Questions for the exam on discipline "Anatomy»
|
|
|
- Tyrone Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Questions for the exam on discipline "Anatomy» OSTEOLOGY AND ARTHROLOGY 1. Bone as an organ: development, structure. Classification of bones. Vertebrae: their structure in different parts of the vertebral column (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal vertebrae), variants and anomalies. Structure of ribs, sternum. 2. Structure of bones of the shoulder girdle (scapula, clavicle). Structure of bones of free part upper limb. The humerus, bones of a forearm (ulna, radius). Bones of the hand. 3. Hip (coxal) bone, femur, patella. Bones of the leg and the foot. 4. Anatomic and biomechanical classification of bone connections (articulations) their functional features. Continuous articulations (or connections - synarthrosis) of bones. Structure of a joint. Classification of synovial joints (diarthrosis) according to the number of articular surfaces, number of axes and shape of articular surfaces, and function. 5. Connections of vertebrae. The vertebral column as a whole: formation of its curvatures, movements. The atlanto-occipital joint, the atlantoaxial joints. Connections (articulations) of the skull bones (continuous connections, temporo-mandibular joint). 6. Connections of ribs with vertebrae and sternum. Thorax as a whole. 7. Connections of bones of shoulder girdle. Connections of free part of upper limb. Shoulder joint. The еlbow joint, connections of bones of forearm. 8. Joints of the hand. The hand as a whole. 9. Connections of pelvic girdle. Pelvis as a whole. Age and sexual features, sizes of female pelvis. Hip joint. 10. The кnee joint, connections of the leg bones and of the foot. THE SKULL 1. Development of the skull in ontogenesis. Individual, age and sexual features of a skull. Variants and anomalies of cranial bones. 2. The skull. Cranial part. Occipital, parietal and frontal bones. Sphenoid bone, its parts, foramina. Temporal bone, structure, its canals. Ethmoid bone. 3. Bones of the facial (visceral) skull: maxilla, mandible, zygomatic, nasal, palatine, lacrimal, inferior nasal concha, vomer, hyoid. 4. The skull as a whole. Calvaria. The base of the skull. Internal and external surfaces. 5. Temporal, infratemporal and pterygo-palatine fossae, their topography. Facial skull. The orbit, bones of walls, apertures. The nasal cavity. The paranasal sinuses. Palatum osseum. MYOLOGY (THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM) 1. General anatomy of muscles, structure of muscles as an organ. Development of skeletal muscles, their classification (according to form, structure, arrangement, etc.). Muscles sinergists and antagonists. The auxiliary apparatus of muscles: fasciae, synovial sheaths and bursae, their structure and function; sesamoid bones: their position and function. Muscles and fasciae of the head: muscles of facial expression (mimic), masticatory muscles. 2. Muscles of the neck. Topography of the neck (Triangles of the neck). Fasciae of the neck. Fasciae spaces of the neck. 3. Muscles and fasciae of the back. 4. Muscles and fasciae of the thorax (chest). Diaphragm. 5. Muscles of the abdomen. 6. The sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle. The linea alba. The inguinal canal, its walls, deep and superficial rings; contents of the inguinal canal. Weak places of the anterior abdominal wall. 7. Muscles and fasciae of the shoulder girdle. Muscles and fasciae of the arm. 8. Muscles of the forearm: anterior group.
