Left Atrial Structural and Functional Remodeling in Hypertensives - An Echocardioghraphic Study
|
|
|
- Amie Marilyn Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 : 5-11 Original Paper Copyright Celsius Left Atrial Structural and Functional Remodeling in Hypertensives - An Echocardioghraphic Study Ioana Petre, Adriana Alexandrescu, Silvia Iancovici, Sebastian Onciul, Oana Florentina Tãutu, Maria Dorobanåu Department of Cardiology, Clinical Emergency Hospital, Bucharest, Romania REZUMAT Remodelarea structuralã æi funcåionalã a atriului stâng la hipertensivi - studiu ecocardiografic Obiective: Acest studiu æi-a propus evaluarea remodelãrii atriului stâng prin metoda ecocardiograficã la pacienåii hipertensivi optim trataåi comparativ cu cei normotensivi. Metode: În studiul nostru au fost înrolati 35 pacienåi cu hipertensiune arterialã esenåialã necomplicatã, trataåi pânã la valoarea åintã (<140/90mmHg). Dimensiunea atriului stâng a fost evaluatã ecocardiografic: diametrele anteroposterior, transversal æi longitudinal, precum æi cele trei volume fazice [maxim (vol max), minim (vol min) æi cel dinainte de contracåia atrialã (vol pre A)] prin metoda Simpson biplan modificatã. Pe baza volumelor au fost calculate fracåiile de golire atrialã activã, pasivã æi totalã. De asemenea a fost analizatã valoarea strainului sistolic longitudinal atrial (media obåinutã din ferestrele apical patru camere æi douã camere) prin metoda speckle tracking, conform standardelor actuale. Rezultatele au fost comparate cu cele ale unui grup control ce a cuprins 37 subiecåi sãnãtoæi. Rezultate: Diametrul anteroposterior, precum æi toate cele trei volume atriale au fost semnficativ mai mari în grupul hipertensivilor faåã de control (39.54±4.6 mm vs 35.43±4.5 mm pentru diametrul anteroposterior, 60.51±14.9 ml vs 45.22±13.4 ml pentru vol max, 25.48±10.3 ml vs 14.64±5.3 ml pentru vol min si 42.14±11.4 vs 24.86±8.5 pentru volpre A, pentru toate p<0.0001). Din punct de vedere al funcåiei fazice atriale, pacienåii hipertensivi au avut fracåiile de golire totalã si pasivã semnficativ mai mici (49.78±8.4% vs 66.05±7.44, p< æi respectiv 44.62±8.36% vs 58.79±8.14%, p<0.0001), dar cu valori similare ale fracåiei de golire activã atrialã, comparativ cu normotensivii. Valorile peak-strainului longitudinal atrial au fost de asemenea semnficativ mai mici la hipertensivi faåã de control (22.7% vs 35.1%, p<0.0001). Concluzie: Hipertensiunea arterialã, chiar forma necomplicatã æi optim tratatã afecteazã funcåia mecanicã a atriului stâng. În grupul de hipertensivi al studiului nostru s-au observat dimensiuni crescute ale atriului stâng faåã de normotensivi, precum æi o alterare a funcåiei atriale globale æi pasive, cu menåinerea funcåiei de pompã a atriului stâng. Disfuncåia atrialã a fost evidenåiatã æi prin alterarea valorii peak-strainului longitudinal atrial. Cuvinte cheie: hipertensiune arterial, atriu stâng, volume atriale, speckle tracking ABSTRACT Objectives: We sought to investigate left atrial (LA) structural and functional abnormalities in a group of optimal treated hypertensives, in comparison to a control group. Methods: This study included 35 prospectively enrolled subjects with treated, uncomplicated, essential hypertension (HTN). Left atrial diameters (anteroposterior, transversal and longitudinal) and left atrial phasic volumes Corresponding author: Ioana Petre, MD Department of Cardiology, Clinical Emergency Hospital, Calea Floreasca, no.8, Bucharest, Romania i_comanescu@yahoo.com
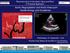
2 6 Ioana Petre et al [maximal (LAV max), minimal (LAV min) and before atrial contraction (LAVpreA)] were assessed by echocardiography and LA emptying functions (LAEF) (global, active and passive) were calculated. Using the current recommendations of speckle tracking technique, peak longitudinal strain of LA walls (PALS)(mean value from apical four chambers and two chambers view) were analysed. The results were compared with a group of 37 age-matched healthy controls. Results: LA anteroposterior diameter as well as all three phasic LA volumes were significantly greater in HTN group (39.54±4.6 mm vs 35.43±4.5 mm for anteroposterior diameter, 60.51±14.9 ml vs 45.22±13.4 ml for LAV max, 25.48±10.3 ml vs 14.64±5.3 ml for LAVmin and 42.14±11.4 vs 24.86±8.5 for LAVpreA, for all p<0.0001), while the transversal and longitudinal diameters were similar. We found significantly lower total and passive EF in hypertensives than in control group (total LAEF 49.78±8.4% vs 66.05±7.44, p<0.001and passive LAEF 44.62±8.36% vs 58.79± 8.14%, p<0.001), but the active LAEF was preserved. The peak systolic strain values were also significantly lower in HTN group versus control (22.7% versus 35.1%, p<0.0001) Conclusion: Hypertension, even correctly treated, affects the mechanical function of left atrium. In our hypertensive group we observed the dilation of left atrium and an altered passive and total atrial function, with preservation of atrial pump function compared to control group. LA dysfunction was also demonstrated through low peak strain values. Key words: hypertension, left atrium, phasic volumes, speckle tracking BACKGROUND Arterial hypertension (HTN) is a common cardiovascular pathology that usually complicates with cardiac dysfunction. HTN alters atrial dynamics significantly, leading to left atrial (LA) morphological and functional abnormalities. Echocardiography proved to be an adequate method of evaluation of LA remodeling, by its means of assessing with accuracy LA size, volumes and its multiple functions. LA size has been consistently shown to be a powerful cardiovascular morbidity and mortality predictor (1-5) and most recently functional assessment of LA has been shown to be at least o marker of cardiovascular outcomes (3,6). Current available