Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Doppler analysis
|
|
|
- Job Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
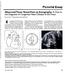
1 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 18: Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Blackwell ORIGINAL Science, PAPERLtd Doppler analysis S.-J. YOO*, J.-Y. MIN and Y.-H. LEE *Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada and Department of Radiology, Samsung Cheil Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea KEYWORDS: Doppler, Fetal echocardiography, Pericardial fluid ABSTRACT Objectives To estimate the incidence of sonographic identification of pericardial fluid in normal fetuses and to evaluate the flow pattern of pericardial fluid by using color and spectral Doppler techniques. Methods We evaluated 27 normal fetuses for the presence of pericardial fluid by using gray-scale two-dimensional and M-mode ultrasound, and color and spectral Doppler techniques. Results Pericardial fluid was detected in 52% of cases by twodimensional and M-mode ultrasound and in 81% of cases by color Doppler. The pericardial fluid moved towards the ventricles during systole and towards the atria during diastole. In 9 of 22 fetuses with pericardial fluid identified by color Doppler, spectral waveforms were obtained. The waveforms confirmed the bidirectional flow pattern identified at color Doppler. In six cases there was monophasic systolic and biphasic diastolic flow. In the remaining three cases, the flow was monophasic during both systole and diastole. Conclusions Pericardial fluid can be identified with color Doppler in the majority of normal fetuses. It characteristically shows bidirectional flow as it moves with ventricular systole and diastole. Spectral waveforms can be obtained from the pericardial fluid. The presence of pericardial fluid per se should not be considered as abnormal. Color-coded pericardial fluid should not be mistaken for coronary artery blood flow. INTRODUCTION A small amount of fluid normally exists in the pericardial space. It facilitates friction-free movement of the beating heart within the pericardial sac. It can be visualized as an echo-free rim along the ventricles and atrioventricular junction at both grayscale two-dimensional and M-mode echocardiography 1,2. DeVore and Horenstein described color Doppler identification of pericardial effusion in the fetus 3. According to their study, pericardial fluid was identifiable with real-time gray-scale and color Doppler ultrasound only in the fetuses with pathological effusion. In the 50 control fetuses, they were unable to identify any fluid collection within the pericardial space with either real-time or color Doppler ultrasound. This is in contrast to the study of Dizon-Townson et al. 2 in which pericardial fluid was identifiable in 71% of normal fetuses by using realtime gray-scale and M-mode echocardiography. The aims of this prospective study were to estimate the incidence of sonographic identification of pericardial fluid in normal fetuses and to evaluate the flow pattern of pericardial fluid by using both color and spectral Doppler techniques. MATERIALS AND METHODS We recruited 30 consecutive fetuses in which no abnormality was found at targeted obstetric sonography. We excluded three fetuses from the final study population because adequate postnatal follow-up data could not be obtained. The gestational age at investigation ranged from 19 to 38 weeks (average, 24.7 weeks). All scans were performed by one investigator (S.Y.) with an ATL HDI 3000 ultrasound machine (Advanced Technology Laboratories, Bothell, WA, USA), using a multifrequency (7 4 or MHz) convex transducer. The fetal heart was first evaluated with two-dimensional ultrasound for the presence of pericardial fluid. As the hypoechoic outer layer of the myocardium could be mistaken for pericardial fluid, the anechoic rim was carefully traced to the cardiac apex to find whether it continued through the ventricular septum 4. If the anechoic rim continued through the ventricular septum, it was considered as a hypoechoic layer of the myocardium. The location of the pericardial fluid seen at two-dimensional ultrasound was recorded. The pericardial fluid was evaluated by M-mode in the four-chamber plane in which the ventricular septum was aligned perpendicular to the ultrasound beam axis (Figure 1) 2. The maximum dimension of the fluid shown at M-mode was measured by using a Correspondence: Dr S.-J. Yoo, Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, 555 University Avenue, Ontario, Toronto, M5G 1X8, Canada ( shi-joon.yoo@sickkids.on.ca) Received , Revised , Accepted ORIGINAL PAPER
