Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
|
|
|
- Gregory Grant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are related. Define homeostasis and explain its importance. Define negative feedback and describe its role in maintaining homeostasis and normal body function. Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry Differentiate between ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds, and describe the importance of hydrogen bonds. Differentiate clearly between an acid and a base. Compare and contrast carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in terms of their building blocks, structures, and functions in the body. Chapter 3: Cells and Tissues Define selective permeability, diffusion (including simple and facilitated diffusion and osmosis), active transport, passive transport, solute pumping, exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic. Describe briefly the process of DNA replication and mitosis. Explain the importance of mitotic cell division. Name the four major tissue types and their chief subcategories. Explain how the four major tissue types differ structurally and functionally. Chapter 4: Skin and Body Membranes List the general functions of each membrane type-cutaneous, mucous, serous, and synovial-and give its location in the body. Name the layers of the skin and describe the characteristics of each. Chapter 5: The Skeletal System List at least three functions of the skeletal system. Explain the role of bone salts and the organic matrix in making bone both hard and flexible. Discuss/describe how the formation of long bones and flat bones is different. Name the three major categories of joints and compare the amount of movement allowed by each. Chapter 6: The Muscular System Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue and indicate where they are found in the body. Describe the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle and explain the role of actin and myosin containing myofilaments. Describe the events of muscle cell contraction. Chapter 7: The Nervous System Define central nervous system and peripheral nervous system and list the major parts of each. Describe the events that lead to the generation of a nerve impulse and its conduction from one neuron to another. Identify and indicate the functions of the major regions of the cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum in the human brain.! 1
2 ! Chapter 8: Special Senses Name the layers of the wall of the eye, and indicate the major function of each; trace the pathway of light through the eye. Identify the structures of the external, middle, and internal ear, and list the functions of each. Name the four basic taste sensations and list factors that modify the sense of taste. Chapter 9: The Endocrine System Define hormone and target organ. Define negative feedback and describe its role in regulating blood levels of the various hormones. List hormones produced by the endocrine glands and discuss their general functions. Chapter 10: Blood Describe the composition of plasma and discuss its importance in the body. List the cell types making up the formed elements, and describe the major functions of each type. Describe the ABO and Rh blood groups. Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Name the elements of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart and describe the pathway of impulses through this system. Compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Explain how the lymphatic system is functionally related to the cardiovascular and immune systems. Describe the protective functions of skin and mucous membranes. Name the two arms of the adaptive defense system and relate each to a specific lymphocyte type (B or T cell). Chapter 13: The Respiratory System Name the organs forming the respiratory passageway from the nasal cavity to the alveoli of the lungs and describe the function of each. Explain how the respiratory muscles cause volume changes that lead to air flow into and out of the lungs. Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. Chapter 14: The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Name the organs of the alimentary canal and accessory digestive organs and identify each on an appropriate diagram or model. List the major enzymes or enzyme groups produced by the digestive organs or accessory glands and name the foodstuffs on which they act. Recognize the uses of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in cell metabolism. Chapter 15: The Urinary System Identify the following regions of a kidney (longitudinal section): hilum, cortex, medulla, medullary pyramids, calyces, pelvis, and renal columns. Describe the process of urine formation, identifying the areas of the nephron that are responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Explain the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone in the regulation of water balance by the kidney. Chapter 16: The Reproductive System Describe the various stages of meiosis. Compare and contrast spermatogenesis and oogenesis. Define fertilization and zygote; explain the prevention of polyspermy. Explain the major events that occur during the menstrual cycle. 2