2 9. Muscles of the forearm: posterior group. 10. Muscles of the hand. 11. Fasciae and topography of the upper limb (The axillary fossa. The canal of the radial nerve. The bony-fibrous (osteo-fibrosus) canals and synovial sheaths of the hand). 12. Muscles of the pelvic girdle. 13. Muscles of the thigh. 14. The muscles of the leg. 15. Muscles of the foot. 16. Fasciae and topography of the lower limb. The structures under the inguinal ligament (muscular and vascular lacunae). The adductor canal, its walls. The femoral triangle. SPLANCHNOLOGY The digestive system 1. Development of the digestive system. The mouth: lips, oral cavity (oral vestibule, hard and soft palate). The teeth (deciduous and permanent), their structure, the dental row, the dental formula and the eruption time of deciduous and permanent teeth. 2. The tongue: development, structure, functions. Salivary glands (the parotid, sublingual and submandibular salivary glands, small salivary glands). 3. The pharynx: structure, parts, topography. The lymphoepithelial (Pyrogov`s) ring of pharynx (ring of tonsils). 4. The esophagus: topography (skelepotopy, syntopy and holotopy), structure, constrictions. 5. The stomach: structure, topography, position (relation) according to peritoneum, ligaments. 6. The small intestine: its parts, topography, position according to peritoneum, structure of its wall (the duodenum, mesenteric part of the small intestine (jejunum and ileum)). 7. The abdominal cavity, its walls. Regions of anterior abdominal wall. The peritoneum, peritoneal cavity, variants of organ position (relation) according to peritoneum. 8. The large intestine: its parts, their topography, position according to peritoneum; the structure of a wall. The caecum: structure, position according to peritoneum, topography of the vermiform appendix. The rectum: topography, position according to peritoneum, the structure of its wall. 9. The liver: structure, topography, ligaments, functions, features of blood supply. 10. The gallbladder. Paths for bile excretion (the ducts of the gallbladder and the liver). 11. The pancreas: topography, structure, ducts, endocrine part, functions. 12. The peritoneal cavity. Topography of the peritoneum in the upper storey of the peritoneal cavity. The lesser omentum and omental, hepatic and pregastric bursae and their walls. 13. Topography of the peritoneum in the middle and lower storeys of the peritoneal cavity. The greater omentum. The recesses, grooves, sinuses of walls of the peritoneal cavity, pouches of the pelvis. UROGENITAL APPARATUS (THE URYNARY SYSTEM. THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM) 1. The kidneys: development, topography, structure, their coats, position according to peritoneum, supporting apparatus, functions. Functional unit of the kidney nephron. Blood supply of the kidneys: intrarenal division of vessels. Excretory apparatus. 2. The ureter, the urinary bladder, their structure, topography, position according to peritoneum. The female urethra. 3. Development of the Reproductive system. Male genital organs. The testis, structure, endocrine part of the testis. The epididymis. 4. The prostate, the seminal vesicles. The bulbo-urethral glands (Cowper`s), their relation to the urethra. 5. The spermatic cord, its components. The ductus (vas) deferens. Semen-conveying ducts (Reproductive system ducts in Males). 6. Male external genital organs (penis, scrotum). The male urethra. 7. Female genital organs. The ovary, topography, structure, position according to the peritoneum, endocrine part of the ovary. The uterine tube: structure, position according to peritoneum. 8. The uterus: parts, topography, ligaments, position according to peritoneum. The vagina: structure, topography, position according to
3 peritoneum. 9. Female external genitalia (pudendum femininum). The perineum: parts. Muscles and fasciae of the perineum (male and female). Peritoneum of the pelvic cavity in the male and female pelvis. Its relation to the rectum, the urinary bladder, the uterus and other organs. THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1. Development of the Respiratory system. Two parts: upper respiratory system and lower respiratory system; two portions: conducting and respiratory. The external nose. The nasal cavity (olfactory and respiratory areas). The paranasal sinuses. 2. The larynx: cartilages, joints, the elastic cone of the larynx, the relief of the internal surface (mucous membrane) of the larynx. Muscles of the larynx, their classification, functions. The trachea and primary bronchi, structure, topography. 3. The lungs: development, topography (skelepotopy, syntopy and holotopy). The segmental structure of the lungs. The roots of right and left lungs: anatomy and topography. Division of bronchi (bronchial tree, alveolar tree), structural and functional unit of the lungs acinus. Blood supply of the lungs. 4. The pleura: parts, borders; the pleural cavity, pleural recesses. The mediastinum: parts, organs of the mediastinum, their topography. CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. General anatomy of blood vessels. The heart: development, structure of the heart. Chambers of the heart: structure. Layers of the heart walls. The features of the myocardium of atria and ventricles. Conducting system of the heart. Topography, projection of borders and valves of the heart on the anterior thoracic wall. Blood supply of the heart, coronary circulation. The pericardium, its topography. The vessels of the pulmonary circulation (general characteristic), their distribution in lungs. The Systemic circulation. 