PROTEIN METABOLISM DEPT OF BIOCHEMISTRY ACS MEDICAL COLLEGE CHENNAI - 77
|
|
|
- Tobias Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROTEIN METABOLISM DEPT OF BIOCHEMISTRY ACS MEDICAL COLLEGE CHENNAI - 77
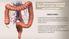
2 DIGESTION & ABSORPTION
3 DIETARY PROTEINS SERVE 3 FUNCTIONS 1. THEIR CONSTITUTENT AMINOACIDS ARE USED FOR SYNTHESIS OF BODY PROTEINS 2. THE CARBON SKELETONS OF THE AMINO ACIDS ARE OXIDISED TO YIELD ENERGY 3. THEIR CARBON & NITROGEN ATOMS MAY BE USED TO SYNTHESISE OTHER N CONTAINING CELLULAR CONSTITUENTS AS WELL AS MANY NON- NITROGEN CONTAINING METABOLITES
4 DIGESTION TAKES PLACE WITH THE HELP OF ENZYMES SECRETED BY 1. STOMACH 2. PANCREAS 3. SMALL INTESTINE
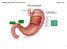
5 1.DIGESTION IN STOMACH ENTERING PROTEINS (+) GASTRIN (+) GASTRIC JUICE (ph ) CONTAINING 1. HCL 2. PEPSINOGEN 3. RENNIN (IN INFANTS)
6 HYDROCHLORIC ACID SECRETED BY PARIETAL CELLS KILLS MICRO-ORGANISMS DENATURES PROTEIN MAKING INTERNAL PEPTIDE BONDS MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO SUBSSEQUENT HYDROLYSIS BY PROTEOSES PROVIDES ACID ENVIRONMENT FOR PEPSIN ACTION
7 PEPSIN SECRETED BY CHIEF CELLS AS PEPSINOGEN INACTIVE PRECURSOR CONVERTED TO ACTIVE PEPSIN BY AUTOCATALYSIS WORKS AT ACIDIC ph CLEAVES PEPTIDE BONDS INVOLVING AROMATIC & ACIDIC AA
8 PEPSINOGEN PEPSIN PEPSIN H + (ph ) DIETARY PROTEIN SMALLER PEPTIDES + AA
9 RENNIN CHYMOSIN / RENNET IMPORTANT IN INFANTS DIGESTIVE PROCESS CLOTTING OF MILK R Ca ++ CASEIN PARACASEIN Ca ++ PARACASEINATE THE PURPOSE OF THIS REACTION IS TO CONVERT MILK INTO MORE SOLID FORM TO PREVENT THE RAPID PASSAGE OF MILK FROM STOMACH OF INFANTS
10 2.DIGESTION IN INTESTINE BY PANCREATIC ENZYMES ACIDIC CONTENTS (CHYME) PASSING INTO SMALL INTESTINE TRIGGERS THE SECRETION OF 1. SECRETIN 2. CHOLECYSTOKININ
11 SECRETIN STIMULATES PANCREAS TO SECRETE BICARBONATE & RELEASE OF PANCREATIC JUICE INTO THE SMALL INTESTINE. NEUTRALISES GASTRIC HCL CHANGING ph FROM
12 CHOLECYSTOKININ STIMULATES SECRETION OF PANCREATIC ENDOPEPTIDASE & EXOPEPTIDASE ENDOPEPTIDASE INCLUDES CHYMOTRYPSIN & ELASTASE, CLEAVING INTERNAL PEPTIDE BONDS EXOPEPTIDASE CLEAVES 1 AA AT A TIME FROM EITHER C OR N END. INCLUDES CARBOXYPEPTIDASE & AMINOPEPTIDASE
13 ACTIVATION OF PANCREATIC PRO-ENZYMES TRYPSINOGEN ENTEROPEPTIDASE TRYPSIN CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN CHYMOTRYPSIN PRO-ELASTASE ELASTASE PROCARBOXYPEPTIDASE CARBOXYPEPTIDASE
14 TRYPSIN HYDROLYSES PEPTIDE BONDS WHOSE CRBOXYL GROUPS ARE CONTRIBUTED NY LYS & ARG RESIDUES CHYMOTRYPSIN-CLEAVES PEPTIDE BONDS INVOLING CARBOXYL GROUP OF AROMATIC AA ELASTASE HYDROLYSES THOSE PEPTIDE BONDS FORMED BY SMALL NON- POLAR AA RESIDUES SUCH AS ALA, SER & GLY THUS 3 ENZYMES HYDROLYSE POLYPEPTIDES TO SMALLER PEPTIDES
15 Degradation of short peptides in the small intestine is continued by an EXOPEPETIDASE- CARBOXYPEPTIDASE which removes the successive carboxy terminal aa residues from peptide 1. CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A RELEASES HYDROPHOBIC AA 2. CARBOXYPEPTIDASE B RELEASES BASIC AA
16 3.DIGESTION IN INTESTINE BY INTESTINAL PROTEOSES The digestion is completed by the PEPTIDASES of the mucosa of the small intestine namely: 1. AMINOPEPTIDASES 2. GROUP OF DIPEPTIDASES
17 AMINO-PEPTIDASE - EXOPEPTIDASE - REQUIRE Mg/Mn - HYDROLYSE PEPTIDE BONDS NEXT TO N-TERMINAL AA OF SHORT PEPTIDES DIPEPTIDASES - COMPLETE THE DIGESTION OF DIPEPTIDES TO FREE AMINO ACIDS
18 ABSORPTION OF AMINOACIDS MOSTLY THRU ACTIVE TRANSPORT 5 SEPARATE SYSTEMS TRANSPORT L- AMINOACIDS FROM INTESTINAL LUMEN INTO INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS THUS AA RELEASED BY DIGESTION PASS FRM GUT THRU HEPATIC PORTAL VEIN TO THE LIVER TRANSPORT SYSTEM ALSO PRESENT IN RENAL SYSTEM
