Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy: A New Way of Thinking. Ji Su Jenny Kim & Logan D. MacLean SRNA, BSN, CCRN DNP Candidates
|
|
|
- Ralf Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy: A New Way of Thinking Ji Su Jenny Kim & Logan D. MacLean SRNA, BSN, CCRN DNP Candidates
2 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
3 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
4 Brief History of Fluid Management Srinivasa, S. & Hill, A. G. (2012). Perioperative fluid administration: historical highlights and implications for practice. Surgical Retrospection, 256(6),
5 Why Should I Care?
6 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
7 Hypovolemia Hypervolemia
8 Hypovolemia Complications Low cardiac output Hypovolemia Decreased tissue perfusion Shock/organ failure Chappell, D., Jacob, M., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Conzen, P., & Rehm, M. (2008). A rational approach to perioperative fluid management. Anesthesiology, 109(4): 723 Brandstrup, B. (2006). Fluid therapy for the surgical patient. Best Practice Research Clinical Anaesthesiology, 20(2), 265.
9 Hypervolemia Complications Respiratory effects GI effects Hypervolemia Coagulation Joshi, G. P. (2018). Intraoperative fluid management. UpToDate. Retrieved February 26, 2018, from Thacker, J. K., Mountford, W. K., Ernst, F. R., Krukas, M. R., & Mythen, M. M. (2016). Perioperative fluid utilization variability and association with outcomes: considerations for enhanced recovery efforts in sample US surgical populations. Annals of Surgery, 263(3), Wound healing
10 Shin, C. H., Long, D. R., McLean, D., Grabitz, S. D., Ladha, K., Timm, F. P., Eikermann, M. (2017). Effects of intraoperative fluid management on postoperative outcomes: a hospital registry study. Annals of Surgery, doi: /SLA
11 Thacker, J. K., Mountford, W. K., Ernst, F. R., Krukas, M. R., & Mythen, M. M. (2016). Perioperative fluid utilization variability and association with outcomes: considerations for enhanced recovery efforts in sample US surgical populations. Annals of Surgery, 263(3),
12 Why Should I Care? Surgical Anesthetics Patient-related Surgical procedure Excessive fluid administration Age > 65 yr Vascular Blood transfusion (>4 units) ASA physical status > 2 Thoracic Residual neuromuscular blockade History of respiratory disease Upper abdominal Intraoperative hypothermia OSA Neurosurgery Use of NG tube Preoperative SpO2 < 96% Head and neck Inadequate ventilator settings History of CHF Emergency procedure Reintervention Surgical duration > 2h Open laparotomy > laparoscopy Futier, E., Marret, E., & Jaber, S. (2014). Perioperative positive pressure ventilation: an integrated approach to improved pulmonary care. Anesthesiology, 121(2), Recent respiratory infection (<1 mo) Partial or total functional dependency Active smoking Alcohol abuse Preoperative sepsis Weight loss > 10% in the last 6 months Preoperative anemia (<10g/dl) Obesity
13 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
14 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
15 Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
16 Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
17 Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
18 Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
19 Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
20 ml Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
21 Fluid Compartments
22 Fluid Compartments 30L 12L 3L
23 Fluid Compartments 30L 12L water Na+ Na+ K+ K+ protein protein 3L
24 Fluid Compartments 30L 12L water Na+ Na+ K+ K+ protein protein water Na+ K+ protein protein 3L
25 Endothelial Glycocalyx Brettner, F., Chappell, D., & Jacob, M. (2012). The concept of the glycocalyx Facts that influence perioperative fluid management. Trends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care,2(4), doi: /j.tacc
26 Endothelial Glycocalyx Brettner, F., Chappell, D., & Jacob, M. (2012). The concept of the glycocalyx Facts that influence perioperative fluid management. Trends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care,2(4), doi: /j.tacc
27 Protect Endothelial Glycocalyx Inhalational Agents (sevoflurane) Plasma proteins Hydrocortisone Etanercept (TNF-a receptor) Antithrombin III Antioxidants Ischemia/Reperfusion Sepsis/Inflammation Hypervolemia ANP Hyperglycemia Surgical Stress Destroy Bashandy, G. M. (2014). Implications of recent accumulating knowledge about endothelial glycocalyx on anesthetic management. Journal of Anesthesia,29(2), doi: /s
28 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
29 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
30 Intra-Operative Fluid Replacement 80kg pt undergoing Exploratory Laparotomy; NPO for past 10 hours Hours Fluid Deficit Maintenance Insensible Losses EBL Urine Output Hourly Total Total Hour (300) 150 1,810 1,810 Hour (900) 50 2,010 3,820 Hour (150) 30 1,240 5,060 mls
31 Maintenance Fluids/Insensible Losses Maintenance Requirements for Different Surgeries Surgical Trauma Fluid Volume Example Surgery Superficial 1-2 ml/kg/hr Peripheral surgery Minimal 3-4 ml/kg/hr Head and neck, hernia, knee surgery Moderate 5-6 ml/kg/hr Major surgery without exposed abdominal contents Severe 8-10 ml/kg/hr (or more) Major abdominal, especially with exposed abdominal contents Barash, P. G., Cullen, B. F., Stoelting, R. K., Cahalan, M. K., Stock, M. C., & Ortega, R. (2013). Clinical Anesthesia, 7 th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
32 Intra-Operative Fluid Replacement 80kg pt undergoing Exploratory Laparotomy; NPO for past 10 hours Hours Fluid Deficit Maintenance Insensible Losses EBL Urine Output Hourly Total Total Hour (300) 150 1,810 1,810 Hour (900) 50 2,010 3,820 Hour (150) 30 1,240 5,060 mls
33 Fundamentals 1. Preoperative fasting patients are hypovolemic due to ongoing insensible perspiration and urinary output 2. Insensible perspiration increases dramatically during surgery due to exposure 3. An unpredictable fluid shift towards the third space requires generous substitution 4. Hypervolemia is harmless because the kidneys regulate the overload
34 Intra-Operative Fluid Replacement 80kg pt undergoing Exploratory Laparotomy; NPO for past 10 hours Hours Fluid Deficit Maintenance Insensible Losses EBL Urine Output Hourly Total Total Hour (300) 150 1,810 1,810 Hour (900) 50 2,010 3,820 Hour (150) 30 1,240 5,060 mls
35 Intra-Operative Fluid Replacement 80kg pt undergoing Exploratory Laparotomy; NPO for past 10 hours Hours Fluid Deficit Maintenance Insensible Losses EBL Urine Output Hourly Total Total Pre-op fasting for 10hrs = No differences between theoretical and actual plasma volumes using indocyanine green (2008) Hour (300) 150 1,810 1,810 Hour (900) 50 2,010 3,820 Pre-op fasting for >8hrs = No differences between pre and post fasting plasma volumes using transthoracic echocardiography (2014) Hour (150) 30 1,240 5,060 mls Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Conzen, P., Finsterer, U., Rehm, M. (2008). Blood volume is normal after pre-operative overnight fasting. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 52(4), Muller, L., Briere, M., Bastide, S., Roger, C., Zoric, L., Seni, G., de La Coussaye, J. E. Ripart, J., & Lefrant, J. Y. (2014). Preoperative fasting does not affect haemodynamic status: a prospective, non-inferiority, echocardiography study. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 112(5),
36 Intra-Operative Fluid Replacement 80kg pt undergoing Exploratory Laparotomy; NPO for past 10 hours Hours Fluid Deficit Maintenance Insensible Losses EBL Urine Output Hourly Total Total Hour (300) 150 1,810 1,810 Hour (900) 50 2,010 3,820 Hour (150) 30 1,240 5,060 mls
37 Maintenance Fluids/Insensible Losses Maintenance Requirements for Different Surgeries Surgical Trauma Fluid Volume Example Surgery Superficial 1-2 ml/kg/hr Peripheral surgery Minimal 3-4 ml/kg/hr Head and neck, hernia, knee surgery Moderate 5-6 ml/kg/hr Major surgery without exposed abdominal contents Severe 8-10 ml/kg/hr (or more) Major abdominal, especially with exposed abdominal contents Barash, P. G., Cullen, B. F., Stoelting, R. K., Cahalan, M. K., Stock, M. C., & Ortega, R. (2013). Clinical Anesthesia, 7 th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Navarro, L. H. C., Bloomstone, J. A., Auler Jr, J. O. C., Cannesson, M., Rocca, G. D., Gan, T. J., Kramer, G. C. (2015). Perioperative fluid therapy: a statement from the international fluid optimization group. Perioperative Medicine, 4(3).
