Test # 2 Review. Nervous System, Energy System, Cardio-respiratory System
|
|
|
- Junior Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test # 2 Review Nervous System, Energy System, Cardio-respiratory System
2 #1 & #2 Proper treatment of Soft Tissue injuries S.H.A.R.P P.I.E.R. Principle Swelling: instantly or over time Heat: increased temperature in the area Altered: tissue will not function properly Red: in colour Pressure: tensor wrap Ice: placed on affected area Elevate: to reduce swelling Restrict: tensors, slings, or crutches Painful: to touch or move
3 #1 Protocol to determine if ligament or tendon injured Pain through an active range of motion usually indicates tendon, whereas pain during passive range of motion Can be confirmed by active range of motion test to rule out tendon
4 he Components of the Nervous System #3 Major components of Nervous system Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Central Nervous System nial Nerves Spinal Nerves Brain Spinal Cord Forebrain Hindbrain Midbrain
5 #4-6 main part of the Central Nervous System The central nervous system (CNS) is divided into two parts: The vertebral column and the spinal cord: Main pathway for information connecting the brain and peripheral nervous system The brain: Main control centre Receives and interprets endless signals Has six main parts: Cerebrum Cerebellum Brain stem Diencephalon Limbic system Reticular activating system
6 #5 - The Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Consists of those parts of the nervous system that lie outside the CNS Carries information in and out of the CNS Includes: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves Contains both autonomic and somatic components
7 #6 - The Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system (ANS): Comprised of two systems: Sympathetic system: Causes localized bodily adjustments to occur Prepares body for emergencies (i.e. releases adrenaline, increases heart rate) Parasympathetic system: Returns body to normal (after it s been altered by the sympathetic system) Systems work in unison
8 # 7 - Somatic Nervous System Somatic nervous system: Handles the muscles in our extremities Contains both afferent and efferent nerve fibres: Afferent nerves: Send information to the CNS Efferent nerves: Send instructions to skeletal muscle PNS receives and processes information
9 #7 - Autonomic and Somatic Nervous Systems
10 #8 - The Reflex Arc (5 parts) t Reflex arc: v Pathway in which the initial stimulus and the corresponding response message travel Five parts to a reflex arc: Receptor Sensory (or afferent) nerve Intermediate nerve fibre Motor (or efferent) nerve Effector organ
11 #9 - Golgi Tendon Organs & Muscle Spindles Golgi Tendon Organs Muscle Spindles Location Position Respond to Sensory neurons Where tendon meets muscle fibre In series with muscle fibre Changes in muscle/ tendon tension 1 2 In belly of muscle fibre Parallel to muscle fibre Changes in muscle length
12 #10 - The Knee-Jerk Reflex (The Patella Reflex) monosynaptic 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 12
13 #10 Proprioception System and stretch reflex.. The Stretch Reflex! Stretch reflex: " Simplest spinal reflex " Depends on the single connection between primary afferent fibres and motor neurons of same muscle " Sequence of nerve impulses and motions (e.g. tapping patella ligament): Receptor muscle senses action of hammer against patella ligament through the muscle spindle s sensory neuron Message transmitted along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord Afferent neuron synapses with the efferent pathway of same muscle Impulse transmitted along efferent pathways to muscle Motor units contract brings about knee-jerk action
14 #11 - The Crossed-Extensor Reflex & Withdrawl reflex : A More Complex Reflex Action (Polysynaptic) 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 60
15 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 3 #12 - What Are the three key Energy Nutrients The food we take in contains three key energy nutrients that are broken down over the course of digestion: Carbohydrates Protein Fats Of these three key nutrients, carbohydrates are our most important source of energy.
