EMBRIOLOGY Intermediate Mesoderm. Becomes the suprarenal glands, gonads, kidneys and associated tubes and vasculature
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM
2
3 EMBRIOLOGY Intermediate Mesoderm Becomes the suprarenal glands, gonads, kidneys and associated tubes and vasculature
4
5
6
7 THE VULVA 1. Mons : a pad of fat overlying the symphysis pubis and covered by skin & hairs. 2. Clitoris: an erectile cavernous structure below the symphysis pubis. formed of a small glans and two corpora cavernosa.
8 THE VULVA 3. Labia Majora: he outer 2 skin folds, raised by underlying fat, and passing back from the mons veneris to the perineum. The outer skin is covered by hairs while the inner medial surface is smooth, hairless and contains sebaceous and sweat glands. 4. Labia Minora: 2 thin folds of modified skin situated medial to the labia majora.
9 THE VULVA 5. The Hymen: a membrane, situated about 2 cm from the vestibule that demarcates the external from the internal genital organs, and partially closes the vaginal orifice.
10 Blood Supply Arterial Supply: Internal pudendal artery: The terminal branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery that ends as the dorsal artery of the clitoris. Branches from the femoral artery, supply the anterior part. Superficial and deep external pudendal arteries. Venous Drainage: The veins draining the vulva form a venous plexus from which veins accompany their corresponding arteries. The veins draining the clitoris join vaginal and vesical venous plexuses.
11 Lymphatic drainage and Nerve Supply Lymphatic Drainage of the vulva From the skin and appendages, to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, to the deep inguinal and femoral lymph nodes of which the lymph node of Cloquet drains the clitoris directly. From the former superficial group, lymphatic channels pass to the deep pelvic nodes including; the external iliac, common iliac, then para-aortic lymph nodes. Nerve Supply of the vulva The vulva is supplied mainly from the pudendalnerve (S 2, 3 & 4). Additional sensory nerves are supplied from; the Ilio-inguinal nerve (L1), the genital branch of genito-femoral nerve (L 1,2), and the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
12 THE VAGINA A fibromuscular tube from the vulva to the uterus forming an angle of 60 with the horizontal plane. Length: anterior wall is 8-9 cm posterior wall is cm Vaginal Fornices: The cervix projects in the upper blind end of the vagina that forms a pouch (vaginal pouch) around the cervix and is divided into four fornices : two lateral, anterior and posterior (deeper) fornices.
13 Anatomical Relations of the Vagina Anteriorly: Upper 1/3: trigone of urinary bladder Lower 2/3: urethra. Posteriorly: Upper 1/3: peritoneum of Douglas pouch. Middle 1/3: ampulla of rectum. Lower 1/3: the perineal body. Laterally: Lower end: Bulbocavernosus muscle, vestibular bulb, and Bartholin gland. 1 cm above orifice: urogenital diaphragm 2½ cm above the orifice: levator ani muscle with the pelvic fascia above it. The lateral fornix gives attachment, to the lower part of the cardinal ligaments. The ureters pass through the cardinal ligaments 1 cm lateral to the vagina.
14 Vaginal Supports Ligaments attached to the upper vagina: Pubocervical ligamentanteriorly, Mackenrodt s ligamentlaterally, Uterosacral ligament posteriorly. Levator ani muscles : pubo-vaginalis part Triangular ligament, and the Perineal membrane. Vaginal fascia:connective tissue fascia that condenses anteriorly forming the vesico-vaginal fascia and posteriorly forming the recto-vaginal fascia.
15 Histology of the Vagina The cut section of the vagina is H shaped with approximation of the anterior to the posterior vaginal walls. It is formed of Three layers; mucosa, formed of squamous epithelium without glands, the musculosa,which is fibromuscular with some fibres from the levator ani inserted into it, and the adventitia, which is connective tissue continuous with the paracolpos.
16 Blood Supply Arterial supply: The vaginal artery (from internal iliac artery) Additional branches from: Middle rectal artery (from internal iliac artery) Inferior rectal artery (from the internal pudendalartery, of the internal iliac artery) Venous drainage: A plexus around the vagina (the vaginal plexus), drain into the internal iliac vein by veins that accompany their corresponding arteries.
17 Lymphatic drainage and Nerve Supply Lymphatic drainage of the vagina lower 1/3 drains to the inguinal lymph nodes, upper 1/3 follows lymphatic drainage of the cervix, middle 1/3, drains in both upper and lower directions. Nerve supply of the vagina: The pudendal nerve gives sensory fibres to the lower vagina.