38 Maintenance Fluids/Insensible Losses Maintenance Requirements for Different Surgeries Surgical Trauma Fluid Volume Example Surgery Superficial 1-2 ml/kg/hr Peripheral surgery Minimal 3-4 ml/kg/hr Head and neck, hernia, knee surgery Moderate 5-6 ml/kg/hr Major surgery without exposed abdominal ml/kg/hr contents Severe 8-10 ml/kg/hr (or more) Evaporation/fluid loss through exposure: Major abdominal, especially with exposed abdominal contents Barash, P. G., Cullen, B. F., Stoelting, R. K., Cahalan, M. K., Stock, M. C., & Ortega, R. (2013). Clinical Anesthesia, 7 th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Navarro, L. H. C., Bloomstone, J. A., Auler Jr, J. O. C., Cannesson, M., Rocca, G. D., Gan, T. J., Kramer, G. C. (2015). Perioperative fluid therapy: a statement from the international fluid optimization group. Perioperative Medicine, 4(3).
39 Fluid Resuscitation Classical Approach 3:1 ratio Recent Findings 1.3:1 to 2:1 ratio The efficacy and safety of colloid resuscitation in the critically ill (2011) Crystalloids versus colloids: exploring differences in fluid requirements by systematic review and meta-regression (2015) Cortes, D. O., Barros, T. G., Njimi, H., Vincent, J. (2015). Crystalloids versus colloids: exploring differences in fluid requirements by systematic review and meta-regression. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 120(2), Hartog, C. S., Bauer, M., & Reinhart, K. (2011). The efficacy and safety of colloid resuscitation in the critically ill. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 120(1),
40 Intra-Operative Fluid Replacement 80kg pt undergoing Exploratory Laparotomy; NPO for past 10 hours Hours Fluid Deficit Maintenance Insensible Losses EBL Urine Output Hourly Total Total Hour (300) 150 1,810 1,810 Hour (900) 50 2,010 3,820 Hour (150) 30 1,240 5,060 mls
41 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
42 Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Map History of Fluid Management Significance of Fluid Management Fluid Compartment Physiology Traditional Theories of Fluid Management Fluid Management Indicators & Interventions
43 Indications and Interventions Scientific Method Traditional Indicators Advanced Indicators Pharmacokinetic Indicator: Volume Effect Crystalloid vs. Colloid
44 Scientific Method Target Indication Therapy Outcome Variable Normovolemia Intravascular Hypovolemia Volume Replacement Blood Volume
45 Scientific Method Target Indication Therapy Outcome Variable Normovolemia Intravascular Hypovolemia Volume Replacement Blood Volume
46 Traditional Indicators BP, HR, CVP Urine output Not sensitive or specific 62 ± ± 7 55 ± 8 HR Blood volume: 3959 ± 387 ml 3501 ± 499ml 3934 ± 500 ml (n = 10) Hct: 0.35 ± ± ± 0.04 Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
47 Advanced Flow Measurements Frank Starling Curve Pulse Pressure Variation (PPV) Stroke Volume Variation (SVV) Limitations Doherty, M., & Buggy, D. J. (2013). Intraoperative Fluids. Survey of Anesthesiology,57(1), doi: /01.sa dc
48 Indications and Interventions Scientific Method Traditional Indicators Advanced Indicators Pharmacokinetic Indicator: Volume Effect Crystalloid vs. Colloid
49 Volume Effect Percentage of infused solution that 2) does not cause interstitial edema 1) remains within circulatory compartment and 30L 12L 3L
50 Volume Effect Percentage of infused solution that 2) does not cause interstitial edema 1) remains within circulatory compartment and Calculation Methods Hematocrit Dilution (98% existing data) Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) 30L 12L 3L
51 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct - Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume - Intravenous volume therapy - New Hct - Calculation of increase in blood volume
52 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume - Intravenous volume therapy - New Hct - Calculation of increase in blood volume
53 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume 5 L * 0.40 = 2 L RCV 5 L - 2 L = 3 L Plasma - Intravenous volume therapy - New Hct - Calculation of increase in blood volume
54 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume 5 L * 0.40 = 2 L RCV 5 L - 2 L = 3 L Plasma - Intravenous volume therapy 1 L Colloid - New Hct - Calculation of increase in blood volume
55 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume 5 L * 0.40 = 2 L RCV 5 L - 2 L = 3 L Plasma - Intravenous volume therapy 1 L Colloid - New Hct Calculation of increase in blood volume
56 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume 5 L * 0.40 = 2 L RCV 5 L - 2 L = 3 L Plasma - Intravenous volume therapy 1 L Colloid - New Hct Calculation of increase in blood volume 2 L RCV = x L Plasma x = 3.7 L Plasma
57 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume 5 L * 0.40 = 2 L RCV 5 L - 2 L = 3 L Plasma - Intravenous volume therapy 1 L Colloid - New Hct Calculation of increase in blood volume 2 L RCV = x L Plasma x = 3.7 L Plasma
58 Volume Effect: Hematocrit Dilution - Initial hct Initial blood volume * initial Hct = Red Cell Volume 5 L * 0.40 = 2 L RCV 5 L - 2 L = 3 L Plasma - Intravenous volume therapy 1 L Colloid +700 ml = 1000 ml Volume Effect of 1L Colloid 70% - New Hct Calculation of increase in blood volume 2 L RCV = x L Plasma x = 3.7 L Plasma
59 Protect Endothelial Glycocalyx Inhalational Agents (sevoflurane) Plasma proteins Hydrocortisone Etanercept (TNF-a receptor) Antithrombin III Antioxidants Ischemia/Reperfusion Sepsis/Inflammation Hypervolemia ANP Hyperglycemia Surgical Stress Destroy Brettner, F., Chappell, D., & Jacob, M. (2012). The concept of the glycocalyx Facts that influence perioperative fluid management. Trends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care,2(4), doi: /j.tacc
60 Volume Effect Percentage of infused solution that 2) does not cause interstitial edema 1) remains within circulatory compartment and Calculation Methods Hematocrit Dilution Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) 30L 12L 3L
61 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
62 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
63 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: Blood Loss: - 1L LR: 4L + 3L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
64 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: Blood Loss: - 1L LR: 4L + 3L BV: 3.5L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
65 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: Blood Loss: - 1L LR: 4L + 3L BV: 3.5L Volume Effect of LR 17% Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
66 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4L Blood Loss: - 1L LR: + 3L Volume Effect of LR 17% BV: 3.5L
67 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4.1 L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
68 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4.1 L Blood Loss: L 6% HES: L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
69 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4.1 L Blood Loss: L 6% HES: L BV: 4.3 L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
70 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4.1 L Blood Loss: L 6% HES: L BV: 4.3 L Volume Effect of Colloid (ANH) 98% Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
71 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) BV: 4.1 L Blood Loss: L 6% HES: L BV: 4.3 L Volume Effect of Colloid (ANH) 98% Vs. Volume Effect (Hct dilution) 127% Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
72 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) 30L water 12L K+ Na+ protein protein water Na+ Na+ K+ K+ protein protein Volume Effect of Colloid (ANH) 98% 3L Vs. Volume Effect (Hct dilution) 127%
73 Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution (ANH) Volume Effect of LR 17% Volume Effect of Colloid (ANH) 98% Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
74 Scientific Method Target Indication Therapy Outcome Variable Normovolemia Intravascular Hypovolemia Volume Replacement Blood Volume
75 Scientific Method Target Indication Therapy Outcome Variable Normovolemia Intravascular Hypovolemia Volume Replacement Blood Volume
76 Volume Loading (VL) BV: 4.2 L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
77 Volume Loading (VL) BV: 4.2 L Blood Loss: --- Albumin: L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
78 Volume Loading (VL) BV: 4.2 L Blood Loss: --- Albumin: L BV: 4.7 L Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
79 Volume Loading (VL) BV: 4.2 L Blood Loss: --- Albumin: L BV: 4.7 L Volume Effect of Colloid (VL) 38% Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
80 Volume Effect is Context Sensitive Volume Effect of Colloid (ANH) 98% Volume Effect of Colloid (VL) 38% Jacob, M., Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Helfen, T., Schuelke, A., Jacob, B.,... Rehm, M. (2012). The intravascular volume effect of Ringers lactate is below 20%: A prospective study in humans. Critical Care,16(3). doi: /cc11344
81 Indications and Interventions Scientific Method Traditional Indicators Advanced Indicators Pharmacokinetic Indicator: Volume Effect Crystalloid vs. Colloid Crystalloid Colloid
82 Why Should I Care? - Hypervolemia and hypovolemia are not benign. - Evidence challenges traditional theories of fluid replacement and indicators. - Integrity of the EGL has many implications for perioperative fluid therapy (namely, hypervolemia, surgical stress, ischemia). - Volume effect is context sensitive. Proper indications matter.