2 Pericardial fluid was identified by two-dimensional ultrasound in 14 fetuses (52%). It was seen all the way around the ventricles and atrioventricular junction in six, along either right or left ventricle in four, along the ventricular apex in three, and at the atrioventricular junction in one. The depth of the pericardial fluid ranged from 0.8 to 2 mm (Figure 1). Color signals were obtained from the pericardial space in 13 of 14 fetuses with visible pericardial fluid at two-dimensional ultrasound (Figure 2a,b). Color signals were also obtained in 9 of 13 fetuses with no identifiable pericardial fluid at twodimensional or M-mode ultrasound. Therefore, pericardial fluid was identifiable by color Doppler in 81% of the whole study population. The optimum velocity setting for color Doppler visualization of pericardial fluid ranged from 14.4 to 44.3 cm/s (19.2 cm/s in 16 cases). Color signals from pericardial fluid, when visible, were towards the ventricular apex during systole and towards the atria during diastole in all cases. Spectral waveforms could be obtained from the pericardial fluid in 9 of 22 fetuses (41%) with visible color signals. The waveforms confirmed the bidirectional flow pattern shown at color Doppler in all cases (Figure 2c). In six of these nine cases, the systolic flow was monophasic and the diastolic flow was biphasic. In the remaining three cases, the flow was monophasic both in systole and in diastole. The peak velocities for systolic and diastolic flows were (average, 22.8) cm/s and (average, 17.4) cm/s, respectively. DISCUSSION Figure 1 M-mode echocardiogram showing pericardial fluid along the left ventricle. The fluid accumulates along the ventricle during the ventricular systolic phase only (arrows). LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle. built-in electronic caliper. When M-mode demonstration of the pericardial fluid was not possible, the maximum thickness of the pericardial fluid shown on a gray-scale image was measured. When it exceeded 2 mm, which is the upper limit of the normal value 1,2, we excluded the fetus from the study population. For Doppler evaluation, the ventricular septum was aligned as parallel as possible with the ultrasound beam axis. Color Doppler sensitivity was maximized at the expense of grayscale image quality by selecting a higher priority setting for color Doppler signals. The velocity limits were adjusted until the pericardial fluid was coded with color signals (Figure 2a,b). The pattern of the pericardial fluid movement during the cardiac cycle was evaluated using a cine-loop display. Finally, spectral waveforms were obtained from the color-coded pericardial fluid, and the peak diastolic and systolic velocities were measured after angle correction (Figure 2c). All babies were delivered after weeks of gestation. None showed any signs of cardiovascular abnormalities either at immediate postnatal physical examination or at more than 6 months of age, according to a telephone interview with the parents. RESULTS A small amount of pericardial fluid is commonly seen at fetal ultrasound during the second and third trimesters 1,2. The fluid measuring 2 mm or less in depth at gray-scale twodimensional or M-mode echocardiography is considered nonpathological. DeVore and Horenstein utilized color Doppler for identification of the pericardial fluid in the fetus 3. They demonstrated that color Doppler signals within the pericardial space were opposite in direction to the color Doppler signals within the ventricles. This phasic movement of the pericardial fluid is secondary to the phasic change in the dimension of the pericardial space. During ventricular systole, the pericardial space around the ventricles expands and the pericardial fluid moves into this expanding space. During ventricular diastole, the pericardial space around the ventricles disappears as the pericardial fluid moves away from the field of view. In our study, spectral waveforms as well as color Doppler signals could be obtained from the moving pericardial fluid. In two thirds of the cases with identifiable spectral waveforms, there was monophasic flow during systole and biphasic flow during diastole. The waveforms from the pericardial fluid coincided with the waveforms from the ventricular outlet and inlet, except that the flow was in the opposite direction. This observation supports the concept that the pericardial fluid moves passively within the pericardial sac secondary to the phasic changes in the atrial and ventricular dimensions. One may claim that the Doppler signals we sampled were from the myocardium. It is very unlikely, however, that Doppler signals from the moving myocardium could be sampled by the conventional Doppler technique that we used. To depict myocardial movement, it is necessary to use the Doppler tissue imaging technique, which requires a low velocity limit to measure a velocity of 15 20cm/s, the lowest wall filter settings and minimal optimal gain 4 6. It is noticeable, on the other hand, that the Doppler waveform from the basal myocardium is similar to that from the pericardial fluid except for its lower peak velocities. The similarity between these two waveforms reflects the fact that the pericardial fluid moves within the confined sac of pericardium secondary to the movement of myocardium. Harada et al. assessed the myocardial tissue Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology 249