3 1. Identify the following endocrine glands, list the hormones produced by each gland, and list the target for each hormone. A. B. C. D. E. 2. Five other glands are shown in the diagram above that aren t identified by a letter. List each of the glands and list the hormone(s) produced by each Describe atomic structure and formation of chemical bonds, including ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds.! 3
4 4. Identify the anterior pituitary hormones that targets the organs/glands shown in the diagram. Additionally, list the posterior pituitary hormones too. A. B. C. D. E. 5. Identify the four leukocytes shown below. List a function for each and identify the granulocytes from the agranulocytes. Additionally, list the missing leukocyte along with its function. A. B. C. D.! 4
5 6. In the heart diagram below, identify the structures involved in the conduction of signals through the heart. A. B. C. D. E. 7. Label the diagram of the heart above with the following terms: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, right ventricle, right A-V valve, left A-V valve, and interventricular septum. 8. Identify the respiratory structures in the diagram below. A. B. C. D. E. 9. Explain the mechanisms of inspiration and expiration of air into and out of the lungs.! 5
6 10. Label each of the various respiratory volumes in the diagram below. Identify the volumes that make up Vital Capacity 11. Explain how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. 12. Identify the following organs of the digestive system. For each organ, list at least one function. A. B. C. D. E.! 6
7 13. Identify the following structure of the nephron. Circle the structure that responds to ADH. A. B. C. D. 14. Sketch and label a long bone. Identify where the yellow and red marrow are located and the function of each marrow. E. 15. List hormones pairs that work as antagonists (for example, insulin and glucagon). 16. List the major highlights of spermatogenesis. Do the same for oogenesis. List the location within the female reproductive system where fertilization occurs. 17. What ovarian structures produce estrogen? Name the second hormone produced by the same structures.! 7
8 18. Sketch and label the major structures of the human eye. 19. Explain the major steps that occur during an action potential and the propagation of a nerve impulse. 20. Explain the major components that make up a monosynaptic reflex arc. 21. List the four macroorganic molecules. For each, list a function and example. 22. List the four main types of tissues found in humans. For each tissue type, list the tissue s major characteristics. 23. Name and describe four types of passive transport. 24. Distinguish between negative and positive feedback mechanisms. 25. Sketch and label a neuron. Explain the difference between multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons.! 8
9 Final Exam Word List Chapter abdominopelvic cavity 2. acid 3. actin 4. action potential 5. active vitamin D 6. ADH 7. adipose tissue 8. adrenaline 9. adrenocorticotropic hormone 10. afferent nerves 11. agglutination 12. alpha cells of pancreas 13. alveoli 14. amino acids 15. amphiarthrotic joint 16. amylase 17. anatomical position 18. anatomy 19. androgens 20. angiotensin 21. antibody classes 22. appendix 23. arachnoid mater 24. areolar tissue 25. arteries 26. arterioles 27. atomic mass 28. auditory tube 29. auricle 30. autonomic nervous system 31. AV bundle 32. AV node 33. axon terminal 34. axons 35. base 36. basophils 37. beta cells of pancreas 38. bicarbonate 39. bicuspid valve 40. bile 41. blastocyst 42. blood cell antigens 43. blood ph 44. brain stem 45. brush border enzymes 46. bulbourethral gland 47. Ca calcaneus 49. calcitonin 50. canaliculli 51. capillaries! 9