2. General anatomy of blood vessels. Distribution of General anatomy of blood vessels. 3. The aorta and its parts. Branches of arch of the aorta. The external carotid artery, its topography, branches and areas, supplied by them. arteries. 4. The internal carotid artery, topography, branches. The subclavian artery: topography, branches and areas supplied by them. Blood supply of the brain and the spinal cord (cervical part). 5. The axillary and brachial arteries: topography, branches and areas, supplied by them. The arteries of the forearm: topography, branches, areas, supplied by them. Collateral blood circulation at the region of the elbow joint. The arteries of the hand. Arterial palmar arches and their branches. Collateral blood circulation (main collateral artery) at the upper limb, practical significance. 6. Thoracic part of the aorta, branches (parietal and visceral). The visceral (paired and unpaired) branches of the abdominal aorta. The parietal (paired and unpaired) branches of the abdominal part of the aorta. Features of their distribution and anastomoses. 7. The common iliac artery, external and internal iliac arteries, their branches. 8. The femoral and the popliteal arteries: topography, branches and areas, supplied by them. Blood supply of the hip and the knee joints. 9. The arteries of the leg: topography, branches and areas, supplied by them. The arteries of the foot: topography, branches and areas, supplied by them. 10. Veins of the Systemic circulation. The superior vena cava, the main tributaries and its topography. The brachiocephalic veins, their formation, tributaries. The azygos and hemiazygos veins. 11. The veins of the brain, the venous blood sinuses of the dura mater, the emissary and diploic veins. Intracranial and extracranial ways of outflow from the brain Superficial and deep veins of the upper limb and their topography 13. The inferior vena cava, sources of its formation and topography. The tributaries of the inferior vena cava and their anastomoses. 14. The common iliаc veins, external and internal iliac veins, their tributaries; venous plexuses of the true pelvis. 15. Superficial and deep veins of the lower limb and their topography. 16. The hepatic portal vein. Its tributaries, their topography; the distribution of portal vein in the liver. Intersystemic and intrasystemic
4 anastomoses of veins (porto-caval, cava-caval anastomoses). 17. The spleen: development, topography, structure, position according to peritoneum, ligaments.
5 NERVOUS SYSTEM Anatomy of cerebrum 1. Anatomic and morphological classifications of the nervous system; its anatomic formations (plexus, ganglions, nerves). 2. Anatomy of spinal cord; meninges of the spinal cord; Intermeningeal spaces. Spinal segment. 3. Anatomic classification of cerebrum. Anatomy of cerebrum. Anatomic of structures of the brainstem part of the cerebrum (medulla oblongata, pons, mesencephalon and diencephalon). 4. Anatomy of medulla oblongata and pons. 5. Anatomy of mesencephalon and diencephalon. 6. Anatomy of cerebellum. 7. Telencephalon. Relief of pallium. Localization of functions in the cortex of hemispheres. Meninges of the cerebrum and their derivates. 8. Basal ganglia. White matter of hemispheres. Internal capsule. 9. Lateral ventricles. III and IV ventricle. Its walls. 10. Rhomboid fossa, its structure, topography of nuclei of the cranial nerves. 11. Classification of conducting tracts of the head and spinal cord. Ascending tracts. 12. Descending conducting tracts of the brain and spinal cord. 13. Anatomy of sense organs. Organ of vision. 14. Anatomy of organs of hearing and balance. Anatomy of sense organs Peripheral nerves 15. Spinal nerve, its branches. Anterior branches of thoracic nerves. 16. Cervical plexus, its branches, areas of innervations. 17. Brachial plexus,, its branches 18. Lumbar and sacro-coccygeal plexus,, its branches 19. Review of cranial nerves. General description. Olfactory, optic, oculomotor, block (trochlea) and abducent nerves. 20. Trigeminal nerve. Branches of trigeminal nerve. 21. Facial nerve. 22. Vestibulo-cochleal and glossopharyngeal nerves. 23. Vagus, accessory and hypoglossal nerves.
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester. (control of theoretical knowledge)
 Pag. 1 / 5 List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester (control of theoretical knowledge) LOCOMOTOR APPARATUS 1. Human Anatomy and its role in medical
Pag. 1 / 5 List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester (control of theoretical knowledge) LOCOMOTOR APPARATUS 1. Human Anatomy and its role in medical
Q U E S T I O N A R Y of Anatomy and Histology for students dental medicine
 Q U E S T I O N A R Y of Anatomy and Histology for students dental medicine I. BONES AND JOINTS 1. Bone structure, development and growth. 2. Joints types: fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, bony union
Q U E S T I O N A R Y of Anatomy and Histology for students dental medicine I. BONES AND JOINTS 1. Bone structure, development and growth. 2. Joints types: fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, bony union
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1.
 Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1. Classification of internal organs. General plan of tubular organs. 2. The
Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1. Classification of internal organs. General plan of tubular organs. 2. The
Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System. A list of the first 3 digits - 72 terms
 1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
ANATOMY. Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks)
 ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS M. PHIL ANATOMY SUMMARY. MCQs: Marks SEQs: Marks. Segment MCQs SEQs
 M. PHIL ANATOMY SUMMARY MCQs: 150 150 Marks SEQs: 15 150 Marks Segment MCQs SEQs Gross Anatomy 35% 35% Microanatomy (Histology) 25% 25% Neuroanatomy 20% 20% Embryology 20% 20% GROSS ANATOMY Table of specification
M. PHIL ANATOMY SUMMARY MCQs: 150 150 Marks SEQs: 15 150 Marks Segment MCQs SEQs Gross Anatomy 35% 35% Microanatomy (Histology) 25% 25% Neuroanatomy 20% 20% Embryology 20% 20% GROSS ANATOMY Table of specification
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Teaching Objectives
 Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Rachana Sareeram. : Classes for 6 months, including examination & result. Study leave + Universrity Exam for 2 months
 Rachana Sareeram It is proposed to divide the 1-½ years of professional course into three terms as envisaged by DAME. The three terms, study leave & periodical exams can be as follows: TTerm 1 Term 2 Term
Rachana Sareeram It is proposed to divide the 1-½ years of professional course into three terms as envisaged by DAME. The three terms, study leave & periodical exams can be as follows: TTerm 1 Term 2 Term
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Topic list for the Anatomy end-semester exam of the First semester Academic year 2018/2019, Autumn term
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5
 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Applied anatomy. Types of ossification & Epiphysis Kinesiology 2
 .General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
.General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Anatomy. A Photographic Atlas. Bearbeitet von Johannes W. Rohen, Chihiro Yokochi, Elke Lütjen-Drecoll
 Anatomy A Photographic Atlas Bearbeitet von Johannes W. Rohen, Chihiro Yokochi, Elke Lütjen-Drecoll 8 2015. Taschenbuch. 560 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 7945 2982 7 Format (B x L): 21 x 29,7 cm Gewicht: 2300
Anatomy A Photographic Atlas Bearbeitet von Johannes W. Rohen, Chihiro Yokochi, Elke Lütjen-Drecoll 8 2015. Taschenbuch. 560 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 7945 2982 7 Format (B x L): 21 x 29,7 cm Gewicht: 2300
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT CENTER. Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department 29/12/2015
 Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Table of Contents: 1 The body. What is anatomy? 4. How can gross anatomy be studied? 4. Important anatomical terms 4. Imaging 7
 Table of Contents: 1 The body What is anatomy? 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? 4 Important anatomical terms 4 Imaging 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques 7 Nuclear medicine imaging 10 Image interpretation
Table of Contents: 1 The body What is anatomy? 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? 4 Important anatomical terms 4 Imaging 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques 7 Nuclear medicine imaging 10 Image interpretation
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY FIRST M.B.B.S. (BATCH ) TEACHING PROGRAMME (January March 2018) 1.00pm 2.00 pm (Demo) Batch A Dr. Uma Batch B Dr.
 HEAD, FACE AND NECK(contd) DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY FIRST M.B.B.S. (BATCH 2017-18) TEACHING PROGRAMME (January March 2018) 9.00-9.30 am (s) Batch B 02/01/18 Thyroid Gland Thyroid gland, Scalene muscles, Subclavian
HEAD, FACE AND NECK(contd) DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY FIRST M.B.B.S. (BATCH 2017-18) TEACHING PROGRAMME (January March 2018) 9.00-9.30 am (s) Batch B 02/01/18 Thyroid Gland Thyroid gland, Scalene muscles, Subclavian
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Academic Year 2017/2018. FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm
 CURRICULUM FOR HUMAN ANATOMY COURSE LAB SESSIONS Academic Year 2017/2018 FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm Category 1: Bones name, type, structure Joints: type, articular
CURRICULUM FOR HUMAN ANATOMY COURSE LAB SESSIONS Academic Year 2017/2018 FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm Category 1: Bones name, type, structure Joints: type, articular
The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p.