18 THE UTERUS A pear shaped hollow muscular organ Measuring around 7.5 x 4.0 x 2.5 cm in the longitudinal, transverse, and anteroposterior diameters. It is slightly larger in the multipara than in the nullipara.
19 Divisions 1. The corpus uteri: Bodythat lies above the internal os Cornu = the area of insertion of the fallopian tubes Fundus lies above the insertion of the tubes. Three structures are attached to the cornu round ligament anteriorly, Fallopian tube centrally, ovarian ligament posteriorly.
20 Divisions 2. The isthmus: an area 4-5 mm in length that lies between the anatomical internal os above, and the histological internal os below. It is lined by low columnar epithelium and few glands. The isthmus expands during pregnancy forming the lower uterine segment (10 cm) during the last trimester.
21 Divisions 3. The cervix: The elongated lower part of the uterus Measuring cm. Divided by the vaginal attachment into supravaginal portion above vaginal portion (portio-vaginalis) below. The external os is round in nulliparas and slit shaped in multiparas.
22 Position The uterus is kept in an anteverted anteflexed position (AVF),with the external os lying at the level of the ischial spines, by the support of the cervical ligaments, endopelvic fascia and pelvic floor muscles (levator ani). Anteversion:The uterus is inclined anteriorly to axis of the vagina. Anteflexion:The body of the uterus is bent forwards upon the cervix.
23 Relations of the Body of the Uterus Anteriorly: The bladder and vesicouterine pouch. Posteriorly: The pouch of Douglas. Laterally: The broad ligament on each side.
24 Relations of cervix Anteriorly: Urinary bladder. Posteriorly: Forms the anterior wall of Douglas pouch. Laterally: 1/2 an inch lateral to the internal os the ureteris crossed by the uterine artery (i.e. ureterbelow the uterine artery). The uterosacral, cardinal, and pubocervical ligaments are attached to its posterior, lateral, and anterior surfaces respectively.
25 Histology of the Uterus Three layers: 1. Endometrium: (mucosa) 2. Myometrium (musculosa) 3. The peritoneal covering or perimetrium
26 Histology of the Uterus Endometrium: Lined by simple cubical or columnar epithelium Contains tubular glands. Shows cyclic changes with the menstrual cycle under the influence of ovarian hormones
27 Histology of the Uterus Myometrium Three layers outer longitudinal muscle layer middle layer of interlacing crisscross muscle fibres surrounding the blood vessels inner circular muscle layer
28 Histology of the Uterus Perimetrium: Anteriorly: firmly attached to the fundusand body till the isthmus where it becomes loose and is reflected on the superior surface of the urinary bladder forming the vesicouterinepouch. Posteriorly: firmly attached to the fundus, body, cervix, and posterior vaginal fornix then is reflected on the pelvic colon forming the Douglas pouch. Laterally: the anterior and posterior peritoneal coverings blend as the anterior and posterior layers of the broad ligaments.
29 Histology of the Cervix Endocervix: Lined by simple columnar epithelium with compound racemose glands or crypts that are liable to chronic infection. It secretes alkaline cervical mucus. Muscle layer: Outer longitudinal and inner circular muscles.(2 layers only) Ectocervix: Formed of stratified squamous epithelium covering the outer portion of the cervix. The junction between squamous and columnar epithelium at the external os is either abrupt or it may form a transitional zone 1-3 mm known as the transformation zone.
30 Blood Supply Arterial supply: THE UTERINE ARTERIES Arise from the anterior division of internal iliac artery. in the base of the broad ligament, crossing above the ureter 1/2 an inch lateral to the supravaginal cervix. 2 branches: An ascending A descending branch
31 Blood Supply The ascending branches pass upwards in a tortuous manner parallel to the lateral border of the uterus between the 2 layers of the broad ligament to end by anastomosing with branches of the ovarian arteries near the uterine cornu. The descending cervical branch supplies the lower cervix.
32 Blood Supply Venous drainage: Starts as a plexus between the 2 layers of the broad ligament (Pampiniform plexus)that communicate with the vesical plexus and drains into the uterine and ovarian veins. Lymphatic drainage: Fundus: To the para-aortic lymph nodes via ovarian vessels. Cornu: To the superficial inguinal lymph nodes via lymphatics of the round ligament. Body: To the internal then external iliac lymph nodes via the uterine vessels. Isthmus: As that of the cervix. Cervix: Two groups of lymphatics: Primary groups: Paracervical, parametrial, obturator, internal and external iliac nodes. Secondary groups: Common iliac, para-aortic, and lateral sacral lymph nodes.
