Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Table 1.
|
|
|
- Victoria Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Table. In vivo echocardiographic assessment of cardiac size and function following transaortic constriction (T) at 7d and 8d. SHM 7d N=6 T 7d N=5 SHM 8d N= T 8d N=6 W, g.± ±.8.6± ±.5 HR, bpm 57±7 5±5 55±7 59±5 IVSd, mm.7±.9.±.7*.67±.5.9±.* LVIDd, mm.67±.6.59±..55±.5.±.5* LVIDs, mm.±..9±..7±.7.9±.8* LVFS 6.9± ±6.78.±5..6±9.9* TSPG, mmhg N/ 8.±5.5 N/ 86.±6.5 HR, heart rate; LVIDd, LV internal dimension at end-diastole; LVIDs, LV internal dimension at end-systole; TSPG, trans-stenotic systolic pressure gradient as the difference between right carotid and left axillary artery systolic pressures. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. *P <.5 by Student s t-test before and after T within the same group.
2 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure LV/W (mg/g) 6 5 p<. p<. 7d T 8d T T T Trichrome staining 7d 8d anp fold change p=. p<. p=. ßmhc fold change 8 6 p=.9 p=.9 p=. 5 5 cola fold change p=. p=.6 p=. p<. cola fold change p<. p=.9 αmhc fold change p=. p=.9 p=.5 7d T 8 d T Supplemental Figure. Transaortic constriction (T) model. () Left ventricle (LV) weight over body weight (W). Data was analyzed by Student s t-test (n=6-8 per group). () Representative trichrome staining of left ventricular wall. () qrt-pr analysis of genes associated with hypertrophy/fibrosis. Data was analyzed by unpaired Student s t-test. Scale bars represent µm.
3 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure % cells in perivascular fibrotic lesion 7d T 6 5 olagfp+;fsp- olagfp+;fsp+ FSP+;olaGFP-;- FSP+;+ +;FSP- DPI FSP DPI FSP D % cells in perivacsular fibrotic lesion 7d T 6 5 olagfp+;αsm+ olagfp+;αsm- αsm+;olgfp-;- αsm+;+ +;αsm- E DPI αsm F % cells in interstitial fibrotic lesion 8d T 5 olagfp+;αsm+ olagfp+;αsm- αsm+;olgfp-;- αsm+;+ +;αsm- Supplemental Figure. Quantification of cell types in fibrotic areas. () Percentages of cells expressing, FSP and in perivascular fibrotic areas. () onfocal image showing FSP+ fibroblasts (arrows) and an FSP+ leukocyte (arrowhead) in a perivascular area. () onfocal image showing FSP labels immune cells (+) and not perivascular fibroblasts in operated mice. (D) Percentages of cells expressing, αsm and in perivascular fibrotic areas. (E) onfocal image showing lack of αsm + fibroblasts in a perivascular area. No ollagenagfp+ cells were +. (F) Percentages of cells expressing, αsm and in interstitial lesions following 8d T. ells were counted in fields each from mice. Histograms represent mean±s.d. Scale bars are µm., coronary artery.
4 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure trl 7d T % % % % 8d T % % PDGFRα.7% 9.5%.5% 5.%.%.% 7d T 8d T vimentin DPI ollagena -GFP merge Fold change compared with endothelium Fold change compared with endothelium 5 5 ddr prolyl--hydroxylase d T 7d T Supplemental Figure. Expression of fibroblast markers by + cells () Representative flow cytometry analysis showing that collagena-gfp+ cells are PDGFRa+ in operated animals and following 7d and 8d T. ll plots/images are representative of at least 5 animals per group. () Represesentative images of vimentin staining in operated animals and following 7d and 8d T. Scale bars represent µm. () qrt-pr data showing expression level of DDR and Prolyl--hydroxylase in + cells versus + endothelial cells sorted from (n=) and 7d T (n=) hearts.
5 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure dult (5w) WT-cre;Rosa-tdT DPI image of atria and RV * * * * Left atrium Right Ventricle E8.5 Tbx8-cre;Rosa-tdT DPI b b b b IVS E8.5 Tbx8-cre;Rosa-tdT DPI c c c LVFW c Supplemental Figure. Distribution of fibroblasts derived from epicardium. () onfocal images of adult Wt-cre lineage traced atria and right ventricle. Fibroblasts were lineage-traced (arrows). (*) Epicardial surface. () onfocal images of E8.5 Tbx8-cre lineage-traced hearts. s seen with Wt-cre, many fibrblasts were ot labelled in the interventricular septum (IVS) (arrows). () vast majority of fibroblasts were labelled in left ventricular free wall (LVFW) of Tbx8-cre lineage-traced hearts (arrows).scale bars represent 5µm.