 The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p. 7 Nuclear medicine imaging p. 10 Image interpretation
The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p. 7 Nuclear medicine imaging p. 10 Image interpretation
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI
 IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
Undergraduate Gross Anatomy: Systems
 Complete Anatomy 2018 + COURSES Undergraduate Gross Anatomy: s Course Outcomes General Education Outcomes A) A Student will be able to use anatomical terms correctly B) A student will be able to identify
Complete Anatomy 2018 + COURSES Undergraduate Gross Anatomy: s Course Outcomes General Education Outcomes A) A Student will be able to use anatomical terms correctly B) A student will be able to identify
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Control center! (set point)! (Change is compared! to the set point.)!
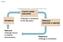 Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax
 Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones
Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
6e Plate# 7e Plate# Plate Title
 6e Plate# 7e Plate# Plate Title 1 8 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 9 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 10 Superficial Arteries and Veins of Face and Scalp 4 11 Skull: Anterior View 5 (replaced) 12
6e Plate# 7e Plate# Plate Title 1 8 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 9 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 10 Superficial Arteries and Veins of Face and Scalp 4 11 Skull: Anterior View 5 (replaced) 12
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Angiology Part 4. Veins. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Table of Contents: SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION PLATES 1-7. Introduction Plates 1-7. Plate 1 Body Planes and Terms of Relationship
 Table of Contents: SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION PLATES 1-7 Introduction Plates 1-7 Plate 1 Body Planes and Terms of Relationship Plate 2 Surface Anatomy: Regions (Anterior view of female) Plate 3 Surface Anatomy:
Table of Contents: SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION PLATES 1-7 Introduction Plates 1-7 Plate 1 Body Planes and Terms of Relationship Plate 2 Surface Anatomy: Regions (Anterior view of female) Plate 3 Surface Anatomy:
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
SKELETON AND JOINTS. MUSCLES. 1. Classification of the bones. The structure of the bone. Bonedevelopment.
 Human morphology department Exam Questions on Human anatomy for the second year students of Medical Faculty for International Students (speciality "Dentistry") (approved at the meeting of the department
Human morphology department Exam Questions on Human anatomy for the second year students of Medical Faculty for International Students (speciality "Dentistry") (approved at the meeting of the department
Kidney Model (Model 3-13)
 Kidney Model (Model 3-13) Kidney Model Blood Vessels (Model 3-29) Segmental Artery Interlobar Artery Renal Artery Renal Vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular Vein Arcuate Artery Interlobar Vein Arcuate
Kidney Model (Model 3-13) Kidney Model Blood Vessels (Model 3-29) Segmental Artery Interlobar Artery Renal Artery Renal Vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular Vein Arcuate Artery Interlobar Vein Arcuate
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
ANATOMY - II. FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX
 ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
The program of the courses of Human Anatomy for 1-st year students. Dentistry faculty
 The program of the courses of Human Anatomy for 1-st year students. Dentistry faculty Osteology and syndesmology. Course 1. The axes, lines, planes and directions of the human body. Kinds of bones. Structure
The program of the courses of Human Anatomy for 1-st year students. Dentistry faculty Osteology and syndesmology. Course 1. The axes, lines, planes and directions of the human body. Kinds of bones. Structure
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy
 Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Introduction to Canine Anatomy and Physiology. Anatomical Vocabulary, Basic Functions and Anatomy of the Dog Lecture 1
 Introduction to Canine Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Vocabulary, Basic Functions and Anatomy of the Dog Lecture 1 1 Lecture Content Basic Anatomical Concepts Anatomy and Physiology terminology Anatomy
Introduction to Canine Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Vocabulary, Basic Functions and Anatomy of the Dog Lecture 1 1 Lecture Content Basic Anatomical Concepts Anatomy and Physiology terminology Anatomy
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
QUESTIONARY OF HUMAN ANATOMY
 QUESTIONARY OF HUMAN ANATOMY for 2 nd Year Dental Medicine Students of the English Language Programme at Medical University Prof. Dr. Paraskev Stoyanov Varna (Academic Years 2014 2015) I. Osteology and
QUESTIONARY OF HUMAN ANATOMY for 2 nd Year Dental Medicine Students of the English Language Programme at Medical University Prof. Dr. Paraskev Stoyanov Varna (Academic Years 2014 2015) I. Osteology and
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