33 Nerve supply of the Uterus The cervix and body are relatively insensitive to touch, cutting and burning. The cervix is sensitive to dilatation and the body is sensitive to distension. Innervations Parasympathetic form S2,3,4 Sympathetic from: T5 and T6 (motor) T10, T11, T12, and L1 (sensory). Both reach the uterus through branches of inferior hypogastric plexus.
34 THE FALLOPIAN TUBE 2 tortuous tubes (10 cm in length) lie in the free upper part of the broad ligament. They blend medially with the cornu of the uterus Laterally their free outer end curves backwards towards the ovary. Their lumen communicates between the uterine and the peritoneal cavities.
35 THE FALLOPIAN TUBE 1. Interstitial part (1 cm):pierces the uterine wall, very narrow, no peritoneal covering, no outer longitudinal muscles. 4 parts 2. Isthmus (2 cm): straight, narrow, thick walled portion lateral to uterus. 3. Ampulla (5 cm): the widest, tortuous, thin walled outer part. 4. Infundibulum (2 cm): trumpet shaped outer end opens into the peritoneal cavity by the tubal ostium. The ostuim is surrounded by fimbriae, one of which is long and directed towards the ovary (fimbria ovarica).
36 Tubal functions Ovum Pick Up, at the time of ovulation, by their free fimbrial end, Transport Of The Ovathrough the tubal lumen, by their peristaltic and ciliary movements, and Production Of Secretionsnecessary for capacitation of the sperm and nutrition of the ova during their journey, by their lining cells.
37 Anatomical Relations Bounded above by loops of intestine belowby the broad ligament and its contents. mediallythey blends with cornu of the uterus while laterally they are bounded by the lateral pelvic wall. The ovaries lie posterior and inferior to the Fallopian tubes at each side.
38 Histology of the Fallopian tubes Mucosa (endosalpnix):arranged into 4-5 main longitudinal ridges that give rise to subsidiary folds or plicae. It is lined by columnar partially ciliated epithelium. Muscle layer:outer longitudinal and inner circular involuntary smooth muscles. It is thick at the isthmus and thin at the ampulla. Serosa (peritoneal covering): The extrauterine part is covered by peritoneum in the upper margin of the broad ligament.
39 Blood Supply & Lymphatic Drainage Arterial supply: branches from both the uterine artery, and the ovarian artery. Venous drainage: Right ovarian vein drains directly into the IVC Left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein. Lymphatic drainage: para-aortic LNs directly via ovarian lymphatics. Nerve supply sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres
40 THE OVARY Almond shaped Lying in the fossa ovarica on the lateral pelvic wall, Measuring 3 x 2 x 1 cm. Not covered by peritoneum. Surface is pearly white and corrugated by the effect or the monthly ovulatory activity.
41 Ovarian Attachments Three attachments: The mesovarium:a peritoneal fold that suspends the ovary to the back of the broad ligament. The infundibulopelivc ligament: suspends the upper pole of the ovary to the lateral pelvic wall and carries the ovarian vessels, nerves and lymphatics. The ovarian ligament:attaches the lower pole to the cornu of the uterus.
42 Anatomical Relations Theovary is bounded mediallyby the Fallopian tube, laterallyby the lateral pelvic wall. superiorly and anteriorlyit is surrounded by the small intestine inferiorly by the ovarian fossa where the ureter and the internal iliac vessels pass.
43 Histology of the Ovary
44 Blood Supply and Lymphatic Drainage Arterial supply: Ovarian artery: Arises from the aorta at the level of L2 and passes through the infundibulopelvic ligament. Ovarian branch from the uterine artery; which anastomose with the ovarian vesels at the broad ligament. Venous drainage: The ovarian veins accompany the arterial supply, and join with the pampiniform plexus of veins and the uterine vein. Lymphatic drainage: to the para-aortic LNs via the ovarian vessels. Nerve supply insensitive except to squeezing on P.V examination. sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves (T10 and T11) through the preaortic plexus that accompany the ovarian vessel.
