Cardiovascular Drugs
|
|
|
- Dorothy Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cardiovascular Drugs Calcium Channel blockers Phenylalkylamine Verapamil Binds to S5-S6 loop and S6 domain.?inactivation/selectivity interference Dihydropyridines Nifedipine i) S5-S6 loop and S6 of domain III; S5-S6 loop domain IV. Don t bind to type T channel Benzothiazepines Diltiazem Binds extracellularly, similar effect to phenylalkylamine; modulates dihydropyridine binding Antidysrhythmics Clonidine Na channel block Binds to open state of channel (only use dependent at high freq. not attainable in heart) Lignocaine Na channel block Binds to inactivatd channels associates and dissociates in duration of normal heart beat thus preventing premature beats. Also binds channels in partially depolarised cells (e.g ischaemia) thus preventing ventricular dysrhythmia after MI Propranolol et al B blockers (useful where increased excitability due to tissue damage) Verapamil Phenylalkylamine Ca channel block Diltiazem Benzothiazepine Ca channel block Congestive heart failure Digoxin, Digitoxin Cardiac glycoside Reduce effect of catecholamines negative inotropic and chronotropic effects. (note sensitisation of tissues to catecholamines after ischaemic damage can create ectopic foci) Inhibits Na/K ATPase thus ^ [Na] reducing gradient for NCX so [Ca] ^ and has + inotropic effect. Also stimulated Vagus via CNS slowing I f (hence its use for atrial dysrhythmia) Side effect = BIGEMINY due to I Na- Ca. Dobutamine B 1 agonist Positive inotropic effect > chronotropic effect. Used for congestive heart failure in absence of hypertension. (sympathomimetics will tend to increase oxygen demand of heart, heart rate (ppte/reveal dysrhythmia, as well as hypertension) Xamoterol Partial B 1 agonist Positive inotropic effect but antagonises excessive symp.
2 Amrinone Milrinone Caffeine, theophylline Bosentan Type III Phosphodiesterase Type III Phosphodiesterase Methylxanthines Endothelin ET A and ET B receptor stimulation. Antagonistic action can reduce symp. activity and thus can make the congestive heart failure worse! Short acting, acute cases, ^camp causing positive inotropic effect. Also causes dilatation of VSM reducing afterload Longer acting, may cause dysrhythmia. Same effects as above. Non selective phosphodiesterase and adenosine A 1 and A 2 s. = Positive inotropic and chronotropic effects. (but may give rise to dysrhythmia) Endothelin mediates contraction by such receptors on VSM cells (although mediates dilatation via ET B on endothelial cell) ACE s Reduce AT II Prevent sodium, thus water, reabsorption in kidney. Angina Pectoris Glyceryl trinitrate Nitrovasodilator Must be taken sublingually (poor stomach absorption) Yields NO which can act via cgmp to vasodilate (not arterioles as already fully dilated) venous vessels and collateral vessels (primarily in ischaemic areas Isosorbide dinitrate Dipyridamole Propranolol Nitrovasodilator Blocks adenosine transporter B adrenoceptor Metabolised in stomach to form isosorbide mononitrate. Same mechanism as above Acts to enhance adenosine action on A 2 receptors on VSM which elicit dilatation in all areas ie results in diverting blood from ischaemic areas coronary steal Reduces sympathetic effects on heart, thus reducing ABP (afterload). But can cause bronchoconstriction and cause vasoconstriction of coronary vessels ( 1 effect unmasked by blocking 2 ) Atenolol 1 Reduces sympathetic effects on heart and reduces afterload Alprenolol Partial B agonist Maintains sympathetic stimulation at low output, but blocks high sympathetic output (used in heart
3 Nifedipine VEGF Gene transfer Clot Lysis Dihydropyridine Ca channel block Angiogenesis failure where sympathetic required to maintain heart function) Reduces Ca entry into VSM cells vasodilatation and reduced afterload (preferentially acts on VSM than cardiac since binds to inactivated form of channel. VSM resting potential more depolarised) Adenoviral or plasmid vector for transient expression; idea to create new blood flow to ischaemic areas. Still in clinical trial stages Streptokinase Anistreplase Urokinase Alteplase; Duteplase Asprin Clopidogrel Aminocaproic acid; tranexamic acid Activates Activates Endogenous Human tissue s COX Anti coagulant Inhibits clot lysis Plasmin yielded from = protease degrading fibrin. In clots. Combination of and anisoylated streptokinase. Anisoyl group must be removed in blood (long t 1/2 ) more prolonged effect than above. Single chain scu-pa released from kidney and hydrolysed to two chain enzymatic tcu- PA form. Both given clinically Single and double chain; act preferentially on bound to fibrin in clots (localising action) Prophylaxis for thrombosis Inhibits binding of ATP to platelets. Shown that use with asprin improves morbidity and mortality Prevent excessive clot lysis which can lead to severe bleeding. Hypolipidaemic agents Lovastatin; Simvastatin HMG CoA Reductase Cholestyramine Bile acid reuptake Clofibrate Lipoprotein lipase Causes liver to increase expression of LDL receptors to scavenge cholesterol from blood for hepatic requirements Anion resin. Liver must uptake more cholesterol from blood to metabolise new bile acids Releases lipids from VLDL > LDL, and they are then stored in fat or metabolised in skeletal muscle