6 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure 5 LVFW IVS DPI VEcadherine-creERT;Rosa-tdT Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT D RV DPI Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT RV DPI Wt-cre;Rosa-tdT E 7d T DPI Tie Supplemental Figure 5. Lack of EndoMT following pressure overload. () Perivascular fibrosis in Tiecre+/-;ollagenaGFP+/;RosaTdt+/- hearts. Following 7d T, as observed for intersitital fibroblasts, perivascular fibroblasts in left ventricular free wall (LVFW) were Tiecre-RosatdT- whereas perivascular fibroblasts in interventricular septum (IVS) were Tiecre-RosatdT+. Similar results were observed at 8d T. Scale bars represent 5mm. () Perivascular fibrosis in VE-cadherin lineage traced heart following 7d T. + coronary endothelial cells were labelled, but not perivascular fibroblasts. Scale bar mm. () Right ventricle (7d T) from Tie-cre lineage traced heart. (D) Equivalent area to inset in () in RV of Wt-creERT lineage traced heart. Similar results were observed at 8d T. Scale bars represent 5µm. (E) ells expressing Tie protein (arrows) were not + fibroblasts in hearts and following 7d T. Similar results were observed at 8d T. Scale bars represent µm.
7 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure 6 Tie-cre SHM F Singlets Rosa-tdT Singlets Rosa-tdT 86.%.%.8%.8% 6.% 9.% 89.6%.%.8% Tie-cre 8d T 9.6%.8% 5.%.%.5%.9%.% D E Singlets SHM Rosa-tdT.6% 7.% 7.5% 5.6%.9% IVS Tie-cre 7d T.%.%.% Tie-cre;Wt-cre 8d T 9.6% of GFP+ Rosa-tdT Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT DPI Edu LVFW d T 6.% of GFP+ DPI leaved-caspase- Supplemental Figure 6. Similar responses of Tie-re and non Tie-re derived fibroblasts to pressure overload () Flow cytometry plot of dissociated left ventricle (LV) + interventricular septum (IVS) from a sham operated Tiecre+/-;collagena-GFP+/-;Rosa-tdT+/- mouse. Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT+, Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT++ and Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT+- populations have been gated and plotted against and expression. oth + populations are negative for and, except a small subset of collagena-gfp+;+ endocardial cells. Tie-cre;Rosa-tdT+;collagena-GFP- cells consist of + endothelial cells and + leukocytes. This is also the case following 7d () and 8d () T. (D) Representative flow cytometry plots showing percentages of labelled (Rosa-tdT+) and non-labelled (Rosa-tdT-) Fs in double Tie- cre;wt-cre lineage traced LV + IVS (representative of mice). (E) Representative images of IVS and LVFW (left ventricular free wall) of sham operated and T operated Tie-cre+/-;collagena-GFP+/-;Rosa-tdT+/- mice d after surgery (PG 76.7±8. mmhg, n=). Hearts were recovered h after EdU injection. Rare EdU+ cells (arrowheads) were never fibroblasts in hearts. Equivalent fibrotic areas that contained EdU+ fibroblasts (arrows) were found in IVS and LVFW. Scale bars are µm. (F) poptotic leaved-caspase + cells were very rare following T and - (see inset). The reporter is cytoplasmic and nuclear, enabling clear identification of fibroblast nuclei (see nucleus to right of aspase + cell inset). Scale bars are µm except insets (5µm). Image taken from 7d post surgery, similar results were observed following d and 8d T.
8 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure 7. Vav-cre;Rosa-tdT+ gate LV+ IVS Singlets - Vav-cre;Rosa-tdT+ gate 7d T 8d T - - Supplemental Figure 7. Vav-cre labelling following pressure overload. () Representative flow cytometry plots showing Vav-cre;Rosa-tdT+ and signals from cell suspensions from LVFW+IVS. >9% of + leukocytes were labelled in Vav-cre lineage traced mice, with almost no labelling outside of this cellular compartment. () Vav-cre lineage traced cells consist invariably of + leukocytes in and following 7d or 8dT, with small sub-populations of + endothelial cell. Each plot is representative of at least mice.