45 UTERINE AND CERVICAL LIGAMENTS Broad ligament Round ligament Ovarian ligament
46 THE BROAD LIGAMENT The broad ligament is a double sheet of peritoneum that extends from the lateral wall of the uterus to the lateral pelvic wall. Its outer upper part forms the infundibulopelvic ligament in which the ovarian vessels traverse there way to the ovary.
47 Contents of the Broad Ligament Round ligament Ovarian vessels Uterine vessels Ureter Parametrial lymphatics and lymph nodes Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves Parametrial pelvic cellular tissue and fascia Embryological remnants of the Wolffian ducts Hydatid cyst of Morgagni Koblet s tubules Epoophoron Paroophoron Gartner s duct
48 The Round Ligament A fibromuscular ligament attached to the uterine cornu. Runs downwards and forwards in between the two leafs of the broad ligament to enter the inguinal canal via the internal inguinal ring and comes out of it at the external inguinal ring to be inserted in the upper part of the labium majus. It pulls the uterus forwards and help keeping it in an anteverted position.
49 The ovarian ligament A fibromuscular ligament that attaches the inner lower pole of the ovary to the cornu of the uterus. It plays no role in pelvic support of the uterus.
50 THE CERVICAL LIGAMENTS
51 Three Pairs of Ligaments Mackenrodt s ligaments(the cardinal ligaments of the cervix): spread out on either side from the lateral surface of the cervix and vagina, in a fan-shaped manner, and are inserted in the lateral pelvic wall. Utero-sacral ligaments: From the cervix and vagina, backwards surrounding the rectum and below the uterosacral folds of peritoneum, to become inserted in the third piece of the sacrum. Pubo-cervical ligaments:extend from the anterior surface of the cervix and vagina, forwards beneath the bladder and surrounding the urethra, to the posterior surface of the pubis.
52
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
The Female and Male External Genitalia. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Pelvis MCQs. Block 1. B. Reproductive organs. C. The liver. D. Urinary bladder. 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: E.
 Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia. Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Urinary Bladder. Prof. Imran Qureshi
 Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal. Yes, with uterine artery (collateral circulation between abdominal +pelvic source)
 Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
~ Bobbitt Laboratories Human Female Genital Organs 1308 RAINEY STREET BURLINGTON, N. C
 56-6935 Human Female Genital Organs ~ Bobbitt Laboratories 1308 RAINEY STREET BURLINGTON, N. C. 27215 Printed in U.S.A. 1974 Bobbitt Laboratories, Inc. BB169357402/356-6935 Human Female Genital Organs
56-6935 Human Female Genital Organs ~ Bobbitt Laboratories 1308 RAINEY STREET BURLINGTON, N. C. 27215 Printed in U.S.A. 1974 Bobbitt Laboratories, Inc. BB169357402/356-6935 Human Female Genital Organs
The Female Reproductive System
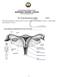 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Pelvis Perineum MCQs. Block 1.1. A. Urinary bladder. B. Rectum. C. Reproductive organs. D. The thigh
 Pelvis Perineum MCQs Block 1.1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The coccygeus B. The levator ani C. The external urethral sphincter D. The internal urethral sphincter E. The obturator
Pelvis Perineum MCQs Block 1.1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The coccygeus B. The levator ani C. The external urethral sphincter D. The internal urethral sphincter E. The obturator
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA
 1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology
 Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Aniko Szabo Hill 1 of 12
 Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale. Category or Criterion. Rationale or Comments (1) (2) (3) (4)
 Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space
 Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Perineum. Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying
 Perineum Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying OUTLINE Subdivision The Layers Urogenital Diaphragm Main Structures inside Superficial & Deep Perineal Spaces Ischioanal Fossa Perineum A narrow region Urogenital
Perineum Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying OUTLINE Subdivision The Layers Urogenital Diaphragm Main Structures inside Superficial & Deep Perineal Spaces Ischioanal Fossa Perineum A narrow region Urogenital
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 The Human Urogenital Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 The Human Urogenital Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان-
 -6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
-6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
Learning objectives. SGD on Functions of Testosterone. Class
 Learning objectives SGD on Functions of Testosterone Class 2016 14-1-2013 Discuss o Process of spermatogenesis. o Sex determination. o Process of maturation of sperms. o Physiology of mature sperms. Discuss
Learning objectives SGD on Functions of Testosterone Class 2016 14-1-2013 Discuss o Process of spermatogenesis. o Sex determination. o Process of maturation of sperms. o Physiology of mature sperms. Discuss
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Objectives. Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble. Disclosures. Anatomy 101. Anterior Abdominal Wall. Arcuate Line. Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C)
