Table of Contents: Section 1 : Development of the Genital Tracts and Functional Relationships of the Gonads
|
|
|
- Laurence Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents: Section 1 : Development of the Genital Tracts and Functional Relationships of the Gonads 1. Genetics and Biology of Early Reproductive Tract Development 2. Homologues of the Internal Genitalia 3. Homologues of External Genitalia 4. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Hormonal Axis 5. Testosterone and Estrogen Synthesis 6. Puberty Normal Sequence 7. Puberty - Abnormalities: Male Gonadal Failure 8. Puberty - Abnormalities: 1-9 Puberty Abnormalities 10. Puberty - Abnormalities: Female Gonadal Failure 11. Puberty - Abnormalities: 12. Intersex: True Hermaphoditism 13. Intersex: Male Pseudohermaphoditism I-Gonadal 14. Intersex: Male Pseudohermaphoditism II-Hormonal 15. Intersex: Female Pseudohermaphoditism Section 2 : The Penis and Male Perineum 1. Pelvic Structures 2. Superficial Fascial Layers 3. Deep Fascial Layers 4. Penile Fascia and Structures 5. Urogenital Diaphragm 6. Blood Supply of Pelvis 7. Blood Supply of Perineum 8. Blood Supply of Testis 9. Lymphatic Drainage of Pelvis and Genitalia 10. Innervation of Genitalia I
2 11. Innervation of Genitalia II and of Perineum 12. Urethra and Penis 13. Erection and Erectile Dysfunction 14. Hypospadias and Epispadias 15. Congenital Valve Formation and Cyst 16. Urethral Anomalies, Verumontanum Disorders 17. Phimosis, Paraphimosis, Strangulation 18. Peyronie s Disease, Priapism, Thrombosis 19. Trauma to Penis and Urethra 20. Urinary Extravasation 21. Balanitis 22. Urethritis 23. Syphilis 24. Chancroid, Lymphogranuloma Venereum 25. Granuloma Inguinale 26. Strictures 27. Warts, Precancerous Lesions, Early Cancer 28. Advanced Carcinoma of the Penis 29. Papilloma, Cancer of Urethra Section 3 : The Scrotum and Testis 1. Scrotal Wall 2. Blood Supply of the Testis 3. Testis, Epididymis and Vas Deferens 4. Testicular Development and Spermatogenesis 5. Descent of the Testis 6. Scrotal Skin Diseases I: Chemical and Infectious 7. Scrotal Skin Diseases II: Scabies and Lice 8. Avulsion, Edema, Hematoma 9. Hydrocele, Spermatocele 10. Varicocele, Hematocele, Torsion 11. Infection, Gangrene 12. Syphilis 13. Elephantiasis 14. Cysts and Cancer of the Scrotum 15. Cryptorchidism 16. Testis Failure I: Primary (Hypergonadotropic) Hypogonadism 17. Testis Failure II: Secondary (Hypogonadotropic) Hypogonadism 18. Testis Failure III: Secondary Hypogonadism Variants 19. Testis Failure IV: Klinefelter Syndrome 20. Testis Failure V: Delayed Puberty 21. Spermatogenic Failure 22. Infection and Abscess of Testis and Epididymis 23. Syphilis and Tuberculosis of the Testis 24. Testicular Tumors I: Seminoma, Embryonal Carcinoma, Yolk Sac Tumors 25. Testicular Tumors II: Teratoma, Choriocarcinoma, In
3 Situ Neoplasia Section 4 : The Seminal Vesicles and Prostate 1. Prostate and Seminal Vesicles 2. Development of Prostate 3. Pelvic and Prostatic Trauma 4. Prostatic Infarct and Cysts 5. Prostatitis 6. Prostatic Tuberculosis and Calculi 7. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy I: Histology 8. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy II: Sites of Hypertrophy and Etiology 9. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy III: Complications and Medical Treatment 10. Carcinoma of Prostate I: Epidemiology, PSA, Staging and Grading 11. Carcinoma of Prostate II: Metastases 12. Carcinoma of Prostate III: Diagnosis, Treatment, Palliation 13. Sarcoma of Prostate 14. Benign Prostate Surgery I--Suprapubic 15. Benign Prostate Surgery II--Retropubic 16. Benign Prostate Surgery III--Perineal 17. Benign Prostate Surgery IV--Transurethral 18. Malignant Prostate Surgery I--Retropubic 19. Malignant Prostate Surgery I--Perineal 20. Malignant Prostate Surgery I-Laparoscopic and Robotic 21. Seminal Vesicle Surgical Approaches 22. Anomalies of the Spermatic Cord Section 5 : Sperm and Ejaculation 1. Anatomy of a Sperm 2. Semen Analysis and Sperm Morphology 3. Azoospermia I: Sperm Production Problems-Genetics 4. Azoospermia II: Excurrent Duct Obstruction 5. Azoospermia III: Reproductive Microsurgery 6. Azoospermia IV: Diagnostic Procedures 7. Therapeutic Sperm Retrieval 8. Ejaculatory Disorders 9. Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction Section 6 : The Vulva 1. External Genitalia 2. Pudendal, pubic and inguinal regions 3. Perineum 4. Lymphatic drainage - external genitalia 5. Blood supply of perineum
4 6. Innervation of external genitalia and perineum 7. Dermatoses 8. Atrophic conditions 9. Circulatory and other disturbances 10. Diabetes, trichomoniasis, moniliasis 11. Vulvar Vestibulitis 12. Gonorrhea 13. Syphilis 14. Chancroid and other infections 15. Cysts 16. Benign tumors 17. Malignant tumors 18. Female Circumcision Section 7 : The Vagina 1. The Vagina 2. Pelvic Diaphragm I - From below 3. Pelvic Diaphragm II - From above 4. Support of pelvic viscera 5. Female urethra 6. Vulva and vagina histology 7. Vagina - cytology 8. Congenital anomalies 9. Imperforate hymen, hematocolpos, fibrous hymen 10. Vaginitis I - Trichomonas, Monilia, Bacterial Vaginosis 11. Vaginitis II - Venereal Infections 12. Vaginitis III - Chemical, traumatic 13. Toxic shock syndrome 14. Trauma 15. Cystocele, urethrocele 16. Rectocele, enterocele 17. Fistulae 18. Atrophic conditions 19. Cysts and Benign Tumors 20. Endometriosis I - Vulva, Vagina, Cervix 21. Malignant Tumors I -Primary 22. Malignant Tumors II - Metastases and Extension Section 8 : The Uterus and Cervix 1. Pelvic Viscera 2. Pelvic Viscera and Support - From Above 3. Blood supply of uterus and pelvic organs 4. Lymphatic drainage I - Pelvis 5. Lymphatic drainage II - Internal genitalia 6. Innervation of internal genitalia 7. Uterus and adnexa 8. Uterine development and musculature 9. Endometrial blood supply
5 10. Endometrial cycle 11. Dysmenorrhea 12. Congenital anomalies 13. Displacements 14. Prolapse 15. Perforation 16. Lacerations, strictures, polyps 17. Cervicitis I - Erosions, external infections 18. Cervicitis II - Gonorrhea, Chlamydial infections 19. Cancer of cervix I - Cytology 20. Cancer of cervix II -Various stages and types 21. Cancer of cervix III - Extension and metastases 22. Causes of uterine bleeding 23. Relationships in endometrial hyperplasia 24. Adenomyosis 25. Asherman s Syndrome (uterine synechia) 26. Endometrial hyperplasia, polyps 27. Myoma (Fibroid) I - Locations 28. Myoma (Fibroid) II - Secondary changes 29. Myoma (Fibroid) III - Degeneration, obstruction 30. Sarcoma 31. Cancer of corpus I - Various stages and types 32. Cancer of corpus II - Histology and extension Section 9 : The Fallopian Tubes 1. Fallopian tubes 2. Congenital anomalies I - Absence. rudiments 3. Congenital anomalies II - Atresia, defects 4. Bacterial routes, parametritis, acute salpingitis I 5. Acute salpingitis II, pyosalpinx 6. Hydrosalpinx 7. Pelvic peritonitis, abscess 8. Chronic salpingitis, adhesions 9. Obstruction following chronic salpingitis 10. Tubo-ovarian abscess 11. Tuberculosis 12. Salpingitis Isthmica Nodosa, carcinoma 13. Para-ovarian or Epoöphoron cyst Section 10 : The Ovaries 1. Ovarian structures and development 2. Endocrine relations during cycle 3. Ovarian cycle 4. Hormonal influence during life 5. Menopause 6. Developmental anomalies 7. Gonadal dysgenesis 8. Physiologic variations, nonneoplastic cysts