10 52. carbohydrates 53. carbonic acid 54. cardiac muscle tissue 55. cardioesophageal sphincter 56. cartilaginous joint 57. cecum 58. cell cycle phases 59. cell membrane 60. central nervous system 61. cerebellum 62. cerebral aqueduct 63. chemotaxis 64. chordae tendineae 65. choroid layer 66. cilia 67. coagulation 68. cochlea 69. collecting duct 70. colon 71. connective tissue 72. cornea 73. corpus callosum 74. corpus luteum 75. cortisol 76. covalent bonds 77. creatine phosphate 78. cutaneous membrane 79. cytoplasm 80. dendrites 81. desmosomes 82. diapedesis 83. diencephalon 84. diploid cell 85. disaccharides 86. distal convoluted tubule 87. DNA base pairing rules 88. DNA replication 89. dorsal cavity 90. ductus deferens 91. duodenum 92. dura mater 93. dynamic equilibrium 94. ear ossicles 95. eccrine glands 96. efferent nerves 97. electrons 98. endocrine system 99. endocytosis 100. endometrium 101. enzymes 102. eosinophils 103. epidermis 104. epididymis 105. epiglottis 106. epinephrine 107. epiphyseal plate 108. epithelial tissue! 10
11 109. erythropoietin (EPO) 110. esophagus 111. estrogen 112. exocytosis 113. expiratory reserve volume 114. facilitated diffusion 115. fascicle 116. fats 117. fertilization 118. fever 119. fibrous joint 120. fibrous tunic of eye 121. formed elements of blood 122. fourth ventricle of brain 123. fovea centralis 124. FSH 125. gallbladder 126. gap junctions 127. gastrin 128. glomerulus 129. glottis 130. glucagon 131. glucocorticoids 132. Golgi apparatus 133. gout 134. Graafian follicle 135. growth hormone 136. haploid cell 137. Haversian canals 138. HCl 139. hematopoiesis 140. homeostasis 141. human chorionic gonadotropin 142. hydrogen bonds 143. hydrostatic pressure 144. hypertonic 145. hypothalamus 146. hypotonic 147. ileocecal valve 148. incus 149. inflammatory response 150. inspiratory reserve volume 151. insulin 152. interatrial septum 153. interferon 154. interstitial cells of testis 155. interstitial fluid 156. interventricular septum 157. ionic bonds 158. iris 159. irritability 160. isotonic 161. isotope 162. keratin 163. lacunae 164. lamellae 165. larynx! 11
12 166. lateral ventricles of brain 167. left atrium 168. left ventricle 169. leukocytes 170. levels of organization in the body 171. LH 172. lipid bilayer 173. lipids 174. liver 175. loop of Henle 176. lymph 177. lymphocytes 178. malleus 179. mediastinum 180. medulla oblongata 181. melanin 182. melatonin 183. metacarpals 184. metatarsals 185. microvilli 186. midbrain 187. mineralocorticoids 188. monocytes 189. monosaccharides 190. morula 191. motor division of nervous system 192. motor unit 193. mucous membrane 194. muscle fiber (cell) 195. muscle tissue 196. myelinated axon 197. myofibril 198. myofilament 199. myometrium 200. myosin 201. natural killer cells 202. negative feedback mechanisms 203. nervous tissue 204. neurolemma 205. neuromuscular junction 206. neurotransmitter 207. neutrons 208. neutrophils 209. nucleic acids 210. osmotic pressure 211. ossification 212. osteoarthritis 213. osteoblasts 214. osteoclast 215. osteocytes 216. osteoporosis 217. oval window 218. ovary 219. ovum 220. oxyhemoglobin 221. oxytocin 222. pancreas! 12
13 223. parasympathetic nervous system 224. pepsin 225. pepsinogens 226. perforins 227. pericardium 228. periosteum 229. peripheral nervous system 230. peritoneum 231. Peyer s patches 232. phagocytes 233. phagocytosis 234. phalanges 235. physiology 236. pia mater 237. pineal gland 238. pinocytosis 239. pituitary gland 240. plasma of blood 241. platelets 242. pleura 243. polar covalent bonds 244. polysaccharides 245. primary bronchi 246. primary oocyte 247. progesterone 248. prolactin 249. proteins 250. protons 251. proximal convoluted tubule 252. pseudostratified epithelium 253. PTH 254. pulmonary artery 255. pulmonary circuit of blood flow 256. pulmonary veins 257. pupil 258. Purkinje fibers 259. pyloric sphincter 260. radioisotope 261. rectum 262. relaxin 263. renal hilus 264. renin 265. rennin 266. retina 267. ribosomes 268. rickets 269. right atrium 270. right ventricle 271. rough ER 272. round window 273. SA node 274. salivary glands 275. sarcolemma 276. sarcomere 277. satellite cells 278. Schwann cells 279. sclera! 13
14 280. secondary oocyte 281. secretin 282. self-antigens 283. semicircular canals 284. seminiferous tubules 285. sensory division of nervous system 286. serous membrane 287. sex chromosomes 288. simple cuboidal epithelium 289. simple squamous epithelium 290. skeletal muscle tissue 291. small intestine 292. smooth ER 293. smooth muscle tissue 294. sodium-potassium pump 295. somatic nervous system 296. spermatid 297. spermatogenesis 298. spiral organ of Corti 299. spleen 300. stapes 301. static equilibrium 302. stratified squamous epithelium 303. striated muscle 304. subarachnoid space 305. surfactant 306. sympathetic nervous system 307. synaptic cleft 308. synovial joint 309. systemic circuit of blood flow 310. T T talus 313. tarsals 314. testosterone 315. thalamus 316. thoracic cavity 317. thymosin 318. thymus gland 319. thyroid cartilage 320. thyroid gland 321. thyroid hormone 322. tidal volume 323. tight junctions 324. tonsils 325. trabeculae 326. trachea 327. trcuspid valve 328. triglycerides 329. tropomyosin 330. troponin 331. tubular reabsorption 332. tubular secretion 333. universal blood donor 334. universal blood recipient 335. ureter 336. urethra! 14