data suggest that the combined evaluation of LA size and function will augment prognostication, being important in clinical setting. (7) MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population In the first study group were included 35 consecutive patientswith well-controlled essential hypertension (blood pressure at initial evaluation <=140/90 mmhg). Two blood pressure measurement were performed 5 minutes apart and the mean value was noted. All patients were under pharmacological treatment. Diabetes mellitus and secondary causes of hypertension were excluded, as well as any other significant cardiac pathology: LV ejection fraction <50%, arrhythmias, pacing, cardiomyopathies, significant valvulopathies (moderate or severe), any history or evidence of ischemic heart disease. Because the left atrium function evaluation needs a high quality acquisition, with a good view of endocardial borders only the patients with optimal echocardiographic views were included. The second group (control subjects) comprised 37 normotensives, with normal clinical exam and echocardiography, with no significant medical history or treatment. Left atrium size and phasic volumes Two dimensional echocardiography was performed, using a VIVID7 (General Electric) machine, with respect of the recommendations of available guidelines. Three LA diameters were measured, using bidimensional method: anteroposterior diameter (from parasternal long axis view), transversal and longitudinal diameter (from apical 4 chamber view). LA volumes were measured from the apical four and two chamber view. For measuring LA volumes we used the Simpson biplane method because it has the advantage of being more objective (by reliance on the computerized summation of discs for the total volume and not requiring input of a specific length for volume calculation). (8) LA volumes were measured at 3 points: - maximal LA volume (LAV max) - the volume that occurs at the end of ventricular systole, just before mitral valve opening (the end of the T wave of the ecg); (Fig.1 and Fig. 2) - minimal LA volume (LAV min) that occurs at mitral valve closure (in telediastole); (Fig. 3 and Fig. 4) - the volume before active atrial contraction (LAV prea) - timed to the onset of the P wave. (Fig. 5 and Fig. 6) The left atrium acts as a reservoir when the valve is closed, as a conduit when the mitral valve is open, until the start of atrial contraction when it acts as a pump. From these volumes total, passive and active emptying fraction (LAEF) were calculated (Table 1), which give important information about atrial functions. All atrial volumes were indexed to body surface area.
3 Left Atrial Structural and Functional Remodeling in Hypertensives Figure 1 and 2. Measuring LA maximal volume (LAV max) at the end of ventricular systole in apical 4c and apical 2c views 3 4 Figure 3 and 4. Measuring LA minimum volume (LAV min) at the end of the dyastole, in apical 4c and 2c views 5 6 Figure 5 and 6. Measuring the LA volume just before atrial contraction (LAV prea) in apical 4c and 2c views Table 1. Volumetric assessment of LA phasic function FUNCTION PARAMETER FORMULA Reservoir Function Total emptying fraction (LAV max-lav min)/lav max x100% Conduit Function Passive Emptying Fraction (LAV max-lav prea)/lav max x100% Pump Function Active Emptying Fraction (LAV prea-lav min)/lavpreax100%
4 8 Ioana Petre et al Two dimensional speckle tracking technique Speckle tracking is a novel echocardiographic method that analyses myocardial motion within a user-defined region of interest, without angle dependency. (6,9) We assessed longitudinal atrial strain, using offline analysis (data from Echopac, GE Medical Systems), after apical 4c and 2c images were recorded. The acquisitions were of good quality, with frame rates of about frames/s, using a narrow sector, optimizing visualization of LA cavity and avoiding foreshortening of the LA. The LA endocardial border was manually traced at endsystole in both apical views; the software generated an automatically epicardial surface tracing, delineating a region of interest of 6 segments in each apical view. The examiner selected a default thickness for the LA myocardium (2-3 mm) and the system performed the wall motion tracking analysis throughout the entire cardiac cycle. Longitudinal strain curves were generated for each atrial segment. The LA strain pattern is characterized by a predominant positive wave that peaks at the end of ventricular systole (PALS), followed by two distinct descending phases in early diastole and late systole. The mean measurements of the six segments was automated generated as a separate white curve (Fig. 7 and Fig. 8). The mean value of all 12 segments of PALS was used in the statistical analysis. Statistical analysis The quantitative continue variables were expressed as mean value ± standard deviation and the categorical variables as percentage. The categorical variables were compared using chisqured test or Fisher test as appropriate. All the p values were 2-tailed, with statistical significance defined by a p value <=0.05. RESULTS Baseline characteristics The general characteristics are summarized in Table 2. The frequency of female individuals was similar in both groups (68.1% comparative to 70%, respective 25 subjects for both groups), but HTN group comprised an Figure 7. Peak systolic atrial strain in apical 4c view (curves and values for 6 atrial segments and the mean white curve) Figure 8. Peak systolic atrial strain in apical 2 view(curves for 6 atrial segments and the mean white curve)