3 velocities in normal fetuses and suggested that tissue Doppler imaging can be utilized for quantitative evaluation of systolic and diastolic function of the ventricles as in postnatal echocardiography 6. It might, then, be worthwhile investigating the effect of ventricular function and pericardial compliance on the Doppler waveform of pericardial fluid or effusion. Although the mechanism is not clear, the outer subpericardial layer of the myocardium is less echoic than the inner subendocardial layer 7. Therefore, the anechoic rim of pericardial fluid should be differentiated from this hypoechoic and sometimes anechoic subpericardial myocardium. The hypoechoic outer myocardial layer characteristically continues through the ventricular septum, where it is sandwiched between the two subendocardial echoic myocardial layers. The anechoic sliver of pericardial fluid is seen peripheral to the hypoechoic myocardial layer. When it is difficult to determine whether the hypoechoic or anechoic rim of the normal fetal heart originates from the pericardial fluid or myocardium 7 9, Doppler examination can be utilized for differentiation. The hypoechoic or anechoic rim originating from the myocardium does not demonstrate any Doppler signals, while the rim originating from the pericardial fluid does. A major concern regarding the presence of an abnormal amount of pericardial fluid is the association with other fetal abnormalities including arrhythmias, anomalies, neoplasms, immune and non-immune hydrops, growth restriction, and chromosomal abnormalites 2. In this context, it is also important to note that pericardial fluid is identifiable sonographically in up to 71% of otherwise normal fetuses 1,2 and that isolated pericardial effusion is not usually associated with an adverse outcome 10,11. DeVore and Horenstein considered that the pericardial fluid identifiable with color Doppler is abnormal because they could not identify any color Doppler signals within the pericardial space in any of their 50 control fetuses 3. Based on this observation, they recommended that the reasons for pericardial fluid accumulation should be sought if abnormal pericardial fluid is detected by color Doppler ultrasound. Their result is contradictory to the result of our present study in which pericardial fluid was identified by color Doppler in 81% of normal fetuses. Our study also demonstrated that color Doppler is more sensitive than gray-scale two-dimensional or M-mode ultrasound in depicting pericardial fluid (81% vs. 52%). Therefore, the pericardial fluid seen on color Doppler is not necessarily more suspicious of a pathological condition than that seen at gray-scale or M-mode echocardiography. Figure 2 Doppler echocardiograms showing bidirectional flow pattern of pericardial fluid (a, b). Color Doppler echocardiograms show that the fluid (arrows) moves towards the ventricular apices during systole (a) and towards the atria during diastole (b). The spectral waveform from the pericardial fluid (c) shows monophasic flow towards the cardiac apex during systole (above the baseline) and biphasic flow away from the apex during diastole (below the baseline). The two peaks of the diastolic flow coincide with the e- and a-waves of the blood flow through the atrioventricular valve. LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle. 250 Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology
4 Figure 3 Color Doppler echocardiograms in systolic (a) and diastolic (b) phases from a fetus with pulmonary atresia and intact ventricular septum. A vessel-like structure with color signals (arrows) is seen along the diaphragmatic surface of the ventricle. The flow is towards the apex in systolic phase (a) and towards the base in diastolic phase (b). We believe that pericardial fluid identified with color Doppler is a normal finding when it does not exceed 2 mm in depth at two-dimensional gray-scale or M-mode echocardiography. On color Doppler, a thin sliver of pericardial fluid is seen as a linear or curvilinear structure along the outer surface of the heart. Therefore, it can be mistaken for a coronary arterial branch. In our earlier experience of a fetus with pulmonary atresia and intact ventricular septum, we identified a tortuous vessel-like structure along the diaphragmatic surface of the heart on color Doppler, and suspected it to be a coronary artery that was dilated because of ventriculocoronary arterial communications (Figure 3). The color Doppler findings of our case were similar to those of Chaoui et al. s case with ventriculocoronary arterial communications 12. In our case, however, postnatal right ventriculography failed to visualize ventriculocoronary arterial communications or dilated arteries. Therefore, we think that we mistook the color-coded pericardial fluid for a dilated coronary artery. By the same token, one should be very cautious when one utilizes visualization of fetal coronary blood flow as an ominous sign of severe uteroplacental insufficiency 13,14. The coronary artery can be differentiated from the pericardial fluid by continuously sweeping the transducer on real-time examination. The coronary arteries are seen only at the expected locations and out of the imaging planes on subtle sweeping of the transducer. The pericardial fluid, on the contrary, is seen not only along the expected courses of the coronary arteries but also in other locations. In summary, pericardial fluid can be identified with color and spectral Doppler, as it moves passively in the pericardial sac