83 THANK YOU!
Fluid management. Dr. Timothy Miller Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center
 Fluid management Dr. Timothy Miller Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center Disclosure Consultant and research funding Edwards Lifesciences Goals of fluid therapy 1. Maintain
Fluid management Dr. Timothy Miller Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center Disclosure Consultant and research funding Edwards Lifesciences Goals of fluid therapy 1. Maintain
Actualités sur le remplissage peropératoire. Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD
 Actualités sur le remplissage peropératoire Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD Fees for lectures, advisory board and consultancy: Fresenius Kabi GmbH B Braun Medical SA Perioperative Fluid Volume Administration
Actualités sur le remplissage peropératoire Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD Fees for lectures, advisory board and consultancy: Fresenius Kabi GmbH B Braun Medical SA Perioperative Fluid Volume Administration
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS. Ahmad AL-zu bi
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS Ahmad AL-zu bi Types of IV fluids Crystalloids colloids Crystalloids Crystalloids are aqueous solutions of low molecular weight ions,with or without glucose. Isotonic, Hypotonic, & Hypertonic
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS Ahmad AL-zu bi Types of IV fluids Crystalloids colloids Crystalloids Crystalloids are aqueous solutions of low molecular weight ions,with or without glucose. Isotonic, Hypotonic, & Hypertonic
Conflicts of Interest
 Anesthesia for Major Abdominal Cancer Resection John E. Ellis MD Adjunct Professor University of Pennsylvania johnellis1700@gmail.com Conflicts of Interest 1 Upper Abdominal Surgery Focus on oncologic
Anesthesia for Major Abdominal Cancer Resection John E. Ellis MD Adjunct Professor University of Pennsylvania johnellis1700@gmail.com Conflicts of Interest 1 Upper Abdominal Surgery Focus on oncologic
The Use of Dynamic Parameters in Perioperative Fluid Management
 The Use of Dynamic Parameters in Perioperative Fluid Management Gerard R. Manecke Jr., M.D. Chief, Cardiac Anesthesia UCSD Medical Center San Diego, CA, USA Thanks to Tom Higgins, M.D. 1 Goals of today
The Use of Dynamic Parameters in Perioperative Fluid Management Gerard R. Manecke Jr., M.D. Chief, Cardiac Anesthesia UCSD Medical Center San Diego, CA, USA Thanks to Tom Higgins, M.D. 1 Goals of today
Les solutés de remplissage. Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD
 Les solutés de remplissage Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD Fees for lectures, advisory board and consultancy: Fresenius Kabi GmbH B Braun Medical SA Fluid Resuscitation Morbidity Procedure Co-morbidities
Les solutés de remplissage Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD Fees for lectures, advisory board and consultancy: Fresenius Kabi GmbH B Braun Medical SA Fluid Resuscitation Morbidity Procedure Co-morbidities
Fluid Balance in an Enhanced Recovery Pathway. Edwin Itenberg, DO, FACS, FASCRS St. Joseph Mercy Oakland MSQC/ASPIRE Meeting April 28, 2017
 Fluid Balance in an Enhanced Recovery Pathway Edwin Itenberg, DO, FACS, FASCRS St. Joseph Mercy Oakland MSQC/ASPIRE Meeting April 28, 2017 No Disclosures 2 Introduction The optimal intravenous fluid regimen
Fluid Balance in an Enhanced Recovery Pathway Edwin Itenberg, DO, FACS, FASCRS St. Joseph Mercy Oakland MSQC/ASPIRE Meeting April 28, 2017 No Disclosures 2 Introduction The optimal intravenous fluid regimen
Perioperative Goal Directed Therapy Improving the Quality of Care for Our Surgical Patients
 Perioperative Goal Directed Therapy Improving the Quality of Care for Our Surgical Patients DESIRÉE CHAPPELL, CRNA ERAS TEAM LEAD NORTON AUDUBON HOSPITAL, LOUISVILLE, KY Disclosure Edwards Lifesciences,
Perioperative Goal Directed Therapy Improving the Quality of Care for Our Surgical Patients DESIRÉE CHAPPELL, CRNA ERAS TEAM LEAD NORTON AUDUBON HOSPITAL, LOUISVILLE, KY Disclosure Edwards Lifesciences,
Presented by: Indah Dwi Pratiwi
 Presented by: Indah Dwi Pratiwi Normal Fluid Requirements Resuscitation Fluids Goals of Resuscitation Maintain normal body temperature In most cases, elevate the feet and legs above the level of the heart
Presented by: Indah Dwi Pratiwi Normal Fluid Requirements Resuscitation Fluids Goals of Resuscitation Maintain normal body temperature In most cases, elevate the feet and legs above the level of the heart
How and why I give IV fluid Disclosures SCA Fluids and public health 4/1/15. Andrew Shaw MB FRCA FCCM FFICM
 How and why I give IV fluid Andrew Shaw MB FRCA FCCM FFICM Professor and Chief Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology Vanderbilt University Medical Center 2015 Disclosures Consultant for Grifols manufacturer of
How and why I give IV fluid Andrew Shaw MB FRCA FCCM FFICM Professor and Chief Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology Vanderbilt University Medical Center 2015 Disclosures Consultant for Grifols manufacturer of
-Cardiogenic: shock state resulting from impairment or failure of myocardium
 Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments
 Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments 2016 1 WHAT WE BELIEVE We believe that clinicians make vital fluid and drug decisions every day with limited and inconclusive information Cheetah
Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments 2016 1 WHAT WE BELIEVE We believe that clinicians make vital fluid and drug decisions every day with limited and inconclusive information Cheetah
Fluids in Sepsis: How much and what type? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Kent Hospital, İzmir Eisenhower Medical Center, USA American Hospital Dubai, UAE
 Fluids in Sepsis: How much and what type? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Kent Hospital, İzmir Eisenhower Medical Center, USA American Hospital Dubai, UAE In critically ill patients: too little fluid Low preload,
Fluids in Sepsis: How much and what type? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Kent Hospital, İzmir Eisenhower Medical Center, USA American Hospital Dubai, UAE In critically ill patients: too little fluid Low preload,
Crystalloid infusion rate during fluid resuscitation from acute haemorrhage
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 99 (2): 212 17 (2007) doi:10.1093/bja/aem165 Advance Access publication June 21, 2007 Crystalloid infusion rate during fluid resuscitation from acute haemorrhage T. Tatara*,
British Journal of Anaesthesia 99 (2): 212 17 (2007) doi:10.1093/bja/aem165 Advance Access publication June 21, 2007 Crystalloid infusion rate during fluid resuscitation from acute haemorrhage T. Tatara*,
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Management of intervention group patients SOP 001
 ` Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Management of intervention group patients SOP 001 Authors: Mark Edwards & Rupert Pearse Authorisation: Rupert Pearse (Chief Investigator) Scope To provide guidance
` Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Management of intervention group patients SOP 001 Authors: Mark Edwards & Rupert Pearse Authorisation: Rupert Pearse (Chief Investigator) Scope To provide guidance
Intraoperative Fluid Management. David G Hovord BA MB BChir FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor University of Michigan
 Intraoperative Fluid Management David G Hovord BA MB BChir FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor University of Michigan Objectives Examine impact of perioperative renal failure, and discuss structure and function
Intraoperative Fluid Management David G Hovord BA MB BChir FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor University of Michigan Objectives Examine impact of perioperative renal failure, and discuss structure and function
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy
 Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
FLUIDS AND SOLUTIONS IN THE CRITICALLY ILL. Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium
 FLUIDS AND SOLUTIONS IN THE CRITICALLY ILL Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium Why do we want to administer fluids? To correct hypovolemia? To increase
FLUIDS AND SOLUTIONS IN THE CRITICALLY ILL Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium Why do we want to administer fluids? To correct hypovolemia? To increase
Images have been removed from the PowerPoint slides in this handout due to copyright restrictions.