5 Left Atrial Structural and Functional Remodeling in Hypertensives 9 Table 2. General characteristics Age (years) 41.4± ±13.4 Gender Female 25(67.6%) 25(71.4%) NS Male 12(32.4%) 10(29.6%) BSA, m² 1.82± ±0.2 NS BP systolic 111± ±17.6 <0.001 diastolic 63±2.3 74±8.1 <0.001 Time from HTN dgn (months) - 33 Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation for numerical data and percentage for categorical data; N: total number from the group; NS: statistically nonsignificant (p>0.05); BSA=body surface area; BP=blood pressure; dgn=diagnosis older population (mean value of 54 ± 13 years in the HTN group and 41 ± 13 years in control group). All the echocardiographic parameters were age and sexmatched. In our HTN group the mean time of arterial HTN diagnosis was 33 months and the mean blood pressure (under treatment) was 129/74 mmhg. LA volumes and diameters LA anteroposterior diameter, as well as all the volumes (Vol max, Vol min and VolpreA) and indexed values were significantly greater in hypertensives, compared to controls (p<0.0001), while the transversal and longitudinal diameters were similar (Table 3). LA active EF was similar between the two groups, while we found significantly lower LA passive and total EF in hypertensives, than in control group (p<0.0001) (Table 4). Peak longitudinal atrial strain The positive peak atrial strain values (the mean value for 12 atrial segments) were also significantly lower in the HTN group versus control, ranging from 22.36% to 44% in control group (with a mean value of 35.2±5.6 % and the most frequent value of 34.5%) and from 8.8% to 43% in HTN group with the mean value of 22.7±13.9 and most often the value of 26%.(Table 5) DISCUSSIONS In the recent years many studies focused on the analysis of the left atrium among hypertensives or patients with atrial arrhythmias, trying to find elements of clinical relevance and new markers of prognosis. LA size proved to be an independent predictor of atrial fibrillation (8,10,11), stroke (12), heart failure (4, 13, 14), prognosis in cardiomyopathies (15, 16) and total as well as cardiovascular mortality (3, 5, 17, 18). LA linear size measurement - the anteroposterior Table 3. LA size (phasic volumes and diameters) LAV prea(ml) 24.86± ±11.4 < LAV prea(ml/m²) 13.62± ±5.86 < LAV max(ml) 45.22± ±14.9 < LAV max(ml/m²) 24.66± ±7.4 < LAV min(ml) 14.64± ±10.3 < LAV min(ml/m²) 8.03± ±5.3 < LA ant-post diam 35.43± ±4.6 < LA longitudinal diam 40.13± ±3.58 NS LA transversal diam 46± ±6.15 NS Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation for numerical data and percentage for categorical data; N: total number from the group; NS: statistically nonsignificant (p>0.05); LA = left atrium; LAV = left atrial volume; max = maximal; min = minimal; prea = before atrial contraction; ant-post = anteroposterior; diam = diameter Table 4. LA phasic emptying fractions LA active EF biplane 40.75± ±11 NS LA passive EF biplane 58.79± ±8.36 < LA total EF biplane 66.05± ±8.4 < Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation for numerical data and percentage for categorical data; N: total number from the group; NS: statistically nonsignificant (p>0.05); LA=left atrium; EF=emptying fraction Table 5. Peak systolic atrial strain (average of 12 atrial segments) PALS (%) 35.2± ±13.9 < Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation for numerical data and percentage for categorical data; N: total number from the group; NS: statistically nonsignificant (p>0.05); PALS = peak atrial longitudinal strain diameter - has been validated in many old studies. This was confirmed also in our study - the anteroposterior diameter being the single increased diameter in HTN group, with a statistical significance comparative to control. However, the current guidelines recommend assessment of LA maximal volume using optimal 4-chamber view and using this value indexed by BSA (LAVI). In our HTN group (patients with optimal treated HTN) comparing LAVI with the reference range from literature we find that 45%(15 subjects) had LA dilatation, the rest of the subjects having a normal LA size. LA dilatation was defined as recommended by the last chamber quantification guideline (19), as LAVI>=34 ml/m²; between them 73.3% (11
6 10 Ioana Petre et al subjects) had only mild dilatation (34-41 ml/m²). The explanation for the preserved LAVI in more of the half of the HTN patients and the mild dilatation in the other half could be the short time of the HTN diagnosis (a mean of 33 months) and the optimal treated HTN. A comprehensive measuring of LA volume using 4-chamber and 2-chamber views (without foreshoretening) at different points of cardiac cycle brings more reliable information about the left atrium structure. As expected, in our study all left atrial biplane volumes (maximal, minimal and prea volumes as well as indexed values) were found to be higher in hypertensive group compared to our normotensive group. Many echocardiographic parameters can be analysed for an accurate prediction of left atrium function. The study of left atrium myocardium mechanics identified three atrial functions: reservoir function, conduit function and contractile function. LA function assessment based on echocardiographic volumetric formula has been used in several studies. Even if there are no validated normal values for emptying fractions, because there were no large multicentric studies, our control EF values were closed to the one reported in the literature. (7,8) Most of the studies among hypertensives demonstrated a decrease in conduit and passive volumes, with an increase in active emptying fraction. (20,2 1). This augmented contractile atrial function is one of the mechanisms compensating for decreased early filling in patients with reduced left ventricular compliance and is considered to becaused by the increase of LA volume (Frank-Starling s law). However, the results in literature about the changes of the phasic LA functions among HTN are inconclusive. For patients with mild hypertension no change was noted in passive emptying or conduit