Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
|
|
|
- Junior Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are related. Define homeostasis and explain its importance. Define negative feedback and describe its role in maintaining homeostasis and normal body function. Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry Differentiate between ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds, and describe the importance of hydrogen bonds. Differentiate clearly between an acid and a base. Compare and contrast carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in terms of their building blocks, structures, and functions in the body. Chapter 3: Cells and Tissues Define selective permeability, diffusion (including simple and facilitated diffusion and osmosis), active transport, passive transport, solute pumping, exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic. Describe briefly the process of DNA replication and mitosis. Explain the importance of mitotic cell division. Name the four major tissue types and their chief subcategories. Explain how the four major tissue types differ structurally and functionally. Chapter 4: Skin and Body Membranes List the general functions of each membrane type-cutaneous, mucous, serous, and synovial-and give its location in the body. Name the layers of the skin and describe the characteristics of each. Chapter 5: The Skeletal System List at least three functions of the skeletal system. Explain the role of bone salts and the organic matrix in making bone both hard and flexible. Discuss/describe how the formation of long bones and flat bones is different. Name the three major categories of joints and compare the amount of movement allowed by each. Chapter 6: The Muscular System Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue and indicate where they are found in the body. Describe the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle and explain the role of actin and myosin containing myofilaments. Describe the events of muscle cell contraction. Chapter 7: The Nervous System Define central nervous system and peripheral nervous system and list the major parts of each. Describe the events that lead to the generation of a nerve impulse and its conduction from one neuron to another. Identify and indicate the functions of the major regions of the cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum in the human brain.! 1
2 ! Chapter 8: Special Senses Name the layers of the wall of the eye, and indicate the major function of each; trace the pathway of light through the eye. Identify the structures of the external, middle, and internal ear, and list the functions of each. Name the four basic taste sensations and list factors that modify the sense of taste. Chapter 9: The Endocrine System Define hormone and target organ. Define negative feedback and describe its role in regulating blood levels of the various hormones. List hormones produced by the endocrine glands and discuss their general functions. Chapter 10: Blood Describe the composition of plasma and discuss its importance in the body. List the cell types making up the formed elements, and describe the major functions of each type. Describe the ABO and Rh blood groups. Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Name the elements of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart and describe the pathway of impulses through this system. Compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Explain how the lymphatic system is functionally related to the cardiovascular and immune systems. Describe the protective functions of skin and mucous membranes. Name the two arms of the adaptive defense system and relate each to a specific lymphocyte type (B or T cell). Chapter 13: The Respiratory System Name the organs forming the respiratory passageway from the nasal cavity to the alveoli of the lungs and describe the function of each. Explain how the respiratory muscles cause volume changes that lead to air flow into and out of the lungs. Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. Chapter 14: The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Name the organs of the alimentary canal and accessory digestive organs and identify each on an appropriate diagram or model. List the major enzymes or enzyme groups produced by the digestive organs or accessory glands and name the foodstuffs on which they act. Recognize the uses of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in cell metabolism. Chapter 15: The Urinary System Identify the following regions of a kidney (longitudinal section): hilum, cortex, medulla, medullary pyramids, calyces, pelvis, and renal columns. Describe the process of urine formation, identifying the areas of the nephron that are responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Explain the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone in the regulation of water balance by the kidney. Chapter 16: The Reproductive System Describe the various stages of meiosis. Compare and contrast spermatogenesis and oogenesis. Define fertilization and zygote; explain the prevention of polyspermy. Explain the major events that occur during the menstrual cycle. 2
3 1. Identify the following endocrine glands, list the hormones produced by each gland, and list the target for each hormone. 2. Five other glands are shown in the diagram above that aren t identified by a letter. List each of the glands and list the hormone(s) produced by each ! 3
4 3. Identify the anterior pituitary hormones that targets the organs/glands shown in the diagram. Additionally, list the posterior pituitary hormones too. 4. Identify the four leukocytes shown below. List a function for each and identify the granulocytes from the agranulocytes. Additionally, list the missing leukocyte along with its function.! 4
5 5. In the heart diagram below, identify the structures involved in the conduction of signals through the heart. 6. Label the diagram of the heart above with the following terms: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, right ventricle, right A-V valve, left A-V valve, and interventricular septum. 7. Identify the respiratory structures in the diagram below. 8. Explain the mechanisms of inspiration and expiration of air into and out of the lungs.! 5
6 9. Label each of the various respiratory volumes in the diagram below. Identify the volumes that make up Vital Capacity 10. Explain how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. 11. Identify the following organs of the digestive system. For each organ, list at least one function.! 6
7 12. Identify the following structure of the nephron. Circle the structure that responds to ADH. 13. Sketch and label a long bone. Identify where the yellow and red marrow are located and the function of each marrow.! 7
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview
 Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES PROGRAMME
 セ @セ@ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): BACHELOR OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION
セ @セ@ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): BACHELOR OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
VirtualSC. Course Detail. Credits: 1 Estimated Completion Time: (This course runs from September-May) Course Description
 Course Detail VirtualSC Course Name: Anatomy and Physiology Course Code: CW326300 Subject: Science Prerequisites: Biology Credits: 1 Estimated Completion Time: (This course runs from September-May) Course
Course Detail VirtualSC Course Name: Anatomy and Physiology Course Code: CW326300 Subject: Science Prerequisites: Biology Credits: 1 Estimated Completion Time: (This course runs from September-May) Course
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review. 3 weeks A&P1, A&P2
 Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Performance Objective Critical Attributes Benchmarks/Assessment. Can the student identify structures and functions of whole systems?