9 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure 8 ge (weeks): nalysis nalysis SHM/T surgery Tamoxifen inductions (5 consecutive days) Recombination efficiency in endothelium Rosa-tdT Singlets 5.7% - 8.8% Supplemental Figure 8. Inductions in VE-cadherin-reERT lineage traced mice () Time line for tamoxifen induction and T procedure on VE-cadherin-reERT+/-;collagena-GFP+/-;Rosa- Tdt+/- mice. () Representative flow cytometry plot showing the percentage of + endothelium labeled in left ventricle (LV) + interventicular septum (IVS) by VEcadherin-creERT following inductions.
10 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure 9 ge (weeks): nalysis /T surgery Tamoxifen inductions ( consecutive days) d T Tbx8-reERT-RosatdT DPI PDGFRα D6 Supplemental Figure 9 Epicardium does not give rise to fibroblasts following pressure overload. () Time course for tamoxifen inductions and /T surgery for Tbx8-reERT+/-;Rosa-tdT+/- mice. () onfocal images showing recombination in epicardium (asterisks) and D6+ mural cells (arrowheads) but not in PDGFRα+ fibroblasts (arrows) of operated mice and following d pressure overload (PG 8±.5 mmhg, n=). Scale bars represent µm.
11 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure Embryonic DPI αsm PDGFRα dult DPI αsm DPI E5.5 Nfatc-cre;Rosa-tdT L PDGFRα PDGFRα DPI LVFW D E5.5 Nfatc-cre;Rosa-tdT DPI IVS Supplemental Figure. Lack of PDGFRα staining in vascular smooth muscle/epicardium and confocal images of E5.5 IVS of Nfatc-cre+/-;+/-;Rosa-tdT+/- embyronic heart. () Embryonic E7.5 left ventricular wall. Epicardium is indicated by arrows. () dult smooth muscle (5 weeks old male) is PDGFRα, wherease epicardial cells (arrows) express PDGFRα. () LVFW displaying extensive labelling of + vessels (arrows). (D) s with Tie-re and VE-cadherin-creERT, Nfatc-cre lineage traced fibroblasts were abundant in IVS (arrows). L, left atrium. Scale bars in and represent µm, Scale bars in and D represent 5µm.
12 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure VE-cadherin-creERT;Rosa-tdT E7.5>E5.5 DPI VE-cadherin-creERT;Rosa-tdT E9.5>E5.5 DPI VE-cadherin-reERT;Rosa-tdT E7.5>E9.5 D VE-cadherin-reERT;Rosa-tdT E7.5>E.5 E OFT R E E RV E VEcadherin Wt DPI VEcadherin Wt Supplemental Figure. Fate of VE-cadherin-reERT lineage traced endocardium. () Tamoxifen induction at E7.5 in VE-cadherin-creERT embryos resulted in labelling of + fibroblasts in the valves and septum (&), and labelling of a small number of fibroblasts in the ventricular wall by E5.5 (, arrows). () Tamoxifen induction at E9.5 resulted in no labelling of fibroblasts, despite a similar degree of labelling of endothelium. () Tamoxifen induction in E7.5 embryos resulted in Rosa-tdT+/- lineage labeling of VE-cadherin immunolabeled endothelial/endocardial cells but not Wt immunolabeled proepicardial cells at E9.5. (D) Inductions at E7.5 and harvesting at E.5 resulted in labeling of atrioventriclar canal cushion (e ) and VE-cadherin+ endocardial/endothelial cells, but not Wt+ epicardial cells (e ). Scale bars are µm except chamber views in () and () that represent µm. OFT= Outflow tract, R= Right atrium.