volumes with an increase in active emptying volume, with an overall LA increase compared with normal (22). On the other hand, extreme dilatation and pathological abnormalities of LA muscle may account for the decreased LA booster function in hypertensive patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (23). In our study we found a decrease in reservoir and passive volumes among hypertensives, but with the preservation of active emptying fraction (without an compensatory response of the contractile atrial function). In a recent study, all LA emptying fractions were decreased in hypertensives (24). Speckle tracking (ST) technique was initially used for the strain evaluation of left ventricle. From 2009 it has been validated as a feasible technique for the assessment of longitudinal myocardial LA deformation. Reference ranges of strain indices were reported by Cameli (25) and were similar with the values from our control group (PALS 42.2±6.1% in Cameli study and 35.2±5.6 %in our study). The advantage brought by speckle tracking is the analysis of every element of atrial function, with a higher frame rate - so a better temporal evaluation at a particular moment from the cardiac cycle. More importantly, the ST strain imaging technique allows detection of LA functional impairment at very early stage, even in the absence of LA enlargement and before clinical appraisal of symptoms. The speckle tracking parameter investigated in our study was the mean value from the 12 atrial segments of the peak longitudinal atrial strain (the positive value from the ventricular systole). In previous studies patients with HTN showed significantly lower values of strain and strain rate during reservoir function compared with controls, even when the LA dimensions were not increased (26), irrespective of left ventricular hypertrophy (27). Consistently with the results from the literature, we found that PALS was reduced among the hypertensives comparing with controls (22.7% versus 35.2%, p<0.0001), with a high statistical significance, demonstrating an altered reservoir function of LA among HTN. Limitations The small number of patients in both groups and the heterogenity of the hypertensives (all classes of hypertension, that were treated with different drug combinations) represent some limitations of this study. Also, we excluded the diabetes mellitus, but we did not analyse the presence of other classical risk factors among the subjects. Between the two groups there was a statistically significant difference of the age of the population. Even we tried to compensate this finding by age-matching all the parameters, the increased age of hypertensives comparing to controls might have influenced the results. We could have had a better evaluation of LA function by analyzing also the other strain parameters and this will be our purpose for the next HTN study. CONCLUSION Hypertension, even well treated, is associated with impaired LA size and function. Using multiple echocardiographic techniques, we found that hypertensive patients have structural and functional LA abnormalities. LA enlargement (increased LA biplane volumes at different cardiac cycles) was closely related to LA dysfunctions. Decreased peak atrial longitudinal systolic strain and total emptying atrial fraction demonstrate an altered LA reservoir function. Also our study has shown a reduced passive EF with preservation of active EF (atrial pump) among hypertensives - results that are not well defined in literature. Our observation onthe close association between LA size and functional impairment is similar with the results of numerous previous studies involving measuring techniques. Our findings suggest that a more thorough echocardiographic evaluation of LA may be necessary and useful along with the choice of antihypertensive drugs and target blood value in hypertension.
7 Left Atrial Structural and Functional Remodeling in Hypertensives 11 Acknowledgement This paper is partly supported by the Sectorial Operational Programme Human Resources Development (SOPHRD), financed by the European Social Fund and the Romanian Government under the contract number POSDRU "/ MENÅIUNE: Aceastã lucrare este paråial sprijinitã de cãtre Programul Operaåional Sectorial Dezvoltarea Resurselor Umane (POSDRU) finanåat din Fondul Social European æi de cãtre Guvernul Romaniei prin contractul nr. POSDRU REFERENCES 1. B. Ristow, S. Ali, M. a Whooley et al, Usefulness of left atrial volume index to predict heart failure hospitalization and mortality in ambulatory patients with coronary heart disease and comparison to left ventricular ejection fraction (from the Heart and Soul Study), Am. J. Cardiol., 2008, 102(1): B. Paul, Left Atrial Volume - A New Index in Echocardiography, JAPI, 2009, 57: S. Gupta, S. A. Matulevicius, C. R. Ayers et al, Left atrial structure and function and clinical outcomes in the general population, Eur. Hear. J., 2013, 34(4): Y. Takemoto, M. E. Barnes, J. B. Seward et al, Usefulness of Left Atrial Volume in Predicting First Congestive Heart Failure in Patients 65 Years of Age With Well-Preserved Left Ventricular Systolic Function, Am. J. Cardiol., 2014, 96(6): A. Rossi, P. L. Temporelli, M. Quintana et al, Independent relationship of left atrial size and mortality in patients with heart failure: an individual patient meta-analysis of longitudinal data (MeRGE Heart Failure), Eur. J. Heart Fail., 2009, 11(10): B. D. Hoit, Left atrial size and function: role in prognosis, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2014, 63(6): G.G. Blume, C.J. Mcleod, M.E.Barnes et al, Left atrial function: physiology, assessment, and clinical implications, Eur. Hear.J., 2011, 12: E.S.Tucay, Left Atrial Volume and Left Atrial Function as Predictor of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation, 