Kingdom Phylum Class Genus. Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta;
|
|
|
- David Malone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. (a) BIOLOGY BY2 Kingdom Phylum Class Genus Planta(e)/ plant(s); 4 Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta; (b) (i) A = Fungi; 2 B = Protoctist(a)/ protoctists/ protists; NOT protozoa (ii) A (reproduce by) spores/ hyphae/ mycelium/ chitin walls/ heterotrophic/ saprophytic/ eukaryotic; Accept description of saprophytic 2 B membrane bound organelles present/ eukaryotic/ no tissue differentiation/ (mainly) single celled organisms/ unicellular; 1 total [8] 10
2 2. (a) loss of water vapour/ evaporation of water; 2 from (surface of) leaf /through stomata; Accept lenticels (b) (i) TWO precautions and TWO reasons Shoot cut under water/inserted under water/flood inside of apparatus with water/ assemble under water; to prevent air entering/ bubbles; Shoot with large number of leaves; to ensure measurable rate of transpiration; Avoid wetting leaves/ ensure leaves are dry; blocks stomata/ reduces rate of transpiration; Leave time for apparatus to settle down; allow plant to adapt to new conditions/ to equilibrate; Seal joints with Vaseline/ ensure screw clip is closed; to prevent air entering apparatus/ prevent leakage; Ensure bubble set at appropriate position/ right hand end; to enable a (suitable) reading to be taken; Reference to not allowing air bubbles to enter = 1 mark ( if no precautions are given) 4 max (c) (i) Sun(light); 1 (d) (ii) Molecules of water moving together/ water pulled up; Because of cohesion of molecules; adhesion to (walls of) {xylem/ hydrophilic lining/ vessel wall}; root pressure {forces/ pushes} water upwards; IGNORE capillarity (i) A= phloem; B= xylem; (ii) {Xylem/ vascular tissue} is at the centre/ xylem is star shaped/ central stele; NOT bundle No vascular bundles/ peripheral vascular bundles in stem; Endodermis visible in root/ no pith; 2 max 2 2 max 2 total [13] 11
3 3. (a) Any 4 Intercostal muscles contract and ribs move up and out; 4 Diaphragm (muscles) contract and diaphragm flattens; (Internal) volume of thorax increases; accept chest reject lungs Pressure in lungs/ thorax decreases; {Higher/ difference in} air pressure outside {forces/ pushes/ moves/ drawn} air into lungs; (b) (i) blood flows across (gills/ filaments/ lamellae/ gill plates) in opposite direction to water; water always has more oxygen than blood/ (oxygen) {diffusion/ concentration} gradient maintained; oxygen passes from water into blood; across entire {gill/ gas exchange} surface; NOT longer higher saturation of blood with oxygen/ more oxygen taken up; 4 (ii) Parallel (flow); 1 (c) (iii) Equilibrium is reached (part way across the gill plates/ lamellae)/{diffusion/ concentration} gradient not maintained; {Lower percentage saturation with/ only 50% saturation} oxygen/ less oxygen uptake/ less diffusion of oxygen; NOT slower gills dry out; prevents oxygen from dissolving on surface of gills; gills may {stick together/not open as easily/ collapse}; decrease in surface area; (Explanation cannot be accepted alone) 2 2 max 3 Total [13] 12
4 4. (a) (i) C/ D; 1 (ii) K and F; 1 (iii) C; 1 (iv) E; 1 (v) F; 1 (vi) J; 1 (b) (i) Herbivorous/ herbivore; 1 (ii) {large/ridged/wm shape} {molars/premolars} for grinding; 3max {diastema/space with no teeth/ gap between teeth} to assist with {chewing/ (tongue to) manipulate food/ cud}; {well developed/ sharp/ long} incisors for {biting/ cutting/ slicing/ tearing} (vegetation); loose articulation/ jaw moves in a {horizontal/ circular} plane; Very small/ no canines; open roots to allow continuous growth of molars; (iii) Four chambered stomach (NOT four stomachs) / rumen/ large caecum; Contain cellulose digesting bacteria/ have cellulase producing bacteria; NOT cellulose eating bacteria Long gut {to allow extra time for digestion of cellulose/ cellulose harder to digest}; Cud is regurgitated for further chewing; 2 4 Total [12] 13
5 5. (a) Parasites (are organisms that) live {on/ in} {another organism/ host} and obtain {nourishment/ nutrients} from it; at the expense of /causing harm to the host; 2 (b) attaches to gut wall by {hooks and suckers/ scolex}; {large/ high/ increased} surface area to volume ratio; {digested products/ nutrients} in host gut absorbed into tapeworm; short diffusion pathway; 3 max 5 Total [5] 14
6 6. (a) (i) sucrose is produced in (photosynthesising) leaf/ leaves are the source of sucrose; sucrose travels in phloem; phloem removed (by the ringing process); sucrose cannot flow to roots/ is blocked; 3 max (ii) amino acids/hormones/ florigen; 1 (b) sucrose used for {cell wall formation/ cell division/ mitosis/ respiration}; {Less/ no} sucrose used (by growing areas/sinks as they have been removed); therefore more will pass down stem; NOT accumulation 2 max (c) sucrose not replaced from above (the ring); so concentration decreases; as movement towards root continues; and sucrose used in respiration/storage/ converted to starch/ growth/ active transport; 3 max 6 Total [9] 15