15 337. uterine tube (fallopian tube) 338. vagina 339. vasopressin 340. veins 341. vena cava 342. vestibule of inner ear 343. villi 344. vital capacity 345. Volkmann s canals 346. voluntary vs. involuntary muscle tissue 347. XX 348. XY 349. yellow marrow 350. Z-disc 351. zygote! 15
Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Semester 2 Review Units 1 thru 16
 Name: Semester 2 Review Units 1 thru 16 Period: 1. Describe the events that occur at a neuromuscular junction. 2. List the four main types of tissues found in humans. For each tissue type, list the tissue
Name: Semester 2 Review Units 1 thru 16 Period: 1. Describe the events that occur at a neuromuscular junction. 2. List the four main types of tissues found in humans. For each tissue type, list the tissue
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview
 Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Animal Structure and Function
 Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Body Structure and Function
 Western Technical College 10806120 Body Structure and Function Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course is designed to provide the students
Western Technical College 10806120 Body Structure and Function Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course is designed to provide the students
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 10 (starting with the auditory system), 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16): Sensory Systems (chapter
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 10 (starting with the auditory system), 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16): Sensory Systems (chapter
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13): Skeletal System (from chapter 5 in the textbook), Nervous System
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13): Skeletal System (from chapter 5 in the textbook), Nervous System
Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2
 The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
3. The structure labelled X is the A. nucleolus. B. mitochondria. C. cell membrane. D. rough endoplasmic reticulum.
 PART A: Multiple Choice Section: Please DO NOT WRITE or MAKE ANY MARKS on this test paper. Put all answers on your SCANTRON CARD. Please make sure that you fill in your Scantron Card correctly: use pencil,
PART A: Multiple Choice Section: Please DO NOT WRITE or MAKE ANY MARKS on this test paper. Put all answers on your SCANTRON CARD. Please make sure that you fill in your Scantron Card correctly: use pencil,
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Anatomy & Physiology (submitted by Matt Osborne) 1 st Nine Weeks
 Days Unit 2, Unit 2, Unit 2, Unit 2, Indiana Standard(s) AP.1.1 AP.1.3 AP.1.4 AP 2.1 AP 2.2 AP 2.3 AP 2.4 AP 1.2 AP 2.5 AP 3.1 Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Anatomy & Physiology (submitted
Days Unit 2, Unit 2, Unit 2, Unit 2, Indiana Standard(s) AP.1.1 AP.1.3 AP.1.4 AP 2.1 AP 2.2 AP 2.3 AP 2.4 AP 1.2 AP 2.5 AP 3.1 Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Anatomy & Physiology (submitted
Autumn 2012 LEARNING OBJECTIVES BIOL&241
 CELL BIOLOGY This is information that you are expected to have or to acquire on your own. I highly recommend that you have a basic understanding of the following before continuing. Please see me if you
CELL BIOLOGY This is information that you are expected to have or to acquire on your own. I highly recommend that you have a basic understanding of the following before continuing. Please see me if you
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Histology. Study of body tissues
 Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System
 Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System Digestive System 1. Secretions from which of the following would have the effect shown in the diagram? A. liver B. mouth C. stomach D. large intestine
Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System Digestive System 1. Secretions from which of the following would have the effect shown in the diagram? A. liver B. mouth C. stomach D. large intestine
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE JANUARY 2000 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE JANUARY 2000 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
BIOLOGY 12 SAMPLE QUESTIONS
 BIOLOGY 12 SAMPLE QUESTIONS The following are examples of the cognitive levels: K (), U ( and Application) and H (). It should be noted that cognitive level does not necessarily reflect level of difficulty.