13 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Figure Fold difference - qrt-pr. postn wisp pdgfrα ddr cola. Fold difference - microarray R =.8 cdh5 (VEcad) pecam cola luster GO Term Gene number Permute P value T EFFET extracellular matrix part(go:) <. FIROLSTS proteinaceous extracellular 7 <. (luster ) matrix(go:5578) metallopeptidase activity(go:87) <. negative regulation of cell death(go:658) 9 <. positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation (GO:86) <. FIROLST SPEIFI (luster ) ENDOTHELIL ELL SPEIFI (luster ) T EFFET FIROLSTS ND ENDOTHELIL ELLS (luster ) extracellular matrix(go:) <. regulation of cartilage 7 <. development(go:65) pattern binding(go:87) 65 <. extracellular matrix part(go:) 65 <. extracellular matrix organization(go:98) 5 <. adherens junction(go:59) 6.5 regulation of small GTPase mediated signal 6.85 transduction(go:556) cell-cell adherens junction(go:59). cadherin binding(go:596).5 regulation of angiogenesis(go:5765).55 cell cycle(go:79) 7 <. cell cycle process(go:) 6 <. cell division(go:5) 9 <. chromosome, centromeric region(go:775) 5 <. chromosome(go:569) 79 <. Supplemental Figure. Genes differentially regulated following pressure overload. () Plot showing correlation between q-rt- PR and microarray fold differences between genes from clusters (T effect on fibroblasts), (fibroblast specific genes) and (endothelial specific genes) of Figure 9. Genes from cluster are cola (D/) and wisp (/). Genes from cluster are cola (/E), ddr (/E), pdgfrα (D/F) and postn (D/). Genes from cluster are cdh5 (VEcadherin) (F/) and pecam (E/) (, TiecreRosatdT+ fibroblasts ;, TiecreRosatdT- fibroblasts ;, TiecreRosatdT+ fibroblasts T; D, TiecreRosatdT- fibroblasts T; E, endothelial cells ; F, endothelial cells T). () Most significant GO-Terms associated with the main gene clusters. () Gene network diagram including genes specifically upregulated in both fibroblast populations following T.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W. Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W
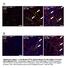 A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles (n = 5). (C) Plasma norepinephrine
 Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and
 Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and Edn1-knockout (Edn1-KO) (c, d) hearts. The boxed areas
Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and Edn1-knockout (Edn1-KO) (c, d) hearts. The boxed areas
Cardiac fibroblasts: more than mechanical support
 Review Article Cardiac fibroblasts: more than mechanical support Stefanie A. Doppler 1, Catarina Carvalho 1, Harald Lahm 1, Marcus-André Deutsch 1,2, Martina Dreßen 1, Nazan Puluca 1, Rüdiger Lange 1,2,
Review Article Cardiac fibroblasts: more than mechanical support Stefanie A. Doppler 1, Catarina Carvalho 1, Harald Lahm 1, Marcus-André Deutsch 1,2, Martina Dreßen 1, Nazan Puluca 1, Rüdiger Lange 1,2,
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
E10.5 E18.5 P2 10w 83w NF1 HF1. Sham ISO. Bmi1. H3K9me3. Lung weight (g)
 Myociyte cross-sectional Relative mrna levels Relative levels Relative mrna levels Supplementary Figures and Legends a 8 6 4 2 Ezh2 E1.5 E18.5 P2 1w 83w b Ezh2 p16 amhc b-actin P2 43w kd 37 86 16 wt mouse
Myociyte cross-sectional Relative mrna levels Relative levels Relative mrna levels Supplementary Figures and Legends a 8 6 4 2 Ezh2 E1.5 E18.5 P2 1w 83w b Ezh2 p16 amhc b-actin P2 43w kd 37 86 16 wt mouse
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography Control (n=4)
 Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
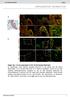 Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Supplemental Information. Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier. to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell
 Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
(a-r) Whole mount X-gal staining on a developmental time-course of hearts from
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Supplementary Figure 1 (a-r) Whole mount X-gal staining on a developmental time-course of hearts from Sema3d +/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ and Sema3d -/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ embryos.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Supplementary Figure 1 (a-r) Whole mount X-gal staining on a developmental time-course of hearts from Sema3d +/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ and Sema3d -/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ embryos.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
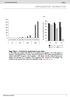 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Heart Development. Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
Control. csarnt -/- Cre, f/f
 ody weight (g) A re,f/f re x f/f f/+ re, f/+ re,f/+ f/f x f/f f/+ cs -/- re, f/f re f/f re, f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen Tamoxifen Tamoxifen W 4W re f/f re, re/ff f/f re f/f re, re/ff f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen
ody weight (g) A re,f/f re x f/f f/+ re, f/+ re,f/+ f/f x f/f f/+ cs -/- re, f/f re f/f re, f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen Tamoxifen Tamoxifen W 4W re f/f re, re/ff f/f re f/f re, re/ff f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Title: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying maternal diabetes-associated risk of congenital heart disease
 1 Supplemental Materials 2 3 Title: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying maternal diabetes-associated risk of congenital heart disease 4 5 6 Authors: Madhumita Basu, 1 Jun-Yi Zhu, 2 Stephanie LaHaye 1,3, Uddalak
