Supplementary Material
|
|
|
- Allen Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental Figure 1. Effect of the strong androgen receptor inhibitor enzalutamide in combination with the second generation mtor inhibitors BEZ235 or INK128 in PC346C, C4-2 and C4-2b cells. (A, B) MTT viability assay of PC346C and C4-2b cells treated with 10nM of BEZ235 alone or in combination with 1uM of enzalutamide. (C, D) MTT viability assay of PC346C and C4-2 cells treated with 25nM of INK128 alone or in combination with 1uM of enzalutamide. C4-2 and C4-2b, which is a sub-cell line of C4-2, were more susceptible to the mtor inhibitors alone or in combination with enzalutamide while PC346C showed little effect to BEZ235 alone or in combination. INK128 was more effective against PC346C but not to the extent of the effect demonstrated in C4-2 cell. 1
2 Supplemental Figure 2. Effect of the mtor inhibitor RAD001 alone on mtor pathway proteins in C4-2 and PC346C cells. Western blot of C4-2 and PC346C treated with RAD001 for different time points up to 4 days depicting the effect of mtor inhibition on the expression and phosphorylation of various proteins. RAD001 alone is sufficient to inhibit mtor activity shown by the decrease phosphorylation of its both direct targets, 4EBP1 and P70S6K but increased eif4e phosphorylation in C4-2. Right panel shows a very low exposure of eif4e phosphorylation in PC-346C cells, where eif4e phosphorylation levels are very high. Supplemental Figure 3. Effect of different mtor inhibitors in the nontumor prostate line prns1-1 transfected with wild type AR. MTT viability assay of PRNS1-1 cells transfected with wild type AR and treated with RAD001, BEZ235 or INK128. The presence of androgen receptor in these cells made them sensitive to mtor inhibitors similar to the transfection of the mutated version (or AR (T877A) demonstrated on figure 3E). 2
3 Supplemental Figure 4. Effect of PTEN over expression on eif4e and Akt phosphorylation and on cell growth in the presence of RAD001 and bicalutamide in C4-2 cells. (A) Western blot of C4-2 cells transfected with empty vector or a plasmid expressing PTEN showing a decrease in phosphorylation of eif4e and Akt. (B-C) MTT viability assay of C4-2 transfected either with control (B) or PTEN overexpression (C) treated with RAD001, Casodex or the combination. 3
4 Supplemental Figure 5. Inhibition of eif4e phosphorylation caused by a Mnk1/2 inhibitor sensitizes CRPC cells to mtor inhibitors and AR antagonists. (A) Western blots of C4-2 cells treated with CGP57380, INK128 and either AR antagonist bicalutamide or enzalutamide and the different combinations for 48 hours. Both AR antagonists increase phosphorylation at Ser209 eif4e which is prevented by addition of the Mnk inhibitor CGP57380 or the strong mtorc1 and C2 inhibitor INK128. (B, C) MTT viability assay of C4-2 and PC346C treated with mtor inhibitor RAD001, AR antagonist enzalutamide and the Mnk inhibitor CGP C4-2 cells are sensitive to mtor inhibition alone, but the resistant cell line PC346C shows decreased viability when Mnk is inhibited by CGP57380 and paired with an mtor inhibitor. (D) Effect of CGP57380, RAD001 or the combination on apoptosis in C4-2 and PC346C measured by Annexin V FITC x PI flow cytometry. 4
5 Supplemental Figure 6. P70S6K phosphorylation inhibition caused by treatment with the Mnk inhibitor CGP Western blots of LNCaP (A), 22Rv1 (B) and CWR-R1 cells (C) treated either with the Mnk inhibitor CGP57380, the mtor C1 and C2 strong inhibitor INK128 or the combination showing effects of Mnk inhibition on P70S6K phosphorylation in PTEN positive (CWR22-R1 and 22Rv1) and negative (LNCaP) cells. (D-E) Western blots of PC346C and C4-2 treated with the PI3K inhibitor BKM120, RAD001, BEZ235, INK128 and the combinations for 48 hours. 5
6 Supplemental Figure 7. mrna transcription levels of the eif4e target proteins surviving, c-myc and Cyclin D1 in C4-2 and PC-346C cells treated with Bicalutamide (BIC), RAD001, or the combination. (A) C4-2 cells were plated in triplicate and treated as shown. mrna expression was determined by qpcr. Data represents mean±s.d. of triplicates, and show the effect of the drug treatments on the expression of survivin, c-myc and cyclin D1. (B) Effect of the same drugs on the expression of the three genes in PC-346C cells. Starred variables represent those significantly different from the corresponding control (p<0.05) as determined by t-test. 6