BIOLOGY 12 SAMPLE QUESTIONS The following are examples of the cognitive levels: K (), U ( and Application) and H (). It should be noted that cognitive level does not necessarily reflect level of difficulty.
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Semester 2 Final Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Semester 2 Final Review Name: Key Cardiovascular 1. Name and define the two cardiovascular circuits. a. Pulmonary-blood to and from the lungs b. Systemic-blood to and from the body
Anatomy and Physiology Semester 2 Final Review Name: Key Cardiovascular 1. Name and define the two cardiovascular circuits. a. Pulmonary-blood to and from the lungs b. Systemic-blood to and from the body
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul)
 TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul) ANATOMY BASICS I. Basic concepts of anatomy a. Spatial terminology 1. Anatomical position 2. Body regions 3. Directional terms 4. Planes b. Structural hierarchy
TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul) ANATOMY BASICS I. Basic concepts of anatomy a. Spatial terminology 1. Anatomical position 2. Body regions 3. Directional terms 4. Planes b. Structural hierarchy
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as:
 3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
2. The waste products of metabolism are eliminated through the process of A) assimilation. B) absorption. C) excretion. D) digestion. E) resorption.
 CH 1 GENERAL ANATOMY 1. Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) grow and reproduce. B) respond and adapt to their environment. C) control the external environment. D) A and B
CH 1 GENERAL ANATOMY 1. Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) grow and reproduce. B) respond and adapt to their environment. C) control the external environment. D) A and B
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1
 INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Descriptive Histology
 Atlas of Descriptive Histology Michael H. Ross University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Wojciech Pawlina Mayo Medical School College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota
Atlas of Descriptive Histology Michael H. Ross University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Wojciech Pawlina Mayo Medical School College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Key Terms. Chapter 1. Chapter 2. acids. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) atomic mass number. atomic number. atomic symbol. atomic weight. bases.
 Key Terms Chapter 1 anatomical position anatomy atoms cells homeostasis homeostatic imbalance negative feedback organ organ system organism physiology plane positive feedback section tissues Chapter 2
Key Terms Chapter 1 anatomical position anatomy atoms cells homeostasis homeostatic imbalance negative feedback organ organ system organism physiology plane positive feedback section tissues Chapter 2
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Biology 12. Examination Booklet 2009/10 Released Exam January 2010 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EXAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO.
 Biology 12 Examination Booklet 2009/10 Released Exam January 2010 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS REFER TO THE RESPONSE BOOKLET. Contents:
Biology 12 Examination Booklet 2009/10 Released Exam January 2010 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS REFER TO THE RESPONSE BOOKLET. Contents:
THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: RESULTS/SCORES FROM LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
 MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Chapter Assessment. Protection, Support, and Locomotion, continued. Understanding Main Ideas (Part A)
 34 Protection, Support, and Locomotion, continued Assessment Understanding Main Ideas (Part A) Write the word or phrase that best completes the statement. 1. Beneath the scab of a wound, begin to multiply
34 Protection, Support, and Locomotion, continued Assessment Understanding Main Ideas (Part A) Write the word or phrase that best completes the statement. 1. Beneath the scab of a wound, begin to multiply
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / /
 Fall 2015 22TBio 142 22THuman Anatomy and Physiology II Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Semester/Year 22TBio 142
Fall 2015 22TBio 142 22THuman Anatomy and Physiology II Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Semester/Year 22TBio 142
January Here it is boys and girls, an exam is coming and you are no doubt studying hard and getting your brain in gear for the big day!