with ventricular systole and diastole. The typical spectral waveform from the pericardial fluid consists of biphasic diastolic flow and monophasic systolic flow, which reflects the pattern of blood flow into and from the ventricles. The presence of pericardial fluid per se should not be considered as abnormal when it does not exceed 2 mm in depth at twodimensional or M-mode echocardiography in the absence of other associated abnormalities. Color-coded pericardial fluid should not be mistaken for coronary artery blood flow. REFERENCES 1 Jeanty P, Romero R, Hobbins JC. Fetal pericardial fluid: a normal finding of the second half of gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984; 149: Dizon-Townson DS, Dildy GA, Clark SL. A prospective evaluation of fetal pericardial fluid in 506 second-trimester low-risk pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1997; 90: DeVore GR, Horenstein J. Color Doppler identification of a pericardial effusion in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994; 4: Garcia MJ, Rodgiguez L, Ares M, Griffin BP, Thomas JD, Klein AL. Differentiation of constrictive pericarditis from restrictive cardiomyopathy: assessment of left ventricular diastolic velocities in longitudinal axis by Doppler tissue imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996; 27: Nagueh SF, Middleton KJ, Kopelen HA, Zoghbi WA, Quiñones MA. Doppler tissue imaging: a noninvasive technique for evaluation of left ventricular relaxation and estimation of filling pressures. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 30: Harada K, Tsuda A, Orino T, Tanaka T, Takada G. Tissue Doppler imaging in the normal fetus. Int J Cardiol 1999; 71: Brown DL, Cartier MS, Emerson DS, Shanklin DR, Smith WC, Felker RE. The peripheral hypoechoic rim of the fetal heart. J Ultrasound Med 1989; 8: Jeanty P. Hypoechoic rim of fetal heart. [Letter to the Editor] J Ultrasound Med 1991; 10: Brown DL, Emerson DS. Peripheral hypoechoic rim of the fetal heart. [Letter to the Editor] J Ultrasound Med 1991; 10: Yagel S, Hurwitz A. Fetal pericardial fluid. [Letter to the Editor] Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985; 15: Di Salvo DN, Brown DL, Doubilet PM, Benson CB, Frates MC. Clinical significance of isolated fetal pericardial effusion. J Ultrasound Med 1994; 13: Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology 251
5 12 Chaoui R, Tennstedt C, Göldner B, Bollmann R. Prenatal diagnosis of ventriculo-coronary communications in a second-trimester fetus using transvaginal and transabdominal color Doppler sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997; 9: Gembruch U, Baschat AA. Demonstration of fetal coronary blood flow by color-coded and pulsed wave Doppler sonography: a possible indicator of severe compromise and impending demise in intrauterine growth retardation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996; 7: Baschat AA, Gembruch U, Reiss I, Gortner L, Diedrich K. Demonstration of fetal coronary blood flow by Doppler ultrasound in relation to arterial and venous flow velocity waveforms and perinatal outcome the heart-sparing effect. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997; 9: Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
The Fetus: Five Top Do Not Miss Diagnoses. Doppler Ultrasound
 The Fetus: Five Top Do Not Miss Diagnoses Doppler Ultrasound Giancarlo Mari, MD, MBA Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, TN
The Fetus: Five Top Do Not Miss Diagnoses Doppler Ultrasound Giancarlo Mari, MD, MBA Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, TN
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI. Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals
 Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals Applications Both maternal uterine and fetal circulations can be studied with doppler sonography Uterine arteries
Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals Applications Both maternal uterine and fetal circulations can be studied with doppler sonography Uterine arteries
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation
 First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding at various stages of pregnancy
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 606 610 Published online 7 October 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1999 Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 606 610 Published online 7 October 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1999 Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding
Sonography of the Fetal Heart: Normal Variants and Pitfalls
 1251 Pictorial Essay Sonography of the Fetal Heart: Normal Variants and Pitfalls Douglas L. Brown,1 Donald N. DiSalvo,1 Mary C. Frates,1 and Ira A. Parness2 3 Sonographic evaluation of the fetal heart
1251 Pictorial Essay Sonography of the Fetal Heart: Normal Variants and Pitfalls Douglas L. Brown,1 Donald N. DiSalvo,1 Mary C. Frates,1 and Ira A. Parness2 3 Sonographic evaluation of the fetal heart
Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus*
 Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Introduction. Cardiac Imaging Modalities MRI. Overview. MRI (Continued) MRI (Continued) Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03
 Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction to Fetal Doppler Echocardiography
 Chapter 32 Introduction to Fetal Doppler Echocardiography Dev Maulik Introduction Evaluation of the fetal heart constitutes one of the critical areas of prenatal diagnosis. Advances in diagnostic medical
Chapter 32 Introduction to Fetal Doppler Echocardiography Dev Maulik Introduction Evaluation of the fetal heart constitutes one of the critical areas of prenatal diagnosis. Advances in diagnostic medical
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
The rapid evolution of echocardiography during the past 25 years
 Evaluation of Myocardial Mechanics in the Fetus by Velocity Vector Imaging Adel K. Younoszai, MD, David E. Saudek, MD, Stephen P. Emery, MD, and James D. Thomas, MD, Denver, Colorado; Cleveland, Ohio;
Evaluation of Myocardial Mechanics in the Fetus by Velocity Vector Imaging Adel K. Younoszai, MD, David E. Saudek, MD, Stephen P. Emery, MD, and James D. Thomas, MD, Denver, Colorado; Cleveland, Ohio;
Coarctation of the aorta: difficulties in prenatal
 7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures and quantitative assessment of the fetal heart
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23; 21: 2 32 Published online 2 December 22 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/uog. Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23; 21: 2 32 Published online 2 December 22 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/uog. Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome
 Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Editorial. Color and pulsed Doppler in fetal echocardiography A. ABUHAMAD
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 1 9 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1096 Editorial Color and pulsed Doppler in fetal echocardiography A. ABUHAMAD
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 1 9 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1096 Editorial Color and pulsed Doppler in fetal echocardiography A. ABUHAMAD
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations
 Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
PIAF study: Placental insufficiency and aortic isthmus flow Jean-Claude Fouron, MD
 Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Persistent Fetal Arrhythmias
 1386 JACC Vol 7. No 6 June 19X6 I3Xh-91 Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Persistent Fetal Arrhythmias JANETTE F. STRASBURGER, MD, JAMES C. HUHTA, MD, FACC, ROBERT J. CARPENTER,
1386 JACC Vol 7. No 6 June 19X6 I3Xh-91 Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Persistent Fetal Arrhythmias JANETTE F. STRASBURGER, MD, JAMES C. HUHTA, MD, FACC, ROBERT J. CARPENTER,
Pulsed Wave Doppler and Color Flow Doppler Evaluation in Healthy Dogs and Dogs with Cardiac Disease
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Veterinary Science and Technology 2016, Volume 5, Issue 2, pp. 256-265, Article ID Sci-446 ISSN 2320-3595 Research Article Open Access Pulsed Wave Doppler
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Veterinary Science and Technology 2016, Volume 5, Issue 2, pp. 256-265, Article ID Sci-446 ISSN 2320-3595 Research Article Open Access Pulsed Wave Doppler
Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of the normal
 Br Heart J 1987;57:528-33 Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of the normal human fetal heart LINDSEY D ALLAN, SUNDER K CHITA, WIDAD AL-GHAZALI, DIANE C CRAWFORD, MICHAEL TYNAN From the Departments of
Br Heart J 1987;57:528-33 Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of the normal human fetal heart LINDSEY D ALLAN, SUNDER K CHITA, WIDAD AL-GHAZALI, DIANE C CRAWFORD, MICHAEL TYNAN From the Departments of
AbnormalThree-VesselView on Sonography: A Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus
 rt Pictorial Essay bnormalthree-vesselview on Sonography: Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus screening tool for major congenital heart diseases [I. 2J. However, anomalies of
rt Pictorial Essay bnormalthree-vesselview on Sonography: Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus screening tool for major congenital heart diseases [I. 2J. However, anomalies of
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
 Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Noninvasive assessment of left ventricular (LV)
 Comparative Value of Tissue Doppler Imaging and M-Mode Color Doppler Mitral Flow Propagation Velocity for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure* Michal Kidawa, MD; Lisa Coignard, MD; Gérard
Comparative Value of Tissue Doppler Imaging and M-Mode Color Doppler Mitral Flow Propagation Velocity for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure* Michal Kidawa, MD; Lisa Coignard, MD; Gérard
4/19/2018. St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT
 St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know. Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts 2/8/2012
 Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
Summary. HVRA s Cardio Vascular Genetic Detailed L2 Obstetrical Ultrasound. CPT 76811, 76825, _ 90% CHD detection. _ 90% DS detection.