16 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. #13 ATP- The Common Energy Molecule To be usable, nutrients in the food we eat need to be reconstituted (or resynthesized) into a universal form of energy a free energy that can then be used for muscle contraction and many other physiological processes. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) The final form this free energy takes is adenosine triphosphate, ATP the common energy molecule for all living things. ATP captures the chemical energy resulting from the breakdown of food and is then used to fuel the various cellular processes in our bodies. 16
17 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. #14 - Approximate Energy Sources for Different Types of Sport Activities 17
18 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. #15a - The Release of Energy from ATP Energy is released when a trailing phosphate atom is broken from the ATP molecule. This results in ADP (adenosine diphosphate plus energy), as in the formula below: ATP > ADP + P + Energy 18
19 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 15 b - Two Energy Systems The anaerobic system occurs without the requirement of oxygen. It can occur in two separate metabolic pathways, one not involving the breakdown of glucose and the other involving the partial breakdown of glucose. The aerobic system, a separate but to some extent overlapping energy system, requires oxygen. It involves many enzymes and several complex sub-pathways, and it leads to the complete breakdown of glucose. (Fats and protein also enter the cycle at this stage.) 10
20 # 16 - Three Metabolic Pathways There are two energy systems (anaerobic and aerobic), but there are three metabolic pathways by which ATP energy reserves are restored. They are: ATP-PC (anaerobic alactic) sprint Glycolysis (anaerobic lactic) 400 meters Cellular respiration marathon In the presence of oxygen, the second pathway (glycolysis) is also the beginning of the third pathway (the aerobic system). 20
21 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. #17 & #18 The Chemical Equation for the ATP-PC Pathway Phosphocreatine (PC) is a high-energy molecule in which the phosphate can be broken off easily and which can be used to convert ADP (adenosine diphosphate) back to ATP. The chemical equation that represents this process is as follows: 21
22 #19, 20 & 21 22
23 #19 b - Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Macronutrients are the human body s direct sources of energy: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Macronutrients supply us with the energy we need for daily life and for physical exercise. Carbohydrates 4 Calories per gram (kilocalories) Protein 4 Calories per gram (kilocalories) Fat 9 Calories per gram (kilocalories) 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 2 3
24 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. #20 b - Muscle Fibre Types and Physical Activity Slow-twitch muscle fibres These are ideal for activities such as longdistance swimming, cycling, and running. Fast-twitch muscle fibres These can activate at a rate two to three times faster than slow-twitch muscles, making them ideal for the fast, powerful muscle contractions needed for activities such as short sprints, powerlifting, and explosive jumping. 24
25 #21 25
26 #22 - % Muscle fibre - Implications for Training For elite athletes, differences in muscle fibre types are often very pronounced. Olympic sprinters, for example, may possess as much as percent fast-twitch muscle fibres. Athletes in marathon-style events may possess that equivalent in slow-twitch fibres. But many factors contribute to an individualʼ s athletic performance. Physiology is just one of them. 26
27 Composed of: Heart Blood vessels Blood #23 - The Cardiovascular System Functions: Delivery of O 2, fuel, and nutrients to the tissues of the body Removal of CO 2 and waste products from the tissues Maintenance of a constant body temperature (thermoregulation) Prevention of infection (immune function)
28 #24 - Tracking the Flow of Blood 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 10
29 #24 & #25 The Flow of Blood through the Heart Blood is delivered to the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve and enters the right ventricle. From there, the blood is pumped through the pulmonary semilunar valve and out through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. The blood returns from the lungs through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium. It then passes through the bicuspid valve and enters into the left ventricle. The blood is then pumped out through the aortic semilunar valve into the aorta and throughout the systemic circulation Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 2 9
30 #26 - Properties of Blood Two main components: Plasma Fluid component of blood (mostly water) Blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) Made in bone marrow Transport O 2 and CO 2 in the blood Transport nutrients and waste Contain hemoglobin White blood cells (leukocytes) Destroy foreign elements Critical in the function of the immune system Platelets Regulate blood clotting Plasma 55% 90% water 7% plasma proteins 3% other (acids, salts) Formed elements 45% >99% red blood cells <1% white blood cells and platelets
31 #27 & #28 CARDIAC TERMS Heart rate (HR) duration of each cardiac cycle Stroke volume(sv) volume of blood ejected by ventricles Cardiac output (Q) HR Î SV = Q Frank-Starling Law: Ability of the heart to stretch and increase the force of contraction LUB-DUB HEART SOUNDS : The lub is the first heart sound, commonly termed S1, and is caused by turbulence caused by the closure of mitral and tricuspid valves at the start of systole. The second sound, dub or S2, is caused by the closure of aortic and pulmonic valves, marking the end of systole.