2012, gov.ph/journal/publication 9. M. Cameli, M. Lisi, F. M. Righini et al, Novel echocardiographic techniques to assess left atrial size, anatomy and function, Cardiovasc. Ultrasound, 2012, 10(1): Y-S Lee, D W Hyun, B C Jung et al, Left atrial volume index as a predictor for occurrence of atrial fibrillation after ablation of typical atrial flutter, Journal of Cardiology, 2010, 56(3): AJ Sanfilippo, VM Abascal, M Sheehan, Atrial enlargment as a consequence of atrial fibrillation. A prospective echocardiographic study, Circulation, 1990, 82: G Piotrowski, M Banach, E. Gerdts et al Left atrial size in hypertension and stroke, J Hypertens, 2011, 29(10): B. Ristow, S. Ali, M. A. Whooley et al, Usefulness of Left Atrial Volume Index to Predict Heart Failure Hospitalization and Mortality in Ambulatory Patients With Coronary Heart Disease and Comparison to Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (from the Heart and Soul Study), Am. J. Cardiol., 2014, 102(1): H. Tamura, T. Watanabe, S. Nishiyama et al, Increased Left Atrial Volume Index Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Patients With Heart Failure, J. Card. Fail., 2014, 17(3): AM Losi, S Betocchi, G Barbati et al, Prognostic significance of left atrial volume dilatation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2009, 22(1): F. Ferreira, A.Galrinho, R.Soares et al, Prognostic valueof left atrial volume in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy, Rev Port Cardiol, 2013; 32: DA Patel, CJ LAvie, RV Milani et al, Clinical Implications of left atrial enlargement: a review, Ochsner J, 2009, 9(4): DA Patel, CJ LAvie, RV Milani et al, Left atrial volume index preditive of mortality independent of left ventricular geometry in a large clinical cohort with preserved ejection fraction, Mayo Clin Proc, 2011, 86(8): R.M. Lang, L.P. Badano, V. Mor-Avi et al, Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging, J Am Soc Echocard, 2015, 28(1) 20. MK Erol, M Yilmaz, M Acikel et al, Left atrial mechanical function in patients with essential hypertension, Acta Cardiol, 2002, 57(5): G. Cioffi, GF Mureddu, C Stefenelli et al, Relationship between left ventricular geometry and let atrial size in patients with systemic hypertension, J Hypertens, 2004, 22: S. Eshoo, S.L.Ross, L.Thomas, Impact of Mild Hypertension on Left Atrial Size and Function, Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2009, 2: Q.Cui, H.Wang, W.Zhang et al, Enhanced Left Atrial Reservoir, Increased Conduit, and Weakened Booster Pump Function in Hypertensive Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation, Hypertension Research, 2008, 31: T-Y Xu, J Sun, A P-W Lee et al, Left atrial Function as Assessed by Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Hypertension, Medicine, 2015, 94(6): M. Cameli, M. Caputo, S. Mondillo et al, Feasibility and reference values of left atrial longitudinal strain imaging by two-dimensional speckle tracking, Cardiovasc. Ultrasound, 2009, 7:6 26. M Sahebjam, A Mazareei, M Lotfi-Tokaldany et al, Comparison of Left Atrial Function between Hypetensive Patients with Normal Atrial Size and Normotensive Subjects Using Strain Rate Imaging, Arch Cardiovasc Imaging, 2014, 2(1):ee N Kokubu, S Yuda, K Tsuchihashi et al, Noninvasive assessement of Left atrial function by strain rate imaging in patients with hypertension: a possible beneficial effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibition on left atrial function, Hypertens Res, 2007; 30(1):13-21
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New?
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function
 II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
THE LEFT ATRIUM HOW CAN ECHO HELP US?
 THE LEFT ATRIUM HOW CAN ECHO HELP US? Dr. Dragos COZMA BACKGROUND Left atrium (LA) dilation can occur in a broad spectrum of cardiovascular diseases including hypertension, left ventricular dysfunction,
THE LEFT ATRIUM HOW CAN ECHO HELP US? Dr. Dragos COZMA BACKGROUND Left atrium (LA) dilation can occur in a broad spectrum of cardiovascular diseases including hypertension, left ventricular dysfunction,
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Prognostic Value of Left Atrial Size and Function
 Prognostic Value of Left Atrial Size and Function James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Conflicts: None
Prognostic Value of Left Atrial Size and Function James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Conflicts: None
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle
 Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
4D Auto LAQ (Left Atrial Quantification)
 4D Auto LAQ (Left Atrial Quantification) Introduction There has been an increased interest in quantification of the left atrium (LA) for various types of diseases; e.g. heart failure, heart valve diseases,
4D Auto LAQ (Left Atrial Quantification) Introduction There has been an increased interest in quantification of the left atrium (LA) for various types of diseases; e.g. heart failure, heart valve diseases,
Left atrial Function In Echocardiography
 Left atrial Function In Echocardiography Pr Erwan DONAL erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Inserm Diastole LA Pressure (mmhg) -t/ 17 LA function 15 A-Loop 13 V-Loop 11 9 7 5 1 2 3 4 20 30 40 50 60 70 LA Volume
Left atrial Function In Echocardiography Pr Erwan DONAL erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Inserm Diastole LA Pressure (mmhg) -t/ 17 LA function 15 A-Loop 13 V-Loop 11 9 7 5 1 2 3 4 20 30 40 50 60 70 LA Volume
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Romanian Journal of Cardiology Vol. 28, No. 3, 2018