4 Nicotinic acid Fish oil Inhibits triglyceride production and VLDL secretion from liver; increases levels of tcu-pa Reduces hypertriglyceridaemia and increased unsaturated FA reduce thrombosis risk (via production of less effective thromboxane) Diuretics Frusemide; bumetanide; piretanide Probenecid Hydrochlorothiazide bendrofluazide xipamide Loop Thiazide Inhibit Na/K/2Cl cotransporter in thick ascending limb. Also mild inhibition of CA and a vasodilatory effect (piretanide shows vasodilatation at sub-diuretic levels). High ceiling diuretic (15-25%) BUT hypokalaemia, metabolic alkalosis, uric acid excretion decrease (gout) Ca and Mg loss ^ Competes for reabsorption with uric acid, thus reducing its reabsorption Inhibit Na/Cl cotransport in early distal tubule, have a mild y effect on CA, and a vasodilatory effect proceeding the diuresis (accompanied by ^ blood glucose level). BUT metabolic alkalosis, hypokalaemia (significant decrease may cause problems if given with cardiac glycosides for congestive heart failure potentiates effect) ^Mg excretion ^Ca reabsorption ^uric acid reabsorption Diazoxide Thiazide Non diuretic thiazide produces vasodilatory effect via opening K ATP. Hence ^ blood glucose levels. Triamterene Amiloride Spironolactone Acetazolamide K Sparing K Sparing K Sparing Carbonic anhydrase Block ENaC with mild diuresis but reduced K loss Can only Block ENaC from apical side - with mild diuresis but reduced K loss. Competes for aldosterones intracellular binding site, preventing its action. Spironolactone metabolised in liver to canrenone (both involved) Effect only significant when under influence of aldosterone, and due to involving gene expression, long rate of onset. Prevents reabsorption of NaHCO 3. in proximal and late distal tubule. Urine ph rises as consequence. BUT must block >99% enzyme to have appreciable effect. Only use now really is glaucoma Mannitol Osmotic Small molecule, filtered but not
5 diuretic reabsorbed. Retains its equivalent of water so increased urine volume with decreased Na reabsorption. Maintains urine flow so good when reduced GFR. Used acutely to reduce cerebral oedema. Renin Angiotensin system Captopril ACE Inhibitor Enalapril ACE Inhibitor Saralasin Partial AT 1 agonist Losartan AT 1 Blocks production of angiotensin II thus leading to a reduction in pre and afterload. Most benefit in congestive heart failure associated with raised renin levels. BUT in hypotensive state can lead to renal failure because no constriction of glomerular efferent arteriole usually mediated by angiotensin II. ALSO bradykinin metabolism dependent on ACE, so ACEi prevent breakdown, so accumulates, some in brain stem and irritates cough reflex area hence dry cough also since Bradykinin is potent vasodilator and induces natriuresis, may add effect. As above. However drug is inactive, must be metabolised in liver to enalaprilat Inhibits the action of angiotensin II, similar effects as above. BUT peptide so cannot be used via oral administration. Not used Non peptide so doesn t have the problem as above. Has similar effects to above Antihypertensive drugs Thiazides, loop, K + sparing, CA s, osmotic Captopril enalapril(at) Propranolol Atenolol Pindolol Phenoxybenzamine phentolamine Diuretics ACE Inhibitors B non slelctive B 1 specific Partial B agonist Non selective Act to reduce blood volume by inducing a natriuresis (thiazides/loop also cause a vasodilatation) Reduce angiotensin II, aldosterone; ^ Na excretion. Decreased bradykinin metabolism may have an effect. BUT dry cough. Often used in combination with a diuretic for ^ effect ^ TPR (B 2 ) decrease CO (B 1 ) so ABP~ over time ABP decreases. BUT bronchoconstriction and coronary constriction. Also depression and insomnia Decreased CO and rennin release. Fewer side effects No effect on rennin; reduced effect on CO. (note xamoterol has no hypertensive effect) Vasodilatation but with reflex tachycardia and ^ rennin release ( 2 block)