1 Supplemental Materials 2 3 Title: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying maternal diabetes-associated risk of congenital heart disease 4 5 6 Authors: Madhumita Basu, 1 Jun-Yi Zhu, 2 Stephanie LaHaye 1,3, Uddalak
Review. Endocardial and Epicardial Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions in Heart Development and Disease
 Review Endocardial and Epicardial Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions in Heart Development and Disease Alexander von Gise, William T. Pu Abstract: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) converts
Review Endocardial and Epicardial Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions in Heart Development and Disease Alexander von Gise, William T. Pu Abstract: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) converts
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Heart Development. Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells. Robert G. Kelly
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly Animal models of heart development
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly Animal models of heart development
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
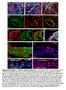 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Supporting Information. Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell. Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
 Supporting Information Table of contents Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell differentiation and cardioprotection (page 2) Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
Supporting Information Table of contents Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell differentiation and cardioprotection (page 2) Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental methods Pericardium In several studies, it has been shown that the pericardium significantly modulates ventricular interaction. 1-4 Since ventricular interaction has
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental methods Pericardium In several studies, it has been shown that the pericardium significantly modulates ventricular interaction. 1-4 Since ventricular interaction has
Supplementary information. The proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptor T-cell death-associated gene 8
 1 Supplementary information 2 3 The proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptor T-cell death-associated gene 8 4 (TDAG8) shows cardioprotective effects against myocardial infarction 5 Akiomi Nagasaka 1+,
1 Supplementary information 2 3 The proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptor T-cell death-associated gene 8 4 (TDAG8) shows cardioprotective effects against myocardial infarction 5 Akiomi Nagasaka 1+,
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Supplementary Information. Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania. through collective production of nitric oxide
 Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Prospect Cardiac Packages. S-Sharp
 Prospect Cardiac Packages S-Sharp B mode: Teichholz: Teichholz formula LV Volume 2D: modified Simpson's rule method ALM: area length method LV Volume (Intg.): integral method M mode: Long axis: Teichholz
Prospect Cardiac Packages S-Sharp B mode: Teichholz: Teichholz formula LV Volume 2D: modified Simpson's rule method ALM: area length method LV Volume (Intg.): integral method M mode: Long axis: Teichholz
5 Working With Measurements
 5 Working With Measurements Measurement Overview Measurements accompanying ultrasound images supplement other clinical procedures available to the attending physician. Accuracy of the measurements is determined
5 Working With Measurements Measurement Overview Measurements accompanying ultrasound images supplement other clinical procedures available to the attending physician. Accuracy of the measurements is determined
Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
doi: /nature14508 Rappsilber et al.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1458 Grosso et al. Barbosa et al. 74 72 45 33 47 7 51 Rappsilber et al. Supplementary Figure 1 a, Venn-Diagram of identified splice factors in the work of Barbossa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1458 Grosso et al. Barbosa et al. 74 72 45 33 47 7 51 Rappsilber et al. Supplementary Figure 1 a, Venn-Diagram of identified splice factors in the work of Barbossa
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk TAC is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2.
 3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
B-Mode measurements protocols:
 Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class IV
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Supplemental Information. Tissue-Resident Macrophages in Pancreatic. Ductal Adenocarcinoma Originate from Embryonic
 Immunity, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Tissue-Resident Macrophages in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Originate from Embryonic Hematopoiesis and Promote Tumor Progression Yu Zhu, John M. Herndon,
Immunity, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Tissue-Resident Macrophages in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Originate from Embryonic Hematopoiesis and Promote Tumor Progression Yu Zhu, John M. Herndon,
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
Fog2 is critical for cardiac function and maintenance of coronary vasculature in the adult mouse heart
 Research article Fog2 is critical for cardiac function and maintenance of coronary vasculature in the adult mouse heart Bin Zhou, 1,2 Qing Ma, 1 Sek Won Kong, 1 Yongwu Hu, 1,3 Patrick H. Campbell, 4 Francis