 Curriculum Standard One: Organization of the Human Body The student will understand how structure and function compliment each other, the nature of homeostasis, and the language of Anatomy. 1A. The student
Curriculum Standard One: Organization of the Human Body The student will understand how structure and function compliment each other, the nature of homeostasis, and the language of Anatomy. 1A. The student
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
4. Describe the body cavities, what organs are found in each and be able to identify them on a diagram.
 Health Science I Final Exam Review 1. Define ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 2. List and describe the characteristics of life 3. Know the levels of organization, from simplest to most complex 4. Describe the body
Health Science I Final Exam Review 1. Define ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 2. List and describe the characteristics of life 3. Know the levels of organization, from simplest to most complex 4. Describe the body
SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL
 Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
Body Structure and Function
 Western Technical College 10806120 Body Structure and Function Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course is designed to provide the students
Western Technical College 10806120 Body Structure and Function Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course is designed to provide the students
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2
 The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Homeostasis. Thermoregulation. Osmoregulation. Excretion. how organisms regulate their body temperature
 Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Township of Ocean Schools
 Township of Ocean Schools Assistant Superintendent Office of Teaching and Learning SPARTAN MISSION: Meeting the needs of all students with a proud tradition of academic excellence. Curriculum Documents
Township of Ocean Schools Assistant Superintendent Office of Teaching and Learning SPARTAN MISSION: Meeting the needs of all students with a proud tradition of academic excellence. Curriculum Documents
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore year. Catalog Description:
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore year. Catalog Description:
Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology
 Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology by Visible Body contains 12 units. Below is a listing of each unit, the chapters within it, and the unit s associated learning objectives.
Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology by Visible Body contains 12 units. Below is a listing of each unit, the chapters within it, and the unit s associated learning objectives.
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Advanced Anatomy and Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Advanced Anatomy
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Advanced Anatomy
General Anatomy & Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
Animal Structure and Function
 Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours)
 PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Learners will explore the structure and function of the major
PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Learners will explore the structure and function of the major
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to describe how the human body is organized by:
 Common Course Number: BSC 1084 MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE Course Title: Functional Human Anatomy Course Catalog Description: Basic human anatomy is for students in Allied Health and Mortuary Science Programs.
Common Course Number: BSC 1084 MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE Course Title: Functional Human Anatomy Course Catalog Description: Basic human anatomy is for students in Allied Health and Mortuary Science Programs.
Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System
 Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System Digestive System 1. Secretions from which of the following would have the effect shown in the diagram? A. liver B. mouth C. stomach D. large intestine
Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System Digestive System 1. Secretions from which of the following would have the effect shown in the diagram? A. liver B. mouth C. stomach D. large intestine
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education
 Date Adopted: July 1, 1980 Date Reviewed: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY
Date Adopted: July 1, 1980 Date Reviewed: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Pacing Guide for 9th Curriculum
 Pacing Guide for 9th Curriculum Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology Length of Course: 36 weeks Week Number Week 1 Chapter COS Objectives Introduction to Class & Lab Safety Biology COS Objective 1 Select
Pacing Guide for 9th Curriculum Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology Length of Course: 36 weeks Week Number Week 1 Chapter COS Objectives Introduction to Class & Lab Safety Biology COS Objective 1 Select
Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes
 Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes 1. What is the model for cell membrane structure called? Why is it called this? 2. What is the function of plasma membrane? 3. Draw one phospholipid, label
Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes 1. What is the model for cell membrane structure called? Why is it called this? 2. What is the function of plasma membrane? 3. Draw one phospholipid, label
Test Review: Animal Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
How do heterotrophs obtain energy from their environment? How do heterotrophs depend on autotrophs for their energy and matter?
 ecurriculum System emap Licensed to: TRUMBULL PUBLIC SCHOOLS COURSE: Honors Biology CODE: UNIT: Unit 9: Animal and Human Biology MAP LEVEL: CONTACT: Doug Winters; Denise Weed; Marty Schaivone GRADE: TIME
ecurriculum System emap Licensed to: TRUMBULL PUBLIC SCHOOLS COURSE: Honors Biology CODE: UNIT: Unit 9: Animal and Human Biology MAP LEVEL: CONTACT: Doug Winters; Denise Weed; Marty Schaivone GRADE: TIME
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Lassen Community College Course Outline. I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body.