 Objectives Hemodynamic Complications and in the Post Surgical Patient Debra Whitney, RN, MSN Hennepin County Medical Center Describe factors that influence hemodynamic stability in the postsurgical patient.
Objectives Hemodynamic Complications and in the Post Surgical Patient Debra Whitney, RN, MSN Hennepin County Medical Center Describe factors that influence hemodynamic stability in the postsurgical patient.
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
L : Line and Tube อ นตรายป องก นได จากการให สารน า
 L : Line and Tube อ นตรายป องก นได จากการให สารน า รศ.นพ.กว ศ กด จ ตตว ฒนร ตน ภาคว ชาศ ลยศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม 3 rd Mini Conference: ความปลอดภ ยในผ ป วย ร วมด วย ช วยได ท กคน ว นท 13-14
L : Line and Tube อ นตรายป องก นได จากการให สารน า รศ.นพ.กว ศ กด จ ตตว ฒนร ตน ภาคว ชาศ ลยศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม 3 rd Mini Conference: ความปลอดภ ยในผ ป วย ร วมด วย ช วยได ท กคน ว นท 13-14
HYPOVOLEMIA AND HEMORRHAGE UPDATE ON VOLUME RESUSCITATION HEMORRHAGE AND HYPOVOLEMIA DISTRIBUTION OF BODY FLUIDS 11/7/2015
 UPDATE ON VOLUME RESUSCITATION HYPOVOLEMIA AND HEMORRHAGE HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OPERATES WITH A SMALL VOLUME AND A VERY EFFICIENT VOLUME RESPONSIVE PUMP. HOWEVER THIS PUMP FAILS QUICKLY WITH VOLUME
UPDATE ON VOLUME RESUSCITATION HYPOVOLEMIA AND HEMORRHAGE HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OPERATES WITH A SMALL VOLUME AND A VERY EFFICIENT VOLUME RESPONSIVE PUMP. HOWEVER THIS PUMP FAILS QUICKLY WITH VOLUME
Clinical Applications of The Pleth. Variability Index (PVI):
 Clinical Applications of The Pleth. Variability Index (PVI): A non invasive and continuous monitoring of fluid responsiveness J.PIRSON, MD 26 nov. 2011 Preoperative hypovolemia after an overnight fasting
Clinical Applications of The Pleth. Variability Index (PVI): A non invasive and continuous monitoring of fluid responsiveness J.PIRSON, MD 26 nov. 2011 Preoperative hypovolemia after an overnight fasting
Reducing Variation in Perioperative Fluid Utilization Results in Improved Surgical Outcomes
 Reducing Variation in Perioperative Fluid Utilization Results in Improved Surgical Outcomes A Quality Improvement and Cost Savings Initiative for Hospitals, Surgeons and Anesthesiologists Hypoperfusion
Reducing Variation in Perioperative Fluid Utilization Results in Improved Surgical Outcomes A Quality Improvement and Cost Savings Initiative for Hospitals, Surgeons and Anesthesiologists Hypoperfusion
ICU treatment of the trauma patient. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen
 ICU treatment of the trauma patient Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen Christian Kleber Surgical Intensive Care Unit - The trauma surgery Perspective Langenbecks
ICU treatment of the trauma patient Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen Christian Kleber Surgical Intensive Care Unit - The trauma surgery Perspective Langenbecks
JOURNAL CLUB: THE FLUIDS DEBATE. Veronica Ueckermann
 JOURNAL CLUB: THE FLUIDS DEBATE Veronica Ueckermann INTRODUCTION The selection and use of resuscitation fluids should be based on physiological principles. However, historically, clinical practice has
JOURNAL CLUB: THE FLUIDS DEBATE Veronica Ueckermann INTRODUCTION The selection and use of resuscitation fluids should be based on physiological principles. However, historically, clinical practice has
Edwards Critical Care Education. Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary
 Edwards Critical Care Education Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary Issue Date: November 2014 Evidence-based, Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy (PGDT) protocols Note: This protocol summary
Edwards Critical Care Education Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary Issue Date: November 2014 Evidence-based, Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy (PGDT) protocols Note: This protocol summary
INTRODUCTION. Dengue is one of the ten leading. Globally 20 million cases/yr. 24,000 deaths/yr. It is important to know the typical and atypical
 DENGUE IN CHILDREN INTRODUCTION Dengue is one of the ten leading causes of hospitalization and death in children. Globally 20 million cases/yr. 24,000 deaths/yr. It is important to know the typical and
DENGUE IN CHILDREN INTRODUCTION Dengue is one of the ten leading causes of hospitalization and death in children. Globally 20 million cases/yr. 24,000 deaths/yr. It is important to know the typical and
The Impact Of Intraoperative Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy
 University of New England DUNE: DigitalUNE Nurse Anesthesia Capstones School of Nurse Anesthesia 6-2017 The Impact Of Intraoperative Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Marc Yacovone University of New England
University of New England DUNE: DigitalUNE Nurse Anesthesia Capstones School of Nurse Anesthesia 6-2017 The Impact Of Intraoperative Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Marc Yacovone University of New England
The surgeon was not always the same, but all data was collected by one of the authors, J.N., which is now mentioned.
 Author's response to reviews Title: Minimal Shedding of the Glycocalyx Layer During Abdominal Hysterectomy. A Preliminary Report Authors: Robert G Hahn (r.hahn@telia.com) Janis Nemme (janis.nemme@gmail.com)
Author's response to reviews Title: Minimal Shedding of the Glycocalyx Layer During Abdominal Hysterectomy. A Preliminary Report Authors: Robert G Hahn (r.hahn@telia.com) Janis Nemme (janis.nemme@gmail.com)
Perioperative Fluid Management in ERPs
 Perioperative Fluid Management in ERPs Robert H. Thiele, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Virginia First Do No Harm Intravenous fluids should be considered a pharmacotherapeutic agent Just like all
Perioperative Fluid Management in ERPs Robert H. Thiele, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Virginia First Do No Harm Intravenous fluids should be considered a pharmacotherapeutic agent Just like all
SHOCK and the Trauma Victim. JP Pretorius Department of Surgery & SICU Steve Biko Academic Hospital.