 Exam Review January 2019 Grade 11 Biology Student Here it is boys and girls, an exam is coming and you are no doubt studying hard and getting your brain in gear for the big day! First of all, you should
Exam Review January 2019 Grade 11 Biology Student Here it is boys and girls, an exam is coming and you are no doubt studying hard and getting your brain in gear for the big day! First of all, you should
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.)
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
This presentation will be posted to the website.
 This presentation will be posted to the website. 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and triggering transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching to the cell membrane
This presentation will be posted to the website. 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and triggering transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching to the cell membrane
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
1. In this process substances move from the nephron to the circulatory system. A. filtration B. reabsorption C. secretion D.
 3rd lecture test 3:30 Sp 08 1. In this process substances move from the nephron to the circulatory system. A. filtration B. reabsorption C. secretion D. excretion 2. Where does secretion take place? A.
3rd lecture test 3:30 Sp 08 1. In this process substances move from the nephron to the circulatory system. A. filtration B. reabsorption C. secretion D. excretion 2. Where does secretion take place? A.
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE NOVEMBER 1998 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE NOVEMBER 1998 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
يراهظلا( يئلاطلا جيسنلا
 Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
1. The Endocrine System is a major controlling system of what body processes?
 SEMESTER 2 1. The Endocrine System is a major controlling system of what body processes? 1. -Mobilizing body defenses 2. Regulating cellular metabolism 3. Maintaining electrolyte balance 2. What mechanism
SEMESTER 2 1. The Endocrine System is a major controlling system of what body processes? 1. -Mobilizing body defenses 2. Regulating cellular metabolism 3. Maintaining electrolyte balance 2. What mechanism
Human Body Systems. The human body consists of 11 major systems.
 Human Body Systems The human body consists of 11 major systems. Systems Skeletal Muscular Cardiovascular or Circulatory Digestive Respiratory Urinary Endocrine Nervous Integumentary Lymphatic or the Immune
Human Body Systems The human body consists of 11 major systems. Systems Skeletal Muscular Cardiovascular or Circulatory Digestive Respiratory Urinary Endocrine Nervous Integumentary Lymphatic or the Immune
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Learning Outcome
 Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
3. Because of homeostasis, large external changes cause internal changes.
 Biology 30S Page 1 I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. In a negative feedback mechanism, an effector is a A) muscle. B) gland. C) answers A) and B) D) none of the above 2. Which of the following is an example
Biology 30S Page 1 I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. In a negative feedback mechanism, an effector is a A) muscle. B) gland. C) answers A) and B) D) none of the above 2. Which of the following is an example
Chapter 25: Urinary System
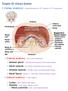 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
VirtualSC. Course Detail. Credits: 1 Estimated Completion Time: (This course runs from September-May) Course Description
 Course Detail VirtualSC Course Name: Anatomy and Physiology Course Code: CW326300 Subject: Science Prerequisites: Biology Credits: 1 Estimated Completion Time: (This course runs from September-May) Course
Course Detail VirtualSC Course Name: Anatomy and Physiology Course Code: CW326300 Subject: Science Prerequisites: Biology Credits: 1 Estimated Completion Time: (This course runs from September-May) Course
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours. Animal Form. AP Biology Rapid Learning Series
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
MULTIPLE CHOICE PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS 1. Organelle X produces proteins. These proteins move through organelle Y toward organelle Z where they are packaged. What are X, Y and Z? 6. Which of the following
MULTIPLE CHOICE PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS 1. Organelle X produces proteins. These proteins move through organelle Y toward organelle Z where they are packaged. What are X, Y and Z? 6. Which of the following
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 2B CELLS
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 2B CELLS Cells/ Structure Cell Type (Epithelial) / Secretion Location(s) Function in Location Neurons -Multipolar -Associative -Bipolar, Unipolar Glial Cells (CNS) -Astrocytes -Microglia
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 2B CELLS Cells/ Structure Cell Type (Epithelial) / Secretion Location(s) Function in Location Neurons -Multipolar -Associative -Bipolar, Unipolar Glial Cells (CNS) -Astrocytes -Microglia
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