32 #29 & #30 Excitation of the Heart Sinoatrial node (SA node): Specialized region of tissue found in wall of right atrium Location where electrical signals are initiated ( pacemaker ) Atrioventricular node (AV node): Passes electrical signal from atria into ventricles Passes electrical signal to the bundle of His (atrioventricular bundle) Bundle of His pass electrical signal to the Purkinje fibres Purkinje fibres pass electrical signal to the myocardium
33 #31 - The Electrical Activity of the Heart Measured using an electrocardiogram (ECG) Graphical representation of electrical sequence of events occurring with each contraction of the heart Each wave generated during contraction is named: P wave: represents depolarization through the atria QRS complex: represents depolarization of the ventricle T wave: represents repolarization of the ventricle
34 # Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 34
35 #33 & # 34 The 6 Causes of Coronary Artery Disease (Atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction) Besides a 1. poor diet, other risk factors associated with coronary artery disease include: 2. smoking, 3. elevated blood lipids, 4. hypertension, 5. family history, and 6. physical inactivity. Each factor individually increases the risk of development of coronary artery disease. When the factors are combined, the risk of coronary artery disease is magnified Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 30
36 #35 - The Respiratory System Composed of structures that allow: Passage of air from outside the body to the lungs Gas exchange to occur Three main functions: Supply O 2 to the blood Remove CO 2 from the blood Regulate blood ph (acid-base balance) istockphoto.com/ Eraxion Divided into two zones: Conductive zone Respiratory zone
37 #36 Different respiration systems (external, internal and cellular) The respiratory system supplies O2 to the blood, removes CO2 from the blood, and regulates blood ph (acid-base balance). All aspects of breathing are closely associated with the overall need of O2, metabolic processes, and muscle activity. External respiration occurs within the lungs and involves the exchange of O2 and CO2. Internal respiration refers to the exchange of gases at the tissue level. Cellular respiration is the process in which the cells use oxygen to generate energy cells use O2 to generate energy Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 37
38 #37 - The Conductive and Respiratory Zones 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 38
39 Expiration # Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 39
40 # 39 - Diffusion The primary factor that mediates gas exchange both at the lung (where blood becomes oxygenated and CO2 is removed) and at the tissue (where O2 is delivered for metabolism and CO2 is removed) is diffusion. Diffusion is the movement of a gas, liquid, or solid from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through random movement. Diffusion can only occur if a difference in concentration exists, and such a difference is called a concentration gradient Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 40
41 #40 - Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation When lactate levels begin to accumulate rapidly in the blood, this is referred to as the onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA). With training, the curve for lactate threshold and OBLA can shift to the right Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 41
42 #41 - Oxygen Deficit and EPOC
43 #42 - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Describes a family of diseases that lead to a reduction in airflow through the respiratory system Often fatal in severe cases Persistent conditions cannot be relieved (quickly or effectively) through the use of medications Individuals experience dyspnea while performing everyday activities Treatment includes: Medication Oxygen therapy Respiratory muscle training
44 # 43 - Training at High Altitude Proponents claim that when such athletes travel to competitions at lower altitudes they will still have a higher concentration of red blood cells for days, and this gives them a competitive advantage. Some athletes live permanently at high altitude, only returning to sea level to compete, but their training may suffer due to less available oxygen for workouts.
45 Final thoughts Final Thoughts 1.Know the multiple choice questions 2.Good Luck on your Exam J
2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 3. What Are Nutrients?