 SHOCK and the Trauma Victim JP Pretorius Department of Surgery & SICU Steve Biko Academic Hospital. Classification of Shock Cardiogenic - Myopathic Arrythmic Mechanical Hypovolaemic - Haemorrhagic Non-haemorrhagic
SHOCK and the Trauma Victim JP Pretorius Department of Surgery & SICU Steve Biko Academic Hospital. Classification of Shock Cardiogenic - Myopathic Arrythmic Mechanical Hypovolaemic - Haemorrhagic Non-haemorrhagic
Edwards Critical Care Education. Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary
 Edwards Critical Care Education Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary Issue Date: March 2013 Evidence-based, Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy (PGDT) protocols Note: This protocol summary
Edwards Critical Care Education Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary Issue Date: March 2013 Evidence-based, Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy (PGDT) protocols Note: This protocol summary
Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018
 Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018 Objectives By the end of this session the learner will
Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018 Objectives By the end of this session the learner will
Anesthesiology in advanced radical surgery. Bruno Carrara Ospedali Riuniti di Bergamo
 Anesthesiology in advanced radical surgery Bruno Carrara Ospedali Riuniti di Bergamo Anesthetic considerations Anesthesiology in advanced radical surgery Anesthesiologists's task is to minimize the contribution
Anesthesiology in advanced radical surgery Bruno Carrara Ospedali Riuniti di Bergamo Anesthetic considerations Anesthesiology in advanced radical surgery Anesthesiologists's task is to minimize the contribution
Blood Management of the Cardiac Patient in the Postoperative Period
 Blood Management of the Cardiac Patient in the Postoperative Period Al Stammers, MSA, CCP, Eric Tesdahl, PhD Andy Stasko MS, CCP, RRT, Linda Mongero, BS, CCP, Sam Weinstein, MD, MBA Goal To examine the
Blood Management of the Cardiac Patient in the Postoperative Period Al Stammers, MSA, CCP, Eric Tesdahl, PhD Andy Stasko MS, CCP, RRT, Linda Mongero, BS, CCP, Sam Weinstein, MD, MBA Goal To examine the
MASSIVE TRANSFUSION DR.K.HITESH KUMAR FINAL YEAR PG DEPT. OF TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
 MASSIVE TRANSFUSION DR.K.HITESH KUMAR FINAL YEAR PG DEPT. OF TRANSFUSION MEDICINE CONTENTS Definition Indications Transfusion trigger Massive transfusion protocol Complications DEFINITION Massive transfusion:
MASSIVE TRANSFUSION DR.K.HITESH KUMAR FINAL YEAR PG DEPT. OF TRANSFUSION MEDICINE CONTENTS Definition Indications Transfusion trigger Massive transfusion protocol Complications DEFINITION Massive transfusion:
Context-sensitive fluid therapy in critical illness
 Tatara Journal of Intensive Care (2016) 4:20 DOI 10.1186/s40560-016-0150-7 REVIEW Context-sensitive fluid therapy in critical illness Tsuneo Tatara Open Access Abstract Microcirculatory alterations are
Tatara Journal of Intensive Care (2016) 4:20 DOI 10.1186/s40560-016-0150-7 REVIEW Context-sensitive fluid therapy in critical illness Tsuneo Tatara Open Access Abstract Microcirculatory alterations are
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Activated partial thromboplastin time abnormality, perioperative approach to, 104 105 Acute kidney injury, perioperative, 89 99 early
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Activated partial thromboplastin time abnormality, perioperative approach to, 104 105 Acute kidney injury, perioperative, 89 99 early
Edwards Critical Care Education. Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary
 Edwards Critical Care Education Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary Issue Date: March 2013 Evidence-based, Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy (PGDT) protocols Note: This protocol summary
Edwards Critical Care Education Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy Protocol Summary Issue Date: March 2013 Evidence-based, Perioperative Goal-Directed Therapy (PGDT) protocols Note: This protocol summary
How to Address an Inappropriately high Mortality Rate? Joe Sharma, MD Associate Professor of Surgery NSQIP Surgical Champion
 How to Address an Inappropriately high Mortality Rate? Joe Sharma, MD Associate Professor of Surgery NSQIP Surgical Champion Disclosure Slide No COI and no disclosures. Hospital Mortality rate : is it
How to Address an Inappropriately high Mortality Rate? Joe Sharma, MD Associate Professor of Surgery NSQIP Surgical Champion Disclosure Slide No COI and no disclosures. Hospital Mortality rate : is it
Initial Resuscitation of Sepsis & Septic Shock
 Initial Resuscitation of Sepsis & Septic Shock Dr. Fatema Ahmed MD (Critical Care Medicine) FCPS (Medicine) Associate professor Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital Is Sepsis a known
Initial Resuscitation of Sepsis & Septic Shock Dr. Fatema Ahmed MD (Critical Care Medicine) FCPS (Medicine) Associate professor Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital Is Sepsis a known
Transfusion & Mortality. Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD
 Transfusion & Mortality Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD Conflict of Interest Disclosure In the past 5 years, I have received honoraria or travel support for consulting or lecturing from the following companies:
Transfusion & Mortality Philippe Van der Linden MD, PhD Conflict of Interest Disclosure In the past 5 years, I have received honoraria or travel support for consulting or lecturing from the following companies:
HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT.
 HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT. Donna M. Sisak, CVT, LVT, VTS (Anesthesia/Analgesia) Seattle Veterinary Specialists Kirkland, WA dsisak@svsvet.com THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT
HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT. Donna M. Sisak, CVT, LVT, VTS (Anesthesia/Analgesia) Seattle Veterinary Specialists Kirkland, WA dsisak@svsvet.com THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Guideline for the perioperative fluid management in children Kieran O Connor Anaesthetics ATICS Date Uploaded: 26/04/2016 Review
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Guideline for the perioperative fluid management in children Kieran O Connor Anaesthetics ATICS Date Uploaded: 26/04/2016 Review
Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? Outline. Outline 29/04/2013
 Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? 18 th October 2012 Richard Seigne Anaesthetist 1 - Non fluid 40% T o t a l b o d y f l u i d 60% NaCl NaCl Intra-cellular fluid 2/3 KCl Interstitial fluid 3/4 of ECF
Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? 18 th October 2012 Richard Seigne Anaesthetist 1 - Non fluid 40% T o t a l b o d y f l u i d 60% NaCl NaCl Intra-cellular fluid 2/3 KCl Interstitial fluid 3/4 of ECF
Burn Resuscitation Formulas. John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX
 Burn Resuscitation Formulas John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX BURN INJURY % Physiologic Change % TBSA burn Stasis BURN VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
Burn Resuscitation Formulas John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX BURN INJURY % Physiologic Change % TBSA burn Stasis BURN VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
R2R: Severe sepsis/septic shock. Surat Tongyoo Critical care medicine Siriraj Hospital
 R2R: Severe sepsis/septic shock Surat Tongyoo Critical care medicine Siriraj Hospital Diagnostic criteria ACCP/SCCM consensus conference 1991 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference
R2R: Severe sepsis/septic shock Surat Tongyoo Critical care medicine Siriraj Hospital Diagnostic criteria ACCP/SCCM consensus conference 1991 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference
Perioperative Fluid Management
 Perioperative Fluid Management A. Scott Keller October 22, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Or 2016 MFMER slide-2 Mr. Anesthesiologist, please don t drown my patient! 2016 MFMER slide-3 Disclosures No relevant
Perioperative Fluid Management A. Scott Keller October 22, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Or 2016 MFMER slide-2 Mr. Anesthesiologist, please don t drown my patient! 2016 MFMER slide-3 Disclosures No relevant
Evidence-Based. Management of Severe Sepsis. What is the BP Target?