7 Supplemental Figure 8. Schematic representation of the mtor signaling pathway and targets of the drugs used on this study. mtor acts in complex with raptor (mtorc1) or with rictor (mtorc2). mtorc1 increases mrna translation by phosphorylation of the downstream target eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eif4e) binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), while mtorc2 activates Akt phosphorylation at Ser473, among other targets. Akt is also phosphorylated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) at Thr308 for complete activation, which can phosphorylate key residues on the androgen receptor (AR). The AR inhibits activation of various kinases including Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) which is activated by AR inhibition by antiandrogens such as bicalutamide and enzalutamide. In the unphosphorylated state, 4E-BP1 binds eif4e and keeps it inactive. 4E-BP1 phosphorylation by mtorc1 releases eif4e which associates with eif4g and eif4a to form the translational initiation complex eif4f. This enables eif4e binding to the m7g cap at the 5 -end of eukaryotic mrnas, which initiates cap-dependent translation. Here, our data indicate that phosphorylation of eif4e at S209 by MAPK-Interacting Kinase 1 and 2 (Mnk1/2) downstream of MAPK activation prevents cap-independent translation, whereas inhibition of Mnk by CGP57380 shifts translation back to a cap-dependent mechanism. 7
Targeted mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for Olaparib pharmacokinetics. For LC/MS/MS of Olaparib pharmacokinetics metabolites were extracted from
 Supplementary Methods: Targeted mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for Olaparib pharmacokinetics For LC/MS/MS of Olaparib pharmacokinetics metabolites were extracted from mouse tumor samples and analyzed as
Supplementary Methods: Targeted mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for Olaparib pharmacokinetics For LC/MS/MS of Olaparib pharmacokinetics metabolites were extracted from mouse tumor samples and analyzed as
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway is dominant over androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells
 Cellular Oncology 32 (2010) 11 27 11 DOI 10.3233/CLO-2009-0487 IOS Press PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway is dominant over androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells Mari Kaarbø a,, Øyvind Løveseter Mikkelsen
Cellular Oncology 32 (2010) 11 27 11 DOI 10.3233/CLO-2009-0487 IOS Press PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway is dominant over androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells Mari Kaarbø a,, Øyvind Løveseter Mikkelsen
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original
 Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
Dox. R26-rtTA Tyr-CreERT2. any ink/arf, no rtta (n=8) ink/arf +/+ (n=5) Day 0 Day 11 Day 18 Day 28
 A 4OHT Dox hraf iip tumors inras ddh 2 O -RT Ink/Arf / Pten l/ l R26-lsl-rtTA Tyr-reERT2 TetO-hRAF V6E Ink/Arf / Pten / R26-rtTA Tyr-reERT2 TetO-hRAF V6E Ink/Arf / Pten / R26-rtTA Tyr-reERT2 TetO-hRAF
A 4OHT Dox hraf iip tumors inras ddh 2 O -RT Ink/Arf / Pten l/ l R26-lsl-rtTA Tyr-reERT2 TetO-hRAF V6E Ink/Arf / Pten / R26-rtTA Tyr-reERT2 TetO-hRAF V6E Ink/Arf / Pten / R26-rtTA Tyr-reERT2 TetO-hRAF
mtor plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions
 Supplementary Information mtor plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions Shyuichiro Matsubara 1, Qiang Ding 1, Yumi Miyazaki 1, Taisaku Kuwahata
Supplementary Information mtor plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions Shyuichiro Matsubara 1, Qiang Ding 1, Yumi Miyazaki 1, Taisaku Kuwahata
Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 28, 2014 Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Outline 1.
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 28, 2014 Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Outline 1.