 What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
Most common fetal cardiac anomalies
 Most common fetal cardiac anomalies Common congenital heart defects CHD % of cardiac defects Chromosomal Infants Fetuses anomaly (%) 22q11 deletion (%) VSD 30 5~10 20~40 10 PS 9 5 (PA w/ VSD) HLHS 7~9
Most common fetal cardiac anomalies Common congenital heart defects CHD % of cardiac defects Chromosomal Infants Fetuses anomaly (%) 22q11 deletion (%) VSD 30 5~10 20~40 10 PS 9 5 (PA w/ VSD) HLHS 7~9
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY. Patient Care. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Patient Care Be able to: Perform and interpret basic TTE and X cardiac Doppler examinations Perform and interpret a comprehensive X TTE and cardiac Doppler examination Perform and interpret a comprehensive
Patient Care Be able to: Perform and interpret basic TTE and X cardiac Doppler examinations Perform and interpret a comprehensive X TTE and cardiac Doppler examination Perform and interpret a comprehensive
Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram
 JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study
 J. Fetal Med. (March 2015) 2:27 32 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0038-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study Aldo L. Schenone
J. Fetal Med. (March 2015) 2:27 32 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0038-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study Aldo L. Schenone
Failing right ventricle
 Failing right ventricle U. Herberg 1, U. Gembruch 2 1 Pediatric Cardiology, 2 Prenatal Diagnostics and Fetal Therapy, University of Bonn, Germany Prenatal Physiology Right ventricle dominant ventricle
Failing right ventricle U. Herberg 1, U. Gembruch 2 1 Pediatric Cardiology, 2 Prenatal Diagnostics and Fetal Therapy, University of Bonn, Germany Prenatal Physiology Right ventricle dominant ventricle
Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus
 ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo M Selvarani Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo M Selvarani Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology,
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Disclosures. Outline. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Introduction. Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart
 Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation
 Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
The Normal Echocardiogram
 The Normal Echocardiogram Pravin V. Patil, MD FACC Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Acknowledgments Dr. Susan Wiegers Dr. Martin Keane Temple Cardiac Sonographers Disclosures No relevant
The Normal Echocardiogram Pravin V. Patil, MD FACC Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Acknowledgments Dr. Susan Wiegers Dr. Martin Keane Temple Cardiac Sonographers Disclosures No relevant
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Basic Echocardiography in Life Support
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Basic Echocardiography in Life Support Page 1 of 7 05/18 ACN 001 679 161 ABN 64 001 679 Basic Echocardiography in Life Support (BELS) Syllabus
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Basic Echocardiography in Life Support Page 1 of 7 05/18 ACN 001 679 161 ABN 64 001 679 Basic Echocardiography in Life Support (BELS) Syllabus
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency
 Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
 Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound. Cardiac Ultrasound
 Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early second trimester by enhanced-flow (e-flow) echocardiography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 652 657 Published online 1 November 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8965 Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 652 657 Published online 1 November 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8965 Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm
 Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Objectives. Introduction 11/2/2015
 Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function
 CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
Practical Echocardiography: ECHOES in the REAL WORLD Know When to Hold Em and When to Fold Em
 Practical Echocardiography: ECHOES in the REAL WORLD Know When to Hold Em and When to Fold Em Introduction The use of ultrasound in private veterinary practice is continuing to grow. The popularity of
Practical Echocardiography: ECHOES in the REAL WORLD Know When to Hold Em and When to Fold Em Introduction The use of ultrasound in private veterinary practice is continuing to grow. The popularity of
Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University
 Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University in St. Louis Goal o To review the imaging criteria of
Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University in St. Louis Goal o To review the imaging criteria of
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Copyright 2017 American College of Emergency Physicians. All rights reserved.