 Evidence-Based Management of Severe Sepsis Michael A. Gropper, MD, PhD Professor and Vice Chair of Anesthesia Director, Critical Care Medicine Chair, Quality Improvment University of California San Francisco
Evidence-Based Management of Severe Sepsis Michael A. Gropper, MD, PhD Professor and Vice Chair of Anesthesia Director, Critical Care Medicine Chair, Quality Improvment University of California San Francisco
Fluid balance in Critical Care
 Fluid balance in Critical Care By Dr HP Shum Nephrologist and Critical Care Physician Department of Intensive Care, PYNEH Fluid therapy is a critical aspect of initial acute resuscitation in critically
Fluid balance in Critical Care By Dr HP Shum Nephrologist and Critical Care Physician Department of Intensive Care, PYNEH Fluid therapy is a critical aspect of initial acute resuscitation in critically
Intra-operative Echocardiography: When to Go Back on Pump
 Intra-operative Echocardiography: When to Go Back on Pump GREGORIO G. ROGELIO, MD., F.P.C.C. OUTLINE A. Indications for Intraoperative Echocardiography B. Role of Intraoperative Echocardiography C. Criteria
Intra-operative Echocardiography: When to Go Back on Pump GREGORIO G. ROGELIO, MD., F.P.C.C. OUTLINE A. Indications for Intraoperative Echocardiography B. Role of Intraoperative Echocardiography C. Criteria
SHOCK Susanna Hilda Hutajulu, MD, PhD
 SHOCK Susanna Hilda Hutajulu, MD, PhD Div Hematology and Medical Oncology Department of Internal Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta Outline Definition Epidemiology Physiology Classes of Shock
SHOCK Susanna Hilda Hutajulu, MD, PhD Div Hematology and Medical Oncology Department of Internal Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta Outline Definition Epidemiology Physiology Classes of Shock
Dr. Nai Shun Tsoi Department of Paediatric and Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong SAR
 Dr. Nai Shun Tsoi Department of Paediatric and Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong SAR A very important aspect in paediatric intensive care and deserve more attention Basic principle is to
Dr. Nai Shun Tsoi Department of Paediatric and Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong SAR A very important aspect in paediatric intensive care and deserve more attention Basic principle is to
Problem Based Learning. Problem. Based Learning
 Problem 2013 Based Learning Problem Based Learning Your teacher presents you with a problem in anesthesia, our learning becomes active in the sense that you discover and work with content that you determine
Problem 2013 Based Learning Problem Based Learning Your teacher presents you with a problem in anesthesia, our learning becomes active in the sense that you discover and work with content that you determine
Cardiothoracic Fellow Expectations Division of Cardiac Anesthesia, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 The fellowship in Cardiothoracic Anesthesia at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is intended to provide the foundation for a career as either an academic cardiothoracic anesthesiologist or clinical
The fellowship in Cardiothoracic Anesthesia at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is intended to provide the foundation for a career as either an academic cardiothoracic anesthesiologist or clinical
Reverse (fluid) resuscitation Should we be doing it? NAHLA IRTIZA ISMAIL
 Reverse (fluid) resuscitation Should we be doing it? NAHLA IRTIZA ISMAIL 65 Male, 60 kg D1 in ICU Admitted from OT intubated Diagnosis : septic shock secondary to necrotising fasciitis of the R lower limb
Reverse (fluid) resuscitation Should we be doing it? NAHLA IRTIZA ISMAIL 65 Male, 60 kg D1 in ICU Admitted from OT intubated Diagnosis : septic shock secondary to necrotising fasciitis of the R lower limb
SHOCK AETIOLOGY OF SHOCK (1) Inadequate circulating blood volume ) Loss of Autonomic control of the vasculature (3) Impaired cardiac function
 SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK. Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital
 SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
Perioperative Management To Prevent Allogeneic Blood Transfusion In Liver Surgery
 AEJ Perioperative Management To Prevent Allogeneic Blood Transfusion In Liver Surgery Robbin Rabbani, CRNA, MS Michele E. Gold, CRNA, PhD Affiliations: This article was written by Robbin as student at
AEJ Perioperative Management To Prevent Allogeneic Blood Transfusion In Liver Surgery Robbin Rabbani, CRNA, MS Michele E. Gold, CRNA, PhD Affiliations: This article was written by Robbin as student at
Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS
 Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS OVERVIEW ER to ICU Transition Early Management Priorities the First 48 hours Organ System Support Complications THE FIRST 48 HOURS Communication Damage
Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS OVERVIEW ER to ICU Transition Early Management Priorities the First 48 hours Organ System Support Complications THE FIRST 48 HOURS Communication Damage
Intraoperative Fluid Administration Is Associated With Perioperative Outcomes in Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis
 2013;108:242 247 Intraoperative Fluid Administration Is Associated With Perioperative Outcomes in Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis OLIVER S. ENG, MD, JULIE GOSWAMI, MD, DIRK
2013;108:242 247 Intraoperative Fluid Administration Is Associated With Perioperative Outcomes in Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Single Center Retrospective Analysis OLIVER S. ENG, MD, JULIE GOSWAMI, MD, DIRK
Intraoperative Fluid Management and Blood Transfusion Essentials
 Intraoperative Fluid Management and Blood Transfusion Essentials Glenn P. Gravlee, M.D. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Denver and Health Sciences Center Body Fluid Distribution Perioperative
Intraoperative Fluid Management and Blood Transfusion Essentials Glenn P. Gravlee, M.D. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Denver and Health Sciences Center Body Fluid Distribution Perioperative
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetaminophen, for geriatric surgical patients, 569 570 Acute kidney injury, critical care issues in geriatric patients with, 555 556
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetaminophen, for geriatric surgical patients, 569 570 Acute kidney injury, critical care issues in geriatric patients with, 555 556
Hypotension after induction, corrected with 20 mg ephedrine x cc LR EBL 250cc Urine output:
 Terry C. Wicks, CRNA, MHS Catawba Valley Medical Center Hickory, North Carolina 63 y.o., 5 2, 88 kg female for hand assisted laparoscopic tranversecolectomy Co-morbidities include: Hypertension controlled
Terry C. Wicks, CRNA, MHS Catawba Valley Medical Center Hickory, North Carolina 63 y.o., 5 2, 88 kg female for hand assisted laparoscopic tranversecolectomy Co-morbidities include: Hypertension controlled
SLCOA National Guidelines
 SLCOA National Guidelines Peri - operative Fluid & Electrolyte Management SLCOA National Guidelines Contents List of Contributors 92 Paediatric fasting guidelines for elective procedures 93 Guidelines
SLCOA National Guidelines Peri - operative Fluid & Electrolyte Management SLCOA National Guidelines Contents List of Contributors 92 Paediatric fasting guidelines for elective procedures 93 Guidelines
Principles of Infusion Therapy: Fluids
 Principles of Infusion Therapy: Fluids Christie Heinzman, MSN, APRN-CNP Acute Care Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center May 22, 2018 Conflict of Interest Disclosure
Principles of Infusion Therapy: Fluids Christie Heinzman, MSN, APRN-CNP Acute Care Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center May 22, 2018 Conflict of Interest Disclosure
Intra-Operative IV Fluid Management: Goal Directed Therapy with Esophageal Doppler Monitoring vs. Standard Weight Based Fluid Therapy
 Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 2016 Intra-Operative
Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 2016 Intra-Operative
What would be the response of the sympathetic system to this patient s decrease in arterial pressure?
 CASE 51 A 62-year-old man undergoes surgery to correct a herniated disc in his spine. The patient is thought to have an uncomplicated surgery until he complains of extreme abdominal distention and pain
CASE 51 A 62-year-old man undergoes surgery to correct a herniated disc in his spine. The patient is thought to have an uncomplicated surgery until he complains of extreme abdominal distention and pain
Dr Alireza Yarahmadi and Dr Arvind Perathur Mercy Medical Center - Winter Retreat Des Moines February 2012
 Dr Alireza Yarahmadi and Dr Arvind Perathur Mercy Medical Center - Winter Retreat Des Moines February 2012 Why screen of OSA prior to surgery? What factors increase the risk? When due to anticipate problems?