6 9. Endometriosis II - Pelvis 10. Infections 11. Serous cystoma and cystadenoma 12. Papillary serous cystadenoma 13. Papilloma, serous adeno- and cystadenofibroma 14. Mucinous cystadenoma 15. Teratomata 16. Adnexal Torsion 17. Feminizing neoplasms 18. Masculinizing neoplasms 19. Endocrinopathies I - Luteinization 20. Endocrinopathies II - Polycystic ovary syndrome 21. Dysgerminoma, Brenner tumor 22. Stromatogenous neoplasms 23. Primary cystic carcinoma 24. Primary solid carcinoma 25. Secondary ovarian carcinoma 26. Diagnosis of ovarian neoplasms 27. Conditions simulating ovarian neoplasms I 28. Conditions simulating ovarian neoplasms II Section 11 : The Ovum and Reproduction 1. The Oocyte and Ovulation 2. Fertilization 3. Genetics of Reproduction 4. Infertility I - Causes 5. Infertility II - Evaluation Female 6. Infertility III - Evaluation Male 7. Recurrent abortion 8. Assisted Reproduction 9. Contraception Section 12 : Pregnancy 1. Implantation and early development of ovum 2. Developmental events of the first trimester 3. Developmental events of the second trimester 4. Developmental events of the third trimester 5. Development of placenta and fetal membranes 6. Circulation in placenta 7. Hormonal fluctuations in pregnancy 8. Ectopic pregnancy I - Tubal pregnancy 9. Ectopic pregnancy II - Rupture, abortion 10. Ectopic pregnancy III - Interstitial, abdominal, ovarian 11. Abortion 12. Cervical insufficiency 13. Multiple gestation 14. Placenta I - Form and structure 15. Placenta II - Numbers, cord, membranes
7 16. Placenta previa 17. Abruptio placentae 18. Placenta accreta 19. Couvelaire uterus, Amniotic fluid embolism 20. Nodular lesions of placenta other than true infarcts 21. Gestational trophoblastic disease 22. Neuropathways in parturition 23. Normal birth 24. Operative vaginal delivery 25. Obstetric lacerations I - Vagina, perineum, vulva 26. Obstetric lacerations II - Fibromuscular support 27. Cesarean delivery 28. Rupture of the uterus 29. Uterine inversion 30. Urinary complications of pregnancy 31. Preeclampsia I - Symptomatology 32. Preeclampsia II -Ophthalmologic changes in preeclampsia and eclampsia 33. Preeclampsia III - Visceral lesions in preeclampsia and eclampsia 34. Preeclampsia IV - Placental infarcts 35. Causes of decreased maternal circulation 36. Intrauterine growth restriction 37. Erythroblastosis fetalis (Rh sensitization) 38. Syphilis 39. Puerperal infection Section 13 : The Mammary Gland 1. Position and structure 2. Blood supply 3. Lymphatic drainage 4. Developmental stages 5. Functional changes and lactation 6. Polythelia, polymastia, hypertrophy 7. Gynecomastia 8. Painful engorgement, puerperal mastitis 9. Galactorrhea 10. Mondor s disease 11. Breast Imaging 12. Fibrocystic change I - Mastodynia 13. Fibrocystic change II - Adenosis 14. Fibrocystic change III - Cystic change 15. Benign fibroadenoma, intracystic papilloma 16. Giant myxoma, sarcoma 17. Breast cancer 18. Intraductal and lobular adenocarcinoma 19. Inflammatory carcinoma
8 20. Hereditary breast disease 21. Paget's disease of the nipple 22. Malignancies of male breast Selected REferences Index
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
reproductive organs. Malignant neoplasms. 4. Inflammatory disorders of female reproductive organs 2 5. Infertility. Family planning.
 Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
MODELS ON PATHOLOGY. Each Rs. 7000/-
 MODELS ON PATHOLOGY. Each Rs. 7000/- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. 1. Myocardial Infraction. 2. Rheumatic Heart Disease. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 1. Chronic Bronchitis. 2. Cystic Fibrosis. 3. Asthma. 4. Collagen -
MODELS ON PATHOLOGY. Each Rs. 7000/- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. 1. Myocardial Infraction. 2. Rheumatic Heart Disease. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 1. Chronic Bronchitis. 2. Cystic Fibrosis. 3. Asthma. 4. Collagen -
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chris Davies & Greg Handley
 Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
DISORDERS OF MALE GENITALS
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Pathology of the female genital tract
 Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase
 Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Log Title: OBRES Gynecologic Case Log
 Log Title: OBRES Gynecologic Case Log Hospital/Institution: (Lookup) Attending Physician (Lookup) Is Patient Pregnant? ( Y or N) MEDRECNO: (text) Date (encounter) (Date) Diagnosis DX GYN Acute Pelvic Pain
Log Title: OBRES Gynecologic Case Log Hospital/Institution: (Lookup) Attending Physician (Lookup) Is Patient Pregnant? ( Y or N) MEDRECNO: (text) Date (encounter) (Date) Diagnosis DX GYN Acute Pelvic Pain
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Breast Carcinoma The Hard Way
 Women s Health Breast Carcinoma The Hard Way C50 - Malignant neoplasm of breast C50.0 Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola C50.01 - Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola, female C50.011 - Malignant
Women s Health Breast Carcinoma The Hard Way C50 - Malignant neoplasm of breast C50.0 Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola C50.01 - Malignant neoplasm of nipple and areola, female C50.011 - Malignant
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Vascular Related Torsion Venous compression Hemorrhagic infarct Young men At night Very painful Can be reduced Scrotal Masses Testicular Tumors (solid
 Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Learning Outcomes: The following list provides the learning objectives that will be covered in the lectures, and tutorials of each week:
 Course Code Course Title ECTS Credits MED-309 Pathology II 6 School Semester Prerequisites Medical School Spring (Semester 6) MED-304 Pathology I Type of Course Field Language of Instruction Required Medicine
Course Code Course Title ECTS Credits MED-309 Pathology II 6 School Semester Prerequisites Medical School Spring (Semester 6) MED-304 Pathology I Type of Course Field Language of Instruction Required Medicine
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
MALE GENITAL SURGICAL PROCEDURES
 Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System TESTES and EPIDIDYMIS Testes produce male gametes (SPERMATOZOA) and male sex hormone TESTOSTERONE Found in pouch of skin called a SCROTUM Size of a small egg Made up of 250 lobules,
Male Reproductive System TESTES and EPIDIDYMIS Testes produce male gametes (SPERMATOZOA) and male sex hormone TESTOSTERONE Found in pouch of skin called a SCROTUM Size of a small egg Made up of 250 lobules,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders
 Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders Episode Overview: 1. Describe the presentation and RF for Adnexal torsion 2. List the imaging findings of adnexal torsion (US vs CT) 3. What is the management of adnexal
Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders Episode Overview: 1. Describe the presentation and RF for Adnexal torsion 2. List the imaging findings of adnexal torsion (US vs CT) 3. What is the management of adnexal
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
The Reproductive System
 The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
2/9/2015. Bartholin Cyst. Vulva: Squamous epithelium skin. Vagina: Squamous epithelium mucosa. Cervix: Ectocervix: squamous Endocervix: glandular
 Vulva: Squamous epithelium skin Bartholin Cyst Vagina: Squamous epithelium mucosa Cervix: Ectocervix: squamous Endocervix: glandular Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal
Vulva: Squamous epithelium skin Bartholin Cyst Vagina: Squamous epithelium mucosa Cervix: Ectocervix: squamous Endocervix: glandular Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal
Hths 2231 Laboratory 14 Alterations in the Reproductive System and STDs
 Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Click on the STD fact-sheet link under activity 1 to complete the information on the STD tables. Write the information on the lab worksheet. Activity #2: Complete
Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Click on the STD fact-sheet link under activity 1 to complete the information on the STD tables. Write the information on the lab worksheet. Activity #2: Complete
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Scrub In. The normal periodic discharge of the endometrial lining in a female is known as:
 Scrub In The normal periodic discharge of the endometrial lining in a female is known as: a. Dysmenorrhea b. Leukorrhea c. Menorrhagia d. Menstruation The scientific name for the beginning of the menses
Scrub In The normal periodic discharge of the endometrial lining in a female is known as: a. Dysmenorrhea b. Leukorrhea c. Menorrhagia d. Menstruation The scientific name for the beginning of the menses
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
[KT 556] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4086
![[KT 556] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4086 [KT 556] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4086](/thumbs/93/114130125.jpg) [KT 556] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4086 FINAL M.B.B.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Time : Three hours Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. What are the causes
[KT 556] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4086 FINAL M.B.B.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Time : Three hours Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. What are the causes
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Development of the urogenital system
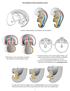 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Male Reproductive System. Anatomy
 Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Female Reproductive System
 21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
3 cell types in the normal ovary
 Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Code Conversion Table for Assisted Reproduction Codes arranged alphanumerically by ICD-10 code within category
 ABDOMEN 568 Abdominal Adhesions K66.0 789 Abdominal Pain NOS R10.9 789.6 Abdominal tenderness (rebound) R10.819 789.3 Mass, abdominal/pelvic R19.00 BREAST 611.72 Breast Lump N63 610.1 Fibrocystic disease
ABDOMEN 568 Abdominal Adhesions K66.0 789 Abdominal Pain NOS R10.9 789.6 Abdominal tenderness (rebound) R10.819 789.3 Mass, abdominal/pelvic R19.00 BREAST 611.72 Breast Lump N63 610.1 Fibrocystic disease
Chapter 15 The Reproductive Systems and Human Development. ANATOMY Loulousis
 Chapter 15 The Reproductive Systems and Human Development ANATOMY Loulousis Overview Main job ensure continuation of the human species Gonads in all sexually reproducing organisms Aid in sexual reproduction
Chapter 15 The Reproductive Systems and Human Development ANATOMY Loulousis Overview Main job ensure continuation of the human species Gonads in all sexually reproducing organisms Aid in sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX
 DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
Reproductive System Disorders
 Reproductive System Disorders Overview Male Infertility Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Prostate Cancer Female Infertility Endometriosis Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Ovarian Cysts Cancer Breast Cervical Uterine
Reproductive System Disorders Overview Male Infertility Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Prostate Cancer Female Infertility Endometriosis Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Ovarian Cysts Cancer Breast Cervical Uterine
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Code Conversion Table for Assisted Reproduction Codes arranged numerically by ICD-9 code