Bhatnagar et al, 2010 Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS T
 Bhatnagar et al, Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS--98-T Supplemental Materials. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure (A) WPE-NA and WPE-NB6 cells were treated with 4 nm of Docetaxel
Bhatnagar et al, Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS--98-T Supplemental Materials. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure (A) WPE-NA and WPE-NB6 cells were treated with 4 nm of Docetaxel
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
 SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Crystal violet assay Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured in media supplemented with % FBS for 7 days. Media were then removed, plates were briefly washed
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Crystal violet assay Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured in media supplemented with % FBS for 7 days. Media were then removed, plates were briefly washed
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer
 Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/Pkb Kinase in the Development of Hormone- Independent Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/Pkb Kinase in the Development of Hormone- Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Linda A. degraffenried, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
AD Award Number: TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/Pkb Kinase in the Development of Hormone- Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Linda A. degraffenried, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
Rationale Design of Combination Therapy in Prostate Cancer: Targeting the AR and PI3K pathways
 Rationale Design of Combination Therapy in Prostate Cancer: Targeting the AR and PI3K pathways Brett S Carver, MD Assistant Attending, Department of Surgery/Urology Prostate Cancer Therapeutics: A Changed
Rationale Design of Combination Therapy in Prostate Cancer: Targeting the AR and PI3K pathways Brett S Carver, MD Assistant Attending, Department of Surgery/Urology Prostate Cancer Therapeutics: A Changed
TITLE: Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors of the Akt Protein Kinase by Modulation of the Pim Kinase Pathway
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0560 TITLE: Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors of the Akt Protein Kinase by Modulation of the Pim Kinase Pathway PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Andrew S. Kraft, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0560 TITLE: Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors of the Akt Protein Kinase by Modulation of the Pim Kinase Pathway PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Andrew S. Kraft, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Aloe-emodin suppresses prostate cancer by targeting the mtor complex 2
 Carcinogenesis vol.33 no.7 pp.1406 1411, 2012 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs156 Advance Access publication April 24, 2012 Aloe-emodin suppresses prostate cancer by targeting the mtor complex 2 Kangdong Liu 1,2,3,
Carcinogenesis vol.33 no.7 pp.1406 1411, 2012 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs156 Advance Access publication April 24, 2012 Aloe-emodin suppresses prostate cancer by targeting the mtor complex 2 Kangdong Liu 1,2,3,
Supplemental Data. Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mtorc2 Assembly and Akt/PKB. Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Supplemental Data Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mtorc2 Assembly and Akt/PKB Dos D. Sarbassov, Siraj M. Ali, Shomit Sengupta, Joon-Ho Sheen, Peggy P. Hsu, Alex F. Bagley, Andrew L. Markhard, and
Supplemental Data Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mtorc2 Assembly and Akt/PKB Dos D. Sarbassov, Siraj M. Ali, Shomit Sengupta, Joon-Ho Sheen, Peggy P. Hsu, Alex F. Bagley, Andrew L. Markhard, and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
FACTORS AFFECTING SKELETAL MUSCLE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE HORSE
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Animal and Food Sciences Animal and Food Sciences 2011 FACTORS AFFECTING SKELETAL MUSCLE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE HORSE Ashley Leigh Wagner University
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Animal and Food Sciences Animal and Food Sciences 2011 FACTORS AFFECTING SKELETAL MUSCLE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE HORSE Ashley Leigh Wagner University
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Mitotic Raptor Promotes mtorc1 Activity, G 2 /M Cell Cycle Progression, and Internal Ribosome Entry Site-Mediated mrna Translation
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, July 2010, p. 3151 3164 Vol. 30, No. 13 0270-7306/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/mcb.00322-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Mitotic Raptor
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, July 2010, p. 3151 3164 Vol. 30, No. 13 0270-7306/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/mcb.00322-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Mitotic Raptor
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy se
 A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
The Changing Role of mtor Kinase in the Maintenance of Protein Synthesis during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 3930 3939 Vol. 85, No. 8 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.01913-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Changing Role of mtor
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 3930 3939 Vol. 85, No. 8 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.01913-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Changing Role of mtor
Targeting Kinases Critical for TMPRSS2-ERG Function in Prostate Cancer
 Targeting Kinases Critical for TMPRSS2-ERG Function in Prostate Cancer Kyle Nakatsuka David Takeda, MD, PhD Lab of William Hahn, M.D., Ph.D. Broad Institute Summer Research Program in Genomics TMPRSS2-ERG
Targeting Kinases Critical for TMPRSS2-ERG Function in Prostate Cancer Kyle Nakatsuka David Takeda, MD, PhD Lab of William Hahn, M.D., Ph.D. Broad Institute Summer Research Program in Genomics TMPRSS2-ERG
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S5. ROS regulated the signaling responses of A. gambiae 4a3B cells to human insulin. (A) 4a3B cells were stimulated with 6000
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Exogenous H 2 O 2 induced rapid activation of ERK in Anopheles stephensi cells. ASE cells were treated with PBS or with 500 mmh 2 O 2 for 5, 30, 60, and 180 min.