Dr Alireza Yarahmadi and Dr Arvind Perathur Mercy Medical Center - Winter Retreat Des Moines February 2012 Why screen of OSA prior to surgery? What factors increase the risk? When due to anticipate problems?
TBSA Burn Estimation Chart Adult Major Burn Clinical Practice Guideline
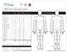 TBSA Burn Estimation Chart Adult Major Burn Clinical Practice Guideline Patient Label Anatomical Subunit Percent Total Percent One Side Anterior Posterior Injury Subtotal 3.5% 2nd and 3rd degree burns
TBSA Burn Estimation Chart Adult Major Burn Clinical Practice Guideline Patient Label Anatomical Subunit Percent Total Percent One Side Anterior Posterior Injury Subtotal 3.5% 2nd and 3rd degree burns
How can the PiCCO improve protocolized care?
 How can the PiCCO improve protocolized care? Azriel Perel Professor and Chairman Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel ESICM, Vienna 2009 Disclosure
How can the PiCCO improve protocolized care? Azriel Perel Professor and Chairman Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel ESICM, Vienna 2009 Disclosure
Resuscitation Before Emergency Surgeries FEIRAN LOU SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER KINGS COUNTY HOSPITAL
 Resuscitation Before Emergency Surgeries FEIRAN LOU SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER KINGS COUNTY HOSPITAL Case 73 yo woman h/o HTN three days abdominal pain and nausea. The pain was diffuse, cramp-like,
Resuscitation Before Emergency Surgeries FEIRAN LOU SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER KINGS COUNTY HOSPITAL Case 73 yo woman h/o HTN three days abdominal pain and nausea. The pain was diffuse, cramp-like,
Nothing to Disclose. Severe Pulmonary Hypertension
 Severe Ronald Pearl, MD, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University Rpearl@stanford.edu Nothing to Disclose 65 year old female Elective knee surgery NYHA Class 3 Aortic stenosis
Severe Ronald Pearl, MD, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University Rpearl@stanford.edu Nothing to Disclose 65 year old female Elective knee surgery NYHA Class 3 Aortic stenosis
Albumina nel paziente critico. Savona 18 aprile 2007
 Albumina nel paziente critico Savona 18 aprile 2007 What Is Unique About Critical Care RCTs patients eligibility is primarily defined by location of care in the ICU rather than by the presence of a specific
Albumina nel paziente critico Savona 18 aprile 2007 What Is Unique About Critical Care RCTs patients eligibility is primarily defined by location of care in the ICU rather than by the presence of a specific
KASHVET VETERINARIAN RESOURCES FLUID THERAPY AND SELECTION OF FLUIDS
 KASHVET VETERINARIAN RESOURCES FLUID THERAPY AND SELECTION OF FLUIDS INTRODUCTION Formulating a fluid therapy plan for the critical small animal patient requires careful determination of the current volume
KASHVET VETERINARIAN RESOURCES FLUID THERAPY AND SELECTION OF FLUIDS INTRODUCTION Formulating a fluid therapy plan for the critical small animal patient requires careful determination of the current volume
Peri-Operative Management: Guidelines for Inpatient Management of Children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Version 02 Approved by Interprofessional Patient Care Committee: September 16, 2016 1.0 Background Children with Sickle Cell are at risk of developing post-operative Acute Chest Syndrome. With improvements
Version 02 Approved by Interprofessional Patient Care Committee: September 16, 2016 1.0 Background Children with Sickle Cell are at risk of developing post-operative Acute Chest Syndrome. With improvements
Fluid resuscitation practices in cardiac surgery patients in the USA: a survey of health care providers
 Aronson et al. Perioperative Medicine (2017) 6:15 DOI 10.1186/s13741-017-0071-6 RESEARCH Fluid resuscitation practices in cardiac surgery patients in the USA: a survey of health care providers Solomon
Aronson et al. Perioperative Medicine (2017) 6:15 DOI 10.1186/s13741-017-0071-6 RESEARCH Fluid resuscitation practices in cardiac surgery patients in the USA: a survey of health care providers Solomon
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE CPD EVENING. Dr Alastair Morgan Wednesday 13 th September 2017
 INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE CPD EVENING Dr Alastair Morgan Wednesday 13 th September 2017 WHAT IS NEW IN ICU? (RELEVANT TO ANAESTHETISTS) Not much! SURVIVING SEPSIS How many deaths in England were thought
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE CPD EVENING Dr Alastair Morgan Wednesday 13 th September 2017 WHAT IS NEW IN ICU? (RELEVANT TO ANAESTHETISTS) Not much! SURVIVING SEPSIS How many deaths in England were thought
The cornerstone of treating patients with hypotension,
 Does the Central Venous Pressure Predict Fluid Responsiveness? An Updated Meta-Analysis and a Plea for Some Common Sense* Paul E. Marik, MD, FCCM 1 ; Rodrigo Cavallazzi, MD 2 Background: Aim: Data Sources:
Does the Central Venous Pressure Predict Fluid Responsiveness? An Updated Meta-Analysis and a Plea for Some Common Sense* Paul E. Marik, MD, FCCM 1 ; Rodrigo Cavallazzi, MD 2 Background: Aim: Data Sources:
Sepsis: Management ANUPOL PANITCHOTE, MD. Division of Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand
 Sepsis: Management ANUPOL PANITCHOTE, MD. Division of Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand Vital signs Symptoms LAB BT > 38.3 or < 36 ๐ C HR > 90 bpm RR > 20 /min
Sepsis: Management ANUPOL PANITCHOTE, MD. Division of Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand Vital signs Symptoms LAB BT > 38.3 or < 36 ๐ C HR > 90 bpm RR > 20 /min
Intra-operative colloid administration increases the clearance of a post-operative fluid load
 Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2009; 53: 311 317 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved r 2009 The Authors Journal compilation r 2009 The Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica Foundation ACTA ANAESTHESIOLOGICA
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2009; 53: 311 317 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved r 2009 The Authors Journal compilation r 2009 The Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica Foundation ACTA ANAESTHESIOLOGICA
Maria B. ALBUJA-CRUZ, MD ALBUMIN: OVERRATED. Surgical Grand Rounds
 Maria B. ALBUJA-CRUZ, MD ALBUMIN: OVERRATED Surgical Grand Rounds ALBUMIN Most abundant plasma protein 1/3 intravascular 50% of interstitial SKIN Synthesized in hepatocytes Transcapillary escape rate COP
Maria B. ALBUJA-CRUZ, MD ALBUMIN: OVERRATED Surgical Grand Rounds ALBUMIN Most abundant plasma protein 1/3 intravascular 50% of interstitial SKIN Synthesized in hepatocytes Transcapillary escape rate COP
AS - EXPERT
 AS - EXPERT 204-009-361 AS - EXPERT 204-009-362 AS - EXPERT 204-009-363 AS - EXPERT 204-009-364 AS - EXPERT 204-009-365 AS - EXPERT 204-009-366 AS - EXPERT 204-009-367 AS - EXPERT 204-009-368 AS - EXPERT
AS - EXPERT 204-009-361 AS - EXPERT 204-009-362 AS - EXPERT 204-009-363 AS - EXPERT 204-009-364 AS - EXPERT 204-009-365 AS - EXPERT 204-009-366 AS - EXPERT 204-009-367 AS - EXPERT 204-009-368 AS - EXPERT
Evaluation of Stroke Volume Variation Obtained by the FloTrac /Vigileo System to Guide Preoperative Fluid Therapy in Patients Undergoing Brain Surgery