7 7. (a) (i) A. Fish/ amphibians show external fertilisation; Fish/ amphibians Reptiles/ birds mammals Reptiles/ birds mammals B. Fertilised {egg/ zygote/ embryo} develops outside body of parent; C. Many eggs/ young produced; D. Ensures some survive; E. Reptiles / Bird / Mammals internal fertilisation; F. This allows gametes to be independent of water; G. Increased chance of fertilisation/ fewer gametes {needed/ wasted}; H. (Evolution of an) amniote egg; I. eggs surrounded by protective shell/ preventing dessication; J. Birds incubate eggs outside mothers body; K. Mammals development inside mothers body; L. Nutrients/ oxygen via placenta; M. Young born well developed; N. Birds/ mammals exhibit parental care; O. Relationship between parental care and number of offspring produced; 7 Total [10] 16
8 (b) A. wall consists of three layers/ diagram of artery + vein labelled correctly; B. smooth endothelial (lining); C. to reduce friction; D. {outer layer/ tunica externa} of collagen ( can be on diagram) E. to resist/prevent overstretching; F. artery has a thick wall to resist pressure; G. contain a thick layer of elastic tissue; H. { for elastic recoil/ small lumen} to maintain pressure; I. Smooth muscles in {small arteries/ arterioles} {regulate blood flow/pressure/ ref to vasoconstriction}; J. arteries closer to the heart have more elastic tissue; K. semilunar valves in aorta/ pulmonary artery; L. Veins have valves to {prevent backflow of blood/ to maintain unidirectional flow}; M. Walls are thin(ner) because blood at lower pressure; N. (skeletal) muscle contraction returns blood to heart; O. Large lumen reduces resistance to flow/ friction; 7 Total [10] 17
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01. Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 A.M. MONDAY, 3 June 2013 1 1 2 hours Question For s use Maximum Mark 1. 8 Mark Awarded 2. 13 3. 13 4. 12 5. 5 1072
Surname Other Names Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 A.M. MONDAY, 3 June 2013 1 1 2 hours Question For s use Maximum Mark 1. 8 Mark Awarded 2. 13 3. 13 4. 12 5. 5 1072
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
IGCSE Biology Revision Answers
 IGCSE Biology Revision Answers Test 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms 1. (b), (c) and (e) 2. Nutrition; respiration 3. (b) and (d) 4. T, F, F, F 5. Nutrition; respiration Metabolism; excretion 7. F,
IGCSE Biology Revision Answers Test 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms 1. (b), (c) and (e) 2. Nutrition; respiration 3. (b) and (d) 4. T, F, F, F 5. Nutrition; respiration Metabolism; excretion 7. F,
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section:
 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
GCE BIOLOGY - BY2. Mark Scheme - January (b) (i) birds; 1. (ii) Borneo {1.61/ 1.62/1.6}; 1
 GCE BIOLOGY - BY Mark Scheme - January 03 (a) A species is a group of organisms that {can interbreed/ reproduce}; (under natural conditions) produce fertile offspring; (b) (i) birds; (ii) Borneo {.6/.6/.6};
GCE BIOLOGY - BY Mark Scheme - January 03 (a) A species is a group of organisms that {can interbreed/ reproduce}; (under natural conditions) produce fertile offspring; (b) (i) birds; (ii) Borneo {.6/.6/.6};
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Circulatory Systems AP Biology
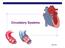 Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad , A.P.
 THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
AP Biology. Circulatory Systems. Exchange of materials. Overcoming limitations of diffusion. Circulatory systems. In circulation
 Circulatory Systems 2008-2009 Exchange of materials nimal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, C ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s easy!
Circulatory Systems 2008-2009 Exchange of materials nimal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, C ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s easy!
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
Trial Examination VCE Biology Unit 1. Written Examination. Question and Answer Booklet. Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes
 Trial Examination 2006 VCE Biology Unit 1 Written Examination Question and Answer Booklet Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes Student s Name: Teacher s Name: Structure of Booklet Section
Trial Examination 2006 VCE Biology Unit 1 Written Examination Question and Answer Booklet Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes Student s Name: Teacher s Name: Structure of Booklet Section
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided
 GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June 2015 Time 1. 30 hours S 3 MOT II Name class/no INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided ANSWERS
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 June 2015 Time 1. 30 hours S 3 MOT II Name class/no INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A, and B Answers to questions in section A, and B must be in spaces provided ANSWERS
UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 148 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Recording of marks Examiners must mark in red ink. One tick
GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 148 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Recording of marks Examiners must mark in red ink. One tick
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2006 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2006 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL
 WARNING: This Question Paper MUST be returned with your answer book(s) at the end of the examination: otherwise marks will be lost. STUDENT NAME SCHOOL L.37 For Examiner s use only Sect. Q. Mark Sect.