19 TRANSPORT SYSTEM Small neutral aminoacids Large neutral aminoacids Basic aa & Cysteine Acidic aminoacids Iminoacid, Glycine AMINOACID TRANSPORTD Ala Ser & Thr Isoleu, Leu, Val,Tyr,Trp,Ph e Arg, Lys, Ornithine, Cys Glutamic acid Aspartic acid Pro, Hydroxy pro, Gly DISORDER HARTNUP Disease CYSTINUTIA GLYCINURIA
20 MEISTER CYCLE GAMMA GLUTAMYL CYCLE AMINO ACID GLUTATHIONE GLUTAMYL AMINOACID CYSTEINYL GLYCINE AMINOACID GLYCINE CYSTEINE GLUTAMYL-CYSTEINE OXOPROLINE GLUTAMATE
Day Date Title Instructor 5 th Ed 6 th Ed. Protein digestion and AA absorption
 Day Date Title Instructor 5 th Ed 6 th Ed 1 Tuesday 18 April 2017 Protein digestion and AA absorption D S Jairajpuri 250 256 250 256 2 Wednesday 19 April 2017 Removal of nitrogen and urea cycle D S Jairajpuri
Day Date Title Instructor 5 th Ed 6 th Ed 1 Tuesday 18 April 2017 Protein digestion and AA absorption D S Jairajpuri 250 256 250 256 2 Wednesday 19 April 2017 Removal of nitrogen and urea cycle D S Jairajpuri
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
100 Points NAME: KEY Lab section:
 ANSC 324 Spring, 2007 EXAM 1 100 Points NAME: KEY Lab section: Instructions: Make sure that you take time to carefully read each question, and then answer the question appropriately. Answers to essay questions
ANSC 324 Spring, 2007 EXAM 1 100 Points NAME: KEY Lab section: Instructions: Make sure that you take time to carefully read each question, and then answer the question appropriately. Answers to essay questions
Summary break down long chain proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids into monomers recall hydrolysis (opposite of dehydration synthesis) (hydro-w
 Summary break down long chain proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids into monomers recall hydrolysis (opposite of dehydration synthesis) (hydro-water lysis-break apart) if not broken down, proteins
Summary break down long chain proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids into monomers recall hydrolysis (opposite of dehydration synthesis) (hydro-water lysis-break apart) if not broken down, proteins
CLASS XI BIOLOGY. Digestion And Absorption. Finish Line & Beyond send your queries to
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
1 Digestion and absorption. Lecture #14 Lecturer: PhD Alexander N. Koval
 1 Digestion and absorption Lecture #14 Lecturer: PhD Alexander N. Koval Presentation of Protein 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 2 Lectures plan 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 3 Overview of Protein Metabolism
1 Digestion and absorption Lecture #14 Lecturer: PhD Alexander N. Koval Presentation of Protein 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 2 Lectures plan 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 3 Overview of Protein Metabolism
AMINO ACIDS NON-ESSENTIAL ESSENTIAL
 Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen
 Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD All images were taken from Lippincott s Biochemistry textbook except where noted Textbook Amino acid metabolism: Biochemistry
Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD All images were taken from Lippincott s Biochemistry textbook except where noted Textbook Amino acid metabolism: Biochemistry
Class XI Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Biology
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
5.3 DIGESTION 5.2 DIGESTION, ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT - BASIC CONCEPT Digestion in the Mouth
 Nutritions' differentiate between the types of absorption and transport of final end products across the intestinal brush border into the portal and lymphatic system. 5.2 DIGESTION, ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT
Nutritions' differentiate between the types of absorption and transport of final end products across the intestinal brush border into the portal and lymphatic system. 5.2 DIGESTION, ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT
Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen
 Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD Medical students-first semester All images were taken from Lippincott s Biochemistry textbook except where noted Amino acids (AAs)
Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD Medical students-first semester All images were taken from Lippincott s Biochemistry textbook except where noted Amino acids (AAs)
L1, 2 : Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates
 L1, 2 : Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates OBJECTIVES: Understand the process of digestion of dietary lipids, protein and carbohydrates including, the organs involved,
L1, 2 : Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates OBJECTIVES: Understand the process of digestion of dietary lipids, protein and carbohydrates including, the organs involved,
BIOCHEMISTRY Protein Metabolism
 BIOCHEMISTRY Protein Metabolism BIOB111 CHEMISTRY & BIOCHEMISTRY Session 25 Session Plan Digestion & Absorption of Proteins Amino Acid Utilization Amino Acid Degradation Transamination Oxidative Deamination
BIOCHEMISTRY Protein Metabolism BIOB111 CHEMISTRY & BIOCHEMISTRY Session 25 Session Plan Digestion & Absorption of Proteins Amino Acid Utilization Amino Acid Degradation Transamination Oxidative Deamination
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 25
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 25 General topics for week 14 Session 25 The metabolism of proteins Students are asked to draw the concept map showing all details of protein metabolism 1 Instructions:
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 25 General topics for week 14 Session 25 The metabolism of proteins Students are asked to draw the concept map showing all details of protein metabolism 1 Instructions:
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
c.uma sankar.kanchipuram.
 NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
Biology. TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption. Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr
 TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Van Kupffer cells (i) Isolets of langerhans B - cells (ii)
TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Van Kupffer cells (i) Isolets of langerhans B - cells (ii)
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr. Diala
 number 30 Done by Dergam Al-Tarawneh Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor Dr. Diala 1 After we ve finished talking about lipids metabolism pathways, today we will start talking about another pathway that takes
number 30 Done by Dergam Al-Tarawneh Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor Dr. Diala 1 After we ve finished talking about lipids metabolism pathways, today we will start talking about another pathway that takes
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Protein Modification Overview DEFINITION The modification of selected residues in a protein and not as a component of synthesis
 Lecture Four: Protein Modification & Cleavage [Based on Chapters 2, 9, 10 & 11 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Protein Modification
Lecture Four: Protein Modification & Cleavage [Based on Chapters 2, 9, 10 & 11 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Protein Modification
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
the following objectives: 1. Describe the environment of the stomach and its relation to protein digestion.