 Objectives Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C) To focus on key anatomy for the gynaecologic surgeon advancing their minimally invasive gynaecologic skills To provide
Objectives Pelvic Anatomy: Staying Out of Trouble Abheha Satkunaratnam MD, FRCS(C) To focus on key anatomy for the gynaecologic surgeon advancing their minimally invasive gynaecologic skills To provide
Female Reproductive System
 21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
Basic Sciences in Obstetrics and Gynecology
 Section One Basic Sciences in Obstetrics and Gynecology 1 Anatomy Teaching is only demonstrating that it is possible, Learning is making it possible for yourself. Anatomy of Female Genital Tract An understanding
Section One Basic Sciences in Obstetrics and Gynecology 1 Anatomy Teaching is only demonstrating that it is possible, Learning is making it possible for yourself. Anatomy of Female Genital Tract An understanding
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra
 Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra Please check our Editing File هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Lecture 2 } و م ن ي ت و ك ع ل ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { Objectives o Describe the course of ureter
Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra Please check our Editing File هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Lecture 2 } و م ن ي ت و ك ع ل ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { Objectives o Describe the course of ureter
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
-15. -Alaa Albandi. -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib. 0 P a g e
 -15 -Alaa Albandi - -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib 0 P a g e In this last lecture, we will talk about the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. Sigmoid colon It has a mesentery called pelvic mesocolon or sigmoidal
-15 -Alaa Albandi - -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib 0 P a g e In this last lecture, we will talk about the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. Sigmoid colon It has a mesentery called pelvic mesocolon or sigmoidal
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Gross anatomy of the urinary system. Done by : razan krishan. slide in bold and book in green
 Gross anatomy of the urinary system Done by : razan krishan slide in bold and book in green Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and
Gross anatomy of the urinary system Done by : razan krishan slide in bold and book in green Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and
Inguinal Canal. It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Present in both sexes
 Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Pelvic Angiogram - Male
 Pelvic Angiogram - Male Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Lateral sacral artery Iliolumbar artery Posterior trunk of internal iliac artery Superior gluteal artery Internal pudendal artery External
Pelvic Angiogram - Male Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Lateral sacral artery Iliolumbar artery Posterior trunk of internal iliac artery Superior gluteal artery Internal pudendal artery External
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 24
 primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
Applied Anatomy For Obstetrics and Gynecology
 Applied Anatomy For Obstetrics and Gynecology Shashank V Parulekar Applied Anatomy For Obstetrics and Gynecology Shashank V Parulekar Professor and Head Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Seth G.
Applied Anatomy For Obstetrics and Gynecology Shashank V Parulekar Applied Anatomy For Obstetrics and Gynecology Shashank V Parulekar Professor and Head Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Seth G.
1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation is the: Endometrium Myometrium Mesometrium Cervical mucosa Rugae 2.
 1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation is the: Endometrium Myometrium Mesometrium Cervical mucosa Rugae 2. The extension of the vaginal lumen around the intravaginal part
1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation is the: Endometrium Myometrium Mesometrium Cervical mucosa Rugae 2. The extension of the vaginal lumen around the intravaginal part
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
The Reproductive System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II The Reproductive System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapters
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II The Reproductive System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapters
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics.
 NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
Urinary system. Urinary system
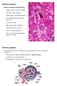 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Rama Nada. - Ensherah Mokheemer. - Ahmed salman. 1 P a g e
 - 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
- 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 21 Female Reproductive System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of female reproductive system
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 21 Female Reproductive System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of female reproductive system
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 1. Introduction I. 2. Lecturers I. 3. Timetable I. 4. Assessment I. 5. Study material II. 6. General information II.