Research article Fog2 is critical for cardiac function and maintenance of coronary vasculature in the adult mouse heart Bin Zhou, 1,2 Qing Ma, 1 Sek Won Kong, 1 Yongwu Hu, 1,3 Patrick H. Campbell, 4 Francis
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x
 Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
Alternatively Activated Macrophages Determine the Repair of the Infarcted
 Alternatively Activated Macrophages Determine the Repair of the Infarcted Adult Murine Heart (Shiraishi et al.) List of Supplemental Materials Supplemental Methods Supplemental Figure 1. Cardiac CD206
Alternatively Activated Macrophages Determine the Repair of the Infarcted Adult Murine Heart (Shiraishi et al.) List of Supplemental Materials Supplemental Methods Supplemental Figure 1. Cardiac CD206
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
SCPA602 Cardiovascular System
 SCPA602 Cardiovascular System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Cardiovascular System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin, Kazumi Fukatsu, and Paul Grossfeld
 Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function 52 Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin,
Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function 52 Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin,
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Imaging Guide Echocardiography
 Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Echocardiography using the Vevo Imaging Systems System Compatibility: This guide contains instructions and suggestions for work on the Vevo2100, VevoLAZR, Vevo 3100
Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Echocardiography using the Vevo Imaging Systems System Compatibility: This guide contains instructions and suggestions for work on the Vevo2100, VevoLAZR, Vevo 3100
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Lect.6 Electrical axis and cardiac vector Cardiac vector: net result Vector that occurs during depolarization of the ventricles Figure:
 Lect.6 Electrical axis and cardiac vector Objectives: 1. State the relationship between the direction of cardiac vector with the direction (-ve, +ve) and amplitude of an ECG waves. 2. Draw diagram indicting
Lect.6 Electrical axis and cardiac vector Objectives: 1. State the relationship between the direction of cardiac vector with the direction (-ve, +ve) and amplitude of an ECG waves. 2. Draw diagram indicting
Morphogenesis of the right ventricle requires myocardial expression of Gata4
 Research article Morphogenesis of the right ventricle requires myocardial expression of Gata4 Elisabeth M. Zeisberg, 1,2 Qing Ma, 3 Amy L. Juraszek, 3,4 Kelvin Moses, 5 Robert J. Schwartz, 5 Seigo Izumo,
Research article Morphogenesis of the right ventricle requires myocardial expression of Gata4 Elisabeth M. Zeisberg, 1,2 Qing Ma, 3 Amy L. Juraszek, 3,4 Kelvin Moses, 5 Robert J. Schwartz, 5 Seigo Izumo,
Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements. Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc.
 Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc. dfuchs@visualsonics.com Instructions This document is a guideline on how to assess cardiac function in rodents imaged
Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc. dfuchs@visualsonics.com Instructions This document is a guideline on how to assess cardiac function in rodents imaged
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
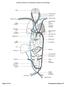 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Declaration of conflict of interest
 Declaration of conflict of interest There is no any potential conflict of interest. There is not any financial commitments or funds from private companies. Roles of heat shock transcription factor 1 gene
Declaration of conflict of interest There is no any potential conflict of interest. There is not any financial commitments or funds from private companies. Roles of heat shock transcription factor 1 gene
Extending the time window of mammalian heart regeneration by thymosin beta 4
 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 18, No 12, 2014 pp. 2417-2424 Extending the time window of mammalian heart regeneration by thymosin beta 4 Liu Rui #, Nie Yu #, Lian Hong, He Feng, Han Chunyong, Meng Jian, Zheng
J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 18, No 12, 2014 pp. 2417-2424 Extending the time window of mammalian heart regeneration by thymosin beta 4 Liu Rui #, Nie Yu #, Lian Hong, He Feng, Han Chunyong, Meng Jian, Zheng
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Hemodynamic Forces Sculpt Developing Heart Valves through a KLF2-WNT9B Paracrine Signaling Axis
 Hemodynamic Forces Sculpt Developing Heart Valves through a KLF2-WNT9B Paracrine Signaling Axis Article Graphical Abstract Endocardial cell (EC) WNT9B WNT9B Wildtype Endocardial Klf2 KO Mesenchymal cell
Hemodynamic Forces Sculpt Developing Heart Valves through a KLF2-WNT9B Paracrine Signaling Axis Article Graphical Abstract Endocardial cell (EC) WNT9B WNT9B Wildtype Endocardial Klf2 KO Mesenchymal cell
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Specimen. Humeral Head. Femoral Head. Objective. Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1
 A B Specimen Humeral Head 2 1 µm 76 µm Femoral Head Objective Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1 A Femoral Head Global Cell Density Superficial Cell Density Cell Number at 1 µm Nuclei /.1
A B Specimen Humeral Head 2 1 µm 76 µm Femoral Head Objective Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1 A Femoral Head Global Cell Density Superficial Cell Density Cell Number at 1 µm Nuclei /.1