6 Prazosin 1 specific Labetolol Nifedipine L-type Ca channel block Minoxidil diazoxide (pinacidil, cromakalim, lemakalim) K channel openers Clonidine 2 /I 1 agonists Guanficine 2 /I 1 agonists Veno/vasodilatation, lack of reflex tachycardia (blockade CNS 1 reduces sympathetic discharge) First dose effect postural hypotension (probably due to venodilatation) Used in pregnancy because reduced transmission across placenta Cardiovascular effects and mild diuretic effect (? Reduce aldosterone release) also antagonise baroreceptor reflexes. Usually combined with blocker to combat reflex tachycardia (decrease TPR) Opens ATP dependent K channels (ATP closes) = hyperpolarisation and relaxation. Side effect minoxidil = hirtuism! Note often combined with blocker and diuretic to combat reflex tachycardia and any increase in blood volume Vasoconstriction topically, vasodilatation systemically; thought to be via imidazoline receptors. Rapid withdrawal may cause problems More potent 2 agonist so > topical vasoconstriction but not very potent antihypertensive (showing dilatation is not 2 mediated) Centrally acting antihypertensives with fewer side effects. Avoid rapid withdrawal Moxonidine I 1 agonists Rilmenidine -methyldopa 2 agonist Converted to -methynoradrenaline which is released as false transmitter. More potent on 2 receptors and acts as partial agonist at 1 receptors. Thus reducing central sympathetic release. Used in pregnancy. Guanethidine Reserpine Hexamethionium trimetaphan Sodium nitroprusside Hydralazine Inhibits uptake into vesicles Ganglion block Depletes NA stores and reduces release. BUT postural hypotension Initial hypertension but consequent depletion of vesicle store BUT severe depression First used. Block all ganglion transmission so many side effects. Hexamethonium used for malignant hypertension. Vasodilator Metabolised to NO used IV in hypertensive emergencies. BUT in solution yields CN so must be stored as powder. Vasodilator Arteriolar vasodilatation.
7
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Cardiovascular drugs
 chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics
 sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
Antihypertensives. Diagnostic category
 Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Congestive Heart Failure - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@vcu.edu Heart failure:
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Congestive Heart Failure - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@vcu.edu Heart failure:
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
PRINCIPLES OF DIURETIC ACTIONS:
 DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS. The Basics of cardiac pharmacology 2007
 WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED. Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics
 Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Therapeutics of Diuretics
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
Drugs Used in Heart Failure. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Antihypertensive Agents
 1. Blood Pressure Regulation Antihypertensive Agents - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@hsc.vcu.edu Frank's formula,
1. Blood Pressure Regulation Antihypertensive Agents - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@hsc.vcu.edu Frank's formula,
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Antihypertensive Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017
 Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension? A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension? A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Diuretics (Saluretics)
 Diuretics (Saluretics) Diuretics increase urine excretion mainly by reabsorption of salts and water from kidney tubules These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at
Diuretics (Saluretics) Diuretics increase urine excretion mainly by reabsorption of salts and water from kidney tubules These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at
Dr. Vishaal Bhat. anti-adrenergic drugs
 Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Chapter / Section / Drug
 2 Cardiovascular System 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs Digoxin Digoxin specific antibody ( DigiFab ) 2.2 Diuretics 2.2.1 Thiazides and related diuretics Indapamide (1 st Line) Bendroflumethiazide Metolazone
2 Cardiovascular System 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs Digoxin Digoxin specific antibody ( DigiFab ) 2.2 Diuretics 2.2.1 Thiazides and related diuretics Indapamide (1 st Line) Bendroflumethiazide Metolazone
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
Antihypertensive Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014
 Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension: A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension: A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D.
 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth
Leading Causes of Death in the U.S. Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Blood flow at rest and exercise
 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Leading Causes of Death in the U.S Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Leading Causes of Death in the U.S Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
 ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
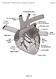 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
b. Describe the pharmacology of centrally acting agents such as clonidine and α methyldopa.