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Left atrial function - novel ecocardiographic markers for detecting atrial fibrillation in hypertensives Ioana etre 1, Silvia Iancovici 2, Sebastian Onciul 1, Oana Florentina Tautu 1,2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Left atrial function - novel ecocardiographic markers for detecting atrial fibrillation in hypertensives Ioana etre 1, Silvia Iancovici 2, Sebastian Onciul 1, Oana Florentina Tautu 1,2,
Conflict of interest: none declared
 The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
LA Function analysis Marcia Barbosa Vice Presidente - Brazilian Soc of Cardiology President-elect - Interamerican Soc of Cardiology
 LA Function analysis Marcia Barbosa Vice Presidente - Brazilian Soc of Cardiology President-elect - Interamerican Soc of Cardiology Belo Horizonte Brazil DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to
LA Function analysis Marcia Barbosa Vice Presidente - Brazilian Soc of Cardiology President-elect - Interamerican Soc of Cardiology Belo Horizonte Brazil DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
Conflict of Interests
 The Left Ventricle: How Should We Quantify Its Size and Function; Is It Time for 3D in Everyone? Roberto M Lang, MD Conflict of Interests Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory
The Left Ventricle: How Should We Quantify Its Size and Function; Is It Time for 3D in Everyone? Roberto M Lang, MD Conflict of Interests Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory
Changes of Left Atrial Phasic Function Assessed by Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in Untreated Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Ultrasound (2012) 20, 220e227 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jmu-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changes of Left Atrial Phasic Function Assessed by Speckle
Journal of Medical Ultrasound (2012) 20, 220e227 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jmu-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changes of Left Atrial Phasic Function Assessed by Speckle
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD
 Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD Ospedale San Pietro Fatebenefratelli Rome, Italy Differential
Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD Ospedale San Pietro Fatebenefratelli Rome, Italy Differential
MAYON VOLCANO: FAST FACTS
 MAYON VOLCANO: FAST FACTS Type of Volcano: Stratovolcano Elevation: 2.46 km Base Diameter: 20 km Base Circumference: 62.8 km Area: 314.1 km 2 Reference: http://www.phivolcs.dost.gov.ph/html/update_vmepd/volcano/volcanolist/mayon.htm
MAYON VOLCANO: FAST FACTS Type of Volcano: Stratovolcano Elevation: 2.46 km Base Diameter: 20 km Base Circumference: 62.8 km Area: 314.1 km 2 Reference: http://www.phivolcs.dost.gov.ph/html/update_vmepd/volcano/volcanolist/mayon.htm
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography
 Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking:
 Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Assessment of cardiac function with 3D echocardiography. Đánh giá chức năng tim bằng siêu âm tim 3D
 Assessment of cardiac function with 3D echocardiography Đánh giá chức năng tim bằng siêu âm tim 3D TS. BS. Nguyễn Thị Thu Hoài Viện Tim Mạch Quốc Gia Việt Nam TỪ SIÊU ÂM M-mode ĐẾN SIÊU ÂM 3D TỪ SIÊU ÂM
Assessment of cardiac function with 3D echocardiography Đánh giá chức năng tim bằng siêu âm tim 3D TS. BS. Nguyễn Thị Thu Hoài Viện Tim Mạch Quốc Gia Việt Nam TỪ SIÊU ÂM M-mode ĐẾN SIÊU ÂM 3D TỪ SIÊU ÂM
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease:
 Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging. Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Temple University School of Medicine
 Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Temple University School of Medicine Measurement of end-diastolic LV internal diameter (LVIDd) made by properly-oriented M-Mode techniques in the Parasternal Long Axis View (PLAX):
Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Temple University School of Medicine Measurement of end-diastolic LV internal diameter (LVIDd) made by properly-oriented M-Mode techniques in the Parasternal Long Axis View (PLAX):
3D-stress echocardiography Bernard Cosyns, MD, PhD
 3D-stress echocardiography Bernard Cosyns, MD, PhD No Disclosure The Pro-Technology bias Sicari et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2006, 4:11 Overview 2D stress echocardiography: main limitations 3D echocardiography:
3D-stress echocardiography Bernard Cosyns, MD, PhD No Disclosure The Pro-Technology bias Sicari et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2006, 4:11 Overview 2D stress echocardiography: main limitations 3D echocardiography:
Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study
 Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study By Julius Caesar D. de Vera, MD Jonnah Fatima B. Pelat, MD Introduction Right ventricle contributes
Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study By Julius Caesar D. de Vera, MD Jonnah Fatima B. Pelat, MD Introduction Right ventricle contributes
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi
 Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION. There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation
 PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
Left Atrial Volume:?Physiologic Model for Cardiovascular Disease Risk.
 Left Atrial Volume:?Physiologic Model for Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Dr Gitura Muriuki Physician Kenyatta National Hospital Aging Epidemic US approx 35m 65yrs plus. Fastest growing cohort 80s. Comorbidities
Left Atrial Volume:?Physiologic Model for Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Dr Gitura Muriuki Physician Kenyatta National Hospital Aging Epidemic US approx 35m 65yrs plus. Fastest growing cohort 80s. Comorbidities
Left atrial dimensions Is left atrial volume calculation always necessary?