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Exogenous H 2 O 2 induced rapid activation of ERK in Anopheles stephensi cells. ASE cells were treated with PBS or with 500 mmh 2 O 2 for 5, 30, 60, and 180 min.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Professor Christopher Proud
 South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute Professor Christopher Proud Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation Professor Christopher G. Proud Nutrition and Metabolism Theme Leader South Australian
South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute Professor Christopher Proud Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation Professor Christopher G. Proud Nutrition and Metabolism Theme Leader South Australian
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
The PI3K/AKT axis. Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia. Introduction
 The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
Supplementary Figure 1. HeliScope CAGE revealed androgen-regulated signaling and differentially regulated promoters in hormone-refractory prostate
 Supplementary Figure 1. HeliScope CAGE revealed androgen-regulated signaling and differentially regulated promoters in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. (a) Cell proliferation of BicR cells in
Supplementary Figure 1. HeliScope CAGE revealed androgen-regulated signaling and differentially regulated promoters in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. (a) Cell proliferation of BicR cells in
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Nutrition & Metabolism Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation PhD & Honours Projects 2018
 Nutrition & Metabolism Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation PhD & Honours Projects 2018 Prof. Proud s laboratory studies the signalling pathways by which hormones, growth factors and nutrients regulate the
Nutrition & Metabolism Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation PhD & Honours Projects 2018 Prof. Proud s laboratory studies the signalling pathways by which hormones, growth factors and nutrients regulate the
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
5K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR1-negative. 5K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR1-positive BAAA BAAA CXCR1-APC BAAA BAAA CXCR1-APC
 A +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-negative BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC B +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-positive BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC C Supplemental Figure. Tumorigenicity of the ALDEFLUOR-positive/CXCR-positive
A +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-negative BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC B +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-positive BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC C Supplemental Figure. Tumorigenicity of the ALDEFLUOR-positive/CXCR-positive
Hui-Kuan Lin, Yueh-Chiang Hu, Lin Yang, Saleh Altuwaijri, Yen-Ta Chen, Hong-Yo Kang, and Chawnshang Chang
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 278, No. 51, Issue of December 19, pp. 50902 50907, 2003 2003 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Suppression
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 278, No. 51, Issue of December 19, pp. 50902 50907, 2003 2003 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Suppression
Akt-dependent Skp2 mrna translation is required for exiting contact inhibition, oncogenesis, and adipogenesis
 The EMBO Journal (2012) 31, 1134 1146 & 2012 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 0261-4189/12 www.embojournal.org Akt-dependent Skp2 mrna translation is required for exiting contact
The EMBO Journal (2012) 31, 1134 1146 & 2012 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 0261-4189/12 www.embojournal.org Akt-dependent Skp2 mrna translation is required for exiting contact
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0045 TITLE: MT 2A Phosphorylation by PKC Mu/PKD Influences Chemosensitivity to Cisplatin in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kethandapatti Balaji, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0045 TITLE: MT 2A Phosphorylation by PKC Mu/PKD Influences Chemosensitivity to Cisplatin in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kethandapatti Balaji, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit
 Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Distinct inhibitory effects on mtor signaling by ethanol and INK128 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
 Mazan-Mamczarz et al. Cell Communication and Signaling (2015) 13:15 DOI 10.1186/s12964-015-0091-0 RESEARCH Open Access Distinct inhibitory effects on mtor signaling by ethanol and INK128 in diffuse large
Mazan-Mamczarz et al. Cell Communication and Signaling (2015) 13:15 DOI 10.1186/s12964-015-0091-0 RESEARCH Open Access Distinct inhibitory effects on mtor signaling by ethanol and INK128 in diffuse large
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Ulises D. Orlando 1,*, Ana F. Castillo 1,*, Melina A. Dattilo 1, Angela R. Solano 1, Paula M. Maloberti 1, Ernesto J.
