heart
 Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
W.S. O. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Repetition: Muscle tissue
 Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations.
 6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart. The Heart
 Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue
 Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue Development of the heart fields h:p://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ index.php?6tle=advanced_- _Heart_Fields! 2 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Bulbus
Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue Development of the heart fields h:p://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ index.php?6tle=advanced_- _Heart_Fields! 2 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Bulbus
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I
 6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
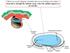 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Development of the Heart and Vasculature
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Development of the Heart and Vasculature Overview vascular system appears (middle of 3 rd week) when the embryo is not able to satisfy its nutrition by diffusion Heart is the first functional
IN THE NAME OF GOD Development of the Heart and Vasculature Overview vascular system appears (middle of 3 rd week) when the embryo is not able to satisfy its nutrition by diffusion Heart is the first functional
Development of the Heart *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
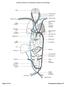 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
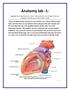 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
Circulatory System: Introduction. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College
 Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Spleen. Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum. Vessel walls. Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels. Artery elastic tissue
 Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
ANATOMY. lecture#: Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi
 ANATOMY 28 lecture#: Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Superior vena -=- Blood inflow part is rough and outflow part is smooth. - _Arch of aorta Pulmonary trunk Tricuspid valve Right auricle Right atrium
ANATOMY 28 lecture#: Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Superior vena -=- Blood inflow part is rough and outflow part is smooth. - _Arch of aorta Pulmonary trunk Tricuspid valve Right auricle Right atrium
Heart & Pericardium. December, 2015
 Heart & Pericardium December, 2015 2 Pericardium Definition Fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and the roots of great vessels Function Restrict excessive movements of the heart as a whole Serve as
Heart & Pericardium December, 2015 2 Pericardium Definition Fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and the roots of great vessels Function Restrict excessive movements of the heart as a whole Serve as
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Bayan Yanes. April/9 th /2013
 Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Large Ventricular Septal Defect with Irreversible Pulmonary Hypertension
 Week 20 Blue Is For Boys Tetralogy of Fallot Presenting Symptoms Child, 4 Cyanosis Exercise Tolerance Failure to thrive Clubbing Lower Sternal Heave Right ventricular hypertrophy Loud ejection systolic
Week 20 Blue Is For Boys Tetralogy of Fallot Presenting Symptoms Child, 4 Cyanosis Exercise Tolerance Failure to thrive Clubbing Lower Sternal Heave Right ventricular hypertrophy Loud ejection systolic
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,700 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,700 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 1 Aortic arch derivatives Aortic arches 2 Pharyngeal and aortic arches 4 th week 3 (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 6 th week (37 days) 4 8th week: transformed into the
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 1 Aortic arch derivatives Aortic arches 2 Pharyngeal and aortic arches 4 th week 3 (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 6 th week (37 days) 4 8th week: transformed into the
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM
 THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM BY REGINALD HUDSON From the Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital Received April 5, 1954 This paper is an elementary study of the normal and abnormal
THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM BY REGINALD HUDSON From the Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital Received April 5, 1954 This paper is an elementary study of the normal and abnormal
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular System Module 3: Heart Anatomy *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49683 1 Cardiovascular System Module 3: Heart Anatomy * Donna Browne Based on Heart Anatomy by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m49683 1 Cardiovascular System Module 3: Heart Anatomy * Donna Browne Based on Heart Anatomy by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Papworth Hospital NHS Trust INTRODUCTION. Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan INTRODUCTION
 Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Anatomy of the Heart
 1 Anatomy of the Heart L. Maximilian Buja Embryologic Development.......................... 3 External Anatomy of the Heart and Great Vessels...... 7 Pericardium.......................................
1 Anatomy of the Heart L. Maximilian Buja Embryologic Development.......................... 3 External Anatomy of the Heart and Great Vessels...... 7 Pericardium.......................................
Read Me. covering the Heart Anatomy. Labs. textbook. use. car: you
 Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Cardiac embryology and anatomy
 Section 1 Anatomy and physiology Chapter 1 Cardiac embryology and anatomy Doris M. Rassl and Martin J. Goddard An appreciation of the normal development of the heart and great vessels and normal adult
Section 1 Anatomy and physiology Chapter 1 Cardiac embryology and anatomy Doris M. Rassl and Martin J. Goddard An appreciation of the normal development of the heart and great vessels and normal adult
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System
 The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
THE VESSELS OF THE HEART
 1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Cardiovascular Respiratory Renal/ Urinary. VOLUME 111 Nervous System. Organ ~ Systems ~
 Cardiovascular Respiratory Renal/ Urinary VOLUME 111 Nervous System Organ ~ Systems ~ Contents Section I: Cardiovascular System Chapter 1. Embryology... 3 Chapter 2. Histology... 13 Chapter 3. Anatomy...
Cardiovascular Respiratory Renal/ Urinary VOLUME 111 Nervous System Organ ~ Systems ~ Contents Section I: Cardiovascular System Chapter 1. Embryology... 3 Chapter 2. Histology... 13 Chapter 3. Anatomy...
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS:
 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
Chapter 20 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: THE HEART
 Chapter 20 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: THE HEART INTRODUCTION A. The cardiovascular system consists of the blood, heart, and blood vessels. B. The heart is the pump that circulates the blood through an
Chapter 20 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: THE HEART INTRODUCTION A. The cardiovascular system consists of the blood, heart, and blood vessels. B. The heart is the pump that circulates the blood through an
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries
 Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic venous anomaly
 World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
- what other structures, besides the heart, does the mediastinum contain?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Paediatric Cardiology. Acyanotic CHD. Prof F F Takawira
 Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