 POLICY Approved April 2017 Guidelines for the Use of Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) in the ED for Cardiac Arrest Approved by the ACEP Board of Directors April 2017 1. Introduction The American
POLICY Approved April 2017 Guidelines for the Use of Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) in the ED for Cardiac Arrest Approved by the ACEP Board of Directors April 2017 1. Introduction The American
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hesham Rashid* Tissue Doppler Imaging CARDIOLOGY Editorial Department of Cardiology, Benha University, Egypt *Corresponding Author: Hesham Rashid, Department of Cardiology, Benha University,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hesham Rashid* Tissue Doppler Imaging CARDIOLOGY Editorial Department of Cardiology, Benha University, Egypt *Corresponding Author: Hesham Rashid, Department of Cardiology, Benha University,
Jong-Won Ha*, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Jae-Yun Moon, Hye-Sun Suh, Seok-Min Kang, Se-Joong Rim, Yangsoo Jang, Namsik Chung, Won-Heum Shim, Seung-Yun Cho
 Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Carotid Duplex Ultrasound SECTION: Vascular Ultrasound ORIGINATOR: Deborah L. Richert, BSVT, RDMS, RVT DATE: October 15, 2015
GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Carotid Duplex Ultrasound SECTION: Vascular Ultrasound ORIGINATOR: Deborah L. Richert, BSVT, RDMS, RVT DATE: October 15, 2015
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC)
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 535 545 Published online 6 May 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1075 Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 535 545 Published online 6 May 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1075 Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography
PERICARDIAL DIAESE. Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University
 PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR
 cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
Introduction to Biomedical Imaging
 Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu Basic principles. Comparison to X-rays Ultrasound > 20kHz
Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu Basic principles. Comparison to X-rays Ultrasound > 20kHz
The Fetal Cardiology Program
 The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Atrioventricular Flow Wave Patterns before and after Birth by Fetal Echocardiography
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.2.85 pissn 1975-4612/ eissn 2005-9655 Copyright 2012 Korean Society of Echocardiography www.kse-jcu.org ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2012;20(2):85-89 Atrioventricular
http://dx.doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.2.85 pissn 1975-4612/ eissn 2005-9655 Copyright 2012 Korean Society of Echocardiography www.kse-jcu.org ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2012;20(2):85-89 Atrioventricular
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers. This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions.
 Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions. This lesson was derived from pages 33 through 42 in the textbook: Ultrasound Transducers Ultrasound Transducers
Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions. This lesson was derived from pages 33 through 42 in the textbook: Ultrasound Transducers Ultrasound Transducers
Influence of Preload Reduction on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Hemodialysis Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
 93 Original Article St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 35, pp. 93 99, 2007 Influence of Preload Reduction on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Hemodialysis Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Sachihiko
93 Original Article St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 35, pp. 93 99, 2007 Influence of Preload Reduction on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Hemodialysis Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Sachihiko
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study
 Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Read Me. covering the Heart Anatomy. Labs. textbook. use. car: you
 Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Diagnostic Ultrasound. Sutiporn Khampunnip, M.D.
 Diagnostic Ultrasound Sutiporn Khampunnip, M.D. Definition of Ultrasound Ultrasound is simply sound waves, like audible sound. High-frequency sound and refers to mechanical vibrations above 20 khz. Human
Diagnostic Ultrasound Sutiporn Khampunnip, M.D. Definition of Ultrasound Ultrasound is simply sound waves, like audible sound. High-frequency sound and refers to mechanical vibrations above 20 khz. Human
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