 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 3 What Are Nutrients? Nutrients are chemical substances obtained from food and used by the body for many different processes. They are the raw materials our bodies
2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 3 What Are Nutrients? Nutrients are chemical substances obtained from food and used by the body for many different processes. They are the raw materials our bodies
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION
 Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION (a) The Reflex Arc ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (b) Proprioception and Proprioceptors 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 What Are Reflexes? Reflexes
Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION (a) The Reflex Arc ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (b) Proprioception and Proprioceptors 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 What Are Reflexes? Reflexes
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Exercise Science Section 7: The Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems
 Exercise Science Section 7: The Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 The Cardiovascular System Composed
Exercise Science Section 7: The Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 The Cardiovascular System Composed
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
NZQA Expiring unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 5. Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy
 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the nervous system and its functions;
Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the nervous system and its functions;
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms
 Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Cardiovascular system progress chart
 Neural muscular system Topic 3A: Characteristics and functions of different muscle fibre types for a variety of sporting activities Term Muscle fibre Slow twitch (type I) Fast oxidative glycolytic (type
Neural muscular system Topic 3A: Characteristics and functions of different muscle fibre types for a variety of sporting activities Term Muscle fibre Slow twitch (type I) Fast oxidative glycolytic (type
1. Know the knee joints anatomical structures
 Final Exam Review 1. Know the knee joints anatomical structures 2. Types of bones and examples! Long " Found in arms and legs! Short " Found in wrists and ankles! Flat " Bones of the skull! Irregular "
Final Exam Review 1. Know the knee joints anatomical structures 2. Types of bones and examples! Long " Found in arms and legs! Short " Found in wrists and ankles! Flat " Bones of the skull! Irregular "
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
(C) Muscles provide structural support, are involved in thermoregulation, but have no effect on organ function.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 13: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 (A) Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable bone,
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 13: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 (A) Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable bone,
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
1. Know the knee joints anatomical structures
 Final Exam Review 1. Know the knee joints anatomical structures 2. Types of bones and examples! Long " Found in arms and legs! Short " Found in wrists and ankles! Flat " Bones of the skull! Irregular "
Final Exam Review 1. Know the knee joints anatomical structures 2. Types of bones and examples! Long " Found in arms and legs! Short " Found in wrists and ankles! Flat " Bones of the skull! Irregular "
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S
 The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
THE STRUCTURE OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1
 THE STRUCTURE OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 250-350g Left of the midline Size of a closed fist Two sides are separated by the septum The pericardium is the
THE STRUCTURE OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 250-350g Left of the midline Size of a closed fist Two sides are separated by the septum The pericardium is the
Chapter 9, Part 2. Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise
 Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Approximately the size of your fist Location. Pericardial physiology
 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Heart. Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat
 Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Chapter 1: Exercise Physiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 1: Exercise Physiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Physiology is the study of the myriad functions in a living organism. Exercise physiology is the study of the ways
Chapter 1: Exercise Physiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Physiology is the study of the myriad functions in a living organism. Exercise physiology is the study of the ways
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 18: The Muscular System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 18: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 A. Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 18: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 A. Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms?
 Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Using Figure 14.1, match the following: 1) Myelin sheath. 1) 2) Cell body of ANS preganglionic neuron. 2)
 Practice Exam 1 AP 2 chapters 14 and 18 Name MATCHING: Match labeled areas with the appropriate terminology from the list below. Figure 14.1 Using Figure 14.1, match the following: 1) Myelin sheath. 1)
Practice Exam 1 AP 2 chapters 14 and 18 Name MATCHING: Match labeled areas with the appropriate terminology from the list below. Figure 14.1 Using Figure 14.1, match the following: 1) Myelin sheath. 1)
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
basic information on the following: mitosis, meiosis, DNA, protein synthesis
 Anatomy and Physiology Review Final Exam Introductory Concepts homeostasis and negative feedback body cavities directional terminology basic information on the following: mitosis, meiosis, DNA, protein
Anatomy and Physiology Review Final Exam Introductory Concepts homeostasis and negative feedback body cavities directional terminology basic information on the following: mitosis, meiosis, DNA, protein
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Conditioning 101. How To Most Effectively Program for Conditioning
 Conditioning 101 How To Most Effectively Program for Conditioning Which Athlete Has a Higher Level of Conditioning? Floyd Mayweather Aaron Rodgers What Is Conditioning? Conditioning is a measure of how
Conditioning 101 How To Most Effectively Program for Conditioning Which Athlete Has a Higher Level of Conditioning? Floyd Mayweather Aaron Rodgers What Is Conditioning? Conditioning is a measure of how
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
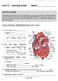 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton. Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node.
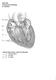 BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
IP: Regulation of Cardiac Output
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