 LEFT ATRIAL ASSESSMENT Left atrial dimensions Is left atrial volume calculation always necessary? Marina Leitman and Zvi Vered ABSTRACT Department of Cardiology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center and Sackler
LEFT ATRIAL ASSESSMENT Left atrial dimensions Is left atrial volume calculation always necessary? Marina Leitman and Zvi Vered ABSTRACT Department of Cardiology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center and Sackler
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial septal aneurysm: A speckle tracking study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2015, Vol. 22, No. 5, 535 540 DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0033 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2015, Vol. 22, No. 5, 535 540 DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0033 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies. Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO PhD European Society of Cardiology 2012
 Relative Apical Sparing of Longitudinal Strain Using 2- Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography is Both Sensitive and Specific for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO
Relative Apical Sparing of Longitudinal Strain Using 2- Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography is Both Sensitive and Specific for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO
Aortic Regurgitation and Aortic Aneurysm - Epidemiology and Guidelines -
 Reconstruction of the Aortic Valve and Root - A Practical Approach - Aortic Regurgitation and Aortic Aneurysm Wednesday 14 th September - 9.45 Practice must always be founded on sound theory. Leonardo
Reconstruction of the Aortic Valve and Root - A Practical Approach - Aortic Regurgitation and Aortic Aneurysm Wednesday 14 th September - 9.45 Practice must always be founded on sound theory. Leonardo
Masked Hypertension and Left Atrial Dysfunction: A Hidden Association
 ORIGINAL PAPER Masked Hypertension and Left Atrial Dysfunction: A Hidden Association Marijana Tadic, MD, PhD; 1,2 Cesare Cuspidi, MD; 3 Jana Radojkovic, MD; 1 Branislav Rihor, MD; 1 Vesna Kocijanic, RN;
ORIGINAL PAPER Masked Hypertension and Left Atrial Dysfunction: A Hidden Association Marijana Tadic, MD, PhD; 1,2 Cesare Cuspidi, MD; 3 Jana Radojkovic, MD; 1 Branislav Rihor, MD; 1 Vesna Kocijanic, RN;
Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size
 2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
 Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Left Atrial Deformation Predicts Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure in Pediatric Heart Transplant Recipients
 DOI: 10.1111/echo.12679 2014, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Echocardiography Left Atrial Deformation Predicts Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure in Pediatric Heart Transplant Recipients Jay Yeh, M.D.,* Ranjit
DOI: 10.1111/echo.12679 2014, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Echocardiography Left Atrial Deformation Predicts Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure in Pediatric Heart Transplant Recipients Jay Yeh, M.D.,* Ranjit
Left atrial function and remodelling in aortic stenosis
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2011) 12, 299 305 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jer006 Left atrial function and remodelling in aortic stenosis Kim O Connor, Julien Magne, Monica Rosca, Luc A. Piérard, and
European Journal of Echocardiography (2011) 12, 299 305 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jer006 Left atrial function and remodelling in aortic stenosis Kim O Connor, Julien Magne, Monica Rosca, Luc A. Piérard, and
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
10/7/2013. Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast. Thanks to our Course Director: Neil J.
 Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies
 Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
New aspects of Echocardiography in Hypertensive Heart Disease. Fausto J. Pinto, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC, FASE
 New aspects of Echocardiography in Hypertensive Heart Disease Fausto J. Pinto, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC, FASE Progressive increase in cardiovascular morbidity (left) and all-cause mortality (right) rates
New aspects of Echocardiography in Hypertensive Heart Disease Fausto J. Pinto, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC, FASE Progressive increase in cardiovascular morbidity (left) and all-cause mortality (right) rates
Prediction of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Left Atrial Size Is Volume Superior to Area or Diameter?
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 5, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.077
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 5, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.077
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography
 Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING M-MODE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function. Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes
 Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Preload Afterload Myocardial Fiber Shortening Circumferential Longitudinal
Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Preload Afterload Myocardial Fiber Shortening Circumferential Longitudinal
Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS
 Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS No disclosures Review 2D Speckle Strain (briefly) Discuss some various patient populations & disease pathways where Strain can be helpful Discuss how to acquire images for Strain
Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS No disclosures Review 2D Speckle Strain (briefly) Discuss some various patient populations & disease pathways where Strain can be helpful Discuss how to acquire images for Strain
2/2/2011. Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? Movement vs Deformation. Doppler Myocardial Velocities. Movement. Deformation.
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain. V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen
 HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation
 Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Basic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function
 WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Basic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function Ritesh Dhar, MD Director, Echocardiography Lab and Staff Cardiologist Intermountain Medical Center Murray, Utah Outline
WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Basic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function Ritesh Dhar, MD Director, Echocardiography Lab and Staff Cardiologist Intermountain Medical Center Murray, Utah Outline
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND LEFT ATRIUM: STRUCTURAL REMODELING AND EVOLUTION OF ARRHYTHMIA PATTERN
 Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: the ugly and the nasty 13 International Meeting February 14-15 th 2019, Bologna ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND LEFT ATRIUM: STRUCTURAL REMODELING AND EVOLUTION OF ARRHYTHMIA
Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: the ugly and the nasty 13 International Meeting February 14-15 th 2019, Bologna ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND LEFT ATRIUM: STRUCTURAL REMODELING AND EVOLUTION OF ARRHYTHMIA
Objectives. Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction
 Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Københavns Universitet
 university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of Inadequate Ventricular Hypertrophy
 Abstract ESC 82445 Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of Inadequate Ventricular Hypertrophy FL. Dini 1, P. Capozza 1, P. Fontanive 2, MG. Delle Donne 1, V. Santonato
Abstract ESC 82445 Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of Inadequate Ventricular Hypertrophy FL. Dini 1, P. Capozza 1, P. Fontanive 2, MG. Delle Donne 1, V. Santonato
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When?
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Ο ΡOΛΟΣ ΤΗΣ ΑΠΕΙΚOΝΙΣΗΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΦΥΣΙΟΛΟΓIΑ - ΥΠΟΣΤΡΩΜΑ ΚΟΛΠΟΙ ΩΤΙΑ ΑΞΙΟΛΟΓΗΣΗ ΟΥΛΗΣ
 Ο ΡOΛΟΣ ΤΗΣ ΑΠΕΙΚOΝΙΣΗΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΦΥΣΙΟΛΟΓIΑ - ΥΠΟΣΤΡΩΜΑ ΚΟΛΠΟΙ ΩΤΙΑ ΑΞΙΟΛΟΓΗΣΗ ΟΥΛΗΣ Κώστας Παπαδόπουλος, Επιμ. Α Καρδιολογίας, Νοσοκομείο Ερυθρός Σταυρός ATRIA ANATOMY Complex anatomy Best knowledge
Ο ΡOΛΟΣ ΤΗΣ ΑΠΕΙΚOΝΙΣΗΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΦΥΣΙΟΛΟΓIΑ - ΥΠΟΣΤΡΩΜΑ ΚΟΛΠΟΙ ΩΤΙΑ ΑΞΙΟΛΟΓΗΣΗ ΟΥΛΗΣ Κώστας Παπαδόπουλος, Επιμ. Α Καρδιολογίας, Νοσοκομείο Ερυθρός Σταυρός ATRIA ANATOMY Complex anatomy Best knowledge
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: Improving Patient Selection and Outcomes
 The Journal of Innovations in Cardiac Rhythm Management, 3 (2012), 899 904 DEVICE THERAPY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: Improving Patient Selection and Outcomes GURINDER S.