 Lassen Community College Course Outline HO-54 Basic Structure and Function of the Human Body 3.0 Units I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body. Recommended
Lassen Community College Course Outline HO-54 Basic Structure and Function of the Human Body 3.0 Units I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body. Recommended
February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701
![February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701](/thumbs/74/69742203.jpg) February 2009 [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks SECTION A (ANATOMY) 1. Describe the uterus under the following heads: a) Situation b) Normal position c) Parts
February 2009 [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks SECTION A (ANATOMY) 1. Describe the uterus under the following heads: a) Situation b) Normal position c) Parts
n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y
 n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS
n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra
 Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
Biology Q4 Homework Questions (revised 3/28/18) What are the three levels of behavior? Please describe and give an example for each.
 Biology Q4 Homework Questions (revised 3/28/18) 20.1 1. How does a Biblical worldview and recognition that others are made in the image of God alter how we treat one another? What are the three levels
Biology Q4 Homework Questions (revised 3/28/18) 20.1 1. How does a Biblical worldview and recognition that others are made in the image of God alter how we treat one another? What are the three levels
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Title: Series Title (if applicable): Format: Copyright Date: ISBN:
 MANITOBA CALL FOR BIOLOGY CURRICULUM CORRELATION FORM Resource ID #(s) Title: Series Title (if applicable): Format: Copyright Date: ISBN: Student Resource Teacher Resource Indicate in the boxes below the
MANITOBA CALL FOR BIOLOGY CURRICULUM CORRELATION FORM Resource ID #(s) Title: Series Title (if applicable): Format: Copyright Date: ISBN: Student Resource Teacher Resource Indicate in the boxes below the
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Physiology Quiz (30 Points)
 Physiology Quiz (30 Points) Name: 1. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses
Physiology Quiz (30 Points) Name: 1. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses
Subject Program. Year : 1º Semester : 1º School Year : 2010/2011
 1 de 9 06-02-2012 09:55 Printed on: 06-02-2012 09:55:01 Subject Program Subject Identification Organic Unity Course : [IS] Informática para a Saúde Degree : Subject/Module : Anatomia e Fisiologia Kind
1 de 9 06-02-2012 09:55 Printed on: 06-02-2012 09:55:01 Subject Program Subject Identification Organic Unity Course : [IS] Informática para a Saúde Degree : Subject/Module : Anatomia e Fisiologia Kind
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Western University: Physiology 2130 Online Course Contents
 Western University: Physiology 2130 Online Course Contents Module 1: Introduction to Physiology Contents Homeostasis Negative Feedback Control Systems Positive Feedback Control Systems Negative and Positive
Western University: Physiology 2130 Online Course Contents Module 1: Introduction to Physiology Contents Homeostasis Negative Feedback Control Systems Positive Feedback Control Systems Negative and Positive
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment. Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane
 Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Anatomy & Homeostasis. Unit 5
 Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
THE DIFINITIVE GUIDE TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (HAP 2).
 THE DIFINITIVE GUIDE TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (HAP 2). Pages 2-49 Lecture 1 notes: Cardiovascular 1. Pages 50-97 Lecture 2 notes: Cardiovascular 2. Pages 98-128 Lecture 3 notes: Respiratory 1. Pages
THE DIFINITIVE GUIDE TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (HAP 2). Pages 2-49 Lecture 1 notes: Cardiovascular 1. Pages 50-97 Lecture 2 notes: Cardiovascular 2. Pages 98-128 Lecture 3 notes: Respiratory 1. Pages
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science
 Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science Mission Statement The Mission of Science Education Is: 1) To nurture an active interest in science that continues throughout life.
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science Mission Statement The Mission of Science Education Is: 1) To nurture an active interest in science that continues throughout life.
Health Science Career Cluster Essentials of Healthcare Course Number:
 Health Science Career Cluster Essentials of Healthcare Course Number: 25.44000 Course Description: Anatomy and Physiology is a vital part of most healthcare post-secondary education programs. The Essentials
Health Science Career Cluster Essentials of Healthcare Course Number: 25.44000 Course Description: Anatomy and Physiology is a vital part of most healthcare post-secondary education programs. The Essentials
Chapter 25: Urinary System
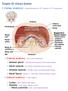 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