 /, Vol. 6, No. 40 Acyl-CoA synthetase-4, a new regulator of mtor and a potential therapeutic target for enhanced estrogen receptor function in receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer Ulises D. Orlando
/, Vol. 6, No. 40 Acyl-CoA synthetase-4, a new regulator of mtor and a potential therapeutic target for enhanced estrogen receptor function in receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer Ulises D. Orlando
This is an Open Access Creative Commons version of an article that appears in:
 This is an Open Access Creative Commons version of an article that appears in: ONCOTARGET The internet address for this paper is: https://publications.icr.ac.uk/15486/ Please direct all emails to: publications@icr.ac.uk
This is an Open Access Creative Commons version of an article that appears in: ONCOTARGET The internet address for this paper is: https://publications.icr.ac.uk/15486/ Please direct all emails to: publications@icr.ac.uk
Scholar Commons. University of South Carolina. Song Gao University of South Carolina. Theses and Dissertations
 University of South Carolina Scholar Commons Theses and Dissertations 2017 The Regulation of Glycoprotein130 Dependent Inflammatory Cytokines one Basal and Mechanical Stimuli Induced Protein Synthesis
University of South Carolina Scholar Commons Theses and Dissertations 2017 The Regulation of Glycoprotein130 Dependent Inflammatory Cytokines one Basal and Mechanical Stimuli Induced Protein Synthesis
Translational regulation of Myeloid Cell Differentiation: Novel Mechanisms and Players PDCD4, DAP5 and eif2α
 Translational regulation of Myeloid Cell Differentiation: Novel Mechanisms and Players PDCD4, DAP5 and eif2α Bulent Ozpolat,M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Department of
Translational regulation of Myeloid Cell Differentiation: Novel Mechanisms and Players PDCD4, DAP5 and eif2α Bulent Ozpolat,M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Department of
Supporting Information. FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce. apoptosis
 1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
Control of Cell Cycle Progression by mtor
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects Graduate Center 5-2015 Control of Cell Cycle Progression by mtor Amrita Chatterjee Graduate Center, City
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects Graduate Center 5-2015 Control of Cell Cycle Progression by mtor Amrita Chatterjee Graduate Center, City
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1. Int6 gene silencing efficiency. (A) Western Blot analysis of Int6 expression at different times after sirna transfection. Int6 expression is strongly silenced in Int6
Supplementary Information Figure S1. Int6 gene silencing efficiency. (A) Western Blot analysis of Int6 expression at different times after sirna transfection. Int6 expression is strongly silenced in Int6
TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/PKB Kinase in the Development of Hormone-Independent Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/PKB Kinase in the Development of Hormone-Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Linda A. degraffenried, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The
AD Award Number: TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/PKB Kinase in the Development of Hormone-Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Linda A. degraffenried, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma
 Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Evaluation of Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor 1 Inhibition as a Treatment for Prostate Cancer: Preclinical Efficacy and Resistance
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2013-12-11 Evaluation of Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor 1 Inhibition as a Treatment for Prostate
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2013-12-11 Evaluation of Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor 1 Inhibition as a Treatment for Prostate
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Brief Critical Review
 Brief Critical Review March 2007: 122 129 Leucine and Protein Synthesis: mtor and Beyond Martha H. Stipanuk, PhD The effects of amino acid intake on protein synthesis in the intact rat appear to be mediated
Brief Critical Review March 2007: 122 129 Leucine and Protein Synthesis: mtor and Beyond Martha H. Stipanuk, PhD The effects of amino acid intake on protein synthesis in the intact rat appear to be mediated
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/333/333ra47/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Androgen receptor antagonists compromise T cell response against prostate cancer leading to early tumor
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/333/333ra47/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Androgen receptor antagonists compromise T cell response against prostate cancer leading to early tumor
Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors
 Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Current development of mtor inhibitors as anticancer agents
 Current development of mtor inhibitors as anticancer agents Sandrine Faivre*, Guido Kroemer and Eric Raymond* Abstract Mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) is a kinase that functions as a master switch