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 5: Protein Digestion by Enzyme Action Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 5: Protein Digestion by Enzyme Action Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Digestion and absorption (I)
 Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
PAPER No. : 16, Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 22, Mechanism of enzyme catalyst reaction (I) Chymotrypsin
 Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Lujain Hamdan. Faisal Nimri ... Diala Abu-Hassan
 31 Lujain Hamdan Faisal Nimri... Diala Abu-Hassan Amino Acids Metabolism Amino acid has an alpha-carbon which is connected to Carboxyl group, Amino group, hydrogen atom and R group which differs from an
31 Lujain Hamdan Faisal Nimri... Diala Abu-Hassan Amino Acids Metabolism Amino acid has an alpha-carbon which is connected to Carboxyl group, Amino group, hydrogen atom and R group which differs from an
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
endopeptidases aminopeptidases carboxypeptidases hydrolyzes a peptide bond somewhere in the middle of the polypeptide
 1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 4 Protein Sequence
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
Ques*ons. Ques*ons 4/11/12. Which macromolecule has the highest energy content?
 Ques*ons Which macromolecule has the highest energy content? How have herbivores adapted to the demands of a largely cellulose diet? Ques*ons Describe the ac*on of the carnassial teeth in carnivores. How
Ques*ons Which macromolecule has the highest energy content? How have herbivores adapted to the demands of a largely cellulose diet? Ques*ons Describe the ac*on of the carnassial teeth in carnivores. How
PROTEIN METABOLISM: NITROGEN CYCLE; DIGESTION OF PROTEINS. Red meat is an important dietary source of protein nitrogen
 PROTEIN METABOLISM: NITROGEN CYCLE; DIGESTION OF PROTEINS Red meat is an important dietary source of protein nitrogen The Nitrogen Cycle and Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen is needed for amino acids, nucleotides,
PROTEIN METABOLISM: NITROGEN CYCLE; DIGESTION OF PROTEINS Red meat is an important dietary source of protein nitrogen The Nitrogen Cycle and Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen is needed for amino acids, nucleotides,
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
NCERT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 91 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Select what is not true of intestinal villi among followings a. They possess microvilli b. They increase the surface area c. They are
91 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Select what is not true of intestinal villi among followings a. They possess microvilli b. They increase the surface area c. They are
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Amino Acids: essential nonessential
 Protein: a component of every living cell provides structure and framework in the body plays a role in fluid balance and acid--base balance used to transport substances through the blood provides 4 cal/g
Protein: a component of every living cell provides structure and framework in the body plays a role in fluid balance and acid--base balance used to transport substances through the blood provides 4 cal/g
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Physiology 12. Overview. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Germann Ch 19
 Physiology 12 The Gastrointestinal Tract Germann Ch 19 Overview 1 Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Physiology 12 The Gastrointestinal Tract Germann Ch 19 Overview 1 Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS
 Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO AIDS 1. The fate of the amino group OO - 3 N 24 1 Key structure s Glutamine (Gln), 5 Gln Glutamate (Glu), 5 Glu a-keto-glutarate, 5 akg AMIDE N 2 O - O - 2 2 2 3 N 2
Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO AIDS 1. The fate of the amino group OO - 3 N 24 1 Key structure s Glutamine (Gln), 5 Gln Glutamate (Glu), 5 Glu a-keto-glutarate, 5 akg AMIDE N 2 O - O - 2 2 2 3 N 2
MAN IN HEALTH AND DISEASES 18 HOURS 27 MARKS
 MAN IN HEALTH AND DISEASES 18 HOURS 27 MARKS HOMEOSTASIS BODY DEFENCE AND IMMUNITY DIGESTION CIRCULATION RESPIRATION EXCRETION NERVOUS SYSTEM DIGESTION DIGESTION Structure of digestive system. Process
MAN IN HEALTH AND DISEASES 18 HOURS 27 MARKS HOMEOSTASIS BODY DEFENCE AND IMMUNITY DIGESTION CIRCULATION RESPIRATION EXCRETION NERVOUS SYSTEM DIGESTION DIGESTION Structure of digestive system. Process
Chapter 6 Reading Guide
 Chapter 6 Reading Guide 1. Describe the structure of an amino acid. 2. What s the difference between an amino acid and a protein? Where do dipeptides, tripeptides and polypeptides fit in? 3. How many amino
Chapter 6 Reading Guide 1. Describe the structure of an amino acid. 2. What s the difference between an amino acid and a protein? Where do dipeptides, tripeptides and polypeptides fit in? 3. How many amino
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Give the dental formula of adult human being? A. Dental formula represents the arrangement of various types of teeth in each half of both the jaws
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Give the dental formula of adult human being? A. Dental formula represents the arrangement of various types of teeth in each half of both the jaws
Ali Yaghi. Yaseen Fatayer. M.Khatatbeh
 6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport. Lecture 2. Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients
 BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport Lecture 2 Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients 1. Overview of digestion & absorption of nutrients 2. Functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract 3. Digestion
BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport Lecture 2 Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients 1. Overview of digestion & absorption of nutrients 2. Functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract 3. Digestion
SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 15, 2011 BILD 2. Nasha 10. (10 points) Josh 2. (10 points) Josh 3. (10 points) Mary 4. (5 points) 8.
 SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 15, 2011 BILD 2 WRITE YOUR NAME ON ALL 7 PAGES. ANSWER ALL 10 QUESTIONS (100 POINTS). CONFINE YOUR ANSWERS TO THE SPACE ALLOWED. If you would like to write on the back of the
SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 15, 2011 BILD 2 WRITE YOUR NAME ON ALL 7 PAGES. ANSWER ALL 10 QUESTIONS (100 POINTS). CONFINE YOUR ANSWERS TO THE SPACE ALLOWED. If you would like to write on the back of the
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Enzyme Regulation I. Dr. Kevin Ahern
 Enzyme Regulation I Dr. Kevin Ahern Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms 1. Allosterism Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms 1. Allosterism 2. Covalent Modification Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms
Enzyme Regulation I Dr. Kevin Ahern Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms 1. Allosterism Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms 1. Allosterism 2. Covalent Modification Enzyme Regulation Mechanisms
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Animal Nutrition. Key Concepts. Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms. What do animals get from food?
 Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts. Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory
 Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Chymotrypsin Lecture. Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin
 Chymotrypsin Lecture Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin What s so great about enzymes? They accomplish large rate accelerations (10 10-10
Chymotrypsin Lecture Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin What s so great about enzymes? They accomplish large rate accelerations (10 10-10
Enzymes for Flavour Development in Dairy Substrates. Presented by: Blanca Camarasa Senior Business Manager
 Enzymes for Flavour Development in Dairy Substrates Presented by: Blanca Camarasa Senior Business Manager Cheese composition Cheese consists of proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, goat,
Enzymes for Flavour Development in Dairy Substrates Presented by: Blanca Camarasa Senior Business Manager Cheese composition Cheese consists of proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, goat,
I. Heterotrophic Processes Figure 1: Stages of Food Processing
 I. Heterotrophic Processes Figure 1: Stages of Food Processing Upon obtaining a food item, it is taken into the body or Ingested. Organisms cannot DIRECTLY utilize the macromolecules in a food item because:
I. Heterotrophic Processes Figure 1: Stages of Food Processing Upon obtaining a food item, it is taken into the body or Ingested. Organisms cannot DIRECTLY utilize the macromolecules in a food item because:
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
The gallbladder. Bile secretion:
 The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Overview. Physiology 1. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Guyton section XI
 Overview Physiology 1 The Gastrointestinal Tract Guyton section XI Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Overview Physiology 1 The Gastrointestinal Tract Guyton section XI Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
CHAPTER 10: REGULATORY STRATEGIES. Traffic signals control the flow of traffic
 CHAPTER 10: REGULATORY STRATEGIES Traffic signals control the flow of traffic INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 10 The activity of enzymes must often be regulated so that they function at the proper time and place.
CHAPTER 10: REGULATORY STRATEGIES Traffic signals control the flow of traffic INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 10 The activity of enzymes must often be regulated so that they function at the proper time and place.