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT 1. Introduction I 2. Lecturers I 3. Timetable I 4. Assessment I 5. Study material II 6. General information II B. STUDY COMPONENT 1. Block XI: Session
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page A. ORGANISATIONAL COMPONENT 1. Introduction I 2. Lecturers I 3. Timetable I 4. Assessment I 5. Study material II 6. General information II B. STUDY COMPONENT 1. Block XI: Session
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL
 ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
Cardiovascular Digestive. Endocrine Integumentary
 General Anatomy Match the Components and Functions with their respective primary Anatomical System COMPONENTS / DESCRIPTION CODE Anatomical System Primary Function 1. Fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles
General Anatomy Match the Components and Functions with their respective primary Anatomical System COMPONENTS / DESCRIPTION CODE Anatomical System Primary Function 1. Fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida. Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS
 NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS IOANNIS VARKARAKIS ASOSCIATE PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY 2 ND DEPT OF UROLOGY NATIONAL & KAPODISTRIAN UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS PENILE GROSS ANATOMY 3 ERECTILE COLUMNS TWO CORPORA CAVERNOSA
NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS IOANNIS VARKARAKIS ASOSCIATE PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY 2 ND DEPT OF UROLOGY NATIONAL & KAPODISTRIAN UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS PENILE GROSS ANATOMY 3 ERECTILE COLUMNS TWO CORPORA CAVERNOSA
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Adductor canal (Subsartorial) or Hunter s canal
 Adductor canal (Subsartorial) or Hunter s canal John Hunter described the exposure and ligation of the femoral artery in this canal for aneurysm of the popliteal artery; this method has the advantage that
Adductor canal (Subsartorial) or Hunter s canal John Hunter described the exposure and ligation of the femoral artery in this canal for aneurysm of the popliteal artery; this method has the advantage that
Clinical pelvic anatomy
 1 Section one Fundamentals Clinical pelvic anatomy Introduction 1 Obstetric anatomy 1 The bony pelvis 1 The pelvic organs during pregnancy 2 The uterus 2 The cervix 3 Additional changes 3 The urinary tract
1 Section one Fundamentals Clinical pelvic anatomy Introduction 1 Obstetric anatomy 1 The bony pelvis 1 The pelvic organs during pregnancy 2 The uterus 2 The cervix 3 Additional changes 3 The urinary tract
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
 The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistance Professor of Anatomy &embryology PELVIS Learning Objectives 1. Bony pelvis, its joints and
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistance Professor of Anatomy &embryology PELVIS Learning Objectives 1. Bony pelvis, its joints and
B) cervix of uterus C) vagina D) rectum. 1. What number illustrates the adnexal area? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 5 C) 8 D) 9
 Pelvis Practice Problems 1. What number illustrates the adnexal area? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 5 C) 8 D) 9 2. What number illustrates the cervix? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 8 C) 5 D) 6 3. Which of the following is
Pelvis Practice Problems 1. What number illustrates the adnexal area? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 5 C) 8 D) 9 2. What number illustrates the cervix? (Fig. 4-64) A) 4 B) 8 C) 5 D) 6 3. Which of the following is
Bony ypelvis. Composition: formed by coccyx, and their articulations Two portions
 Pelvis Bony ypelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations Two portions Greater pelvis Lesser pelvis Terminal line ( pelvic inlet): formed by promontory of sacrum,
Pelvis Bony ypelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations Two portions Greater pelvis Lesser pelvis Terminal line ( pelvic inlet): formed by promontory of sacrum,
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O.
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
Anatomy of the renal system. Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi
 Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
HUMAN REPRODUCTION SYSTEM
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION SYSTEM The human reproductive system usually involves internal fertilization by sexual intercourse. During this process, the male inserts his erect penis into the female's vagina and
HUMAN REPRODUCTION SYSTEM The human reproductive system usually involves internal fertilization by sexual intercourse. During this process, the male inserts his erect penis into the female's vagina and
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Anatomy Review File اللهم ال سهل إال ماجعلته سهال وأنت تجعل الحزن
 Anatomy Review File اللهم ال سهل إال ماجعلته سهال وأنت تجعل الحزن إذا شئت سهال This work was done by: Alanoud Abuhaimed Dania Alkelabi Ghada Alothaim Jawaher Abanumy Rawan AlWadee Wejdan Alzeid Mohanad
Anatomy Review File اللهم ال سهل إال ماجعلته سهال وأنت تجعل الحزن إذا شئت سهال This work was done by: Alanoud Abuhaimed Dania Alkelabi Ghada Alothaim Jawaher Abanumy Rawan AlWadee Wejdan Alzeid Mohanad
Slide Read the tables it is about the difference between male & female pelvis.
 I didn t include the slides, this is only what the doctor read or said because he skipped a lot of things because we took it previously, very important to go back to the slides (*there is an edited version)
I didn t include the slides, this is only what the doctor read or said because he skipped a lot of things because we took it previously, very important to go back to the slides (*there is an edited version)
The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska
 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The reproductive system is designed to perpetuate the species
27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The reproductive system is designed to perpetuate the species