Current development of mtor inhibitors as anticancer agents Sandrine Faivre*, Guido Kroemer and Eric Raymond* Abstract Mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) is a kinase that functions as a master switch
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Protein SD Units (P-value) Cluster order
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE AND FIGURES Table S1. Signature Phosphoproteome of CD22 E12 Transgenic Mouse BPL Cells. T-test vs. Other Protein SD Units (P-value) Cluster order ATPase (Ab-16) 1.41 0.000880 1 mtor
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE AND FIGURES Table S1. Signature Phosphoproteome of CD22 E12 Transgenic Mouse BPL Cells. T-test vs. Other Protein SD Units (P-value) Cluster order ATPase (Ab-16) 1.41 0.000880 1 mtor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3866
 Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
PIK3CA mutations enable targeting of a breast tumor dependency through mtor-mediated MCL-1 translation
 CANCER PIK3CA mutations enable targeting of a breast tumor dependency through mtor-mediated MCL-1 translation 2016 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement
CANCER PIK3CA mutations enable targeting of a breast tumor dependency through mtor-mediated MCL-1 translation 2016 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement
TITLE: Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer by Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Organoselenium Compounds. Medical Center Hershey, PA 17033
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-08-1-0297 TITLE: Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer by Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Organoselenium Compounds PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nicole Facompre CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-08-1-0297 TITLE: Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer by Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Organoselenium Compounds PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nicole Facompre CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Cell cycle-dependent activity of the novel dual PI3K-MTORC1/2 inhibitor NVP-BGT226 in acute leukemia
 Kampa-Schittenhelm et al. Molecular Cancer 2013, 12:46 RESEARCH Open Access Cell cycle-dependent activity of the novel dual PI3K-MTORC1/2 inhibitor NVP-BGT226 in acute leukemia Kerstin Maria Kampa-Schittenhelm
Kampa-Schittenhelm et al. Molecular Cancer 2013, 12:46 RESEARCH Open Access Cell cycle-dependent activity of the novel dual PI3K-MTORC1/2 inhibitor NVP-BGT226 in acute leukemia Kerstin Maria Kampa-Schittenhelm
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
The nuclear import of ribosomal proteins is regulated by mtor
 /, Vol. 5, No. 20 The nuclear import of ribosomal proteins is regulated by mtor Dubek Kazyken 1,2, Yelimbek Kaz 1,2, Vladimir Kiyan 1,2, Assylbek A. Zhylkibayev 1,2, Chien-Hung Chen 1, Nitin K. Agarwal
/, Vol. 5, No. 20 The nuclear import of ribosomal proteins is regulated by mtor Dubek Kazyken 1,2, Yelimbek Kaz 1,2, Vladimir Kiyan 1,2, Assylbek A. Zhylkibayev 1,2, Chien-Hung Chen 1, Nitin K. Agarwal
Megan S. Lim MD PhD. Translating Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Malignant Lymphoma into Clinical Application
 Translating Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Malignant Lymphoma into Clinical Application Megan S. Lim MD PhD FRCPC Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Proteomics is a multi-faceted
Translating Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Malignant Lymphoma into Clinical Application Megan S. Lim MD PhD FRCPC Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Proteomics is a multi-faceted
Expanded View Figures
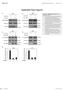 MO reports PR3 dephosphorylates TZ Xian-o Lv et al xpanded View igures igure V1. PR3 dephosphorylates and inactivates YP/TZ., Overexpression of tight junction proteins Pals1 () or LIN7 () has no effect
MO reports PR3 dephosphorylates TZ Xian-o Lv et al xpanded View igures igure V1. PR3 dephosphorylates and inactivates YP/TZ., Overexpression of tight junction proteins Pals1 () or LIN7 () has no effect
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
Review Article Mammalian target of rapamycin: a central node of complex signaling cascades
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2011;4(5):476-495 www.ijcep.com /IJCEP1106002 Review Article Mammalian target of rapamycin: a central node of complex signaling cascades Yoh Dobashi, Yasutaka Watanabe 1, Chihiro
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2011;4(5):476-495 www.ijcep.com /IJCEP1106002 Review Article Mammalian target of rapamycin: a central node of complex signaling cascades Yoh Dobashi, Yasutaka Watanabe 1, Chihiro
PI3K Inhibitors in Follicular Lymphoma. Anas Younes, M.D. chief, Lymphoma Service Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
 PI3K Inhibitors in Follicular Lymphoma Anas Younes, M.D. chief, Lymphoma Service Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center PI3K Pathway mutations do correlate with pathway activation in lymphoma How to measure
PI3K Inhibitors in Follicular Lymphoma Anas Younes, M.D. chief, Lymphoma Service Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center PI3K Pathway mutations do correlate with pathway activation in lymphoma How to measure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
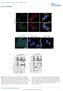 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