Lab #12: Digestive Physiology
 Background In order for the nutrients in food to be absorbed, they must first be broken down into particles that are small enough to be transported through carrier proteins into the epithelial cells that
Background In order for the nutrients in food to be absorbed, they must first be broken down into particles that are small enough to be transported through carrier proteins into the epithelial cells that
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
Part III => METABOLISM and ENERGY. 3.5 Protein Catabolism 3.5a Protein Degradation 3.5b Amino Acid Breakdown 3.5c Urea Cycle
 Part III => METABOLISM and ENERGY 3.5 Protein Catabolism 3.5a Protein Degradation 3.5b Amino Acid Breakdown 3.5c Urea Cycle Section 3.5a: Protein Degradation Synopsis 3.5a - Dietary proteins are degraded
Part III => METABOLISM and ENERGY 3.5 Protein Catabolism 3.5a Protein Degradation 3.5b Amino Acid Breakdown 3.5c Urea Cycle Section 3.5a: Protein Degradation Synopsis 3.5a - Dietary proteins are degraded
Amino Acids and Proteins (2) Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Amino Acids and Proteins (2) Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih 1 Some important biologically active peptides 2 Proteins The word protein is derived from Greek word, proteios which means primary. As the
Amino Acids and Proteins (2) Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih 1 Some important biologically active peptides 2 Proteins The word protein is derived from Greek word, proteios which means primary. As the
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens
 Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Gastrointestinal Physiology. Secretion
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Contemporary Nutrition
 Contemporary Nutrition Chapter 6 Proteins Overview of Protein Body is made up of thousands of substances that are made of proteins Each protein has own unique structure and function More than 300 different
Contemporary Nutrition Chapter 6 Proteins Overview of Protein Body is made up of thousands of substances that are made of proteins Each protein has own unique structure and function More than 300 different
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition. 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations
 Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 15 Friday 26 Feb. 1
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 15 Friday 26 Feb. 1 Illustration of a Polypeptide amino acids peptide bonds Review Polypeptide (chain) See textbook, Fig 5.21, p. 82 for a more clear illustration Folding and
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 15 Friday 26 Feb. 1 Illustration of a Polypeptide amino acids peptide bonds Review Polypeptide (chain) See textbook, Fig 5.21, p. 82 for a more clear illustration Folding and
Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes
 Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 5.2 Definition of the mechanism 1. The sequence from substrate(s) to product(s) : Reaction steps 2. The rates at which the complex are interconverted 3.
Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 5.2 Definition of the mechanism 1. The sequence from substrate(s) to product(s) : Reaction steps 2. The rates at which the complex are interconverted 3.
1. Overview of Animal Nutrition
 Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Lab Activity 30. Digestive Enzymes. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 30 Digestive Enzymes Portland Community College BI 233 Cellular Reactions All molecular bonds have energy barriers that prevent spontaneous breakdown Enzymes lowering these activation energy
Lab Activity 30 Digestive Enzymes Portland Community College BI 233 Cellular Reactions All molecular bonds have energy barriers that prevent spontaneous breakdown Enzymes lowering these activation energy
Chapter 21 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 21 Lecture Outline Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes! Introduction! Proteins are biomolecules that contain many amide bonds, formed by joining amino acids. Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University
Chapter 21 Lecture Outline Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes! Introduction! Proteins are biomolecules that contain many amide bonds, formed by joining amino acids. Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University
- Most nutrients are absorbed before reaching the ileum. - Colon is responsible for final removal of electrolytes and water.
 University of Jordan Department of physiology and Biochemistry Gastro-Intestinal physiology, Medical, Pt III. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Academic year:
University of Jordan Department of physiology and Biochemistry Gastro-Intestinal physiology, Medical, Pt III. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Academic year:
Chapter 4. Chapter 4: Digestion and Absorption
 Chapter 4 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 4: Digestion and Absorption Press the space bar or click the mouse to build each
Chapter 4 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 4: Digestion and Absorption Press the space bar or click the mouse to build each
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