 112.1 Vulvavaginitis-Candidiasis B37.3 180 Cancer,cervix (canal) C53.0 182 Cancer, endometrium C54.1 183 Cancer, ovarian C56.9 218 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus D25.0 218.1 Intramural leiomyoma of uterus
112.1 Vulvavaginitis-Candidiasis B37.3 180 Cancer,cervix (canal) C53.0 182 Cancer, endometrium C54.1 183 Cancer, ovarian C56.9 218 Submucous leiomyoma of uterus D25.0 218.1 Intramural leiomyoma of uterus
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Code Conversion Table for Assisted Reproduction Codes arranged alphabetically by desriptor
 568 Abdominal Adhesions K66.0 789 Abdominal Pain NOS R10.9 633 Abdominal pregnancy O00.0 789.6 Abdominal tenderness (rebound) R10.819 793.5 Abnormal Radiology exam (HSG, USG) R93.8 792.2 Abnormal Sperm
568 Abdominal Adhesions K66.0 789 Abdominal Pain NOS R10.9 633 Abdominal pregnancy O00.0 789.6 Abdominal tenderness (rebound) R10.819 793.5 Abnormal Radiology exam (HSG, USG) R93.8 792.2 Abnormal Sperm
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Genito Urinary Pathology
 Duration: 5 Weeks (25 days) Genito Urinary Pathology Concepts Objectives Time T/L Activity Dept. Comments 3/SBM-5/01 Kidneys and the urinary tract a. Auto regulation of renal blood flow b. The basic functional
Duration: 5 Weeks (25 days) Genito Urinary Pathology Concepts Objectives Time T/L Activity Dept. Comments 3/SBM-5/01 Kidneys and the urinary tract a. Auto regulation of renal blood flow b. The basic functional
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
POST - DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE. Anatomy : Male and Female genital tract
 POST - DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE DURATION OF THE COURSE : TWO YEARS Detailed syllabus: Part 1 Basic Sciences: Anatomy : Male and Female genital tract Physiology Endocrinology
POST - DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE DURATION OF THE COURSE : TWO YEARS Detailed syllabus: Part 1 Basic Sciences: Anatomy : Male and Female genital tract Physiology Endocrinology
Question Bank III - BHMS
 Question Bank III - BHMS Sub:- Ob/Gy -Paper-II 1. Give the definition of Puberty. 2. Enumerate five important physical changes evident during puberty. 3. Write down the vaginal changes during puberty.
Question Bank III - BHMS Sub:- Ob/Gy -Paper-II 1. Give the definition of Puberty. 2. Enumerate five important physical changes evident during puberty. 3. Write down the vaginal changes during puberty.
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 22: The Reproductive System
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 22: The Reproductive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 60 year old man who recently had a urinary tract infection that was treated and resolved has returned complaining of increased
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 22: The Reproductive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 60 year old man who recently had a urinary tract infection that was treated and resolved has returned complaining of increased
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Chapter 7. Male Reproductive System
 Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System 1 Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents Sexual reproduction introduces new gene
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System 1 Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents Sexual reproduction introduces new gene
Lecture 28, The Reproductive System
 Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Anatomy of Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
College of Medicine Department of Medical Education Curriculum Development and Research Unit WEEK 1 REPRODUCTION BLOCK (Female)
 Week (1 ) 10/03/2019 to 14/03/2019 WEEK 1 REPRODUCTION BLOCK (Female) FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM & DEVELOPMENT 10 March 2019 8:00-9:00am 11 March 2019 8:00-10:00am 12 March 2019 13 March 2019 14 March
Week (1 ) 10/03/2019 to 14/03/2019 WEEK 1 REPRODUCTION BLOCK (Female) FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM & DEVELOPMENT 10 March 2019 8:00-9:00am 11 March 2019 8:00-10:00am 12 March 2019 13 March 2019 14 March
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