The Journal of Innovations in Cardiac Rhythm Management, 3 (2012), 899 904 DEVICE THERAPY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: Improving Patient Selection and Outcomes GURINDER S.
Beginner s Guide to Strain: What should be in your lab in Disclosures
 Beginner s Guide to Strain: What should be in your lab in 2018 Bonita Anderson DMU (Cardiac), MApplSc (Med Ultrasound), ACS, AMS, FASE None Disclosures Calculation of Strain Strain can be Positive Strain
Beginner s Guide to Strain: What should be in your lab in 2018 Bonita Anderson DMU (Cardiac), MApplSc (Med Ultrasound), ACS, AMS, FASE None Disclosures Calculation of Strain Strain can be Positive Strain
Atrial dysfunction and chronotropic incompetence
 Pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction Atrial dysfunction and chronotropic incompetence Vojtech Melenovsky IKEM, Prague, Czech Republic DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST :
Pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction Atrial dysfunction and chronotropic incompetence Vojtech Melenovsky IKEM, Prague, Czech Republic DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST :
Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied
 9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
The rapid evolution of echocardiography during the past 25 years
 Evaluation of Myocardial Mechanics in the Fetus by Velocity Vector Imaging Adel K. Younoszai, MD, David E. Saudek, MD, Stephen P. Emery, MD, and James D. Thomas, MD, Denver, Colorado; Cleveland, Ohio;
Evaluation of Myocardial Mechanics in the Fetus by Velocity Vector Imaging Adel K. Younoszai, MD, David E. Saudek, MD, Stephen P. Emery, MD, and James D. Thomas, MD, Denver, Colorado; Cleveland, Ohio;
EDITOR S PICK CURRENT STATUS OF FULLY AUTOMATED SOFTWARE WITH THREE-DIMENSIONAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY FOR THE QUANTIFICATION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 ITOR S PICK This paper, courtesy of Yang and Takeuchi, provides a timely and well-considered update on the current status of fully-automated software with three-dimensional echocardiography for quantifying
ITOR S PICK This paper, courtesy of Yang and Takeuchi, provides a timely and well-considered update on the current status of fully-automated software with three-dimensional echocardiography for quantifying
DISCLOSURE. Myocardial Mechanics. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Off Label Usage
 7th Annual Team Echocardiography: The Heart of Cardiovascular Medicine Tissue Doppler, Strain, Speckle: What? How? Christopher J Kramer RDCS Aurora Medical Group Advanced Cardiovascular Services, Aurora
7th Annual Team Echocardiography: The Heart of Cardiovascular Medicine Tissue Doppler, Strain, Speckle: What? How? Christopher J Kramer RDCS Aurora Medical Group Advanced Cardiovascular Services, Aurora
Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction
 Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction JC Eicher, G Laurent, O Barthez, A Mathé, G Bertaux, JE Wolf Heart Failure Treatment Unit, Rhythmology and
Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction JC Eicher, G Laurent, O Barthez, A Mathé, G Bertaux, JE Wolf Heart Failure Treatment Unit, Rhythmology and
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK- BENIGN OR A HARBINGER OF HEART FAILURE? PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR?
 LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK- BENIGN OR A HARBINGER OF HEART FAILURE? PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? Juan Cinca Department and Chair of Cardiology Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK- BENIGN OR A HARBINGER OF HEART FAILURE? PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? Juan Cinca Department and Chair of Cardiology Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Myocardial Performance Index in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
 Arch Iranian Med 2008; 11 (5): 497 501 Original Article Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Myocardial Performance Index in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Daryoosh Javidi MD
Arch Iranian Med 2008; 11 (5): 497 501 Original Article Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Myocardial Performance Index in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Daryoosh Javidi MD
Dominic Y. Leung, MBBS, PhD; Melissa Leung, MBBS, PhD Department of Cardiology, Liverpool Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
 Original Article Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 Early detection of left ventricular dysfunction in diabetes Dominic Y. Leung, MBBS, PhD; Melissa Leung, MBBS, PhD Department of Cardiology, Liverpool Hospital,
Original Article Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 Early detection of left ventricular dysfunction in diabetes Dominic Y. Leung, MBBS, PhD; Melissa Leung, MBBS, PhD Department of Cardiology, Liverpool Hospital,
Introduction. In Jeong Cho, MD, Wook Bum Pyun, MD and Gil Ja Shin, MD ABSTRACT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.4.145 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology The Influence of the Left Ventricular Geometry on the Left
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.4.145 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology The Influence of the Left Ventricular Geometry on the Left
On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding
 Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
Prof. Samir Morcos Rafla Alexandria Univ. Cardiology Dept.
 Obesity as a risk factor for Atrial Fibrillation Prof. Samir Morcos Rafla Alexandria Univ. Cardiology Dept. CardioAlex 2010 smrafla@hotmail.com 1 Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United
Obesity as a risk factor for Atrial Fibrillation Prof. Samir Morcos Rafla Alexandria Univ. Cardiology Dept. CardioAlex 2010 smrafla@hotmail.com 1 Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United
Echo assessment of the failing heart
 Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