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2012; 40: 1175 1181 [first published online as 40(3) 11] Evaluation of Stroke Volume Variation Obtained by the FloTrac /Vigileo System to Guide Preoperative
The Journal of International Medical Research 2012; 40: 1175 1181 [first published online as 40(3) 11] Evaluation of Stroke Volume Variation Obtained by the FloTrac /Vigileo System to Guide Preoperative
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type A Acute coronary syndrome, perioperative oxygen in, 599 600 Acute lung injury (ALI). See Lung injury and Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type A Acute coronary syndrome, perioperative oxygen in, 599 600 Acute lung injury (ALI). See Lung injury and Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
PREVENT COMPLICATIONS IN MAJOR SURGERY
 PREVENT COMPLICATIONS IN MAJOR SURGERY Dept of Anesthesia and ICM (Prof. G. Della Rocca) Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria University of Udine. Udine, Italy CLINICAL TRIAL OF SURVIVORS CARDIORESPIRATORY
PREVENT COMPLICATIONS IN MAJOR SURGERY Dept of Anesthesia and ICM (Prof. G. Della Rocca) Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria University of Udine. Udine, Italy CLINICAL TRIAL OF SURVIVORS CARDIORESPIRATORY
福島県立医科大学学術成果リポジトリ. Title laparoscopic adrenalectomy in patie pheochromocytoma. Midori; Iida, Hiroshi; Murakawa, Ma
 福島県立医科大学学術成果リポジトリ Examination of the usefulness of no Title variation monitoring for adjusting laparoscopic adrenalectomy in patie pheochromocytoma Isosu, Tsuyoshi; Obara, Shinju; Oha Author(s) Atsuyuki;
福島県立医科大学学術成果リポジトリ Examination of the usefulness of no Title variation monitoring for adjusting laparoscopic adrenalectomy in patie pheochromocytoma Isosu, Tsuyoshi; Obara, Shinju; Oha Author(s) Atsuyuki;
Management of Shock. Scott Provost, MD University of Utah
 Management of Shock Scott Provost, MD University of Utah Shock Serious, life-threatening medical condition where insufficient blood flow reaches the body tissues! Condition of severe impairment of tissue
Management of Shock Scott Provost, MD University of Utah Shock Serious, life-threatening medical condition where insufficient blood flow reaches the body tissues! Condition of severe impairment of tissue
Dengue Fever & Dengue Shock Syndrome. 07-May-18 PLES / SLCP 1
 Dengue Fever & Dengue Shock Syndrome 07-May-18 PLES / SLCP 1 Objectives Early diagnosis Pathophysiology of DHF Proper management How to avoid complications Case 07-May-18 PLES / SLCP 2 Febrile Phase High
Dengue Fever & Dengue Shock Syndrome 07-May-18 PLES / SLCP 1 Objectives Early diagnosis Pathophysiology of DHF Proper management How to avoid complications Case 07-May-18 PLES / SLCP 2 Febrile Phase High
EFFECT OF ALBUMIN ADMINISTRATION PRIOR TO GRAFT REPERFUSION ON THE SEVERITY OF REPERFUSION SYNDROME DURING LIVING RELATED LIVER TRANSPLANTATION
 46 EFFECT OF ALBUMIN ADMINISTRATION PRIOR TO GRAFT REPERFUSION ON THE SEVERITY OF REPERFUSION SYNDROME DURING LIVING RELATED LIVER TRANSPLANTATION Abdel Moniem M. Mohamed*, Ahmed R. Brakat*, Tarek A. Tawfeek**,
46 EFFECT OF ALBUMIN ADMINISTRATION PRIOR TO GRAFT REPERFUSION ON THE SEVERITY OF REPERFUSION SYNDROME DURING LIVING RELATED LIVER TRANSPLANTATION Abdel Moniem M. Mohamed*, Ahmed R. Brakat*, Tarek A. Tawfeek**,
Use of Blood Lactate Measurements in the Critical Care Setting
 Use of Blood Lactate Measurements in the Critical Care Setting John G Toffaletti, PhD Director of Blood Gas and Clinical Pediatric Labs Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center Chief, VAMC
Use of Blood Lactate Measurements in the Critical Care Setting John G Toffaletti, PhD Director of Blood Gas and Clinical Pediatric Labs Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center Chief, VAMC
Perioperative Pulmonary Management. Objectives
 Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consult Conference Perioperative Pulmonary Management Frank Jacono, MD May 5, 2017 Objectives Definition of post-operative pulmonary complications (PPC) Risk factors
Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consult Conference Perioperative Pulmonary Management Frank Jacono, MD May 5, 2017 Objectives Definition of post-operative pulmonary complications (PPC) Risk factors
Case Scenario 3: Shock and Sepsis
 Name: Molly Boyle 1. Define the term shock (Lewis textbook): Shock is a syndrome characterized by decreased perfusion and impaired metabolism. Shock can have a number of causes that result in damage to
Name: Molly Boyle 1. Define the term shock (Lewis textbook): Shock is a syndrome characterized by decreased perfusion and impaired metabolism. Shock can have a number of causes that result in damage to
Full Disclosure. The case for why it matters. Goal-directed Fluid Resuscitation
 Goal-directed Fluid Resuscitation Christopher G. Choukalas, MD, MS Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco I own no stocks Full Disclosure The case for why
Goal-directed Fluid Resuscitation Christopher G. Choukalas, MD, MS Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco I own no stocks Full Disclosure The case for why
Is the patient at risk for blood loss of 1000 mls? Avoid these Guidelines. Avoid these Guidelines. Yes. Yes. Yes. Yes. Yes
 Clinical Guidelines Acute rmovolemic Hemodilution Guidelines for Cardiac Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Date: 12-30-2012 Is the patient at risk for blood loss of 1000 mls?
Clinical Guidelines Acute rmovolemic Hemodilution Guidelines for Cardiac Surgery Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Date: 12-30-2012 Is the patient at risk for blood loss of 1000 mls?
Fluids and electrolytes: the basics
 Fluids and electrolytes: the basics This document is based on the handout from the Surgery for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical
Fluids and electrolytes: the basics This document is based on the handout from the Surgery for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical
FLUID THERAPY: IT S MORE THAN JUST LACTATED RINGERS
 FLUID THERAPY: IT S MORE THAN JUST LACTATED RINGERS Elisa M. Mazzaferro, MS, DVM, PhD, DACVECC Cornell University Veterinary Specialists, Stamford, CT, USA Total body water constitutes approximately 60%
FLUID THERAPY: IT S MORE THAN JUST LACTATED RINGERS Elisa M. Mazzaferro, MS, DVM, PhD, DACVECC Cornell University Veterinary Specialists, Stamford, CT, USA Total body water constitutes approximately 60%
25. Fluid Management and Renal Function During a Laparoscopic Case Done Under CO 2 Pneumoperitoneum
 25. Fluid Management and Renal Function During a Laparoscopic Case Done Under CO 2 Pneumoperitoneum Gamal Mostafa, M.D. Frederick L. Greene, M.D. Minimally invasive surgery aims to attenuate the stress
25. Fluid Management and Renal Function During a Laparoscopic Case Done Under CO 2 Pneumoperitoneum Gamal Mostafa, M.D. Frederick L. Greene, M.D. Minimally invasive surgery aims to attenuate the stress
Prediction of dilutional acidosis based on the revised classical dilution concept for bicarbonate
 J Appl Physiol 98: 62 71, 2005; doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00292.2004. Prediction of dilutional acidosis based on the revised classical dilution concept for bicarbonate Werner Lang and Rolf Zander Institut
J Appl Physiol 98: 62 71, 2005; doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00292.2004. Prediction of dilutional acidosis based on the revised classical dilution concept for bicarbonate Werner Lang and Rolf Zander Institut