WARNING: This Question Paper MUST be returned with your answer book(s) at the end of the examination: otherwise marks will be lost. STUDENT NAME SCHOOL L.37 For Examiner s use only Sect. Q. Mark Sect.
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level *4900384293* IOLOGY 5090/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 dditional Materials:
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level *4900384293* IOLOGY 5090/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 dditional Materials:
Name GLOSSARY. Carrier protein a molecule in the cell membrane that allows materials to pass through it
 2 GLOSSARY Active transport movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
2 GLOSSARY Active transport movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
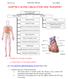 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory),
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2439575101* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core May/June 2010 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2439575101* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core May/June 2010 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
1b. Credit: State the chemical elements present in carbohydrates, proteins and fats. See table below
 1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
1 Living organisms: variety and common features
 Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
BIOLOGY - BY2. No. Answer Mark. (ii) 1 egg 1 mark for both (not: zygote) 7 adult/imago 2-6 nymphs (allow: instar) 2
 BIOLOGY - BY. (a) (i) Incomplete metamorphosis (ii) egg mark for both (not: zygote) 7 adult/imago -6 nymphs (allow: instar) (b) (i) Complete metamorphosis (ii) A Egg B Larva (allow: maggot) C Pupa (allow:
BIOLOGY - BY. (a) (i) Incomplete metamorphosis (ii) egg mark for both (not: zygote) 7 adult/imago -6 nymphs (allow: instar) (b) (i) Complete metamorphosis (ii) A Egg B Larva (allow: maggot) C Pupa (allow:
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes
 Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
A level Biology Preparation Work
 A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Nutrition in Heterotrophs
 Nutrition in Heterotrophs Required Nutrients Water Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Makes up ~90% of some animals Makes up a major portion of many body parts Humans require at least
Nutrition in Heterotrophs Required Nutrients Water Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Makes up ~90% of some animals Makes up a major portion of many body parts Humans require at least
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
3/27/2015. A. Interactions and coordination between organs provide essential biological activities.
 EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme. F211, AS Biology. May 2013 OCR
 Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme F211, AS Biology May 2013 OCR This mark scheme only deduce how the paper could be marked according to previous ones Question I. a.) i.) [2 marks] A nucleus B chloroplast
Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme F211, AS Biology May 2013 OCR This mark scheme only deduce how the paper could be marked according to previous ones Question I. a.) i.) [2 marks] A nucleus B chloroplast
Y10 POS Combined BIOLOGY 3Y
 08-9 Y0 POS Combined BIOLOGY Y Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 7... Contraception Evaluate hormonal and non- hormonal contraception...6 Fertility hormones FSH & LH IVF Issues surrounding IVF...
08-9 Y0 POS Combined BIOLOGY Y Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 7... Contraception Evaluate hormonal and non- hormonal contraception...6 Fertility hormones FSH & LH IVF Issues surrounding IVF...
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/21 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL
 Write your Examination Number here 2007. M. 43 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 12 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00
Write your Examination Number here 2007. M. 43 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 12 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
Topic Page: Circulatory system
 Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
* * Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level. BIOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2014.
 *9130719436* ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level IOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft
*9130719436* ambridge International Examinations ambridge Ordinary Level IOLOGY 5090/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2014 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 www.xtremepapers.com International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice OTOER/NOVEMER SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials:
www.xtremepapers.com International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice OTOER/NOVEMER SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials:
c Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology Part 1
 c ngel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 iology Grade 11 uration: 03 hours Part 1 Index No:- 1 The cell wall of a plant cell is removed using an enzyme. What would happen
c ngel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 iology Grade 11 uration: 03 hours Part 1 Index No:- 1 The cell wall of a plant cell is removed using an enzyme. What would happen
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS
 UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0924559665* BIOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 Core May/June 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0924559665* BIOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 Core May/June 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on the
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum
Chapter 10 EXCRETION
 Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/01
 MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2003 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean
MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2003 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *4543376409* UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
*4543376409* UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/11 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *4625240491* IOLOGY 0610/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education *4625240491* IOLOGY 0610/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2011 dditional Materials: RE THESE INSTRUTIONS
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
231/2 BIOLOGY (2017) PAPER 2(Theory)
 231/2 BIOLOGY (2017) PAPER 2(Theory) 1 MARKING SCHEME 1. (a) Albinism; sickle cell anaemia; Haemophilia; colour blindness; b) (i) Inversion Occurs when chromatids break at two places; and when rejoining
231/2 BIOLOGY (2017) PAPER 2(Theory) 1 MARKING SCHEME 1. (a) Albinism; sickle cell anaemia; Haemophilia; colour blindness; b) (i) Inversion Occurs when chromatids break at two places; and when rejoining