 B. 13 Antihypertensive drugs a. Classify the modes of action of the antihypertensive drugs. central sympathetic tone inhibitors α 2 agonists β antagonists peripheral sympathetic antagonists α blockers
B. 13 Antihypertensive drugs a. Classify the modes of action of the antihypertensive drugs. central sympathetic tone inhibitors α 2 agonists β antagonists peripheral sympathetic antagonists α blockers
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
Angina Pectoris. Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room
 Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS. Lecture 5
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
β adrenergic blockade, a renal perspective Prof S O McLigeyo
 β adrenergic blockade, a renal perspective Prof S O McLigeyo Carvedilol Third generation β blocker (both β 1 and β 2 ) Possesses α 1 adrenergic blocking properties. β: α blocking ratio 7:1 to 3:1 Antioxidant
β adrenergic blockade, a renal perspective Prof S O McLigeyo Carvedilol Third generation β blocker (both β 1 and β 2 ) Possesses α 1 adrenergic blocking properties. β: α blocking ratio 7:1 to 3:1 Antioxidant
Renal physiology II. Basic renal processes. Dr Alida Koorts BMS
 Renal physiology II Basic renal processes Dr Alida Koorts BMS 7-12 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Basic renal processes 1. filtration 2. reabsorption 3. secretion Glomerular filtration The filtration
Renal physiology II Basic renal processes Dr Alida Koorts BMS 7-12 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Basic renal processes 1. filtration 2. reabsorption 3. secretion Glomerular filtration The filtration
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Hypertension: pathophysiology and treatment
 Hypertension: pathophysiology and treatment P Foëx DPhil FRCA FMedSci JW Sear PhD FRCA Arterial hypertension is a major cause of morbidity and mortality because of its association with coronary heart disease,
Hypertension: pathophysiology and treatment P Foëx DPhil FRCA FMedSci JW Sear PhD FRCA Arterial hypertension is a major cause of morbidity and mortality because of its association with coronary heart disease,
Low Efficacy Diuretics. Potassium sparing diuretics. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Osmotic diuretics. Miscellaneous
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
Introduction. Factors affecting blood pressure: 1-COP = HR X SV mainly affect SBP. 2-TPR = diameter of arterioles X viscosity of blood affect DBP
 Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
CONGESTIVE CARDIAC FAILURE. Dr.T.Rajathilagam, M.D., S.R.M. Medical College
 CONGESTIVE CARDIAC FAILURE Dr.T.Rajathilagam, M.D., S.R.M. Medical College HEART FUNCTIONS Your heart is an amazing powerhouse that pumps and circulates 5 or 6 gallons of blood each minute through your
CONGESTIVE CARDIAC FAILURE Dr.T.Rajathilagam, M.D., S.R.M. Medical College HEART FUNCTIONS Your heart is an amazing powerhouse that pumps and circulates 5 or 6 gallons of blood each minute through your
Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy
 Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Overview Mechanism of cardiovascular drugs Indications and clinical use in cardiology Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin
Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Overview Mechanism of cardiovascular drugs Indications and clinical use in cardiology Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin
Water Reabsorption and the Effect of Diuretics on Urine Formation Patricia J. Clark, Ph.D. Department of Biology, IUPUI
 Water Reabsorption and the Effect of Diuretics on Urine Formation Patricia J. Clark, Ph.D. Department of Biology, IUPUI This activity may be done in conjunction with a more traditional urinalysis lab.
Water Reabsorption and the Effect of Diuretics on Urine Formation Patricia J. Clark, Ph.D. Department of Biology, IUPUI This activity may be done in conjunction with a more traditional urinalysis lab.
New classification of HT Systolic Diastolic Normal <120 <80 Prehypertension Stage1HT Stage 2 HT >160 or >100
 Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
Drugs act on Cardiovascular system (Heart Failure)
 Drugs act on Cardiovascular system (Heart Failure) Dr Laith M Abbas Al-Huseini M.B.Ch.B, M.Sc., M.Res., Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics efinition and Pathophysiology Heart failure (HF)
Drugs act on Cardiovascular system (Heart Failure) Dr Laith M Abbas Al-Huseini M.B.Ch.B, M.Sc., M.Res., Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics efinition and Pathophysiology Heart failure (HF)
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
 Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Goals of Acute Heart Failure Therapy Alleviate
Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Goals of Acute Heart Failure Therapy Alleviate
Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure (CHF) Inotropics and Other Agents. Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D.
 Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure (CHF) Inotropics and Other Agents Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure (CHF) Inotropics and Other Agents Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Heart Failure Treatments
 Heart Failure Treatments Past & Present www.philippelefevre.com Background Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Sudden
Heart Failure Treatments Past & Present www.philippelefevre.com Background Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Sudden
Hypertension: an overview of recommended treatment John Vann Jones PhD, FRCP
 Drug review Hypertension Hypertension: an overview of recommended treatment John Vann Jones PhD, FRCP Skyline Imaging Ltd Professor Vann Jones provides an overview of the wide range of antihypertensive
Drug review Hypertension Hypertension: an overview of recommended treatment John Vann Jones PhD, FRCP Skyline Imaging Ltd Professor Vann Jones provides an overview of the wide range of antihypertensive
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
DIURETICS. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 DIURETICS Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Classification of Diuretics The best way to classify diuretics is to look for their Site of action in the nephron A. Diuretics that inhibit transport in the Proximal
DIURETICS Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Classification of Diuretics The best way to classify diuretics is to look for their Site of action in the nephron A. Diuretics that inhibit transport in the Proximal
Therapeutic Uses of Diuretics
 DIURETICS Diuretics are drugs that promote the output of urine excreted by the Kidneys. The primary action of most diuretics is the direct inhibition of a + transport at one or more of the four major anatomical
DIURETICS Diuretics are drugs that promote the output of urine excreted by the Kidneys. The primary action of most diuretics is the direct inhibition of a + transport at one or more of the four major anatomical
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Treatment of T Angina reatment of By Ali Alalawi
 Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
5mg/5mL Liquid 25mg Tablets 50mg Tablets 100mg Tablets 50mg/5mL Suspension Special standardise strength 25mg Tablets
 Chapter 2- Cardiovascular Category Drug name Strength / dose / form BCU 2.1 Positive Inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac Digoxin 62.5 microgram Tablets Glycosides 125 microgram Tablets 250 microgram Tablets
Chapter 2- Cardiovascular Category Drug name Strength / dose / form BCU 2.1 Positive Inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac Digoxin 62.5 microgram Tablets Glycosides 125 microgram Tablets 250 microgram Tablets
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Table 1. Diuretics. Drugs Mechanisms of Action Indications Adverse Drug Effects. Table 2. Electrolyte Modifiers.
 Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2017 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2017 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Drug Therapy of Heart Failure. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014
 Drug Therapy of Heart Failure Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Drug Therapy of Heart Failure Definition of Heart Failure Causes Classifications
Drug Therapy of Heart Failure Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Drug Therapy of Heart Failure Definition of Heart Failure Causes Classifications
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Prof. Ramzy H. El Mawardy. Cairo Egypt 2009
 Prof. Ramzy H. El Mawardy Ain Shams University Cairo Egypt 2009 Burden of HRN is increasing worldwide = 7 billion individuals. BP control is still poor = 60.70%. Global risk assessment is essential in
Prof. Ramzy H. El Mawardy Ain Shams University Cairo Egypt 2009 Burden of HRN is increasing worldwide = 7 billion individuals. BP control is still poor = 60.70%. Global risk assessment is essential in
Composition: Each Tablet contains. Pharmacokinetic properties:
 Composition: Each Tablet contains Torsemide 5/10/20/40/100mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Torsemide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak serum concentrations are achieved within 1 hour
Composition: Each Tablet contains Torsemide 5/10/20/40/100mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Torsemide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak serum concentrations are achieved within 1 hour
Drug treatment for primary hypertension
 7 Drug treatment for primary hypertension PRACTICAL PRESCRIBING IN HYPERTENSION 7.1 Which drugs should be used first-line? 70 7.2 What is an appropriate interval before assessing the response to therapy?
7 Drug treatment for primary hypertension PRACTICAL PRESCRIBING IN HYPERTENSION 7.1 Which drugs should be used first-line? 70 7.2 What is an appropriate interval before assessing the response to therapy?
Dysrhythmias. Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics. EKG Parameters. Dysrhythmias. Components of an ECG Wave. Dysrhythmias
 Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Chapter 20. Drugs Affecting Circulation: Antihypertensives, Antianginals, Antithrombotics
 Chapter 20 Drugs Affecting Circulation: Antihypertensives, Antianginals, Antithrombotics Epidemiology and Etiology of Hypertension Primary: Unknown etiology Secondary: Due to known disease process Adversely
Chapter 20 Drugs Affecting Circulation: Antihypertensives, Antianginals, Antithrombotics Epidemiology and Etiology of Hypertension Primary: Unknown etiology Secondary: Due to known disease process Adversely
Pharmacology. Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs)
 Lecture 7 (year3) Dr Noor Al-Hasani Pharmacology University of Baghdad College of dentistry Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs) Atherosclerotic disease of the coronary arteries,
Lecture 7 (year3) Dr Noor Al-Hasani Pharmacology University of Baghdad College of dentistry Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs) Atherosclerotic disease of the coronary arteries,
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter 15 Diuretic Agents
 Chapter 15 Diuretic Agents Diuretics Diuretics are agents that increase the rate of urine formation and salt excretion. Diuresis = increased water formation, but the term is also used to indicate increased
Chapter 15 Diuretic Agents Diuretics Diuretics are agents that increase the rate of urine formation and salt excretion. Diuresis = increased water formation, but the term is also used to indicate increased
